United States Department of Education on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States Department of Education is a
"The Educational Legacy of Ronald Reagan"
, Summer 2004 v. 82 n. 4 p. 256
 Under President
Under President
online
Department of Education
on
Department of Education
in the
Department of Education
reports and recommendations from the Government Accountability Office
ERIC Digests
– Informational digests on educational topics produced by the U.S. Department of Education before 1983. * *
United States Government Manual, Department of Education
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Department Of Education
Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
-level department of the United States government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
. It began operating on May 4, 1980, having been created after the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
was split into the Department of Education and the Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
by the Department of Education Organization Act
The Department of Education Organization Act is a United States federal law enacted in 1979.
Purpose
Congress established the United States Department of Education (ED) with the Department of Education Organization Act. Under the law, ED's missio ...
, which President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
signed into law on October 17, 1979.
The Department of Education is administered by the United States Secretary of Education
The United States secretary of education is the head of the U.S. Department of Education. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States, and the federal government, on policies, programs, and activities re ...
. It has 4,400 employees - the smallest staff of the Cabinet agencies - and an annual budget of $68 billion. The President's 2023 Budget request is for 88.3 billion, which includes funding for children with disabilities (IDEA
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of being ...
), pandemic recovery, early childhood education, Pell Grants
A Pell Grant is a subsidy the U.S. federal government provides for students who need it to pay for college. Federal Pell Grants are limited to students with financial need, who have not earned their first bachelor's degree, or who are enrolled i ...
, Title I
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) was passed by the 89th United States Congress and signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on April 11, 1965. Part of Johnson's "War on Poverty", the act has been one of the most far-rea ...
, work assistance, among other programs. Its official abbreviation is ED ("DoE" refers to the United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
) but is also abbreviated informally as "DoEd".
Purpose and functions
Unlike the systems of many other countries,education in the United States
Education in the United States is provided in public and private schools and by individuals through homeschooling. State governments set overall educational standards, often mandate standardized tests for K–12 public school systems and sup ...
is decentralized. Due to the courts and lawmakers' interpretation of the 10th Amendment, this means the federal government and Department of Education are not involved in determining curricula or educational standards or establishing schools or colleges. The Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA) oversees schools located on American military bases and the Department of the Interior's Bureau of Indian Education supports tribally-controlled schools. The quality of higher education institutions and their degrees are maintained through an informal private process known as accreditation
Accreditation is the independent, third-party evaluation of a conformity assessment body (such as certification body, inspection body or laboratory) against recognised standards, conveying formal demonstration of its impartiality and competence to ...
, over which the Department of Education has no direct public jurisdictional control.
The Department identifies four key functions:
* Establishing policies on federal financial aid for education, and distributing as well as monitoring those funds.
* Collecting data on America's schools and disseminating research.
* Focusing national attention on key educational issues.
* Prohibiting discrimination and ensuring equal access to education.
The Department of Education is a member of the United States Interagency Council on Homelessness
The United States Interagency Council on Homelessness (USICH) is an independent federal agency within the U.S. executive branch that leads the implementation of the federal strategic plan to prevent and end homelessness. USICH is advised by a Co ...
, and works with federal partners to ensure proper education for homeless and runaway youth in the United States.
Budget
For 2006, the ED discretionary budget was $56 billion and the mandatory budget contained $23 billion. In 2009 it received additional ARRA funding of $102 billion. As of 2011, the discretionary budget is $70 billion.History
Establishment
The Department's origin goes back to 1867, when PresidentAndrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a Dem ...
signed legislation for a Department of Education. It was seen as a way to collect information and statistics about the nation's schools and provide advice to schools in the same way the Department of Agriculture helped farmers. The Department was originally proposed by Henry Barnard
Henry Barnard (January 24, 1811 – July 5, 1900) was an American educationalist and reformer.
Biography
He was born in Hartford, Connecticut on January 24, 1811 and attended Wilbraham & Monson Academy. He graduated from Yale University in 1 ...
and leaders of the National Teachers Association (renamed the National Education Association
The National Education Association (NEA) is the largest labor union in the United States. It represents public school teachers and other support personnel, faculty and staffers at colleges and universities, retired educators, and college stud ...
). Barnard served as the first commissioner of education but resigned when the office was reconfigured as a bureau in the Department of Interior known as the United States Office of Education
The Office of Education, at times known as the Department of Education and the Bureau of Education, was a small unit in the Federal government of the United States, Federal Government of the United States within the United States Department of the ...
due to concerns it would have too much control over local schools.
