Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of
mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's
fifteenth-most populous country. One of two
communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
s in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
to the north, and
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
and
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
to the west. It shares
maritime borders with
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
through the
Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
, and the
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
,
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, and
Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
through the
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
. Its capital is
Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
and its largest city is
Ho Chi Minh City
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
.
Vietnam was inhabited by the
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the
Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta () is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in Northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word for "red" or "crimson". T ...
in modern-day
northern Vietnam
Northern Vietnam or '' Tonkin'' () is one of three geographical regions in Vietnam. It consists of three geographic sub-regions: the Northwest (Vùng Tây Bắc), the Northeast (Vùng Đông Bắc), and the Red River Delta (Đồng Bằng Sôn ...
. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subsequently under
Chinese rule from 111 BC until the
first dynasty emerged in 939. Successive
monarchical dynasties absorbed Chinese influences through
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
and
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, and
expanded southward to the
Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( or simply ), also known as the Western Region () or South-western region (), is the list of regions of Vietnam, region in southwestern Vietnam where the Mekong, Mekong River River delta, approaches and empties into the sea th ...
,
conquering Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from ...
. During most of the 17th and 18th centuries, Vietnam was effectively divided into two domains of
Đàng Trong
Đàng Trong ( chữ Nôm: 唐冲, lit. "Inner Circuit"), also known as Nam Hà (, "South of the River"), was the South region of Vietnam, under the lordship of the Nguyễn clan, later enlarged by the Vietnamese southward expansion. The word '' ...
and
Đàng Ngoài
Đàng Ngoài ( vi-hantu, 唐外, lit. "Outer Land"), also known as Tonkin, Bắc Hà (北河, "North of the River") or '' Kingdom of Annam'' (安南國) by foreigners, was an area in northern Đại Việt (now Vietnam) during the 17th and 18t ...
. The
Nguyễn
Nguyễn (阮) (sometimes abbreviated as Ng̃) is the most common surname of the Vietnamese people.
Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as ''Nguyen''.
By some estimates 30 to 39 percent of Vietnamese peopl ...
—the last imperial dynasty—surrendered to
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
in 1883. In 1887, its territory was integrated into
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
as three separate regions. In the immediate aftermath of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the
Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (, ) is the common and abbreviated name of the League for Independence of Vietnam ( or , ; ), which was a Communist Party of Vietnam, communist-led national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1 ...
, a coalition front led by the communist revolutionary
Ho Chi Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first President of Vietnam, president of the ...
, launched the
August Revolution
The August Revolution (), also known as the August General Uprising (), was a revolution led by the Việt Minh against the Empire of Vietnam from 16 August to 2 September 1945. The Empire of Vietnam was led by the Nguyễn dynasty and was ...
and
declared Vietnam's independence from the
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
in 1945.
Vietnam went through
prolonged warfare in the 20th century. After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, France returned to reclaim colonial power in the
First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam, and alternatively internationally as the French-Indochina War) was fought between French Fourth Republic, France and Việ ...
, from which Vietnam emerged victorious in 1954. As a result of the
treaties signed between the Viet Minh and France, Vietnam was also separated into two parts. The
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
began shortly after, between the communist
North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; ; VNDCCH), was a country in Southeast Asia from 1945 to 1976, with sovereignty fully recognized in 1954 Geneva Conference, 1954. A member of the communist Eastern Bloc, it o ...
, supported by the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and the anti-communist
South Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered Diplomatic recognition, international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the ...
, supported by the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Upon the
North Vietnamese victory in 1975, Vietnam reunified as a
unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
that self-designated as a
socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. This article is about states that refer to themselves as socialist states, and not specifically ...
under the
Communist Party of Vietnam
The Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) is the founding and sole legal party of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Founded in 1930 by Hồ Chí Minh, the CPV became the ruling party of North Vietnam in 1954 and then all of Vietnam after the col ...
(CPV) in 1976. An ineffective
planned economy
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, ...
, a trade embargo by the
West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, and wars with
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
crippled the country further. In 1986, the CPV initiated
economic and political reforms similar to the
Chinese economic reform
Reform and opening-up ( zh, s=改革开放, p=Gǎigé kāifàng), also known as the Chinese economic reform or Chinese economic miracle, refers to a variety of economic reforms termed socialism with Chinese characteristics and socialist marke ...
, transforming the country to a
socialist-oriented market economy
The socialist-oriented market economy ( Vietnamese: ''Kinh tế thị trường định hướng xã hội chủ nghĩa'') is the official title given to the current economic system in Vietnam by the ruling Communist Party. It is described ...
. The reforms facilitated Vietnamese reintegration into the
global economy
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans in the world, referring to the global economic system, which includes all economic activities conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, econ ...
and
politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
.
Vietnam is a
developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
with a lower-middle-income economy. It has
high levels of corruption,
censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governmen ...
,
environmental issues
Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans (human impact on the environment) or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot recov ...
and a poor
human rights record. It is part of international and intergovernmental institutions including the
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
, the
APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC ) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economy , economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of Association of Southeast Asia ...
, the
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
, the
OIF, and the
WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
. It has assumed a seat on the
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
twice.
Etymology
The name (,
chữ Hán
( , ) are the Chinese characters that were used to write Literary Chinese in Vietnam, Literary Chinese (; ) and Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary in Vietnamese language, Vietnamese. They were officially used in Vietnam after the Red River Delta region ...
: ), literally "Viet South", means per Vietnamese word order "Viet of the South";
meanwhile, per
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary ...
word order, "Việt Nam" ambiguously means either "South of the Viet"
[; reproduced in ] or "Viet people's Southern country".
A variation of the name,
Nanyue
Nanyue ( zh, c=南越 or 南粵, p=Nányuè, cy=, j=Naam4 Jyut6, l=Southern Yue, , ), was an ancient kingdom founded in 204 BC by the Chinese general Zhao Tuo, whose family (known in Vietnamese as the Triệu dynasty) continued to rule until ...
(or Nam Việt, ), was first documented in the 2nd century BC. The term "" (Yue) () in
Early Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the ''Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The S ...
was first written using the
logograph
In a written language, a logogram (from Ancient Greek 'word', and 'that which is drawn or written'), also logograph or lexigraph, is a written character that represents a semantic component of a language, such as a word or morpheme. Chines ...
"戉" for an axe (a homophone), in
oracle bone
Oracle bones are pieces of ox scapula and turtle plastron which were used in pyromancya form of divinationduring the Late Shang period () in ancient China. '' Scapulimancy'' is the specific term if ox scapulae were used for the divination, ''p ...
and bronze inscriptions of the late
Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
( BC), and later as "越". At that time, it referred to a people or chieftain to the northwest of the Shang. In the early 8th century BC, a tribe on the middle
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
were called the
Yangyue, a term later used for peoples further south.
Between the 7th and 4th centuries BC, 'Yue'/'Việt' referred to the
State of Yue
Yue (), also known as Yuyue ( or ), was a state in ancient China which existed during the first millennium BC the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods of China's Zhou dynasty in the modern provinces of Zhejiang, Shanghai and Jiangsu ...
in the lower Yangtze basin and its people. From the 3rd century BC, the term was used for the non-Chinese populations of southern China and northern Vietnam, with particular ethnic groups called
Minyue
Minyue (; Pinyin: ''Mǐnyuè, Mínyuè'') was an ancient kingdom in what is now the Fujian province in southern China. It was a contemporary of the Han dynasty, and was later annexed by the Han empire as the Southward expansion of the Han dynas ...
,
Ouyue, Luoyue (Vietnamese:
Lạc Việt
The Lạc Việt or Luoyue ( or ; ← Middle Chinese: *''lɑk̚-ɦʉɐt̚'' ← Old Chinese *''râk-wat'') were an ancient conglomeration of peoples inhabiting northern Vietnam, particularly the ancient Red River Delta, from approximately 700 B ...
), etc., collectively called the
Baiyue
The Baiyue, Hundred Yue, or simply Yue, were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of southern China and northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair, body tattoos, fine swo ...
(Bách Việt, ).
The term 'Baiyue'/'Bách Việt' first appeared in the book ''
Lüshi Chunqiu
The ''Lüshi Chunqiu'' (), also known in English as ''Master Lü's Spring and Autumn Annals'', is an encyclopedic Chinese classic text compiled around 239BC under the patronage of late pre-imperial Qin Chancellor Lü Buwei. In the evaluati ...
'' compiled around 239 BC. By the 17th and 18th centuries AD, educated Vietnamese apparently referred to themselves as ''người Việt'' (Viet people) or ''người Nam'' (southern people).
The form () is first recorded in the 16th-century oracular poem ''
Sấm Trạng Trình''. The name has also been found on 12
stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
s carved in the 16th and 17th centuries, including one at Bao Lam Pagoda in
Hải Phòng
Haiphong or Hai Phong (, ) is the third-largest city in Vietnam and is the principal port city of the Red River Delta. The municipality has an area of , consisting of 8 List of urban districts of Vietnam, urban districts, 6 Huyện, rural distri ...
that dates to 1558. In 1802,
Nguyễn Phúc Ánh
Gia Long (Chữ hán: 嘉隆) ( (''North''), (''South''); 8 February 1762 – 3 February 1820), born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh (阮暎), was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last dynasty of Vietnam, whi ...
(who later became Emperor Gia Long) established the
Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (, chữ Nôm: 茹阮, chữ Hán: 朝阮) was the last List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, preceded by the Nguyễn lords and ruling unified Vietnam independently from 1802 until French protectorate in 1883 ...
. In the second year of his rule, Gia Long asked the
Jiaqing Emperor
The Jiaqing Emperor (13 November 1760 – 2 September 1820), also known by his temple name Emperor Renzong of Qing, personal name Yongyan, was the sixth emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fifth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. He was ...
of the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
to confer on him the title 'King of Nam Việt / Nanyue' ( in Chinese character) after seizing power in Annam. Emperor Jiaqing refused because the name was related to
Zhao Tuo
Zhao Tuo (), rendered as Triệu Đà in Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, was a Qin dynasty Chinese general and first emperor of Nanyue. He participated in the conquest of the Baiyue peoples of Guangdong, Guangxi and Northern Vietnam. After ...
's Nanyue, which included the regions of
Guangxi
Guangxi,; officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang Province, Hà Giang, Cao Bằn ...
and
Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
in southern China, so he decided to call the area "Việt Nam" instead, meaning per
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary ...
word order "land to the south of the Viet land" (
Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
: ) but the Vietnamese just understood "Việt Nam" as either, also per Classical Chinese word-order, "Viet people's Southern country" (
Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
: )
or even "Viet of the South", per Vietnamese word order.
Between 1804 and 1813, the name Vietnam was used officially by Emperor Gia Long. It was revived in the early 20th century in
Phan Bội Châu
Phan Bội Châu (; 26 December 1867 – 29 October 1940), born Phan Văn San, courtesy name Hải Thụ (later changed to Sào Nam), was a pioneer of 20th century Vietnamese nationalism. In 1904, he formed a revolutionary organization called ...
's ''
History of the Loss of Vietnam
''History of the Loss of Vietnam'' (, ) is a Literary Chinese book written by Phan Bội Châu, the leading Vietnamese anti-colonial revolutionary of the early 20th century, in 1905 while he was in Japan.Spencer C. Tucker ''The Encyclopedia of the ...
'', and later by the
Vietnamese Nationalist Party (VNQDĐ). The country was usually called Annam until 1945, when the
imperial government
The name imperial government () denotes two organs, created in 1500 and 1521, in the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation to enable a unified political leadership, with input from the Princes. Both were composed of the empero ...
in
Huế
Huế (formerly Thừa Thiên Huế province) is the southernmost coastal Municipalities of Vietnam, city in the North Central Coast region, the Central Vietnam, Central of Vietnam, approximately in the center of the country. It borders Quảng ...
adopted .
History
Prehistory and early history
Archaeological excavations have revealed the existence of humans in what is now Vietnam as early as the
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
age. Stone artefacts excavated in
Gia Lai province
Gia Lai is a northern mountainous Provinces of Vietnam, province in the Central Highlands (Vietnam), Central Highlands region, the Central Vietnam, Central of Vietnam. It borders Kon Tum province, Kon Tum in the north, Quảng Ngãi province, Qu ...
have been claimed to date to 780,000 years ago, based on associated find of
tektite
Tektites () are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Franz Eduard Suess (1867–1941), son of Eduar ...
s, however this claim has been challenged because tektites are often found in archaeological sites of various ages in Vietnam. ''
Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' fossils dating to around 500,000 BC have been found in caves in
Lạng Sơn
Lạng Sơn () is a city in far Northern Vietnam, and the capital of Lạng Sơn Province. It is accessible by road and rail from Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital, and it is the northernmost point on National Route 1.
History
Due to its geograph ...
and
Nghệ An provinces in northern Vietnam. The oldest ''
Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' fossils from mainland Southeast Asia are of
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
provenance, and include isolated tooth fragments from Tham Om and Hang Hum. Teeth attributed to ''Homo sapiens'' from the
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
have been found at Dong Can, and from the Early
Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
at Mai Da Dieu, Lang Gao and Lang Cuom. Areas comprising what is now Vietnam participated in the
Maritime Jade Road
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Pri ...
, as ascertained by archaeological research.
By about 1,000 BC, the development of wet-
rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
cultivation in the
Ma River
Ma, MA, or mA may refer to:
Academia
* Master of Arts, a degree award
* Marin Academy, a high school in San Rafael, California
* Menlo-Atherton High School, a public high school in Atherton, California
* Minnehaha Academy, a private high sch ...
and
Red River floodplains led to the flourishing of
Đông Sơn culture
The Dong Son culture, Dongsonian culture, or the Lạc Việt culture (named for modern village Đông Sơn, a village in Thanh Hóa, Vietnam) was a Bronze Age culture in ancient Vietnam centred at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam ...
, notable for its
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
casting used to make elaborate bronze
Đông Sơn drums. This culture spread to the rest of
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, including
Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
, throughout the first millennium BC.
Dynastic Vietnam

