Vortex Ring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
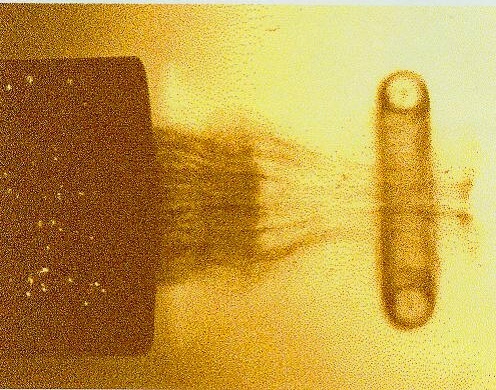 A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a
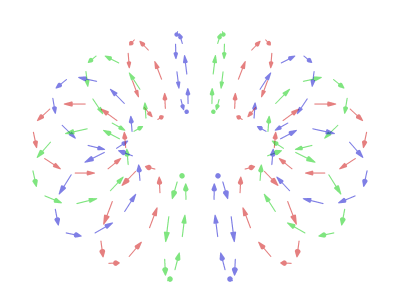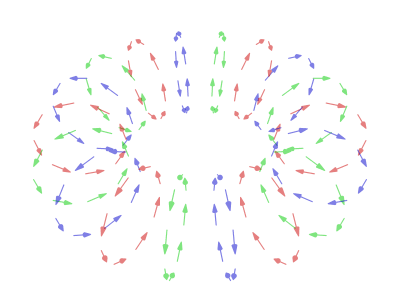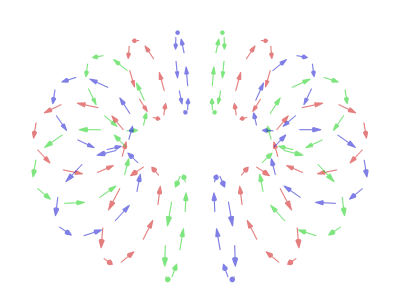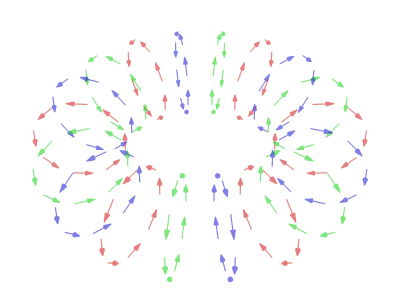 In a typical vortex ring, the fluid particles move in roughly circular paths around an imaginary circle (the ''core'') that is perpendicular to those paths. As in any vortex, the velocity of the fluid is roughly constant except near the core, so that the
In a typical vortex ring, the fluid particles move in roughly circular paths around an imaginary circle (the ''core'') that is perpendicular to those paths. As in any vortex, the velocity of the fluid is roughly constant except near the core, so that the
Physics Central, American Physical Society . Accessed January 2011.
 Air vortices can form around the main rotor of a helicopter, causing a dangerous condition known as vortex ring state (VRS) or "settling with power". In this condition, air that moves down through the rotor turns outward, then up, inward, and then down through the rotor again. This re-circulation of flow can negate much of the lifting force and cause a catastrophic loss of altitude. Applying more power (increasing collective pitch) serves to further accelerate the downwash through which the main-rotor is descending, exacerbating the condition.
Air vortices can form around the main rotor of a helicopter, causing a dangerous condition known as vortex ring state (VRS) or "settling with power". In this condition, air that moves down through the rotor turns outward, then up, inward, and then down through the rotor again. This re-circulation of flow can negate much of the lifting force and cause a catastrophic loss of altitude. Applying more power (increasing collective pitch) serves to further accelerate the downwash through which the main-rotor is descending, exacerbating the condition.
 There has been research and experiments on the existence of separated vortex rings (SVR) such as those formed in the wake of the pappus of a dandelion. This special type of vortex ring effectively stabilizes the seed as it travels through the air and increases the lift generated by the seed. Compared to a standard vortex ring, which is propelled downstream, the axially symmetric SVR remains attached to the pappus for the duration of its flight and uses drag to enhance the travel. These dandelion seed structures have been used to create tiny battery-free wireless sensors that can float in the wind and be dispersed across a large area.
