United States Census Bureau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the  Article One of the United States Constitution (section II) directs the
Article One of the United States Constitution (section II) directs the
. US Census Bureau. In 1954, various acts were codified into Title 13 of the U.S. Code. By law, the Census Bureau must count everyone and submit state population totals to the U.S. President by December 31 of any year ending in a zero. States within the Union receive the results in the spring of the following year.

 Since 1903, the official census-taking agency of the United States government has been the Bureau of the Census. The Census Bureau is headed by a director, assisted by a deputy director and an executive staff composed of the associate directors.
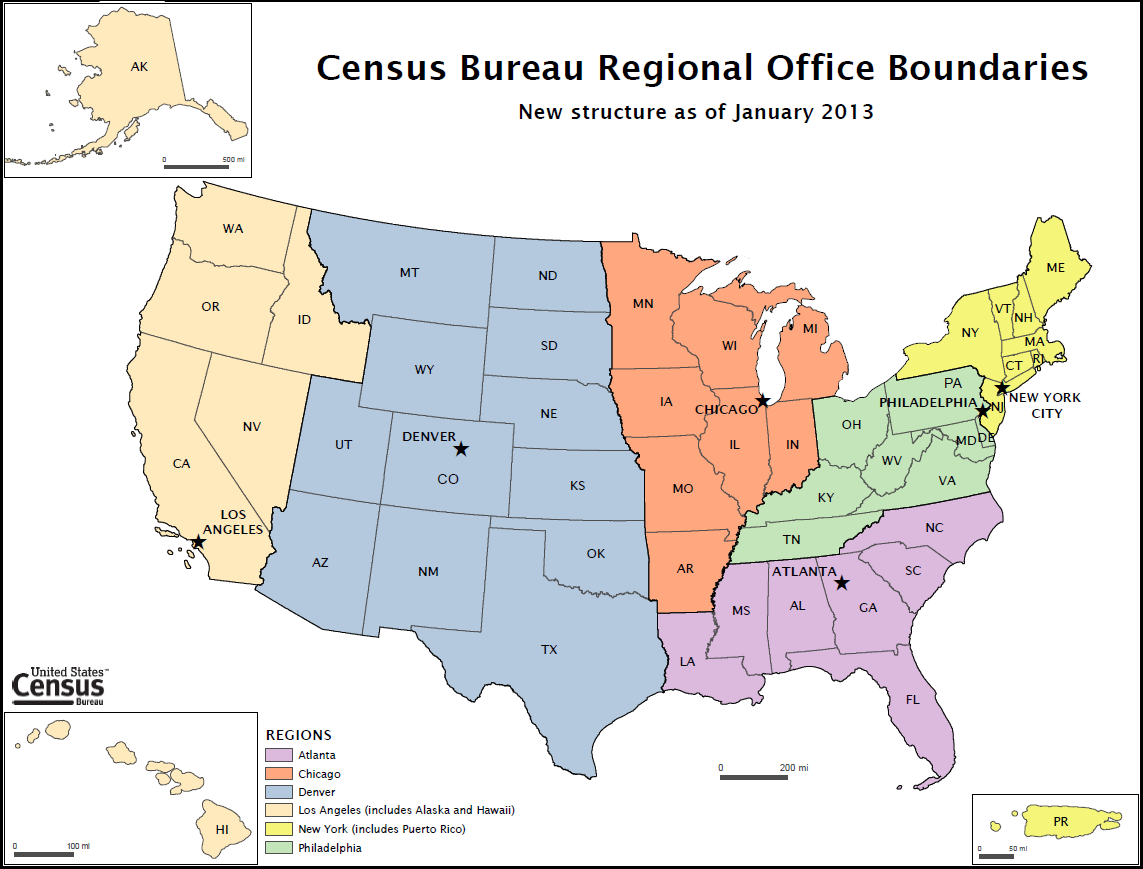
The Census Bureau headquarters has been in Suitland, Maryland, since 1942. A new headquarters complex completed there in 2007 supports over 4,000 employees. The bureau operates regional offices in 6 cities:
Since 1903, the official census-taking agency of the United States government has been the Bureau of the Census. The Census Bureau is headed by a director, assisted by a deputy director and an executive staff composed of the associate directors.