According to Vietnamese legends,
Hồng Bàng dynasty
The Hồng Bàng period (), also called the Hồng Bàng dynasty,Pelley, p. 151 was a legendary ancient period in Vietnamese historiography, spanning from the beginning of the rule of Kinh Dương Vương over the kingdom of Văn Lang (initia ...
of the
Hùng kings first established in 2879 BC is considered the first state established in Vietnam (then known as Xích Quỷ and later
Văn Lang). Văn Lang was established by
Lạc Việt
The Lạc Việt or Luoyue ( or ; ← Middle Chinese: *''lɑk̚-ɦʉɐt̚'' ← Old Chinese *''râk-wat'') were an ancient conglomeration of peoples inhabiting northern Vietnam, particularly the ancient Red River Delta, from approximately 700 B ...
tribes, who were likely a confederacy of multilingual
Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
and
Kra-Dai speakers that occupied the
Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta () is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in Northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word for "red" or "crimson". T ...
in northern Vietnam.
In 257 BC, the last Hùng king was defeated by Thục Phán. He consolidated the
Lạc Việt
The Lạc Việt or Luoyue ( or ; ← Middle Chinese: *''lɑk̚-ɦʉɐt̚'' ← Old Chinese *''râk-wat'') were an ancient conglomeration of peoples inhabiting northern Vietnam, particularly the ancient Red River Delta, from approximately 700 B ...
and
Âu Việt
The Âu Việt or Ouyue () were an ancient conglomeration of Baiyue tribes living in what is today the mountainous regions of northernmost Vietnam, western Guangdong, and northern Guangxi, China, since at least the third century BCE. They were b ...
tribes, who came from southern China, to form the
Âu Lạc
Âu Lạc (chữ Hán: 甌貉 (Peripheral Records/Volume 1:6a): "王既併文郎國,改國號曰甌貉國。""The King then annexed the Văn Lang nation, changed the nation's name to Âu Lạc nation."/甌駱; (Volume 113): "且南方卑濕� ...
, proclaiming himself
An Dương Vương
An Dương Vương (), personal name Thục Phán, was the founding king and the only ruler of the kingdom of Âu Lạc, an ancient state centered in the Red River Delta. As the leader of the Âu Việt tribes, he defeated the last Hùng ki ...
.
In 179 BC, a Chinese general named
Zhao Tuo
Zhao Tuo (), rendered as Triệu Đà in Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, was a Qin dynasty Chinese general and first emperor of Nanyue. He participated in the conquest of the Baiyue peoples of Guangdong, Guangxi and Northern Vietnam. After ...
("Triệu Đà") defeated An Dương Vương and consolidated Âu Lạc into
Nanyue
Nanyue ( zh, c=南越 or 南粵, p=Nányuè, cy=, j=Naam4 Jyut6, l=Southern Yue, , ), was an ancient kingdom founded in 204 BC by the Chinese general Zhao Tuo, whose family (known in Vietnamese as the Triệu dynasty) continued to rule until ...
. However, Nanyue was itself
incorporated into the empire of the Chinese
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
in 111 BC after the
Han–Nanyue War
The Han conquest of Nanyue was a military conflict between the Han Empire and the Nanyue kingdom in modern Guangdong, Guangxi, and Northern Vietnam. During the reign of Emperor Wu, Imperial Han military forces formally launched a punitive ca ...
. For the next thousand years, what is now northern Vietnam remained mostly under
Chinese rule. Early independence movements, such as those of the
Trưng Sisters
The Trưng sisters ( (), 𠄩婆徵, literally "Two Ladies amed Amed or AMED may refer to:
*Amed (Bali), a town in Bali, Indonesia
*Amedisys Home Health and Hospice Care, a home health and hospice care company in the US, NASDAQ abbreviation AMED
* Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
*Amed Ber, a t ...
Trưng",
14 – c. 43) were Luoyue military leaders who ruled for three years after Trung sisters' rebellion, commanding a rebellion of Luoyue tribes and other tribes in ...
and
Lady Triệu
Lady Triệu (, , Chữ Nôm: , died 248 AD) or Triệu Ẩu (, Chữ Hán: ) was a female warrior in 3rd century Vietnam who managed, for a time, to resist the rule of the Chinese Eastern Wu dynasty. She is also called , although her actual giv ...
, were temporarily successful, though the region gained a longer period of independence as Vạn Xuân under the
Anterior Lý dynasty between AD 544 and 602. By the early 10th century, northern Vietnam had gained autonomy, but not sovereignty, under the
Khúc family.
In AD 938, the Vietnamese lord
Ngô Quyền
Ngô Quyền ( vi-hantu, 吳權) (April 17, 898 – February 14, 944), often referred to as Tiền Ngô Vương (前吳王; "First King of Ngô"), was a warlord who later became the founding king of the Ngô dynasty of Vietnam. He reigned fro ...
defeated the forces of the Chinese
Southern Han
Southern Han ( zh , t = 南漢 , p = Nán Hàn , j=Naam4 Hon3; 917–971), officially Han ( zh , t = 漢 , links=no), originally Yue ( zh , c = 越 , links=no), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms that existed during the ...
state at
Bạch Đằng River
The Bạch Đằng River (, ), also called Bạch Đằng Giang (from ), ''white wisteria river'', is a river in northern Vietnam, located near Hạ Long Bay. It flows through Yên Hưng District of Quảng Ninh province and the district Th� ...
and achieved full independence for Vietnam in 939 after a millennium of Chinese domination. By the 960s, the dynastic
Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), was a Vietnamese monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day Hanoi. Its early name, Đại Cồ Việt,(ch ...
(''Great Viet'') kingdom was established, Vietnamese society enjoyed a golden era under the Lý and
Trần
Trần (陳) or Tran is the second most common Vietnamese surname after Nguyen. More than 10% of all Vietnamese people share this surname.
History
The Tran ruled the Trần dynasty, a golden era in Vietnam, and successfully repelled the Mongol ...
dynasties. During the rule of the Trần dynasty, Đại Việt repelled three
Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
. Meanwhile, the
Mahāyāna
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main ex ...
branch of
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
flourished and became the state religion. Following the 1406–7
Ming–Hồ War, which overthrew the
Hồ dynasty
The Hồ dynasty (Vietnamese: , chữ Nôm: 茹胡; Vietnamese: ''triều'' ''Hồ'', chữ Hán: wikt:朝, 朝wikt:胡, 胡), officially Đại Ngu (; chữ Hán: 大虞), was a short-lived List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty cons ...
, Vietnamese independence was
interrupted briefly by the Chinese
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
, but was restored by
Lê Lợi
Lê Lợi (, chữ Hán: 黎利; 10 September 1385 – 5 October 1433), also known by his temple name as Lê Thái Tổ (黎太祖) and by his pre-imperial title Bình Định vương (平定王; "Prince of Pacification"), was a Vietnamese peopl ...
, the founder of the
Lê dynasty
The Lê dynasty, also known in historiography as the Later Lê dynasty (, chữ Hán: 朝後黎, chữ Nôm: 茹後黎), officially Đại Việt (; Chữ Hán: 大越), was the longest-ruling List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, h ...
. The Vietnamese polity reached their zenith in the Lê dynasty of the 15th century, especially during the reign of emperor
Lê Thánh Tông
Lê Thánh Tông (黎聖宗; 25 August 1442 – 3 March 1497), personal name Lê Hạo, temple name Thánh Tông, courtesy name Tư Thành, was an emperor of Đại Việt, reigning from 1460 to 1497, the fifth and the longest-reigning empero ...
(1460–1497). Between the 11th and 18th centuries, the Vietnamese polity expanded southward in a gradual process known as ("Southward expansion"), eventually conquering the kingdom of
Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from ...
and part of the
Khmer Kingdom.
From the 16th century onward, civil strife and frequent political infighting engulfed much of Đại Việt. First, the Chinese-supported
Mạc dynasty
The Mạc dynasty (; Hán-Nôm: 茹 莫/ 朝 莫) (1527–1677), officially Đại Việt (Chữ Hán: 大越), was a Vietnamese dynasty which ruled over a unified Vietnam between 1527 and 1540, and northern Vietnam from 1540 until 1593. The M ...
challenged the Lê dynasty's power. After the Mạc dynasty was defeated, the Lê dynasty was nominally reinstalled. Actual power, however, was divided between the northern
Trịnh lords Trịnh is a Vietnamese family name
In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full na ...
and the southern
Nguyễn lords
The Nguyễn lords (, 主阮; 1558–1777, 1780–1802), also known as the Nguyễn clan (; ), were Nguyễn dynasty's forerunner and a feudal noble clan ruling southern Đại Việt in the Revival Lê dynasty. The Nguyễn lords were membe ...
, who engaged in a
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
for more than four decades before a truce was called in the 1670s. Vietnam was divided into North (Trịnh) and South (Nguyễn) from 1600 to 1777. During this period, the Nguyễn expanded into the
Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( or simply ), also known as the Western Region () or South-western region (), is the list of regions of Vietnam, region in southwestern Vietnam where the Mekong, Mekong River River delta, approaches and empties into the sea th ...
, annexing the
Central Highlands and the Khmer lands in the Mekong Delta. The division of the country ended a century later when the
Tây Sơn brothers helped Trịnh to end Nguyễn, they also established new dynasty and ended Trịnh. However, their rule did not last long, and they were defeated by the remnants of the Nguyễn lords, led by
Nguyễn Ánh
Gia Long (Chữ Hán, Chữ hán: 嘉隆) ( (''Hanoi, North''), (''Ho Chi Minh City, South''); 8 February 1762 – 3 February 1820), born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh (阮暎), was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynas ...
. Nguyễn Ánh unified Vietnam, and established the
Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (, chữ Nôm: 茹阮, chữ Hán: 朝阮) was the last List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, preceded by the Nguyễn lords and ruling unified Vietnam independently from 1802 until French protectorate in 1883 ...
, ruling under the name
Gia Long
Gia Long (Chữ Hán, Chữ hán: 嘉隆) ( (''Hanoi, North''), (''Ho Chi Minh City, South''); 8 February 1762 – 3 February 1820), born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh (阮暎), was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynas ...
.
French Indochina
In the 1500s, the
Portuguese explored the Vietnamese coast and reportedly erected a
stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
on the
Chàm Islands to mark their presence. By 1533, they began landing in the Vietnamese delta but were forced to leave because of local turmoil and fighting. They also had less interest in the territory than they did in China and Japan. After they had settled in
Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by p ...
and
Nagasaki
, officially , is the capital and the largest Cities of Japan, city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
Founded by the Portuguese, the port of Portuguese_Nagasaki, Nagasaki became the sole Nanban trade, port used for tr ...
to begin the profitable Macau–Japan trade route, the Portuguese began to involve themselves in trade with
Hội An
Hội An () is a city of approximately 120,000 people in Vietnam's Quảng Nam Province, registered as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1999. Along with the Cù Lao Chàm archipelago, it is part of the Cù Lao Chàm-Hội An Biosphere Reserve ...
. Portuguese traders and
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
missionaries under the ''
Padroado
The ''Padroado'' (, "patronage") was an arrangement between the Holy See and the Kingdom of Portugal and later the Portuguese Republic, through a series of concordats by which the Holy See delegated the administration of the local churches and g ...
'' system were active in both Vietnamese realms of ''
Đàng Trong
Đàng Trong ( chữ Nôm: 唐冲, lit. "Inner Circuit"), also known as Nam Hà (, "South of the River"), was the South region of Vietnam, under the lordship of the Nguyễn clan, later enlarged by the Vietnamese southward expansion. The word '' ...
'' (
Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer t ...
or Quinan) and ''
Đàng Ngoài
Đàng Ngoài ( vi-hantu, 唐外, lit. "Outer Land"), also known as Tonkin, Bắc Hà (北河, "North of the River") or '' Kingdom of Annam'' (安南國) by foreigners, was an area in northern Đại Việt (now Vietnam) during the 17th and 18t ...
'' (
Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
) in the 17th century. The
Dutch also tried to establish contact with Quinan in 1601 but failed to sustain a presence there after several violent encounters with the locals. The
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(VOC) only managed to establish official relations with Tonkin in the spring of 1637 after leaving
Dejima
or Deshima, in the 17th century also called , was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan, that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1858). For 220 years, it was the central con ...
in Japan to establish trade for
silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
. Meanwhile, in 1613, the first
English attempt to establish contact with Hội An failed following a violent incident involving the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
. By 1672 the English did establish relations with Tonkin and were allowed to reside in
Phố Hiến.
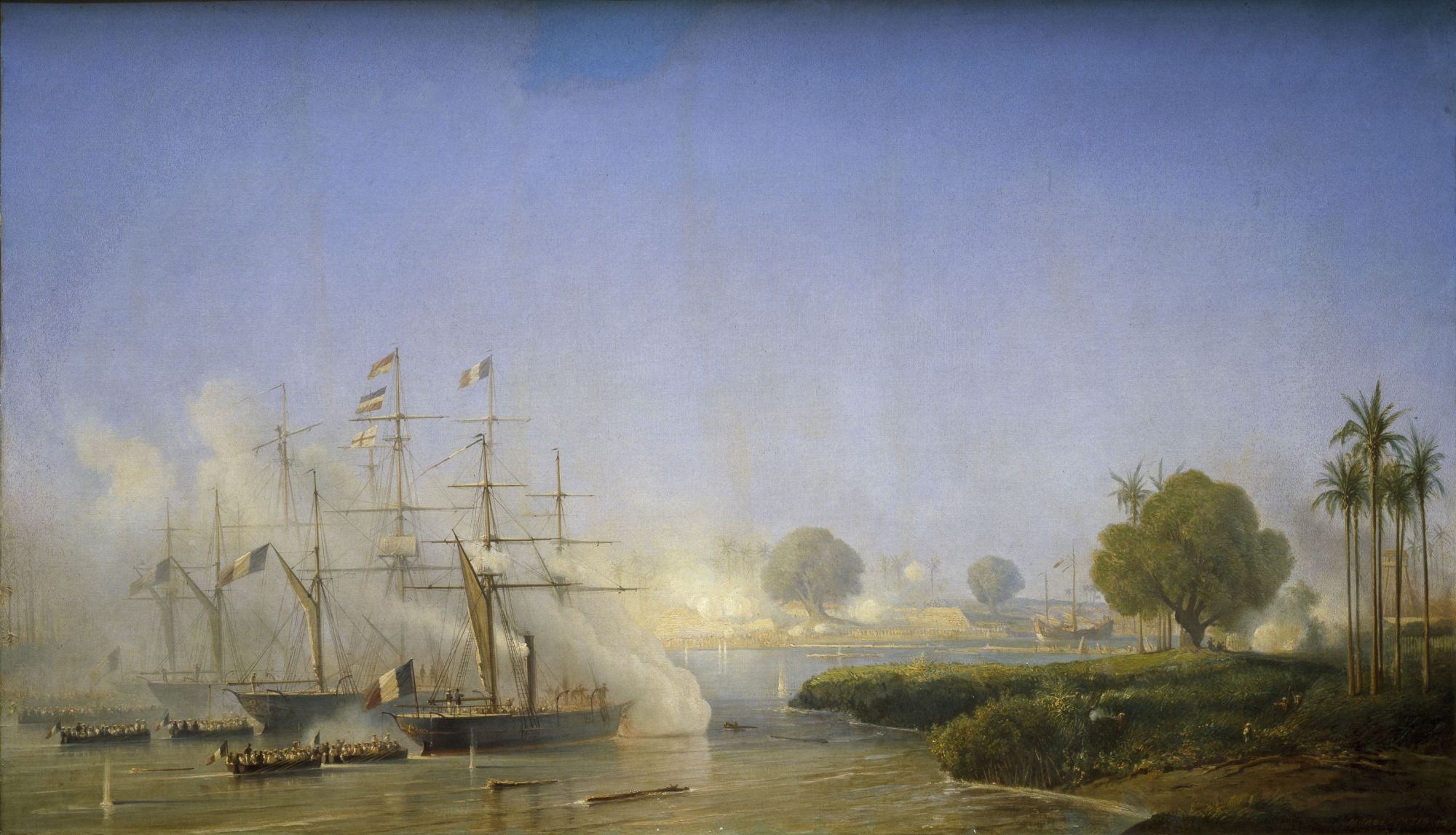

Between 1615 and 1753, French traders also engaged in trade in Vietnam. The first French missionaries arrived in 1658, under the Portuguese ''Padroado''. From its foundation, the
Paris Foreign Missions Society
The Society of Foreign Missions of Paris (, , MEP) is a Catholic Missionary order, missionary organization. It is not a religious institute, but an organization of secular clergy, secular priests and Laity, lay persons dedicated to missionary wo ...
under
''Propaganda Fide'' actively sent missionaries to Vietnam, entering Cochinchina first in 1664 and Tonkin first in 1666. Spanish
Dominicans
Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ...
joined the Tonkin mission in 1676, and
Franciscans
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest conte ...
were in Cochinchina from 1719 to 1834. The Vietnamese authorities began to feel threatened by continuous
Christianisation
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individu ...
activities. After several Catholic missionaries were detained, the
French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
intervened in 1843 to free them, as the kingdom was perceived as
xenophobic
Xenophobia (from (), 'strange, foreign, or alien', and (), 'fear') is the fear or dislike of anything that is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression that is based on the perception that a conflict exists between an in-gr ...
. In a series of conquests from 1859 to 1885,
France eroded Vietnam's sovereignty. At the
siege of Tourane in 1858, France was aided by
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
(with Filipino,
Latin American
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizenship, citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their Latin American diaspora, diasporas are Metroethnicity, ...
, and Spanish troops from the
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
) and perhaps some Tonkinese Catholics. After the
1862 Treaty, and especially after France completely conquered
Lower Cochinchina in 1867, the
Văn Thân movement of scholar-gentry class arose and committed violence against
Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
across central and northern Vietnam.
Between 1862 and 1867, the southern third of the country became the
French colony of Cochinchina. By 1884, the entire country was under French rule, with the central and northern parts of Vietnam separated into the two protectorates of
Annam and
Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
. The three entities were formally integrated into the union of
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
in 1887. The French administration imposed significant political and cultural changes on Vietnamese society. A Western-style system of modern education introduced new
humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humanism" ha ...
values. Most French settlers in Indochina were concentrated in Cochinchina, particularly in
Saigon
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
, and in
Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
, the colony's capital.
During the early colonial period, guerrillas of the royalist
Cần Vương movement
The Cần Vương (, chữ Hán: , ) movement was a large-scale Vietnamese insurgency between 1885 and 1896 against French colonial rule. Its objective was to expel the French and install the Hàm Nghi Emperor as the leader of an independent V ...
rebelled against French rule and massacred around a third of
Vietnam's Christian population. Anti-Catholic violence persisted in Nam Định, Quảng Trị, and Bình Định during the 1880s. The French strategy for pacification in Vietnam relied more on alliances with local notables than on Christian missions to establish control and manage resistance. The French developed a
plantation economy to promote export of
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
,
indigo
InterGlobe Aviation Limited (d/b/a IndiGo), is an India, Indian airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana, India. It is the largest List of airlines of India, airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 64.1% domestic market ...
,
tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of south-western China and nor ...
and
coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
. However, they largely ignored the increasing demands for civil rights and
self-government
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any ...
. An increasing dissatisfaction, even led to half-hearted, badly co-ordinated, and still worsely executed plots to oust the French, like the infamous
Hanoi Poison Plot
The Poisoning at Hanoi Citadel ( Vietnamese: ''Hà Thành đầu độc;'' Chữ Hán: 河城投毒) was a poisoning plot which occurred in 1908 when a group of Vietnamese indigenous tirailleurs attempted to poison the entire French colonial a ...
of 1908. Another large-scale rebellion, the
Thái Nguyên uprising
Cài () is a Chinese-language surname that derives from the name of the ancient Cai state. In 2019 it was the 38th most common surname in China, but the 9th most common in Taiwan (as of 2018), where it is usually romanized as "Tsai" (based on ...
in 1917, was also suppressed heavily.
A nationalist political movement soon emerged, with leaders like
Phan Bội Châu
Phan Bội Châu (; 26 December 1867 – 29 October 1940), born Phan Văn San, courtesy name Hải Thụ (later changed to Sào Nam), was a pioneer of 20th century Vietnamese nationalism. In 1904, he formed a revolutionary organization called ...
,
Phan Châu Trinh
Phan Châu Trinh (Chữ Hán: 潘周楨, 9 September 1872 – 24 March 1926), courtesy name Tử Cán (梓幹), pen name Tây Hồ (西湖) or Hi Mã (希馬), was an early 20th-century Vietnamese nationalist and reformer. He sought to end Franc ...
,
Phan Đình Phùng
Phan Đình Phùng (; 1847January 21, 1896) was a Vietnamese revolutionary who led rebel armies against French colonial forces in Vietnam. He was the most prominent of the Confucian court scholars involved in anti-French military campaign ...
, Emperor
Hàm Nghi
Emperor Hàm Nghi (, vi-hantu, lit. "entirely right", 3 August 1871 – 14 January 1944), personal name Nguyễn Phúc Ưng Lịch (), also Nguyễn Phúc Minh, was the eighth emperor of the Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty. He reigned for only one ...
, and
Hồ Chí Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first president of the Democratic Republic ...
fighting or calling for independence. This resulted in the 1930
Yên Bái mutiny
The Yên Bái mutiny () or officially Yên Báy general uprising () was an uprising of Vietnamese soldiers in the Troupes coloniales, French colonial army on 10 February 1930. This took place in collaboration with civilian supporters who were mem ...
by the
Vietnamese Nationalist Party (VNQDĐ), which the French quashed. The mutiny split the independence movement, as many leading members converted to
communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
.
The French maintained full control of their colonies until World War II, when the
war in the Pacific
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War or the Pacific Theatre, was the Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the Empire of Japan and the Allies of World War II, Allies in East Asia, East and Southeast As ...
led to the
Japanese invasion of French Indochina
The , () was a short undeclared military confrontation between Japan and Vichy France in northern French Indochina. Fighting lasted from 22 to 26 September 1940; the same time as the Battle of South Guangxi in the Sino-Japanese War, which was ...
in 1940. Afterwards, the
Japanese Empire
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From 1910 to ...
was allowed to station its troops in Vietnam while the pro-
Vichy French
Vichy France (; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was a French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II, established as a result of the French capitulation after the defeat against G ...
colonial administration continued. Japan exploited Vietnam's natural resources to support its military campaigns, culminating in a
full-scale takeover of the country in March 1945. This led to the
Vietnamese Famine of 1945
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
which killed up to two million people.
First Indochina War
In 1941, the
Việt Minh
The Việt Minh (, ) is the common and abbreviated name of the League for Independence of Vietnam ( or , ; ), which was a communist-led national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Vi ...
, a national liberation movement based on a
communist ideology
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, d ...
, emerged under the Vietnamese revolutionary leader
Hồ Chí Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first president of the Democratic Republic ...
. The Việt Minh sought independence for Vietnam from France and the end of the
Japanese occupation. After the military defeat of Japan in World War II and the fall of its sponsored government
Empire of Vietnam
The Empire of Vietnam (; Literary Chinese and Japanese language, Contemporary Japanese: ; Japanese language, Modern Japanese: ) was a short-lived Japanese puppet state, puppet state of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan between March 11 and Abdicat ...
in August 1945, Saigon's administrative services collapsed and chaos, riots, and murder were widespread. The Việt Minh occupied
Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
and proclaimed a provisional government, which asserted national independence on 2 September.
In July 1945, the
Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
had decided to divide Indochina at the
16th parallel to allow
Chiang Kai-shek of the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
to receive the Japanese surrender in the north while Britain's
Lord Louis Mountbatten
Admiral of the Fleet Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (born Prince Louis of Battenberg; 25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979), commonly known as Lord Mountbatten, was a British statesman, Royal Navy off ...
received their surrender in the south. The Allies agreed that Indochina still belonged to France.