There has been research and experiments on the existence of separated vortex rings (SVR) such as those formed in the wake of the pappus of a dandelion. This special type of vortex ring effectively stabilizes the seed as it travels through the air and increases the lift generated by the seed. Compared to a standard vortex ring, which is propelled downstream, the axially symmetric SVR remains attached to the pappus for the duration of its flight and uses drag to enhance the travel. These dandelion seed structures have been used to create tiny battery-free wireless sensors that can float in the wind and be dispersed across a large area.
with
and where is the
YouTube video of Vortex ring cannon
Fluid dynamics lecture covering vortices
Toy Box Physics: Vortices, Air Cannons, and Mushroom Clouds
Thesis on vortex ring formation and interactions
Vortex half-ring in a pool
More experiments with vortex rings in a pool
 A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal.
Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, and in microbursts.
A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relatively long distance, carrying the spinning fluid with it.
Structure
 In a typical vortex ring, the fluid particles move in roughly circular paths around an imaginary circle (the ''core'') that is perpendicular to those paths. As in any vortex, the velocity of the fluid is roughly constant except near the core, so that the
In a typical vortex ring, the fluid particles move in roughly circular paths around an imaginary circle (the ''core'') that is perpendicular to those paths. As in any vortex, the velocity of the fluid is roughly constant except near the core, so that the angular velocity
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an objec ...
increases towards the core, and most of the vorticity (and hence most of the energy dissipation) is concentrated near it.
Unlike a sea wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, water wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result from the wind blowing over the water surface. The contact distance in the direction o ...
, whose motion is only apparent, a moving vortex ring actually carries the spinning fluid along. Just as a rotating wheel lessens friction between a car and the ground, the poloidal flow of the vortex lessens the friction between the core and the surrounding stationary fluid, allowing it to travel a long distance with relatively little loss of mass and kinetic energy, and little change in size or shape. Thus, a vortex ring can carry mass much further and with less dispersion than a jet of fluid. That explains, for instance, why a smoke ring keeps traveling long after any extra smoke blown out with it has stopped and dispersed. These properties of vortex rings are exploited in the vortex ring gun for riot control and vortex ring toy
An air vortex cannon is a toy that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices are able to ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres.
...
s such as the air vortex cannon
An air vortex cannon is a toy that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices are able to ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres.
...
s.Physics in a Toroidal Vortex: Air CannonPhysics Central, American Physical Society . Accessed January 2011.
Formation
Formation process
The formation of vortex rings has fascinated the scientific community for more than a century, starting with William Barton Rogers who made sounding observations of the formation process of air vortex rings in air, air rings in liquids, and liquid rings in liquids. In particular, William Barton Rogers made use of the simple experimental method of letting a drop of liquid fall on a free liquid surface; a falling colored drop of liquid, such as milk or dyed water, will inevitably form a vortex ring at the interface due to thesurface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
.
A method proposed by G. I. Taylor
Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor OM FRS FRSE (7 March 1886 – 27 June 1975) was a British physicist and mathematician, and a major figure in fluid dynamics and wave theory. His biographer and one-time student, George Batchelor, described him as ...
to generate a vortex ring is to impulsively start a disk from rest. The flow separates to form a cylindrical vortex sheet and by artificially dissolving the disk, one is left with an isolated vortex ring. This is the case when someone is stirring their cup of coffee with a spoon and observing the propagation of a half-vortex in the cup.
In a laboratory, vortex rings are formed by impulsively discharging fluid through a sharp-edged nozzle or orifice. The impulsive motion of the piston/cylinder system is either triggered by an electric actuator or by a pressurized vessel connected to a control valve. For a nozzle geometry, and at first approximation, the exhaust speed is uniform and equal to the piston speed. This is referred as a parallel starting jet. It is possible to have a conical nozzle in which the streamlines at the exhaust are directed toward the centerline. This is referred as a converging starting jet. The orifice geometry which consists in an orifice plate covering the straight tube exhaust, can be considered as an infinitely converging nozzle but the vortex formation differs considerably from the converging nozzle, principally due to the absence of boundary layer in the thickness of the orifice plate throughout the formation process. The fast moving fluid (A) is therefore discharged into a quiescent fluid (B). The shear imposed at the interface between the two fluids slows down the outer layer of the fluid (A) relatively to the centerline fluid. In order to satisfy the Kutta condition
The Kutta condition is a principle in steady-flow fluid dynamics, especially aerodynamics, that is applicable to solid bodies with sharp corners, such as the trailing edges of airfoils. It is named for German mathematician and aerodynamicist Mar ...
, the flow is forced to detach, curl and roll-up in the form of a vortex sheet. Later, the vortex sheet detaches from the feeding jet and propagates freely downstream due to its self-induced kinematics. This is the process commonly observed when a smoker forms smoke rings from their mouth, and how vortex ring toys work.
