War Of 1812 Forts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or
 The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century
The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century

 The earliest evidence of
The earliest evidence of  In Western Europe, since the late 18th century, more than 150 conflicts and about 600 battles have taken place.World War One – A New Kind of War , Part II
In Western Europe, since the late 18th century, more than 150 conflicts and about 600 battles have taken place.World War One – A New Kind of War , Part II
, From ''14 – 18 Understanding the Great War'', by Stéphane Audoin-Rouzeau, Annette Becker During the 20th century, war resulted in a dramatic intensification of the pace of social changes, and was a crucial catalyst for the emergence of the political Left as a force to be reckoned with.: "War in this century became an essential precondition for the emergence of a numerically powerful Left, moving it from the margins to the very center of European politics during 1917–18 and of all world affairs after 1941".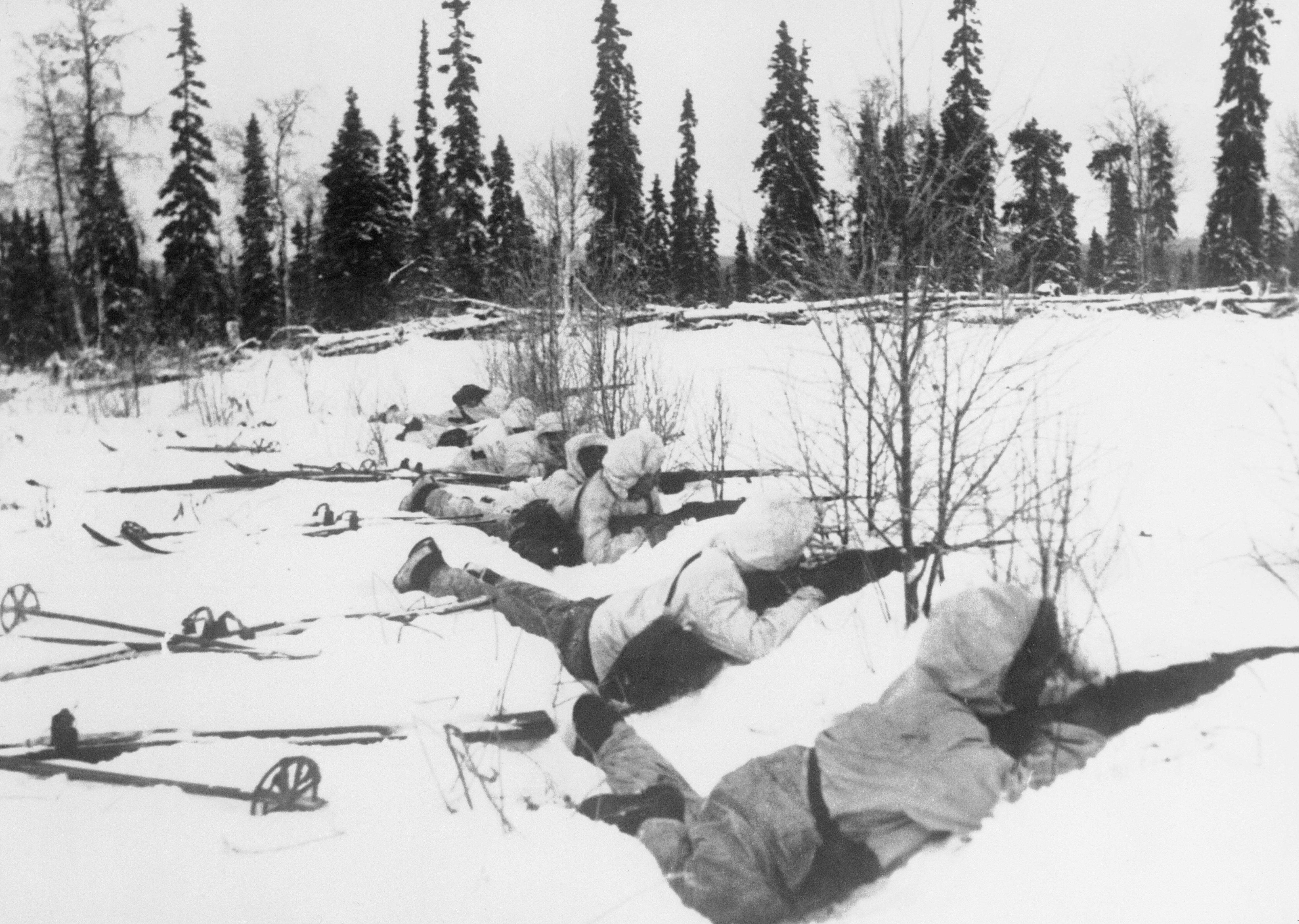 In 1947, in view of the rapidly increasingly destructive consequences of modern warfare, and with a particular concern for the consequences and costs of the newly developed atom bomb, Albert Einstein famously stated, "I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones." Nuclear Age Peace Foundation paper
Mao Zedong urged the socialist camp not to fear
In 1947, in view of the rapidly increasingly destructive consequences of modern warfare, and with a particular concern for the consequences and costs of the newly developed atom bomb, Albert Einstein famously stated, "I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones." Nuclear Age Peace Foundation paper
Mao Zedong urged the socialist camp not to fear  The Human Security Report 2005 documented a significant decline in the number and severity of armed conflicts since the end of the
The Human Security Report 2005 documented a significant decline in the number and severity of armed conflicts since the end of the
 * Asymmetric warfare is a conflict between
* Asymmetric warfare is a conflict between

 Throughout the course of human history, the average number of people dying from war has fluctuated relatively little, being about 1 to 10 people dying per 100,000. However, major wars over shorter periods have resulted in much higher casualty rates, with 100-200 casualties per 100,000 over a few years. While conventional wisdom holds that casualties have increased in recent times due to technological improvements in warfare, this is not generally true. For instance, the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) had about the same number of casualties per capita as World War I, although it was higher during World War II (WWII). That said, overall the number of casualties from war has not significantly increased in recent times. Quite to the contrary, on a global scale the time since WWII has been unusually peaceful.
Throughout the course of human history, the average number of people dying from war has fluctuated relatively little, being about 1 to 10 people dying per 100,000. However, major wars over shorter periods have resulted in much higher casualty rates, with 100-200 casualties per 100,000 over a few years. While conventional wisdom holds that casualties have increased in recent times due to technological improvements in warfare, this is not generally true. For instance, the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) had about the same number of casualties per capita as World War I, although it was higher during World War II (WWII). That said, overall the number of casualties from war has not significantly increased in recent times. Quite to the contrary, on a global scale the time since WWII has been unusually peaceful.
White
 Additionally, it has been estimated anywhere from 18% to 54% of Vietnam war veterans suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder.
Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all white American males aged 13 to 43 died in the American Civil War, including about 6% in the North and approximately 18% in the South. The war remains the deadliest conflict in American history, resulting in the deaths of 620,000 military personnel. United States military casualties of war since 1775 have totaled over two million. Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilized in World War I, 8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured.
Additionally, it has been estimated anywhere from 18% to 54% of Vietnam war veterans suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder.
Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all white American males aged 13 to 43 died in the American Civil War, including about 6% in the North and approximately 18% in the South. The war remains the deadliest conflict in American history, resulting in the deaths of 620,000 military personnel. United States military casualties of war since 1775 have totaled over two million. Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilized in World War I, 8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured.
 During
During
''TIME''. In addition, if it were not for modern medical advances there would be thousands more dead from disease and infection. For instance, during the Seven Years' War, the Royal Navy reported it conscripted 184,899 sailors, of whom 133,708 (72%) died of disease or were 'missing'. It is estimated that between 1985 and 1994, 378,000 people per year died due to war.
 Most wars have resulted in significant loss of life, along with destruction of infrastructure and resources (which may lead to
Most wars have resulted in significant loss of life, along with destruction of infrastructure and resources (which may lead to
 World War II was the most financially costly conflict in history; its belligerents cumulatively spent about a trillion U.S. dollars on the war effort (as adjusted to 1940 prices).