But as the French were weakened by the
German occupation
German-occupied Europe, or Nazi-occupied Europe, refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly militarily occupied and civil-occupied, including puppet states, by the (armed forces) and the government of Nazi Germany at ...
,
British-Indian forces and the remaining Japanese
Southern Expeditionary Army Group
The was a general army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. It was responsible for all military operations in South East Asian and South West Pacific campaigns of World War II. Its military symbol was NA.
The Southern Expediti ...
were used to maintain order and help France reestablish control through the
1945–1946 War in Vietnam. Hồ initially chose to take a moderate stance to avoid military conflict with France, asking the French to withdraw their colonial administrators and for French professors and engineers to help build a modern independent Vietnam. But the
Provisional Government of the French Republic
The Provisional Government of the French Republic (PGFR; , GPRF) was the provisional government of Free France between 3 June 1944 and 27 October 1946, following the liberation of continental France after Operations ''Overlord'' and ''Drago ...
did not act on these requests, including the idea of independence, and dispatched the
French Far East Expeditionary Corps
The French Far East Expeditionary Corps (, CEFEO) was a colonial expeditionary force of the French Union Army that was initially formed in French Indochina in 1945 during the Pacific War. The CEFEO later fought and lost in the First Indochina Wa ...
to restore colonial rule. This resulted in the Việt Minh launching a guerrilla campaign against the French in late 1946. The resulting
First Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam, and alternatively internationally as the French-Indochina War) was fought between French Fourth Republic, France and Việ ...
lasted until July 1954. The defeat of French colonialists and
Vietnamese loyalists in the 1954
battle of Điện Biên Phủ
The Battle of Điện Biên Phủ was a climactic confrontation of the First Indochina War that took place between 13 March and 7 May 1954. It was fought between the forces of the French Union and Viet Minh.
The French began an operation to in ...
allowed Hồ to negotiate a ceasefire from a favourable position at the subsequent
Geneva Conference.
The colonial administration was thereby ended and French Indochina was dissolved under the Geneva Accords of 21 July 1954 into three countries—Vietnam, and the kingdoms of
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
and
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
. Vietnam was further divided into North and South administrative regions at the
Demilitarised Zone
A demilitarized zone (DMZ or DZ) is an area in which treaties or agreements between states, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities, or personnel. A DZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary ...
, roughly along the
17th parallel north
Following are circles of latitude between the 15th parallel north and the 20th parallel north:
16th parallel north
The 16th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 16 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, As ...
(pending elections scheduled for July 1956). A 300-day period of free movement was permitted, during which almost a million northerners, mainly Catholics, moved south, fearing persecution by the communists. This migration was in large part aided by the United States military through
Operation Passage to Freedom
Operation Passage to Freedom was a term used by the United States Navy to describe the propaganda effort and the assistance in transporting 310,000 Vietnamese civilians, soldiers and non-Vietnamese members of the French Army from communist No ...
. The
partition of Vietnam
Partition may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Partition'' (1987 film), directed by Ken McMullen
* ''Partition'' (2007 film), directed by Vic Sarin
* '' Partition: 1947'', or ''Viceroy's House'', a 2017 film
Music
* Par ...
by the Geneva Accords was not intended to be permanent, and stipulated that Vietnam would be reunited after the elections. But in 1955, the southern State of Vietnam's prime minister,
Ngô Đình Diệm
Ngô Đình Diệm ( , or ; ; 3 January 1901 – 2 November 1963) was a South Vietnamese politician who was the final prime minister of the State of Vietnam (1954–1955) and later the first president of South Vietnam ( Republic of ...
, toppled
Bảo Đại
Bảo Đại (, vi-hantu, , , 22 October 191331 July 1997), born Nguyễn Phúc (Phước) Vĩnh Thụy (), was the 13th and final emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam. From 1926 to 1945, he was ''de jure'' em ...
in a fraudulent
referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
organised by his brother
Ngô Đình Nhu
James (Giacôbê) Ngô Đình Nhu (7 October 19102 November 1963) was a Vietnamese archivist and politician. He was the younger brother and State Counsellor of South Vietnam's first president, Ngô Đình Diệm. Although he held no formal exe ...
, and proclaimed himself president of the
Republic of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with it ...
. This effectively replaced the internationally recognised
State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam (; chữ Hán: 國家越南; ) was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as an associated state of the French Union and later as an independent state (from 20 July 1954 to 26 October 1955). The s ...
by the
Republic of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with it ...
in the south—supported by the United States, France,
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
,
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and Thailand—and Hồ's
Democratic Republic of Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; ; VNDCCH), was a country in Southeast Asia from 1945 to 1976, with sovereignty fully recognized in 1954. A member of the communist Eastern Bloc, it opposed the French-suppor ...
in the north, supported by the Soviet Union, Sweden,
Khmer Rouge
The Khmer Rouge is the name that was popularly given to members of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK), and by extension to Democratic Kampuchea, which ruled Cambodia between 1975 and 1979. The name was coined in the 1960s by Norodom Sihano ...
, and the
People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
Vietnam War
From 1953 to 1956, the
North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; ; VNDCCH), was a country in Southeast Asia from 1945 to 1976, with sovereignty fully recognized in 1954 Geneva Conference, 1954. A member of the communist Eastern Bloc, it o ...
ese government instituted
agrarian reforms including "
rent reduction" and "
land reform
Land reform (also known as agrarian reform) involves the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership, land use, and land transfers. The reforms may be initiated by governments, by interested groups, or by revolution.
Lan ...
", which resulted in significant
political repression
Political repression is the act of a state entity controlling a citizenry by force for political reasons, particularly for the purpose of restricting or preventing the citizenry's ability to take part in the political life of a society, thereby ...
. This included 13,500 to as many as 100,000 executions. In the South, Diệm countered North Vietnamese subversion (including the assassination of over 450 South Vietnamese officials in 1956) by detaining tens of thousands of suspected communists in "political reeducation centres". This programme incarcerated many non-communists, but was successful at curtailing
communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
activity in the country, if only for a time. The North Vietnamese government claimed that 2,148 people were killed in the process by November 1957. The pro-Hanoi
Việt Cộng
The Viet Cong (VC) was an epithet and umbrella term to refer to the communist-driven armed movement and united front organization in South Vietnam. It was formally organized as and led by the National Liberation Front of South Vietnam, and ...
began a guerrilla campaign in
South Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered Diplomatic recognition, international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the ...
in the late 1950s to overthrow Diệm's government. From 1960, the Soviet Union and North Vietnam signed treaties providing for further Soviet military support.

In 1963, Buddhist discontent with Diệm's Catholic regime erupted into
mass demonstrations, leading to a violent government crackdown. This led to the
collapse of Diệm's relationship with the United States, and ultimately to a
1963 coup in which
he and Nhu were assassinated. The Diệm era was followed by more than a dozen successive military governments, before the pairing of Air Marshal
Nguyễn Cao Kỳ
Nguyễn Cao Kỳ (; 8 September 1930 – 23 July 2011) was a South Vietnamese military officer and politician who served as the chief of the Republic of Vietnam Air Force in the 1960s, before leading the nation as the prime minister of Sout ...
and General
Nguyễn Văn Thiệu
Nguyễn Văn Thiệu (; 5 April 1923 – 29 September 2001) was a South Vietnam, South Vietnamese military officer and politician who was the Leaders of South Vietnam, president of South Vietnam from 1967 to 1975. He was a general in the Repub ...
took control in mid-1965. Thiệu gradually outmaneuvered Kỳ and cemented his grip on power in fraudulent elections in 1967 and 1971. During this political instability, the communists began to gain ground. To support South Vietnam's struggle against the communist insurgency, the United States used the 1964
Gulf of Tonkin incident as a pretext for increasing its contribution of military advisers. US forces became involved in ground combat operations by 1965, and at their peak several years later, numbered more than 500,000. The US also engaged in
sustained aerial bombing. Meanwhile, China and the Soviet Union provided North Vietnam with significant material aid and 15,000 combat advisers. Communist forces supplying the Việt Cộng carried supplies along the
Hồ Chí Minh trail, which passed through
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
.
The communists attacked South Vietnamese targets during the 1968
Tết Offensive. The campaign failed militarily, but shocked the American establishment and turned US public opinion against the war. During the offensive, communist troops
massacred over 3,000 civilians at
Huế
Huế (formerly Thừa Thiên Huế province) is the southernmost coastal Municipalities of Vietnam, city in the North Central Coast region, the Central Vietnam, Central of Vietnam, approximately in the center of the country. It borders Quảng ...
. Facing an increasing casualty count,
rising domestic opposition to the war, and growing international condemnation, the US began
withdrawing from ground combat roles in the early 1970s. This also entailed an unsuccessful effort to
strengthen and stabilise South Vietnam. Following the
Paris Peace Accords
The Paris Peace Accords (), officially the Agreement on Ending the War and Restoring Peace in Viet Nam (), was a peace agreement signed on January 27, 1973, to establish peace in Vietnam and end the Vietnam War. It took effect at 8:00 the follo ...
of 27 January 1973, all American combat troops were withdrawn by 29 March 1973. In December 1974, North Vietnam
captured the province of
Phước Long and started a
full-scale offensive, culminating in the
fall of Saigon
The fall of Saigon, known in Vietnam as Reunification Day (), was the capture of Saigon, the capital of South Vietnam, by North Vietnam on 30 April 1975. As part of the 1975 spring offensive, this decisive event led to the collapse of the So ...
on 30 April 1975. South Vietnam was ruled by a
provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, a transitional government or provisional leadership, is a temporary government formed to manage a period of transition, often following state collapse, revoluti ...
for 14 months under North Vietnamese control.
Reunification and reforms
On 2 July 1976, North and South Vietnam were merged to form the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The war had devastated Vietnam and killed 966,000 to 3.8 million people. A 1974 US Senate subcommittee estimated nearly 1.4 million
Vietnamese civilians were killed or wounded between 1965 and 1974—including 415,000 killed. In its aftermath, under
Lê Duẩn
Lê Duẩn (; 7 April 1907 – 10 July 1986) was a Vietnamese communist politician. He rose in the party hierarchy in the late 1950s and became General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (VCP) at the 3rd Natio ...
's administration, there were no mass executions of South Vietnamese who had collaborated with the US or the defunct South Vietnamese government, confounding Western fears, but up to 300,000 South Vietnamese were sent to
reeducation camps, where many endured torture, starvation, and disease while being forced to perform hard labour. The government embarked on a mass campaign of
collectivisation
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-o ...
of farms and factories. Many fled the country following the conclusion of the war. In 1978, in response to the
Khmer Rouge
The Khmer Rouge is the name that was popularly given to members of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK), and by extension to Democratic Kampuchea, which ruled Cambodia between 1975 and 1979. The name was coined in the 1960s by Norodom Sihano ...
government of Cambodia ordering massacres of Vietnamese residents in the border villages in the districts of
An Giang
An Giang is a province of Vietnam. It is located in the Mekong Delta, in the country's southwestern part.
Geography
An Giang is located in the upper reaches of the Mekong Delta. The Hậu Giang and Tiền Giang branches of the Mekong River ...
and
Kiên Giang, the Vietnamese military
invaded Cambodia and removed them from power after occupying
Phnom Penh
Phnom Penh is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Cambodia, most populous city of Cambodia. It has been the national capital since 1865 and has grown to become the nation's primate city and its political, economic, industr ...
. The intervention was a success, resulting in the establishment of a new, pro-Vietnam socialist government, the
People's Republic of Kampuchea
The People's Republic of Kampuchea (PRK) was a partially recognised state in Southeast Asia which existed from 1979 to 1989. It was a satellite state of Vietnam, founded in Cambodia by the Vietnamese-backed Kampuchean United Front for Nationa ...
, which ruled until 1989. However, this worsened relations with China, which had supported the Khmer Rouge. China later launched a
brief incursion into northern Vietnam in 1979, causing Vietnam to rely even more heavily on Soviet economic and military aid, while mistrust of the
Chinese government
The government of the People's Republic of China is based on a system of people's congress within the parameters of a Unitary state, unitary communist state, in which the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP) enacts its policies through people's ...
escalated.
At the
Sixth National Congress of the
Communist Party of Vietnam
The Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) is the founding and sole legal party of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Founded in 1930 by Hồ Chí Minh, the CPV became the ruling party of North Vietnam in 1954 and then all of Vietnam after the col ...
(CPV) in December 1986, reformist politicians replaced the "old guard" government with new leadership. The reformers were led by 71-year-old
Nguyễn Văn Linh
Nguyễn Văn Linh (; 1 July 1915 – 27 April 1998) was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician. Nguyễn Văn Linh was the general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam from 1986 to 1991 and a political leader of the Vietcong during ...
, who became the party's new general secretary. He and the reformers implemented a series of market reforms known as ("Renovation") that carefully managed the transition from a
planned economy
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, ...
to a "
socialist-oriented market economy
The socialist-oriented market economy ( Vietnamese: ''Kinh tế thị trường định hướng xã hội chủ nghĩa'') is the official title given to the current economic system in Vietnam by the ruling Communist Party. It is described ...
". Although the authority of the state remained unchallenged under ''Đổi Mới'', the government encouraged
private ownership
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
of farms and factories, economic deregulation, and foreign investment, while maintaining control over strategic industries. Subsequently, Vietnam's economy achieved strong growth in agricultural and industrial production, construction, exports, and foreign investment, although these reforms also resulted in a rise in income inequality and gender disparities.
In 2021,
General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam
The general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam Central Committee (), simply and informally the party general secretary or just general secretary (, TBT), is the contemporary title for the holder of the highest office within the Commu ...
,
Nguyễn Phú Trọng
Nguyễn Phú Trọng ( ; 14 April 194419 July 2024) was a Vietnamese politician and political theorist who served as general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam from 2011 until his death in 2024. As the head of the party's Secretaria ...
, was re-elected for his third term in office, meaning he was Vietnam's most powerful leader in decades. He died 19 July 2024, and was followed by
Tô Lâm
Tô Lâm (; born 10 July 1957) is a Vietnamese politician and former police officer who has served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam, general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) since August 2024 and the 13th p ...
as General Secretary of the Communist Party.
Geography