Secondary effects are likely to modify the formation process of vortex rings. Firstly, at the very first instants, the velocity profile at the exhaust exhibits extrema near the edge causing a large vorticity flux into the vortex ring. Secondly, as the ring grows in size at the edge of the exhaust, negative vorticity is generated on the outer wall of the generator which considerably reduces the circulation accumulated by the primary ring. Thirdly, as the boundary layer inside the pipe, or nozzle, thickens, the velocity profile approaches the one of a Poiseuille flow and the centerline velocity at the exhaust is measured to be larger than the prescribed piston speed. Last but not least, in the event the piston-generated vortex ring is pushed through the exhaust, it may interact or even merge with the primary vortex, hence modifying its characteristic, such as circulation, and potentially forcing the transition of the vortex ring to turbulence.
Vortex ring structures are easily observable in nature. For instance, a mushroom cloud formed by a nuclear explosion or a volcano irruption, has a vortex ring-like structure. Vortex rings are also seen in many different biological flows; blood is discharged into the left ventricle of the human heart in the form of a vortex ring and jellyfishes or squids were shown to propel themselves in water by periodically discharging vortex rings in the surrounding. Finally, for more industrial applications, the synthetic jet which consists in periodically-formed vortex rings, was proved to be an appealing technology for flow control, heat and mass transfer and thrust generation
Vortex formation number
Prior to Gharib ''et al.'' (1998), few studies had focused on the formation of vortex rings generated with long stroke-to-diameter ratios , where is the length of the column of fluid discharged through the exhaust and is the diameter of the exhaust. For short stroke ratios, only one isolated vortex ring is generated and no fluid is left behind in the formation process. For long stroke ratios, however, the vortex ring is followed by some energetic fluid, referred as the trailing jet. On top of showing experimental evidence of the phenomenon, an explanation of the phenomenon was provided in terms of energy maximisation invoking a variational principle first reported by Kelvin and later proven by Benjamin (1976), or Friedman & Turkington (1981). Ultimately, Gharib ''et al.'' (1998) observed the transition between these two states to occur at a non-dimensional time , or equivalently a stroke ratio , of about 4. The robustness of this number with respect to initial and boundary conditions suggested the quantity to be a universal constant and was thus named ''formation number''. The phenomenon of 'pinch-off', or detachment, from the feeding starting jet is observed in a wide range of flows observed in nature. For instance, it was shown that biological systems such as the human heart or swimming and flying animals generate vortex rings with a stroke-to-diameter ratio close to the formation number of about 4, hence giving ground to the existence of an optimal vortex ring formation process in terms of propulsion, thrust generation and mass transport. In particular, the squid '' lolliguncula brevis'' was shown to propel itself by periodically emitting vortex rings at a stroke-ratio close to 4. Moreover, in another study by Gharib ''et al'' (2006), the formation number was used as an indicator to monitor the health of the human heart and identify patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.Other examples
Vortex ring state in helicopters
 Air vortices can form around the main rotor of a helicopter, causing a dangerous condition known as vortex ring state (VRS) or "settling with power". In this condition, air that moves down through the rotor turns outward, then up, inward, and then down through the rotor again. This re-circulation of flow can negate much of the lifting force and cause a catastrophic loss of altitude. Applying more power (increasing collective pitch) serves to further accelerate the downwash through which the main-rotor is descending, exacerbating the condition.
Air vortices can form around the main rotor of a helicopter, causing a dangerous condition known as vortex ring state (VRS) or "settling with power". In this condition, air that moves down through the rotor turns outward, then up, inward, and then down through the rotor again. This re-circulation of flow can negate much of the lifting force and cause a catastrophic loss of altitude. Applying more power (increasing collective pitch) serves to further accelerate the downwash through which the main-rotor is descending, exacerbating the condition.
In the human heart
A vortex ring is formed in the left ventricle of the human heart during cardiac relaxation ( diastole), as ajet
Jet, Jets, or The Jet(s) may refer to:
Aerospace
* Jet aircraft, an aircraft propelled by jet engines
** Jet airliner
** Jet engine
** Jet fuel
* Jet Airways, an Indian airline
* Wind Jet (ICAO: JET), an Italian airline
* Journey to Enceladus a ...
of blood enters through the mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-w ...
. This phenomenon was initially observed in vitro and subsequently strengthened by analyses based on color Doppler mapping
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associa ...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
. Some recent studies have also confirmed the presence of a vortex ring during rapid filling
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence.
Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascad ...
phase of diastole and implied that the process of vortex ring formation can influence mitral annulus
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-w ...
dynamics.
