Western Xia coinage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The
The
宁夏首次出土篆书乾祐元宝。
朱 浒 盛世隆泉 Published: 25 April 2016 by Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of
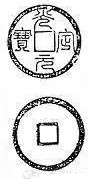 In early September of the year 1984 a cache of old cash coins was unearthed in the
In early September of the year 1984 a cache of old cash coins was unearthed in the
 For a long it was believed that the Guangding Yuanbao cash coins produced towards the very end of the Western Xia period were the only cash coins with seal script inscriptions produced by the empire. However, in the 2012, a Chinese farmer had uncovered a cache of Western Xia era cash coins in Tongxin County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and among these cash coins was a unique Qianyou Yuanbao (乾佑元寶) with a seal script inscription. This cash coin has a diameter of 25.4 millimeters, a thickness of 1.5 millimeters and has a weight of 3.3 grams, its inscription is read clockwise.
Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of
For a long it was believed that the Guangding Yuanbao cash coins produced towards the very end of the Western Xia period were the only cash coins with seal script inscriptions produced by the empire. However, in the 2012, a Chinese farmer had uncovered a cache of Western Xia era cash coins in Tongxin County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and among these cash coins was a unique Qianyou Yuanbao (乾佑元寶) with a seal script inscription. This cash coin has a diameter of 25.4 millimeters, a thickness of 1.5 millimeters and has a weight of 3.3 grams, its inscription is read clockwise.
Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of

 The
The Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
was a Tangut-led Chinese dynasty
Dynasties in Chinese history, or Chinese dynasties, were Hereditary monarchy, hereditary Monarchy, monarchical regimes that ruled over China during much of History of China, its history. From the Yu the Great#Historicity, legendary inauguration ...
which ruled over what are now the northwestern Chinese subdivisions of Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
, Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
, eastern Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
, northern Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichu ...
, northeastern Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, southwest Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, and southernmost Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
from 1032 until 1227 when they were destroyed by the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
. The country was established by the Tangut people;1984 "Who are the Tanguts? Remarks on Tangut Ethnogenesis and the Ethnonym Tangut." Journal of Asian History 18:1: 78-89.1994 "Hsi-Hsia." The Cambridge History of China, Volume 6. Eds. Denis C. Twitchett and Herbert Franke. Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
likewise its earliest coins were escribed with Tangut characters, while later they would be written in Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
. Opposed to Song dynasty coins that often read top-bottom-right-left, Western Xia coins exclusively read clockwise. Despite the fact that coins had been cast for over a century and a half, very little were actually produced and coins from Western Xia are a rarity today. S.W. Bushell "The Hsi Hsia Dynasty of Tangut, Their Money and Peculiar Script" (Journal of the North China Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society
The Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, commonly known as the Royal Asiatic Society (RAS), was established, according to its royal charter of 11 August 1824, to further "the investigation of subjects connected with and for the en ...
Vol.XXX (1895-1896) pp. 142-160. Although the Western Xia cast their own coins barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists distingu ...
remained widely used.
Originally from 1053 until 1068 the inscription of its cash coins
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-immed ...
were exclusively written in the Tangut script, and between 1068 and 1206 coins were cast with both Tangut and Chinese inscriptions, but after 1206 only Chinese characters were used. Compared to Liao dynasty coinage
The Liao dynasty was a Khitan-led dynasty of China that ruled over parts of Northern China, Manchuria, the Mongolian Plateau, northern Korean Peninsula, and what is modern-day Russian Far East from 916 until 1125 when it was conquered by the ...
, coins from Western Xia were cast in superior quality, though only bronze and iron coins produced between 1149 and 1193 were cast in high quantities.
After Western Xia was annexed by the Mongols, Tangut inscriptions appeared only on a single Yuan dynasty coin.