The Census Bureau headquarters has been in Suitland, Maryland, since 1942. A new headquarters complex completed there in 2007 supports over 4,000 employees. The bureau operates regional offices in 6 cities:
 The 1890 census was the first to use the electric tabulating machines invented by
The 1890 census was the first to use the electric tabulating machines invented by
United States Census Bureau
Census Bureau
in the Federal Register
USCB population estimates
USCB History
* * * ;72-year rule
PDF of Availability of Census Records About Individuals
PDF of Letter from Census Bureau Director, Roy V. Peel to Archivist of the United States, Wayne C. Grover, concerning the 72-year lapse between collection and release of decennial census records
PDF of Letter from Archivist of the United States, Wayne C. Grover to Census Bureau Director Roy V. Peel, in reply to Peel's August 1952 letter
{{Authority control 1903 establishments in Washington, D.C. United States census Government agencies established in 1903 National statistical services Organizations based in Washington, D.C. Statistical organizations in the United States Federal Statistical System of the United States
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
and economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
. The Census Bureau is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce
The United States Department of Commerce is an executive department of the U.S. federal government concerned with creating the conditions for economic growth and opportunity. Among its tasks are gathering economic and demographic data for busin ...
and its director
Director may refer to:
Literature
* ''Director'' (magazine), a British magazine
* ''The Director'' (novel), a 1971 novel by Henry Denker
* ''The Director'' (play), a 2000 play by Nancy Hasty
Music
* Director (band), an Irish rock band
* ''D ...
is appointed by the President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
.
The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the U.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
to the states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses make informed decisions. The information provided by the census informs decisions on where to build and maintain schools, hospitals, transportation infrastructure, and police and fire departments.
In addition to the decennial census, the Census Bureau continually conducts over 130 surveys and programs a year, including the American Community Survey, the U.S. Economic Census, and the Current Population Survey
The Current Population Survey (CPS) is a monthly survey of about 60,000 U.S. households conducted by the United States Census Bureau for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS uses the data to publish reports early each month called the Em ...
.USCB DOC-D1026 QVC Manual 01/03/09 Furthermore, economic and foreign trade indicators released by the federal government typically contain data produced by the Census Bureau.
Legal mandate
 Article One of the United States Constitution (section II) directs the
Article One of the United States Constitution (section II) directs the population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
be enumerated at least once every ten years and the resulting counts used to set the number of members from each state in the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
and, by extension, in the Electoral College. The Census Bureau now conducts a full population count every ten years in years ending with a zero and uses the term " decennial" to describe the operation. Between censuses, the Census Bureau makes population estimates and projections.
In addition, Census data directly affects how more than $400 billion per year in federal and state funding is allocated to communities for neighborhood improvements, public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
, education, transportation and more. The Census Bureau is mandated with fulfilling these obligations: the collecting of statistics about the nation, its people, and economy. The Census Bureau's legal authority is codified in Title 13 of the United States Code
Title 13 of the United States Code outlines the role of the United States Census in the United States Code.
Chapters
* : Administration
* : Collection and Publication of Statistics
* : Censuses
* : Offenses and Penalties
* : Collection and ...
.
The Census Bureau also conducts surveys on behalf of various federal government and local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
agencies on topics such as employment, crime, health, consumer expenditures, and housing. Within the bureau, these are known as "demographic surveys" and are conducted perpetually between and during decennial (10-year) population counts. The Census Bureau also conducts economic surveys of manufacturing, retail, service, and other establishments and of domestic governments.