The
World War II was the most financially costly conflict in history; its belligerents cumulatively spent about a trillion U.S. dollars on the war effort (as adjusted to 1940 prices).
The
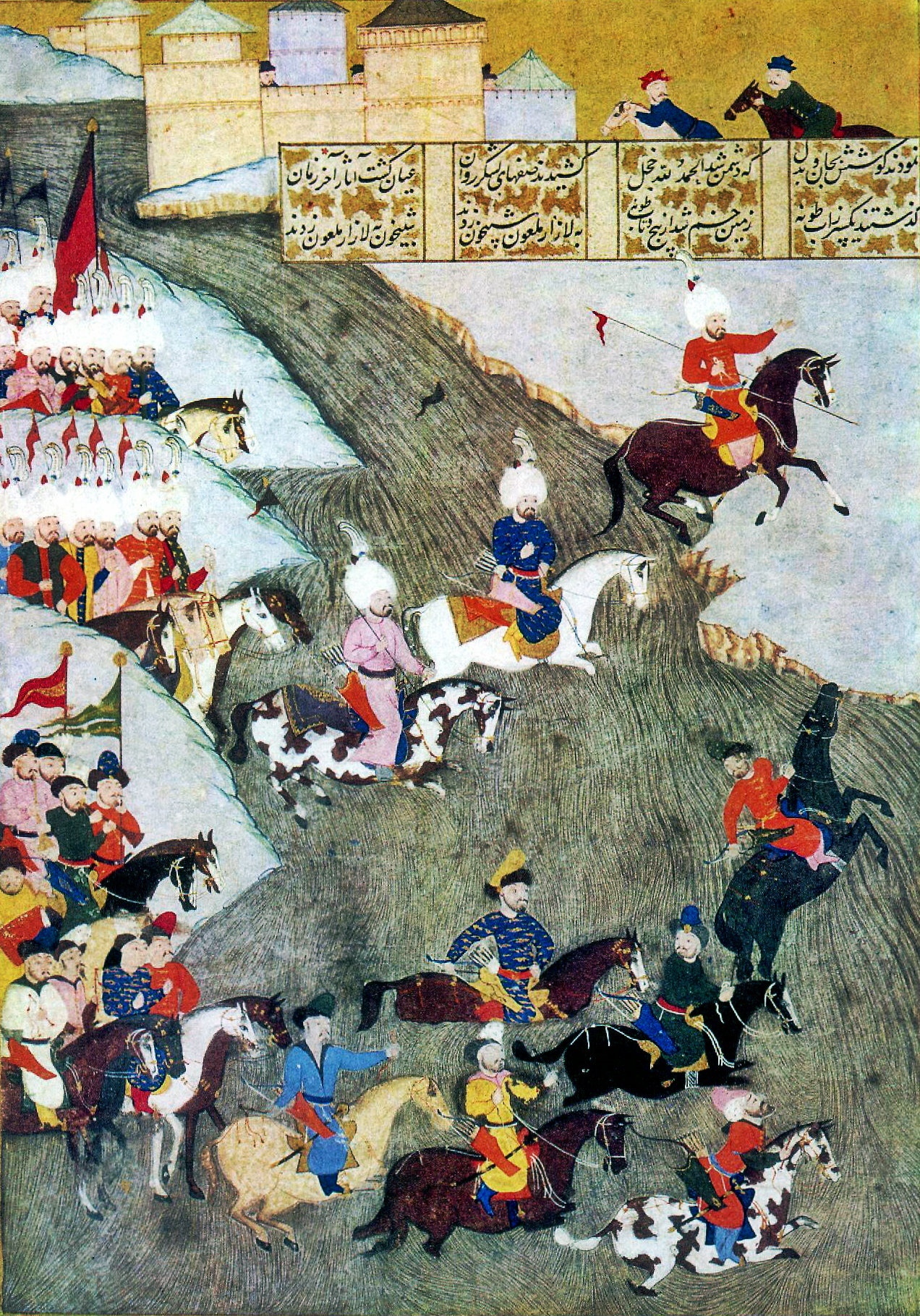 There are many theories about the motivations for war, but no consensus about which are most common. Carl von Clausewitz said, 'Every age has its own kind of war, its own limiting conditions, and its own peculiar preconceptions.'
There are many theories about the motivations for war, but no consensus about which are most common. Carl von Clausewitz said, 'Every age has its own kind of war, its own limiting conditions, and its own peculiar preconceptions.'
 Several theories concern the evolutionary origins of warfare. There are two main schools: One sees organized warfare as emerging in or after the Mesolithic as a result of complex social organization and greater population density and competition over resources; the other sees human warfare as a more ancient practice derived from common animal tendencies, such as territoriality and sexual competition.
The latter school argues that since warlike behavior patterns are found in many primate species such as
Several theories concern the evolutionary origins of warfare. There are two main schools: One sees organized warfare as emerging in or after the Mesolithic as a result of complex social organization and greater population density and competition over resources; the other sees human warfare as a more ancient practice derived from common animal tendencies, such as territoriality and sexual competition.
The latter school argues that since warlike behavior patterns are found in many primate species such as  Crofoot and Wrangham have argued that warfare, if defined as group interactions in which "coalitions attempt to aggressively dominate or kill members of other groups", is a characteristic of most human societies. Those in which it has been lacking "tend to be societies that were politically dominated by their neighbors".''Mind the Gap: Tracing the Origins of Human Universals'' By Peter M. Kappeler, Joan B. Silk, 2009, Chapter 8, "Intergroup Aggression in Primates and Humans; The Case for a Unified Theory", Margaret C. Crofoot and Richard W. Wrangham
Ashley Montagu strongly denied universalistic instinctual arguments, arguing that social factors and childhood socialization are important in determining the nature and presence of warfare. Thus, he argues, warfare is not a universal human occurrence and appears to have been a historical invention, associated with certain types of human societies. Montagu's argument is supported by ethnographic research conducted in societies where the concept of aggression seems to be entirely absent, e.g. the Chewong and Semai of the Malay peninsula. Bobbi S. Low has observed correlation between warfare and education, noting societies where warfare is commonplace encourage their children to be more aggressive.
Crofoot and Wrangham have argued that warfare, if defined as group interactions in which "coalitions attempt to aggressively dominate or kill members of other groups", is a characteristic of most human societies. Those in which it has been lacking "tend to be societies that were politically dominated by their neighbors".''Mind the Gap: Tracing the Origins of Human Universals'' By Peter M. Kappeler, Joan B. Silk, 2009, Chapter 8, "Intergroup Aggression in Primates and Humans; The Case for a Unified Theory", Margaret C. Crofoot and Richard W. Wrangham
Ashley Montagu strongly denied universalistic instinctual arguments, arguing that social factors and childhood socialization are important in determining the nature and presence of warfare. Thus, he argues, warfare is not a universal human occurrence and appears to have been a historical invention, associated with certain types of human societies. Montagu's argument is supported by ethnographic research conducted in societies where the concept of aggression seems to be entirely absent, e.g. the Chewong and Semai of the Malay peninsula. Bobbi S. Low has observed correlation between warfare and education, noting societies where warfare is commonplace encourage their children to be more aggressive.
 Malthusian theories see expanding population and scarce resources as a source of violent conflict.
Malthusian theories see expanding population and scarce resources as a source of violent conflict.
 According to Heinsohn, who proposed youth bulge theory in its most generalized form, a youth bulge occurs when 30 to 40 percent of the males of a nation belong to the "fighting age" cohorts from 15 to 29 years of age. It will follow periods with total fertility rates as high as 4–8 children per woman with a 15–29-year delay.
Heinsohn saw both past "Christianist" European colonialism and imperialism, as well as today's Islamist civil unrest and terrorism as results of high birth rates producing youth bulges. Among prominent historical events that have been attributed to youth bulges are the role played by the historically large youth cohorts in the rebellion and revolution waves of early modern Europe, including the French Revolution of 1789, and the effect of economic depression upon the largest German youth cohorts ever in explaining the rise of Nazism in Germany in the 1930s. The 1994 Rwandan genocide has also been analyzed as following a massive youth bulge.
