Whistler Blackcomb is a
ski resort
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area – a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In N ...
located in
Whistler, British Columbia
Whistler ( Lillooet/Ucwalmícwts: Cwitima, ; Squamish/Sḵwx̱wú7mesh: Sḵwiḵw, ) is a resort municipality in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mo ...
, Canada. By many measures it is the largest ski resort in
North America and has the greatest uphill lift capacity. It features the
Peak 2 Peak Gondola for moving between
Whistler and
Blackcomb mountains at the top. With all of this capacity, Whistler Blackcomb is also often the busiest ski resort, often surpassing 2 million visitors a year.
Whistler was originally conceived as part of a bid to win the
1968 Winter Olympics. Although the bid failed, construction started anyway and the resort opened for the first time in January 1966. Blackcomb mountain, originally a separate entity, opened for business in December 1980. The two resorts underwent a period of intense rivalry through the 1980s and 90s, with constant upgrades and improvements that were unseen at other resorts. By the mid-1990s the area was repeatedly named the best resort in many skiing magazines.
Intrawest
Intrawest Resorts Holdings, Inc was a developer and operator of destination resorts and a luxury adventure travel company. The company was founded in 1976 as a privately funded real estate development company. In 2006, Intrawest was purchased by ...
, the BC real estate firm that developed Blackcomb, purchased Whistler in 1997 and fully merged their operations in 2003.
Whistler Blackcomb was the centrepiece of a renewed bid on the part of nearby Vancouver for the
2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May Doan Nancy GreeneWayne Gr ...
, which they won in July 2003. Whistler Blackcomb hosted the
alpine skiing events, including the men's and women's Olympic and Paralympic alpine skiing disciplines of
downhill,
Super-G
Super giant slalom, or super-G, is a racing discipline of alpine skiing. Along with the faster downhill, it is regarded as a "speed" event, in contrast to the technical events giant slalom and slalom. It debuted as an official World Cup event ...
,
slalom,
giant slalom
Giant slalom (GS) is an alpine skiing and alpine snowboarding discipline. It involves skiing between sets of poles ("gates") spaced at a greater distance from each other than in slalom but less than in Super-G.
Giant slalom and slalom make up t ...
and
super combined
Combined is an event in alpine ski racing. A traditional combined competition consists of one run of downhill and two runs of slalom, each discipline runs on separate days. The winner is the skier with the fastest aggregate time. (Until the 1990 ...
. In contrast with Cypress Mountain – which hosted the freestyle skiing and all snowboard events, and was plagued with a lack of fresh, natural snow during the Olympics leading to many complaints about hill quality – Whistler Blackcomb had the second-highest snowfall on record with 1,432 cm (over 14 metres) by the end of the 2009/10 season.
Over the next decade, Intrawest expanded by purchasing additional ski resorts across North America, before expanding into golf and other resorts as well. Whistler Village, widely recognized for its livable design, formed the basis of similar
Tyrolian-inspired developments at their expanding series of resorts, as well as other resorts that hired Intrawest to build similar developments on their behalf. In 2010 Intrawest sold off much of its 75% interest in Whistler Blackcomb Resort via a public share offering.
On August 8, 2016, American company
Vail Resorts
Vail Resorts, Inc. is an American mountain resort company headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado. The company is divided into three divisions. The mountain segment owns and operates 40 mountain resorts in four countries, Vail Resorts Hospitality o ...
bought Whistler Blackcomb Holdings for C$1.39 billion.
Nippon Cable
is a Japanese corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo and is engaged in the design, production and installation of jig-back and material ropeways, gondola lifts, funiculars, chairlifts, car parking systems, ramp elevators and amusement pa ...
's minority interest in Whistler Blackcomb resort has continued throughout the ownership changes, by way of ownership of a 25% interest of the Whistler and Blackcomb partnerships.
Description
The ski areas at Whistler and Blackcomb are situated on two ridge-lines running roughly northwest to southeast. The two are separated by a deep valley with Fitzsimmons Creek running along the valley floor. The main base area at Whistler Village is located on the northwest end of this valley, where Fitzsimmons Creek flows into the larger Green River, which forms a floodplain running north-south just to the west of the village area. The Sea-to-Sky Highway runs along the Green River valley. The ski runs generally run northwest towards the village area, or into the valley area between the two ridges. A small number of runs are located on the south side of the Whistler ridge, where they run to the Creekside Base area, some distance south of the main Whistler Village.
Whistler Mountain is the basis of the southern of the two ridges, on the right when looking at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski area from Whistler Village. It has a summit elevation of . The total vertical drop is and skiable inbound terrain. Whistler is served by a total of 19 lifts; 2 gondolas, 5 high-speed detachable quad chair lifts, 2 high-speed detachable sixpack chair lifts, 2 fixed grip triple chair lifts, 1 T-bar (called T-bars but parallel T-Bar was removed however towers and stations still mostly stand) and 7 carpet lifts. It also hosts the drive station for the
Peak 2 Peak Gondola connecting it with Blackcomb mountain to the north. There are 4 on-hill restaurants, as well as a children's ski school. It is served by two base areas: Whistler Creek also known as creekside, the original base on its southwest flank, and Whistler Village on its northwest flank.
Blackcomb Mountain is the northern ridge, on the left when viewed from the village. It has a lift-serviced elevation of at the top of the 7th Heaven chair – Blackcomb Mountain itself is higher at , but unlike Whistler, the peak is not lift-served. Blackcomb has a higher skiable vertical, at , but less in-bound skiing area at . It is served by 15 lifts; 2 gondolas, 6 high-speed quads, 1 fixed-grip triple and 7 surface lifts (1 T-Bar and 5 carpet lifts), as well as the end-station for the Peak 2 Peak. Blackcomb is the location of the world-famous "Couloir Extreme" run, which is one of the top ten steep in-bounds runs in the world according to
Skiing Magazine
''Skiing'' was an American magazine devoted to skiing that was in print publication from 1948 until 2017. It was one of the two largest circulation magazines for skiers.
Early years
Merrill Hastings launched ''Rocky Mountain Skiing'' in 1948, a ...
. Originally called the Saudan Couloir by local skiers even before it was part of the ski area, the company eventually had to drop the name when
extreme skier
Extreme skiing is performed on long, steep (typically from 45 to 60+ degrees, or grades of 100 to 170 percent) slopes in mountainous terrain. The French coined the term 'Le Ski Extreme' in the 1970s. The first practitioners include Swiss skier ...
Sylvain Saudan
Sylvain Saudan (born 23 September 1936 in Lausanne, Switzerland) is an extreme skier, dubbed "skier of the impossible." He is noted for skiing down large and steep mountains, including those in the Himalayas. In 2007 he survived a helicopter crash ...
complained about the unauthorised use of his name.
The two previously separate ski areas of Whistler and Blackcomb were integrated into one operation in 1997 after
Intrawest
Intrawest Resorts Holdings, Inc was a developer and operator of destination resorts and a luxury adventure travel company. The company was founded in 1976 as a privately funded real estate development company. In 2006, Intrawest was purchased by ...
merged with Whistler Mountain Ski Corporation. Ticketing, pass, and access control systems for the two ski areas were fully integrated in 2003. Together, Whistler and Blackcomb form the largest ski area in North America at . Either mountain alone would be in the top-five in terms of size.