Between 1790 and 1840, the census was taken by marshals
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
of the judicial districts
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
. The Census Act of 1840 established a central office which became known as the Census Office. Several acts followed that revised and authorized new censuses, typically at the 10-year intervals. In 1902, the temporary Census Office was moved under the Department of Interior, and in 1903 it was renamed the Census Bureau under the new Department of Commerce and Labor
The United States Department of Commerce and Labor was a short-lived Cabinet department of the United States government, which was concerned with fostering and supervising big business.
Origins and establishment
Calls in the United States for ...
. The department was intended to consolidate overlapping statistical agencies, but Census Bureau officials were hindered by their subordinate role in the department.
An act in 1920 changed the date and authorized manufacturing censuses every two years and agriculture censuses every 10 years. In 1929, a bill was passed mandating the House of Representatives be reapportioned based on the results of the 1930 Census.History 1920. US Census Bureau. In 1954, various acts were codified into Title 13 of the U.S. Code. By law, the Census Bureau must count everyone and submit state population totals to the U.S. President by December 31 of any year ending in a zero. States within the Union receive the results in the spring of the following year.
Data collection
Census regions and divisions
The United States Census Bureau defines four statistical regions, with nine divisions. The Census Bureau regions are "widely used...for data collection and analysis"."The National Energy Modeling System: An Overview 2003" (Report #:DOE/EIA-0581, October 2009). United States Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration. The Census Bureau definition is pervasive. Regional divisions used by the United States Census Bureau: * Region 1:Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
** Division 1: New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
(Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont)
** Division 2: Mid-Atlantic (New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania)
* Region 2: Midwest (Prior to June 1984, the Midwest Region was designated as the North Central Region.)
** Division 3: East North Central (Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin)
** Division 4: West North Central (Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota)
* Region 3: South
** Division 5: South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
(Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, Washington D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
, and West Virginia)
** Division 6: East South Central (Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Tennessee)
** Division 7: West South Central (Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas)
* Region 4: West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
** Division 8: Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually highe ...
(Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming)
** Division 9: Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
(Alaska, California, Hawaii, Oregon, and Washington)
The current system was introduced for the 1910 census, but other ways of grouping states were used historically by the Census Bureau. The first of these was introduced after the 1850 census by statistician and later census superintendent J. D. B. De Bow. He published a compendium where the states and territories were grouped into five "great division", namely the Middle, New England, the Northwestern, the Southern, and the Southwestern. Unsatisfied with this system, De Bow devised another one four years later, with states and territories grouped into an Eastern, Interior, and Western "great section", each divided into a northern and southern half called "great divisions". In the following decades, several other systems were used, until the current one was introduced in 1910. This system has seen only minor changes: The North region was divided into a Northeast and a North Central region in 1940, Alaska and Hawaii were both added to the Pacific division in the West region upon statehood in 1959, and the North Central region was renamed the Midwest in 1984.
Uses of census data
Many federal, state, local and tribal governments use census data to: * Decide the location of new housing and public facilities, * Examine the demographic characteristics of communities, states, and the US, * Plan transportation systems and roadways, * Determine quotas and creation of police and fire precincts, and * Create localized areas for elections, schools, utilities, etc. * Gathers population information every 10 yearsData stewardship
The United States Census Bureau is committed to confidentiality and guarantees non-disclosure of any addresses or personal information related to individuals or establishments. Title 13 of theU.S. Code
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the ...
establishes penalties for the disclosure of this information. All Census employees must sign an affidavit
An ( ; Medieval Latin for "he has declared under oath") is a written statement voluntarily made by an ''affiant'' or '' deponent'' under an oath or affirmation which is administered by a person who is authorized to do so by law. Such a stateme ...
of non-disclosure prior to employment.
The bureau cannot share responses, addresses or personal information with anyone, including the United States or foreign governments, or law enforcement agencies such as the IRS
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service for the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting U.S. federal taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax ...
or the FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
or Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cri ...