Vietnam is located on the eastern
Indochinese Peninsula between the latitudes
8° and
24°N, and the longitudes
102° and
110°E. It covers a total area of
or .
The combined length of the country's land boundaries is , and its coastline is long. At its narrowest point in the central
Quảng Bình province
Quảng Bình was formerly a southern coastal Provinces of Vietnam, province in the North Central Coast region, the Central Vietnam, Central of Việt Nam, Vietnam. It borders Hà Tĩnh province, Hà Tĩnh to the north, Quảng Trị province, ...
, the country is as little as across, though it widens to around in the north. Vietnam's land is mostly hilly and densely forested, with level land covering no more than 20%. Mountains account for 40% of the country's land area, and tropical forests cover around 42%. The Red River Delta in the north, a flat, roughly triangular region covering , is smaller but more intensely developed and more densely populated than the
Mekong River Delta
The Mekong Delta ( or simply ), also known as the Western Region () or South-western region (), is the region in southwestern Vietnam where the Mekong River approaches and empties into the sea through a network of distributaries. The Mekong d ...
in the south. Once an inlet of the
Gulf of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin ( northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern co ...
, it has been filled in over the millennia by riverine
alluvial deposits. The delta, covering about , is a low-level plain no more than
above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level ...
at any point. It is criss-crossed by a maze of rivers and canals, which carry so much sediment that the delta advances into the sea every year. The
exclusive economic zone of Vietnam covers in the
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
.
Southern Vietnam is divided into coastal lowlands, the mountains of the
Annamite Range
The Annamite Range (; ) is a major mountain range of Mainland Southeast Asia, extending approximately through Laos, Vietnam, and a small area in northeast Cambodia.
Geography
The highest points of the Annamite Range are the -high Phou Bia, th ...
, and extensive forests. Comprising five relatively flat plateaus of
basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
soil, the highlands account for 16% of the country's
arable land
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of a ...
and 22% of its total forested land. The soil in much of the southern part of Vietnam is relatively low in nutrients as a result of intense cultivation. Several minor
earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s have been recorded. The northern part of the country consists mostly of highlands and the Red River Delta.
Fansipan (also known as Phan Xi Păng), which is located in
Lào Cai province, is the highest mountain in Vietnam, standing high. From north to south Vietnam, the country also has
numerous islands;
Phú Quốc
Phú Quốc () is the largest island in Vietnam. Phú Quốc and nearby islands, along with the distant Thổ Chu Islands, are part of Kiên Giang Province as Phú Quốc City; Vietnam's first island municipality. The island has a total area o ...
is the largest. The
Hang Sơn Đoòng Cave is considered the largest known cave passage in the world since its discovery in 2009. The
Ba Bể Lake and
Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of wat ...
River are the largest lake and longest river in the country.
Climate
Due to differences in latitude and the marked variety in
topographical relief, Vietnam's climate tends to vary considerably for each region. During the winter or dry season, extending roughly from November to April, the
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
winds usually blow from the northeast along the Chinese coast and across the Gulf of Tonkin, picking up considerable moisture. The average annual temperature is generally higher in the plains than in the mountains, especially in southern Vietnam compared to the north. Temperatures vary less in the southern plains around Ho Chi Minh City and the Mekong Delta, ranging from between over the year. In Hanoi and the surrounding areas of the Red River Delta, the temperatures are much lower between . Seasonal variations in the mountains, plateaus, and the northernmost areas are much more dramatic, with temperatures varying from in December and January to in July and August. During winter, snow occasionally falls over the highest peaks of the far northern mountains near the Chinese border. Vietnam receives high rates of
precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
in the form of rainfall with an average amount from during the monsoon seasons; this often causes flooding, especially in the cities with poor drainage systems. The country is also affected by
tropical depression
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s,
tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its lo ...
s and
typhoon
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for a ...
s. Vietnam is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change, with 55% of its population living in low-elevation coastal areas.
Biodiversity

As the country is located within the
Indomalayan realm
The Indomalayan realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms. It extends across most of South and Southeast Asia and into the southern parts of East Asia.
Also called the Oriental realm by biogeographers, Indomalaya spreads all over the Ind ...
, Vietnam is one of twenty-five countries considered to possess a uniquely high level of
biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
. This was noted in the country's National Environmental Condition Report in 2005. It is ranked 16th worldwide in biological diversity, being home to approximately 16% of the world's species. 15,986 species of
flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
have been identified in the country, of which 10% are
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
. Vietnam's
fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
includes 307
nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
species, 200
oligochaeta
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of soft-bodied animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadril ...
, 145
acarina
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as ea ...
, 113
springtail
Springtails (class Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern Hexapoda, hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three lineages are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have in ...
s, 7,750 insects, 260 reptiles, and 120 amphibians. There are 840 birds and 310 mammals are found in Vietnam, of which 100 birds and 78 mammals are endemic. Vietnam has two
World Natural Heritage Sites—the
Hạ Long Bay and
Phong Nha-Kẻ Bàng National Park Phong may refer to:
Computer graphics
*Phong shading
*Phong reflection model
* Blinn–Phong shading model
* Bui Tuong Phong - creator of the Phong shading interpolation method and reflection model.
Other
* Phong-Kniang language
* Nam Phong ...
—together with nine
biosphere reserves
Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific program, launched in 1971 by UNESCO, that aims to establish a scientific basis for the 'improvement of relationships' between people and their environments.
MAB engages w ...
, including
Cần Giờ Mangrove Forest,
Cát Tiên,
Cát Bà,
Kiên Giang, the Red River Delta, Mekong Delta,
Western Nghệ An,
Cà Mau
Cà Mau () is a city in southern Vietnam. It is the capital of Cà Mau province, a province in the Mekong Delta region, in the southernmost part of Vietnam's inland territory (mainland). The city is characterised by its system of transport cana ...
, and
Cu Lao Cham Marine Park.
Vietnam is also home to 1,438 species of freshwater
microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic scale, microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine life, marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellul ...
, constituting 9.6% of all microalgae species, as well as 794 aquatic
invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s and 2,458 species of sea fish. In recent years, 13
genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
, 222 species, and 30
taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
of flora have been newly described in Vietnam. Six new mammal species, including the
saola
The saola (''Pseudoryx nghetinhensis''), also called spindlehorn, Asian unicorn, or infrequently, Vu Quang bovid, is a forest-dwelling bovid native to the Annamite Range in Vietnam and Laos. It was described in 1993 following a discovery of ...
,
giant muntjac
The giant muntjac (''Muntiacus vuquangensis''), sometimes referred to as the large-antlered muntjac, is a species of muntjac deer. It is the largest muntjac species and was discovered in 1994 in Vũ Quang, Hà Tĩnh Province of Vietnam and in c ...
and
Tonkin snub-nosed monkey have also been discovered, along with one new bird species, the endangered
Edwards's pheasant. In the late 1980s, a small population of
Javan rhinoceros
The Javan rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros sondaicus''), Javan rhino, Sunda rhinoceros or lesser one-horned rhinoceros is a critically endangered member of the genus ''Rhinoceros'', of the rhinoceros family Rhinocerotidae, and one of the five remainin ...
was found in Cát Tiên National Park. However, the last individual of the species in Vietnam was reportedly shot in 2010. In agricultural
genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
, Vietnam is one of the world's twelve original
cultivar
A cultivar is a kind of Horticulture, cultivated plant that people have selected for desired phenotypic trait, traits and which retains those traits when Plant propagation, propagated. Methods used to propagate cultivars include division, root a ...
centres. The Vietnam National Cultivar Gene Bank preserves 12,300 cultivars of 115 species. The Vietnamese government spent US$49.07 million on the preservation of biodiversity in 2004 alone and has established 126 conservation areas, including 30
national parks
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
.

In Vietnam, wildlife
poaching
Poaching is the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the huntin ...
has become a major concern. In 2000, a
non-governmental organisation
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
(NGO) called
Education for Nature – Vietnam was founded to instill in the population the importance of wildlife conservation in the country. In the years that followed, another NGO called GreenViet was formed by Vietnamese youngsters for the enforcement of wildlife protection. Through collaboration between the NGOs and local authorities, many local poaching syndicates were crippled by their leaders' arrests. A study released in 2018 revealed Vietnam is a destination for the illegal export of
rhinoceros
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
horns from
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
due to the demand for them as a medicine and a status symbol.
The main environmental concern that persists in Vietnam today is the legacy of the use of the chemical
herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
Agent Orange
Agent Orange is a chemical herbicide and defoliant, one of the tactical uses of Rainbow Herbicides. It was used by the U.S. military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1962 to 1971. T ...
, which continues to cause
birth defect
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth de ...
s and many health problems in the Vietnamese population. In the southern and central areas affected most by the chemical's use during the Vietnam War, nearly 4.8 million Vietnamese people have been exposed to it and suffered from its effects. In 2012, approximately 50 years after the war, the US began a US$43 million joint clean-up project in the former chemical storage areas in Vietnam to take place in stages. Following the completion of the first phase in
Đà Nẵng
Da Nang or DanangSee also Danang Dragons (, ) is the list of cities in Vietnam, fifth-largest city in Vietnam by municipal population. It lies on the coast of the Western Pacific Ocean of Vietnam at the mouth of the Hàn River (Vietnam), Hàn R ...
in late 2017, the US announced its commitment to clean other sites, especially in the heavily impacted site of
Biên Hòa
Biên Hòa (Northern accent: , Southern accent: ) is the capital city of Đồng Nai Province, Vietnam, and is part of the Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area. Situated northeast of Ho Chi Minh City (also known as Saigon), Biên Hòa is connect ...
.
The Vietnamese government spends over
VNĐ10 trillion each year ($431.1 million) for monthly allowances and the physical rehabilitation of victims of the chemicals. In 2018, the Japanese engineering group
Shimizu Corporation
is an architecture, architectural, civil engineering and General contractor, general contracting firm. It has annual sales of approximately US$15 billion and has been widely recognized as one of the top 5 contractors in Japan and among the top 2 ...
, working with Vietnamese military, built a plant for the treatment of soil polluted by Agent Orange. Plant construction costs were funded by the company itself. One of the long-term plans to restore southern Vietnam's damaged
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s is through the use of
reforestation
Reforestation is the practice of restoring previously existing forests and woodlands that have been destroyed or damaged. The prior forest destruction might have happened through deforestation, clearcutting or wildfires. Three important purpose ...
efforts. The Vietnamese government began doing this at the end of the war. It started by replanting
mangrove forest
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangrove trees cannot withsta ...
s in the Mekong Delta regions and in
Cần Giờ outside Hồ Chí Minh City, where mangroves are important to ease (though not eliminate) flood conditions during monsoon seasons. The country had a 2019
Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 47 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 5.35/10, ranking it 104th globally out of 172 countries.
Apart from herbicide problems,
arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
in the
ground water
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidat ...
in the Mekong and Red River Deltas has also become a major concern. And most notoriously,
unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance (UXO, sometimes abbreviated as UO) and unexploded bombs (UXBs) are explosive weapons (bombs, shell (projectile), shells, grenades, land mines, naval mines, cluster munition, and other Ammunition, munitions) that did not e ...
s (UXO) pose dangers to humans and wildlife—another bitter legacy from the long wars. As part of the continuous campaign to
demine/remove UXOs, several international
bomb removal agencies from the United Kingdom, Denmark,
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
and the US have been providing assistance. The Vietnam government spends over VNĐ1 trillion ($44 million) annually on demining operations and additional hundreds of billions of đồng for treatment, assistance, rehabilitation, vocational training and resettlement of the victims of UXOs.
Government and politics
Vietnam is a
unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
that self-designates as a
socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
, one of the two communist states (the other being
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
) in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. Although Vietnam remains officially committed to
socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
as its defining creed, its economic policies have grown increasingly
capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
, with ''
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. M ...
'' characterising its leadership as "ardently capitalist communists". Under the
constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, the
Communist Party of Vietnam
The Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) is the founding and sole legal party of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Founded in 1930 by Hồ Chí Minh, the CPV became the ruling party of North Vietnam in 1954 and then all of Vietnam after the col ...
(CPV) asserts their role in all sectors of the country's politics. The
president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
is the elected
head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
and the
commander-in-chief of the military, serving as the chairman of the Council of Supreme Defence and Security, and holds the second highest office in Vietnam as well as performing executive functions and state appointments and setting policy.
The
general secretary
Secretary is a title often used in organizations to indicate a person having a certain amount of authority, Power (social and political), power, or importance in the organization. Secretaries announce important events and communicate to the org ...
of the CPV performs numerous key administrative functions, controlling the party's national organisation. The
prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
is the
head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
, presiding over a council of ministers composed of five deputy prime ministers and the heads of 26 ministries and commissions. Only political organisations affiliated with or endorsed by the CPV are permitted to contest elections in Vietnam. These include the
Vietnamese Fatherland Front
The Vietnam Fatherland Front (VFF, alternatively Vietnamese Fatherland Front; ) is constitutionally an integral component in the political structure of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and an umbrella group of mass movements and political coa ...
and worker and
trade union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
ist parties.

The
National Assembly of Vietnam
The National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (N.A.; ) is the Unicameralism, unicameral parliament and the highest body of state power of Socialist Republic of Vietnam, Vietnam. The National Assembly is the only branch of governmen ...
is the
unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature consisting of one house or assembly that legislates and votes as one. Unicameralism has become an increasingly common type of legislature, making up nearly ...
supreme state organ of power composed of 500 members. Headed by a
chairman
The chair, also chairman, chairwoman, or chairperson, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the gro ...
, it is superior to both the executive and judicial organs, with all government ministers being appointed from members of the National Assembly. The
Supreme People's Court of Vietnam
The Supreme People's Court of Vietnam () is the highest court of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The Supreme People's Court is one of the two institutions at the apex of the judicial system of Vietnam, with the other body being the Supr ...
, headed by a chief justice, is the country's highest
court of appeal
An appellate court, commonly called a court of appeal(s), appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to Hearing (law), hear a Legal case, case upon appeal from a trial court or other ...
, though it is also answerable to the National Assembly. Beneath the Supreme People's Court stand the
provincial municipal courts and many
local courts.
Military courts
A court-martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of members of the arme ...
possess special jurisdiction in matters of
state security. Vietnam maintains the
death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
for numerous offences.
In 2023, a three-person collective leadership was responsible for governing Vietnam. President
Võ Văn Thưởng, Prime Minister
Phạm Minh Chính (since 2021) and the most powerful leader
Nguyễn Phú Trọng
Nguyễn Phú Trọng ( ; 14 April 194419 July 2024) was a Vietnamese politician and political theorist who served as general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam from 2011 until his death in 2024. As the head of the party's Secretaria ...
(since 2011) as the Communist Party of Vietnam's General Secretary. On 22 May 2024,
Tô Lâm
Tô Lâm (; born 10 July 1957) is a Vietnamese politician and former police officer who has served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam, general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) since August 2024 and the 13th p ...
, who previously served as the
Minister of Public Security, was voted as the president of Vietnam by the National Assembly, after Võ Văn Thưởng resigned in March of the same year due to corruption charges against him. On 3 August 2024, Tô Lâm, who is also serving as the president, was elected by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam as the general secretary following the death of Nguyễn Phú Trọng on 19 July 2024. On 21 October 2024, the National Assembly appointed
army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
general
Lương Cường
Lương Cường (; born 15 August 1957) is a Vietnamese politician and former army General officer, general who is currently serving as the 14th president of Vietnam since October 2024. He also served as the permanent Member of the Secretariat s ...
as president, succeeding Tô Lâm.
Administrative divisions
Vietnam is divided into 57
provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
(,
chữ Hán
( , ) are the Chinese characters that were used to write Literary Chinese in Vietnam, Literary Chinese (; ) and Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary in Vietnamese language, Vietnamese. They were officially used in Vietnam after the Red River Delta region ...
: ). There are also six
municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
(), which are administratively on the same level as provinces.