Over the years, the office remained relatively small, operating under different titles and housed in various agencies, including the United States Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the ma ...
and the former United States Department of Health Education and Welfare (DHEW) (now the United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
(DHHS)). An unsuccessful attempt at creating a Department of Education, headed by a Secretary of Education
An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ...
, came with the Smith–Towner Bill in 1920.
In 1939, the organization (then a bureau) was transferred to the Federal Security Agency, where it was renamed as the Office of Education. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
promulgated "Reorganization Plan No. 1 of 1953." The Federal Security Agency was abolished and most of its functions were transferred to the newly formed DHEW.
In 1979, President Carter advocated for creating a cabinet-level Department of Education. Carter's plan was to transfer most of the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare's education-related functions to the Department of Education. Carter also planned to transfer the education-related functions of the departments of Defense, Justice, Housing and Urban Development, and Agriculture, as well as a few other federal entities. Among the federal education-related programs that were not proposed to be transferred were Headstart, the Department of Agriculture's school lunch and nutrition programs, the Department of the Interior's Native Americans' education programs, and the Department of Labor's education and training programs.
Upgrading Education to cabinet-level status in 1979 was opposed by many in the Republican Party, who saw the department as unconstitutional
Constitutionality is said to be the condition of acting in accordance with an applicable constitution; "Webster On Line" the status of a law, a procedure, or an act's accordance with the laws or set forth in the applicable constitution. When l ...
, arguing that the Constitution doesn't mention ''education'', and deemed it an unnecessary and illegal federal bureaucratic intrusion into local affairs. However, many see the department as constitutional under the Commerce Clause
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amon ...
, and that the funding role of the department is constitutional under the Taxing and Spending Clause
The Taxing and Spending Clause (which contains provisions known as the General Welfare Clause and the Uniformity Clause), Article I, Section 8, Clause 1 of the United States Constitution, grants the federal government of the United States it ...
. The National Education Association
The National Education Association (NEA) is the largest labor union in the United States. It represents public school teachers and other support personnel, faculty and staffers at colleges and universities, retired educators, and college stud ...
supported the bill, while the American Federation of Teachers
The American Federation of Teachers (AFT) is the second largest teacher's labor union in America (the largest being the National Education Association). The union was founded in Chicago. John Dewey and Margaret Haley were founders.
About 60 per ...
opposed it.
As of 1979, the Office of Education had 3,000 employees and an annual budget of $12 billion. Congress appropriated to the Department of Education an annual budget of $14 billion and 17,000 employees when establishing the Department of Education. During the 1980 presidential campaign, Gov. Reagan called for the total elimination of the U.S. Department of Education, severe curtailment of bilingual education, and massive cutbacks in the federal role in education. Once in office, President Reagan significantly reduced its budget. Educational Horizons"The Educational Legacy of Ronald Reagan"
, Summer 2004 v. 82 n. 4 p. 256
Early history
The Republican Party platform of 1980 called for the elimination of the Department of Education created under Carter, and PresidentRonald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
promised during the 1980 presidential election to eliminate it as a cabinet post, but he was not able to do so with a Democratic House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
. In the 1982 State of the Union
The State of the Union Address (sometimes abbreviated to SOTU) is an annual message delivered by the president of the United States to a joint session of the United States Congress near the beginning of each calendar year on the current conditio ...
Address, he pledged: "The budget plan I submit to you on Feb. 8 will realize major savings by dismantling the Department of Education."
By 1984 the GOP had dropped the call for elimination from its platform, and with the election of President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
in 1988, the Republican position evolved in almost lockstep with that of the Democrats, with Goals 2000
The National Educational Goals, also known as the Goals 2000 Act were set by the U.S. Congress in the 1990s to set goals for standards-based education reform. The intent was for certain criteria to be met by the millennium (2000). Many of these go ...
a virtual joint effort.
After the Newt Gingrich-led "revolution" in 1994 had taken control of both Houses of Congress, federal control of and spending on education soared. That trend continued unabated despite the fact that the Republican Party made abolition of the department a cornerstone of 1996 platform and campaign promises, calling it an inappropriate federal intrusion into local, state, and family affairs. The GOP platform read: "The Federal government has no constitutional authority to be involved in school curricula or to control jobs in the market place. This is why we will abolish the Department of Education, end federal meddling in our schools, and promote family choice at all levels of learning."