The mountains are accessed via four gondolas and one high-speed quads: Blackcomb Excalibur Gondola, Whistler Mountain Village Gondola, and Fitzsimmons Express in the village, the Blackcomb Gondola in Blackcomb Base/Upper Village, and the Whistler Creekside Gondola to the south in the Creekside area. The primary skiing terrain starts about one-third up the mountains. Ski-outs to the valley are usually possible during the months of December through April. The mid- and upper- areas are serviced by 10 high-speed detachable chairs and 5 fixed-grip lifts made by
Lift Engineering,
Doppelmayr and
Poma
Poma, incorporated as Pomagalski S.A., and sometimes referred to as the Poma Group, is a French company which manufactures cable-driven lift systems, including fixed and detachable chairlifts, gondola lifts, funiculars, aerial tramways, peo ...
. Two
T-bars service the
Horstman Glacier and the Whistler alpine regions and take skiers to the entrance to Blackcomb Glacier. The overall lift capacity, 65,507 skiers per hour, is the greatest in North America.
Before 2008 the only connection between the two mountains was via the village. The opening of the
Peak 2 Peak Gondola on 12 December 2008 connected the two mountains at approximately . The lift has a total length of and the longest unsupported span for a lift of its kind in the world at while also having the highest ground clearance for a lift of its kind, above the valley floor.
Whistler Village, which is part of the Resort Municipality of Whistler, a geo-political entity not directly associated with the resort company's operation, is situated at the base of the Whistler Mountain Village Gondola and Blackcomb Excalibur Gondola. The village incorporates community services, shops, entertainment venues, restaurants, bars, hotels, condominiums and vacation properties. The village is above sea level, and is located from
Vancouver International Airport
Vancouver International Airport is an international airport located on Sea Island in Richmond, British Columbia, serving the city of Vancouver and the Lower Mainland region. It is located from Downtown Vancouver. It is the second busies ...
.
Microsoft
Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was release to manufacturing, released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Wind ...
is codenamed "Whistler" after this ski resort, as many Microsoft employees skied at this resort during its development. According to the original release planning at Microsoft, the "Windows release after Whistler will be codenamed Blackcomb". However, so much work was planned into the "Blackcomb" release, and it was clear that it couldn’t all be done in one release cycle. So, selected portions and features were extracted and put into an interim release codenamed "Longhorn", which is the name of a bar situated between the Whistler and Blackcomb mountains and which finally released later as
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of ...
. "Longhorn" was originally planned to be released in 2003, as shown by multiple trailers and "Blackcomb" towards 2006. However in 2004, due to a development that no longer really had a clear direction, the Longhorn development have been reset with more reasonable visions and directions, putting aside a bunch of planned features and concentrating on the essential. In March 2006, When the Vista development was almost complete, the "Blackcomb" project was renamed to "Vienna". However, so many features have been postponed into it after the development reset in 2004 that its objectives became very unrealistic, which lead to its cancelation. A new project, codenamed "Windows 7" was set up in its place, which aimed to make minor improvements to the core Windows Vista experience and address the negative feedback Vista faced.
History
Early visitors
The valley area between Whistler and Blackcomb was first surveyed and documented in 1858 by
Hudson's Bay men looking for an alternate route into the Cariboo area further north. Although little-used at the time, the route would later become one of the many paths used during the Gold Rush at the turn of the century. Known as the
Pemberton Trail, the route followed a path similar to the
Sea-to-Sky Highway, leading past the Whistler area to the present day town of
Pemberton. In the 1860s British Naval surveyors named the mountain "London Mountain," but it soon garnered the nickname "Whistler" because of the shrill whistle made by the
Western Hoary Marmot
The hoary marmot (''Marmota caligata'') is a species of marmot that inhabits the mountains of northwest North America. Hoary marmots live near the tree line on slopes with grasses and forbs to eat and rocky areas for cover.
It is the largest N ...
s who lived among the rocks. Four lakes paralleled the route of Trail, the highest then being known as Summit Lake. However, there was another Summit Lake in BC, and in 1910 the name was changed to its current form, Alta Lake.
[''Walking'']
One of the first permanent residents in the Alta Lake area was trapper John Millar, who set up a cabin next to the trail just south of the base of the mountain. During a trip to sell furs in Vancouver in 1911, Millar stopped at the Horseshoe Bar & Grill for dinner. The cook was Alex Philip from Maine, and Millar invited Philip to join him for dinner. Millar was a storyteller, and during the conversations that followed, he invited Philip to visit the Alta area. Alex and his wife Myrtle visited what was then known as Summit Lake several times over the next few years, and in 1913 they purchased of land on the northwest corner of Alta Lake for $700.
[
]
Rainbow Lodge and other early resorts
By 1914, the Philip's Rainbow Lodge fishing resort was completed with four bedrooms, a large living/dining area and a kitchen. The resort was named for the Rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coast ...
that were the main attraction of the resort.[ That same year, the Pacific Great Eastern Railway (PGE) reached the lake, from Squamish. Executives of the PGE suggested the Lodge host fishermen from Vancouver, which was now less than two days away (from three or more) via steamship to Squamish and then the PGE to Alta Lake. A standard rate of $2 for a week was applied, and the very first group arrived with 25 people. The resort was a hit.][ Millar left when the railway arrived, looking to get further away from civilization.
Building followed demand, and over time the lodge grew to include an additional 45 buildings (cabins, tennis courts, general store, post office) and could accommodate 100 people. It became the most popular west coast resort for 30 years.][''History''] The Philips operated the Lodge until 1948 when they sold it to Alec and Audrey Greenwood. The main Lodge burnt down in 1977, but today the area has been preserved as Rainbow Park. The Philips both remained in the valley until their deaths. Alex died in 1968 at the age of 86, and Myrtle died in 1986 at the age of 95.[
Following the successful launch of Rainbow Lodge, several other tourist resorts set up in the valley. Russell Anderson Jordan opened the Alta Lake Hotel which burned down in 1930, and replaced it with Jordan's Lodge on nearby Nita Lake. Bert and Agnes Harrop built Harrop's Point in the 1920s. This became the Cypress Lodge in 1945 under its then-owner Dick Fairhurst, who built new cabins and a main lodge in the early 1960s. In 1972 the property was purchased by the Canadian Youth Hostel Association and it remained the Whistler Hostel until it was closed in 2010 when the association (now Hosteling International) opened a new, larger hostel. The original building is still standing today, home to the point artists centre and the Whistler sailing club. Cecilia and John Mansell moved to Alta Lake in 1945 and built the Hillcrest Lodge near today's Lakeside Park on Alta Lake. They sold it in 1965 to the Mason Family and others who operated it as Mount Whistler Lodge for skiers. The main lodge was burnt in a fire practice by the fire department in 1986.][
There was some commercial use of the London Mountain area as well. Logging had been carried out for some time, but the arrival of the railway in 1914 made this much more profitable and for several years there were a few sizable mills and lumber operations: The Barrs at Parkhurst Mill on Green Lake (to the north), and the Gebharts with the Rainbow Lumber Company on Alta Lake. The fur trade remained for some time, later supplanted by a mink and marten farm. Jimmy Fitzsimmons ran a prospecting support company, which led to mining surveys up Fitzsimmons Valley. The shafts can still be found on the Singing Pass trail.][
]
Olympic dreams
In 1960 the Canadian Olympic Association visited the west coast looking for potential sites for a future 1968 Winter Olympics. They initially looked at a site on Diamond Head just north of Squamish, which was already developed to the extent of a single chairlift. However, they concluded that the area simply couldn't be developed properly, "it just wasn't the right terrain for a world-class resort."[ Franz Wilhelmsen, a local businessman who had married into the ]Seagram family
Joseph Emm Seagram (April 15, 1841 – August 18, 1919) was a Canadian distillery founder, politician, philanthropist, and major owner of thoroughbred racehorses.