History
Following the establishment of the Western Xia state, the Tangut people, in an effort to revive their original ethnic and national culture, had rejected bothChinese characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
and Chinese fashion
Chinese clothing includes both the traditional hanfu and modern variations of indigenous Chinese dress as recorded by the artifacts and some traditional arts of Chinese culture. Chinese clothing has been shaped through its dynastic traditions, as ...
.“China Numismatics” (2016年1期)宁夏首次出土篆书乾祐元宝。
朱 浒 盛世隆泉 Published: 25 April 2016 by Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of
East China Normal University
East China Normal University (ECNU) is a comprehensive Public university, public research university in Shanghai, China. It was formed in 1951 by the merger of the Great China University (est. 1924) and Kwang Hua University (est. 1925) and origin ...
(华东师范大学艺术研究所) Retrieved: 20 June 2017. (in Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language of ...
using Simplified Chinese characters
Simplified Chinese characters are standardized Chinese characters used in mainland China, Malaysia and Singapore, as prescribed by the ''Table of General Standard Chinese Characters''. Along with traditional Chinese characters, they are one o ...
) The Tangut people had soon created an indigenous writing system, this writing system was exclusively used on the earlier Western Xia era cash coins. These early Tangut cash coins had inscriptions like śjɨj ljo ljɨ̣ dzjɨj () and tha nej ljɨ̣ dzjɨj (). The Tangut script inscription on these early Western Xia cash coins always read clockwise (top-right-bottom-left), with all of these coins having inscriptions that translate into English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
as "Precious Coin of the" followed by the reign title. Cash coins with Tangut inscriptions are known to have been produced during six different reign periods, but it's possible that more variants have been produced.
Cash coins with Tangut inscriptions have been discovered in the modern era such as the Zhengde Baoqian type in the year 1999.
During the Qianyou period (1139–1193) of the reign of Emperor Renzong the political and military stability as well as the growing economy in Western Xia had allowed for the country to prosper. Emperor Renzong would hold education in a high esteem and was responsible for the establishment of schools including an Imperial Academy. Emperor Renzong had further established an imperial examination
The imperial examination (; lit. "subject recommendation") refers to a civil-service examination system in Imperial China, administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by ...
system in the style of that of the Chinese Empire. During the Qianyou era the Tangut government had also gained greater respect for both Confucian philosophy
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
and the culture of the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (960–1279 AD) was a culturally rich and sophisticated age for China. It saw great advancements in the visual arts, music, literature, and philosophy. Officials of the ruling bureaucracy, who underwent a strict and extensive exa ...
. Much art from the Western Xia Empire, including its coinage was largely based on that from China.
This era also saw the production of Song dynasty-style cash coins, these Song dynasty-style cash coins also followed the Song tradition of casting “Matched Coins” (對錢, ''duì qián'', 對品, ''duì pǐn'', 和合錢, ''hé hé qián''), where two or more different Chinese calligraphy
Chinese calligraphy is the writing of Chinese characters as an art form, combining purely visual art and interpretation of the literary meaning. This type of expression has been widely practiced in China and has been generally held in high est ...
styles were used on cash coins that had the same Chinese era title (or reign period).
These Chinese calligraphic styles included clerical script
The clerical script (; Japanese: 隷書体, ''reishotai''; Korean: 예서 (old spelling 례서); Vietnamese: lệ thư), sometimes also chancery script, is a style of Chinese writing which evolved from the late Warring States period to the Qi ...
, regular script
Regular script (; Hepburn: ''kaisho''), also called (), (''zhēnshū''), (''kǎitǐ'') and (''zhèngshū''), is the newest of the Chinese script styles (popularized from the Cao Wei dynasty c. 200 AD and maturing stylistically around the ...
, running script
Semi-cursive script (), also known as running hand script, is a style of calligraphy which emerged in China during the Han dynasty (3rd century BC – 3rd century AD). The style is used to write Chinese characters and is abbreviated slightly w ...
, grass script
Cursive script (; , ''sōshotai''; , ''choseo''; ), often mistranslated as grass script, is a script style used in Chinese and East Asian calligraphy. It is an umbrella term for the cursive variants of the clerical script and the regular scri ...
