Water (chemical formula ) is an
inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemist ...
, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and
nearly colorless chemical substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
, which is the main constituent of
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's
hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
and the
fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
s of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a
solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
). It is vital for all known forms of
life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energ ...
, despite not providing
food, energy or organic
micronutrient
Micronutrients are nutrient, essential dietary elements required by organisms in varying quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for exam ...
s. Its
chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ...
, H
2O, indicates that each of its
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
s contains one
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
and two
hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
s, connected by
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
s. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H
2O at
standard temperature and pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union o ...
.
A number of natural states of water exist. It forms
precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
in the form of rain and
aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog o ...
s in the form of
fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
.
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may co ...
s consist of suspended droplets of water and
ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
, its solid state. When finely divided,
crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line ice may precipitate in the form of
snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
. The gaseous state of water is
steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization ...
or
water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
.
Water covers about 71% of the Earth's surface, with seas and oceans making up most of the water volume on earth (about 96.5%).
Small portions of water occur as
groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
(1.7%), in the
glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
and the
ice caps
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
of
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
and
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
(1.7%), and in the air as
vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (British English and Canadian English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critic ...
, clouds (consisting of ice and liquid water suspended in air), and
precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
(0.001%).
Water moves continually through the
water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
of
evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
,
transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth a ...
(
evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpi ...
),
condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
, precipitation, and
runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock market ...
, usually reaching the sea.
Water plays an important role in the
world economy
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system, which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, ...
. Approximately 70% of the freshwater used by
humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
goes to agriculture.
Fishing in salt and fresh water bodies has been, and continues to be a major source of food for many parts of the world, providing 6.5% of global protein. Much of the long-distance trade of commodities (such as oil, natural gas, and manufactured products) is
transported by boats through seas, rivers, lakes, and canals. Large quantities of water, ice, and steam are used for cooling and heating, in industry and homes. Water is an excellent solvent for a wide variety of substances both mineral and organic; as such it is widely used in industrial processes, and in cooking and washing. Water, ice and snow are also central to many sports and other forms of entertainment, such as swimming, pleasure boating, boat racing, surfing, sport fishing, diving,
ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
and skiing.
Etymology
The word ''water'' comes from
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, from
Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
*''watar'' (source also of
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It i ...
,
Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Friesl ...
,
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
,
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
,
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, ,
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
(), from
Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
*''wod-or'', suffixed form of root *''wed-'' ("water"; "wet"). Also
cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
, through the Indo-European root, with
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(, from Ancient Greek , ''hýdōr,'' whence English "hydro-"),
Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
(),
Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, and
Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
.
History
Properties

Water () is a
polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemist ...
. At
room temperature
Colloquially, "room temperature" is a range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings. It feels comfortable to a person when they are wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on ...
it is a
taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
less and
odor
An odor (American English) or odour (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds ...
less
liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
, nearly
colorless with a
hint of blue. This simplest
hydrogen chalcogenide Hydrogen chalcogenides (also chalcogen hydrides or hydrogen chalcides) are binary compounds of hydrogen with chalcogen atoms (elements of group 16: oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium). Water, the first chemical compound in this series ...
is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" for its ability to dissolve many substances. This allows it to be the "
solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
of life": indeed, water as found in nature almost always includes various dissolved substances, and special steps are required to obtain chemically
pure water
Purified water is water that has been mechanically filtered or processed to remove impurities and make it suitable for use. Distilled water was, formerly, the most common form of purified water, but, in recent years, water is more frequently puri ...
. Water is the only common substance to exist as a
solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount o ...
, liquid, and
gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
in normal terrestrial conditions.
States

Along with ''oxidane'', ''water'' is one of the two official names for the chemical compound ; it is also the liquid phase of . The other two common
states of matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, ...
of water are the solid phase,
ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
, and the gaseous phase,
water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
or
steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization ...
. The addition or removal of heat can cause
phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of ...
s:
freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid o ...
(water to ice),
melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which incre ...
(ice to water),
vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomen ...
(water to vapor),
condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
(vapor to water),
sublimation (ice to vapor) and
deposition (vapor to ice).
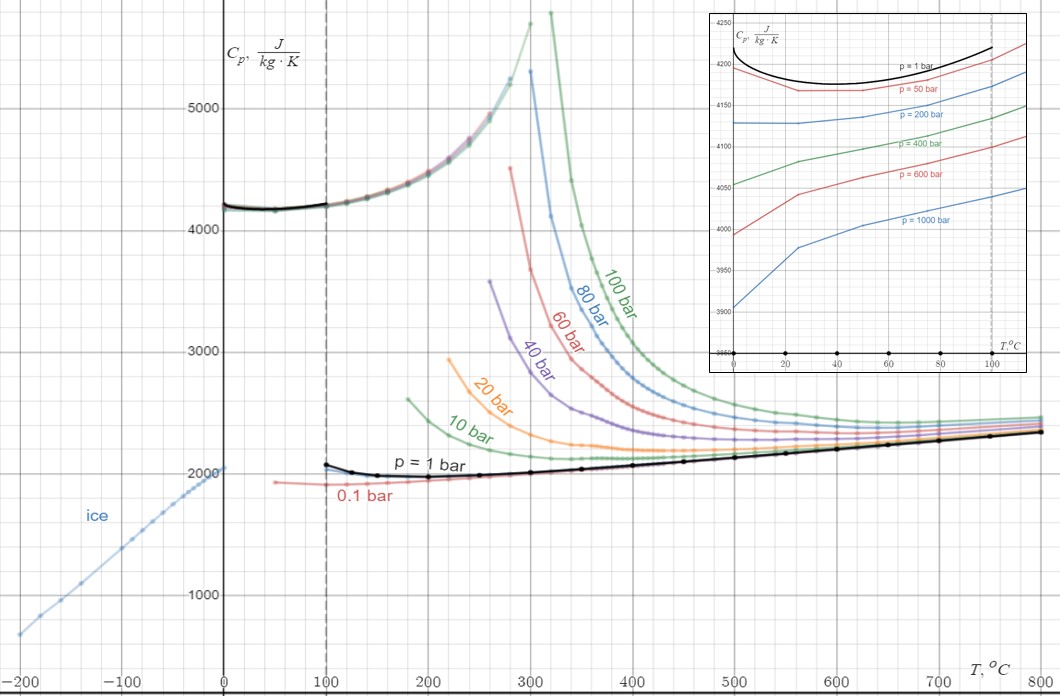
Density
Water differs from most liquids in that it becomes less
dense
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically ...
as it freezes. In 1 atm pressure, it reaches its maximum density of at , or almost at almost .
The density of ice is , an expansion of 9%. This expansion can exert enormous pressure, bursting pipes and cracking rocks.
In a lake or ocean, water at sinks to the bottom, and ice forms on the surface, floating on the liquid water. This ice insulates the water below, preventing it from freezing solid. Without this protection, most aquatic organisms residing in lakes would perish during the winter.
Magnetism
Water is a
diamagnetic
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted ...
material.
Though interaction is weak, with superconducting magnets it can attain a notable interaction.
Phase transitions
At a pressure of one
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
(atm), ice melts or water freezes (solidifies) at ) and water boils or vapor condenses at . However, even below the boiling point, water can change to vapor at its surface by
evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
(vaporization throughout the liquid is known as
boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. Th ...
). Sublimation and deposition also occur on surfaces.
[ For example, ]frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
is deposited on cold surfaces while snowflake
A snowflake is a single ice crystal that has achieved a sufficient size, and may have amalgamated with others, which falls through the Earth's atmosphere as snow.Knight, C.; Knight, N. (1973). Snow crystals. Scientific American, vol. 228, no. ...
s form by deposition on an aerosol particle or ice nucleus. In the process of freeze-drying
Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product and lowering pressure, removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by most conve ...
, a food is frozen and then stored at low pressure so the ice on its surface sublimates.Clausius–Clapeyron relation
The Clausius–Clapeyron relation, named after Rudolf Clausius and Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron, specifies the temperature dependence of pressure, most importantly vapor pressure, at a discontinuous phase transition between two phases of matter ...