In 2000, the Republican Liberty Caucus
The Republican Liberty Caucus (RLC) is a political action organization dedicated to promoting the ideals of Individual freedom, individual liberty, limited government and free market economics within the Republican Party (United States), Republi ...
passed a resolution to abolish the Department of Education. Abolition of the organization was not pursued under the George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
administration, which made reform of federal education a key priority of the president's first term. In 2008 and 2012, presidential candidate Ron Paul campaigned in part on an opposition to the department.
Later history
 Under President
Under President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
, the department primarily focused on elementary and secondary education, expanding its reach through the No Child Left Behind Act. The department's budget increased by $14 billion between 2002 and 2004, from $46 billion to $60 billion.
On March 23, 2007, President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
signed into law , which designates the ED Headquarters building as the Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building
The Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building is a federal office building in Washington, D.C., which serves as the headquarters of the United States Department of Education.
History
Construction of the building started in 1959 and ...
.
In December 2015 President Barack Obama instituted the Every Student Succeeds Act
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) is a US law passed in December 2015 that governs the United States K–12 public education policy. The law replaced its predecessor, the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB), and modified but did not eliminate pr ...
, which reauthorized the Elementary Secondary Education Act. “In December 2015, the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) was signed into law, reauthorizing the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) and replacing the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB). ESEA, the federal law that authorizes federal funding for K-12 schools, represents the nation’s commitment to equal educational opportunity for all students and has influenced the education of millions of children."
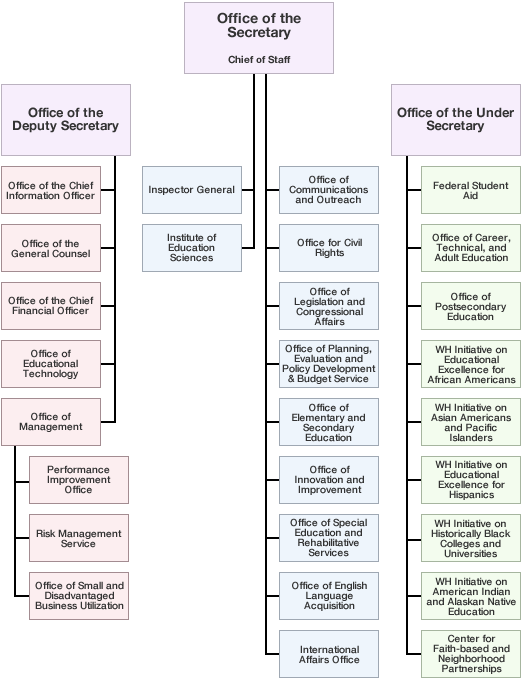
Organization

See also
* Council for Higher Education Accreditation *Educational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population refers to the highest level of education completed. The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the pop ...
* Free Application for Federal Student Aid
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a form completed by current and prospective college students (undergraduate and graduate) in the United States to determine their eligibility for student financial aid.
The FAFSA is differ ...
* FICE code The FICE code is a six-digit identification code used to identify institutions of higher education in the United States. It was initially used to identify schools doing business with the Office of Education during the early sixties. It is named af ...
* Federal Student Aid
Federal Student Aid (FSA), an office of the U.S. Department of Education, is the largest provider of student financial aid in the United States. Federal Student Aid provides student financial assistance in the form of grants, loans, and work-s ...
* National Diffusion Network
The National Diffusion Network (United States, 1974–1995) was the first federally sponsored effort to identify and spread to America's schools innovative education programs. The program was created administratively by the then-Office of Educa ...
* School Improvement Grant
School Improvement Grants (SIGs) are grants awarded by the U.S. Department of Education to state education agencies (SEAs) under Section 1003(g) of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 (aka ESEA, reauthorized by the No Child Left B ...
* Title 34 of the Code of Federal Regulations
CFR Title 34 - Education is one of fifty titles comprising the United States Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Title 34 is the principal set of rules and regulations issued by federal agencies of the United States regarding education
Edu ...
* National Endowment for the Humanities
The National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) is an independent federal agency of the U.S. government, established by thNational Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities Act of 1965(), dedicated to supporting research, education, preserv ...
Related legislation
* 1965:Elementary and Secondary Education Act
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) was passed by the 89th United States Congress and signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on April 11, 1965. Part of Johnson's "War on Poverty", the act has been one of the most far-re ...
(ESEA)
* 1965: Higher Education Act of 1965
The Higher Education Act of 1965 (HEA) () was legislation signed into United States law on November 8, 1965, as part of President Lyndon Johnson's Great Society domestic agenda. Johnson chose Texas State University (then called " Southwest Te ...