Early life
Joseph Seagram was born April 15, 1841 at Fisher's Mills, near Hespeler, ...
, had already come to the same conclusions when he had been scouting areas for a new ski resort. He met with the COA and convinced them to look further north in the London Mountain area, "And they were impressed."[
Encouraged by their positive reviews, Wilhelmsen organized the Garibaldi Olympic Development Association (GODA) to make a formal bid. At this time there was no road, no electricity, and no piped water or sewer in Alta Lake. Their bid for the Olympics was unsurprisingly rejected, and the Canadian bid was given to ]Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, maki ...
, who came in a close second place to Grenoble
lat, Gratianopolis
, commune status = Prefecture and commune
, image = Panorama grenoble.png
, image size =
, caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint- ...
. Undaunted, Wilhelmsen decided to press ahead with development of a resort.[
In 1962 the Garibaldi Lifts Limited was formed with Franz Wilhelmsen as President. It had two main objectives, to finance and supervise required land/business studies, and to erect and operate ski lifts on London Mountain. The company had little experience in ski operations, so they hired Willy Schaeffler, a well known developer, to help them. Schaeffler proved as enthusiastic about London Mountain as COA and GODA had been. Schaeffler returned and wrote a good feasibility study about the Alta area, which had no mining claims.][
From 1962 to 1965 Garibaldi Lifts raised funds and began development of the ski area on the south side of the mountain. The government agreed that they would set aside a plot at the base of the mountain for Garibaldi Lifts to buy, and agreed to bring the highway to the base of the mountain if they could raise enough money. By 1965 they had reached their goal of raising $800,000 and started planning for development. However, they were not happy with the name, and on August 27, 1965 London Mountain officially became Whistler Mountain.][
By 1965 the Provincial Government had completed a narrow gravel road from Vancouver. Electricity arrived the same year with the installation of a substation along the lines from ]Bridge River
The Bridge River is an approximately long river in southern British Columbia. It flows south-east from the Coast Mountains. Until 1961, it was a major tributary of the Fraser River, entering that stream about six miles upstream from the town of ...
. Everything was in place, and the Alta area became a hive of development.[ GODA made a bid for the ]1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Europe ...
, but Banff won again and eventually lost to Japan.[
]
Whistler opens
By the fall of 1965 the ski area featured a four-person gondola to the mountain's mid-station, a double chairlift to the alpine tree line (the Red Chair), and two T-bars, all provided by GMD Mueller GMD may refer to:
* Ben Slimane Airport, in Morocco
* Gambian dalasi, the currency of Gambia by ISO 4217 code
* Game (retailer), a British video game retailer
* GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase, in enzymology
* General material designation, in li ...
. In addition, a day lodge was constructed and six ski runs cut into the hill. Whistler officially opened for skiing for the first time on January 15, 1966. The new mountain won instant acclaim for its vertical drop, good snow conditions, and huge alpine area. The only problem at the time was the road, it was a dirt logging track, which was only plowed on Saturday, to the detriment of Friday travelers.[
With real infrastructure in place, in 1968 GODA made another bid for the ]1976 Winter Olympics
The 1976 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XII Olympic Winter Games (german: XII. Olympische Winterspiele, french: XIIes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Innsbruck 1976 ( bar, Innschbruck 1976, label= Austro-Bavarian), was a ...
, and this time the joint Vancouver/Garibaldi won the Canadian nomination. However, in 1970 when Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
won the voting for the 1976 Summer Olympics
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
, Vancouver/Garibaldi was removed from further consideration and the games eventually went to Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the United ...
, Colorado. In a stunning turn of events, Denver turned down the games after winning the bidding. The games were then offered to the other North American entry, Vancouver/Garibaldi, but political turmoil due to the recent change in government led to their bid being withdrawn as well, and in desperation the IOC returned the games to Innsbruck for a second time in a row.
The gravel road was paved to Whistler in 1966, and on to Pemberton in 1969. The Blue and Green chairlifts were added in 1970, providing access to additional terrain. In 1972 these were joined by the Olive and Orange chairlifts. A parallel lift to the Green Chair to alleviate crowds came in 1974, and the Little Red Chair came in 1978. The Roundhouse, an on-mountain lodge and restaurant, was completed in 1980. This new lodge provided respite for cold skiers who had survived the long ride up on the Red Chair.
Whistler Village
In 1974 the provincial New Democratic Party of British Columbia
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
was interested in developing tourism and took a number of steps affecting Whistler. At the time, the Alta Lake area was overdeveloped, so the government instituted a development freeze while they studied the problem. The only solution was to continue development in another location. They quickly decided to focus on the table between Whistler and Blackcomb, about 4 km to the north of the existing facilities on Alta Lake. At that time this was the site of the Alta Lake dump, and the remains of a Volkswagen Van Volkswagen Bus or Volkswagen Van is a type of vehicle produced by Volkswagen/Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles.
There have been a number of notable versions of it produced.
Volkswagen Bus light commercial vehicles
Six generations of Volkswagen Transp ...
are still buried under the modern village.[
In 1975 the ]Resort Municipality of Whistler
Whistler ( Lillooet/Ucwalmícwts: Cwitima, ; Squamish/Sḵwx̱wú7mesh: Sḵwiḵw, ) is a resort municipality in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mount ...
(RMOW) was formed, the first Resort Municipality in Canada and also the first place in British Columbia since Canadian prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
where bars were allowed to be open on Sunday. The act also created the Whistler Village Land Company who would oversee all development of the new Whistler Village. In 1977 the provincial government named Al Raine the Provincial Ski Area Co-ordinator, in charge of expanding BC's skiing capabilities. Raine was previously National Coach for the Canadian Women's Ski Team, and was married to famous Canadian skier Nancy Greene. Raine saw the potential in developing Blackcomb Mountain
Blackcomb Peak ( Ucwalmícwts: Tsíqten) is a mountain located east of Whistler, British Columbia that forms the boundary between the Whistler Blackcomb ski resort and Garibaldi Provincial Park. Like Whistler Mountain, it is located on the edge ...