Youth bulge theory has been subjected to statistical analysis by the World Bank, Population Action International, and the Berlin Institute for Population and Development. Youth bulge theories have been criticized as leading to racial, gender and age discrimination.
According to Heinsohn, who proposed youth bulge theory in its most generalized form, a youth bulge occurs when 30 to 40 percent of the males of a nation belong to the "fighting age" cohorts from 15 to 29 years of age. It will follow periods with total fertility rates as high as 4–8 children per woman with a 15–29-year delay.
Heinsohn saw both past "Christianist" European colonialism and imperialism, as well as today's Islamist civil unrest and terrorism as results of high birth rates producing youth bulges. Among prominent historical events that have been attributed to youth bulges are the role played by the historically large youth cohorts in the rebellion and revolution waves of early modern Europe, including the French Revolution of 1789, and the effect of economic depression upon the largest German youth cohorts ever in explaining the rise of Nazism in Germany in the 1930s. The 1994 Rwandan genocide has also been analyzed as following a massive youth bulge.
Youth bulge theory has been subjected to statistical analysis by the World Bank, Population Action International, and the Berlin Institute for Population and Development. Youth bulge theories have been criticized as leading to racial, gender and age discrimination.
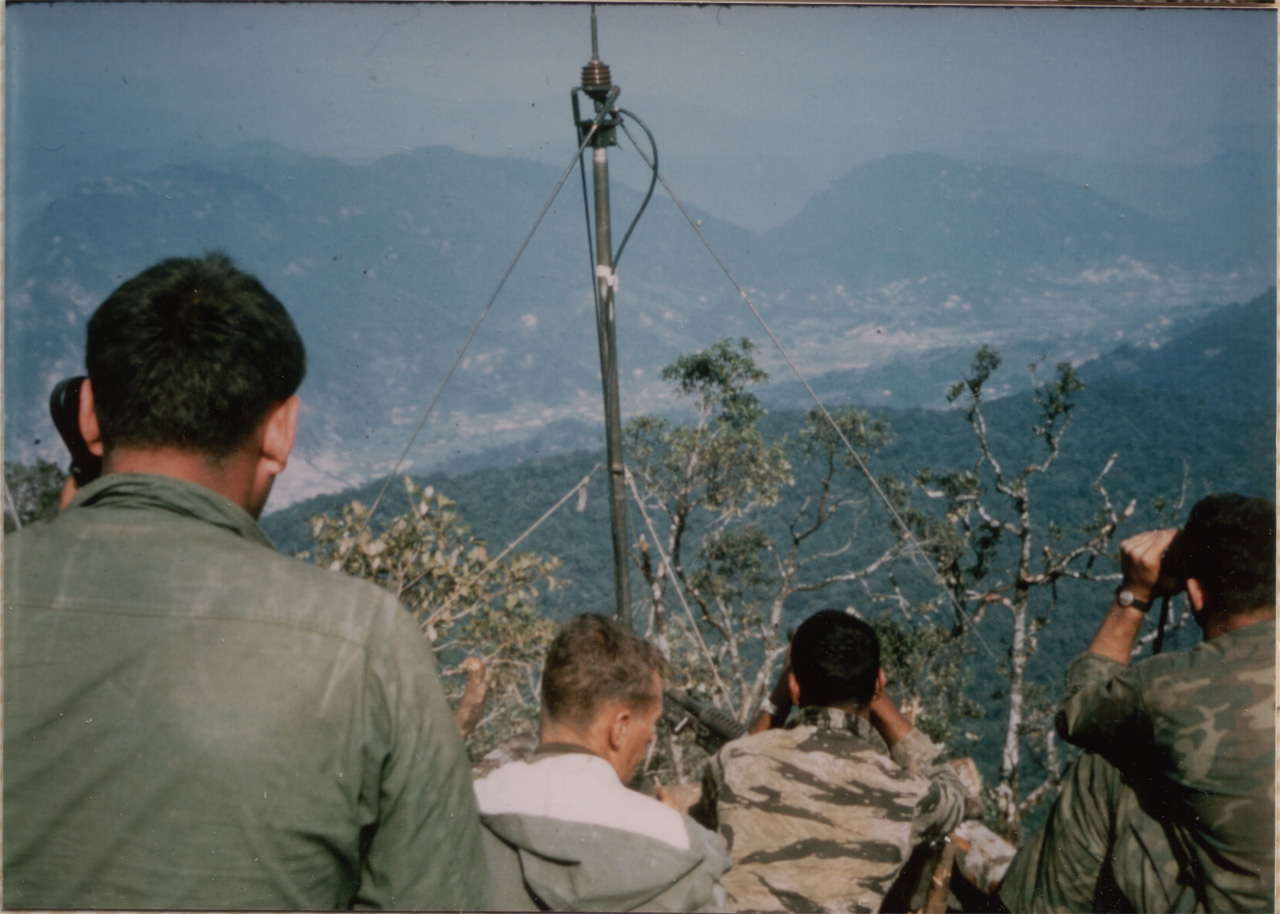 Rationalism is an
Rationalism is an  " Information asymmetry with incentives to misrepresent" occurs when two countries have secrets about their individual capabilities, and do not agree on either: who would win a war between them, or the magnitude of state's victory or loss. For instance, Geoffrey Blainey argues that war is a result of miscalculation of strength. He cites historical examples of war and demonstrates, "war is usually the outcome of a diplomatic crisis which cannot be solved because both sides have conflicting estimates of their bargaining power." Thirdly, bargaining may fail due to the states' inability to make credible commitments.
Within the rationalist tradition, some theorists have suggested that individuals engaged in war suffer a normal level of
" Information asymmetry with incentives to misrepresent" occurs when two countries have secrets about their individual capabilities, and do not agree on either: who would win a war between them, or the magnitude of state's victory or loss. For instance, Geoffrey Blainey argues that war is a result of miscalculation of strength. He cites historical examples of war and demonstrates, "war is usually the outcome of a diplomatic crisis which cannot be solved because both sides have conflicting estimates of their bargaining power." Thirdly, bargaining may fail due to the states' inability to make credible commitments.
Within the rationalist tradition, some theorists have suggested that individuals engaged in war suffer a normal level of
 The morality of war has been the subject of debate for thousands of years.
The two principal aspects of ethics in war, according to the just war theory, are '' jus ad bellum'' and '' jus in bello''.
''Jus ad bellum'' (right to war), dictates which unfriendly acts and circumstances justify a proper authority in declaring war on another nation. There are six main criteria for the declaration of a just war: first, any just war must be declared by a lawful authority; second, it must be a just and righteous cause, with sufficient gravity to merit large-scale violence; third, the just belligerent must have rightful intentions – namely, that they seek to advance good and curtail evil; fourth, a just belligerent must have a reasonable chance of success; fifth, the war must be a last resort; and sixth, the ends being sought must be proportional to means being used.
'' Jus in bello'' (right in war), is the set of ethical rules when conducting war. The two main principles are proportionality and discrimination. Proportionality regards how much force is necessary and morally appropriate to the ends being sought and the injustice suffered. The principle of discrimination determines who are the legitimate targets in a war, and specifically makes a separation between combatants, who it is permissible to kill, and non-combatants, who it is not. Failure to follow these rules can result in the loss of legitimacy for the just-war-belligerent.
The morality of war has been the subject of debate for thousands of years.
The two principal aspects of ethics in war, according to the just war theory, are '' jus ad bellum'' and '' jus in bello''.
''Jus ad bellum'' (right to war), dictates which unfriendly acts and circumstances justify a proper authority in declaring war on another nation. There are six main criteria for the declaration of a just war: first, any just war must be declared by a lawful authority; second, it must be a just and righteous cause, with sufficient gravity to merit large-scale violence; third, the just belligerent must have rightful intentions – namely, that they seek to advance good and curtail evil; fourth, a just belligerent must have a reasonable chance of success; fifth, the war must be a last resort; and sixth, the ends being sought must be proportional to means being used.