:
where and are the molar volume
In chemistry and related fields, the molar volume, symbol ''V''m, or \tilde V of a substance is the ratio of the volume occupied by a substance to the amount of substance, usually given at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar ...
s of the liquid and solid phases, and is the molar latent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process — usually a first-order phase transition.
Latent heat can be understo ...
of melting. In most substances, the volume increases when melting occurs, so the melting temperature increases with pressure. However, because ice is less dense than water, the melting temperature decreases.subglacial lake
A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where gravitational pressure decreases the pressure melting point ...
s.
The Clausius-Clapeyron relation also applies to the boiling point, but with the liquid/gas transition the vapor phase has a much lower density than the liquid phase, so the boiling point increases with pressure. Water can remain in a liquid state at high temperatures in the deep ocean or underground. For example, temperatures exceed in Old Faithful
Old Faithful is a cone geyser in Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, United States. It was named in 1870 during the Washburn–Langford–Doane Expedition and was the first geyser in the park to be named. It is a highly predictable geotherma ...
, a geyser in Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
. In hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s, the temperature can exceed .
At sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
, the boiling point of water is . As atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, the boiling point decreases by 1 °C every 274 meters. High-altitude cooking
High-altitude cooking is cooking done at altitudes that are considerably higher than sea level. At elevated altitudes, any cooking that involves boiling or steaming generally requires compensation for lower temperatures because the boiling point ...
takes longer than sea-level cooking. For example, at , cooking time must be increased by a fourth to achieve the desired result. (Conversely, a pressure cooker
Pressure cooking is the process of cooking food under high pressure steam and water or a water-based cooking liquid, in a sealed vessel known as a ''pressure cooker''. High pressure limits boiling, and creates higher cooking temperatures which c ...
can be used to decrease cooking times by raising the boiling temperature.)
In a vacuum, water will boil at room temperature.
Triple and critical points
 On a pressure/temperature
On a pressure/temperature phase diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous ...
(see figure), there are curves separating solid from vapor, vapor from liquid, and liquid from solid. These meet at a single point called the triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the subli ...
, where all three phases can coexist. The triple point is at a temperature of and a pressure of ; it is the lowest pressure at which liquid water can exist. Until 2019, the triple point was used to define the Kelvin temperature scale
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its metric prefix, prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based eng ...
.supercritical fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous so ...
. It can be gradually compressed or expanded between gas-like and liquid-like densities; its properties (which are quite different from those of ambient water) are sensitive to density. For example, for suitable pressures and temperatures it can mix freely with nonpolar compounds, including most organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s. This makes it useful in a variety of applications including high-temperature electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outco ...
and as an ecologically benign solvent or catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
in chemical reactions involving organic compounds. In Earth's mantle, it acts as a solvent during mineral formation, dissolution and deposition.
Phases of ice and water
The normal form of ice on the surface of Earth is Ice Ih
Photograph showing details of an ice cube under magnification. Ice Ih is the form of ice commonly seen on Earth.
Phase space of ice Ih with respect to other ice phases.
Ice Ih (hexagonal ice crystal) (pronounced: ice one h, also known as ice-p ...
, a phase that forms crystals with hexagonal symmetry. Another with cubic crystalline symmetry, Ice Ic
Ice Ic (pronounced "ice one c" or "ice I see") is a metastable cubic crystalline variant of ice. Hans König was the first to identify and deduce the structure of ice Ic. The oxygen atoms in ice Ic are arranged in a diamond structure; it is extr ...
, can occur in the upper atmosphere. As the pressure increases, ice forms other crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric pat ...
s. As of 2019, 17 have been experimentally confirmed and several more are predicted theoretically (see Ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
). The 18th form of ice, ice XVIII, a face-centred-cubic, superionic ice phase, was discovered when a droplet of water was subject to a shock wave that raised the water's pressure to millions of atmospheres and its temperature to thousands of degrees, resulting in a structure of rigid oxygen atoms in which hydrogen atoms flowed freely.graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. , ice forms a square lattice.
The details of the chemical nature of liquid water are not well understood; some theories suggest that its unusual behaviour is due to the existence of 2 liquid states.
Taste and odor
Pure water is usually described as tasteless and odorless, although humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
have specific sensors that can feel the presence of water in their mouths,[Edmund T. Rolls (2005). ''Emotion Explained''. Oxford University Press, Medical. , 9780198570035.] and frogs are known to be able to smell it.[R. Llinas, W. Precht (2012), ''Frog Neurobiology: A Handbook''. Springer Science & Business Media. , 9783642663161] However, water from ordinary sources (including bottled mineral water) usually has many dissolved substances, that may give it varying tastes and odors. Humans and other animals have developed senses that enable them to evaluate the potability
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ag ...
of water in order to avoid water that is too salty or putrid
Putrefaction is the fifth stage of death, following pallor mortis, algor mortis, rigor mortis, and livor mortis. This process references the breaking down of a body of an animal, such as a human, post-mortem. In broad terms, it can be viewed ...
.
Color and appearance
Pure water is visibly blue due to absorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
* Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which ...
of light in the region c. 600–800 nm. The color can be easily observed in a glass of tap-water placed against a pure white background, in daylight. The principal absorption bands responsible for the color are overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
s of the O–H stretching vibrations
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such ...
. The apparent intensity of the color increases with the depth of the water column, following Beer's law. This also applies, for example, with a swimming pool when the light source is sunlight reflected from the pool's white tiles.
In nature, the color may also be modified from blue to green due to the presence of suspended solids or algae.
In industry, near-infrared spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research incl ...
is used with aqueous solutions as the greater intensity of the lower overtones of water means that glass cuvette
A cuvette ( French: cuvette = "little vessel") is a small tube-like container with straight sides and a circular or square cross section. It is sealed at one end, and made of a clear, transparent material such as plastic, glass, or fused quartz. ...
s with short path-length may be employed. To observe the fundamental stretching absorption spectrum of water or of an aqueous solution in the region around 3,500 cm (2.85 μm) a path length of about 25 μm is needed. Also, the cuvette must be both transparent around 3500 cm and insoluble in water; calcium fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities. ...
is one material that is in common use for the cuvette windows with aqueous solutions.
The Raman-active fundamental vibrations may be observed with, for example, a 1 cm sample cell.
Aquatic plant
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ...
s, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, and other photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
organisms can live in water up to hundreds of meters deep, because sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
can reach them.
Practically no sunlight reaches the parts of the oceans below of depth.
The refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
of liquid water (1.333 at ) is much higher than that of air (1.0), similar to those of alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which ...
s and ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
, but lower than those of glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known ...
(1.473), benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
(1.501), carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non ...
(1.627), and common types of glass (1.4 to 1.6). The refraction index of ice (1.31) is lower than that of liquid water.
Polar molecule
 In a water molecule, the hydrogen atoms form a 104.5° angle with the oxygen atom. The hydrogen atoms are close to two corners of a tetrahedron centered on the oxygen. At the other two corners are ''
In a water molecule, the hydrogen atoms form a 104.5° angle with the oxygen atom. The hydrogen atoms are close to two corners of a tetrahedron centered on the oxygen. At the other two corners are ''lone pairs
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
'' of valence electrons that do not participate in the bonding. In a perfect tetrahedron, the atoms would form a 109.5° angle, but the repulsion between the lone pairs is greater than the repulsion between the hydrogen atoms. The O–H bond length is about 0.096 nm.
Other substances have a tetrahedral molecular structure, for example, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Eart ...
() and hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
(). However, oxygen is more electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
(holds on to its electrons more tightly) than most other elements, so the oxygen atom retains a negative charge while the hydrogen atoms are positively charged. Along with the bent structure, this gives the molecule an electrical dipole moment
The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system, that is, a measure of the system's overall polarity. The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb-meter (C⋅m). The ...
and it is classified as a polar molecule
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
.