Bubble rings
Releasing air underwater forms bubble rings, which are vortex rings of water with bubbles (or even a single donut-shaped bubble) trapped along its axis line. Such rings are often produced byscuba diver
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for "Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chris ...
s and dolphins.
Separated vortex rings
 There has been research and experiments on the existence of separated vortex rings (SVR) such as those formed in the wake of the pappus of a dandelion. This special type of vortex ring effectively stabilizes the seed as it travels through the air and increases the lift generated by the seed. Compared to a standard vortex ring, which is propelled downstream, the axially symmetric SVR remains attached to the pappus for the duration of its flight and uses drag to enhance the travel. These dandelion seed structures have been used to create tiny battery-free wireless sensors that can float in the wind and be dispersed across a large area.
There has been research and experiments on the existence of separated vortex rings (SVR) such as those formed in the wake of the pappus of a dandelion. This special type of vortex ring effectively stabilizes the seed as it travels through the air and increases the lift generated by the seed. Compared to a standard vortex ring, which is propelled downstream, the axially symmetric SVR remains attached to the pappus for the duration of its flight and uses drag to enhance the travel. These dandelion seed structures have been used to create tiny battery-free wireless sensors that can float in the wind and be dispersed across a large area.
Theory
Historical studies
The formation of vortex rings has fascinated the scientific community for more than a century, starting with William Barton Rogers who made sounding observations of the formation process of air vortex rings in air, air rings in liquids, and liquid rings in liquids. In particular, William Barton Rogers made use of the simple experimental method of letting a drop of liquid fall on a free liquid surface; a falling colored drop of liquid, such as milk or dyed water, will inevitably form a vortex ring at the interface due to the surface tension. Vortex rings were first mathematically analyzed by the German physicist Hermann von Helmholtz, in his 1858 paper ''On Integrals of the Hydrodynamical Equations which Express Vortex-motion''.Circular vortex lines
For a single zero-thickness vortex ring, the vorticity is represented by aDirac delta function
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution ( distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire ...
as where denotes the coordinates of the vortex filament of strength in a constant half-plane. The Stokes stream function
In fluid dynamics, the Stokes stream function is used to describe the streamlines and flow velocity in a three-dimensional incompressible flow with axisymmetry. A surface with a constant value of the Stokes stream function encloses a streamtube, ...
is:complete elliptic integral of the first kind
In integral calculus, an elliptic integral is one of a number of related functions defined as the value of certain integrals, which were first studied by Giulio Fagnano and Leonhard Euler (). Their name originates from their originally arising in ...
and is the complete elliptic integral of the second kind
In integral calculus, an elliptic integral is one of a number of related functions defined as the value of certain integrals, which were first studied by Giulio Fagnano and Leonhard Euler (). Their name originates from their originally arising i ...
. BEWARE that Mathematica decided on their own to change the argument of Elliptic Integrals to the SQUARE of \lambda)
A circular vortex line is the limiting case of a thin vortex ring. Because there is no core thickness, the speed of the ring is infinite, as well as the kinetic energy. The hydrodynamic impulse can be expressed in term of the strength, or 'circulation' , of the vortex ring as .
Thin-core vortex rings
The discontinuity introduced by theDirac delta function
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution ( distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire ...
prevents the computation of the speed and the kinetic energy of a circular vortex line. It is however possible to estimate these quantities for a vortex ring having a finite small thickness. For a thin vortex ring, the core can be approximated by a disk of radius which is assumed to be infinitesimal compared to the radius of the ring , i.e. . As a consequence, inside and in the vicinity of the core ring, one may write: , and , and, in the limit of , the elliptic integrals can be approximated by and .
For a uniform vorticity distribution in the disk, the Stokes stream function
In fluid dynamics, the Stokes stream function is used to describe the streamlines and flow velocity in a three-dimensional incompressible flow with axisymmetry. A surface with a constant value of the Stokes stream function encloses a streamtube, ...
can therefore be approximated by
The resulting circulation
Circulation may refer to:
Science and technology
* Atmospheric circulation, the large-scale movement of air
* Circulation (physics), the path integral of the fluid velocity around a closed curve in a fluid flow field
* Circulatory system, a bio ...
, hydrodynamic impulse and kinetic energy are
It is also possible to find the translational ring speed (which is finite) of such isolated thin-core vortex ring:
which finally results in the well-known expression found by Kelvin and published in the English translation by Tait of von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, ...
