Verrucarin A on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Verrucarin A is a chemical compound that belongs in the class of
trichothecenes
The trichothecenes are a large family of chemically related mycotoxins. They are produced by various species of ''Fusarium'', ''Myrothecium'', ''Trichoderma''/''Podostroma'', '' Trichothecium'', ''Cephalosporium'', '' Verticimonosporium'', and '' ...
, a group of sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations. Biochemical modificatio ...
toxins produced by several fungi, namely from the ''Fusarium
''Fusarium'' is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil mi ...
'' species, that are responsible for infecting food grains. It was first described in 1962. Within the skeleton of the basic trichothecene structure, the olefin and epoxide are crucial for toxicity; ester functionalities and hydroxyl groups often contribute to the toxicity, thereby rendering verrucarin A as one of the most lethal examples. The mechanism of action for this class of toxins mainly inhibits protein biosynthesis by preventing peptidyl transferase activity. Although initially thought to be potentially useful as anticancer therapeutics, numerous examples of trichothecene derivatives were shown to be too toxic for clinical use.
Biosynthesis
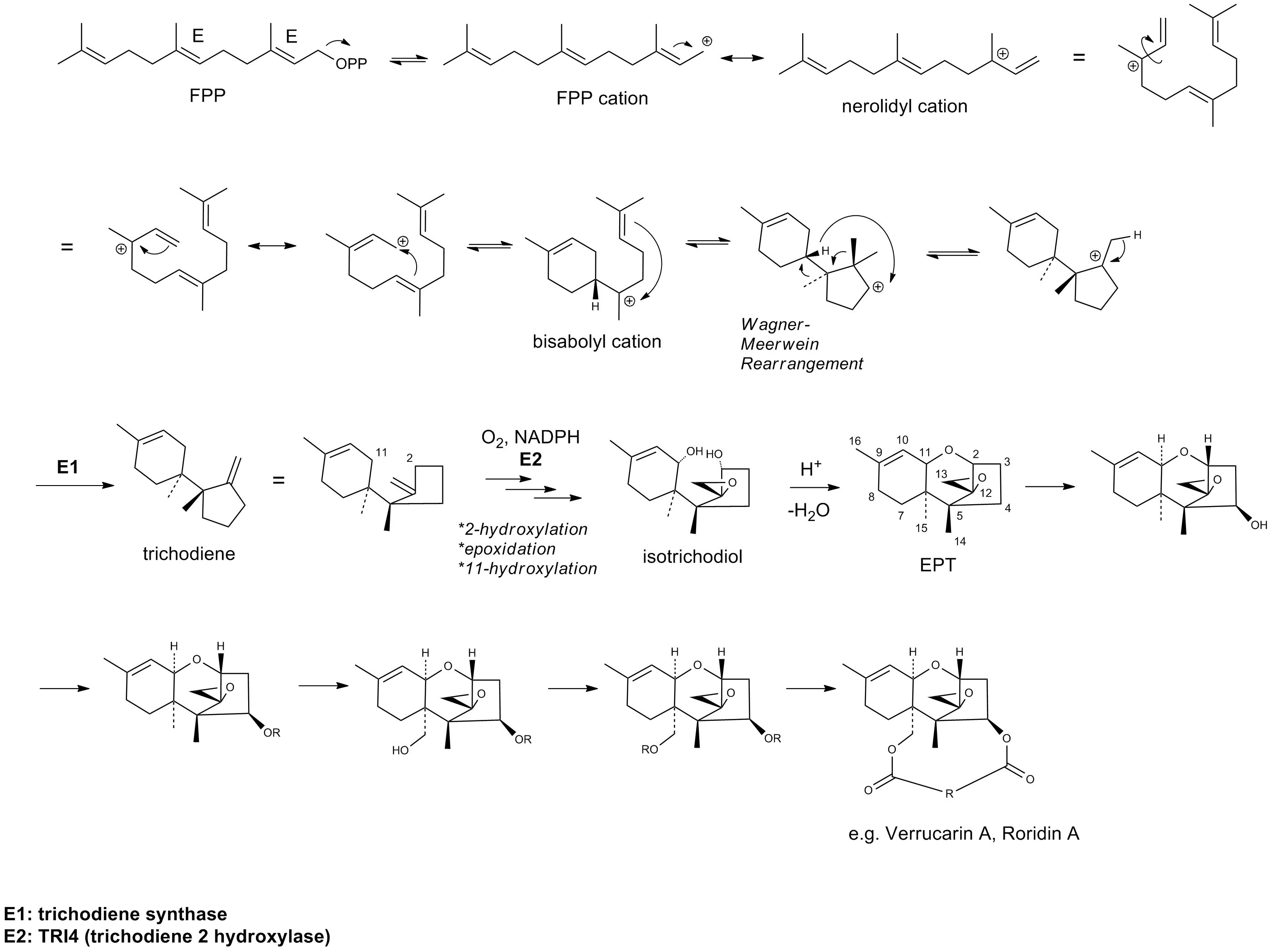
Verrucarin A is classified as a type D trichothecene based on its substitution pattern in the 12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-ene (EPT) core structure. Type D differs from types A, B and C by containing an additional ring linking the C-4 and C-15 position. Trichothecenes are generally formed via the mevalonate pathway beginning with the precursor farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP). After cyclization of FPP to form trichodiene, TRI4 encodes acytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are ...
enzyme to catalyze a series of oxygenation events. Upon the addition of three oxygens at C-2, C-11 and the C-12,13 epoxide, the intermediate isotrichodiol is formed. Isotrichodiol then isomerizes, yielding the tricothecane EPT core structure. Subsequently, it is proposed that a series of hydroxylations and acylations occur at C-15 and C-4 which then cyclize at these carbons.
:
References
{{Reflist Sesquiterpenes