, then part of the Garibaldi Provincial Park, and joined the Whistler city council. The Blackcomb area was currently zoned for logging, but Raine and Greene successfully lobbied the government to remove the zoning and allow development as a ski area.[
In 1977 the Municipality hired Sutcliffe Griggs Moodie Development Consultants to design a layout for Whistler Village's development. However, their design was considered too conventional and allowed too much car traffic. Raine recommended Eldon Beck, who had been the primary designer at Vail, celebrated for its layout. Beck's designs included a pedestrian Main Street Village Stroll and an elevated covered walkway system, limiting all vehicles to the outside of the developed area. To this day the village retains this basic design in spite of dramatic expansions, and has won worldwide acclaim in architecture circles.][
In January 1978, of ]crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it ...
were given to the Whistler municipality to develop the town centre. The first sod for the village was turned on August 18, 1978 by first Mayor Pat Carleton. By 1979 many amenities were in place, including Municipal Hall, Fire Hall, Health Care Centre, and Elementary School. Phase 1 expansion included 11 parcels in the modern Village Square area, including the Whistler Conference Centre, a variety of hotels, restaurants, grocery store, hardware store, etc. An enormous underground garage was built to support all of the buildings in the area, completed before any construction could start above it.[ The first hotel, the Blackcomb Lodge, anchors the Village Square area to this day.
]
Blackcomb opens
In 1978 a call for bids was issued to develop Blackcomb for skiing. The bidding to develop Blackcomb was contested by two companies, the Aspen Skiing Company, and the newly formed Blackcomb Skiing Enterprises (BSE).[ Aspen, having recently developed the Fortress Mountain Resort in Alberta, won the contest. A new company, Fortress Mountain Resorts, was formed with a 50–50 partnership between Aspen and the Business Development Bank of Canada. The new competition, paid for partially by tax dollars, was not initially appreciated by Whistler.
Initial development of the mountain included four triple chairlifts (later named Cruiser, Stoker, Catskinner and Fitzsimmons) and one double chairlift, all supplied by Lift Engineering (Yan Lifts). The double chair was installed on the lower Gear Jammer run where the tube park is located today and was used as a beginner chair at a reduced speed. This area was also the first area to get permanent underground snow making pipes supplying snow making guns up the south side of the run. At the time the lifts were referred to only by number.
Blackcomb opened for skiing on December 6, 1980,][ along with the newly constructed village. To ensure guests could continue to easily access Whistler from the new village, three triple ]chairlift
An elevated passenger ropeway, or chairlift, is a type of aerial lift, which consists of a continuously circulating steel wire rope loop strung between two end terminals and usually over intermediate towers, carrying a series of chairs. Th ...
s were added to Whistler for the same season; the Village, Olympic, and Black Chairs which met up with the top of the Orange chair at the top of the men's downhill course. Whistler's original base at Alta Lake began to be referred to as Whistler Creek, or Creekside, after the creek that runs through the area.
Competition and buildout
Throughout the 1980s the two ski areas competed strongly for ticket sales among the village visitors, which led to a rapid buildout of new lifts that opened new areas and improved ride times.
In 1982, "Chair 6" (later rebranded Jersey Cream) opened in the Horstman Creek drainage on Blackcomb. Whistler cut new trails along the northern flank of the mountain. In 1983 Blackcomb acquired a used T-Bar from Fortress Mountain and installed it on a south-facing slope, in full view of Whistler Mountain. This 7th lift was coined the Seventh Heaven T-Bar and gave access to high alpine and glaciated terrain. It also gave Blackcomb the highest lift-serviced vertical drop of any ski area in North America, with the top of the lift at . Blackcomb promoted themselves as the "Mile High Mountain".
Whistler responded in 1986 with the opening of the Peak Chair to the summit of Whistler Mountain at , acquiring a Poma triple chairlift from the closed Pikes Peak
Pikes Peak is the highest summit of the southern Front Range of the Rocky Mountains, in North America. The ultra-prominent fourteener is located in Pike National Forest, west of downtown Colorado Springs, Colorado. The town of Manitou Sp ...
ski area in Colorado. Although not as high as Seventh Heaven, this lift opened up Whistler Mountain's alpine terrain, and allowed access to the Harmony Bowl area. The new terrain made Whistler the largest alpine ski area in North America.[
Skiers could buy a Blackcomb pass, a Whistler pass, or a Dual Mountain pass. Locals loved when tourists would ask "Where is Dual Mountain?"][
]
Intrawest buys Blackcomb
 In 1986, Blackcomb's assets and real estate rights were bought by fledgling real estate developer
In 1986, Blackcomb's assets and real estate rights were bought by fledgling real estate developer Intrawest
Intrawest Resorts Holdings, Inc was a developer and operator of destination resorts and a luxury adventure travel company. The company was founded in 1976 as a privately funded real estate development company. In 2006, Intrawest was purchased by ...
. Intrawest was an early developer of timeshare
A timeshare (sometimes called vacation ownership) is a property with a divided form of ownership or use rights. These properties are typically resort condominium units, in which multiple parties hold rights to use the property, and each owne ...
listings, and saw the potential in developing the ski resort with condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
assets as a timeshare destination.[''Intrawest'']
Intrawest immediately carried out massive upgrades on Blackcomb. They started by moving the Seventh Heaven T-Bar across the ridge to the Horstman Glacier, still running up to the peak, and supplemented it with the Showcase T-Bar to service Blackcomb Glacier. Doppelmayr replaced Seventh Heaven in its original alignment with a high-speed quad chairlift, and built two additional high-speed quads, the Wizard and Solar Coaster lifts, which cut the ride time from the base area to Rendezvous from 45 minutes to 15. The Rendezvous Restaurant was redubbed Base 2 and the moniker moved to the restaurant at the top of the Solar Coaster lift.
Renewed competition
In response to Blackcomb Mountain's construction of three high-speed quads, Whistler Mountain undertook one of the biggest ski-lift construction projects ever realized in Canada at the time, the construction of the Whistler Express Gondola. Carrying passengers vertically and horizontally over 63 support towers, the lift opened on November 24, 1988. In 1990 Whistler began upgrading its aging fleet of fixed grip chairlifts with the addition of its first high-speed quad chairlift. The Green Chair Express, which replaced the two Green Chairs, was built by Lift Engineering (Yan), and substantially cut long lift queues in the Green area of the mountain. A year later, Whistler Mountain replaced three double chairlifts and the original Creekside gondola with two high-speed quad chairlifts, the Quicksilver Express and Redline Express lifts, also built by Lift Engineering. In 1994, the Blue Chair was removed and replaced with a Poma
Poma, incorporated as Pomagalski S.A., and sometimes referred to as the Poma Group, is a French company which manufactures cable-driven lift systems, including fixed and detachable chairlifts, gondola lifts, funiculars, aerial tramways, peo ...
high speed quad named the Harmony Express, providing access to Little Whistler Peak.
In 1994, Blackcomb made what would be its last major lift expansion until 2018 with the replacement of the lower mountain triple chairlifts. Stoker was replaced with a high speed quad in a longer alignment known as the Excelerator Express, while Fitzsimmons and Cruiser were replaced with the Excalibur Gondola. The second is dubbed by some as the "gondola to nowhere" since it does not connect with any restaurant or access additional terrain. However, it allowed rapid access to Blackcomb for Whistler Village traffic, who previously had to take three or four chairlifts to Rendezvous (Fitzsimmons, Stoker, Cruiser, and Jersey Cream, with 3 of those being slower chairs; or Fitzsimmons, Wizard and Solar Coaster). The Excelerator also opened up a vast area of intermediate-difficulty terrain to the left of Solar Coaster and below Jersey Cream that was previously neglected and under-utilized, because skiers who traveled those slopes frequently had to go all the way to the bottom of the mountain, which was over-skied and icy.