Water is a good polar solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
, that dissolves many salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively cha ...
and hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are no ...
organic molecules such as sugars and simple alcohols such as ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
. Water also dissolves many gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
—the latter giving the fizz of carbonated
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids.
In inorganic ch ...
beverages, sparkling wine
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne regi ...
s and beers. In addition, many substances in living organisms, such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s, DNA and polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s, are dissolved in water. The interactions between water and the subunits of these biomacromolecules shape protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduci ...
, DNA base pairing, and other phenomena crucial to life (hydrophobic effect
The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and exclude water molecules. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar ...
).
Many organic substances (such as fats and oils
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple e ...
and alkanes
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which ...
) are hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
, that is, insoluble in water. Many inorganic substances are insoluble too, including most metal oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
s, sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds lar ...
s, and silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is al ...
s.
Hydrogen bonding
 Because of its polarity, a molecule of water in the liquid or solid state can form up to four
Because of its polarity, a molecule of water in the liquid or solid state can form up to four hydrogen bonds
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
with neighboring molecules. Hydrogen bonds are about ten times as strong as the Van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and th ...
that attracts molecules to each other in most liquids. This is the reason why the melting and boiling points of water are much higher than those of other analogous compounds like hydrogen sulfide. They also explain its exceptionally high specific heat capacity
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
(about 4.2 J/g/K), heat of fusion
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a so ...
(about 333 J/g), heat of vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. T ...
(), and thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
(between 0.561 and 0.679 W/m/K). These properties make water more effective at moderating Earth's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
, by storing heat and transporting it between the oceans and the atmosphere. The hydrogen bonds of water are around 23 kJ/mol (compared to a covalent O-H bond at 492 kJ/mol). Of this, it is estimated that 90% is attributable to electrostatics, while the remaining 10% is partially covalent.
These bonds are the cause of water's high surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
and capillary forces. The capillary action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, any external forces li ...
refers to the tendency of water to move up a narrow tube against the force of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
. This property is relied upon by all vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They al ...
s, such as trees.
Self-ionization
Water is a weak solution of hydronium hydroxide – there is an equilibrium ⇔ + , in combination with solvation of the resulting hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is d ...
ions.
Electrical conductivity and electrolysis
Pure water has a low electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allow ...
, which increases with the dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
of a small amount of ionic material such as common salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of Salt (chemistry), salts; salt in the form of a natural crystallinity, crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. ...
.
Liquid water can be split into the elements hydrogen and oxygen by passing an electric current through it—a process called electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
. The decomposition requires more energy input than the heat released by the inverse process (285.8 kJ/ mol, or 15.9 MJ/kg).
Mechanical properties
Liquid water can be assumed to be incompressible for most purposes: its compressibility ranges from 4.4 to in ordinary conditions. Even in oceans at 4 km depth, where the pressure is 400 atm, water suffers only a 1.8% decrease in volume.viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
of water is about 10 Pa· s or 0.01 poise at , and the speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as w ...
in liquid water ranges between depending on temperature. Sound travels long distances in water with little attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable att ...
, especially at low frequencies (roughly 0.03 dB/km for 1 k Hz), a property that is exploited by cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
and humans for communication and environment sensing (sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect o ...
).[UK National Physical Laboratory]
Calculation of absorption of sound in seawater
. Online site, last accessed on 28 September 2016.
Reactivity
Metallic elements which are more electropositive
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
than hydrogen, particularly the alkali metals
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
and alkaline earth metals
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar pr ...
such as lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
and cesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that ar ...
displace hydrogen from water, forming hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. I ...
s and releasing hydrogen. At high temperatures, carbon reacts with steam to form carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
and hydrogen.
On Earth
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout the Earth. The study of the distribution of water is hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary p ...
. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
is hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aquif ...
, of glaciers is glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climato ...
, of inland waters is limnology
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristi ...
and distribution of oceans is oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
. Ecological processes with hydrology are in the focus of ecohydrology
Ecohydrology (from Greek , ''oikos'', "house(hold)"; , ''hydōr'', "water"; and , '' -logia'') is an interdisciplinary scientific field studying the interactions between water and ecological systems. It is considered a sub discipline of hydrology, ...
.
The collective mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of a planet is called the hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
. Earth's approximate water volume (the total water supply of the world) is .bodies of water
A body of water or waterbody (often spelled water body) is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as p ...
, such as an ocean, sea, lake, river, stream, canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
, pond, or puddle
A puddle is a small accumulation of liquid, usually water, on a surface. It can form either by pooling in a depression on the surface, or by surface tension upon a flat surface.
A puddle is generally shallow enough to walk through, and too sma ...
. The majority of water on Earth is seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
. Water is also present in the atmosphere in solid, liquid, and vapor states. It also exists as groundwater in aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
s.
Water is important in many geological processes. Groundwater is present in most rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
, and the pressure of this groundwater affects patterns of faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
. Water in the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
is responsible for the melt that produces volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
es at subduction zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
s. On the surface of the Earth, water is important in both chemical and physical weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), ...
processes. Water, and to a lesser but still significant extent, ice, are also responsible for a large amount of sediment transport
Sediment transport is the movement of solid particles (sediment), typically due to a combination of gravity acting on the sediment, and/or the movement of the fluid in which the sediment is entrained. Sediment transport occurs in natural system ...
that occurs on the surface of the earth. Deposition of transported sediment forms many types of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s, which make up the geologic record
The geologic record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata. That is, deposits laid down by volcanism or by deposition of sediment derived from weathering detritus (clays, sand ...
of Earth history
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologi ...
.
Water cycle
 The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) is the continuous exchange of water within the
The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) is the continuous exchange of water within the hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
, between the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
water, surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land forming terrestrial (inland) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surface water is produced by prec ...
, groundwater, and plants.
Water moves perpetually through each of these regions in the ''water cycle'' consisting of the following transfer processes:
* evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
from oceans and other water bodies into the air and transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth a ...
from land plants and animals into the air.
* precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
, from water vapor condensing from the air and falling to the earth or ocean.
* runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock market ...
from the land usually reaching the sea.
Most water vapors found mostly in the ocean returns to it, but winds carry water vapor over land at the same rate as runoff into the sea, about 47 Tt per year whilst evaporation and transpiration happening in land masses also contribute another 72 Tt per year. Precipitation, at a rate of 119 Tt per year over land, has several forms: most commonly rain, snow, and hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
, with some contribution from fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
and dew
Dew is water in the form of droplets that appears on thin, exposed objects in the morning or evening due to condensation.
As the exposed surface cools by radiating its heat, atmospheric moisture condenses at a rate greater than that at wh ...
. Dew is small drops of water that are condensed when a high density of water vapor meets a cool surface. Dew usually forms in the morning when the temperature is the lowest, just before sunrise and when the temperature of the earth's surface starts to increase. Condensed water in the air may also refract
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomeno ...
sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
to produce rainbow
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows c ...
s.
Water runoff often collects over watersheds flowing into rivers. Through erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
, runoff shapes the environment creating river valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers ...
s and deltas
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rarel ...
which provide rich soil and level ground for the establishment of population centers. A flood occurs when an area of land, usually low-lying, is covered with water which occurs when a river overflows its banks or a storm surge happens. On the other hand, drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. This occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation either due to its topography or due to its location in terms of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
.
Water resources
Water resources are natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
s of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
or irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
water. Water occurs as both "stocks" and "flows". Water can be stored as lakes, water vapor, groundwater or aquifers, and ice and snow. Of the total volume of global freshwater, an estimated 69 percent is stored in glaciers and permanent snow cover; 30 percent is in groundwater; and the remaining 1 percent in lakes, rivers, the atmosphere, and biota. The length of time water remains in storage is highly variable: some aquifers consist of water stored over thousands of years but lake volumes may fluctuate on a seasonal basis, decreasing during dry periods and increasing during wet ones. A substantial fraction of the water supply for some regions consists of water extracted from water stored in stocks, and when withdrawals exceed recharge, stocks decrease. By some estimates, as much as 30 percent of total water used for irrigation comes from unsustainable withdrawals of groundwater, causing groundwater depletion
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. Groundwater depletion is comparable to a bank account in which mor ...