'' Jus in bello'' (right in war), is the set of ethical rules when conducting war. The two main principles are proportionality and discrimination. Proportionality regards how much force is necessary and morally appropriate to the ends being sought and the injustice suffered. The principle of discrimination determines who are the legitimate targets in a war, and specifically makes a separation between combatants, who it is permissible to kill, and non-combatants, who it is not. Failure to follow these rules can result in the loss of legitimacy for the just-war-belligerent.
 The just war theory was foundational in the creation of the United Nations and in international law's regulations on legitimate war.
Fascism, and the ideals it encompasses, such as Pragmatism, racism, and social Darwinism, hold that violence is good. Pragmatism holds that war and violence can be good if it serves the ends of the people, without regard for universal morality. Racism holds that violence is good so that a master race can be established, or to purge an inferior race from the earth, or both. Social Darwinism asserts that violence is sometimes necessary to weed the unfit from society so civilization can flourish. These are broad archetypes for the general position that the ends justify the means. Lewis Coser, U.S. conflict theorist and sociologist, argued conflict provides a function and a process whereby a succession of new equilibriums are created. Thus, the struggle of opposing forces, rather than being disruptive, may be a means of balancing and maintaining a social structure or society.
The just war theory was foundational in the creation of the United Nations and in international law's regulations on legitimate war.
Fascism, and the ideals it encompasses, such as Pragmatism, racism, and social Darwinism, hold that violence is good. Pragmatism holds that war and violence can be good if it serves the ends of the people, without regard for universal morality. Racism holds that violence is good so that a master race can be established, or to purge an inferior race from the earth, or both. Social Darwinism asserts that violence is sometimes necessary to weed the unfit from society so civilization can flourish. These are broad archetypes for the general position that the ends justify the means. Lewis Coser, U.S. conflict theorist and sociologist, argued conflict provides a function and a process whereby a succession of new equilibriums are created. Thus, the struggle of opposing forces, rather than being disruptive, may be a means of balancing and maintaining a social structure or society.
 Religious groups have long formally opposed or sought to limit war as in the Second Vatican Council document ''Gaudiem et Spes'': "Any act of war aimed indiscriminately at the destruction of entire cities of extensive areas along with their population is a crime against God and man himself. It merits unequivocal and unhesitating condemnation."
Anti-war movements have existed for every major war in the 20th century, including, most prominently, World War I, World War II, and the Vietnam War. In the 21st century, worldwide anti-war movements occurred in response to the United States invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq. Protests opposing the War in Afghanistan occurred in Europe, Asia, and the United States.
Religious groups have long formally opposed or sought to limit war as in the Second Vatican Council document ''Gaudiem et Spes'': "Any act of war aimed indiscriminately at the destruction of entire cities of extensive areas along with their population is a crime against God and man himself. It merits unequivocal and unhesitating condemnation."
Anti-war movements have existed for every major war in the 20th century, including, most prominently, World War I, World War II, and the Vietnam War. In the 21st century, worldwide anti-war movements occurred in response to the United States invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq. Protests opposing the War in Afghanistan occurred in Europe, Asia, and the United States.
''Defining War for the 21st Century,''
online
* Pauketat, Timothy (2005). ''North American Archaeology''. Blackwell Publishing. * * * Sponsel, Leslie; Gregor, Thomas (1994). ''Anthropology of Peace and Nonviolence.'' Lynne Rienner Publishing. *
An Interactive map of all the battles fought around the world in the last 4,000 years
Timeline of wars on Histropedia
* {{Authority control Dispute resolution Ethics Violence
paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carr ...
groups such as mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. Warfare refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties.
While some war studies scholars consider war a universal and ancestral aspect of human nature, others argue it is a result of specific socio-cultural, economic or ecological circumstances.
Etymology
 The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century
The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
words ''wyrre'' and ''werre'', from Old French ''werre'' (also ''guerre'' as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish *''werra'', ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic *''werzō'' 'mixture, confusion'. The word is related to the Old Saxon ''werran'', Old High German ''werran'', and the German ''verwirren'', meaning "to confuse", "to perplex", and "to bring into confusion".
History
 The earliest evidence of
The earliest evidence of prehistoric warfare
Prehistoric warfare refers to war that occurred between societies without recorded history.
The existence — and even the definition — of war in humanity's hypothetical state of nature has been a controversial topic in the history of ideas at ...
is a Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
cemetery in Jebel Sahaba, which has been determined to be approximately 14,000 years old. About forty-five percent of the skeletons there displayed signs of violent death.Keeley, Lawrence H: ''War Before Civilization: The Myth of the Peaceful Savage''. p. 37. Since the rise of the state some 5,000 years ago, military activity has occurred over much of the globe. The advent of gunpowder and the acceleration of technological advances led to modern warfare. According to Conway W. Henderson, "One source claims that 14,500 wars have taken place between 3500 BC and the late 20th century, costing 3.5 billion lives, leaving only 300 years of peace (Beer 1981: 20)." An unfavorable review of this estimate mentions the following regarding one of the proponents of this estimate: "In addition, perhaps feeling that the war casualties figure was improbably high, he changed 'approximately 3,640,000,000 human beings have been killed by war or the diseases produced by war' to 'approximately 1,240,000,000 human beings...&c.'" The lower figure is more plausible, but could still be on the high side considering that the 100 deadliest acts of mass violence between 480 BC and 2002 AD (wars and other man-made disasters with at least 300,000 and up to 66 million victims) claimed about 455 million human lives in total. Primitive warfare is estimated to have accounted for 15.1% of deaths and claimed 400 million victims. Added to the aforementioned figure of 1,240 million between 3500 BC and the late 20th century, this would mean a total of 1,640,000,000 people killed by war (including deaths from famine and disease caused by war) throughout the history and pre-history of mankind. For comparison, an estimated 1,680,000,000 people died from infectious diseases in the 20th century.
In '' War Before Civilization'', Lawrence H. Keeley, a professor at the University of Illinois, says approximately 90–95% of known societies throughout history engaged in at least occasional warfare, and many fought constantly.
Keeley describes several styles of primitive combat such as small raids, large raids, and massacres. All of these forms of warfare were used by primitive societies, a finding supported by other researchers. Keeley explains that early war raids were not well organized, as the participants did not have any formal training. Scarcity of resources meant defensive works were not a cost-effective way to protect the society against enemy raids.Keeley, Lawrence H: ''War Before Civilization: The Myth of the Peaceful Savage''. p. 55.
William Rubinstein wrote "Pre-literate societies, even those organised in a relatively advanced way, were renowned for their studied cruelty...'archaeology yields evidence of prehistoric massacres more severe than any recounted in ethnography .e., after the coming of the Europeans'"
 In Western Europe, since the late 18th century, more than 150 conflicts and about 600 battles have taken place.World War One – A New Kind of War , Part II
In Western Europe, since the late 18th century, more than 150 conflicts and about 600 battles have taken place.World War One – A New Kind of War , Part II, From ''14 – 18 Understanding the Great War'', by Stéphane Audoin-Rouzeau, Annette Becker During the 20th century, war resulted in a dramatic intensification of the pace of social changes, and was a crucial catalyst for the emergence of the political Left as a force to be reckoned with.: "War in this century became an essential precondition for the emergence of a numerically powerful Left, moving it from the margins to the very center of European politics during 1917–18 and of all world affairs after 1941".
 In 1947, in view of the rapidly increasingly destructive consequences of modern warfare, and with a particular concern for the consequences and costs of the newly developed atom bomb, Albert Einstein famously stated, "I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones." Nuclear Age Peace Foundation paper
Mao Zedong urged the socialist camp not to fear
In 1947, in view of the rapidly increasingly destructive consequences of modern warfare, and with a particular concern for the consequences and costs of the newly developed atom bomb, Albert Einstein famously stated, "I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones." Nuclear Age Peace Foundation paper
Mao Zedong urged the socialist camp not to fear nuclear war
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear w ...
with the United States since, even if "half of mankind died, the other half would remain while imperialism would be razed to the ground and the whole world would become socialist."