Provinces are subdivided into
provincial municipalities (, 'city under province'),
township
A township is a form of human settlement or administrative subdivision. Its exact definition varies among countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, this tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, Canad ...
s () and
counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
(), which are in turn subdivided into towns () or
communes
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
().
Centrally controlled municipalities are subdivided into
district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
s () and counties, which are further subdivided into
wards ().
Foreign relations
Throughout its history, Vietnam's main foreign relationship has been with various Chinese dynasties. Following the partition of Vietnam in 1954, North Vietnam maintained relations with the
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, South Vietnam maintained relations with the
Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While ...
. Despite these differences, Vietnam's sovereign principles and insistence on cultural independence have been laid down in numerous documents over the centuries before its independence. These include the 11th-century patriotic poem "''
Nam quốc sơn hà
''Nam quốc sơn hà'' (, ) is a famous 10th- to 11th-century Vietnamese patriotic poem. Dubbed "Vietnam's first Declaration of Independence", it asserts the sovereignty of Vietnam's rulers over its lands. The poem was first dictated to be read ...
''" and the 1428 proclamation of independence "''
Bình Ngô đại cáo''". Though China and Vietnam are now formally at peace,
significant territorial tensions remain between the two countries over the South China Sea. Vietnam holds membership in 63 international organisations, including the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
(UN),
Association of Southeast Asian Nations
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 Sovereign state, states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its ...
(ASEAN),
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 121 countries that Non-belligerent, are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded with the view to advancing interests of developing countries in the context of Cold W ...
(NAM),
International Organisation of the Francophonie (La Francophonie), and
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
(WTO). It also maintains relations with over 650 non-governmental organisations. As of 2010 Vietnam had established diplomatic relations with 178 countries.
Vietnam's current foreign policy is to consistently implement a policy of independence, self-reliance, peace, co-operation, and development, as well openness, diversification,
multilateralisation with international relations. The country declares itself a friend and partner of all countries in the international community, regardless of their political affiliation, by actively taking part in international and regional cooperative development projects. Since the 1990s, Vietnam has taken several key steps to restore diplomatic ties with capitalist
Western countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also constitute the West. ...
. It already had relations with communist Western countries in the decades prior. Relations with the United States
began improving in August 1995 with both states upgrading their ''
liaison
Liaison or Liaisons may refer to:
General usage
* Affair, an unfaithful sexual relationship
* Collaboration
* Co-operation
* Liaison, an egg-based thickening used in cooking
Arts and entertainment
* Liaisons (''Desperate Housewives''), a 2007 ...
'' offices to embassy status. As diplomatic ties between the two governments grew, the United States opened a
consulate general
A consul is an official representative of a government who resides in a foreign country to assist and protect citizens of the consul's country, and to promote and facilitate commercial and diplomatic relations between the two countries.
A consu ...
in Ho Chi Minh City while Vietnam opened
its consulate in San Francisco. Full diplomatic relations were also restored with New Zealand, which opened its embassy in Hanoi in 1995; Vietnam established an embassy in
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
in 2003. President of the United States,
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
, made a historic visit to Vietnam in November 2000. He was the first U.S. leader ever to officially visit Hanoi and the first to visit Vietnam since U.S. troops withdrew from the country in 1975.
Pakistan also reopened its embassy in Hanoi in October 2000, with Vietnam reopening its embassy in
Islamabad
Islamabad (; , ; ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's tenth-most populous city with a population of over 1.1 million and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital Territory. Bu ...
in December 2005 and trade office in
Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
in November 2005. In May 2016, US President
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
further normalised relations with Vietnam after he announced the lifting of an arms
embargo
Economic sanctions or embargoes are commercial and financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of coercion that attempts to get an actor to change its behavior throu ...
on sales of lethal arms to Vietnam. Despite their historical past, today Vietnam is considered to be a potential ally of the United States, especially in the geopolitical context of the
territorial disputes in the South China Sea
Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, the People's Republic of China (PRC), Taiwan (Republic of China/ROC), and Vietnam have conflicting island and maritime claims in the South China Sea. The disputes involve the islands, reefs, banks, ...
and in containment of
Chinese expansionism
Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of Chinese history, especially under the dynasties of Han, Tang, Yuan, and Qing. Chinese expansionism as a motivation or even coherent phenomenon has been contentiously discussed in re ...
.
Military
The
Vietnam People's Armed Forces
The Vietnam People's Armed Forces () are the armed uniformed services and national security forces of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, and should not be confused with the People’s Army of Vietnam. Being placed under the political leadership ...
consists of the
Vietnam People's Army
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
(VPA), the
Vietnam People's Public Security
The People's Public Security of Vietnam (), alternatively the People's Public Security Forces (PPS; - CAND), also recognized as the Vietnamese police, Vietnamese Police or by its Vietnamese short name (), is the national police and the main ...
and the Vietnam Self-Defence Militia. The VPA is the official name for the active military services of Vietnam, and is subdivided into the
Vietnam People's Ground Forces, the
Vietnam People's Navy
The Vietnam People's Navy (VPN; ), internally the Naval Service (), also known as the Vietnamese People's Navy or simply Vietnam/Vietnamese Navy (), is the naval branch of the Vietnam People's Army and is responsible for the protection of the ...
, the
Vietnam People's Air Force
The Vietnam People's Air Force (VPAF; ), officially the Air Defence - Air Force Service (ADAF Service; ) or the Vietnam Air Force (), is the Aerial warfare, aerial, Anti-aircraft warfare, air and Space warfare, space defence service branch of ...
, the
Vietnam Border Guard and the
Vietnam Coast Guard. The VPA has an active manpower of around 450,000, but its total strength, including paramilitary forces, may be as high as 5,000,000. In 2015, Vietnam's
military expenditure totalled approximately US$4.4 billion, equivalent to around 8% of its total government spending. Joint military exercises and war games have been held with
Brunei
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with ...
, India, Japan, Laos, Russia,
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
and the US. In 2017, Vietnam signed the UN treaty on the
Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Human rights and sociopolitical issues
Vietnam's pre-1986 communist system has been described either as
totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a political system and a form of government that prohibits opposition from political parties, disregards and outlaws the political claims of individual and group opposition to the state, and completely controls the public sph ...
or not totalitarian but autocratic. Since 1986, Vietnam retreated from totalitarianism to authoritarianism, with the
freedom of assembly
Freedom of assembly, sometimes used interchangeably with the freedom of association, is the individual right or ability of individuals to peaceably assemble and collectively express, promote, pursue, and defend their ideas. The right to free ...
,
association,
expression,
press and
religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
as well as civil society activism still tightly restricted.
Under the current constitution, the CPV is the only party allowed to rule, the operation of all other political parties being outlawed. Other human rights issues concern
freedom of association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membe ...
,
freedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The rights, right to freedom of expression has been r ...
,
freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty, also known as freedom of religion or belief (FoRB), is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice ...
, and
freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic Media (communication), media, especially publication, published materials, shoul ...
. In 2009, Vietnamese lawyer
Lê Công Định was arrested and charged with the capital crime of
subversion
Subversion () refers to a process by which the values and principles of a system in place are contradicted or reversed in an attempt to sabotage the established social order and its structures of Power (philosophy), power, authority, tradition, h ...
; several of his associates were also arrested.
Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
described him and his arrested associates as
prisoners of conscience
A prisoner of conscience (POC) is anyone imprisoned because of their race, sexual orientation, religion, or political views. The term also refers to those who have been imprisoned or persecuted for the nonviolent expression of their conscienti ...
. Vietnam has also suffered from human trafficking and related issues.
Economy

Throughout the history of Vietnam, its economy has been based largely on
agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
—primarily
wet rice cultivation.
Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
, an important material in the production of
aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, is mined in central Vietnam. Since reunification, the country's economy is shaped primarily by the CPV through
Five Year Plans decided upon at the plenary sessions of the Central Committee and national congresses. The
collectivisation
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-o ...
of farms, factories, and capital goods was carried out as part of the establishment of central planning, with millions of people working for state enterprises. Under strict state control, Vietnam's economy continued to be plagued by inefficiency,
corruption in state-owned enterprises, poor quality and underproduction. With the decline in economic aid from its main trading partner, the Soviet Union, following the erosion of the
Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
in the late 1980s, and the subsequent
collapse of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
, as well as the negative impacts of the post-war
trade embargo imposed by the United States, Vietnam began to liberalise its trade by
devaluing its exchange rate to increase exports and embarked on a policy of economic development.

In 1986, the
Sixth National Congress of the CPV introduced
socialist-oriented market economic reforms as part of the reform programme.
Private ownership
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
began to be encouraged in industry, commerce and agriculture and state enterprises were
restructured
Restructuring or Reframing is the corporate management term for the act of reorganizing the legal, ownership, operational, or other structures of a company for the purpose of making it more profitable, or better organized for its present needs. ...
to operate under market constraints. This led to the five-year economic plans being replaced by the socialist-oriented market mechanism. As a result of these reforms, Vietnam achieved approximately 8% annual
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
(GDP) growth between 1990 and 1997. The United States ended its economic embargo against Vietnam in early 1994. Although the
1997 Asian financial crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide eco ...
caused an economic slowdown to 4–5% growth per year, its economy began to recover in 1999, and grew at around 7% per year from 2000 to 2005, one of the fastest in the world.
[; this article refers to the so-called " Vent for surplus" theory of international trade.] On 11 January 2007, Vietnam became the 150th member of the
WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
(World Trade Organization). According to the
General Statistics Office of Vietnam
The General Statistics Office of Vietnam (GSO; ) is an agency under the Ministry of Finance, performing the function of the state management for statistics; conducting statistical activities and providing social and economic information to org ...
(GSO), growth remained strong despite the
late-2000s global recession, holding at 6.8% in 2010. Vietnam's year-on-year inflation rate reached 11.8% in December 2010 and the currency, the
Vietnamese đồng
The dong (; ; ; sign: ₫ or informally đ and sometimes Đ in Vietnamese; code: VND) is the currency of Vietnam, in use since 3 May 1978. It is issued by the State Bank of Vietnam. The dong was also the currency of the predecessor states of ...
, was devalued three times.
Deep
poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
, defined as the percentage of the population living on less than $1 per day, has declined significantly in Vietnam and the relative poverty rate is now less than that of China, India and the
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. This decline can be attributed to
equitable economic policies aimed at improving
living standards
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available to an individual, community or society. A contributing factor to an individual's quality of life, standard of living is generally concerned with objective metrics outside ...
and preventing the rise of
inequality
Inequality may refer to:
* Inequality (mathematics), a relation between two quantities when they are different.
* Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups
** Income inequality, an unequal distribution of i ...
. These policies have included egalitarian land distribution during the initial stages of the ''Đổi Mới'' programme, investment in poorer remote areas, and subsidising of education and healthcare. Since the early 2000s, Vietnam has applied sequenced trade liberalisation, a two-track approach opening some sectors of the economy to international markets. Manufacturing,
information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
and high-tech industries now form a large and fast-growing part of the national economy. Although Vietnam is a relative newcomer to the
oil industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest volume products ...
, it is the third-largest oil producer in Southeast Asia with a total 2011 output of . In 2010, Vietnam was ranked as the eighth-largest crude
petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
producer in the Asia and Pacific region. The US bought the biggest share of Vietnam's exports, while
goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
from China were the most popular Vietnamese import.
Based on findings by the
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
(IMF) in 2022, the
unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
rate in Vietnam was 2.3%, the
nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance ...
US$406.452 billion, and a nominal
GDP per capita
This is a list of countries by nominal GDP per capita. GDP per capita is the total value of a country's finished goods and services (gross domestic product) divided by its total population (per capita).
Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is ...
$4,086.
Besides the
primary sector economy,
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
has contributed significantly to Vietnam's economic growth with 7.94 million foreign visitors recorded in 2015.
Agriculture

As a result of several
market liberalization measures, Vietnam has become a major exporter of agricultural products. It is now the world's largest producer of
cashew
Cashew is the common name of a tropical evergreen tree ''Anacardium occidentale'', in the family Anacardiaceae. It is native to South America and is the source of the cashew nut and the cashew apple, an accessory fruit. The tree can grow as t ...
nuts, with a one-third global share; the largest producer of
black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter ...
, accounting for one-third of the world's market; and the second-largest
rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
exporter in the world after
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
since the 1990s. Subsequently, Vietnam is also the world's second largest exporter of
coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
. The country has the highest proportion of land use for
permanent crop
Permanent crop means that the land continues to produce year after year, without the farmer needing to replant fields after each harvest.
Traditionally, "arable land" included any land suitable for the growing of crops, even if it was actually be ...
s together with other states in the
Greater Mekong Subregion
The Greater Mekong Subregion, (GMS) or just Greater Mekong, is a trans-national region of the Mekong River basin in Southeast Asia. The region is home to more than 300 million people. It came into being with the launch of a development program i ...
. Other primary exports include
tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of south-western China and nor ...
,
rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
and fishery products. Agriculture's share of Vietnam's GDP has fallen in recent decades, declining from 42% in 1989 to 20% in 2006 as production in other sectors of the economy has risen.
Seafood
The overall fisheries production of Vietnam from capture fisheries and
aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
was 5.6 million MT in 2011 and 6.7 million MT in 2016. The output of Vietnam's fisheries sector has seen strong growth, which could be attributed to the continued expansion of the aquaculture sub-sector.
Science and technology

In 2010, Vietnam's total state spending on science and technology amounted to roughly 0.45% of its GDP. Vietnamese scientists have made many significant contributions in various fields of study, most notably in
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
.
Hoàng Tụy
Hoàng Tụy (7 December 1927 – 14 July 2019) was a prominent Vietnamese applied mathematician. He was considered one of two founders of the mathematical institutions of Vietnam; the other was Lê Văn Thiêm.
Career
Hoàng Tụy's early car ...
pioneered the
applied mathematics
Applied mathematics is the application of mathematics, mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and Industrial sector, industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a ...
field of
global optimisation
Global optimization is a branch of operations research, applied mathematics, and numerical analysis that attempts to find the global maximum and minimum, minimum or maximum of a function or a set of functions on a given set. It is usually describ ...
in the 20th century, while
Ngô Bảo Châu
Ngô Bảo Châu (, born June 28, 1972) is a Vietnamese-French mathematician at the University of Chicago, best known for proving the fundamental lemma for automorphic forms (proposed by Robert Langlands and Diana Shelstad). He is the first Vie ...
won the 2010
Fields Medal
The Fields Medal is a prize awarded to two, three, or four mathematicians under 40 years of age at the International Congress of Mathematicians, International Congress of the International Mathematical Union (IMU), a meeting that takes place e ...
for his proof of
fundamental lemma in the theory of automorphic forms. Since the establishment of the
Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology
The Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST; ) is the largest and most prominent research institute in Vietnam. It was founded on 20 May 1975 as the Vietnam Academy of Science, then subsequently assumed its current name in 2008. Its infra ...
(VAST) by the government in 1975, the country is working to develop its first national
space flight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such a ...
programme especially after the completion of the infrastructure at the Vietnam Space Centre (VSC) in 2018. Vietnam has also made significant advances in the development of
robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s, such as the
TOPIO
TOPIO ("TOSY PIng Pong Playing RobOt") is a bipedal humanoid robot designed to play table tennis against a human being. It has been developed since 2005 by TOSY, a robotics firm in Vietnam. It was publicly demonstrated at the Tokyo International R ...
humanoid model. One of Vietnam's main
messaging apps
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
,
Zalo
Zalo is a Vietnamese instant messaging multi-platform service developed by VNG Corporation. Zalo is also used in other countries outside of Vietnam, including the United States, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Germany, Myanmar and Singapore.
As ...
, was developed by Vương Quang Khải, a Vietnamese
hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals and solves problems by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hackersomeone with knowledge of bug (computing), bugs or exp ...
who later worked with the country's largest
information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
service company, the
FPT Group
FPT, officially the FPT Corporation (; "FPT" stands for ''Financing and Promoting Technology''), is the largest information technology service company in Vietnam with operations spanning three fundamental sectors: Technology, Telecommunications ...
.