.
Seawater and tides
Seawater contains about 3.5% sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
on average, plus smaller amounts of other substances. The physical properties of seawater differ from fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
in some important respects. It freezes at a lower temperature (about ) and its density increases with decreasing temperature to the freezing point, instead of reaching maximum density at a temperature above freezing. The salinity of water in major seas varies from about 0.7% in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
to 4.0% in the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. (The Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
, known for its ultra-high salinity levels of between 30 and 40%, is really a salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
.)
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s are the cyclic rising and falling of local sea levels caused by the tidal force
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomen ...
s of the Moon and the Sun acting on the oceans. Tides cause changes in the depth of the marine and estuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
water bodies and produce oscillating currents known as tidal streams. The changing tide produced at a given location is the result of the changing positions of the Moon and Sun relative to the Earth coupled with the effects of Earth rotation and the local bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water de ...
. The strip of seashore that is submerged at high tide and exposed at low tide, the intertidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species o ...
, is an important ecological product of ocean tides.
Effects on life
 From a
From a biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
standpoint, water has many distinct properties that are critical for the proliferation of life. It carries out this role by allowing organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s to react in ways that ultimately allow replication. All known forms of life depend on water. Water is vital both as a solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
in which many of the body's solutes dissolve and as an essential part of many metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
processes within the body. Metabolism is the sum total of anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-do ...
and catabolism
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipids, ...
. In anabolism, water is removed from molecules (through energy requiring enzymatic chemical reactions) in order to grow larger molecules (e.g., starches, triglycerides, and proteins for storage of fuels and information). In catabolism, water is used to break bonds in order to generate smaller molecules (e.g., glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids to be used for fuels for energy use or other purposes). Without water, these particular metabolic processes could not exist.
Water is fundamental to photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthetic cells use the sun's energy to split off water's hydrogen from oxygen. Hydrogen is combined with (absorbed from air or water) to form glucose and release oxygen. All living cells use such fuels and oxidize the hydrogen and carbon to capture the sun's energy and reform water and in the process (cellular respiration).
Water is also central to acid-base neutrality and enzyme function. An acid, a hydrogen ion (, that is, a proton) donor, can be neutralized by a base, a proton acceptor such as a hydroxide ion () to form water. Water is considered to be neutral, with a pH (the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration) of 7. Acids
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
have pH values less than 7 while bases have values greater than 7.
Aquatic life forms
Earth surface waters are filled with life. The earliest life forms appeared in water; nearly all fish live exclusively in water, and there are many types of marine mammals, such as dolphins and whales. Some kinds of animals, such as amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. Plants such as kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwat ...
and algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
grow in the water and are the basis for some underwater ecosystems. Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
is generally the foundation of the ocean food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), det ...
.
Aquatic vertebrates must obtain oxygen to survive, and they do so in various ways. Fish have gills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
instead of lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of th ...
, although some species of fish, such as the lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
, have both. Marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reli ...
s, such as dolphins, whales, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes wea ...
s, and seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
need to surface periodically to breathe air. Some amphibians are able to absorb oxygen through their skin. Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of modifications to survive in poorly oxygenated waters including breathing tubes (see insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
and mollusc siphons) and gills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
(''Carcinus
''Carcinus'' ( '' Karkinos'') is a genus of crabs, which includes ''Carcinus maenas'', an important invasive species, and '' C. aestuarii'', a species endemic to the Mediterranean Sea.
''Carcinus maenas''
''C. maenas'' is among the 100 "worl ...
''). However, as invertebrate life evolved in an aquatic habitat most have little or no specialization for respiration in water.
Effects on human civilization
 Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways;
Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways; Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, one of the so-called cradles of civilization
A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was created by mankind independent of other civilizations in other locations. The formation of urban settlements (cities) is the primary characteristic of a society that c ...
, was situated between the major rivers Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
; the ancient society of the Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
depended entirely upon the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
. The early Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
(c. 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE) developed along the Indus River and tributaries that flowed out of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
. Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
was also founded on the banks of the Italian river Tiber
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the Riv ...
. Large metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big c ...
es like Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
, Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
owe their success in part to their easy accessibility via water and the resultant expansion of trade. Islands with safe water ports, like Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, have flourished for the same reason. In places such as North Africa and the Middle East, where water is more scarce, access to clean drinking water was and is a major factor in human development.
Health and pollution
 Water fit for human consumption is called
Water fit for human consumption is called drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
or potable water. Water that is not potable may be made potable by filtration or distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separation process, separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distilla ...
, or by a range of other methods. More than 660 million people do not have access to safe drinking water.
Water that is not fit for drinking but is not harmful to humans when used for swimming or bathing is called by various names other than potable or drinking water, and is sometimes called safe water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ag ...
, or "safe for bathing". Chlorine is a skin and mucous membrane irritant that is used to make water safe for bathing or drinking. Its use is highly technical and is usually monitored by government regulations (typically 1 part per million (ppm) for drinking water, and 1–2 ppm of chlorine not yet reacted with impurities for bathing water). Water for bathing may be maintained in satisfactory microbiological condition using chemical disinfectants such as chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
or ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
or by the use of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
light.
Water reclamation
Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting municipal wastewater (sewage) or industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. Types of reuse include: ...
is the process of converting wastewater (most commonly sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
, also called municipal wastewater) into water that can be reuse
Reuse is the action or practice of using an item, whether for its original purpose (conventional reuse) or to fulfill a different function ( creative reuse or repurposing). It should be distinguished from recycling, which is the breaking down of u ...
d for other purposes. There are 2.3 billion people who reside in nations with water scarcities, which means that each individual receives less than of water annually. of municipal wastewater are produced globally each year.hydrologic cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly const ...
, but pressures over access to it result from the naturally uneven distribution in space and time, growing economic demands by agriculture and industry, and rising populations. Currently, nearly a billion people around the world lack access to safe, affordable water. In 2000, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
established the Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenniu ...
for water to halve by 2015 the proportion of people worldwide without access to safe water and sanitation. Progress toward that goal was uneven, and in 2015 the UN committed to the Sustainable Development Goals of achieving universal access to safe and affordable water and sanitation by 2030. Poor water quality and bad sanitation are deadly; some five million deaths a year are caused by water-related diseases. The World Health Organization estimates that safe water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ag ...
could prevent 1.4 million child deaths from diarrhoea each year.
In developing countries, 90% of all Sewage, municipal wastewater still goes untreated into local rivers and streams. Some 50 countries, with roughly a third of the world's population, also suffer from medium or high water scarcity and 17 of these extract more water annually than is recharged through their natural water cycles. The strain not only affects surface freshwater bodies like rivers and lakes, but it also degrades groundwater resources.
Human uses

Agriculture
The most substantial human use of water is for agriculture, including irrigated agriculture, which accounts for as much as 80 to 90 percent of total human water consumption. In the United States, 42% of freshwater withdrawn for use is for irrigation, but the vast majority of water "consumed" (used and not returned to the environment) goes to agriculture.
As a scientific standard
On 7 April 1795, the gram was defined in France to be equal to "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to a cube of one-hundredth of a meter, and at the temperature of melting ice". For practical purposes though, a metallic reference standard was required, one thousand times more massive, the kilogram. Work was therefore commissioned to determine precisely the mass of one liter of water. In spite of the fact that the decreed definition of the gram specified water at —a highly reproducible ''temperature''—the scientists chose to redefine the standard and to perform their measurements at the temperature of highest water ''density'', which was measured at the time as .
The Kelvin temperature scale of the International System of Units, SI system was based on the triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the subli ...
of water, defined as exactly , but as of May 2019 is based on the Boltzmann constant instead. The scale is an absolute temperature scale with the same increment as the Celsius temperature scale, which was originally defined according to the boiling point (set to ) and melting point (set to ) of water.