A distinctive feature of war since 1945 is that combat has largely been a matter of civil wars and insurgencies. The major exceptions were the Korean War, the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, the Iran–Iraq War, the Gulf War, the Eritrean–Ethiopian War, and the Russo-Ukrainian War.
 The Human Security Report 2005 documented a significant decline in the number and severity of armed conflicts since the end of the
The Human Security Report 2005 documented a significant decline in the number and severity of armed conflicts since the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
in the early 1990s. However, the evidence examined in the 2008 edition of the Center for International Development and Conflict Management's "Peace and Conflict" study indicated the overall decline in conflicts had stalled.
Types of warfare
 * Asymmetric warfare is a conflict between
* Asymmetric warfare is a conflict between belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meaning ...
s of drastically different levels of military capability or size.
* Biological warfare, or germ warfare, is the use of weaponized biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
* Chemical warfare
Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare, biological warfare and radiological warfare, which together make up CBRN, the military acronym ...
involves the use of weaponized chemicals in combat. Poison gas as a chemical weapon was principally used during World War I, and resulted in over a million estimated casualties, including more than 100,000 civilians.
* Cold warfare is an intense international rivalry without direct military conflict, but with a sustained threat of it, including high levels of military preparations, expenditures, and development, and may involve active conflicts by indirect means, such as economic warfare, political warfare, covert operation
A covert operation is a military operation intended to conceal the identity of (or allow plausible deniability by) the party that instigated the operation. Covert operations should not be confused with clandestine operations, which are performe ...
s, espionage, cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyber attacks against an enemy state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, manipulation or economic war ...
, or proxy wars.
* Conventional warfare is declared war between states in which nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
, biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
, or chemical weapons are not used or see limited deployment.
* Cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyber attacks against an enemy state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, manipulation or economic war ...
involves the actions by a nation-state or international organization to attack and attempt to damage another nation's information systems.
* Insurgency is a rebellion against authority, when those taking part in the rebellion are not recognized as belligerents (lawful combatants). An insurgency can be fought via counterinsurgency, and may also be opposed by measures to protect the population, and by political and economic actions of various kinds aimed at undermining the insurgents' claims against the incumbent regime.
* Information warfare is the application of destructive force on a large scale against information assets and systems, against the computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s and networks that support the four critical infrastructures (the power grid, communications, financial, and transportation).
* Nuclear warfare is warfare in which nuclear weapons are the primary, or a major, method of achieving capitulation.
* Total war is warfare by any means possible, disregarding the laws of war, placing no limits on legitimate military targets, using weapons and tactics resulting in significant civilian casualties, or demanding a war effort requiring significant sacrifices by the friendly civilian population.
* Unconventional warfare, the opposite of conventional warfare, is an attempt to achieve military victory through acquiescence, capitulation, or clandestine support for one side of an existing conflict.
Aims
Entities contemplating going to war and entities considering whether to end a war may formulate ''war aims'' as an evaluation/propaganda tool. War aims may stand as a proxy for national-military resolve.Definition
Fried defines war aims as "the desired territorial, economic, military or other benefits expected following successful conclusion of a war".Classification
Tangible/intangible aims: * Tangible war aims may involve (for example) the acquisition of territory (as in the German goal of Lebensraum in the first half of the 20th century) or the recognition of economic concessions (as in the Anglo-Dutch Wars). * Intangible war aims – like the accumulation of credibility or reputation – may have more tangible expression ("conquest restores prestige, annexation increases power"). Explicit/implicit aims: * Explicit war aims may involve published policy decisions. * Implicit war aims can take the form of minutes of discussion, memoranda and instructions. Positive/negative aims: * "Positive war aims" cover tangible outcomes. * "Negative war aims" forestall or prevent undesired outcomes. War aims can change in the course of conflict and may eventually morph into "peace conditions" – the minimal conditions under which a state may cease to wage a particular war.Effects

Military and civilian casualties in recent human history
Largest by death toll
The deadliest war in history, in terms of the cumulative number of deaths since its start, is World War II, from 1939 to 1945, with 60–85 million deaths, followed by the Mongol conquests at up to 60 million. As concerns a belligerent's losses in proportion to its prewar population, the most destructive war inmodern history
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
may have been the Paraguayan War (see Paraguayan War casualties). In 2013 war resulted in 31,000 deaths, down from 72,000 deaths in 1990. In 2003, Richard Smalley identified war as the sixth biggest problem (of ten) facing humanity for the next fifty years. War usually results in significant deterioration of infrastructure and the ecosystem, a decrease in social spending, famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
, large-scale emigration from the war zone, and often the mistreatment of prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
or civilians. For instance, of the nine million people who were on the territory of the Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
in 1941, some 1.6 million were killed by the Germans in actions away from battlefields, including about 700,000 prisoners of war, 500,000 Jews, and 320,000 people counted as partisans (the vast majority of whom were unarmed civilians). Another byproduct of some wars is the prevalence of propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
by some or all parties in the conflict, and increased revenues by weapons manufacturers.
Three of the ten most costly wars, in terms of loss of life, have been waged in the last century. These are the two World Wars, followed by the Second Sino-Japanese War (which is sometimes considered part of World War II, or as overlapping). Most of the others involved China or neighboring peoples. The death toll of World War II, being over 60 million, surpasses all other war-death-tolls.McFarlane, Alan: ''The Savage Wars of Peace: England, Japan and the Malthusian Trap'', Blackwell 2003, ,
– cited bWhite
On military personnel
Military personnel subject to combat in war often suffer mental and physical injuries, including depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, disease, injury, and death. Swank and Marchand's World War II study found that after sixty days of continuous combat, 98% of all surviving military personnel will become psychiatric casualties. Psychiatric casualties manifest themselves in fatigue cases, confusional states, conversion hysteria, anxiety, obsessional and compulsive states, and character disorders. During
During Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's retreat from Moscow, more French military personnel died of typhus than were killed by the Russians. Of the 450,000 soldiers who crossed the Neman on 25 June 1812, less than 40,000 returned. More military personnel were killed from 1500 to 1914 by typhus than from military action.War and Pestilence''TIME''. In addition, if it were not for modern medical advances there would be thousands more dead from disease and infection. For instance, during the Seven Years' War, the Royal Navy reported it conscripted 184,899 sailors, of whom 133,708 (72%) died of disease or were 'missing'. It is estimated that between 1985 and 1994, 378,000 people per year died due to war.
On civilians
 Most wars have resulted in significant loss of life, along with destruction of infrastructure and resources (which may lead to
Most wars have resulted in significant loss of life, along with destruction of infrastructure and resources (which may lead to famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
, disease, and death in the civilian population). During the Thirty Years' War in Europe, the population of the Holy Roman Empire was reduced by 15 to 40 percent. Civilians in war zones may also be subject to war atrocities such as genocide, while survivors may suffer the psychological aftereffects of witnessing the destruction of war. War also results in lower quality of life and worse health outcomes. A medium-sized conflict with about 2,500 battle deaths reduces civilian life expectancy by one year and increases infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
by 10% and malnutrition by 3.3%. Additionally, about 1.8% of the population loses access to drinking water.
Most estimates of World War II casualties indicate around 60 million people died, 40 million of whom were civilians. Deaths in the Soviet Union were around 27 million. Since a high proportion of those killed were young men who had not yet fathered any children, population growth in the postwar Soviet Union was much lower than it otherwise would have been.
