|
Li Fanwen
Li Fanwen () (born November 1932) is a Chinese linguist and Tangutologist. Biography Li Fanwen was born in Xixiang County, Shaanxi in November 1932. After leaving school, he worked for several years before going to Beijing to study Tibetan at the Central College for Nationalities, from which he graduated in 1956. He stayed on at the college as a research student in the History department until he graduated in 1959. By this time, he had become fascinated with the extinct and only semi-deciphered Tangut script, and in 1960 he decided to move to Yinchuan in Ningxia, the former capital of the Tangut Empire, to devote himself to Tangut studies, but his wife was unwilling to accompany him, so they divorced. When Li Fanwen arrived at Ningxia, he was disappointed to find that there were no opportunities to study the Tangut script and language, and instead he was assigned to Ningxia Education College to research the Hui people. Two years later, he was reassigned to the Ningxia Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xixiang County
Xixiang County () is a county under the administration of Hanzhong City, in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Sichuan province to the southwest. Its administrative center, Xixiang, formerly known as Hsihsiang, lies on the Muma River. The county contains fourteen towns, eleven townships, and covers an area of . Administrative divisions As 2019, Xixiang County is divided to 2 subdistricts and 15 towns. ;Subdistricts * Chengbei Subdistrict () * Chengnan Subdistrict () ;Towns Climate Economy In the 19th century and early 20th century the area produced silk which was exported to Gansu. Transportation Xixiang is served by the Yangpingguan–Ankang Railway The Yangpingguan–Ankang railway or Yang'an railway (), is a single-track, electrified railroad in China between Yangpingguan and Ankang in southern Shaanxi Province. The line, in length, follows the upper reaches of the Han River and was .... The Muma River supports small boat traffic. Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningxia University
Ningxia University () is a public university located in Yinchuan, China. It is co-administrated by Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China. It is a member of the former Project 211 and a Chinese state Double First Class University, included in the Double First Class University Plan identified by the Ministry of Education. The school was founded in 1958. In the end of 1997, Ningxia Institute of Technology and Yinchuan Normal College (including Ningxia Education College) were merged into the university. In February 2002, it was merged with Ningxia Agricultural College, and formed the new Ningxia University. It currently comprises three campuses. It consists of more than 2,600 teachers and staff, over 50% of them are formal instructors. More than half of the instructors hold intermediate to senior titles, 52% of them with masters or doctors degrees. 15 teachers receives special subsidies of the State Council, and 17 were elected int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing University
Peking University (PKU; ) is a public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education. Peking University was established as the Imperial University of Peking in 1898 when it received its royal charter by the Guangxu Emperor. A successor of the older ''Guozijian'' Imperial College, the university's romanized name 'Peking' retains the older transliteration of 'Beijing' that has been superseded in most other contexts. Perennially ranked as one of the top academic institutions in China and the world; as of 2021 Peking University was ranked 16th globally and 1st in the Asia-Pacific & emerging countries by Times Higher Education, while as of 2022 it was ranked 12th globally and 1st in Asia by QS University Rankings. Throughout its history, Peking University has had an important role "at the center of major intellectual movements" in China. Abolished of its status as a royal institution after the fall of the Qing dynasty and the Xinhai Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