According to the
UNESCO Institute for Statistics
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication.
The UIS was established in 1999. ...
, Vietnam devoted 0.19% of its GDP to science research and development in 2011. Vietnam was ranked 44th in the
Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for and success in innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a Britis ...
in 2024, it has increased its ranking considerably since 2012, where it was ranked 76th. Between 2005 and 2014, the number of Vietnamese scientific publications recorded in Thomson Reuters'
Web of Science
The Web of Science (WoS; previously known as Web of Knowledge) is a paid-access platform that provides (typically via the internet) access to multiple databases that provide reference and citation data from academic journals, conference proceedi ...
increased at a rate well above the average for Southeast Asia, albeit from a modest starting point. Publications focus mainly on
life science
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, respon ...
s (22%),
physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
(13%) and
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
(13%), which is consistent with recent advances in the production of diagnostic equipment and shipbuilding.
Tourism
Tourism is an important element of economic activity in the nation, contributing 7.5% of the total GDP. Vietnam hosted roughly 13 million tourists in 2017, an increase of 29.1% over the previous year, making it one of the fastest growing tourist destinations in the world. The vast majority of the tourists in the country, some 9.7 million, came from Asia; namely China (4 million),
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
(2.6 million), and Japan (798,119). Vietnam also attracts large numbers of visitors from Europe, with almost 1.9 million visitors in 2017; most European visitors came from Russia (574,164), followed by the United Kingdom (283,537), France (255,396), and Germany (199,872). Other significant international arrivals by nationality include the United States (614,117) and Australia (370,438).
The most visited destinations in Vietnam are the largest city, Ho Chi Minh City, with over 5.8 million international arrivals, followed by Hanoi with 4.6 million and
Hạ Long
Hạ Long ( , ) is a first-class provincial city and the capital city of Quảng Ninh province, Vietnam. It was found in 1993, when the old capital, Hòn Gai, was merged with Bãi Cháy, the main tourist area. The city mainly lies on Hạ L ...
, including Hạ Long Bay with 4.4 million arrivals. All three are ranked in the top 100 most visited cities in the world. Vietnam is home to eight
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
. In 2018, ''
Travel + Leisure
Travel + Leisure Co. (formerly Wyndham Destinations, Inc., and Wyndham Worldwide Corporation) is an American timeshare company headquartered in Orlando, Florida. It develops, sells, and manages timeshare properties under several vacation owners ...
'' ranked
Hội An
Hội An () is a city of approximately 120,000 people in Vietnam's Quảng Nam Province, registered as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1999. Along with the Cù Lao Chàm archipelago, it is part of the Cù Lao Chàm-Hội An Biosphere Reserve ...
as one of the world's top 15 best destinations to visit.
Transport
Much of Vietnam's modern transportation network can trace its roots to the French colonial era when it was used to facilitate the transportation of
raw material
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials/Intermediate goods that are feedstock for future finished ...
s to its main ports. It was extensively expanded and modernised following the partition of Vietnam. Vietnam's road system includes national roads administered at the central level, provincial roads managed at the provincial level, district roads managed at the district level, urban roads managed by cities and towns and commune roads managed at the commune level. In 2010, Vietnam's road system had a total length of about of which are
asphalt
Asphalt most often refers to:
* Bitumen, also known as "liquid asphalt cement" or simply "asphalt", a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete
* Asphalt concrete, a mixture of bitumen with coarse and fine aggregates, u ...
roads comprising national, provincial and district roads. The length of the national road system is about with of its length paved. The provincial road system has around of paved roads while district roads are paved.
Bicycles, motorcycles and
motor scooter
A scooter (motor scooter) is a motorcycle with an underbone or step-through frame, a seat, a transmission that shifts without the operator having to operate a clutch lever, a platform for their feet, and with a method of operation that emph ...
s remain the most popular forms of road transport in the country, a legacy of the French, though the number of privately owned cars has been increasing in recent years. Public buses operated by private companies are the main mode of long-distance travel for much of the population.
Traffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
s remain the major safety issue of Vietnamese transportation with an average of 30 people losing their lives daily.
Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s, resulting in m ...
is a growing problem in both Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City especially with the growth of individual car ownership. Vietnam's primary cross-country rail service is the
Reunification Express from Ho Chi Minh City to Hanoi, a distance of nearly . From Hanoi, railway lines branch out to the northeast, north, and west; the eastbound line runs from Hanoi to Hạ Long Bay, the northbound line from Hanoi to
Thái Nguyên, and the northeast line from Hanoi to Lào Cai. In 2009, Vietnam and Japan signed a deal to build a
high-speed railway
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated railway track, tracks. While there is ...
—
shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. It was initially built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond lon ...
(bullet train)—using Japanese technology. Vietnamese engineers were sent to Japan to receive training in the operation and maintenance of high-speed trains. The planned railway will be a -long express route serving a total of 23 stations, including Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, with 70% of its route running on bridges and through tunnels. The trains will travel at a maximum speed of per hour. Plans for the high-speed rail line, however, have been postponed after the Vietnamese government decided to prioritise the development of both the
Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
and
Ho Chi Minh City
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
metros and expand road networks instead.
Vietnam operates 20 major civil airports, including three international gateways:
Noi Bai in Hanoi,
Da Nang International Airport in Đà Nẵng and
Tan Son Nhat in Ho Chi Minh City. Tan Son Nhat is the country's largest airport handling the majority of international passenger traffic. According to a government-approved plan, Vietnam will have another seven international airports by 2025, including
Vinh International Airport,
Phu Bai International Airport
Phu Bai International Airport is located just south of the central city of Huế, the former capital of Vietnam.
History
On October 30, 2005, Phú Bài Airport officially welcomed its first international flight since it was allowed to recei ...
,
Cam Ranh International Airport,
Phu Quoc International Airport
Phu Quoc International Airport is an international airport that serves Phú Quốc Island, in southern Vietnam. It covers nearly 900 hectares of land area in the commune of Dương Tơ, about south of the administrative centre of Phú Quốc C ...
,
Cat Bi International Airport,
Can Tho International Airport, and
Long Thanh International Airport
Long Thanh International Airport is an international airport under construction in Long Thành district, Đồng Nai province, Vietnam, approximately east of Ho Chi Minh City. It will be the second airport to serve the Ho Chi Minh City met ...
. The planned Long Thanh International Airport will have an annual service capacity of 100 million passengers once it becomes fully operational in 2025.
Vietnam Airlines
Vietnam Airlines () is the flag carrier of Vietnam. The airline was founded in 1956 and later established as a Government-owned corporation, state-owned enterprise in April 1989. Vietnam Airlines is headquartered in Long Biên district, Hanoi ...
, the state-owned national airline, maintains a fleet of 86 passenger aircraft and aims to operate 170 by 2020. Several private airlines also operate in Vietnam, including
Air Mekong,
Bamboo Airways
Bamboo Airways JSC () is a Vietnamese airline founded in 2017. Commencing operations in January 2019, this carrier declared that it would be following the "hybrid airline" model. Bamboo Airways operates a fleet of the narrowbody Airbus A320, A320 ...
,
Jetstar Pacific Airlines,
VASCO and
VietJet Air
Vietjet Aviation Joint Stock Company (), operating as VietJet Air or Vietjet, is a Vietnamese low-cost airline based in Hanoi. It was the first privately owned airline to be established in Vietnam, being granted its initial approval to operate ...
. As a coastal country, Vietnam has many major sea ports, including
Cam Ranh
Cam Ranh () is a port-city in Southern Khánh Hòa Province, in the South Central Coast region of Vietnam.
History
Cam Ranh, known in the ancient Ede language as Kăm Mran, is a land closely associated with the development of the Champa cult ...
, Đà Nẵng,
Hải Phòng
Haiphong or Hai Phong (, ) is the third-largest city in Vietnam and is the principal port city of the Red River Delta. The municipality has an area of , consisting of 8 List of urban districts of Vietnam, urban districts, 6 Huyện, rural distri ...
, Ho Chi Minh City,
Hạ Long
Hạ Long ( , ) is a first-class provincial city and the capital city of Quảng Ninh province, Vietnam. It was found in 1993, when the old capital, Hòn Gai, was merged with Bãi Cháy, the main tourist area. The city mainly lies on Hạ L ...
,
Qui Nhơn
Quy Nhon ( ) is a coastal city in Bình Định province in central Vietnam. It is composed of 16 wards and five communes with a total of . Quy Nhon was the capital of the former Bình Định province. As of 2022 its population was 481.110. H ...
,
Vũng Tàu
Vũng Tàu (''Hanoi accent:'' , ''Saigon accent:'' ) is an important port city in southern Vietnam. It serves as the maritime port of Ho Chi Minh City, the largest city in Vietnam. Vũng Tàu covers of area and consists of 16 urban wards and on ...
,
Cửa Lò and
Nha Trang
Nha Trang ( or ; ) is a coastal city and capital of Khánh Hòa Province, on the South Central Coast of Vietnam. It is bounded on the north by Ninh Hoà town, on the south by Cam Ranh city and on the west by Diên Khánh District. The city had ...
. Further inland, the country's extensive network of rivers plays a key role in rural transportation with over of navigable
waterway
A waterway is any Navigability, navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other ways. A first distinction is ...
s carrying ferries, barges and
water taxi
A water taxi or a water bus is a boat used to provide public transport, public or private transport, usually, but not always, in an Urban area, urban environment. Service may be scheduled with multiple stops, operating in a simil ...
s.
Energy
Vietnam's energy sector is dominated largely by the state-controlled
Vietnam Electricity Group (EVN). As of 2017, EVN made up about 61.4% of the country's power generation system with a total power capacity of 25,884
MW. Other energy sources are
PetroVietnam
Petrovietnam (PVN), formally the Vietnam National Industry - Energy Group () and formerly the Vietnam Oil and Gas Group ( or ), is the state-owned national oil, gas and energy industry corporation of Vietnam. Petrovietnam has developed ra ...
(4,435 MW),
Vinacomin
Vinacomin (Vietnam National Coal and Mineral Industries Group, ) is a Vietnamese mining company. The industrial conglomerate focuses on coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal ...
(1,785 MW) and 10,031 MW from
build–operate–transfer
Build–operate–transfer (BOT) or build–own–operate–transfer (BOOT) is a form of project delivery method, usually for large-scale infrastructure projects, wherein a private entity receives a concession (contract), concession from the public ...
(BOT) investors.
Most of Vietnam's power is generated by either
hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
or
fossil fuel power such as
coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
,
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
and
gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as ...
, while
diesel,
small hydropower and renewable energy supplies the remainder. The Vietnamese government had planned to develop a
nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
as the path to establish
another source for electricity from
nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
. The plan was abandoned in late 2016 when a majority of the National Assembly voted to oppose the project due to widespread public concern over
radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is uni ...
.
The household gas sector in Vietnam is dominated by PetroVietnam, which controls nearly 70% of the country's domestic market for
liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas, also referred to as liquid petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas), is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, Butane, ''n''-butane and isobutane. It can also contain some ...
(LPG). Since 2011, the company also operates five renewable energy power plants including the Nhơn Trạch 2 Thermal Power Plant (750 MW), Phú Quý Wind Power Plant (6 MW), Hủa Na Hydro-power Plant (180 MW), Dakdrinh Hydro-power Plant (125 MW) and Vũng Áng 1 Thermal Power Plant (1,200 MW).
According to statistics from
BP, Vietnam is listed among the 52 countries that have
proven crude oil reserves. In 2015 the reserve was approximately 4.4 billion barrels ranking Vietnam first place in Southeast Asia, while the
proven gas reserves were about 0.6 trillion cubic metres (tcm) and ranking it third in Southeast Asia after
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
and
Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
.
Telecommunication
Telecommunications services in Vietnam are wholly provided by the Vietnam Post and Telecommunications General Corporation (now the
VNPT
Vietnam Posts and Telecommunications Group (), Trade name, operating as its initialism VNPT, is a telecommunications company, owned by the Ministry of Finance (Vietnam), Ministry of Finance, and was once the national post office of Vietnam. Ac ...
Group) which is a
state-owned
State ownership, also called public ownership or government ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, property, or enterprise by the national government of a country or state, or a public body representing a community, as opposed to ...
company. The VNPT retained its monopoly until 1986. The telecom sector was reformed in 1995 when the Vietnamese government began to implement a competitive policy with the creation of two domestic telecommunication companies, the Military Electronic and Telecommunication Company (
Viettel
The Military Industry and Telecoms Group (), Trade name, trading as Viettel or Viettel Group (), is a Vietnamese State-owned enterprise, state-owned multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications, technology and manufacturing C ...
, which is wholly owned by the Vietnamese Ministry of Defence) and the Saigon Post and Telecommunication Company (SPT or SaigonPostel), with 18% of it owned by VNPT. VNPT's monopoly was finally ended by the government in 2003 with the issuance of a decree. By 2012, the top three telecom operators in Vietnam were Viettel,
Vinaphone and
MobiFone. The remaining companies included:
EVNTelecom, Vietnammobile and
S-Fone. With the shift towards a more
market-orientated economy, Vietnam's telecommunications market is continuously being reformed to attract
foreign investment, which includes the supply of services and the establishment of nationwide telecom infrastructure.
Water supply and sanitation

Vietnam has 2,360 rivers with an average annual discharge of 310 billion
m3. The rainy season accounts for 70% of the year's discharge. Most of the country's urban
water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
systems have been developed without proper management within the last 10 years. Based on a 2008 survey by the Vietnam Water Supply and Sewerage Association (VWSA), existing water production capacity exceeded demand, but service coverage is still sparse. Most of the clean water supply infrastructure is not widely developed. It is only available to a small proportion of the population with about one third of 727 district towns having some form of piped water supply. There is also concern over the safety of existing water resources for urban and rural water supply systems. Most industrial factories release their untreated
wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
directly into the water sources. Where the government does not take measures to address the issue, most domestic wastewater is discharged, untreated, back into the environment and pollutes the
surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
.
In recent years, there have been some efforts and collaboration between local and foreign universities to develop access to safe water in the country by introducing
water filtration systems. There is a growing concern among local populations over the serious public health issues associated with water contamination caused by pollution as well as the
high levels of arsenic in
groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
sources. The government of Netherlands has been providing aid focusing its investments mainly on water-related sectors including
water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, ...
projects. Regarding
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
, 78% of Vietnam's population has access to
"improved" sanitation—94% of the urban population and 70% of the rural population. However, there are still about 21 million people in the country lacking access to "improved" sanitation according to a survey conducted in 2015. In 2018, the construction ministry said the country's water supply, and drainage industry had been applying hi-tech methods and
information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
(IT) to sanitation issues but faced problems like limited funding, climate change, and pollution. The health ministry has also announced that water inspection units will be established nationwide beginning in June 2019. Inspections are to be conducted without notice, since there have been many cases involving health issues caused by poor or polluted water supplies as well unhygienic conditions reported every year.
Demographics
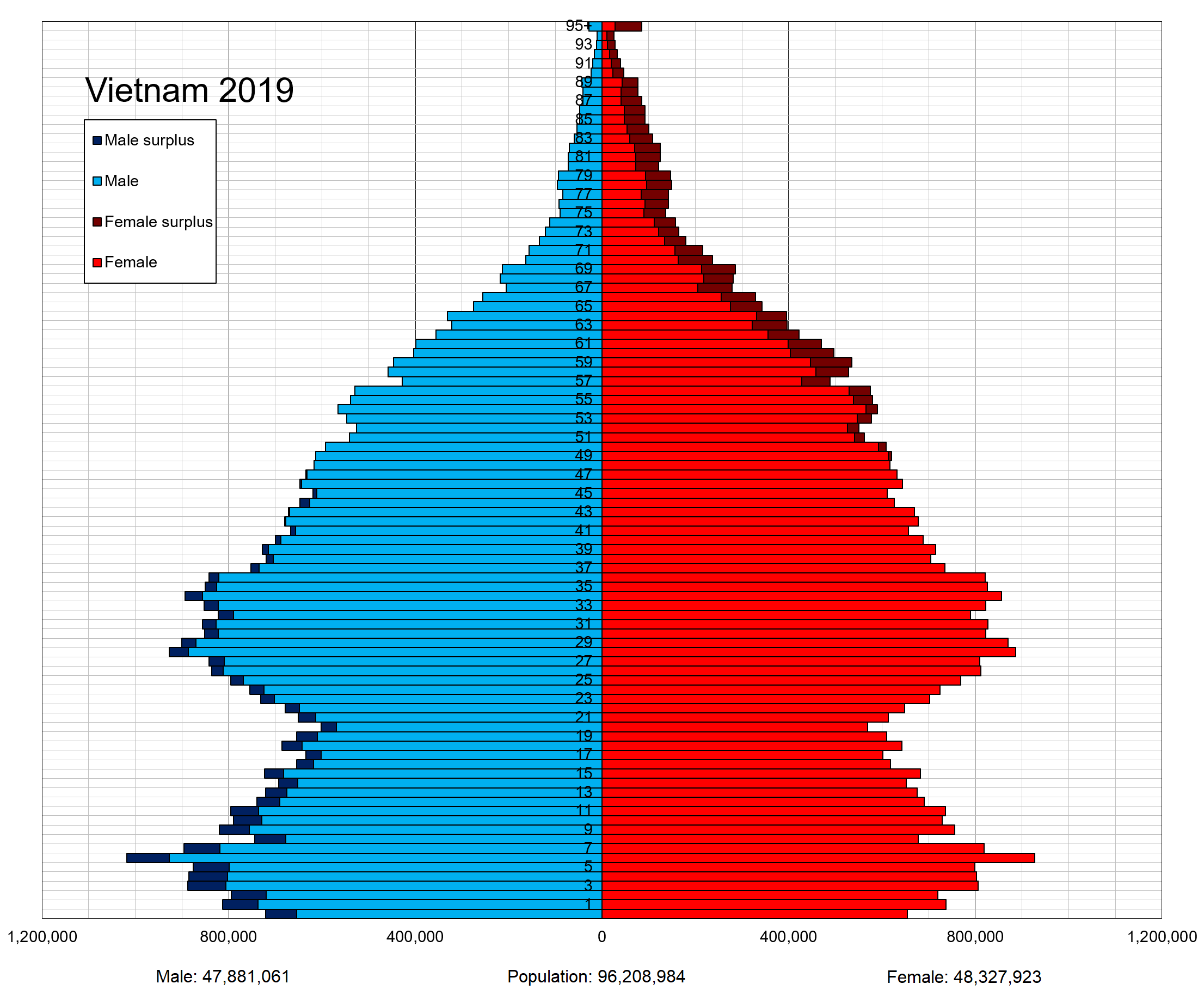
, the population of Vietnam stands at approximately million people. The population had grown significantly from the 1979 census, which showed the total population of reunified Vietnam to be 52.7 million. According to the 2019 census, the country's population was 96,208,984. Based on the 2019 census, 65.6% of the Vietnamese population live in rural areas while only 34.4% live in urban areas. The average growth rate of the urban population has recently increased which is attributed mainly to migration and rapid urbanisation. The dominant Viet people, Viet or Kinh ethnic group constitute 82,085,826 people or 85.32% of the population. Most of their population is concentrated in the country's alluvial fans, alluvial deltas and coastal plains. As a majority ethnic group, the Kinh possess significant political and economic influence over the country. Despite this, Vietnam is also home to various ethnic groups, of which Ethnic groups in Vietnam, 54 are officially recognised, including the Hmong people, Hmong, Yao people, Dao, Tay people, Tày, Thai people in Vietnam, Thái and Nùng people, Nùng. Many ethnic minorities such as the Muong people, Muong, who are closely related to the Kinh, dwell in the highlands which cover two-thirds of Vietnam's territory.
Since the partition of Vietnam, the population of the
Central Highlands was almost exclusively Degar (including more than 40 tribal groups); however, the South Vietnamese government at the time enacted a programme of resettling Kinh in indigenous areas. The Hoa people, Hoa (ethnic Overseas Chinese, Chinese) and Khmer Krom people are mainly lowlanders. Throughout Vietnam's history, many Chinese people, largely from South China, migrated to the country as administrators, merchants and even refugees. Since the reunification in 1976, an increase of communist policies nationwide resulted in the nationalisation and confiscation of property especially from the Hoa in the south and the wealthy in cities. This led many of them to leave Vietnam.
Urbanisation
The number of people who live in urbanised areas in 2019 is 33,122,548 people (with the urbanisation rate at 34.4%). Since 1986, Vietnam's urbanisation rates have surged rapidly after the Vietnamese government implemented the Đổi Mới economic programme, changing the system into a socialist one and liberalising property rights. As a result, Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City (the two major cities in the Red River Delta and Southeast regions respectively) increased their share of the total urban population from 8.5% and 24.9% to 15.9% and 31% respectively. The Vietnamese government, through its Ministry of Construction (Vietnam), construction ministry, forecasts the country will have a 45% urbanisation rate by 2020 although it was confirmed to only be 34.4% according to the 2019 census. Urbanisation is said to have a positive correlation with economic growth. Any country with higher urbanisation rates has a higher GDP growth rate. Furthermore, the urbanisation movement in Vietnam is mainly between the rural areas and the country's Southeast region. Ho Chi Minh City has received a large number of migrants due mainly to better weather and economic opportunities.
A study also shows that rural-to-urban area migrants have a higher standard of living than both non-migrants in rural areas and non-migrants in urban areas. This results in changes to economic structures. In 1985, agriculture made up 37.2% of Vietnam's GDP; in 2008, that number had declined to 18.5%. In 1985, industry made up only 26.2% of Vietnam's GDP; by 2008, that number had increased to 43.2%. Urbanisation also helps to improve basic services which increase people's standards of living. Access to electricity grew from 14% of total households with electricity in 1993 to above 96% in 2009. In terms of access to fresh water, data from 65 utility companies shows that only 12% of households in the area covered by them had access to the water network in 2002; by 2007, more than 70% of the population was connected. Though urbanisation has many benefits, it has some drawbacks since it creates more traffic, and air and water pollution.
Many Vietnamese use mopeds for transportation, since they are relatively cheap and easy to operate. Their large numbers have been known to cause traffic congestion and air pollution in Vietnam. In the capital city alone, the number of mopeds increased from 0.5 million in 2001 to 4.7 million in 2013. With rapid development, factories have sprung up which indirectly pollute the air and water, for example in the 2016 Vietnam marine life disaster. The government is intervening and attempting solutions to decrease air pollution by decreasing the number of motorcycles while increasing public transportation. It has introduced more regulations for waste handling. The amount of solid waste generated in urban areas of Vietnam has increased by more than 200% from 2003 to 2008. Industrial solid waste accounted for 181% of that increase. One of the government's efforts includes attempting to promote campaigns that encourage locals to sort municipal solid waste, household waste, since waste sorting is still not practised by most of Vietnamese society.
Languages
The national language of the country is
Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
, a tonal Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic language (Mon–Khmer), which is spoken by the majority of the population. Vietnam's minority groups speak a variety of languages, including: Tày language, Tày, Muong language, Mường, Cham language, Cham, Khmer language, Khmer, Chinese, Nung language (Tai), Nùng, and Hmong language, Hmong. The Montagnard (Vietnam), Montagnard peoples of the
Central Highlands also speak a number of distinct languages, some belonging to the Austroasiatic and others to the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian language families. In recent years, a number of Vietnamese sign languages, sign languages have developed in the major cities.