. "Providing quality data, for public good—while respecting individual privacy and, at the same time, protecting confidentiality—is the Census Bureau's core responsibility"; "Keeping the public's trust is critical to the Census's ability to carry out the mission as the leading source of quality data about the Nation's people and economy." Only after 72 years does the information collected become available to other agencies or the general public. Seventy-two years was picked because usually by 72 years since the census is taken, most participants would be deceased.
Despite these guarantees of confidentiality, the Census Bureau has some history of disclosures to other government agencies. In 1918, the Census Bureau released individual information regarding several hundred young men to the Justice Department and Selective Service
The Selective Service System (SSS) is an independent agency of the United States government that maintains information on U.S. citizens and other U.S. residents potentially subject to military conscription (i.e., the draft) and carries out contin ...
system for the purpose of prosecutions for draft evasion. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the United States Census Bureau assisted the government's Japanese American internment efforts by providing confidential neighborhood information on Japanese-Americans
are Americans of Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 census, they have declined in number to constitute the sixth largest Asi ...
. The bureau's role was denied for decades but was finally proven in 2007.
United States census data are valuable for the country's political parties; Democrats and Republicans are highly interested in knowing the accurate number of persons in their respective districts. These insights are often linked to financial and economic strategies that are central to federal, state and city investments for locations of particular populations. Such apportionments are designed to distribute political power across neutral spatial allocations; however, "because so much is at stake, the census also runs the risk of being politicized."
Such political tensions highlight the complexity of identity
Identity may refer to:
* Identity document
* Identity (philosophy)
* Identity (social science)
* Identity (mathematics)
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Identity'' (1987 film), an Iranian film
* ''Identity'' (2003 film), ...
and classification; some argue that unclear results from the population data "is due to distortions brought about by political pressures." One frequently used example includes ambiguous ethnic counts, which often involves underenumeration and/or undercounting of minority populations. Ideas about race, ethnicity and identity have also evolved in the United States, and such changes warrant examination of how these shifts have impacted the accuracy of census data over time.
The United States Census Bureau began pursuing technological innovations to improve the precision of its census data collection in the 1980s. Robert W. Marx, the Chief of the Geography Division of the USCB teamed up with the U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
and oversaw the creation of the Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing
Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing, or TIGER, or TIGER/Line is a format used by the United States Census Bureau to describe land attributes such as roads, buildings, rivers, and lakes, as well as areas such as census tra ...
(TIGER) database system. Census officials were able to evaluate the more sophisticated and detailed results that the TIGER system produced; furthermore, TIGER data is also available to the public. And while the TIGER system does not directly amass demographic data, as a geographic information system (GIS), it can be used to merge demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
to conduct more accurate geospatial and mapping analysis.
In July 2019 the Census Bureau deprecated American FactFinder, which was decommissioned in March 2020 after 20 years of being the agency's primary tool for data dissemination. The new platform is data.census.gov.
Ongoing surveys
Throughout the decade between censuses, the bureau conducts surveys to produce a general view and comprehensive study of the United States' social and economic conditions. Staff from the Current Surveys Program conduct over 130 ongoing and special surveys about people and their characteristics. A network of professional field representatives gathers information from a sample of households, responding to questions about employment, consumer expenditures, health, housing, and other topics. Surveys conducted between decades:Other surveys conducted
The Census Bureau collects information in many other surveys and provides the data to the survey sponsor for release. These sponsors include: * Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) * Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) *Bureau of Transportation Statistics
The Bureau of Transportation Statistics (BTS), part of the United States Department of Transportation, is a government office that compiles, analyzes, and publishes information on the nation's transportation systems across various modes; and str ...
(BTS)
* Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
* National Center for Education Statistics (NCES)
* National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS)
* National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
(NSF)
* Social Security Administration
The United States Social Security Administration (SSA) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that administers Social Security, a social insurance program consisting of retirement, disability and survivor benefits. To qualify ...