(HEA) (Pub. L. No. 89-329)
* 1974: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 (FERPA or the Buckley Amendment) is a United States federal law that governs the access to educational information and records by public entities such as potential employers, publicly funded e ...
(FERPA)
* 1974: Equal Educational Opportunities Act of 1974
The Equal Educational Opportunities Act (EEOA) of 1974 is a federal law of the United States of America. It prohibits discrimination against faculty, staff, and students, including racial segregation of students, and requires school districts ...
(EEOA)
* 1975: Education for All Handicapped Children Act
The Education for All Handicapped Children Act (sometimes referred to using the acronyms EAHCA or EHA, or Public Law (PL) 94-142 was enacted by the United States Congress in 1975. This act required all public schools accepting federal funds to p ...
(EHA) (Pub. L. No. 94-142)
* 1978: Protection of Pupil Rights Amendment
* 1980: Department of Education Organization Act
The Department of Education Organization Act is a United States federal law enacted in 1979.
Purpose
Congress established the United States Department of Education (ED) with the Department of Education Organization Act. Under the law, ED's missio ...
(Pub. L. No. 96-88)
* 1984: Equal Access Act
The Equal Access Act is a United States federal law passed as Title VIII of the Education for Economic Security Act in 1984 to compel federally funded public secondary schools to provide equal access to extracurricular student clubs. Lobbied for ...
* 1990: The Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy and Campus Crime Statistics Act (Clery Act)
* 1994: Improving America's Schools Act of 1994 {{Infobox U.S. legislation
, shorttitle = Improving America's Schools Act of 1994
, othershorttitles = {{unbulleted list, Alaska Native Educational Equity, Support and Assistance Act, Albert Einstein Distinguished Educator Fellowship Act o ...
* 2001: No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB)
* 2004: Individuals with Disabilities Education Act
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a piece of American legislation that ensures students with a disability are provided with a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) that is tailored to their individual needs. IDEA wa ...
(IDEA)
* 2005: Higher Education Reconciliation Act of 2005 (HERA) (Pub. L. No. 109-171)
* 2006: Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Improvement Act
* 2007: America COMPETES Act
* 2008: Higher Education Opportunity Act (HEOA) (Pub. L. No. 110-315)
* 2009: Race to the Top
Race to the Top (R2T, RTTT or RTT) was a $4.35 billion United States Department of Education competitive grant created to spur and reward innovation and reforms in state and local district K–12 education. Funded as part of the American Recovery ...
* 2009: Student Aid and Fiscal Responsibility Act
The Student Aid and Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2009 (SAFRA; ) is a bill introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives of the 111th United States Congress by Congressman George Miller that would expand federal Pell Grants to a maximum of $ ...
* 2010: Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
The Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (, ) is a law that was enacted by the 111th United States Congress, by means of the reconciliation process, in order to amend the Affordable Care Act (ACA) (). The law includes the ...
* 2015: Every Student Succeeds Act
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) is a US law passed in December 2015 that governs the United States K–12 public education policy. The law replaced its predecessor, the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB), and modified but did not eliminate pr ...
(ESSA)
References
Further reading
* Radin, Beryl A., and Willis D. Hawley (1988). ''Politics of Federal Reorganization: Creating the U.S. Department of Education'', * Heffernan, Robert V. (2001). ''Cabinetmakers: Story of the Three-Year Battle to Establish the U.S. Department of Education'',Primary sources
* ''Examining the Policies and Priorities of the U.S. Department of Education. Hearing before the Committee on Education and Labor. U.S. House of Representatives, One Hundred Sixteenth Congress, First Session (April 10, 2019).'' (2020online
External links
*Department of Education
on
USAspending.gov ttp://www.usaspending.gov USASpending.govis a database of spending by the United States federal government.
History
Around the time of the Act's passage, OMB Watch, a government watchdog group, was developing a site that would do essentially eve ...
Department of Education
in the
Federal Register
The ''Federal Register'' (FR or sometimes Fed. Reg.) is the official journal of the federal government of the United States that contains government agency rules, proposed rules, and public notices. It is published every weekday, except on feder ...
Department of Education
reports and recommendations from the Government Accountability Office
ERIC Digests
– Informational digests on educational topics produced by the U.S. Department of Education before 1983. * *
United States Government Manual, Department of Education
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Department Of Education
Department Of Education
An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ...
Education ministries
Government agencies established in 1979
Education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...