Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 4 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Space Launch Complex 4 (SLC-4) is a launch and landing site at
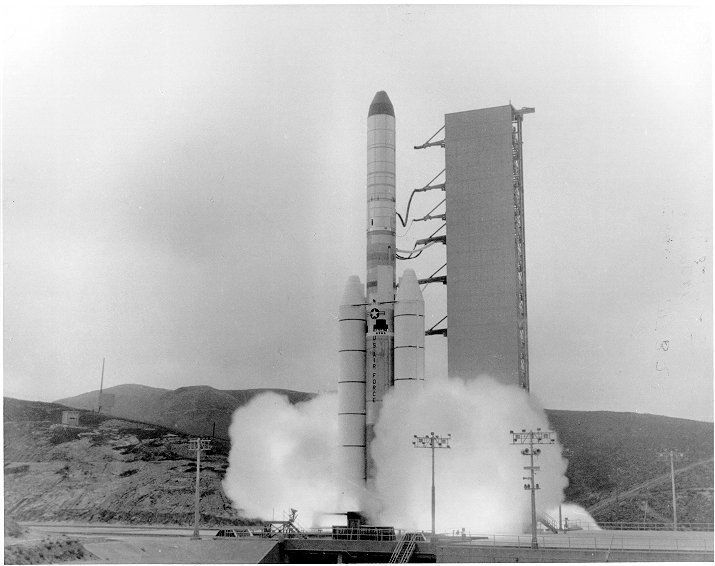



Vandenberg Space Force Base
Vandenberg Space Force Base , previously Vandenberg Air Force Base, is a United States Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County, California. Established in 1941, Vandenberg Space Force Base is a space launch base, launching spacecraft from th ...
, California, U.S. It has two pads, both of which are used by SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
for Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
, one for launch operations, and other as Landing Zone 4 (LZ-4) for SpaceX landings.
The complex was previously used by Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
and Titan rockets between 1963 and 2005. It consisted of two launch pad
A launch pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term ''launch pad'' can be used to describe just the central launch platform ( mobile launcher platform), or the entir ...
s, SLC-4W and SLC-4E, which were formerly designated PALC-2-3 and PALC-2-4 respectively. Both pads were built for use by Atlas-Agena
The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first five Mariner uncrew ...
rockets, but were later rebuilt to handle Titan rockets. The designation SLC-4 was applied at the time of the conversion to launch Titan launch vehicles.
Both pads at Space Launch Complex 4 are currently leased by SpaceX. SLC-4E is leased as a launch site for the Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
rocket, which first flew from Vandenberg on 29 September 2013, following a 24-month refurbishment program which had started in early 2011. SpaceX began a five-year lease of Launch Complex 4 West in February 2015 in order to use that area as a ''landing'' pad to bring back VTVL
Vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) is a form of takeoff and landing for rockets. Multiple VTVL craft have flown. The most widely known and commercially successful VTVL rocket is SpaceX's Falcon 9 first stage.
VTVL technologies were deve ...
return-to-launch-site (RTLS) first-stage boosters of the reusable Falcon 9 launch vehicle. That pad was later named by SpaceX as Landing Zone 4 and first used operationally for a Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
booster landing in 2018.
SLC-4E
Atlas-Agena
The first launch from PALC2-4 occurred on 14 August 1964, when a KH-7 satellite was launched by an Atlas-Agena D. After 27 Atlas-Agena launches, the last of which was on 4 June 1967, the complex was deactivated.
Titan IIID
During 1971 the complex was reactivated and refurbished for use by the Martin MariettaTitan III
Titan was a family of United States expendable rockets used between 1959 and 2005. The Titan I and Titan II were part of the US Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) fleet until 1987. The space launch vehicle versions contribut ...
launch vehicles. The Titan IIID
The Titan IIID or Titan 3D was an American expendable launch system, part of the Titan rocket family. Titan IIID was flown 22 times with KH-9 and KH-11 satellites between 1971 and 1982, all successful launches. Essentially a Titan IIIC with the ...
made its maiden flight from SLC-4E on 15 June 1971, launching the first KH-9 Hexagon
KH-9 (BYEMAN codename HEXAGON), commonly known as Big Bird or KeyHole-9, p.32 Big Bird was a series of photographic reconnaissance satellites launched by the United States between 1971 and 1986. Of twenty launch attempts by the National Recon ...
satellite. The first KH-11 Kennan
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 19 ...
satellite was launched from the complex on 19 December 1976. All 22 Titan IIIDs were launched from SLC-4E, with the last occurring on 17 November 1982.