(SSA)
Organizational structure
 Since 1903, the official census-taking agency of the United States government has been the Bureau of the Census. The Census Bureau is headed by a director, assisted by a deputy director and an executive staff composed of the associate directors.
The Census Bureau headquarters has been in Suitland, Maryland, since 1942. A new headquarters complex completed there in 2007 supports over 4,000 employees. The bureau operates regional offices in 6 cities:
Since 1903, the official census-taking agency of the United States government has been the Bureau of the Census. The Census Bureau is headed by a director, assisted by a deputy director and an executive staff composed of the associate directors.
The Census Bureau headquarters has been in Suitland, Maryland, since 1942. A new headquarters complex completed there in 2007 supports over 4,000 employees. The bureau operates regional offices in 6 cities: New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
, Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, and Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
. The National Processing Center is in Jeffersonville, Indiana. Additional temporary processing facilities facilitate the decennial census, which employs more than a million people. The cost of the 2000 Census was $4.5 billion. During the years just prior to the decennial census, parallel census offices, known as "Regional Census Centers" are opened in the field office cities. The decennial operations are carried out from these facilities. The Regional Census Centers oversee the openings and closings of smaller "Area Census Offices" within their collection jurisdictions. In 2020, Regional Census Centers oversaw the operation of 248 Area Census Offices, The estimated cost of the 2010 Census is $14.7 billion.
On January 1, 2013, the Census Bureau consolidated its twelve regional offices into six. Increasing costs of data collection, changes in survey management tools such as laptops and the increasing use of multi-modal surveys (i.e. internet, telephone, and in-person) led the Bureau to consolidate. The six regional offices that closed were Boston, Charlotte, Dallas, Detroit, Kansas City and Seattle. The remaining regional offices are New York City, Philadelphia, Chicago, Atlanta, Denver, and Los Angeles.
The Census Bureau also runs the Census Information Center cooperative program that involves 58 "national, regional, and local non-profit organizations". The CIC program aims to represent the interests of underserved communities.
Computer equipment
 The 1890 census was the first to use the electric tabulating machines invented by
The 1890 census was the first to use the electric tabulating machines invented by Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, i ...
. For 1890–1940 details, see In 1946, knowing of the bureau's funding of Hollerith and, later, Powers, John Mauchly
John William Mauchly (August 30, 1907 – January 8, 1980) was an American physicist who, along with J. Presper Eckert, designed ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, as well as EDVAC, BINAC and UNIVAC I, the first ...
approached the bureau about early funding for UNIVAC
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company an ...
development. A UNIVAC I
The UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer design for business application produced in the United States. It was designed principally by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, the inven ...
computer was accepted by the bureau in 1951.
Handheld computers (HHC)
Historically, the census information was gathered by census takers going door-to-door collecting information in a ledger. Beginning in 1970 information was gathered via mailed forms. To reduce paper usage, reduce payroll expense and acquire the most comprehensive list of addresses ever compiled, 500,000 handheld computers (HHCs) (specifically designed, single-purpose devices) were used for the first time in 2009 during the address canvassing portion of the 2010 Decennial Census Project. Projected savings were estimated to be over $1 billion.Security precautions
The HHC was manufactured by Harris Corporation, an establishedDepartment of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
contractor, via a controversial contract with the Department of Commerce. Secured access via a fingerprint swipe guaranteed only the verified user could access the unit. A GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
capacity was integral to the daily address management and the transfer of gathered information. Of major importance was the security and integrity of the populace's private information.
Success and failure
Enumerators (information gatherers) that had operational problems with the device understandably made negative reports. During the 2009 Senate confirmation hearings forRobert Groves
Robert Martin Groves (born September 27, 1948) is an American sociologist and expert in survey methodology who has served as the Provost of Georgetown University in Washington, D.C. since August 2012. He also served as the Director of the Un ...