Natural water consists mainly of the isotopes hydrogen-1 and oxygen-16, but there is also a small quantity of heavier isotopes oxygen-18, oxygen-17, and hydrogen-2 (deuterium). The percentage of the heavier isotopes is very small, but it still affects the properties of water. Water from rivers and lakes tends to contain less heavy isotopes than seawater. Therefore, standard water is defined in the Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water specification.
For drinking

 The human body contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size. To function properly, the body requires between of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though the British Dietetic Association advises that 2.5 liters of total water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration, including 1.8 liters (6 to 7 glasses) obtained directly from beverages. Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather.
The human body contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size. To function properly, the body requires between of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though the British Dietetic Association advises that 2.5 liters of total water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration, including 1.8 liters (6 to 7 glasses) obtained directly from beverages. Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather. An original recommendation for water intake in 1945 by the Food and Nutrition Board of the U.S. National Research Council read: "An ordinary standard for diverse persons is 1 milliliter for each calorie of food. Most of this quantity is contained in prepared foods." The latest dietary reference intake report by the U.S. National Research Council in general recommended, based on the median total water intake from US survey data (including food sources): for men and of water total for women, noting that water contained in food provided approximately 19% of total water intake in the survey.
Specifically, pregnant and breastfeeding women need additional fluids to stay hydrated. The US Institute of Medicine recommends that, on average, men consume and women ; pregnant women should increase intake to and breastfeeding women should get 3 liters (12 cups), since an especially large amount of fluid is lost during nursing. Also noted is that normally, about 20% of water intake comes from food, while the rest comes from drinking water and beverages (Caffeine, caffeinated included). Water is excreted from the body in multiple forms; through urine and feces, through sweating, and by exhalation of water vapor in the breath. With physical exertion and heat exposure, water loss will increase and daily fluid needs may increase as well.
Humans require water with few impurities. Common impurities include metal salts and oxides, including copper, iron, calcium and lead, and/or harmful bacteria, such as ''Vibrio''. Some solutes are acceptable and even desirable for taste enhancement and to provide needed electrolytes.
The single largest (by volume) freshwater resource suitable for drinking is Lake Baikal in Siberia.
An original recommendation for water intake in 1945 by the Food and Nutrition Board of the U.S. National Research Council read: "An ordinary standard for diverse persons is 1 milliliter for each calorie of food. Most of this quantity is contained in prepared foods." The latest dietary reference intake report by the U.S. National Research Council in general recommended, based on the median total water intake from US survey data (including food sources): for men and of water total for women, noting that water contained in food provided approximately 19% of total water intake in the survey.
Specifically, pregnant and breastfeeding women need additional fluids to stay hydrated. The US Institute of Medicine recommends that, on average, men consume and women ; pregnant women should increase intake to and breastfeeding women should get 3 liters (12 cups), since an especially large amount of fluid is lost during nursing. Also noted is that normally, about 20% of water intake comes from food, while the rest comes from drinking water and beverages (Caffeine, caffeinated included). Water is excreted from the body in multiple forms; through urine and feces, through sweating, and by exhalation of water vapor in the breath. With physical exertion and heat exposure, water loss will increase and daily fluid needs may increase as well.
Humans require water with few impurities. Common impurities include metal salts and oxides, including copper, iron, calcium and lead, and/or harmful bacteria, such as ''Vibrio''. Some solutes are acceptable and even desirable for taste enhancement and to provide needed electrolytes.
The single largest (by volume) freshwater resource suitable for drinking is Lake Baikal in Siberia.
Washing
Transportation
Chemical uses
Water is widely used in chemical reactions as a solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
or reactant and less commonly as a solute or catalyst. In inorganic reactions, water is a common solvent, dissolving many ionic compounds, as well as other polar compounds such as ammonia and Hydrogen chalcogenide, compounds closely related to water. In organic reactions, it is not usually used as a reaction solvent, because it does not dissolve the reactants well and is amphoteric (acidic ''and'' basic) and nucleophilic. Nevertheless, these properties are sometimes desirable. Also, acceleration of Diels-Alder reactions by water has been observed. Supercritical water has recently been a topic of research. Oxygen-saturated supercritical water combusts organic pollutants efficiently. Water vapor is used for some processes in the chemical industry. An example is the production of acrylic acid from acrolein, propylene and propane. The possible effect of water in these reactions includes the physical and chemical interaction of water with the catalyst and the chemical reaction of water with the reaction intermediates.
Heat exchange
Water and steam are a common fluid used for heat exchanger, heat exchange, due to its availability and high Heat capacity of water, heat capacity, both for cooling and heating. Cool water may even be naturally available from a lake or the sea. It is especially effective to transport heat through vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomen ...
and condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
of water because of its large latent heat of vaporization. A disadvantage is that metals commonly found in industries such as steel and copper are oxidation, oxidized faster by untreated water and steam. In almost all thermal power stations, water is used as the working fluid (used in a closed-loop between boiler, steam turbine, and condenser), and the coolant (used to exchange the waste heat to a water body or carry it away by evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
in a cooling tower). In the United States, cooling power plants is the largest use of water.["Water Use in the United States"](_blank)
''National Atlas''.
In the nuclear power industry, water can also be used as a neutron moderator. In most nuclear reactors, water is both a coolant and a moderator. This provides something of a passive safety measure, as removing the water from the reactor also void coefficient, slows the nuclear reaction down. However other methods are favored for stopping a reaction and it is preferred to keep the nuclear core covered with water so as to ensure adequate cooling.
Fire considerations
 Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good Fire fighting#Use of water, fire extinguishing fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid.
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a steam explosion, which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as coal, charcoal, or coke (fuel), coke graphite, decompose the water, producing water gas.
The power of such explosions was seen in the Chernobyl disaster, although the water involved in this case did not come from fire-fighting but from the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of a reaction between steam and hot zirconium.
Some metallic oxides, most notably those of
Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good Fire fighting#Use of water, fire extinguishing fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid.
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a steam explosion, which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as coal, charcoal, or coke (fuel), coke graphite, decompose the water, producing water gas.
The power of such explosions was seen in the Chernobyl disaster, although the water involved in this case did not come from fire-fighting but from the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of a reaction between steam and hot zirconium.
Some metallic oxides, most notably those of alkali metals
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
and alkaline earth metals
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar pr ...
, produce so much heat on reaction with water that a fire hazard can develop. The alkaline earth oxide Calcium oxide, quicklime is a mass-produced substance that is often transported in paper bags. If these are soaked through, they may ignite as their contents react with water.
Recreation
 Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, surfing and Underwater diving, diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and
Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, surfing and Underwater diving, diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
, are played on ice. Lakesides, beaches and water parks are popular places for people to go to relax and enjoy recreation. Many find the sound and appearance of flowing water to be calming, and fountains and other flowing water structures are popular decorations. Some keep fish and other flora and fauna inside aquariums or ponds for show, fun, and companionship. Humans also use water for snow sports such as skiing, sledding, snowmobiling or snowboarding, which the require the water to be at a low temperature either as ice or crystallized into snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
.
Water industry
The water industry provides drinking water and wastewater services (including sewage treatment) to households and industry. Water supply facilities include water wells, cisterns for rainwater harvesting, water supply networks, and water purification facilities, water tanks, water towers, water pipes including old Aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts. Atmospheric water generators are in development.
Drinking water is often collected at spring (hydrosphere), springs, extracted from artificial Boring (earth), borings (wells) in the ground, or pumped from lakes and rivers. Building more wells in adequate places is thus a possible way to produce more water, assuming the aquifers can supply an adequate flow. Other water sources include rainwater collection. Water may require purification for human consumption. This may involve the removal of undissolved substances, dissolved substances and harmful microbes. Popular methods are filter (water), filtering with sand which only removes undissolved material, while Water chlorination, chlorination and boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. Th ...
kill harmful microbes. Distillation does all three functions. More advanced techniques exist, such as reverse osmosis. Desalination of abundant seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
is a more expensive solution used in coastal arid climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
s.