This competition had driven development of the two mountains at a rate no other resorts could come close to matching. In 1992, ''Snow Country Magazine'' voted Whistler the Number One Ski Resort in North America. Similar No. 1 rankings quickly followed from other major magazines, and between 1992 and 2000 it won No. 1 ranking from one of the major magazines every year. In 1996, it became the only resort in history to be simultaneously named No. 1 by ''Snow Country'', ''SKI'' and ''Skiing'' magazines.[
]
Intrawest buys Whistler
 In 1997, the Whistler Mountain Ski Corporation was also bought out by
In 1997, the Whistler Mountain Ski Corporation was also bought out by Intrawest
Intrawest Resorts Holdings, Inc was a developer and operator of destination resorts and a luxury adventure travel company. The company was founded in 1976 as a privately funded real estate development company. In 2006, Intrawest was purchased by ...
.[
Like their expansion on Blackcomb, Intrawest immediately started a major build-out on Whistler. The Quicksilver lift was replaced with a ]Poma
Poma, incorporated as Pomagalski S.A., and sometimes referred to as the Poma Group, is a French company which manufactures cable-driven lift systems, including fixed and detachable chairlifts, gondola lifts, funiculars, aerial tramways, peo ...
gondola, the Creekside Gondola, while the Green Chair Express and Redline lifts were removed and replaced with Doppelmayr high-speed quad chair lifts, aptly named the Emerald Express and Big Red Express lifts. The original Roundhouse was demolished and a new lodge built in its place. Around this time Intrawest began marketing the two mountains as one large ski area under the name "Whistler-Blackcomb". On April 20, 1999, Whistler Blackcomb became the first North American ski resort to top 2 million skier visits in one season.
1998 saw the replacement of the Peak Chair with a high-speed quad. The original Peak Chair was renamed Franz's Chair and moved parallel to Big Red with a return station approximately halfway up Big Red's lift line. Franz's runs primarily in early and late season, when lower altitudes are not well covered. The Black Chair was replaced with a high-speed quad, the Garbanzo Express. The Fitzsimmons Express was added in 2000, following the line of the long-gone Village Chair and roughly paralleling the lower part of the gondola. The top of Fitzsimmons and the bottom of Garbanzo are co-located in the Village Gondola Olympic station area, providing extra lift capacity from the Whistler Village to the top of the mid-mountain zone in addition to the gondola itself. It is the second lift with the Fitszimmons name, the original lift being a triple chairlift replaced by Stage 1 of the Excalibur Gondola in 1994.
Starting in 2000, Intrawest started redeveloping the Creekside area with new village layout. Throughout, Intrawest also extensively developed the summertime attractions, notably golf and mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and p ...
. Today, Whistler Blackcomb averages 2 million visitors during the ski season, but another 2.5 during the summer.[
Whistler Blackcomb's 2006/2007 season saw Doppelmayr construct the Symphony Express, a high speed quad that begins towards the bottom of the Symphony Amphitheater and carries riders to the top of Piccolo. One of the original names suggested for this lift was Piccolo Express.
A more ambitious upgrade was the Peak 2 Peak Gondola, opened to provide a direct connection between the Roundhouse on Whistler and Rendezvous on Blackcomb. Peak-to-Peak opened for the first time on December 12, 2008, but low snowfall meant it was rockbound at the time. The first summer operation day was June 6, 2009.
]
Renewed Olympic bid
 As Whistler Blackcomb continued to win awards – eight consecutive by 2000 – the resort formed the basis of a renewed Olympics bid, this time for the
As Whistler Blackcomb continued to win awards – eight consecutive by 2000 – the resort formed the basis of a renewed Olympics bid, this time for the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May Doan Nancy GreeneWayne Gr ...
. Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, maki ...
also bid for the Canadian entry, as their equipment from the 1988 Winter Olympics
)
, nations = 57
, athletes = 1,423 (1,122 men, 301 women)
, events = 46 in 6 sports (10 disciplines)
, opening = February 13, 1988
, closing = February 28, 1988
, opened_by = Governor General Jeanne Sauvé
, cauldron ...
was already in place and allowed them to offer a low-cost bid, as did Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Communauté métrop ...
, which lost the 2002 bid. Calgary was eliminated in close voting on November 21, 1998, and Vancouver-Whistler won the second round of voting on December 3. In IOC voting Pyeongchang, South Korea
Pyeongchang (; in full, ''Pyeongchang-gun'' ; ) is a county in the province of Gangwon-do, South Korea, located in the Taebaek Mountains region. It is home to several Buddhist temples, including Woljeongsa. It is about east southeast of Se ...
won the initial round, which eliminated Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
, but in the second round on July 2, 2003, they won every one of Salzburg's supporters and bested Pyeongchang 56-53.
Reorganization
In 2006 Intrawest was purchased by the alternative asset management firm, Fortress Investment Group
Fortress Investment Group is an American investment management firm based in New York City. Fortress was founded as a private equity firm in 1998 by Wes Edens, Rob Kauffman, and Randal Nardone. When Fortress launched on the NYSE in February ...
. Three weeks before the opening of the 2010 Olympics, Fortress failed to make payment on its loan used to buy out Intrawest. This caused its creditors to force Intrawest to divest itself of several of its resort holdings in 2009 and 2010 which included a partial sale of Whistler Blackcomb, in order to reduce its debt load. This was achieved through a public offering of shares of Whistler Blackcomb Holdings Inc on the Toronto Stock Exchange in 2010. The net outcome of the reorganization is that Whistler Blackcomb Holdings is the managing partner and controls 75% of the partnerships which own the assets of Whistler Blackcomb. The remaining 25% of the partnerships are owned by Nippon Cable
is a Japanese corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo and is engaged in the design, production and installation of jig-back and material ropeways, gondola lifts, funiculars, chairlifts, car parking systems, ramp elevators and amusement pa ...
. Intrawest sold its remaining 24% stake in Whistler Blackcomb to KSL Capital Partners in 2012.
2010 Olympic Games
For the 2010 Winter Olympics, Whistler hosted the alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether ...
events. The men's skiing took place on the Dave Murray Downhill course, while women's skiing took place on a new course, which started on Wild Card, cut across Jimmy's Joker to Franz's Run and connected at the bottom of the Dave Murray Downhill. In order to serve the spectators and judges who needed to travel only to the timing area a short distance above the Creekside base, a temporary high-speed quad was built by Doppelmayr, known as the Timing Flats Express, in the Creekside base. This alleviated demand on the main gondola and other lifts that serve the starting areas, much higher up the mountain. After the Olympics, it was dismantled and sold to Sunshine Village, Alberta and replaced the Strawberry chair.
Blackcomb hosted the bobsled
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Fede ...
, luge and skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
events at The Whistler Sliding Centre. Whistler Olympic Park
The Whistler Olympic Park is the location of the Nordic events facilities for the 2010 Winter Olympics and is located in the Madeley Creek basin in the Callaghan Valley, west of Whistler, British Columbia, Canada. The facility hosted the biathlon, ...
hosted Olympic and Paralympic biathlon
The biathlon is a winter sport that combines cross-country skiing and rifle shooting. It is treated as a race, with contestants skiing through a cross-country trail whose distance is divided into shooting rounds. The shooting rounds are not ti ...
, cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreatio ...
