|
Titan IIID
The Titan IIID or Titan 3D was an American expendable launch system, part of the Titan rocket family. Titan IIID was flown 22 times with KH-9 and KH-11 satellites between 1971 and 1982, all successful launches. Essentially a Titan IIIC with the Transstage removed, it was designed for heavy LEO payloads. The Titan IIID first flew on 15 June 1971, launching the first KH-9 satellite. It was retired from service in 1982, and replaced by the uprated Titan 34D. All launches occurred from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to: * Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name * USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida * Vandenberg Sp .... Launch history References External links Titan (rocket family) Military equipment introduced in the 1970s {{rocket-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expendable Launch System
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are either destroyed during reentry or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of several multistage rocket, rocket stages that are discarded sequentially as their fuel is exhausted and the vehicle gains altitude and speed. As of 2022, most satellites and List of crewed spacecraft, human spacecraft are currently launched on ELVs. ELVs are simpler in design than reusable launch systems and therefore may have a lower production cost. Furthermore, an ELV can use its entire fuel supply to accelerate its payload, offering greater payloads. ELVs are proven technology in widespread use for many decades. ELVs are usable only once, and therefore have a significantly higher per-launch cost than modern (post-Space Transportation System, STS) reusable vehicles. Current operators Arianespace China ISRO JAXA Roscosmos United States Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LR-91
The LR91 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine, which was used on the second stages of Titan intercontinental ballistic missiles and launch vehicles. While the original version - the LR91-3 - ran on RP-1/LOX (as did the companion LR87-3) on the Titan I, the models that propelled the Titan II and later were switched to Aerozine 50/ N2O4. This engine was vacuum optimized and ran the gas-generator cycle. The thrust chamber used fuel for regenerative cooling, with separate ablative skirt. The LR87, which was used for the Titan first stage, was used as a template for the LR91. Early LR91 engines used on the Titan I burned RP-1 and liquid oxygen. Because liquid oxygen is cryogenic, it could not be stored in the missile for long periods of time, and had to be loaded before the missile could be launched. For the Titan II, the engine was converted to use Aerozine-50 and nitrogen tetroxide, which are hypergolic and storable at room temperature. This allowed Titan II missil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
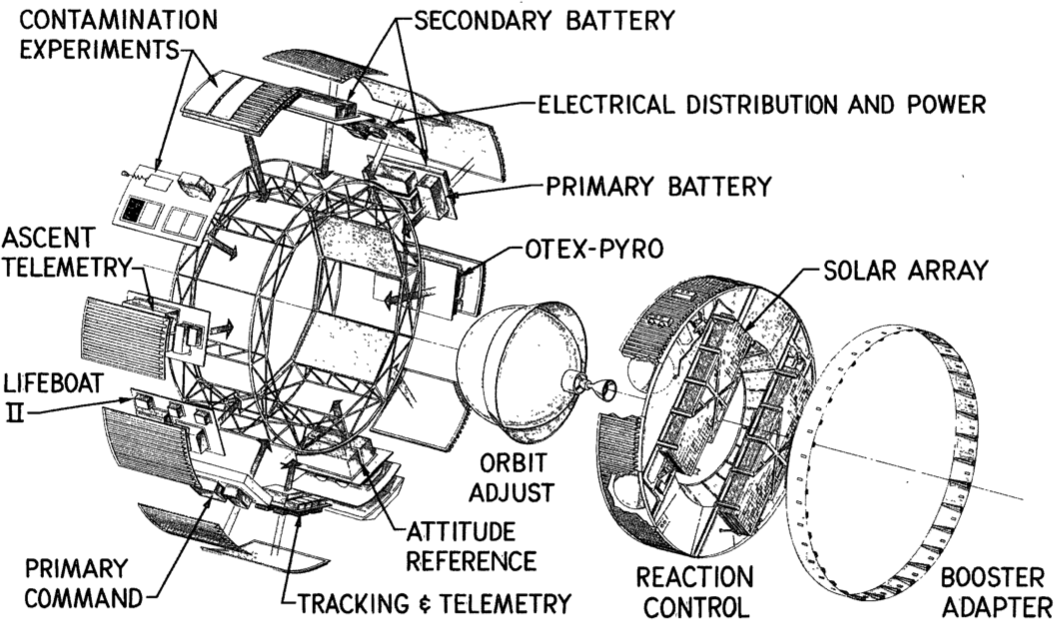
KH-9 HEXAGON
KH-9 (BYEMAN codename HEXAGON), commonly known as Big Bird or KeyHole-9, p.32 Big Bird was a series of photographic reconnaissance satellites launched by the United States between 1971 and 1986. Of twenty launch attempts by the National Reconnaissance Office, all but one were successful. Photographic film aboard the KH-9 was sent back to Earth in recoverable film return capsules for processing and interpretation. The highest ground resolution achieved by the main cameras of the satellite was . Another source says "images in the "better-than-one-foot" category" for the last "Gambit" missions. They are also officially known as the Broad Coverage Photo Reconnaissance satellites (Code 467), built by Lockheed Corporation for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The satellites were an important factor in determining Soviet military capabilities and in the acquisition of accurate intelligence for the formulation of U.S. national policy decisions as well as deployment of U.S. fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan 34D