Economic
Once a war has ended, losing nations are sometimes required to pay war reparations to the victorious nations. In certain cases, land is ceded to the victorious nations. For example, the territory of Alsace-Lorraine has been traded between France and Germany on three different occasions. Typically, war becomes intertwined with the economy and many wars are partially or entirely based on economic reasons. Following World War II, consensus opinion for many years amongst economists and historians was that war can stimulate a country's economy as evidenced by the U.S's emergence from theGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, though modern economic analysis has thrown significant doubt on these views. In most cases, such as the wars of Louis XIV, the Franco-Prussian War, and World War I, warfare primarily results in damage to the economy of the countries involved. For example, Russia's involvement in World War I took such a toll on the Russian economy that it almost collapsed and greatly contributed to the start of the Russian Revolution of 1917.
World War II
 World War II was the most financially costly conflict in history; its belligerents cumulatively spent about a trillion U.S. dollars on the war effort (as adjusted to 1940 prices).
The
World War II was the most financially costly conflict in history; its belligerents cumulatively spent about a trillion U.S. dollars on the war effort (as adjusted to 1940 prices).
The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
of the 1930s ended as nations increased their production of war materials.
By the end of the war, 70% of European industrial infrastructure was destroyed. Property damage in the Soviet Union inflicted by the Axis invasion was estimated at a value of 679 billion rubles. The combined damage consisted of complete or partial destruction of 1,710 cities and towns, 70,000 villages/hamlets, 2,508 church buildings, 31,850 industrial establishments, of railroad, 4100 railroad stations, 40,000 hospitals, 84,000 schools, and 43,000 public libraries.
Theories of motivation
 There are many theories about the motivations for war, but no consensus about which are most common. Carl von Clausewitz said, 'Every age has its own kind of war, its own limiting conditions, and its own peculiar preconceptions.'
There are many theories about the motivations for war, but no consensus about which are most common. Carl von Clausewitz said, 'Every age has its own kind of war, its own limiting conditions, and its own peculiar preconceptions.'
Psychoanalytic
Dutchpsychoanalyst
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek language, Greek: + . is a set of Theory, theories and Therapy, therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a bo ...
Joost Meerloo held that, "War is often...a mass discharge of accumulated internal rage (where)...the inner fears of mankind are discharged in mass destruction."
, A. M. Meerloo, M.D. ''The Rape of the Mind'' (2009) p. 134, Progressive Press,
Other psychoanalysts such as E.F.M. Durban and John Bowlby have argued human beings are inherently violent. This aggressiveness is fueled by displacement and projection
Projection, projections or projective may refer to:
Physics
* Projection (physics), the action/process of light, heat, or sound reflecting from a surface to another in a different direction
* The display of images by a projector
Optics, graphic ...
where a person transfers his or her grievances into bias and hatred against other races, religions
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, tran ...
, nations or ideologies. By this theory, the nation state preserves order in the local society while creating an outlet for aggression through warfare.
The Italian psychoanalyst Franco Fornari, a follower of Melanie Klein, thought war was the paranoid or projective "elaboration" of mourning. Fornari thought war and violence develop out of our "love need": our wish to preserve and defend the sacred object to which we are attached, namely our early mother and our fusion with her. For the adult, nations are the sacred objects that generate warfare. Fornari focused upon sacrifice as the essence of war: the astonishing willingness of human beings to die for their country, to give over their bodies to their nation.
Despite Fornari's theory that man's altruistic desire for self-sacrifice for a noble cause is a contributing factor towards war, few wars have originated from a desire for war among the general populace. Far more often the general population has been reluctantly drawn into war by its rulers. One psychological theory that looks at the leaders is advanced by Maurice Walsh. He argues the general populace is more neutral towards war and wars occur when leaders with a psychologically abnormal disregard for human life are placed into power. War is caused by leaders who seek war such as Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
and Hitler. Such leaders most often come to power in times of crisis when the populace opts for a decisive leader, who then leads the nation to war.
Evolutionary
 Several theories concern the evolutionary origins of warfare. There are two main schools: One sees organized warfare as emerging in or after the Mesolithic as a result of complex social organization and greater population density and competition over resources; the other sees human warfare as a more ancient practice derived from common animal tendencies, such as territoriality and sexual competition.
The latter school argues that since warlike behavior patterns are found in many primate species such as
Several theories concern the evolutionary origins of warfare. There are two main schools: One sees organized warfare as emerging in or after the Mesolithic as a result of complex social organization and greater population density and competition over resources; the other sees human warfare as a more ancient practice derived from common animal tendencies, such as territoriality and sexual competition.
The latter school argues that since warlike behavior patterns are found in many primate species such as chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
s, Analysis of chimpanzee war behavior as well as in many ant species, Scholarly comparisons between human and ant wars group conflict may be a general feature of animal social behavior. Some proponents of the idea argue that war, while innate, has been intensified greatly by developments of technology and social organization such as weaponry and states.
Psychologist and linguist Steven Pinker argued that war-related behaviors may have been naturally selected in the ancestral environment due to the benefits of victory. He also argued that in order to have credible deterrence against other groups (as well as on an individual level), it was important to have a reputation for retaliation, causing humans to develop instincts for revenge
Revenge is committing a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance, be it real or perceived. Francis Bacon described revenge as a kind of "wild justice" that "does... offend the law ndputteth the law out of office." Pr ...
as well as for protecting a group's (or an individual's) reputation (" honor").
Economic
War can be seen as a growth of economic competition in a competitive international system. In this view wars begin as a pursuit of markets for natural resources and for wealth. War has also been linked to economic development by economic historians and development economists studying state-building and fiscal capacity. While this theory has been applied to many conflicts, such counter arguments become less valid as the increasing mobility of capital and information level the distributions of wealth worldwide, or when considering that it is relative, not absolute, wealth differences that may fuel wars. There are those on the extreme right of the political spectrum who provide support, fascists in particular, by asserting a natural right of a strong nation to whatever the weak cannot hold by force. Some centrist, capitalist, world leaders, including Presidents of the United States and U.S. Generals, expressed support for an economic view of war.Marxist
TheMarxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
theory of war is quasi-economic in that it states all modern wars are caused by competition for resources and markets between great ( imperialist) powers, claiming these wars are a natural result of capitalism. Marxist economists Karl Kautsky, Rosa Luxemburg
Rosa Luxemburg (; ; pl, Róża Luksemburg or ; 5 March 1871 – 15 January 1919) was a Polish and naturalised-German revolutionary socialist, Marxist philosopher and anti-war activist. Successively, she was a member of the Proletariat party, ...
, Rudolf Hilferding and Vladimir Lenin theorized that imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
was the result of capitalist countries needing new markets
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
* Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
* Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, a ...
. Expansion of the means of production is only possible if there is a corresponding growth in consumer demand. Since the workers in a capitalist economy would be unable to fill the demand, producers must expand into non-capitalist markets to find consumers for their goods, hence driving imperialism.
Demographic
Demographic theories can be grouped into two classes, Malthusian and youth bulge theories:Malthusian
Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
in 1095, on the eve of the First Crusade, advocating Crusade as a solution to European overpopulation, said:
This is one of the earliest expressions of what has come to be called the Malthusian theory of war, in which wars are caused by expanding populations and limited resources. Thomas Malthus (1766–1834) wrote that populations always increase until they are limited by war, disease, or famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
The violent herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria, Mali, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
and other countries in the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
region have been exacerbated by land degradation and population growth.
Youth bulge
Cultural
Geoffrey Parker argues that what distinguishes the "Western way of war" based in Western Europe chiefly allows historians to explain its extraordinary success in conquering most of the world after 1500:The Western way of war rests upon five principal foundations: technology, discipline, a highly aggressive military tradition, a remarkable capacity to innovate and to respond rapidly to the innovation of others and—from about 1500 onward—a unique system of war finance. The combination of all five provided a formula for military success....The outcome of wars has been determined less by technology, then by better war plans, the achievement of surprise, greater economic strength, and above all superior discipline.Parker argues that Western armies were stronger because they emphasized discipline, that is, "the ability of a formation to stand fast in the face of the enemy, where they're attacking or being attacked, without giving way to the natural impulse of fear and panic." Discipline came from drills and marching in formation, target practice, and creating small "artificial kinship groups: such as the company and the platoon, to enhance psychological cohesion and combat efficiency.
