Virtual Life on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Artificial life (often abbreviated ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine 
 Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.
Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches. 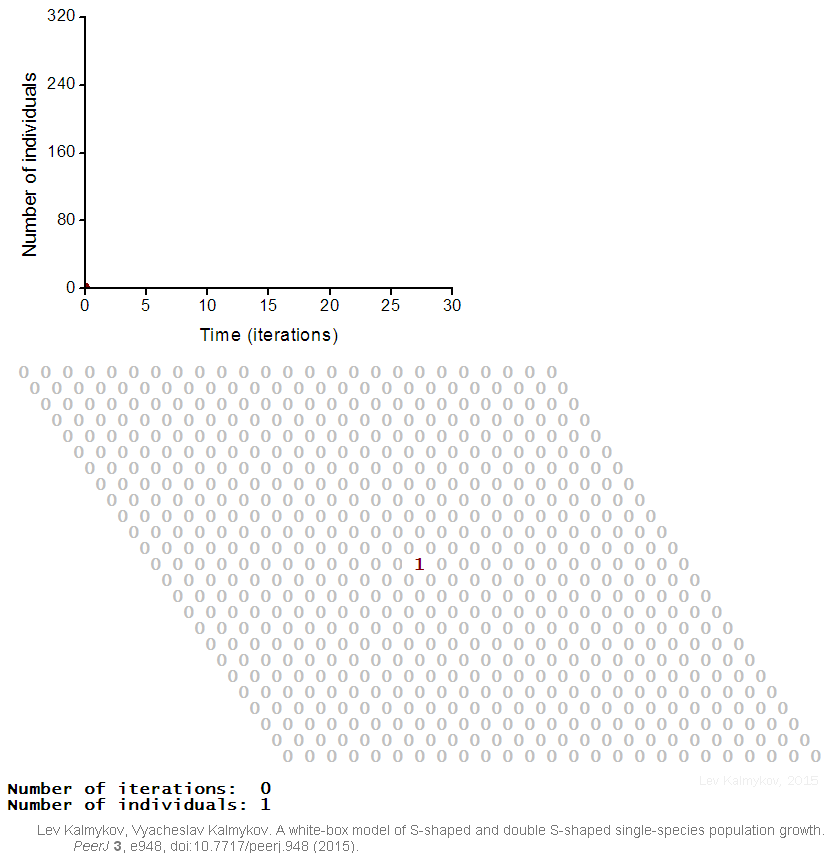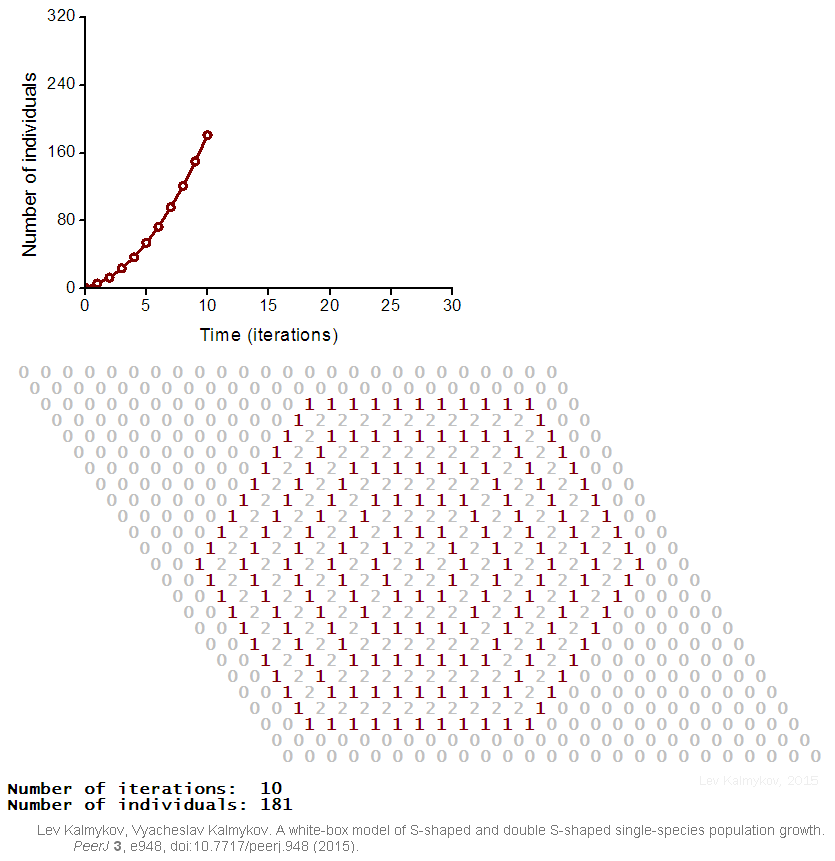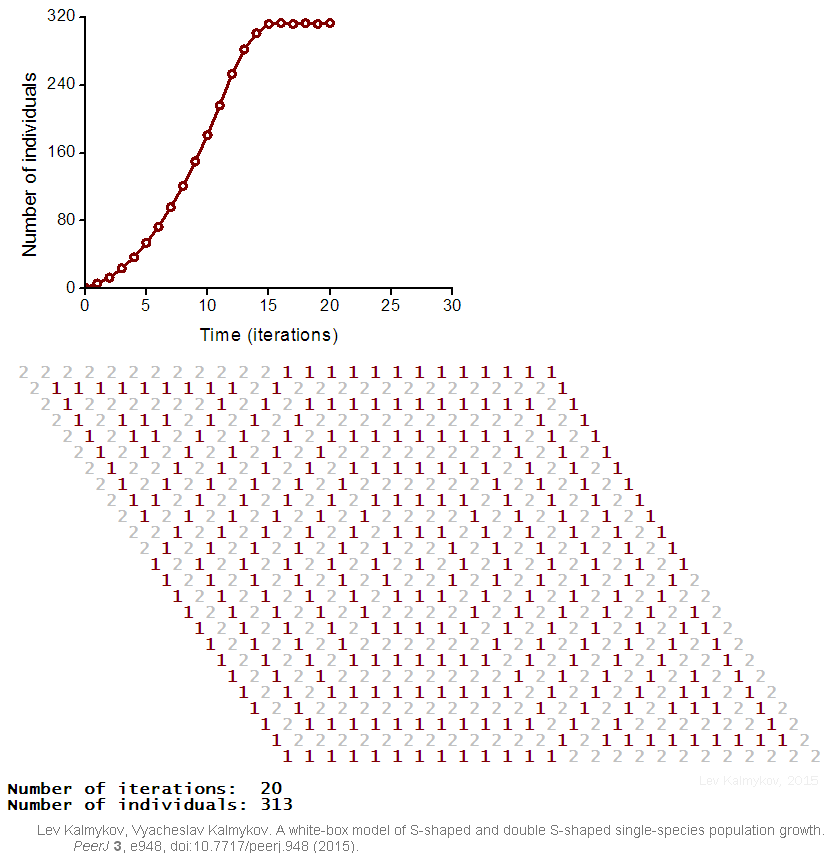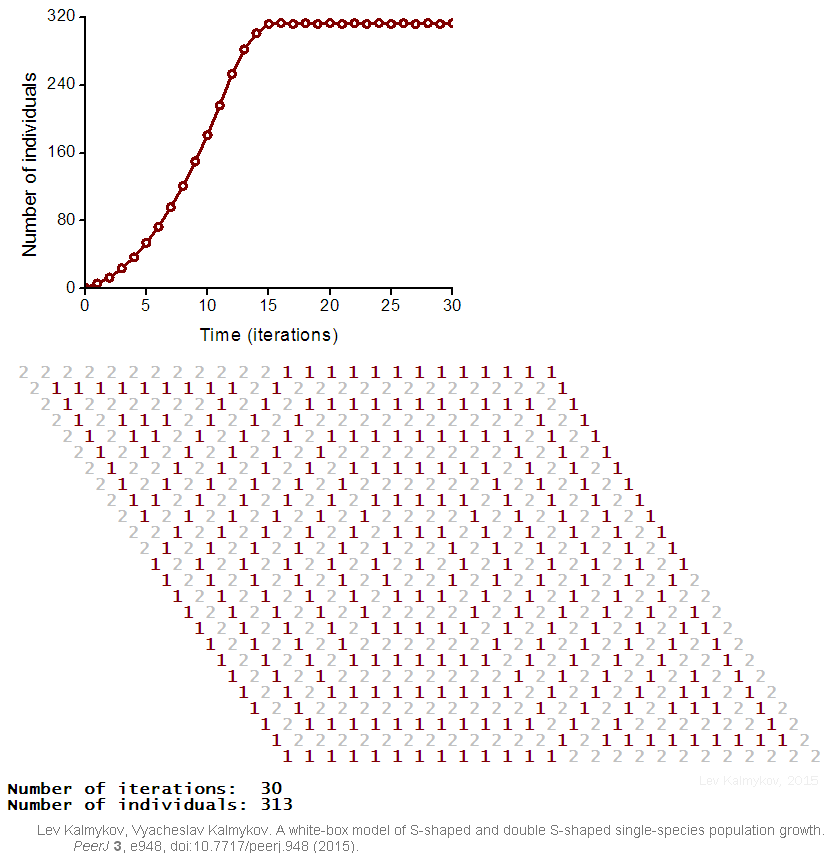 Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical ontology of the object under study. The white-box modeling represents an automatic hyper-logical inference from the first principles because it is completely based on the deterministic logic and axiomatic theory of the subject. The purpose of the white-box modeling is to derive from the basic axioms a more detailed, more concrete mechanistic knowledge about the dynamics of the object under study. The necessity to formulate an intrinsic axiomatic system of the subject before creating its white-box model distinguishes the cellular automata models of white-box type from cellular automata models based on arbitrary logical rules. If cellular automata rules have not been formulated from the first principles of the subject, then such a model may have a weak relevance to the real problem.
Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical ontology of the object under study. The white-box modeling represents an automatic hyper-logical inference from the first principles because it is completely based on the deterministic logic and axiomatic theory of the subject. The purpose of the white-box modeling is to derive from the basic axioms a more detailed, more concrete mechanistic knowledge about the dynamics of the object under study. The necessity to formulate an intrinsic axiomatic system of the subject before creating its white-box model distinguishes the cellular automata models of white-box type from cellular automata models based on arbitrary logical rules. If cellular automata rules have not been formulated from the first principles of the subject, then such a model may have a weak relevance to the real problem.

International Society of Artificial Life''Artificial Life''
journal, at MIT Press Journal
a virtual environment lab {{Authority control Simulation
system
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, ...
s related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American theoretical biologist, in 1986. In 1987 Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: ''soft'', from software; ''hard'', from hardware; and '' wet'', from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena.

Overview
Artificial life studies the fundamental processes ofliving system
Living systems are open self-organizing life forms that interact with their environment. These systems are maintained by flows of information, energy and matter.
In the last few decades, some scientists have proposed that a general living systems ...
s in artificial environments in order to gain a deeper understanding of the complex information processing that define such systems. These topics are broad, but often include evolutionary dynamics, emergent properties of collective systems, biomimicry
Biomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from grc, βίος (''bios''), life, and μίμησ ...
, as well as related issues about the philosophy of the nature of life and the use of lifelike properties in artistic works.
Philosophy
The modeling philosophy of artificial life strongly differs from traditional modeling by studying not only "life-as-we-know-it" but also "life-as-it-might-be". A traditional model of a biological system will focus on capturing its most important parameters. In contrast, an alife modeling approach will generally seek to decipher the most simple and general principles underlying life and implement them in a simulation. The simulation then offers the possibility to analyse new and different lifelike systems. Vladimir Georgievich Red'ko proposed to generalize this distinction to the modeling of any process, leading to the more general distinction of "processes-as-we-know-them" and "processes-as-they-could-be". At present, the commonly accepteddefinition of life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy t ...
does not consider any current alife simulations or software to be alive, and they do not constitute part of the evolutionary process of any ecosystem. However, different opinions about artificial life's potential have arisen:
* The ''strong alife'' (cf. Strong AI
Strong artificial intelligence may refer to:
"Strong Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an artificial intelligence that constructs mental abilities, thought processes, and functions that are impersonated from the human brain. It is more of a phil ...
) position states that "life is a process which can be abstracted away from any particular medium" ( John von Neumann) . Notably, Tom Ray declared that his program Tierra is not simulating life in a computer but synthesizing it.
* The ''weak alife'' position denies the possibility of generating a "living process" outside of a chemical solution. Its researchers try instead to simulate life processes to understand the underlying mechanics of biological phenomena.
Software-based ("soft")
Techniques
* Cellular automata were used in the early days of artificial life, and are still often used for ease of scalability and parallelization. Alife and cellular automata share a closely tied history. * Artificial neural networks are sometimes used to model the brain of an agent. Although traditionally more of an artificial intelligence technique, neural nets can be important for simulatingpopulation dynamics
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems.