The Titan 34D was a United States expendable launch vehicle used to launch a number of satellites for military applications. Service history Derived from the Titan III, the Titan 34D featured Stage 1 and Stage 2 stretched with more powerful UA1206 solid motors. A variety of upper stages were available, including the Inertial Upper Stage, the Transfer Orbit Stage, and the Transtage. The Titan 34D made its maiden flight in the year of 1982 on the 30th of October with two DSCS defense communications satellites for the United States Department of Defense (DOD). All of the launches were conducted from either LC-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station or SLC-4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base. Overall, fifteen launches were carried out, of which three failed. 1985 failure, Titan 34D-7 The first failure was a launch of a KH-11 photoreconnaissance satellite in the year 1985 on the 28th of August. The core stage suffered a propulsion system malfunction and was destroyed by Range Saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Astronautica
The ''Encyclopedia Astronautica'' is a reference web site on space travel. A comprehensive catalog of vehicles, technology, astronauts, and flights, it includes information from most countries that have had an active rocket research program, from Robert Goddard to the NASA Space Shuttle and the Soviet Buran programme. Founded in 1994 and maintained for most of its existence by space enthusiast and author Mark Wade. He has been collecting such information for most of his life. Between 1996 and 2000 the site was hosted by '' Friends and Partners in Space''. The site is no longer updated or maintained and is now considered as partially unreliable. Although it contains a great deal of information, not all of it is correct. Reception and accolades The American Astronautical Society gave the site the Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History which "recognizes exceptional, sustained efforts to inform and educate on spaceflight and its history through one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan IIIC
The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar, though the spaceplane was cancelled before it could fly. The majority of the launcher's payloads were DoD satellites, for military communications and early warning, though one flight ( ATS-6) was performed by NASA. The Titan IIIC was launched exclusively from Cape Canaveral while its sibling, the Titan IIID, was launched only from Vandenberg AFB. History The Titan rocket family was established in October 1955 when the Air Force awarded the Glenn L. Martin Company (later Martin Marietta and now Lockheed Martin) a contract to build an intercontinental ballistic missile (SM-68). It became known as the Titan I, the nation's first two-stage ICBM, and replaced the Atlas ICBM as the second underground, vertically stored, silo-based ICBM. Both stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
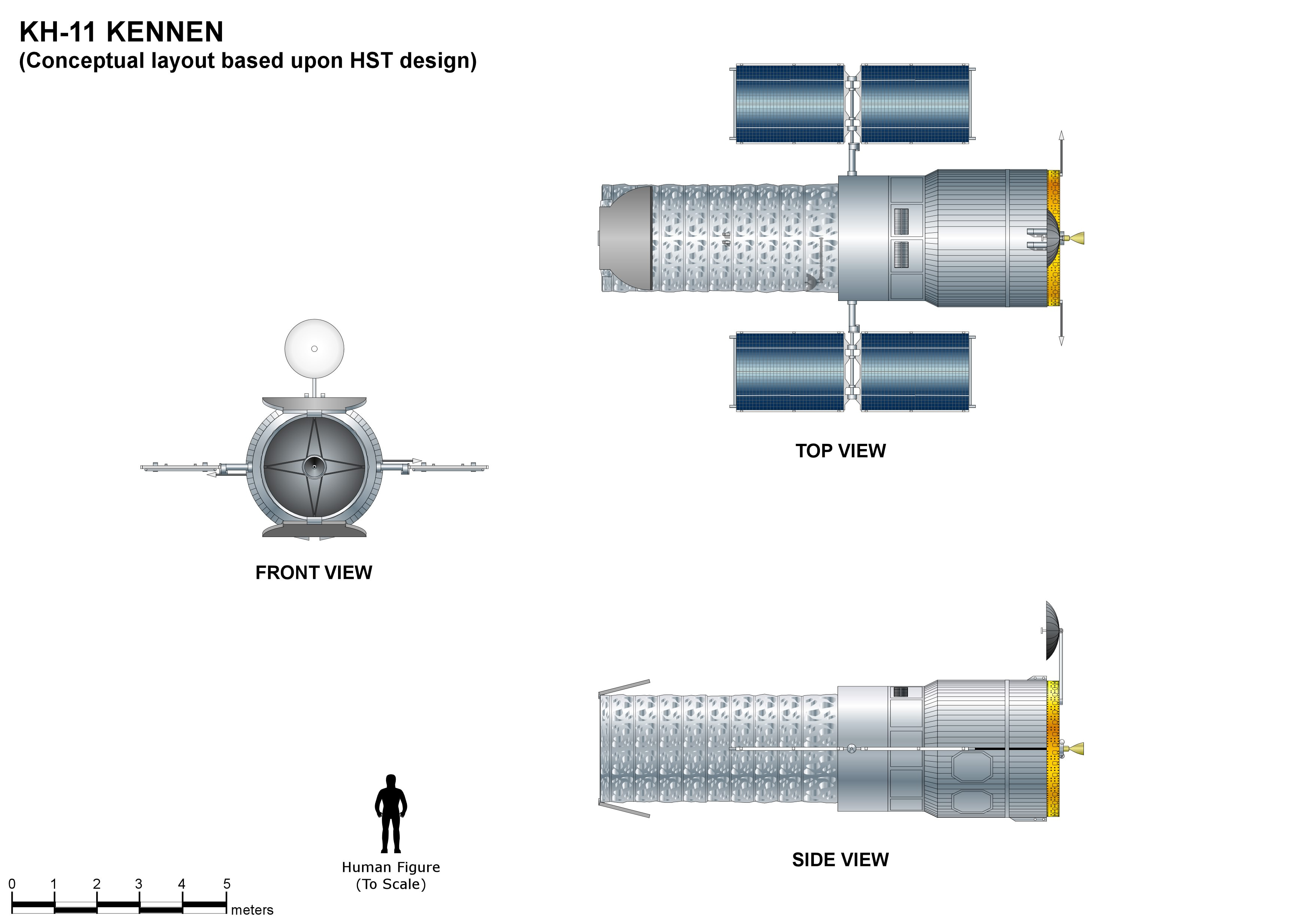
KH-11
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and so offer real-time optical observations. Later KH-11 satellites have been referred to by outside observers as KH-11B or KH-12, and by the names "Advanced KENNEN", "Improved Crystal" and "Ikon". Official budget documents refer to the latest generation of electro-optical satellites as ''Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System''. The Key Hole series was officially discontinued in favor of a random numbering scheme after repeated public references to KH-7 GAMBIT, KH-8 GAMBIT 3, KH-9 HEXAGON, and KH-11 KENNEN satellites. The capabilities of the KH-11 are highly classified, as are images they produce. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KH-9