, President Obama's Census Director appointee, there was much mention of problems but very little criticism of the units. In rural areas, the sparsity of cell phone towers caused problems with data transmission to and from the HHC. Since the units were updated nightly with important changes and updates, operator implementation of proper procedure was imperative.
Notable alumni
* John Shaw Billings *Rattan Chand
Rattan Chand is an Indian former senior bureaucrat who has served Government of India at various positions for more than 35 years. Apart from working at senior positions in Government of India he has also been a resource person to USAID, World ...
* W. Edwards Deming
William Edwards Deming (October 14, 1900 – December 20, 1993) was an American engineer, statistician, professor, author, lecturer, and management consultant. Educated initially as an electrical engineer and later specializing in mathematical ...
* Davis Rich Dewey
Davis Rich Dewey (April 7, 1858December 13, 1942) was an American economist and statistician.
He was born at Burlington, Vermont. Like his well-known younger brother, John Dewey, he was educated at the University of Vermont and Johns Hopkins Unive ...
* Halbert L. Dunn
Halbert L. Dunn, Doctor of Medicine, M.D. (1896–1975) was the leading figure in establishing a national vital statistics (government records), vital statistics system in the United States and is known as the "father of the Wellness (alternative ...
* Murray Feshbach
Murray Feshbach (August 8, 1929 – October 25, 2019) was an American scholar focusing on the demographics of the Soviet Union and demographics of Russia, including population, health, and environment. He was a Senior Scholar at the Woodrow Wils ...
* Robert Groves
Robert Martin Groves (born September 27, 1948) is an American sociologist and expert in survey methodology who has served as the Provost of Georgetown University in Washington, D.C. since August 2012. He also served as the Director of the Un ...
* Henry Gannett
Henry Gannett (August 24, 1846 – November 5, 1914) was an American geographer who is described as the "father of mapmaking in America."Evans, Richard Tranter; Frye, Helen M. (2009).History of the Topographic Branch (Division) (PDF). ''U.S. Geo ...
* Morris H. Hansen
Morris Howard Hansen (1910–1990) was an American statistician. While at the United States Census Bureau, he was one of the first to develop methods for statistical sampling and made contributions in many areas of surveys and censuses.
Biogra ...
* Joseph Adna Hill
Joseph Adna Hill (1860–1938) was an American statistician, born at Stewartstown, New Hampshire. Hill was descended from "an elite, old-line New England family," and attended many well-regarded educational institutions: after graduating from ...
* Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, i ...
* Leslie Kish
Leslie Kish (born László Kiss, July 27, 1910 – October 7, 2000) was a Hungarian-American statistician and survey methodologist.. Reprint of an obituary from ''International Statistical Institute (ISI) Newsletter'', Volume 25, No. 73.
Life a ...
* John Wesley Langley
* Bernard Malamud
Bernard Malamud (April 26, 1914 – March 18, 1986) was an American novelist and short story writer. Along with Saul Bellow, Joseph Heller, and Philip Roth, he was one of the best known American Jewish authors of the 20th century. His baseba ...
* Thomas Commerford Martin
Thomas Commerford Martin (July 22, 1856 – May 17, 1924) was an American electrical engineer and editor.
Martin was born in Limehouse, England. His father worked with Lord Kelvin and other pioneers of submarine telegraph cables, and Martin worke ...
* Warren Mitofsky
Warren J. Mitofsky (September 17, 1934 – September 1, 2006) was an American political pollster.
Mitofsky graduated in 1957 from Guilford College and was executive director of the CBS News election and survey unit from 1967 to 1990. He also prev ...
* Ivan Petrof
Ivan Petrof (1842? - 1896) (commonly spelled "Petroff" in sources) was a Russian-born soldier, writer, and translator who for many years was regarded as a major authority on Alaska. According to historian Terrence Cole, Petrof "holds the distinc ...
* Cyrus Guernsey Pringle
Cyrus Guernsey Pringle (May 6, 1838 – May 25, 1911) was an American botanist who spent a career of 35 years cataloguing the plants of North America. He was a prolific collector and accomplished botanical explorer.