The distribution of drinking water is done through municipal water systems, tanker delivery or as bottled water. Governments in many countries have programs to distribute water to the needy at no charge.
Reducing usage by using drinking (potable) water only for human consumption is another option. In some cities such as Hong Kong, seawater is extensively used for flushing toilets citywide in order to Water conservation, conserve freshwater resources.
Water pollution, Polluting water may be the biggest single misuse of water; to the extent that a pollutant limits other uses of the water, it becomes a waste of the resource, regardless of benefits to the polluter. Like other types of pollution, this does not enter standard accounting of market costs, being conceived as externality, externalities for which the market cannot account. Thus other people pay the price of water pollution, while the private firms' profits are not redistributed to the local population, victims of this pollution. Pharmaceuticals consumed by humans often end up in the waterways and can have detrimental effects on marine biology, aquatic life if they bioaccumulation, bioaccumulate and if they are not biodegradable.
Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater are typically treated at wastewater treatment plants. Mitigation of polluted surface runoff is addressed through a variety of prevention and treatment techniques. (''See'' Surface runoff#Mitigation and treatment.)
Industrial applications
Many industrial processes rely on reactions using chemicals dissolved in water, suspension of solids in water slurry, slurries or using water to dissolve and extract substances, or to wash products or process equipment. Processes such as mining, chemical pulping, pulp bleaching, paper manufacturing, textile production, dyeing, printing, and cooling of power plants use large amounts of water, requiring a dedicated water source, and often cause significant water pollution.
Water is used in power generation. Hydroelectricity is electricity obtained from hydropower. Hydroelectric power comes from water driving a water turbine connected to a generator. Hydroelectricity is a low-cost, non-polluting, renewable energy source. The energy is supplied by the motion of water. Typically a dam is constructed on a river, creating an artificial lake behind it. Water flowing out of the lake is forced through turbines that turn generators.
Pressurized water is used in Hydrodemolition, water blasting and water jet cutters. Also, high pressure water guns are used for precise cutting. It works very well, is relatively safe, and is not harmful to the environment. It is also used in the cooling of machinery to prevent overheating, or prevent saw blades from overheating.
Water is also used in many industrial processes and machines, such as the steam turbine and heat exchanger, in addition to its use as a chemical solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
. Discharge of untreated water from industrial uses is water pollution, pollution. Pollution includes discharged solutes (chemical pollution) and discharged coolant water (thermal pollution). Industry requires pure water for many applications and uses a variety of purification techniques both in water supply and discharge.
Food processing

 Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for dishwashing. Water also plays many critical roles within the field of food science.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as air pressure, which is in turn affected by altitude. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure that occurs at higher elevations. One mole (unit), mole of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by , and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by ; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.
Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for dishwashing. Water also plays many critical roles within the field of food science.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as air pressure, which is in turn affected by altitude. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure that occurs at higher elevations. One mole (unit), mole of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by , and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by ; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.
Medical use
Water for injection is on the World Health Organization's World Health Organization's list of essential medicines, list of essential medicines.
Distribution in nature
In the universe
 Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. The formation of stars is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined" around a quasar located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence".
Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. The formation of stars is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined" around a quasar located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence".
Water vapor
Water is present as vapor in:
* Solar atmosphere, Atmosphere of the Sun: in detectable trace amounts[Water Found in Extrasolar Planet's Atmosphere](_blank)
– Space.com Tau Boötis b, HAT-P-11b,[Andersson, Jonas (June 2012)]
Water in stellar atmospheres "Is a novel picture required to explain the atmospheric behavior of water in red giant stars?"
Lund Observatory, Lund University, Sweden
* Circumstellar disks: including those of more than half of T Tauri stars such as AA Tauri
Liquid water
Liquid water is present on Earth, covering 71% of its surface.
Water ice
Water is present as ice on:
 * Water on Mars, Mars: under the regolith and at the poles.
* Earth–Moon system: mainly as ice sheets on Earth and in Lunar craters and volcanic rocks NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.
* Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres
* Water on Mars, Mars: under the regolith and at the poles.
* Earth–Moon system: mainly as ice sheets on Earth and in Lunar craters and volcanic rocks NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.
* Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres[ (supporting online material, table S1)]
* Pluto–Charon (moon), Charon system
Exotic forms
Water and other volatiles probably comprise much of the internal structures of Uranus and Neptune and the water in the deeper layers may be in the form of ionic water in which the molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and deeper still as superionic water in which the oxygen crystallizes, but the hydrogen ions float about freely within the oxygen lattice.[Weird water lurking inside giant planets](_blank)
, ''New Scientist'', 1 September 2010, Magazine issue 2776.
Water and planetary habitability
The existence of liquid water, and to a lesser extent its gaseous and solid forms, on Earth are vital to the existence of Organism, life on Earth as we know it. The Earth is located in the habitable zone of the Solar System; if it were slightly closer to or farther from the Sun (about 5%, or about 8 million kilometers), the conditions which allow the three forms to be present simultaneously would be far less likely to exist.
Earth's gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
allows it to hold an Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere. Water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere provide a temperature buffer (greenhouse effect) which helps maintain a relatively steady surface temperature. If Earth were smaller, a thinner atmosphere would allow temperature extremes, thus preventing the accumulation of water except in polar ice caps (as on Mars).
The surface temperature of Earth has been relatively constant through geologic time despite varying levels of incoming solar radiation (insolation), indicating that a dynamic process governs Earth's temperature via a combination of greenhouse gases and surface or atmospheric albedo. This proposal is known as the Gaia hypothesis.
The state of water on a planet depends on ambient pressure, which is determined by the planet's gravity. If a planet is sufficiently massive, the water on it may be solid even at high temperatures, because of the high pressure caused by gravity, as it was observed on exoplanets Gliese 436 b and GJ 1214 b.
Law, politics, and crisis
 Water politics is politics affected by water and water resources. Water, particularly fresh water, is a strategic resource across the world and an important element in many political conflicts. It causes health impacts and damage to biodiversity.
Access to safe drinking water has improved over the last decades in almost every part of the world, but approximately one billion people still lack access to safe water and over 2.5 billion lack access to adequate sanitation.
Water politics is politics affected by water and water resources. Water, particularly fresh water, is a strategic resource across the world and an important element in many political conflicts. It causes health impacts and damage to biodiversity.
Access to safe drinking water has improved over the last decades in almost every part of the world, but approximately one billion people still lack access to safe water and over 2.5 billion lack access to adequate sanitation.sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
disposal.
Organizations concerned with water protection include the International Water Association (IWA), WaterAid, Water 1st, and the American Water Resources Association. The International Water Management Institute undertakes projects with the aim of using effective water management to reduce poverty. Water related conventions are United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea and Ramsar Convention. World Day for Water takes place on 22 March and World Oceans Day on 8 June.
In culture
Religion
 Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Faiths that incorporate ritual washing (Ritual purification, ablution) include Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, the Rastafari movement, Shinto, Taoism, and Wicca. Immersion (or aspersion or affusion) of a person in water is a central sacrament of Christianity (where it is called baptism); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (''Ghusl''), Judaism (''mikvah'') and Sikhism (''Amrit Sanskar''). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after washing certain parts of the body using clean water (''wudu''), unless water is unavailable (see ''Tayammum''). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of ''misogi'').
In Christianity, holy water is water that has been sanctified by a priest for the purpose of baptism, the Blessing (Roman Catholic Church), blessing of persons, places, and objects, or as a means of repelling evil.
In Zoroastrianism, water (''aban, āb'') is respected as the source of life.
Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Faiths that incorporate ritual washing (Ritual purification, ablution) include Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, the Rastafari movement, Shinto, Taoism, and Wicca. Immersion (or aspersion or affusion) of a person in water is a central sacrament of Christianity (where it is called baptism); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (''Ghusl''), Judaism (''mikvah'') and Sikhism (''Amrit Sanskar''). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after washing certain parts of the body using clean water (''wudu''), unless water is unavailable (see ''Tayammum''). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of ''misogi'').