's paper:
Spherical vortices
Hill's spherical vortex is an example of steady vortex flow and may be used to model vortex rings having a vorticity distribution extending to the centerline. More precisely, the model supposes a linearly distributed vorticity distribution in the radial direction starting from the centerline and bounded by a sphere of radius as: where is the constant translational speed of the vortex. Finally, theStokes stream function
In fluid dynamics, the Stokes stream function is used to describe the streamlines and flow velocity in a three-dimensional incompressible flow with axisymmetry. A surface with a constant value of the Stokes stream function encloses a streamtube, ...
of Hill's spherical vortex can be computed and is given by:
The above expressions correspond to the stream function describing a steady flow. In a fixed frame of reference, the stream function of the bulk flow having a speed should be added.
The circulation
Circulation may refer to:
Science and technology
* Atmospheric circulation, the large-scale movement of air
* Circulation (physics), the path integral of the fluid velocity around a closed curve in a fluid flow field
* Circulatory system, a bio ...
, the hydrodynamic impulse and the kinetic energy can also be calculated in terms of the translational speed and radius :
Such a structure or an electromagnetic equivalent has been suggested as an explanation for the internal structure of ball lightning. For example, Shafranov used a magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) analogy to Hill's stationary fluid mechanical vortex to consider the equilibrium conditions of axially symmetric MHD configurations, reducing the problem to the theory of stationary flow of an incompressible fluid. In axial symmetry, he considered general equilibrium for distributed currents and concluded under the Virial Theorem that if there were no gravitation, a bounded equilibrium configuration could exist only in the presence of an azimuthal current.
Fraenkel-Norbury model
The Fraenkel-Norbury model of isolated vortex ring, sometimes referred as the standard model, refers to the class of steady vortex rings having a linear distribution of vorticity in the core and parametrised by the mean core radius , where is the area of the vortex core and is the radius of the ring. Approximate solutions were found for thin-core rings, i.e. , and thick Hill's-like vortex rings, i.e. , Hill's spherical vortex having a mean core radius of precisely . For mean core radii in between, one must rely on numerical methods. Norbury (1973) found numerically the resulting steady vortex ring of given mean core radius, and this for a set of 14 mean core radii ranging from 0.1 to 1.35. The resulting streamlines defining the core of the ring were tabulated, as well as the translational speed. In addition, the circulation, the hydrodynamic impulse and the kinetic energy of such steady vortex rings were computed and presented in non-dimensional form.Instabilities
A kind of azimuthal radiant-symmetric structure was observed by Maxworthy when the vortex ring traveled around a critical velocity, which is between the turbulence and laminar states. Later Huang and ChanHuang, J., Chan, K.T. (2007) ''Dual-Wavelike Instability in Vortex Rings'', Proc. 5th IASME/WSEAS Int. Conf. Fluid Mech. & Aerodyn., Greece reported that if the initial state of the vortex ring is not perfectly circular, another kind of instability would occur. An elliptical vortex ring undergoes an oscillation in which it is first stretched in the vertical direction and squeezed in the horizontal direction, then passes through an intermediate state where it is circular, then is deformed in the opposite way (stretched in the horizontal direction and squeezed in the vertical) before reversing the process and returning to the original state.See also
*Air vortex cannon
An air vortex cannon is a toy that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices are able to ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres.
...
* Bubble ring – underwater vortex ring
* Mushroom cloud
* Toroidal moment
A toroidal moment is an independent term in the multipole expansion of electromagnetic fields besides magnetic and electric multipoles. In the electrostatic multipole expansion, all charge and current distributions can be expanded into a complete ...
* Vortex ring gun
* Vortex ring toy
An air vortex cannon is a toy that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices are able to ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres.
...
References
External links
YouTube video of Vortex ring cannon
Fluid dynamics lecture covering vortices
Toy Box Physics: Vortices, Air Cannons, and Mushroom Clouds
Thesis on vortex ring formation and interactions
Vortex half-ring in a pool
Dianna Cowern
Dianna Leilani Cowern (born May 4, 1989) is an American science communicator. She is a YouTuber; she uploads videos to her YouTube channel ''Physics Girl'' explaining various physical phenomena. She worked in partnership with the PBS Digital Stu ...
(Physics Girl), YouTube
More experiments with vortex rings in a pool
Dianna Cowern
Dianna Leilani Cowern (born May 4, 1989) is an American science communicator. She is a YouTuber; she uploads videos to her YouTube channel ''Physics Girl'' explaining various physical phenomena. She worked in partnership with the PBS Digital Stu ...
(Physics Girl), YouTube
{{DEFAULTSORT:Vortex Ring
Aerodynamics
Aviation risks
Helicopter aerodynamics
Vortices