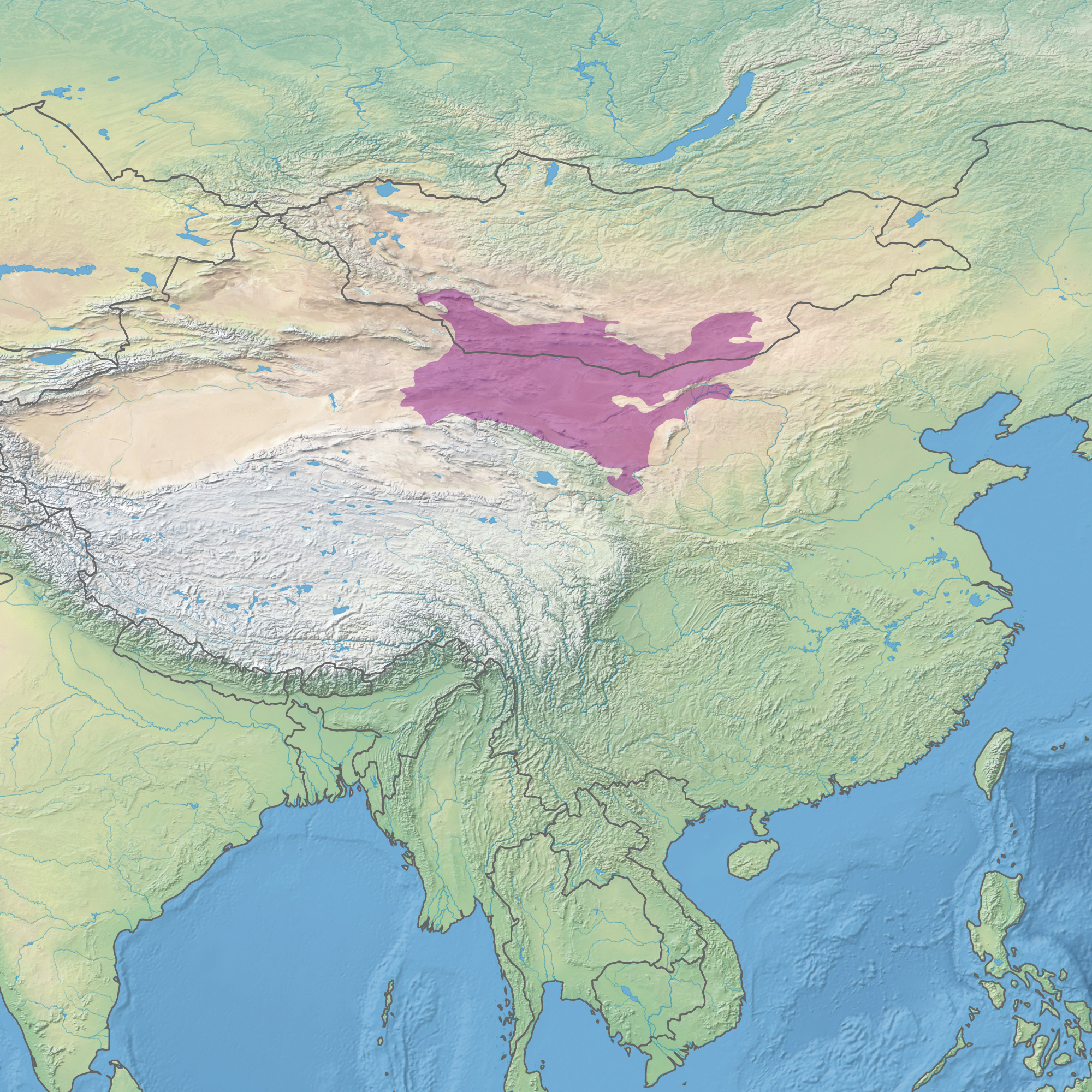
Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China that existed from 1038 to 1227. At its peak, the dynasty ruled over the modern-day northwestern Chinese provinces of Ningxia, Gansu, eastern Qinghai, northern Shaanxi, northeastern Xinjiang, and southwest Inner Mongolia, and southernmost Outer Mongolia, measuring about . Its capital was Xingqing (modern Yinchuan), until its destruction by the Mongols in 1227. Most of its written records and architecture were destroyed, so the founders and history of the empire remained obscure until 20th-century research in China and the West. The Western Xia occupied the area around the Hexi Corridor, a stretch of the Silk Road, the most important trade route between northern China and Central Asia. They made significant achievements in literature, art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gong Hwang Cherng
Gong Hwang-cherng () (1934–2010) was a Taiwanese linguist who specialized in Sino-Tibetan comparative linguistics and the phonetic reconstruction of Tangut and Old Chinese. He was born on 10 December 1934 at Yunlin County in Taiwan, and graduated from National Taiwan Normal University in 1958 with a degree in English. He earned his PhD in 1975 from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich in Germany, and was a research fellow and later professor at Academia Sinica in Taiwan. He was elected an honorary member of the Linguistic Society of America in 2001, and an academician of Academia Sinica in 2002. In 2006, he received a life achievement award from the Linguistic Society of Taiwan Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis .... Works * Gong Huang-cherng (1977). "y guzangwen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishida Tatsuo
was a professor at Kyoto University. His work encompasses research on a variety of Tibeto-Burman languages, he made great contributions in particular to the deciphering of the Tangut language. Biography Born in Osaka, Nishida graduated from the Kyoto University Faculty of Letters in 1951. In 1958 he became assistant professor at Kyoto University. During his studies Ishihama Juntarō and Izui Hisanosuke had a formative impact on him.Yabu, Shirō 藪 司郎 (2014). “Professor Nishida, Tatsuo and the study of Tibeto-Burman languages.” ''Memoirs of the research department of the Toyo Bunko'' 72: 180. In 1958 he was awarded the Japan Academy Prize. In 1962 he received his PhD for his study of Tangut characters. In 1992 he retired as a professor. In 1994 he received the Asahi Award, and in 2005 the Kyoto Culture Prize Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Zhenyu
Luo Zhenyu or Lo Chen-yü (August 8, 1866 – May 14, 1940), courtesy name Shuyun (叔蘊), was a Chinese classical scholar, philologist, epigrapher, antiquarian and Qing loyalist. Biography A native of Huai'an, Luo began to publish works of agriculture in Shanghai after the First Sino-Japanese War. With his friends, he set up ''Dongwen Xueshe'' (), a Japanese language teaching school in 1896. One of the students was Wang Guowei. Luo first visited Japan in 1901 to study the Japanese educational system. From 1906 onwards, he held several different government posts, mostly related to agriculture. From April 1909 to February 1912 he was president of the Imperial Agricultural College. Being a loyalist to the Qing Dynasty, he fled to Japan after the Xinhai Revolution, residing in Kyoto and doing some research on Chinese archaeology. He returned to Tianjin in China in 1919, taking part in political activities aimed at restoration of deposed Qing Emperor Puyi. Luo eventually rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Fuyi