, and rarely seal script
Seal script, also sigillary script () is an ancient style of writing Chinese characters that was common throughout the latter half of the 1st millennium BC. It evolved organically out of the Zhou dynasty bronze script. The Qin variant of seal ...
.
List of coins produced by the Western Xia
Thecash coins
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-immed ...
produced under the Western Xia were cast in either Tangut or Chinese.
Coins with Tangut inscriptions:in Li Fanwen (), Xia-Han Zidian () Tangut-Chinese Dictionary(Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
: Zhongguo Shehui Kexue Chubanshe, 1997).
Coins with Chinese inscriptions:
Usage of seal script on Western Xia cash coins
Many Chinese and other Oriental coin catalogues through the centuries had documented the cash coins that were cast by the Western Xia Empire to be in regular script or running scripts but not in seal script. This changed in September of the year 1984 with the discovery of a seal script Guangding Yuanbao cash coin and again in 2012 with the discovery of a seal script Qianyou Yuanbao cash coin. While a multitude of seal script Guangding Yuanbao cash coins have been discovered, only a single Qianyou Yuanbao cash coin has been known to exist. Today these newly discovered variants have been added to newer Chinese coin catalogues as variants of the "matched cash coins" of the Western Xia Empire. In the modern era the discovery of a new Chinese coin variety is a rare occurrence to happen, so the discovery of the seal script Qianyou Yuanbao has caused a great amount of excitement among Chinese cash coinage collectors.Guangding Yuanbao
 In early September of the year 1984 a cache of old cash coins was unearthed in the
In early September of the year 1984 a cache of old cash coins was unearthed in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1 ...
, among these cash coins was a Guangding Yuanbao (光定元寶) with an inscription that was written in seal script
Seal script, also sigillary script () is an ancient style of writing Chinese characters that was common throughout the latter half of the 1st millennium BC. It evolved organically out of the Zhou dynasty bronze script. The Qin variant of seal ...
. These cash coins were unearthed due to Helanshan flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
s which occurred near Yinchuan
Yinchuan (, ; ) is the capital of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China, and was the capital of the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty. It has an area of and a total population of 2,859,074 according to the 2020 Chinese census, and its built- ...
, which was historically known as Xingqing
Xingqing District (, Xiao'erjing: ) is one of three District (China), urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Yinchuan, the capital of Ningxia, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Northwest China, Northwest China, bordering Inner Mongolia to th ...
and was the capital city of the Western Xia Empire. Among the cash coins unearthed during this event were Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
, Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
, Song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetitio ...
, Khitan Liao
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yel� ...
, Jurchen Jin Jurchen may refer to:
* Jurchen people, Tungusic people who inhabited the region of Manchuria until the 17th century
** Haixi Jurchens, a grouping of the Jurchens as identified by the Chinese of the Ming Dynasty
** Jianzhou Jurchens, a grouping of ...
, and many other types of cash coins. The rarest earlier documented coins found after these flash floods were Liao dynasty coins and gold coins, but at the time the seal script Guangding Yuanbao was never seen before and thought to be unique. This first seal script Guangding Yuanbao cash coin has a diameter of 25.3 millimeters, a thickness of 1.4 millimeters, and a weight of 4.3 grams.
In the year 2002 a second specimen was dug up in the province of Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichu ...
, this was followed by the discovery of a third specimen found in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
. Later excavations in the Tongxin County
Tongxin County (, Xiao'erjing: طْوثٍ ثِيًا) is a county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Wuzhong in the central part of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, bordering Gansu province ...
, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region had brought this number up to more than ten.