The French language, a legacy of colonial rule, is spoken by many educated Vietnamese as a second language, especially among those educated in the former
South Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered Diplomatic recognition, international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the ...
, where it was a principal language in administration, education and commerce. Vietnam remains a full member of the
International Organisation of the Francophonie () and education has revived some interest in the language. Russian language, Russian, and to a lesser extent German, Czech language, Czech and Polish language, Polish are known among some northern Vietnamese whose families had ties with the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. With improved relations with Western countries and recent reforms in Vietnamese administration, English has been increasingly used as a second language and the study of English is now obligatory in most schools either alongside or in place of French. The popularity of Japanese, Korean language, Korean, and Mandarin Chinese have also grown as the country's ties with other East Asian nations have strengthened. Third-graders can choose one of seven languages (English, Russian, French, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, German) as their first foreign language. In Vietnam's Education in Vietnam, high school graduation examinations, students can take their foreign language exam in one of the above-mentioned languages.
Religion
Under Article 70 of the 1992 Constitution of Vietnam, all citizens enjoy freedom of religion, freedom of belief and religion. All religions are equal before the law and each place of worship is protected under Vietnamese state law. Religious beliefs cannot be misused to undermine state law and policies. According to a 2007 survey 81% of Vietnamese people Atheism, did not believe in a god. Based on government findings in 2009, the number of religious people increased by 932,000. The official statistics, presented by the Vietnamese government to the United Nations special rapporteur in 2014, indicate the overall number of followers of recognised religions is about 24 million of a total population of almost 90 million. According to the General Statistics Office of Vietnam in 2019, Buddhism in Vietnam, Buddhists account for 4.79% of the total population, Catholic Church in Vietnam, Catholics 6.1%, Protestantism in Vietnam, Protestants 1.0%, Hòa Hảo, Hoahao Buddhists 1.02%, and Caodaism followers 0.58%. Other religions includes Islam, Baháʼí Faith, Bahaʼís and Hinduism, representing less than 0.2% of the population.
The majority of Vietnamese do not follow any organised religion, though many of them observe some form of Vietnamese folk religion.
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
as a system of social and ethical philosophy still has certain influences in modern Vietnam. Mahāyāna Buddhism, Mahāyāna is the dominant branch of Buddhism, while Theravada is practised mostly by the Khmer minority. About 8 to 9% of the population is Christian—made up of Roman Catholics and Protestants. Catholicism was introduced to Vietnam in the 16th century and was firmly established by Society of Jesus, Jesuits missionaries (mainly Portuguese and Italian) in the 17th centuries from nearby Portuguese Macau. French missionaries (from the
Paris Foreign Missions Society
The Society of Foreign Missions of Paris (, , MEP) is a Catholic Missionary order, missionary organization. It is not a religious institute, but an organization of secular clergy, secular priests and Laity, lay persons dedicated to missionary wo ...
) together with Spanish missionaries (from the Dominican Order of the neighbouring Spanish East Indies) actively sought converts in the 18th, 19th, and first half of the 20th century. A significant number of Vietnamese people, especially in the South, are also adherents of two indigenous religions of syncretic Caodaism and quasi-Buddhist Hòa Hảo, Hoahaoism. Protestantism was only recently spread by American and Canadian missionaries in the 20th century; the largest Protestant denomination is the Evangelical Church of Vietnam – South, Evangelical Church of Vietnam. Around 770,000 of the country's Protestants are members of ethnic minorities, particularly the highland Montagnard (Vietnam), Montagnards and Hmong people. Although it is one of the country's minority religions, Protestantism is the fastest-growing religion in Vietnam, expanding at a rate of 600% in recent decades. Several other minority faiths exist in Vietnam, these include: Bani, Sunni Islam, Sunni and Non-denominational Muslim, non-denominational sections of Islam which is practised primarily among the ethnic Chams, Cham minority. There are also a few Kinh adherents of Islam, other minority adherents of Baha'i, as well as Hinduism in Southeast Asia#Vietnam, Hindus among the Cham's.
Education
Vietnam has an extensive state-controlled network of schools, colleges, and universities and a growing number of privately run and partially privatised institutions. General education in Vietnam is divided into five categories: kindergarten, elementary schools, middle schools, high schools, and universities. A large number of public schools have been constructed across the country to raise the national literacy rate, which stood at 90% in 2008. Most universities are located in major cities of Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City with the country's education system continuously undergoing a series of reforms by the government. Basic education in the country is relatively free for the poor although some families may still have trouble paying tuition fees for their children without some form of public or private assistance. Regardless, Vietnam's school enrolment is among the highest in the world. The number of colleges and universities increased dramatically in the 2000s from 178 in 2000 to 299 in 2005. In higher education, the government provides subsidised loans for students through the national bank, although there are deep concerns about access to the loans as well the burden on students to repay them. Since 1995, enrolment in higher education has grown tenfold to over 2.2 million with 84,000 lecturers and 419 institutions of higher education. A number of foreign universities operate private campuses in Vietnam, including Harvard University (United States) and the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology Vietnam, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (Australia). The government's strong commitment to education has fostered significant growth but still need to be sustained to retain academics. In 2018, a decree on university autonomy allowing them to operate independently without ministerial control is in its final stages of approval. The government will continue investing in education especially for the poor to have access to basic education.
Health

By 2015, 97% of the population had access to improved water sources. In 2016, Vietnam's national life expectancy stood at 80.9 years for women and 71.5 for men, and the infant mortality rate was 17 per 1,000 live births. Since the partition, North Vietnam has established a public health system that has reached down to the Hamlet (place), hamlet level. After the national reunification in 1975, a nationwide health service was established. In the late 1980s, the quality of healthcare declined to some degree as a result of budgetary constraints, a shift of responsibility to the provinces and the introduction of charges. Inadequate funding has also contributed to a shortage of nurses, midwives and hospital beds; in 2000, Vietnam had only 24.7 hospital beds per 10,000 people before declining to 23.7 in 2005 as stated in the annual report of Ministry of Health (Vietnam), Vietnamese Health Ministry. The controversial use of herbicides as a chemical weapon by the United States Armed Forces, US military during the war left tangible, long-term Effects of Agent Orange on the Vietnamese people, impacts upon the Vietnamese people that persist in the country today. For instance, it led to three million Vietnamese people suffering health problems, one million birth defects caused directly by exposure to the chemical and 24% of Vietnam's land being defoliated.
Since the early 2000s, Vietnam has made significant progress in combating malaria. The malaria mortality rate fell to about five per cent of its 1990s equivalent by 2005 after the country introduced improved antimalarial drugs and treatment. Tuberculosis (TB) cases, however, are on the rise. TB has become the second most infectious disease in the country after respiratory disease, respiratory-related illness. With an intensified vaccination programme, better hygiene and foreign assistance, Vietnam hopes to reduce sharply the number of TB cases and new TB infections. In 2004, government subsidies covering about 15% of health care expenses. That year, the United States announced Vietnam would be one of 15 states to receive funding as part of its global AIDS relief plan. By the following year, Vietnam had diagnosed 101,291 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cases, of which 16,528 progressed to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS); 9,554 have died. The actual number of HIV-positive individuals is estimated to be much higher. On average between 40 and 50 new infections are reported daily in the country. In 2007, 0.4% of the population was estimated to be infected with HIV and the figure has remained stable since 2005. More global aid is being delivered through The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria to fight the spread of the disease in the country. In September 2018, the Hanoi People's Committee urged the citizens of the country to stop eating dog meat, dog and cat meat as it can cause diseases like rabies and leptospirosis. More than 1,000 stores in the capital city of Hanoi were found to be selling both meats. The decision prompted positive comments among Vietnamese on social media, though some noted that the consumption of dog meat will remain an ingrained habit among many people.
Culture
Vietnamese culture is considered part of the Sinosphere. Vietnam's culture has developed over the centuries from indigenous ancient
Đông Sơn culture
The Dong Son culture, Dongsonian culture, or the Lạc Việt culture (named for modern village Đông Sơn, a village in Thanh Hóa, Vietnam) was a Bronze Age culture in ancient Vietnam centred at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam ...
with wet rice cultivation as its economic base. Some elements of the nation's culture have Chinese origins, drawing on elements of
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
, Mahayana, Mahāyāna Buddhism, and Taoism in its traditional political system and philosophy. Vietnamese society is structured around (ancestral villages); all Vietnamese mark a Giỗ Tổ Hùng Vương, common ancestral anniversary on the tenth day of the third lunar calendar, lunar month. The influence of Chinese culture such as the Cantonese culture, Cantonese, Hakka culture, Hakka, Hokkien culture, Hokkien, and Hainanese cultures is more evident in the north where Buddhism is strongly entwined with popular culture. Despite this, there are Chinatowns in the south, such as in , where many Chinese have interracial marriage, intermarried with Kinh and are indistinguishable among them. In the central and southern parts of Vietnam, traces of Champa and Khmer culture are evidenced through the remains of ruins, artefacts as well within their population as the successor of the ancient Sa Huỳnh culture. In recent centuries, Western cultures have become popular among recent generations of Vietnamese.

The traditional focuses of Vietnamese culture are based on humanity () and harmony () in which family and community values are highly regarded. Vietnam reveres a number of key cultural symbols, such as the Vietnamese dragon which is derived from crocodile and snake imagery; Vietnam's national father, is depicted as a holy dragon. The is a holy bird representing Vietnam's national mother . Other prominent images that are also revered are the turtle, water buffalo, buffalo and horse. Many Vietnamese also believe in the supernatural and Spiritualism (beliefs), spiritualism where illness can be brought on by a curse or Witchcraft, sorcery or caused by non-observance of a religious ethic. Traditional medical practitioners, amulets and other forms of spiritual protection and religious practices may be employed to treat the ill person. In the modern era, the cultural life of Vietnam has been deeply influenced by government-controlled media and cultural programmes. For many decades, foreign cultural influences, especially those of Western origin, were shunned. But since the recent reformation, Vietnam has seen a greater exposure to neighbouring Southeast Asian, East Asian as well to Western culture and media.
The main Vietnamese formal dress, the , is worn for special occasions such as weddings and religious festivals. White is the required uniform for girls in many high schools across the country. Other examples of traditional Vietnamese clothing include the , a four-piece woman's dress; the , a form of the in five-piece form, mostly worn in the north of the country; the , a woman's undergarment; the , rural working "pyjamas" for men and women; the , a formal brocade tunic for government receptions; and the , a variant of the worn by grooms at weddings. Traditional headwear includes the standard conical , the "lampshade-like" , and the traditional turban, . In tourism, a number of popular cultural destinations include the former Imperial City of Huế, the World Heritage Sites of Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng National Park, and , coastal regions such as Nha Trang, the caves of Hạ Long Bay and the Marble Mountains (Vietnam), Marble Mountains.
Literature
Vietnamese literature has centuries-deep history and the country has a rich tradition of folk literature based on the typical six–to-eight-verse poetic form () called which usually focuses on village ancestors and heroes. Written literature has been found dating back to the 10th century Ngô dynasty, with notable ancient authors including , , and . Some literary genres play an important role in theatrical performance, such as in . Some poetic unions have also been formed in Vietnam, such as the . Vietnamese literature has been influenced by Western styles in recent times, with the first literary transformation movement of emerging in 1932. Vietnamese folk literature is an intermingling of many forms. It is not only an oral tradition, but a mixing of three media: hidden (only retained in the memory of folk authors), fixed (written), and shown (performed). Folk literature usually exists in many versions, passed down orally, and has unknown authors. Myths consist of stories about supernatural beings, heroes, and creator gods, and reflect the viewpoint of ancient people about human life. They consist of creation stories, stories about their origins ( and ), culture heroes (Sơn Tinh – Thủy Tinh, and ) which are referred to as a mountain and water spirit respectively and many other folklore tales.
Music
Traditional Vietnamese music varies between the country's northern and southern regions. Northern classical music is Vietnam's oldest musical form and is traditionally more formal. The origins of Vietnamese classical opera () can be traced to the Mongol invasions in the 13th century when the Vietnamese captured a Chinese opera troupe. Throughout its history, Vietnam has been the most heavily impacted by the Music of China, Chinese musical tradition along with those of Japan, Korea and Mongolia. is the most popular form of imperial court music, is a form of generally satirical musical theatre, while or ( singing) is a type of Vietnamese folk music. (alternate singing) is popular in the former Hà Bắc province (which is now divided into and provinces) and across Vietnam. Another form of music called or is used to invoke spirits during ceremonies. is a modern form of Vietnamese folk music which arose in the 1950s, while (also known as ) is a popular folk music. can be thought of as the southern style of . There is a range of traditional instruments, including the (a monochord zither), the (a two-stringed fiddle with coconut body), and the (a two-stringed fretted moon lute). In recent times, there have been some efforts at mixing Vietnamese traditional music—especially folk music—with modern music to revive and promote national music in the modern context and educate the younger generations about Vietnam's traditional musical instruments and singing styles. Bolero#Vietnam, Bolero music has gained popularity in the country since the 1930s, albeit with a different style—a combination of traditional Vietnamese music with Western elements. In the 21st century, the modern Vietnamese pop music industry known as V-pop incorporates elements of many popular genres worldwide, such as electronic music, electronic, dance music, dance and contemporary R&B, R&B.
Media