History
Population dynamics has traditionally been the dominant branch of mathematical biology, which has ...
of organisms that can ''learn''. The symbiosis between learning and evolution is central to theories about the development of instincts in organisms with higher neurological complexity, as in, for instance, the Baldwin effect.
*Neuroevolution
Neuroevolution, or neuro-evolution, is a form of artificial intelligence that uses evolutionary algorithms to generate artificial neural networks (ANN), parameters, and rules. It is most commonly applied in artificial life, general game playing ...
Notable simulators
This is a list of artificial life/ digital organism simulators, organized by the method of creature definition.Program-based
Program-based simulations contain organisms with a complex DNA language, usually Turing complete. This language is more often in the form of a computer program than actual biological DNA. Assembly derivatives are the most common languages used. An organism "lives" when its code is executed, and there are usually various methods allowing self-replication. Mutations are generally implemented as random changes to the code. Use of cellular automata is common but not required. Another example could be an artificial intelligence and multi-agent system/program.Module-based
Individual modules are added to a creature. These modules modify the creature's behaviors and characteristics either directly, by hard coding into the simulation (leg type A increases speed and metabolism), or indirectly, through the emergent interactions between a creature's modules (leg type A moves up and down with a frequency of X, which interacts with other legs to create motion). Generally, these are simulators that emphasize user creation and accessibility over mutation and evolution.Parameter-based
Organisms are generally constructed with pre-defined and fixed behaviors that are controlled by various parameters that mutate. That is, each organism contains a collection of numbers or other ''finite'' parameters. Each parameter controls one or several aspects of an organism in a well-defined way.Neural net–based
These simulations have creatures that learn and grow using neural nets or a close derivative. Emphasis is often, although not always, on learning rather than on natural selection.Complex systems modeling
Mathematical models of complex systems are of three types: black-box (phenomenological), white-box (mechanistic, based on the first principles) and grey-box (mixtures of phenomenological and mechanistic models). In black-box models, the individual-based (mechanistic) mechanisms of a complex dynamic system remain hidden. Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.
Black-box models are completely nonmechanistic. They are phenomenological and ignore a composition and internal structure of a complex system. Due to the non-transparent nature of the model, interactions of subsystems cannot be investigated. In contrast, a white-box model of a complex dynamic system has ‘transparent walls’ and directly shows underlying mechanisms. All events at the micro-, meso- and macro-levels of a dynamic system are directly visible at all stages of a white-box model's evolution. In most cases, mathematical modelers use the heavy black-box mathematical methods, which cannot produce mechanistic models of complex dynamic systems. Grey-box models are intermediate and combine black-box and white-box approaches.  Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical ontology of the object under study. The white-box modeling represents an automatic hyper-logical inference from the first principles because it is completely based on the deterministic logic and axiomatic theory of the subject. The purpose of the white-box modeling is to derive from the basic axioms a more detailed, more concrete mechanistic knowledge about the dynamics of the object under study. The necessity to formulate an intrinsic axiomatic system of the subject before creating its white-box model distinguishes the cellular automata models of white-box type from cellular automata models based on arbitrary logical rules. If cellular automata rules have not been formulated from the first principles of the subject, then such a model may have a weak relevance to the real problem.
Creation of a white-box model of complex system is associated with the problem of the necessity of an a priori basic knowledge of the modeling subject. The deterministic logical cellular automata are necessary but not sufficient condition of a white-box model. The second necessary prerequisite of a white-box model is the presence of the physical ontology of the object under study. The white-box modeling represents an automatic hyper-logical inference from the first principles because it is completely based on the deterministic logic and axiomatic theory of the subject. The purpose of the white-box modeling is to derive from the basic axioms a more detailed, more concrete mechanistic knowledge about the dynamics of the object under study. The necessity to formulate an intrinsic axiomatic system of the subject before creating its white-box model distinguishes the cellular automata models of white-box type from cellular automata models based on arbitrary logical rules. If cellular automata rules have not been formulated from the first principles of the subject, then such a model may have a weak relevance to the real problem.

Hardware-based ("hard")
Hardware-based artificial life mainly consist of ''robots'', that is, automatically guidedmachine
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to na ...
s able to do tasks on their own.
Biochemical-based ("wet")
Biochemical-based life is studied in the field of synthetic biology. It involves research such as the creation ofsynthetic DNA
In September 2021, Synthetic Genomics Inc. (SGI), a private company located in La Jolla, California, changed its name to Viridos. The company is focused on the field of synthetic biology, especially harnessing photosynthesis with micro algae to ...