Rationalist
 Rationalism is an
Rationalism is an international relations theory
International relations theory is the study of international relations (IR) from a theoretical perspective. It seeks to explain causal and constitutive effects in international politics. Ole Holsti describes international relations theories as a ...
or framework. Rationalism (and Neorealism (international relations)) operate under the assumption that states or international actors are rational, seek the best possible outcomes for themselves, and desire to avoid the costs of war. Under one game theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions among rational agents. Myerson, Roger B. (1991). ''Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict,'' Harvard University Press, p.&nbs1 Chapter-preview links, ppvii–xi It has appli ...
approach, rationalist theories posit all actors can bargain, would be better off if war did not occur, and likewise seek to understand why war nonetheless reoccurs. Under another rationalist game theory without bargaining, the peace war game, optimal strategies can still be found that depend upon number of iterations played. In "Rationalist Explanations for War", James Fearon
James D. Fearon (born 1963) is the Theodore and Francis Geballe Professor of Political Science at Stanford University; he is known for his work on the theory of civil wars, international bargaining, war's inefficiency puzzle, audience costs, and ...
examined three rationalist explanations for why some countries engage in war:
* Issue indivisibilities
* Incentives to misrepresent or information asymmetry
* Commitment problems
"Issue indivisibility" occurs when the two parties cannot avoid war by bargaining, because the thing over which they are fighting cannot be shared between them, but only owned entirely by one side or the other.
 " Information asymmetry with incentives to misrepresent" occurs when two countries have secrets about their individual capabilities, and do not agree on either: who would win a war between them, or the magnitude of state's victory or loss. For instance, Geoffrey Blainey argues that war is a result of miscalculation of strength. He cites historical examples of war and demonstrates, "war is usually the outcome of a diplomatic crisis which cannot be solved because both sides have conflicting estimates of their bargaining power." Thirdly, bargaining may fail due to the states' inability to make credible commitments.
Within the rationalist tradition, some theorists have suggested that individuals engaged in war suffer a normal level of
" Information asymmetry with incentives to misrepresent" occurs when two countries have secrets about their individual capabilities, and do not agree on either: who would win a war between them, or the magnitude of state's victory or loss. For instance, Geoffrey Blainey argues that war is a result of miscalculation of strength. He cites historical examples of war and demonstrates, "war is usually the outcome of a diplomatic crisis which cannot be solved because both sides have conflicting estimates of their bargaining power." Thirdly, bargaining may fail due to the states' inability to make credible commitments.
Within the rationalist tradition, some theorists have suggested that individuals engaged in war suffer a normal level of cognitive bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the objective input, m ...
, but are still "as rational as you and me". According to philosopher Iain King, "Most instigators of conflict overrate their chances of success, while most participants underrate their chances of injury...." King asserts that "Most catastrophic military decisions are rooted in GroupThink" which is faulty, but still rational.
The rationalist theory focused around bargaining is currently under debate. The Iraq War proved to be an anomaly that undercuts the validity of applying rationalist theory to some wars.
Political science
The statistical analysis of war was pioneered byLewis Fry Richardson
Lewis Fry Richardson, FRS (11 October 1881 – 30 September 1953) was an English mathematician, physicist, meteorologist, psychologist, and pacifist who pioneered modern mathematical techniques of weather forecasting, and the application of si ...
following World War I. More recent databases of wars and armed conflict have been assembled by the Correlates of War Project, Peter Brecke and the Uppsala Conflict Data Program.
The following subsections consider causes of war from system, societal, and individual levels of analysis. This kind of division was first proposed by Kenneth Waltz in '' Man, the State, and War'' and has been often used by political scientists since then.
System-level
There are several differentinternational relations theory
International relations theory is the study of international relations (IR) from a theoretical perspective. It seeks to explain causal and constitutive effects in international politics. Ole Holsti describes international relations theories as a ...
schools. Supporters of realism in international relations argue that the motivation of states is the quest for security, and conflicts can arise from the inability to distinguish defense from offense, which is called the security dilemma.
Within the realist school as represented by scholars such as Henry Kissinger and Hans Morgenthau, and the neorealist school represented by scholars such as Kenneth Waltz and John Mearsheimer, two main sub-theories are:
# Balance of power theory: States have the goal of preventing a single state from becoming a hegemon, and war is the result of the would-be hegemon's persistent attempts at power acquisition. In this view, an international system with more equal distribution of power is more stable, and "movements toward unipolarity are destabilizing." However, evidence has shown power polarity
Polarity may refer to:
Science
*Electrical polarity, direction of electrical current
*Polarity (mutual inductance), the relationship between components such as transformer windings
* Polarity (projective geometry), in mathematics, a duality of ord ...
is not actually a major factor in the occurrence of wars.
# Power transition theory: Hegemons impose stabilizing conditions on the world order, but they eventually decline, and war occurs when a declining hegemon is challenged by another rising power or aims to preemptively suppress them. On this view, unlike for balance-of-power theory, wars become ''more'' probable when power is more equally distributed. This "power preponderance" hypothesis has empirical support.
The two theories are not mutually exclusive and may be used to explain disparate events according to the circumstance.
Liberalism as it relates to international relations emphasizes factors such as trade, and its role in disincentivizing conflict which will damage economic relations. Realists respond that military force may sometimes be at least as effective as trade at achieving economic benefits, especially historically if not as much today. Furthermore, trade relations which result in a high level of dependency may escalate tensions and lead to conflict. Empirical data on the relationship of trade to peace are mixed, and moreover, some evidence suggests countries at war don't necessarily trade less with each other.
Societal-level
* Diversionary theory, also known as the "scapegoat hypothesis", suggests the politically powerful may use war to as a diversion or to rally domestic popular support. This is supported by literature showing out-group hostility enhances in-group bonding, and a significant domestic "rally effect" has been demonstrated when conflicts begin. However, studies examining the increased use of force as a function of need for internal political support are more mixed. U.S. war-time presidential popularity surveys taken during the presidencies of several recent U.S. leaders have supported diversionary theory. More recently studies (Lebow 2008, Lindemann 2010) demonstrated that striving for self-esteem (i.e. virile self images), and recognition as a Great Power or non-recognition (exclusion and punishment of great powers, denying traumatic historical events) is a principal cause of international conflict and war.Individual-level
These theories suggest differences in people's personalities, decision-making, emotions, belief systems, and biases are important in determining whether conflicts get out of hand. For instance, it has been proposed that conflict is modulated bybounded rationality
Bounded rationality is the idea that rationality is limited when individuals make decisions, and under these limitations, rational individuals will select a decision that is satisfactory rather than optimal.
Limitations include the difficulty of ...
and various cognitive biases, such as prospect theory.
Ethics
 The morality of war has been the subject of debate for thousands of years.
The two principal aspects of ethics in war, according to the just war theory, are '' jus ad bellum'' and '' jus in bello''.
''Jus ad bellum'' (right to war), dictates which unfriendly acts and circumstances justify a proper authority in declaring war on another nation. There are six main criteria for the declaration of a just war: first, any just war must be declared by a lawful authority; second, it must be a just and righteous cause, with sufficient gravity to merit large-scale violence; third, the just belligerent must have rightful intentions – namely, that they seek to advance good and curtail evil; fourth, a just belligerent must have a reasonable chance of success; fifth, the war must be a last resort; and sixth, the ends being sought must be proportional to means being used.
'' Jus in bello'' (right in war), is the set of ethical rules when conducting war. The two main principles are proportionality and discrimination. Proportionality regards how much force is necessary and morally appropriate to the ends being sought and the injustice suffered. The principle of discrimination determines who are the legitimate targets in a war, and specifically makes a separation between combatants, who it is permissible to kill, and non-combatants, who it is not. Failure to follow these rules can result in the loss of legitimacy for the just-war-belligerent.