Early life
He was born on M ...
* Richard M. Scammon
Richard Montgomery Scammon (July 17, 1915 – April 27, 2001) was an American author, political scientist and elections scholar. He served as Director of the U.S. Bureau of the Census from 1961 to 1965. Afterwards, he worked for decades direc ...
* Thelma Strabel
* Howard Sutherland
Howard Sutherland (September 8, 1865March 12, 1950) was an American politician. He was a Republican who represented West Virginia in both houses of the United States Congress.
Sutherland was born near Kirkwood, Missouri. He lived in Missouri un ...
See also
*List of U.S. states and territories by population
The states and territories included in the United States Census Bureau's statistics for the United States (population, ethnicity, religion, and most other categories) include the 50 states and the District of Columbia ( Washington, D.C.). Sep ...
* List of metropolitan statistical areas
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
* List of United States cities by population
This is a list of the most populous incorporated places of the United States. As defined by the United States Census Bureau, an "incorporated place" includes a variety of designations, including city, town, village, borough, and municipal ...
* List of United States counties and county equivalents
This article lists the 3,243 counties and county equivalents of the United States. The 50 states of the United States are divided into 3,007 ''counties'', political and geographic subdivisions of a state; 236 other local governments and geographi ...
* United States Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
**Primary statistical area
The United States federal government defines and delineates the nation's metropolitan areas for statistical purposes, using a set of standard statistical area definitions. the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) defined and delineated 39 ...
(list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
)
**Combined statistical area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
(list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
)
** Core-based statistical area (list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
)
***Metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
(list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
)
*** Micropolitan statistical area (list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
)
** List of United States urban areas
This is a list of urban areas in the United States as defined by the United States Census Bureau, ordered according to their 2010 census populations. An ''urbanized area'' (UA) is an urban area with population of 50,000 or more; an ''urban cluste ...
* PATCOB
PATCOB (Professional, Administrative, Technical, Clerical, Other white collar, and Blue collar) are occupational categories established by Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). They are used for statistical reporting on data collected by ...
* Title 13 of the United States Code
Title 13 of the United States Code outlines the role of the United States Census in the United States Code.
Chapters
* : Administration
* : Collection and Publication of Statistics
* : Censuses
* : Offenses and Penalties
* : Collection and ...
* Title 15 of the Code of Federal Regulations Title 15 is the portion of the Code of Federal Regulations that governs Commerce and Foreign Trade within the United States. It is available in digital or printed form.
Title 15 comprises three volumes, and is divided into four Subtitles:
* Subtit ...
* Director of the United States Census Bureau
The Director of the Bureau of the Census is the chief administrator of the United States Census Bureau (USCB). The officeholder is appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate and assisted by the Deput ...
* Data.gov
Data.gov is a U.S. Government website launched in late May 2009 by the Federal Chief Information Officer (CIO) of the United States, Vivek Kundra. Data.gov aims to improve public access to high value, machine readable datasets generated by t ...
* USAFacts
USAFacts is a non-profit organization and website that provides data and reports on the United States population, its government's finances, and government's impact on society. It was launched in 2017.
History and background
USAFacts was fou ...
References
External links
United States Census Bureau
Census Bureau
in the Federal Register
USCB population estimates
USCB History
* * * ;72-year rule
PDF of Availability of Census Records About Individuals
PDF of Letter from Census Bureau Director, Roy V. Peel to Archivist of the United States, Wayne C. Grover, concerning the 72-year lapse between collection and release of decennial census records
PDF of Letter from Archivist of the United States, Wayne C. Grover to Census Bureau Director Roy V. Peel, in reply to Peel's August 1952 letter
{{Authority control 1903 establishments in Washington, D.C. United States census Government agencies established in 1903 National statistical services Organizations based in Washington, D.C. Statistical organizations in the United States Federal Statistical System of the United States