, Nordic combined
Nordic combined is a winter sport in which athletes compete in cross-country skiing and ski jumping. The Nordic combined at the Winter Olympics has been held since the first ever Winter Olympics in 1924, while the FIS Nordic Combined World Cup ...
and ski jumping
Ski jumping is a winter sport in which competitors aim to achieve the farthest jump after sliding down on their skis from a specially designed curved ramp. Along with jump length, competitor's aerial style and other factors also affect the fin ...
, some distance to the south of the Creekside area in the Callaghan Valley.
The British Columbia government paid $600 million for major upgrades to the Sea-to-Sky Highway, which carried the majority of visitors to the alpine sites.
Notable accomplishments for Whistler athletes in the 2010 Olympic Games:
Ashleigh McIvor won the first gold ever in Ski Cross, an inaugural Olympic event;
Maëlle Ricker won gold in Snowboard Cross;
Siblings Mike and Britt Janyk competed in alpine skiing events on the mountain they grew up skiing;
Ski cross athlete Julia Murray, daughter of Dave Murray, competed in her first of likely many Olympic Games.
2010s
Summer 2010 had two lift construction projects at Creekside Base. The Timing Flats Express, used for passenger transport for the games, was removed and rebuilt as the Strawberry Express at Sunshine Village, Alberta, Canada. The second project was the construction of the Kadenwood Gondola, providing access to the Kadenwood Estate Homes from the Creekside base. Built by Doppelmayr-CTEC, it is a pulse gondola with 8 passenger cabins in two groups of 2.
Whistler Blackcomb announced plans on January 18, 2013 regarding plans for two high-speed detachable chairlift installations for the 2013–2014 Season. Ultimately, Doppelmayr constructed a new high speed six pack to replace the Harmony Express lift, upgrading its capacity from 2,400 to 3,600 persons per hour. The lift was installed ahead of the 2013–2014 winter season in the same location as the existing quad lift. Leitner-Poma reinstalled the original Harmony Express equipment in the Crystal Ridge zone of Blackcomb as the Crystal Ridge Express lift, replacing the shorter and slower Crystal triple chair lift. While the Crystal Ridge Express ends at the same location as that of the removed triple at Crystal Hut, it starts lower down the mountain just below the Blackcomb Glacier Road near the base of Rock n' Roll. The lift line for this lift had been cut many years prior in anticipation of construction, and allows for the runs in this area to be lapped without needing to return to the Excelerator Express.
In 2014, new 8 person cabins were bought to upgrade the Village Gondola, the existing cabins having been in service since 1988. Sigma, a subsidiary of Leitner-Poma who originally installed the lift, were contracted to produce the new cabins.
In May 2015, Whistler Blackcomb announced that both mountains would be declared smoke-free environments, President and CEO Dave Brownlie was quoted as saying "We have made the decision...to preserve the pristine alpine environment our guests come here for,". He continued to highlight a need for a safer workplace for employees and experience for guests, "We also recognize as a leader in the outdoor adventure and wellness industry and as the largest employer in the Whistler community, we have a responsibility to our guests and staff to provide a safe and healthy environment for work and play. We believe implementing this new policy aligns with this goal."
In April 2016, a $345-million three-phase development plan, named 'Renaissance,' was announced by the mountain, described as the "largest and most exciting investment in the Company's history." On-mountain improvements to skiing and snowboard activities includes a replacement of the Magic Chair with a new high-speed lift and the addition of night skiing in the same area during phase one. Additionally, during phase two and three the Franz, Catskinner, and Olympic chairs will be replaced with new high-speed lifts, a new gondola will be constructed from Creekside Base on Whistler Mountain, two new chairlifts will be added in Bagel and Khyber Bowls, and two new high-speed lifts will replace Wizard and Solar Coaster. The Renaissance developments reflect many of the proposals included in the resort master plan updated at the end of 2013.
Additional projects part of Renaissance include a 163,000-square-foot water park with water slides, a mountain roller coaster, a suspension bridge atop Whistler Mountain's peak, expansion of Whistler Mountain Bike Park, new parking facilities and housing developments, a new 'Blackcomb Grind' hiking trail, and a revitalization of Blackcomb's base. The start of this project will be subject to government approval and the renegotiation of the Company's master development agreements and negotiation of a proposed business partnership with local First Nations. Once approval is granted, Phase One projects and expansions will take two years to construct.
On August 8, 2016, it was announced that Whistler Blackcomb Holdings, which owned 75% of the Whistler and Blackcomb partnerships, would be sold to Vail Resorts
Vail Resorts, Inc. is an American mountain resort company headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado. The company is divided into three divisions. The mountain segment owns and operates 40 mountain resorts in four countries, Vail Resorts Hospitality o ...
of Colorado for C$1.4 billion, which also saw the addition of the resort to the Epic Pass.
For 2018, Doppelmayr carried out two major lift projects. On Blackcomb, a new two-stage ten passenger gondola replaced the Wizard Express and Solar Coaster chairlifts, with a midway turn station where the predecessor quads met. Like the Whistler Village and Excalibur Gondolas, it was built so that the two segments can be operated as one continuous lift or as two separate lifts. While this happened, the Emerald Express on Whistler was replaced with a high-speed six pack, and similar to Harmony five years earlier, the original lift was relocated to Blackcomb where it replaced the Catskinner lift. The Catskinner Express runs on a modified alignment compared to its predecessor, starting below the Magic Castle whereas the triple started at the base of the Nintendo Terrain Park.
Major Events
*2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May Doan Nancy GreeneWayne Gr ...
* FIS Freestyle World Ski Championships 2001
*FIS Snowboarding World Championships 2005 The FIS Snowboarding World Championships 2005 took place between January 16 and January 22 in Whistler-Blackcomb, near Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The venues would be part of the 2010 Winter Olympics at Cypress Mountain.
Results
Men' ...
*FIS Alpine Ski World Cup
The FIS Alpine Ski World Cup is the top international circuit of alpine skiing competitions, launched in 1966 by a group of ski racing friends and experts which included French journalist Serge Lang and the alpine ski team directors from France ...
– 1975
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. ...
, 1982
Events January
* January 1 – In Malaysia and Singapore, clocks are adjusted to the same time zone, UTC+8 (GMT+8.00).
* January 13 – Air Florida Flight 90 crashes shortly after takeoff into the 14th Street Bridge in Washington, D.C., Un ...
, 1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast As ...
, 1986
The year 1986 was designated as the International Year of Peace by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
**Aruba gains increased autonomy from the Netherlands by separating from the Netherlands Antilles.
**Spain and Portugal enter ...
, 1989
File:1989 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Cypress structure collapses as a result of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, killing motorists below; The proposal document for the World Wide Web is submitted; The Exxon Valdez oil tanker ru ...
, 1993
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peace ...
, 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson Ma ...
, 1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake strike ...
, 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing ...
* FIS Freestyle Skiing World Cup – 1982
Events January
* January 1 – In Malaysia and Singapore, clocks are adjusted to the same time zone, UTC+8 (GMT+8.00).
* January 13 – Air Florida Flight 90 crashes shortly after takeoff into the 14th Street Bridge in Washington, D.C., Un ...
, 1991
File:1991 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Boris Yeltsin, elected as Russia's first president, waves the new flag of Russia after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, orchestrated by Soviet hardliners; Mount Pinatubo erupts in the ...