. The term "wet" is an extension of the term " wetware". Efforts toward "wet" artificial life focus on engineering live minimal cells from living bacteria '' Mycoplasma laboratorium'' and in building non-living biochemical cell-like systems from scratch.
In May 2019, researchers reported a new milestone in the creation of a new synthetic Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic o ...
(possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria '' Escherichia coli'', by reducing the natural number of 64 codon
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
s in the bacterial genome to 59 codons instead, in order to encode 20 amino acids.
Open problems
;How does life arise from the nonliving? *Generate a molecular proto-organism in vitro. *Achieve the transition to life in anartificial chemistry An artificial chemistryW. Banzhaf and L. YamamotoArtificial Chemistries MIT Press, 2015.
P. DittrichArtificial chemistry (AC)In A. R. Meyers (ed.), Computational Complexity: Theory, Techniques, and Applications, pp. 185-203, Springer, 2012.P. Dittri ...
in silico
In biology and other experimental sciences, an ''in silico'' experiment is one performed on computer or via computer simulation. The phrase is pseudo-Latin for 'in silicon' (correct la, in silicio), referring to silicon in computer chips. It ...
.
*Determine whether fundamentally novel living organizations can exist.
*Simulate a unicellular organism over its entire life cycle.
*Explain how rules and symbols are generated from physical dynamics in living systems.
;What are the potentials and limits of living systems?
*Determine what is inevitable in the open-ended evolution of life.
*Determine minimal conditions for evolutionary transitions from specific to generic response systems.
*Create a formal framework for synthesizing dynamical hierarchies at all scales.
*Determine the predictability of evolutionary consequences of manipulating organisms and ecosystems.
*Develop a theory of information processing
Information processing is the change (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an observer. As such, it is a process that ''describes'' everything that happens (changes) in the universe, from the falling of a rock (a change in posit ...
, information flow, and information generation for evolving systems.
;How is life related to mind, machines, and culture?
*Demonstrate the emergence of intelligence and mind in an artificial living system.
*Evaluate the influence of machines on the next major evolutionary transition of life.
*Provide a quantitative model of the interplay between cultural and biological evolution.
*Establish ethical principles for artificial life.
Related subjects
#Agent-based modeling
An agent-based model (ABM) is a computational model for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents (both individual or collective entities such as organizations or groups) in order to understand the behavior of a system and what ...
is used in artificial life and other fields to explore emergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergence ...
in systems.
# Artificial intelligence has traditionally used a top down approach, while alife generally works from the bottom up.
#Artificial chemistry An artificial chemistryW. Banzhaf and L. YamamotoArtificial Chemistries MIT Press, 2015.
P. DittrichArtificial chemistry (AC)In A. R. Meyers (ed.), Computational Complexity: Theory, Techniques, and Applications, pp. 185-203, Springer, 2012.P. Dittri ...
started as a method within the alife community to abstract the processes of chemical reactions.
# Evolutionary algorithms are a practical application of the weak alife principle applied to optimization problems. Many optimization algorithms have been crafted which borrow from or closely mirror alife techniques. The primary difference lies in explicitly defining the fitness of an agent by its ability to solve a problem, instead of its ability to find food, reproduce, or avoid death. The following is a list of evolutionary algorithms closely related to and used in alife:
#* Ant colony optimization
#* Bacterial colony optimization
#*Genetic algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to gene ...
#* Genetic programming
#*Swarm intelligence
Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, in ...
# Multi-agent system – A multi-agent system is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents within an environment.
# Evolutionary art uses techniques and methods from artificial life to create new forms of art.
# Evolutionary music uses similar techniques, but applied to music instead of visual art.
# Abiogenesis and the origin of life sometimes employ alife methodologies as well.
#Quantum artificial life
Quantum artificial life is the application of quantum algorithms with the ability to simulate biological behavior. Quantum computing, Quantum computers offer many potential improvements to processes performed on classical computers, including mach ...
applies quantum algorithms to artificial life systems.
History
Criticism
Alife has had a controversial history. John Maynard Smith criticized certain artificial life work in 1994 as "fact-free science".See also
References
External links
*International Society of Artificial Life
journal, at MIT Press Journal
a virtual environment lab {{Authority control Simulation