Titan 34D
The complex was then refurbished to accommodate the Martin MariettaTitan 34D
The Titan 34D was a United States expendable launch vehicle used to launch a number of satellites for military applications.
Service history
Derived from the Titan III, the Titan 34D featured Stage 1 and Stage 2 stretched with more powerful U ...
. Seven Titan 34Ds were launched between 20 June 1983, and 6 November 1988.
SLC-4E hosted one of the most dramatic launch accidents in US history when a Titan 34D-9 carrying a KH-9 photoreconnaissance satellite exploded a few hundred feet above the pad on 18 April 1986. The enormous blast showered the launch complex with debris and toxic propellant (hydrazine and dinitrogen tetroxide), resulting in extensive damage. 16 months after the accident, the pad was back in commission when it hosted a successful launch of a KH-11 satellite.

Titan IV
The last Titan variant to use the complex was theTitan IV
Titan IV was a family of heavy-lift space launch vehicles developed by Martin Marietta and operated by the United States Air Force from 1989 to 2005. Launches were conducted from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and Vandenberg Air Forc ...
, starting on 8 March 1991, with the launch of Lacrosse 2
Lacrosse or Onyx is a series of terrestrial radar imaging reconnaissance satellites operated by the United States National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). While not officially confirmed by the NRO or the Government of the United States prior to 200 ...
. On 19 October 2005, the last flight of a Titan rocket occurred, when a Titan IVB was launched from SLC-4E, with an Improved Crystal
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 19 ...
satellite. Following this launch, the complex was deactivated, having been used for 68 launches.

Falcon 9
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
refurbished SLC–4E for Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
launches in a 24-month process that began in early 2011. The draft environmental impact assessment
Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) is the assessment of the environmental consequences of a plan, policy, program, or actual projects prior to the decision to move forward with the proposed action. In this context, the term "environmental imp ...
with a finding of "no significant impact" was published in February 2011. Demolition began on the pad's fixed and mobile service towers in summer 2011.
By late 2012, SpaceX anticipated that the initial launch from the Vandenberg pad would be in 2013, with the larger variant Falcon 9 v1.1
Falcon 9 v1.1 was the second version of SpaceX's Falcon 9 orbital launch vehicle. The rocket was developed in 2011–2013, made its maiden launch in September 2013, and its final flight in January 2016. The Falcon 9 rocket was fully designed ...
.
As the pad was nearing completion in February 2013, the first launch was scheduled for summer 2013, but was delayed until September 2013.
Launch history
Statistics
Atlas (1964–1967)
Titan IIID / 34D (1971–1988)
Titan IV (1991–2005)
Falcon 9 (since 2013)
Upcoming launches
SLC-4W
SLC-4W started operations in 1963 as Space Launch Complex 4W, and continued as an operational launch site through 2003. In 2015, SpaceX started conversion of the launch site into Landing Zone LZ-4. Landing operations commenced in 2018 at LZ-4.SLC-4W Launch history
Statistics
By rocket type
= Atlas-Agena
= The first launch to use what is now SLC-4 occurred on 12 July 1963, when an Atlas LV-3 Agena-D launched the firstKH-7 Gambit
BYEMAN codenamed GAMBIT, the KH-7 (Air Force Program 206) was a reconnaissance satellite used by the United States from July 1963 to June 1967. Like the older CORONA system, it acquired imagery intelligence by taking photographs and returning ...
reconnaissance satellite, from PALC-2-3. Twelve Atlas-Agenas launches were conducted from PALC-2-3, with the last occurring on 12 March 1965.