Qianyou Yuanbao
 For a long it was believed that the Guangding Yuanbao cash coins produced towards the very end of the Western Xia period were the only cash coins with seal script inscriptions produced by the empire. However, in the 2012, a Chinese farmer had uncovered a cache of Western Xia era cash coins in Tongxin County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and among these cash coins was a unique Qianyou Yuanbao (乾佑元寶) with a seal script inscription. This cash coin has a diameter of 25.4 millimeters, a thickness of 1.5 millimeters and has a weight of 3.3 grams, its inscription is read clockwise.
Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of
For a long it was believed that the Guangding Yuanbao cash coins produced towards the very end of the Western Xia period were the only cash coins with seal script inscriptions produced by the empire. However, in the 2012, a Chinese farmer had uncovered a cache of Western Xia era cash coins in Tongxin County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and among these cash coins was a unique Qianyou Yuanbao (乾佑元寶) with a seal script inscription. This cash coin has a diameter of 25.4 millimeters, a thickness of 1.5 millimeters and has a weight of 3.3 grams, its inscription is read clockwise.
Dr. Zhu Hu (朱浒) of the Art Research Institute of East China Normal University
East China Normal University (ECNU) is a comprehensive Public university, public research university in Shanghai, China. It was formed in 1951 by the merger of the Great China University (est. 1924) and Kwang Hua University (est. 1925) and origin ...
published in “Volume One of China Numismatics” () an assessment of this cash coin. According to Dr. Zhu Hu this cash coin is inspired by the seal script "matched cash coins" from the Northern Song dynasty. Dr. Zhu Hu notes that the seal script character "You" (祐) is written in the same method as that of the Jingyou Yuanbao (景祐元寶), Jiayou Yuanbao (嘉祐元寶), and the Yuanyou Tongbao (元祐通寶) cash issued by the Song dynasty in the course of a century from the tenth century until the twelfth century. While the seal script characters "Yuan" (元) and "Bao" (寶) similar to the "Yuan" and "Bao" characters found on the Xuanhe Yuanbao (宣和元寶), and its "Bao" (寶) character looks similar to that of the seal script version of the Zhenghe Tongbao (政和通寶).
The discovery of this unique seal script Qianyou Yuanbao cash coin also means that this inscription is the only Western Xia Empire cash coin that is known to exist in three different Chinese calligraphic varieties, in the form of regular script, running script, and seal script.
According to Gary Ashkenazy from the website ''Primaltrek'', he claims that the fact that this unique seal script Qianyou Yuanbao cash coin is very well-made, in his opinion lends credence to the speculation that this coin might have been cast as a trial piece, or pattern coin
A pattern coin is a coin which has not been approved for release, but produced to evaluate a proposed coin design. They are often off-metal strike (using metals of lower value to test out the dies), to proof standard or piedforts. Many coin col ...
, and that only very few cash coins with this inscription and calligraphic style might have been actually cast for general circulation.
Differences in style between the seal script Guangding Yuanbao and Qianyou Yuanbao cash coins
The seal script "Yuan" (元) character of the Guangding Yuanbao cash coins tends to have more "twists and turns" than the more "dignified" version of the "Yuan" on the seal script version of the Qianyou Yuanbao, furthermore, the "Yuan" character inscribed on the bottom of the Guangding Yuanbao touches the rim of the coin, which the "Yuan" on the Qianyou Yuanbao doesn't touch the rim of the coin. Another difference between these two cash coins is the fact that the "crown" of the seal script "Bao" (宝) character of the Guangding Yuanbao has a more "square" shape compared to the more "round" shape of the "Bao" found on the seal script version of the Qianyou Yuanbao. All of these differentiating characteristics are also found on the seal script "matched cash coins" produced by the Song dynasty.Hoards of Western Xia cash coins
* In the year 1972 a Da'an Baoqian (大安寶錢, ) cash coin withTangut script
The Tangut script ( Tangut: ; ) was a logographic writing system, used for writing the extinct Tangut language of the Western Xia dynasty. According to the latest count, 5863 Tangut characters are known, excluding variants. The Tangut character ...
was found at the Liao Shangjing site, Lindong
Lindong () is a town in the Balin Left Banner, Chifeng, within the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. The town has an area of , and a population of 68,000, according to a 2020 publication by the Balin Left Banner ...