In Christianity, holy water is water that has been sanctified by a priest for the purpose of baptism, the Blessing (Roman Catholic Church), blessing of persons, places, and objects, or as a means of repelling evil.
In Zoroastrianism, water (''aban, āb'') is respected as the source of life.
Philosophy
 The Ancient Greek philosopher Empedocles saw Water (classical element), water as one of the four classical elements (along with fire, earth, and Air (classical element), air), and regarded it as an ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Thales, whom Aristotle portrayed as an astronomer and an engineer, theorized that the earth, which is denser than water, emerged from the water. Thales, a monist, believed further that all things are made from water. Plato believed that the shape of water is an icosahedron – flowing easily compared to the cube-shaped earth.
The theory of the Humorism, four bodily humors associated water with phlegm, as being cold and moist. The Water (classical element), classical element of water was also one of the Five elements (Chinese philosophy), five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy (along with earth (classical element), earth, fire (classical element), fire, wood (classical element), wood, and metal (classical element), metal).
Some traditional and popular Asian philosophy, Asian philosophical systems take water as a role-model. James Legge's 1891 translation of the ''Dao De Jing'' states, "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed." ''Guanzi (text), Guanzi'' in the "Shui di" 水地 chapter further elaborates on the symbolism of water, proclaiming that "man is water" and attributing natural qualities of the people of different Chinese regions to the character of local water resources.
The Ancient Greek philosopher Empedocles saw Water (classical element), water as one of the four classical elements (along with fire, earth, and Air (classical element), air), and regarded it as an ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Thales, whom Aristotle portrayed as an astronomer and an engineer, theorized that the earth, which is denser than water, emerged from the water. Thales, a monist, believed further that all things are made from water. Plato believed that the shape of water is an icosahedron – flowing easily compared to the cube-shaped earth.
The theory of the Humorism, four bodily humors associated water with phlegm, as being cold and moist. The Water (classical element), classical element of water was also one of the Five elements (Chinese philosophy), five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy (along with earth (classical element), earth, fire (classical element), fire, wood (classical element), wood, and metal (classical element), metal).
Some traditional and popular Asian philosophy, Asian philosophical systems take water as a role-model. James Legge's 1891 translation of the ''Dao De Jing'' states, "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed." ''Guanzi (text), Guanzi'' in the "Shui di" 水地 chapter further elaborates on the symbolism of water, proclaiming that "man is water" and attributing natural qualities of the people of different Chinese regions to the character of local water resources.
Folklore
"Living water" features in Germanic and Slavic Folklore, folktales as a means of bringing the dead back to life. Note the Grimms' Fairy Tales, Grimm fairy-tale ("The Water of Life (German fairy tale), The Water of Life") and the Russian dichotomy of and . The Fountain of Youth represents a related concept of Magic (supernatural), magical waters allegedly preventing aging.
Art and activism
Painter and activist Fredericka Foster curated ''The Value of Water'', at the Cathedral of St. John the Divine in New York City, which anchored a year-long initiative by the Cathedral on our dependence on water. The largest exhibition to ever appear at the Cathedral, it featured over forty artists, including Jenny Holzer, Robert Longo, Mark Rothko, William Kentridge, April Gornik, Kiki Smith, Pat Steir, William Kentridge, Alice Dalton Brown, Teresita Fernandez and Bill Viola. Foster created Think About Water, an ecological collective of artists who use water as their subject or medium. Members include Basia Irland, Aviva Rahmani, Betsy Damon, Diane Burko, Leila Daw, Stacy Levy, Charlotte Coté, Meridel Rubenstein, Stacy Levy, Anna Macleod, and Aviva Rahmani.
To mark the 10th anniversary of access to water and sanitation being declared a human right by the UN, the charity WaterAid commissioned ten visual artists to show the impact of clean water on people's lives.
Dihydrogen monoxide parody
Water's technically correct but rarely used chemical name, dihydrogen monoxide, has been used in a series of hoaxes and pranks that mock scientific illiteracy. This began in 1983, when an April Fools' Day article appeared in a newspaper in Durand, Michigan. The false story consisted of safety concerns about the substance.
See also
*
* is a collection of the chemical and physical properties of water.
* (fear of water)
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
Works cited
*
*
Further reading
* Debenedetti, PG., and HE Stanley, "Supercooled and Glassy Water", ''Physics Today'' 56 (6), pp. 40–46 (2003)
Downloadable PDF (1.9 MB)
* Gleick, PH., (editor), ''The World's Water: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources''. Island Press, Washington, D.C. (published every two years, beginning in 1998.
The World's Water, Island Press
*
Journal of Contemporary Water Research & Education
* Postel, S., ''Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity''. W.W. Norton and Company, New York. 1992
* Reisner, M., ''Cadillac Desert: The American West and Its Disappearing Water''. Penguin Books, New York. 1986.
United Nations World Water Development Report
. Produced every three years.
* St. Fleur, Nicholas
. "The water you drink is older than the planet you're standing on." ''The New York Times'' (15 April 2016)
External links
OECD Water statistics
The World's Water Data Page
FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT
Water science school
(USGS)
Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources
America Water Resources Association
Water on the web
Water structure and science
"Why water is one of the weirdest things in the universe"
''Ideas'', BBC, Video, 3:16 minutes, 2019
The chemistry of water
(NSF special report)
* [https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/molecule-that-made-us ''H2O: The Molecule That Made Us''], a 2020 PBS documentary
{{Authority control
Water,
Articles containing video clips
Hydrogen compounds
Inorganic solvents
Liquids
Materials that expand upon freezing
Nuclear reactor coolants
Oxides
Oxygen compounds
 In a water molecule, the hydrogen atoms form a 104.5° angle with the oxygen atom. The hydrogen atoms are close to two corners of a tetrahedron centered on the oxygen. At the other two corners are ''
In a water molecule, the hydrogen atoms form a 104.5° angle with the oxygen atom. The hydrogen atoms are close to two corners of a tetrahedron centered on the oxygen. At the other two corners are ''
 The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) is the continuous exchange of water within the
The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) is the continuous exchange of water within the  Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways;
Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways;  Water fit for human consumption is called
Water fit for human consumption is called 
 The human body contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size. To function properly, the body requires between of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though the British Dietetic Association advises that 2.5 liters of total water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration, including 1.8 liters (6 to 7 glasses) obtained directly from beverages. Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather.
Healthy kidneys can excrete 0.8 to 1 liter of water per hour, but stress such as exercise can reduce this amount. People can drink far more water than necessary while exercising, putting them at risk of water intoxication (hyperhydration), which can be fatal. The popular claim that "a person should consume eight glasses of water per day" seems to have no real basis in science. Studies have shown that extra water intake, especially up to at mealtime, was associated with weight loss. Adequate fluid intake is helpful in preventing constipation.
The human body contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size. To function properly, the body requires between of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though the British Dietetic Association advises that 2.5 liters of total water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration, including 1.8 liters (6 to 7 glasses) obtained directly from beverages. Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather.
Healthy kidneys can excrete 0.8 to 1 liter of water per hour, but stress such as exercise can reduce this amount. People can drink far more water than necessary while exercising, putting them at risk of water intoxication (hyperhydration), which can be fatal. The popular claim that "a person should consume eight glasses of water per day" seems to have no real basis in science. Studies have shown that extra water intake, especially up to at mealtime, was associated with weight loss. Adequate fluid intake is helpful in preventing constipation.
 Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good Fire fighting#Use of water, fire extinguishing fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid.
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a steam explosion, which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as coal, charcoal, or coke (fuel), coke graphite, decompose the water, producing water gas.
The power of such explosions was seen in the Chernobyl disaster, although the water involved in this case did not come from fire-fighting but from the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of a reaction between steam and hot zirconium.
Some metallic oxides, most notably those of
Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good Fire fighting#Use of water, fire extinguishing fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid.
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a steam explosion, which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as coal, charcoal, or coke (fuel), coke graphite, decompose the water, producing water gas.