= Titan IIIB
= Following this, it was rebuilt as SLC-4W, a Titan launch complex. The first Titan launch from SLC-4W was aTitan IIIB
Titan IIIB was the collective name for a number of derivatives of the Titan II ICBM and Titan III launch vehicle, modified by the addition of an Agena upper stage. It consisted of four separate rockets. The Titan 23B was a basic Titan II with an ...
, on 29 July 1966. All 68 Titan IIIB launches occurred from SLC-4W, with the last on 12 February 1987.

= Titan 23G
= After the retirement of the Titan IIIB, it became aTitan 23G
The Titan 23G, Titan II(23)G, Titan 2(23)G or Titan II SLV was an American expendable launch system derived from the LGM-25C Titan II intercontinental ballistic missile. Retired Titan II missiles were converted by Martin Marietta, into which the ...
launch site, and twelve Titan II launches, using the 23G orbital configuration, were conducted between 5 September 1988 and 18 October 2003. Following the retirement of the Titan 23G, SLC-4W was deactivated. 93 rockets were launched from SLC-4W.
SLC-4W was the site of the launch of Clementine
A clementine (''Citrus × clementina'') is a tangor, a citrus fruit hybrid between a willowleaf mandarin orange ( ''C.'' × ''deliciosa'') and a sweet orange (''C. × sinensis''), named in honor of Clément Rodier, a French missionary who fir ...
, the only spacecraft to be launched from Vandenberg to the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, which was launched by a Titan 23G on 25 January 1994.
Launch timeline 1963–2003
LZ-4
Development History
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
signed a five-year lease of Launch Complex 4W in February 2015, in order to use the area to land reusable launch vehicles at the pad. The location is being used for vertical landing of Return-To-Launch-Site (RTLS) first-stage boosters of the Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
rockets that are launched from the adjacent SLC-4E launch pad.
This novel use of SLC-4W had initially surfaced in July 2014 when ''NASASpaceFlight.com
''NASASpaceflight.com'' is a private news website and forum which launched in 2005, covering Human spaceflight, crewed and Uncrewed spacecraft, uncrewed spaceflight and aerospace engineering news. Its original reporting has been referenced by v ...
'' published that SpaceX was considering leasing SLC-4W for use as a RTLS vertical-landing facility for reusable first-stage boosters.
Principal structures on the pad were demolished in September 2014 as construction of the landing pad began and was completed sometime around 2017.
Landing Outcomes (Falcon 9)
Detailed landing history
SpaceX has perfected RTLS landings on two landing pads that it has built atCape Canaveral Space Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station ...
. It was initially thought that the booster used to launch a fourth batch of ten Iridium NEXT
The Iridium satellite constellation provides L band voice and data information coverage to satellite phones, pagers and integrated transceivers over the entire surface of Earth. Iridium Communications owns and operates the constellation, addi ...
satellites in December 2017 would be the first to land at Vandenberg AFB but this mission was ultimately performed in expendable mode. In July 2018, SpaceX applied for a permit to the Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction ...
(FCC) for post-landing communications with a first stage of a Falcon 9 rocket at SLC-4W, pointing to a possible landing sometime in September 2018, possibly for the SAOCOM 1A
SAOCOM (Satélite Argentino de Observación COn Microondas, Spanish for Argentine Microwaves Observation Satellite) is an Earth observation satellite constellation of Argentina's space agency CONAE. Two satellites are already orbiting the Ea ...
mission although this was later rescheduled for 8 October 2018 (UTC). A few weeks prior to this first landing attempt it was known to the public, again via FCC permits and also public warnings about sonic booms in the area, that SpaceX had renamed this pad as Landing Zone 4. Finally, this pad was first used for a rocket booster landing of a first stage of a Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX.
The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payl ...
launch vehicle in October 2018, recovering the booster that had just launched the Argentinian SAOCOM 1A
SAOCOM (Satélite Argentino de Observación COn Microondas, Spanish for Argentine Microwaves Observation Satellite) is an Earth observation satellite constellation of Argentina's space agency CONAE. Two satellites are already orbiting the Ea ...
satellite.
References
External links
* * {{SpaceX Vandenberg Space Force Base SpaceX facilities Space Launch Complex 4 Space Launch Complex 4