, 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment building in Amsterdam after two of its engines ...
, 1993
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peace ...
, 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson Ma ...
, 1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake strike ...
, 1996
File:1996 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: A bomb explodes at Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, set off by a radical anti-abortionist; The center fuel tank explodes on TWA Flight 800, causing the plane to crash and killing everyone on b ...
, 1997
File:1997 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The movie set of ''Titanic'', the highest-grossing movie in history at the time; ''Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'', is published; Comet Hale-Bopp passes by Earth and becomes one of ...
, 1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 – The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently s ...
, 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school s ...
, 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from ...
, 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a multi-national coalition in an invasion of Afghanistan ...
, 2002
File:2002 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 2002 Winter Olympics are held in Salt Lake City; Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother and her daughter Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon die; East Timor gains independence from Indonesia and ...
Major Lifts
Winter Lifts
Summer Lifts
Terrain Aspects
*North: 55%
*West: 40%
*East: 2%
*South: 3%
Other facilities
Whistler Mountain Bike Park
 The Whistler Mountain Bike Park celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2008. Having consistently grown since its inception, it sees an average of 100,000 bikers each summer.
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park uses the Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo quad chairlifts, as well as the Whistler Village
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2008. Having consistently grown since its inception, it sees an average of 100,000 bikers each summer.
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park uses the Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo quad chairlifts, as well as the Whistler Village Gondola
The gondola (, ; vec, góndoła ) is a traditional, flat-bottomed Venetian rowing boat, well suited to the conditions of the Venetian lagoon. It is typically propelled by a gondolier, who uses a rowing oar, which is not fastened to the hull ...
and Creekside Gondola to shuttle bikers to around midstation, at . The park has 47+ trails for all skill levels totaling 250 km + of trails. There are smooth trails with gentle banked corners for beginners, steep twisty trails for intermediates, tight trails with jumps and stunts for advanced riders, and challenging trails with giant jumps, drops, and root-strewn terrain for the experts.
 During the summer, high speed quad chairlifts (Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo) used by the bike park have every second chair replaced with a bike rack. These racks fit four bikes, three in grooves and one on a hook on the side of the chair. The bikers then get on the next chair which is a normal passenger carrier.
The bike park has three zones: the Fitzsimmons Zone (the lower zone), the Garbanzo Zone (the upper zone) and the Creekside Zone. All riders take either the Village
During the summer, high speed quad chairlifts (Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo) used by the bike park have every second chair replaced with a bike rack. These racks fit four bikes, three in grooves and one on a hook on the side of the chair. The bikers then get on the next chair which is a normal passenger carrier.
The bike park has three zones: the Fitzsimmons Zone (the lower zone), the Garbanzo Zone (the upper zone) and the Creekside Zone. All riders take either the Village Gondola
The gondola (, ; vec, góndoła ) is a traditional, flat-bottomed Venetian rowing boat, well suited to the conditions of the Venetian lagoon. It is typically propelled by a gondolier, who uses a rowing oar, which is not fastened to the hull ...
or the Fitzsimmons quad to the Olympic Station area. Then intermediate and advanced riders can take the Garbanzo quad up further to the Garbanzo zone. Garbanzo riders can then return to midstation or Whistler Village, the base of the bike park. The Creekside Zone can be accessed via the Creekside Gondola or by riding through the Garbanzo Zone. From the top of Garbanzo to the village is an impressive vertical descent; eclipsed only by the descent from the top gondola station or the top of the Peak Chair, the highest accessible point on the mountain. "A-Line" is the most well-known track. The Boneyard Slopestyle Course is part of the Fitzsimmons Zone and is located at the very bottom of the bike park, visible from the base of Whistler Mountain. The Boneyard features a collection of high-intermediate and advanced slopestyle features, including drops, dirt jumps, and more.
Each summer since 2004, the park hosts Crankworx, the largest annual freeride mountain biking competition in North America. Another major competition, Harvest Huckfest, was held there each fall from 2002 to 2008.
Whistler Blackcomb's Tube Park
For the 2005–06 ski season, Blackcomb Mountain opened the Tube Park to allow for recreational tubing at the resort. The tube park is located at Base II alongside the Village Run.
Incidents
Quicksilver Express grip failure, December 23, 1995
The lift operator on the Quicksilver lift pressed the button to make a routine stop, to allow a fallen skier to get out of the way of the unloading ramp. Instead, the emergency brake activated, sending shockwaves down the cable. Grips on at least two of the chairs slipped, and caused chairs to slide down the cable and slam into each other. In all, eight were injured, and two were killed in one of the worst ski lift accidents in North America.[Nixon, Emily ]
Disaster and Emergency Management: The Quicksilver Chairlift Incident
'', Graduating Essay, University of Victoria, Geography Dept., April 2004
The lift's manufacturer, Lift Engineering/Yan, entered bankruptcy after the incident in July 1996. The cause was found to be a design fault in the Yan detachable grip. The Quicksilver lift was removed and replaced by the Creekside Gondola. The other two Yan high speed quads on Whistler, Greenline and Redline, were replaced with Doppelmayr high speed quads the year after that, with all new terminals, grips and chairs, and renamed as the Emerald Express and Big Red Express respectively.
Excalibur Gondola Collapse, December 16, 2008
The Excalibur gondola had a major malfunction on December 16, 2008, when the upper portion of one of the lift towers detached and collapsed, causing several of the gondola cabins to drop near to the ground, leaving 53 people trapped on the lower section of the lift line. Firefighters rescued passengers from a cabin dangling over Fitzsimmons Creek, and from another gondola that landed on a bus shelter. The third cabin had crashed into the trees, narrowly missing a condominium. Twelve people suffered minor injuries. According to Whistler-Blackcomb, a joint in the tower separated due to the buildup of ice from water that had seeped into the tower. The undamaged upper half of the lift running from Blackcomb's Base 2 was reopened on Saturday December 20. After repairs were made to the collapsed tower, the whole lift was back in service on Wednesday December 24.
Harmony Express grip failure, February 18, 2009
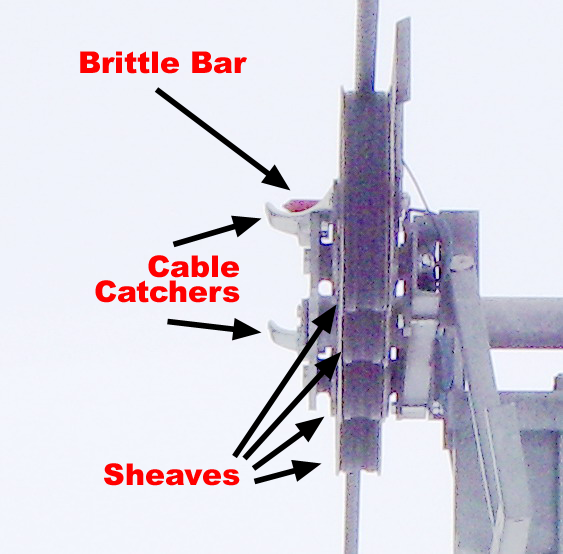 The lift operations team on Whistler's Harmony Express had been experiencing some problems with the lift during the day of Wednesday February 18, 2009. That night, a grooming machine operator found a chair had fallen from the lift at tower 11.