The power of such explosions was seen in the Chernobyl disaster, although the water involved in this case did not come from fire-fighting but from the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of a reaction between steam and hot zirconium.
Some metallic oxides, most notably those of  Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, surfing and Underwater diving, diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and
Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, surfing and Underwater diving, diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and 
 Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for dishwashing. Water also plays many critical roles within the field of food science.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as air pressure, which is in turn affected by altitude. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure that occurs at higher elevations. One mole (unit), mole of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by , and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by ; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.
Solutes in water also affect water activity that affects many chemical reactions and the growth of microbes in food. Water activity can be described as a ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a solution to the vapor pressure of pure water. Solutes in water lower water activity—this is important to know because most bacterial growth ceases at low levels of water activity. Not only does microbial growth affect the safety of food, but also the preservation and shelf life of food.
Water hardness is also a critical factor in food processing and may be altered or treated by using a chemical ion exchange system. It can dramatically affect the quality of a product, as well as playing a role in sanitation. Water hardness is classified based on concentration of calcium carbonate the water contains. Water is classified as soft if it contains less than 100 mg/L (UK) or less than 60 mg/L (US).
According to a report published by the Water Footprint organization in 2010, a single kilogram of beef requires of water; however, the authors also make clear that this is a global average and circumstantial factors determine the amount of water used in beef production.
Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for dishwashing. Water also plays many critical roles within the field of food science.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as air pressure, which is in turn affected by altitude. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure that occurs at higher elevations. One mole (unit), mole of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by , and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by ; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.
Solutes in water also affect water activity that affects many chemical reactions and the growth of microbes in food. Water activity can be described as a ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a solution to the vapor pressure of pure water. Solutes in water lower water activity—this is important to know because most bacterial growth ceases at low levels of water activity. Not only does microbial growth affect the safety of food, but also the preservation and shelf life of food.
Water hardness is also a critical factor in food processing and may be altered or treated by using a chemical ion exchange system. It can dramatically affect the quality of a product, as well as playing a role in sanitation. Water hardness is classified based on concentration of calcium carbonate the water contains. Water is classified as soft if it contains less than 100 mg/L (UK) or less than 60 mg/L (US).
According to a report published by the Water Footprint organization in 2010, a single kilogram of beef requires of water; however, the authors also make clear that this is a global average and circumstantial factors determine the amount of water used in beef production.
 Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. The formation of stars is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined" around a quasar located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence".
Water has been detected in interstellar clouds within the Milky Way. Water probably exists in abundance in other galaxies, too, because its components, hydrogen, and oxygen, are among the most abundant elements in the universe. Based on models of the formation and evolution of the Solar System and that of other star systems, most other planetary systems are likely to have similar ingredients.
Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. The formation of stars is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined" around a quasar located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence".
Water has been detected in interstellar clouds within the Milky Way. Water probably exists in abundance in other galaxies, too, because its components, hydrogen, and oxygen, are among the most abundant elements in the universe. Based on models of the formation and evolution of the Solar System and that of other star systems, most other planetary systems are likely to have similar ingredients.
 * Water on Mars, Mars: under the regolith and at the poles.
* Earth–Moon system: mainly as ice sheets on Earth and in Lunar craters and volcanic rocks NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.
* Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres
* Jupiter's moons: Europa (moon), Europa's surface and also that of Ganymede (moon), Ganymede and Callisto (moon), Callisto
* Saturn: in the Rings of Saturn, planet's ring system and on the surface and mantle of Titan (moon), Titan and Enceladus (moon), Enceladus (supporting online material, table S1)
* Pluto–Charon (moon), Charon system
* Comets and other related Kuiper belt and Oort cloud objects
And is also likely present on:
* Mercury (planet), Mercury's poles
* Tethys (moon), Tethys
* Water on Mars, Mars: under the regolith and at the poles.
* Earth–Moon system: mainly as ice sheets on Earth and in Lunar craters and volcanic rocks NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.
* Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres
* Jupiter's moons: Europa (moon), Europa's surface and also that of Ganymede (moon), Ganymede and Callisto (moon), Callisto
* Saturn: in the Rings of Saturn, planet's ring system and on the surface and mantle of Titan (moon), Titan and Enceladus (moon), Enceladus (supporting online material, table S1)
* Pluto–Charon (moon), Charon system
* Comets and other related Kuiper belt and Oort cloud objects
And is also likely present on:
* Mercury (planet), Mercury's poles
* Tethys (moon), Tethys
 Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Faiths that incorporate ritual washing (Ritual purification, ablution) include Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, the Rastafari movement, Shinto, Taoism, and Wicca. Immersion (or aspersion or affusion) of a person in water is a central sacrament of Christianity (where it is called baptism); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (''Ghusl''), Judaism (''mikvah'') and Sikhism (''Amrit Sanskar''). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after washing certain parts of the body using clean water (''wudu''), unless water is unavailable (see ''Tayammum''). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of ''misogi'').
In Christianity, holy water is water that has been sanctified by a priest for the purpose of baptism, the Blessing (Roman Catholic Church), blessing of persons, places, and objects, or as a means of repelling evil.
In Zoroastrianism, water (''aban, āb'') is respected as the source of life.
Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Faiths that incorporate ritual washing (Ritual purification, ablution) include Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, the Rastafari movement, Shinto, Taoism, and Wicca. Immersion (or aspersion or affusion) of a person in water is a central sacrament of Christianity (where it is called baptism); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (''Ghusl''), Judaism (''mikvah'') and Sikhism (''Amrit Sanskar''). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after washing certain parts of the body using clean water (''wudu''), unless water is unavailable (see ''Tayammum''). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of ''misogi'').
In Christianity, holy water is water that has been sanctified by a priest for the purpose of baptism, the Blessing (Roman Catholic Church), blessing of persons, places, and objects, or as a means of repelling evil.
In Zoroastrianism, water (''aban, āb'') is respected as the source of life.
 The Ancient Greek philosopher Empedocles saw Water (classical element), water as one of the four classical elements (along with fire, earth, and Air (classical element), air), and regarded it as an ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Thales, whom Aristotle portrayed as an astronomer and an engineer, theorized that the earth, which is denser than water, emerged from the water. Thales, a monist, believed further that all things are made from water. Plato believed that the shape of water is an icosahedron – flowing easily compared to the cube-shaped earth.
The theory of the Humorism, four bodily humors associated water with phlegm, as being cold and moist. The Water (classical element), classical element of water was also one of the Five elements (Chinese philosophy), five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy (along with earth (classical element), earth, fire (classical element), fire, wood (classical element), wood, and metal (classical element), metal).
Some traditional and popular Asian philosophy, Asian philosophical systems take water as a role-model. James Legge's 1891 translation of the ''Dao De Jing'' states, "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed." ''Guanzi (text), Guanzi'' in the "Shui di" 水地 chapter further elaborates on the symbolism of water, proclaiming that "man is water" and attributing natural qualities of the people of different Chinese regions to the character of local water resources.
The Ancient Greek philosopher Empedocles saw Water (classical element), water as one of the four classical elements (along with fire, earth, and Air (classical element), air), and regarded it as an ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Thales, whom Aristotle portrayed as an astronomer and an engineer, theorized that the earth, which is denser than water, emerged from the water. Thales, a monist, believed further that all things are made from water. Plato believed that the shape of water is an icosahedron – flowing easily compared to the cube-shaped earth.
The theory of the Humorism, four bodily humors associated water with phlegm, as being cold and moist. The Water (classical element), classical element of water was also one of the Five elements (Chinese philosophy), five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy (along with earth (classical element), earth, fire (classical element), fire, wood (classical element), wood, and metal (classical element), metal).
Some traditional and popular Asian philosophy, Asian philosophical systems take water as a role-model. James Legge's 1891 translation of the ''Dao De Jing'' states, "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed." ''Guanzi (text), Guanzi'' in the "Shui di" 水地 chapter further elaborates on the symbolism of water, proclaiming that "man is water" and attributing natural qualities of the people of different Chinese regions to the character of local water resources.