Luo may refer to: Luo peoples and languages *Luo peoples, an ethno-linguistic group of eastern and central Africa **Luo people of Kenya and Tanzania or Joluo, an ethnic group in western Kenya, eastern Uganda, and northern Tanzania. ***Luoland, the tribal homeland of the group immediately above *Luo languages, a dozen languages spoken by the Luo peoples **Luo language (Kenya and Tanzania) or Dholuo **Southern Luo, a dialect cluster of Uganda and neighboring countries *Luo language (Cameroon), a nearly extinct language of Cameroon - not associated with Luo languages above People *Luo (surname) (羅), Chinese surname *Luò (surname) (駱), Chinese surname *Jing Jing Luo, Chinese composer *Luo Changqing, killed in the 2019 Hong Kong protests *Michael Luo (born 1976), American journalist *Show Lo (born 1979), Taiwanese singer, dancer and actor Geography *Luo (state), a Chinese feudal state, 11th–7th centuries B.C. *Luo River (Henan) (洛河, Luohe), a tributary of the Yellow River, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Chinese History
The National Museum of China () flanks the eastern side of Tiananmen Square in Beijing, China. The museum's mission is to educate about the arts and history of China. It is directed by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the People's Republic of China. History The museum was established in 2003 by the merging of the two separate museums that had occupied the same building since 1959: the Museum of the Chinese Revolution in the northern wing (originating in the Office of the National Museum of the Revolution founded in 1950 to preserve the legacy of the 1949 revolution) and the National Museum of Chinese History in the southern wing (with origins in both the Beijing National History Museum, founded in 1949, and the Preliminary Office of the National History Museum, founded in 1912, tasked to safeguard China's larger historical legacy). The building was completed in 1959 as one of the Ten Great Buildings celebrating the ten-year anniversary of the founding of the People's Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai (; 5 March 1898 – 8 January 1976) was a Chinese statesman and military officer who served as the first Premier of the People's Republic of China, premier of the People's Republic of China from 1 October 1949 until his death on 8 January 1976. Zhou served under Chairman Mao Zedong and helped the Chinese Communist Party, Communist Party rise to power, later helping consolidate its control, form its Foreign policy of China, foreign policy, and develop the Economy of China, Chinese economy. As a diplomat, Zhou served as the Chinese Foreign Minister of the People's Republic of China, foreign minister from 1949 to 1958. Advocating peaceful coexistence with Western Bloc, the West after the Korean War, he participated in the Geneva Conference (1954), 1954 Geneva Conference and the 1955 Bandung Conference, and helped orchestrate 1972 Nixon visit to China, Richard Nixon's 1972 visit to China. He helped devise policies regarding disputes with the United States, Taiwan, the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helan Mountains
The Helan Mountains, frequently called Alashan Mountains in older sources, are an isolated desert mountain range forming the border of Inner Mongolia's Alxa League and Ningxia. They run north-south parallel to the north-flowing Yellow River in the Ordos Loop section. The river is mostly east of the mountains, but in the north it crosses without making a significant gorge and flows on the west side. To the west lies the extremely arid Tengger Desert, while to the east is an irrigated area beside the Yellow River, in which lie the cities of Yinchuan and Shizuishan - a little further east of which lies the Mu Us portion of the Ordos Desert. To the north lies the Inner Mongolian city of Wuhai. They are about 200 km from north to south, from 15 to 50 km wide and average about 2000 meters in altitude (the Yellow River here is about 1,100 meters above sea level). Their highest peak is . Emerging wine industry With the increasing popularity of Ningxia wines, the Chinese aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)