At the tops of the lift towers are a series of wheels known as sheaves, or sheave trains as there are almost always more than one in a row. Towers typically have two sheave trains, one for the uphill-moving side of the cable loop, and one for the downhill side. Upon inspection the next morning, maintenance crews discovered that the sheave train on the downhill side of tower 11 had failed, and that the sheave had turned into the path of a chair and forced it off the cable. The cause was later determined to be a failed bolt, and all of the bolts were replaced.
The lift reopened on Sunday, February 22, 2009. The affected chair No. 37 was temporarily removed from operation; it has since been replaced.
The lift operations team on Whistler's Harmony Express had been experiencing some problems with the lift during the day of Wednesday February 18, 2009. That night, a grooming machine operator found a chair had fallen from the lift at tower 11.
At the tops of the lift towers are a series of wheels known as sheaves, or sheave trains as there are almost always more than one in a row. Towers typically have two sheave trains, one for the uphill-moving side of the cable loop, and one for the downhill side. Upon inspection the next morning, maintenance crews discovered that the sheave train on the downhill side of tower 11 had failed, and that the sheave had turned into the path of a chair and forced it off the cable. The cause was later determined to be a failed bolt, and all of the bolts were replaced.
The lift reopened on Sunday, February 22, 2009. The affected chair No. 37 was temporarily removed from operation; it has since been replaced.
Whistler T-Bars summer maintenance incident, August 31, 2009
On Monday, August 31, 2009, two Lift Maintenance employees were injured when the lift began to move, after being given the go-ahead while a maintenance person was safety-harnessed to the tower. The person remained attached to both the tower and the maintenance carrier while the second employee was secured to the carrier. The safety harness ended up pulling so hard on the maintenance carrier, the carrier became detached from the cable and dropped to the rocky ground below, severely injuring the worker in it. The employee hanging from the tower only received bruises.
Big Red Express Bolt Failure, December 6, 2009
On Sunday, December 6, 2009, at 8:55 am, a passenger aboard the Big Red Express on Whistler Mountain noticed that a sheave train had broken off Tower 31 and had fallen to the ground. They immediately notified the lift operator at the top terminal (2 towers away) and Whistler Blackcomb Lift Maintenance department. After almost a 30-minute inspection, they determined the issue was not severe enough to evacuate the lift. The lift was run at low speed to evacuate all passengers. All passengers were finally off the lift just before 10 am. The lift was closed down for the day, repaired, and back in operation Monday, December 7.
Photographs
File:Blackcomb Mountain-2007.jpg, A view of 7th Heaven on Blackcomb Mountain from Whistler Mountain.
File:Blackcomb 1.jpg
File:Whistler Mountain 1.jpg
File:Whistler Mountain 3.jpg
File:Whistler Panorama -2007.jpg, Panorama of the two mountains
File:BlackcombWizardExpressLift.jpg, The Wizard Express quad lift at the base of Blackcomb mountain (since removed)
File:Jersey Cream Whistler BC Canada.JPG, View from top of Jersey Cream run with Jersey Cream Bowl in the background
File:Whistler Peak Panorama.jpg, 360 degree panorama from the top of Whistler Peak
File:The Couloir Run on Blackcomb Mountain.jpg, The Couloir Run on Blackcomb Mountain
See also
* Whistler, British Columbia
Whistler ( Lillooet/Ucwalmícwts: Cwitima, ; Squamish/Sḵwx̱wú7mesh: Sḵwiḵw, ) is a resort municipality in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mo ...
(the Resort Municipality of Whistler)
* Whistler Mountain
Whistler Mountain is a mountain in the Fitzsimmons Range of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, located on the northwestern edge of Garibaldi Provincial Park. It is the location of the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort and the town of Whi ...
(the geographical feature)
* Blackcomb Peak (the geographical feature)
* Garibaldi Provincial Park
* Peak 2 Peak Gondola
* Intrawest
Intrawest Resorts Holdings, Inc was a developer and operator of destination resorts and a luxury adventure travel company. The company was founded in 1976 as a privately funded real estate development company. In 2006, Intrawest was purchased by ...
* Jack Souther
References
Further reading
* (''Stats'')
"Mountain Stats"
Whistler Blackcomb home page
* (''History'')
Whistler Blackcomb home page
* (''Look'')
"A Look at Whistler History"
Whistler Museum & Archives Society
* (''Walking''), "2010 Village Olympic Walking Tour", Whistler Museum & Archives Society
* (''Intrawest'')
"Intrawest Corporation Quick Facts"
Intrawest Corp.
External links
Vancouver2010.com profile
Whistler Blackcomb official site
{{Intrawest resorts
Venues of the 2010 Winter Olympics
Olympic alpine skiing venues
Ski areas and resorts in British Columbia
Whistler, British Columbia
Vail Resorts
Companies formerly listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange
 In 1986, Blackcomb's assets and real estate rights were bought by fledgling real estate developer
In 1986, Blackcomb's assets and real estate rights were bought by fledgling real estate developer  In 1997, the Whistler Mountain Ski Corporation was also bought out by
In 1997, the Whistler Mountain Ski Corporation was also bought out by  As Whistler Blackcomb continued to win awards – eight consecutive by 2000 – the resort formed the basis of a renewed Olympics bid, this time for the
As Whistler Blackcomb continued to win awards – eight consecutive by 2000 – the resort formed the basis of a renewed Olympics bid, this time for the  The Whistler Mountain Bike Park celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2008. Having consistently grown since its inception, it sees an average of 100,000 bikers each summer.
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park uses the Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo quad chairlifts, as well as the Whistler Village
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2008. Having consistently grown since its inception, it sees an average of 100,000 bikers each summer.
The Whistler Mountain Bike Park uses the Fitzsimmons and Garbanzo quad chairlifts, as well as the Whistler Village  The lift operations team on Whistler's Harmony Express had been experiencing some problems with the lift during the day of Wednesday February 18, 2009. That night, a grooming machine operator found a chair had fallen from the lift at tower 11.
At the tops of the lift towers are a series of wheels known as sheaves, or sheave trains as there are almost always more than one in a row. Towers typically have two sheave trains, one for the uphill-moving side of the cable loop, and one for the downhill side. Upon inspection the next morning, maintenance crews discovered that the sheave train on the downhill side of tower 11 had failed, and that the sheave had turned into the path of a chair and forced it off the cable. The cause was later determined to be a failed bolt, and all of the bolts were replaced.
The lift reopened on Sunday, February 22, 2009. The affected chair No. 37 was temporarily removed from operation; it has since been replaced.
The lift operations team on Whistler's Harmony Express had been experiencing some problems with the lift during the day of Wednesday February 18, 2009. That night, a grooming machine operator found a chair had fallen from the lift at tower 11.
At the tops of the lift towers are a series of wheels known as sheaves, or sheave trains as there are almost always more than one in a row. Towers typically have two sheave trains, one for the uphill-moving side of the cable loop, and one for the downhill side. Upon inspection the next morning, maintenance crews discovered that the sheave train on the downhill side of tower 11 had failed, and that the sheave had turned into the path of a chair and forced it off the cable. The cause was later determined to be a failed bolt, and all of the bolts were replaced.
The lift reopened on Sunday, February 22, 2009. The affected chair No. 37 was temporarily removed from operation; it has since been replaced.