Vietnam's media sector is regulated by the government under the 2004 Law on Publication. It is generally perceived that the country's media sector is controlled by the government and follows the official communist party line, though some newspapers are relatively outspoken. The Voice of Vietnam (VOV) is the official state-run national radio broadcasting service, broadcasting internationally via shortwave using rented transmitters in other countries and providing broadcasts from its website, while Vietnam Television (VTV) is the national television broadcasting company. Since 1997, Vietnam has regulated public internet access extensively using both legal and technical means. The resulting lockdown is widely referred to as the "Internet censorship in Vietnam, Bamboo Firewall". The collaborative project OpenNet Initiative classifies Vietnam's level of online political censorship to be "pervasive", while Reporters Without Borders (RWB) considers Vietnam to be one of 15 global "internet enemies". Though the government of Vietnam maintains that such censorship is necessary to safeguard the country against obscene or sexually explicit content, many political and religious websites that are deemed to be undermining state authority are also blocked.
Cuisine
Traditionally, Vietnamese cuisine is based around five fundamental taste "elements" (): spicy (metal), sour (wood), salty (water), bitter (fire) and sweet (earth). Common ingredients include fish sauce, shrimp paste, soy sauce, rice, fresh herbs, fruits and vegetables. Vietnamese recipes use cymbopogon, lemongrass, ginger, mentha, mint, Vietnamese mint, eryngium foetidum, long coriander, Saigon cinnamon, bird's eye chilli, lime (fruit), lime and basil leaves. Traditional Vietnamese cooking is known for its fresh ingredients, minimal use of oil and reliance on herbs and vegetables; it is considered one of the healthiest cuisines worldwide. The use of meats such as pork, beef and chicken was relatively limited in the past. Instead freshwater fish, crustaceans (particularly crabs), and molluscs became widely used. Fish sauce, soy sauce, prawn sauce and limes are among the main flavouring ingredients. Vietnam has a strong street food culture, with 40 popular dishes commonly found throughout the country. Many notable Vietnamese dishes such as (salad roll), (rice noodle roll), (rice vermicelli soup) and noodles originated in the north and were introduced to central and southern Vietnam by northern migrants. Local foods in the north are often less spicy than southern dishes, as the colder northern climate limits the production and availability of spices. Black pepper is frequently used in place of chilli pepper, chillis to produce spicy flavours. Vietnamese drinks in the south also are usually served cold with ice cubes, especially during the annual hot seasons; in contrast, in the north hot drinks are more preferable in a colder climate. Some examples of basic Vietnamese drinks include (Vietnamese iced coffee), (egg coffee), (salted pickled lime juice), (glutinous rice wine), (sugarcane juice) and (Vietnamese lotus tea).
Holidays and festivals
The country has eleven national recognised holidays. These include: New Year's Day on 1 January; Vietnamese New Year () from the last day of the last lunar month to fifth day of the first lunar calendar, lunar month; Hùng Kings' Festival on the 10th day of the third lunar month; Reunification Day on 30 April; International Workers' Day on 1 May; and National Day (Vietnam), National Day on 2 September. During , many Vietnamese from the major cities will return to their villages for family reunions and to pray for dead ancestors. Older people will usually give the young a (red envelope) while special holiday food, such as (rice cake) in a square shape together with variety of dried fruits, are presented in the house for visitors. Many other festivals are celebrated throughout the seasons, including the , and various temple and nature festivals. In the highlands, Elephant racing, Elephant Race Festivals are held annually during the spring; riders will ride their elephants for about and the winning elephant will be given sugarcane. Traditional Vietnamese weddings remain widely popular.
Sports
The Vovinam, and are widespread in Vietnam, while association football, football is the country's most popular sport. Its Vietnam national football team, national team won the ASEAN Football Championship in 2008 AFF Championship, 2008, 2018 AFF Championship, 2018 and 2024 ASEAN Championship, 2024; and reached the 2007 AFC Asian Cup, 2019 AFC Asian Cup knockout stage#Vietnam vs Japan, quarter-finals of 2019 AFC Asian Cup, its junior team of Vietnam national under-23 football team, under-23 became the runners-up of 2018 AFC U-23 Championship and reached fourth place in Football at the 2018 Asian Games, 2018 Asian Games, while the Vietnam national under-20 football team, under-20 managed to qualify the 2017 FIFA U-20 World Cup for the first time in their football history. And the Vietnam national under-17 football team, under-17 achieved the fourth place per 10 Teams of the 2000 AFC U-16 Championship. The Vietnam women's national football team, women's national football team had first appearance at the FIFA Women's World Cup in 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup, 2023, became the first 11-a-side national football team to participate in a World Cup tournament, and also traditionally dominates the Football at the Southeast Asian Games#Women's tournament, Southeast Asian Games, along with its chief rival, Thailand women's national football team, Thailand. Other Western sports such as badminton, tennis, volleyball, ping-pong and chess are also widely popular. Vietnam has participated in the Summer Olympic Games since Vietnam at the 1952 Summer Olympics, 1952. After the partition of the country in 1954, only South Vietnam competed in the games, sending athletes to the Vietnam at the 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956 and Vietnam at the 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 Olympics. Since the reunification of Vietnam in 1976, it has competed as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, attending every Summer Olympics from 1988 Summer Olympics, 1988 onwards. The present Vietnam Olympic Committee was formed in 1976 and recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) in 1979. Vietnam has never participated in the Winter Olympic Games. In 2016, Vietnam won their first gold medal at the Olympics. Basketball has become an increasingly popular sport in Vietnam, especially in
Ho Chi Minh City
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025.
The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigo ...
,
Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
and .
Vietnam basketball
Vietnam Online. Accessed 19 February 2020.
See also
* Index of Vietnam-related articles
* Outline of Vietnam
Notes
References
Sources
Print
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Legislation and government source
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Academic publications
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
News and magazines
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Websites
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Free content
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Vietnam profile
from BBC News
Vietnam
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. (CIA)
Vietnam
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' (archived 3 October 2012)
Vietnam
at ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
*
Key Development Forecasts for Vietnam
from International Futures
Government
Portal of the Government of Vietnam
Communist Party of Vietnam
– official website (in Vietnamese)
National Assembly
– the Vietnamese legislative body
General Statistics Office
Ministry of Foreign Affairs
(archived 5 October 2013)
Media and censorship
* Robert N. Wilkey
''The John Marshall Journal of Computer and Information Law''. Vol. XX, No. 4. Summer 2002. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
Tourism
Official tourism website
Miscellaneous
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{coord, 16, N, 108, E, display=title
1976 establishments in Vietnam
Communist states
Countries in Asia
Member states of ASEAN
Member states of the United Nations
One-party states
Republics
Southeast Asian countries
States and territories established in 1976
Vietnam,
Tiger Cub Economies
 According to Vietnamese legends,
According to Vietnamese legends,  Between 1615 and 1753, French traders also engaged in trade in Vietnam. The first French missionaries arrived in 1658, under the Portuguese ''Padroado''. From its foundation, the
Between 1615 and 1753, French traders also engaged in trade in Vietnam. The first French missionaries arrived in 1658, under the Portuguese ''Padroado''. From its foundation, the  But as the French were weakened by the
But as the French were weakened by the  In 1963, Buddhist discontent with Diệm's Catholic regime erupted into mass demonstrations, leading to a violent government crackdown. This led to the collapse of Diệm's relationship with the United States, and ultimately to a 1963 coup in which he and Nhu were assassinated. The Diệm era was followed by more than a dozen successive military governments, before the pairing of Air Marshal
In 1963, Buddhist discontent with Diệm's Catholic regime erupted into mass demonstrations, leading to a violent government crackdown. This led to the collapse of Diệm's relationship with the United States, and ultimately to a 1963 coup in which he and Nhu were assassinated. The Diệm era was followed by more than a dozen successive military governments, before the pairing of Air Marshal  Vietnam is located on the eastern Indochinese Peninsula between the latitudes 8° and 24°N, and the longitudes 102° and 110°E. It covers a total area of or . The combined length of the country's land boundaries is , and its coastline is long. At its narrowest point in the central
Vietnam is located on the eastern Indochinese Peninsula between the latitudes 8° and 24°N, and the longitudes 102° and 110°E. It covers a total area of or . The combined length of the country's land boundaries is , and its coastline is long. At its narrowest point in the central  As the country is located within the
As the country is located within the  In Vietnam, wildlife
In Vietnam, wildlife  Provinces are subdivided into provincial municipalities (, 'city under province'),
Provinces are subdivided into provincial municipalities (, 'city under province'),  In 1986, the Sixth National Congress of the CPV introduced socialist-oriented market economic reforms as part of the reform programme.
In 1986, the Sixth National Congress of the CPV introduced socialist-oriented market economic reforms as part of the reform programme.  As a result of several market liberalization measures, Vietnam has become a major exporter of agricultural products. It is now the world's largest producer of
As a result of several market liberalization measures, Vietnam has become a major exporter of agricultural products. It is now the world's largest producer of  In 2010, Vietnam's total state spending on science and technology amounted to roughly 0.45% of its GDP. Vietnamese scientists have made many significant contributions in various fields of study, most notably in
In 2010, Vietnam's total state spending on science and technology amounted to roughly 0.45% of its GDP. Vietnamese scientists have made many significant contributions in various fields of study, most notably in  According to the
According to the  Vietnam has 2,360 rivers with an average annual discharge of 310 billion m3. The rainy season accounts for 70% of the year's discharge. Most of the country's urban
Vietnam has 2,360 rivers with an average annual discharge of 310 billion m3. The rainy season accounts for 70% of the year's discharge. Most of the country's urban  , the population of Vietnam stands at approximately million people. The population had grown significantly from the 1979 census, which showed the total population of reunified Vietnam to be 52.7 million. According to the 2019 census, the country's population was 96,208,984. Based on the 2019 census, 65.6% of the Vietnamese population live in rural areas while only 34.4% live in urban areas. The average growth rate of the urban population has recently increased which is attributed mainly to migration and rapid urbanisation. The dominant Viet people, Viet or Kinh ethnic group constitute 82,085,826 people or 85.32% of the population. Most of their population is concentrated in the country's alluvial fans, alluvial deltas and coastal plains. As a majority ethnic group, the Kinh possess significant political and economic influence over the country. Despite this, Vietnam is also home to various ethnic groups, of which Ethnic groups in Vietnam, 54 are officially recognised, including the Hmong people, Hmong, Yao people, Dao, Tay people, Tày, Thai people in Vietnam, Thái and Nùng people, Nùng. Many ethnic minorities such as the Muong people, Muong, who are closely related to the Kinh, dwell in the highlands which cover two-thirds of Vietnam's territory.
Since the partition of Vietnam, the population of the Central Highlands was almost exclusively Degar (including more than 40 tribal groups); however, the South Vietnamese government at the time enacted a programme of resettling Kinh in indigenous areas. The Hoa people, Hoa (ethnic Overseas Chinese, Chinese) and Khmer Krom people are mainly lowlanders. Throughout Vietnam's history, many Chinese people, largely from South China, migrated to the country as administrators, merchants and even refugees. Since the reunification in 1976, an increase of communist policies nationwide resulted in the nationalisation and confiscation of property especially from the Hoa in the south and the wealthy in cities. This led many of them to leave Vietnam.
, the population of Vietnam stands at approximately million people. The population had grown significantly from the 1979 census, which showed the total population of reunified Vietnam to be 52.7 million. According to the 2019 census, the country's population was 96,208,984. Based on the 2019 census, 65.6% of the Vietnamese population live in rural areas while only 34.4% live in urban areas. The average growth rate of the urban population has recently increased which is attributed mainly to migration and rapid urbanisation. The dominant Viet people, Viet or Kinh ethnic group constitute 82,085,826 people or 85.32% of the population. Most of their population is concentrated in the country's alluvial fans, alluvial deltas and coastal plains. As a majority ethnic group, the Kinh possess significant political and economic influence over the country. Despite this, Vietnam is also home to various ethnic groups, of which Ethnic groups in Vietnam, 54 are officially recognised, including the Hmong people, Hmong, Yao people, Dao, Tay people, Tày, Thai people in Vietnam, Thái and Nùng people, Nùng. Many ethnic minorities such as the Muong people, Muong, who are closely related to the Kinh, dwell in the highlands which cover two-thirds of Vietnam's territory.
Since the partition of Vietnam, the population of the Central Highlands was almost exclusively Degar (including more than 40 tribal groups); however, the South Vietnamese government at the time enacted a programme of resettling Kinh in indigenous areas. The Hoa people, Hoa (ethnic Overseas Chinese, Chinese) and Khmer Krom people are mainly lowlanders. Throughout Vietnam's history, many Chinese people, largely from South China, migrated to the country as administrators, merchants and even refugees. Since the reunification in 1976, an increase of communist policies nationwide resulted in the nationalisation and confiscation of property especially from the Hoa in the south and the wealthy in cities. This led many of them to leave Vietnam.
 The French language, a legacy of colonial rule, is spoken by many educated Vietnamese as a second language, especially among those educated in the former
The French language, a legacy of colonial rule, is spoken by many educated Vietnamese as a second language, especially among those educated in the former  The traditional focuses of Vietnamese culture are based on humanity () and harmony () in which family and community values are highly regarded. Vietnam reveres a number of key cultural symbols, such as the Vietnamese dragon which is derived from crocodile and snake imagery; Vietnam's national father, is depicted as a holy dragon. The is a holy bird representing Vietnam's national mother . Other prominent images that are also revered are the turtle, water buffalo, buffalo and horse. Many Vietnamese also believe in the supernatural and Spiritualism (beliefs), spiritualism where illness can be brought on by a curse or Witchcraft, sorcery or caused by non-observance of a religious ethic. Traditional medical practitioners, amulets and other forms of spiritual protection and religious practices may be employed to treat the ill person. In the modern era, the cultural life of Vietnam has been deeply influenced by government-controlled media and cultural programmes. For many decades, foreign cultural influences, especially those of Western origin, were shunned. But since the recent reformation, Vietnam has seen a greater exposure to neighbouring Southeast Asian, East Asian as well to Western culture and media.
The main Vietnamese formal dress, the , is worn for special occasions such as weddings and religious festivals. White is the required uniform for girls in many high schools across the country. Other examples of traditional Vietnamese clothing include the , a four-piece woman's dress; the , a form of the in five-piece form, mostly worn in the north of the country; the , a woman's undergarment; the , rural working "pyjamas" for men and women; the , a formal brocade tunic for government receptions; and the , a variant of the worn by grooms at weddings. Traditional headwear includes the standard conical , the "lampshade-like" , and the traditional turban, . In tourism, a number of popular cultural destinations include the former Imperial City of Huế, the World Heritage Sites of Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng National Park, and , coastal regions such as Nha Trang, the caves of Hạ Long Bay and the Marble Mountains (Vietnam), Marble Mountains.
The traditional focuses of Vietnamese culture are based on humanity () and harmony () in which family and community values are highly regarded. Vietnam reveres a number of key cultural symbols, such as the Vietnamese dragon which is derived from crocodile and snake imagery; Vietnam's national father, is depicted as a holy dragon. The is a holy bird representing Vietnam's national mother . Other prominent images that are also revered are the turtle, water buffalo, buffalo and horse. Many Vietnamese also believe in the supernatural and Spiritualism (beliefs), spiritualism where illness can be brought on by a curse or Witchcraft, sorcery or caused by non-observance of a religious ethic. Traditional medical practitioners, amulets and other forms of spiritual protection and religious practices may be employed to treat the ill person. In the modern era, the cultural life of Vietnam has been deeply influenced by government-controlled media and cultural programmes. For many decades, foreign cultural influences, especially those of Western origin, were shunned. But since the recent reformation, Vietnam has seen a greater exposure to neighbouring Southeast Asian, East Asian as well to Western culture and media.
The main Vietnamese formal dress, the , is worn for special occasions such as weddings and religious festivals. White is the required uniform for girls in many high schools across the country. Other examples of traditional Vietnamese clothing include the , a four-piece woman's dress; the , a form of the in five-piece form, mostly worn in the north of the country; the , a woman's undergarment; the , rural working "pyjamas" for men and women; the , a formal brocade tunic for government receptions; and the , a variant of the worn by grooms at weddings. Traditional headwear includes the standard conical , the "lampshade-like" , and the traditional turban, . In tourism, a number of popular cultural destinations include the former Imperial City of Huế, the World Heritage Sites of Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng National Park, and , coastal regions such as Nha Trang, the caves of Hạ Long Bay and the Marble Mountains (Vietnam), Marble Mountains.