The morality of war has been the subject of debate for thousands of years.
The two principal aspects of ethics in war, according to the just war theory, are '' jus ad bellum'' and '' jus in bello''.
''Jus ad bellum'' (right to war), dictates which unfriendly acts and circumstances justify a proper authority in declaring war on another nation. There are six main criteria for the declaration of a just war: first, any just war must be declared by a lawful authority; second, it must be a just and righteous cause, with sufficient gravity to merit large-scale violence; third, the just belligerent must have rightful intentions – namely, that they seek to advance good and curtail evil; fourth, a just belligerent must have a reasonable chance of success; fifth, the war must be a last resort; and sixth, the ends being sought must be proportional to means being used.
'' Jus in bello'' (right in war), is the set of ethical rules when conducting war. The two main principles are proportionality and discrimination. Proportionality regards how much force is necessary and morally appropriate to the ends being sought and the injustice suffered. The principle of discrimination determines who are the legitimate targets in a war, and specifically makes a separation between combatants, who it is permissible to kill, and non-combatants, who it is not. Failure to follow these rules can result in the loss of legitimacy for the just-war-belligerent.
 The just war theory was foundational in the creation of the United Nations and in international law's regulations on legitimate war.
Fascism, and the ideals it encompasses, such as Pragmatism, racism, and social Darwinism, hold that violence is good. Pragmatism holds that war and violence can be good if it serves the ends of the people, without regard for universal morality. Racism holds that violence is good so that a master race can be established, or to purge an inferior race from the earth, or both. Social Darwinism asserts that violence is sometimes necessary to weed the unfit from society so civilization can flourish. These are broad archetypes for the general position that the ends justify the means. Lewis Coser, U.S. conflict theorist and sociologist, argued conflict provides a function and a process whereby a succession of new equilibriums are created. Thus, the struggle of opposing forces, rather than being disruptive, may be a means of balancing and maintaining a social structure or society.
The just war theory was foundational in the creation of the United Nations and in international law's regulations on legitimate war.
Fascism, and the ideals it encompasses, such as Pragmatism, racism, and social Darwinism, hold that violence is good. Pragmatism holds that war and violence can be good if it serves the ends of the people, without regard for universal morality. Racism holds that violence is good so that a master race can be established, or to purge an inferior race from the earth, or both. Social Darwinism asserts that violence is sometimes necessary to weed the unfit from society so civilization can flourish. These are broad archetypes for the general position that the ends justify the means. Lewis Coser, U.S. conflict theorist and sociologist, argued conflict provides a function and a process whereby a succession of new equilibriums are created. Thus, the struggle of opposing forces, rather than being disruptive, may be a means of balancing and maintaining a social structure or society.
Limiting and stopping
 Religious groups have long formally opposed or sought to limit war as in the Second Vatican Council document ''Gaudiem et Spes'': "Any act of war aimed indiscriminately at the destruction of entire cities of extensive areas along with their population is a crime against God and man himself. It merits unequivocal and unhesitating condemnation."
Anti-war movements have existed for every major war in the 20th century, including, most prominently, World War I, World War II, and the Vietnam War. In the 21st century, worldwide anti-war movements occurred in response to the United States invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq. Protests opposing the War in Afghanistan occurred in Europe, Asia, and the United States.
Religious groups have long formally opposed or sought to limit war as in the Second Vatican Council document ''Gaudiem et Spes'': "Any act of war aimed indiscriminately at the destruction of entire cities of extensive areas along with their population is a crime against God and man himself. It merits unequivocal and unhesitating condemnation."
Anti-war movements have existed for every major war in the 20th century, including, most prominently, World War I, World War II, and the Vietnam War. In the 21st century, worldwide anti-war movements occurred in response to the United States invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq. Protests opposing the War in Afghanistan occurred in Europe, Asia, and the United States.
Pauses
During a war, brief pauses of violence may be called for, and further agreed to ceasefire, temporary cessation, humanitarian pauses and corridors, days of tranquility, de-confliction arrangements. There a number of disadvantages, obstacles and hesitations against implementing such pauses such as a humanitarian corridor. Pauses in conflict are also ill-advised; reasons such as "delay of defeat" and the "weakening of credibility". Natural causes for a pause may include events such as the 2019 coronavirus pandemic.See also
*Outline of war
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to war:
War – organised and often prolonged armed conflict that is carried out by states or non-state actors – is characterised by extreme violence, social disruption, an ...
* Grey-zone (international relations)
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * Butler, Smedley (1935). '' War is a Racket''. * Chagnon, N. (1983). ''The Yanomamo''. Holt, Rinehart & Winston. * Clausewitz, Carl Von (1976). ''On War'', Princeton University Press * Codevilla, Angelo (2005). ''No Victory, No Peace''. Rowman and Littlefield * * * * * Fry, Douglas (2005). ''The Human Potential for Peace: An Anthropological Challenge to Assumptions about War and Violence''. Oxford University Press. * Fry, Douglas (2009). ''Beyond War''. Oxford University Press. * Gat, Azar (2006). ''War in Human Civilization''. Oxford University Press. * * Howell, Signe; Willis, Roy (1990). ''Societies at Peace: Anthropological Perspectives.'' London: Routledge. * * *Keegan, John
Sir John Desmond Patrick Keegan (15 May 1934 – 2 August 2012) was an English military historian, lecturer, author and journalist. He wrote many published works on the nature of combat between prehistory and the 21st century, covering land, ...
(1994). '' A History of Warfare''. Pimlico.
* Keeley, Lawrence (1996). ''War Before Civilization'', Oxford University Press.
*
* Kelly, Raymond C. (2000). ''Warless Societies and the Origin of War,'' University of Michigan Press.
* Kemp, Graham; Fry, Douglas (2004). ''Keeping the Peace.'' New York: Routledge.
*
* Lebow, Richard Ned (2008). ''A Cultural Theory of International Relations''. Cambridge University Press.
* Lindemann, Thomas (2010). ''Causes of War. The Struggle for Recognition''. Colchester, ECPR Press
*
* McIntosh, Jane (2002). ''A Peaceful Realm: The Rise and Fall of the Indus Civilization.'' Oxford, UK: Westview Press.
* Metz, Steven and Cuccia, Philip R. (2011)''Defining War for the 21st Century,''
Strategic Studies Institute
The Strategic Studies Institute (SSI) is the U.S. Army's institute for strategic and national security research and analysis. It is part of the U.S. Army War College. SSI conducts strategic research and analysis to support the U.S. Army War Co ...
, U.S. Army War College.
* Montagu, Ashley (1978). ''Learning Nonaggression.'' New York: Oxford University Press.
* Otterbein, Keith (2004). ''How War Began''. College Station TX: Texas A&M University Press.
* Parker, Geoffrey, ed. (2008) ''The Cambridge Illustrated History of Warfare: The Triumph of the West'' (Cambridge University Press, 1995, revised 2008online
* Pauketat, Timothy (2005). ''North American Archaeology''. Blackwell Publishing. * * * Sponsel, Leslie; Gregor, Thomas (1994). ''Anthropology of Peace and Nonviolence.'' Lynne Rienner Publishing. *
Strachan, Hew
Sir Hew Francis Anthony Strachan ( ), (born 1 September 1949) is a British military historian, well known for his leadership in scholarly studies of the British Army and the history of the First World War. He is currently professor of internat ...
(2013). ''The Direction of War''. Cambridge University Press.
* Turchin, P. (2005). ''War and Peace and War: Life Cycles of Imperial Nations''. NY: Pi Press.
* Van Creveld, Martin. ''The Art of War: War and Military Thought'' London: Cassell, Wellington House
* Wade, Nicholas (2006). ''Before the Dawn'', New York: Penguin.
* Walzer, Michael (1977). '' Just and Unjust Wars''. Basic Books.
External links
An Interactive map of all the battles fought around the world in the last 4,000 years
Timeline of wars on Histropedia
* {{Authority control Dispute resolution Ethics Violence