, Baarin Left Banner
Baarin Left Banner ( Mongolian: ''Baɣarin Jegün qosiɣu''; ), or Bairin, is a banner of eastern Inner Mongolia, China, under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Chifeng. The banner spans an area of 6,644 square kilometers, and ...
, Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
.
See also
*History of Chinese currency
The history of Chinese currency spans more than 3000 years. Currency of some type has been used in China since the Neolithic age which can be traced back to between 3000 and 4500 years ago. Cowry shells are believed to have been the earliest ...
* Zhou dynasty coinage
Chinese coinage during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods includes some of the earliest coins produced in the world. However, they were mostly not the typical round shape of modern coins. They included cowrie shells, Ant-nose coin ...
* Ancient Chinese coinage
Ancient Chinese coinage includes some of the earliest known coins. These coins, used as early as the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BCE), took the form of imitations of the cowrie shells that were used in ceremonial exchanges. The ...
* Liao dynasty coinage
The Liao dynasty was a Khitan-led dynasty of China that ruled over parts of Northern China, Manchuria, the Mongolian Plateau, northern Korean Peninsula, and what is modern-day Russian Far East from 916 until 1125 when it was conquered by the ...
* Southern Song dynasty coinage
The Southern Song dynasty refers to an era of the Song dynasty after Kaifeng was captured by the Jurchen Jin dynasty in 1127. The government of the Song was forced to establish a new capital city at Lin'an (present day Hangzhou) which wasn't n ...
* Jin dynasty coinage (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty was a Jurchen-led dynasty of China that ruled over northern China and Manchuria from 1115 until 1234. After the Jurchens defeated the Liao dynasty and the Northern Song dynasty, they would continue to use their coins for da ...
* Yuan dynasty coinage
The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-ruled Chinese dynasty which existed from 1271 to 1368. After the conquest of the Western Xia, Western Liao, and Jin dynasties they allowed for the continuation of locally minted copper currency, as well as allowi ...
* Ming dynasty coinage
Chinese coinage in the Ming dynasty saw the production of many types of coins. During the Ming dynasty of China, the national economy was developed and its techniques of producing coinage were advanced. One early period example is the Bronze ...
* Qing dynasty coinage
Qing dynasty coinage (; Manchu: ; Möllendorff: ''Daicing jiha'') was based on a bimetallic standard of copper and silver coinage. The Manchu-led Qing dynasty was established in 1636 and ruled over China proper from 1644 until it was overthro ...
Notes
References
Sources
* 1994. “西夏的衡制與幣制 Xixia de hengzhi yu bizhi (The weight and coin systems of the West Xia)” 《中國錢幣》 Zhongguo qianbi / China Numanistics 1994.1: 3-8,17, 81 (inMandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
)
* 2002. “西夏货币制度概述 (The Outline of monetary system of West Xia dynasty).” 《中國錢幣》 Zhongguo qianbi / China Numanistics 2002.3:43-46 (in Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
)
* Hartill, David (September 22, 2005). ''Cast Chinese Coins.'' Trafford
Trafford is a metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England, with an estimated population of 235,493 in 2017. It covers Retrieved on 13 December 2007. and includes the area of Old Trafford and the towns of Altrincham, Stretford, Ur ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
: Trafford Publishing. .
* Niú Dáshēng (牛达生) ''Research into Western Xia Coins.'' (2013)
{{Western Xia topics
Coinage
Coinage may refer to:
* Coins, standardized as currency
* Neologism, coinage of a new word
* ''COINage'', numismatics magazine
* Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin
* Protologism, coinage of a seldom used new term
See also
* Coining (disambiguatio ...
Tangut history
Coins of China
Cash coins
Currencies of China
Medieval currencies
Chinese numismatics