KH-9 (BYEMAN codename HEXAGON), commonly known as Big Bird or KeyHole-9, p.32 Big Bird was a series of photographic reconnaissance satellites launched by the United States between 1971 and 1986. Of twenty launch attempts by the National Reconnaissance Office, all but one were successful. Photographic film aboard the KH-9 was sent back to Earth in recoverable film return capsules for processing and interpretation. The highest ground resolution achieved by the main cameras of the satellite was . Another source says "images in the "better-than-one-foot" category" for the last "Gambit" missions. They are also officially known as the Broad Coverage Photo Reconnaissance satellites (Code 467), built by Lockheed Corporation for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The satellites were an important factor in determining Soviet military capabilities and in the acquisition of accurate intelligence for the formulation of U.S. national policy decisions as well as deployment of U.S. fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expendable Launch System
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are either destroyed during reentry or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of several multistage rocket, rocket stages that are discarded sequentially as their fuel is exhausted and the vehicle gains altitude and speed. As of 2022, most satellites and List of crewed spacecraft, human spacecraft are currently launched on ELVs. ELVs are simpler in design than reusable launch systems and therefore may have a lower production cost. Furthermore, an ELV can use its entire fuel supply to accelerate its payload, offering greater payloads. ELVs are proven technology in widespread use for many decades. ELVs are usable only once, and therefore have a significantly higher per-launch cost than modern (post-Space Transportation System, STS) reusable vehicles. Current operators Arianespace China ISRO JAXA Roscosmos United States Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerozine 50
__NOTOC__ Aerozine 50 is a 50:50 mix by weight of hydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH), originally developed in the late 1950s by Aerojet General Corporation as a storable, high-energy, hypergolic fuel for the Titan II ICBM rocket engines. Aerozine continues in wide use as a rocket fuel, typically with dinitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer, with which it is hypergolic. Aerozine 50 is more stable than hydrazine alone, and has a higher density and boiling point than UDMH alone. Pure hydrazine has a higher performance than Aerozine 50, but an unacceptable freezing point. By mixing pure hydrazine with UDMH, hydrazine's inconveniently high freezing point of 2 °C is lowered through freezing-point depression. In addition, UDMH is a more stable molecule; this reduces the chances of straight hydrazine decomposing unexpectedly, increasing safety and allowing the blend to be used as a coolant in regeneratively cooled engines. This type of fuel is mainly used for inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Marietta
The Martin Marietta Corporation was an American company founded in 1961 through the merger of Glenn L. Martin Company and American-Marietta Corporation. In 1995, it merged with Lockheed Corporation to form Lockheed Martin. History Martin Marietta formed in 1961 by the merger of the Glenn L. Martin Company and American-Marietta Corporation. Martin, based in Baltimore, was primarily an aerospace concern with a recent focus on missiles, namely its Titan program. American-Marietta was headquartered in Chicago and produced paints, dyes, metallurgical products, construction materials, and other goods. In 1982, Martin Marietta was subject to a hostile takeover bid by the Bendix Corporation, headed by William Agee. Bendix bought the majority of Martin Marietta shares and in effect owned the company. However, Martin Marietta's management used the short time separating ownership and control to sell non-core businesses and launch its own hostile takeover of Bendix (known as the Pac-M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp''2 hybrid orbitals of the two NO2 un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |