Ulysses (spacecraft) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Ulysses'' ( , ) was a robotic space probe whose primary mission was to orbit the Sun and study it at all latitudes. It was launched in 1990 and made three "fast latitude scans" of the Sun in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2007/2008. In addition, the probe studied several comets. ''Ulysses'' was a joint venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the United States'
 The spacecraft was designed by ESA and built by Dornier Systems, a German aircraft manufacturer. The body was roughly a box, approximately in size. The box mounted the dish antenna and the GPHS-RTG radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) power source. The box was divided into noisy and quiet sections. The noisy section abutted the RTG; the quiet section housed the instrument electronics. Particularly "loud" components, such as the preamps for the radio dipole, were mounted outside the structure entirely, and the box acted as a Faraday cage.
''Ulysses'' was spin-stabilised about its z-axis which roughly coincides with the axis of the dish antenna. The RTG, whip antennas, and instrument boom were placed to stabilize this axis, with the spin rate nominally at 5 rpm. Inside the body was a
The spacecraft was designed by ESA and built by Dornier Systems, a German aircraft manufacturer. The body was roughly a box, approximately in size. The box mounted the dish antenna and the GPHS-RTG radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) power source. The box was divided into noisy and quiet sections. The noisy section abutted the RTG; the quiet section housed the instrument electronics. Particularly "loud" components, such as the preamps for the radio dipole, were mounted outside the structure entirely, and the box acted as a Faraday cage.
''Ulysses'' was spin-stabilised about its z-axis which roughly coincides with the axis of the dish antenna. The RTG, whip antennas, and instrument boom were placed to stabilize this axis, with the spin rate nominally at 5 rpm. Inside the body was a
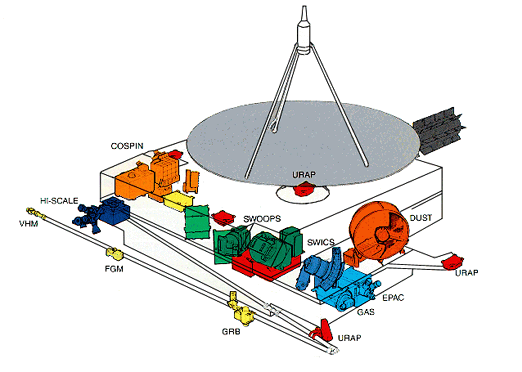
 The twelve different Instruments came from ESA and NASA. The first design was based on two probes, one by NASA and one by ESA, but the probe of NASA was defunded and in the end the instruments of the cancelled probe were mounted on Ulyssses.
* Radio/Plasma antennas: Two beryllium copper antennas were unreeled outwards from the body, perpendicular to the RTG and spin axis. Together this dipole spanned 72 meters (236.2 ft). A third antenna, of hollow beryllium copper, was deployed from the body, along the spin axis opposite the dish. It was a monopole antenna, 7.5 meters (24.6 ft) long. These measured radio waves generated by plasma releases, or the plasma itself as it passed over the spacecraft. This receiver ensemble was sensitive from DC to 1 MHz.
* Experiment Boom: A third type of boom, shorter and much more rigid, extended from the last side of the spacecraft, opposite the RTG. This was a hollow carbon-fiber tube, of 50 mm (2 in.) diameter. It can be seen in the photo as the silver rod stowed alongside the body. It carried four types of instruments: a solid-state X-ray instrument, composed of two silicon detectors, to study X-rays from solar flares and Jupiter's aurorae; the Gamma-Ray Burst experiment, consisting of two CsI scintillator crystals with photomultipliers; two different
The twelve different Instruments came from ESA and NASA. The first design was based on two probes, one by NASA and one by ESA, but the probe of NASA was defunded and in the end the instruments of the cancelled probe were mounted on Ulyssses.
* Radio/Plasma antennas: Two beryllium copper antennas were unreeled outwards from the body, perpendicular to the RTG and spin axis. Together this dipole spanned 72 meters (236.2 ft). A third antenna, of hollow beryllium copper, was deployed from the body, along the spin axis opposite the dish. It was a monopole antenna, 7.5 meters (24.6 ft) long. These measured radio waves generated by plasma releases, or the plasma itself as it passed over the spacecraft. This receiver ensemble was sensitive from DC to 1 MHz.
* Experiment Boom: A third type of boom, shorter and much more rigid, extended from the last side of the spacecraft, opposite the RTG. This was a hollow carbon-fiber tube, of 50 mm (2 in.) diameter. It can be seen in the photo as the silver rod stowed alongside the body. It carried four types of instruments: a solid-state X-ray instrument, composed of two silicon detectors, to study X-rays from solar flares and Jupiter's aurorae; the Gamma-Ray Burst experiment, consisting of two CsI scintillator crystals with photomultipliers; two different


 Until ''Ulysses'', the Sun had only been observed from low solar latitudes. The Earth's orbit defines the ecliptic plane, which differs from the Sun's equatorial plane by only 7.25°. Even spacecraft directly orbiting the Sun do so in planes close to the ecliptic because a direct launch into a high-inclination solar orbit would require a prohibitively large launch vehicle.
Several spacecraft (
Until ''Ulysses'', the Sun had only been observed from low solar latitudes. The Earth's orbit defines the ecliptic plane, which differs from the Sun's equatorial plane by only 7.25°. Even spacecraft directly orbiting the Sun do so in planes close to the ecliptic because a direct launch into a high-inclination solar orbit would require a prohibitively large launch vehicle.
Several spacecraft (
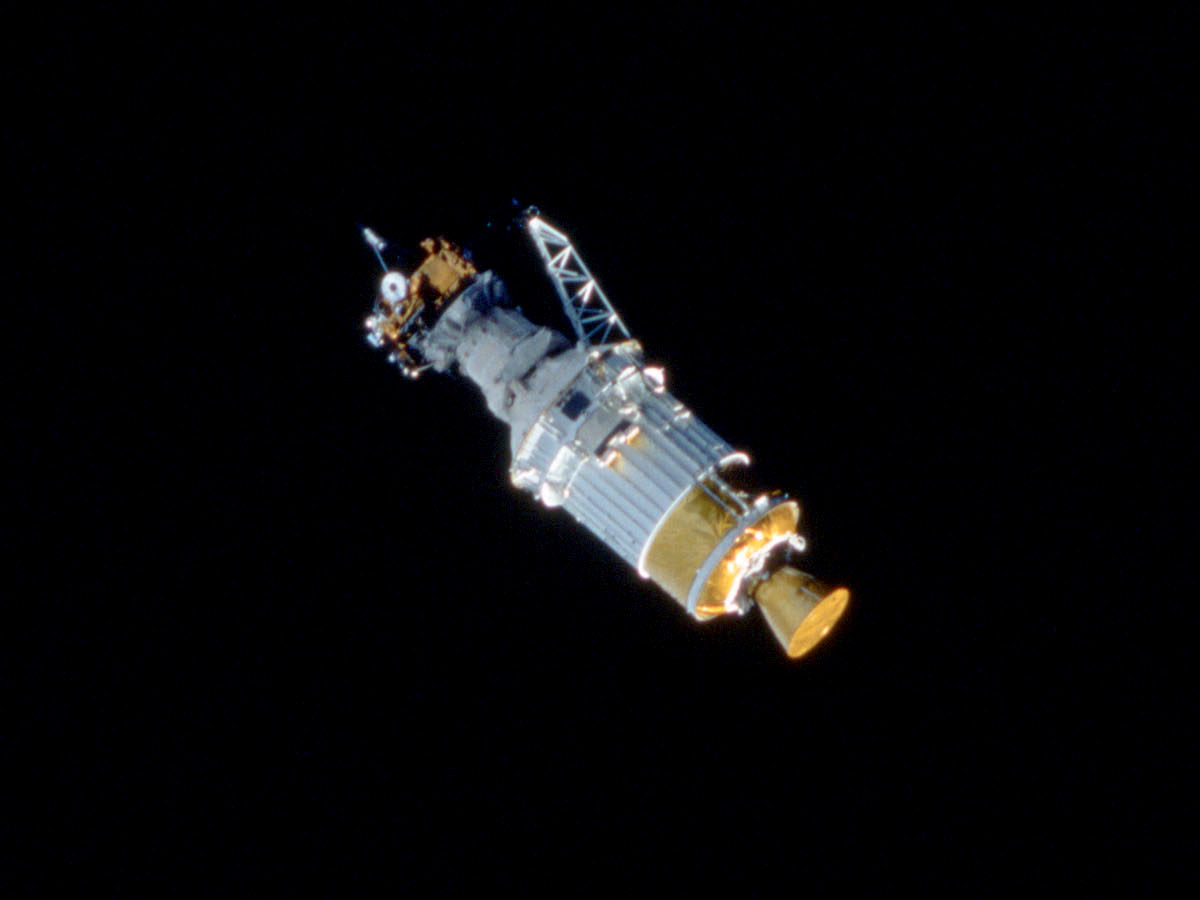 ''Ulysses'' was deployed into low Earth orbit from the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. From there, it was propelled on a trajectory to Jupiter by a combination of solid rocket motors. This upper stage consisted of a two-stage
''Ulysses'' was deployed into low Earth orbit from the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. From there, it was propelled on a trajectory to Jupiter by a combination of solid rocket motors. This upper stage consisted of a two-stage
 It arrived at Jupiter on 8 February 1992 for a
It arrived at Jupiter on 8 February 1992 for a
/ref>
/ref>
 ESA's Science Program Committee approved the fourth extension of the ''Ulysses'' mission to March 2004 thereby allowing it to operate over the Sun's poles for the third time in 2007 and 2008. After it became clear that the power output from the spacecraft's RTG would be insufficient to operate science instruments and keep the attitude control fuel,
ESA's Science Program Committee approved the fourth extension of the ''Ulysses'' mission to March 2004 thereby allowing it to operate over the Sun's poles for the third time in 2007 and 2008. After it became clear that the power output from the spacecraft's RTG would be insufficient to operate science instruments and keep the attitude control fuel,
 During cruise phases, ''Ulysses'' provided unique data. As the only spacecraft out of the ecliptic with a gamma-ray instrument, ''Ulysses'' was an important part of the InterPlanetary Network (IPN). The IPN detects gamma ray bursts (GRBs); since gamma rays cannot be focused with mirrors, it was very difficult to locate GRBs with enough accuracy to study them further. Instead, several spacecraft can locate the burst through multilateration. Each spacecraft has a gamma-ray detector, with readouts noted in tiny fractions of a second. By comparing the arrival times of gamma showers with the separations of the spacecraft, a location can be determined, for follow-up with other telescopes. Because gamma rays travel at the speed of light, wide separations are needed. Typically, a determination came from comparing: one of several spacecraft orbiting the Earth, an inner-Solar-system probe (to Mars, Venus, or an
During cruise phases, ''Ulysses'' provided unique data. As the only spacecraft out of the ecliptic with a gamma-ray instrument, ''Ulysses'' was an important part of the InterPlanetary Network (IPN). The IPN detects gamma ray bursts (GRBs); since gamma rays cannot be focused with mirrors, it was very difficult to locate GRBs with enough accuracy to study them further. Instead, several spacecraft can locate the burst through multilateration. Each spacecraft has a gamma-ray detector, with readouts noted in tiny fractions of a second. By comparing the arrival times of gamma showers with the separations of the spacecraft, a location can be determined, for follow-up with other telescopes. Because gamma rays travel at the speed of light, wide separations are needed. Typically, a determination came from comparing: one of several spacecraft orbiting the Earth, an inner-Solar-system probe (to Mars, Venus, or an
ESA ''Ulysses'' website
ESA ''Ulysses'' mission operations website
ESA ''Ulysses'' Home page
NASA/JPL ''Ulysses'' website
''Ulysses'' Measuring Mission Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060928042857/http://ulysses-ops.jpl.esa.int/ulsfct/rgpCafe/solsys/solsys.html Where is ''Ulysses' now!
Max Planck Institute ''Ulysses'' website
Interview with ''Ulysses'' Mission Operations Manager Nigel Angold on Planetary Radio
Interactive 3D visualisation of Ulysses Jupiter gravity assist and polar orbit around the Sun
{{Authority control European Space Agency space probes NASA space probes Missions to the Sun Missions to Jupiter Derelict satellites in heliocentric orbit Missions to comets Spacecraft launched by the Space Shuttle Derelict space probes Spacecraft launched in 1990 Spacecraft decommissioned in 2009 Solar space observatories
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA), under leadership of ESA with participation from Canada's National Research Council. The last day for mission operations on ''Ulysses'' was 30 June 2009.
To study the Sun at all latitudes, the probe needed to change its orbital inclination and leave the plane of the Solar System. To change the orbital inclination of a spacecraft to about 80° requires a large change in heliocentric velocity, the energy to achieve which far exceeded the capabilities of any launch vehicle. To reach the desired orbit around the Sun, the mission's planners chose a gravity assist maneuver around Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...
, but this Jupiter encounter meant that ''Ulysses'' could not be powered by solar cells. The probe was powered instead by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG).
The spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ...
was originally named ''Odysseus'', because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to study the solar poles. It was renamed ''Ulysses'', the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
translation of "Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odysse ...
", at ESA's request in honor not only of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of ...
's mythological hero but also of Dante's character in the ''Inferno''. ''Ulysses'' was originally scheduled for launch in May 1986 aboard the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' on STS-61-F
STS-61-F was a NASA Space Shuttle mission planned to launch on 15 May 1986 using ''Challenger''. It was canceled after ''Challenger'' was destroyed earlier that year.
Crew
Mission objectives
The main objective of STS-61-F was to deploy ...
. Due to the 28 January 1986 loss of ''Challenger'', the launch of ''Ulysses'' was delayed until 6 October 1990 aboard ''Discovery'' (mission STS-41).
Spacecraft
 The spacecraft was designed by ESA and built by Dornier Systems, a German aircraft manufacturer. The body was roughly a box, approximately in size. The box mounted the dish antenna and the GPHS-RTG radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) power source. The box was divided into noisy and quiet sections. The noisy section abutted the RTG; the quiet section housed the instrument electronics. Particularly "loud" components, such as the preamps for the radio dipole, were mounted outside the structure entirely, and the box acted as a Faraday cage.
''Ulysses'' was spin-stabilised about its z-axis which roughly coincides with the axis of the dish antenna. The RTG, whip antennas, and instrument boom were placed to stabilize this axis, with the spin rate nominally at 5 rpm. Inside the body was a
The spacecraft was designed by ESA and built by Dornier Systems, a German aircraft manufacturer. The body was roughly a box, approximately in size. The box mounted the dish antenna and the GPHS-RTG radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) power source. The box was divided into noisy and quiet sections. The noisy section abutted the RTG; the quiet section housed the instrument electronics. Particularly "loud" components, such as the preamps for the radio dipole, were mounted outside the structure entirely, and the box acted as a Faraday cage.
''Ulysses'' was spin-stabilised about its z-axis which roughly coincides with the axis of the dish antenna. The RTG, whip antennas, and instrument boom were placed to stabilize this axis, with the spin rate nominally at 5 rpm. Inside the body was a hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
fuel tank. Hydrazine monopropellant was used for course corrections inbound to Jupiter, and later used exclusively to repoint the spin axis (and thus, the antenna) at Earth. The spacecraft was controlled by eight thrusters in two blocks. Thrusters were pulsed in the time domain to perform rotation or translation. Four sun sensors detected orientation. For fine attitude control, the S-band antenna feed was mounted slightly off-axis. This offset feed combined with the spacecraft spin introduced an apparent oscillation to a radio signal transmitted from Earth when received on board the spacecraft. The amplitude and phase of this oscillation were proportional to the orientation of the spin axis relative to the Earth direction. This method of determining the relative orientation is called conical scanning and was used by early radars for automated tracking of targets and was also very common in early infrared guided missiles.
The spacecraft used S-band for uplinked commands and downlinked telemetry, through dual redundant 5-watt transceivers. The spacecraft used X-band for science return (downlink only), using dual 20 watts TWTAs until the failure of the last remaining TWTA in January 2008. Both bands used the dish antenna with prime-focus feeds, unlike the Cassegrain Cassegrain may refer to
* Cassegrain reflector, a design used in telescopes
* Cassegrain antenna, a type of parabolic antenna
* Cassegrain (crater), on the Moon
* a Belgian canned vegetables producer now part of Bonduelle S.A.
People :
* Guillaume ...
feeds of most other spacecraft dishes.
Dual tape recorders, each of approximately 45-megabit capacity, stored science data between the nominal eight-hour communications sessions during the prime and extended mission phases.
The spacecraft was designed to withstand both the heat of the inner Solar System and the cold at Jupiter's distance. Extensive blanketing and electric heaters protected the probe against the cold temperatures of the outer Solar System.
Multiple computer systems (CPUs/microprocessors/Data Processing Units) are used in several of the scientific instruments, including several radiation-hardened RCA CDP1802 microprocessors. Documented 1802 usage includes dual-redundant 1802s in the COSPIN, and at least one 1802 each in the GRB, HI-SCALE, SWICS, SWOOPS and URAP instruments, with other possible microprocessors incorporated elsewhere.
Total mass at launch was , of which 33.5 kg was hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
propellant used for attitude control and orbit correction.
Instruments

 The twelve different Instruments came from ESA and NASA. The first design was based on two probes, one by NASA and one by ESA, but the probe of NASA was defunded and in the end the instruments of the cancelled probe were mounted on Ulyssses.
* Radio/Plasma antennas: Two beryllium copper antennas were unreeled outwards from the body, perpendicular to the RTG and spin axis. Together this dipole spanned 72 meters (236.2 ft). A third antenna, of hollow beryllium copper, was deployed from the body, along the spin axis opposite the dish. It was a monopole antenna, 7.5 meters (24.6 ft) long. These measured radio waves generated by plasma releases, or the plasma itself as it passed over the spacecraft. This receiver ensemble was sensitive from DC to 1 MHz.
* Experiment Boom: A third type of boom, shorter and much more rigid, extended from the last side of the spacecraft, opposite the RTG. This was a hollow carbon-fiber tube, of 50 mm (2 in.) diameter. It can be seen in the photo as the silver rod stowed alongside the body. It carried four types of instruments: a solid-state X-ray instrument, composed of two silicon detectors, to study X-rays from solar flares and Jupiter's aurorae; the Gamma-Ray Burst experiment, consisting of two CsI scintillator crystals with photomultipliers; two different
The twelve different Instruments came from ESA and NASA. The first design was based on two probes, one by NASA and one by ESA, but the probe of NASA was defunded and in the end the instruments of the cancelled probe were mounted on Ulyssses.
* Radio/Plasma antennas: Two beryllium copper antennas were unreeled outwards from the body, perpendicular to the RTG and spin axis. Together this dipole spanned 72 meters (236.2 ft). A third antenna, of hollow beryllium copper, was deployed from the body, along the spin axis opposite the dish. It was a monopole antenna, 7.5 meters (24.6 ft) long. These measured radio waves generated by plasma releases, or the plasma itself as it passed over the spacecraft. This receiver ensemble was sensitive from DC to 1 MHz.
* Experiment Boom: A third type of boom, shorter and much more rigid, extended from the last side of the spacecraft, opposite the RTG. This was a hollow carbon-fiber tube, of 50 mm (2 in.) diameter. It can be seen in the photo as the silver rod stowed alongside the body. It carried four types of instruments: a solid-state X-ray instrument, composed of two silicon detectors, to study X-rays from solar flares and Jupiter's aurorae; the Gamma-Ray Burst experiment, consisting of two CsI scintillator crystals with photomultipliers; two different magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
s, a helium vector magnetometer and a fluxgate magnetometer; and a two-axis magnetic search coil antenna measured AC magnetic fields.
* Body-Mounted Instruments: Detectors for electrons, ions, neutral gas, dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
, and cosmic rays were mounted on the spacecraft body around the quiet section.
* Lastly, the radio communications link could be used to search for gravitational waves (through Doppler shifts) and to probe the Sun's atmosphere through radio occultation. No gravitational waves were detected.
* Total instrument mass was 55 kg.
* Magnetometer (MAG): MAG measured the magnetic field in the heliosphere. Measurements of Jupiter's magnetic field were also performed.
* Solar Wind Plasma Experiment (SWOOPS): detected the solar wind at all solar distances and latitudes and in three dimensions. It measured positive ions and electrons.
* Solar Wind Ion Composition Instrument (SWICS): determined composition, temperature and speed of the atoms and ions that comprise the solar wind.
* Unified Radio and Plasma Wave Instrument (URAP): picked up radio waves from the Sun and electromagnetic waves generated in the solar wind close to the spacecraft.
* Energetic Particle Instrument (EPAC) and GAS: EPAC investigated the energy, fluxes and distribution of energetic particles in the heliosphere. GAS studied the uncharged gases (helium) of interstellar origin.
* Low-Energy Ion and Electron Experiment (HI-SCALE): investigated the energy, fluxes and distribution of energetic particles in the heliosphere.
* Cosmic Ray and Solar Particle Instrument (COSPIN): investigated the energy, fluxes and distribution of energetic particles and galactic cosmic rays in the heliosphere.
* Solar X-ray and Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst Instrument (GRB): studied cosmic gamma ray bursts and X-rays from solar flares.
* Dust Experiment (DUST): Direct measurements of interplanetary and interstellar dust grains to investigate their properties as functions of the distance from the Sun and solar latitude.
Mission
Planning


 Until ''Ulysses'', the Sun had only been observed from low solar latitudes. The Earth's orbit defines the ecliptic plane, which differs from the Sun's equatorial plane by only 7.25°. Even spacecraft directly orbiting the Sun do so in planes close to the ecliptic because a direct launch into a high-inclination solar orbit would require a prohibitively large launch vehicle.
Several spacecraft (
Until ''Ulysses'', the Sun had only been observed from low solar latitudes. The Earth's orbit defines the ecliptic plane, which differs from the Sun's equatorial plane by only 7.25°. Even spacecraft directly orbiting the Sun do so in planes close to the ecliptic because a direct launch into a high-inclination solar orbit would require a prohibitively large launch vehicle.
Several spacecraft (Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Ma ...
, Pioneer 11, and ''Voyagers 1'' and ''2'') had performed gravity assist maneuvers in the 1970s. Those maneuvers were to reach other planets also orbiting close to the ecliptic, so they were mostly in-plane changes. However, gravity assists are not limited to in-plane maneuvers; a suitable flyby of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...
could produce a significant plane change. An Out-Of-The-Ecliptic mission (OOE) was thereby proposed. ''See article'' Pioneer H.
Originally, two spacecraft were to be built by NASA and ESA, as the International Solar Polar Mission. One would be sent over Jupiter, then under the Sun. The other would fly under Jupiter, then over the Sun. This would provide simultaneous coverage. Due to cutbacks, the U.S. spacecraft was cancelled in 1981. One spacecraft was designed, and the project recast as ''Ulysses,'' due to the indirect and untried flight path. NASA would provide the Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG) and launch services, ESA would build the spacecraft assigned to Astrium GmbH, Friedrichshafen, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
(formerly Dornier Systems). The instruments would be split into teams from universities and research institutes in Europe and the United States. This process provided the 12 instruments on board.
The changes delayed launch from February 1983 to May 1986 when it was to be deployed by the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' (boosted by the proposed Centaur G Prime
Shuttle-Centaur was a version of the Centaur upper stage rocket designed to be carried aloft inside the Space Shuttle and used to launch satellites into high Earth orbits or probes into deep space. Two variants were developed: Centaur G-Prime, ...
upper stage. However, the ''Challenger'' disaster forced a two-and-a-half year stand down of the shuttle fleet, mandated the cancellation of the Centaur-G upper stage, and pushed the launch date to October 1990.
Launch
 ''Ulysses'' was deployed into low Earth orbit from the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. From there, it was propelled on a trajectory to Jupiter by a combination of solid rocket motors. This upper stage consisted of a two-stage
''Ulysses'' was deployed into low Earth orbit from the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. From there, it was propelled on a trajectory to Jupiter by a combination of solid rocket motors. This upper stage consisted of a two-stage Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
IUS
__NOTOC__
''Ius'' or ''Jus'' (Latin, plural ''iura'') in ancient Rome was a right to which a citizen (''civis'') was entitled by virtue of his citizenship ('' civitas''). The ''iura'' were specified by laws, so ''ius'' sometimes meant law. As on ...
(Inertial Upper Stage), plus a McDonnell Douglas PAM-S ( Payload Assist Module-Special). The IUS was inertially stabilised and actively guided during its burn. The PAM-S was unguided and it and ''Ulysses'' were spun up to 80 rpm for stability at the start of its burn. On burnout of the PAM-S, the motor and spacecraft stack was yo-yo de-spun (weights deployed at the end of cables) to below 8 rpm prior to separation of the spacecraft. On leaving Earth, the spacecraft became the fastest ever artificially-accelerated spacecraft, and held that title until the ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' probe was launched.
On its way to Jupiter, the spacecraft was in an elliptical non- Hohmann transfer orbit. At this time, ''Ulysses'' had a low orbital inclination to the ecliptic.
Jupiter swing-by

 It arrived at Jupiter on 8 February 1992 for a
It arrived at Jupiter on 8 February 1992 for a swing-by maneuver
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the p ...
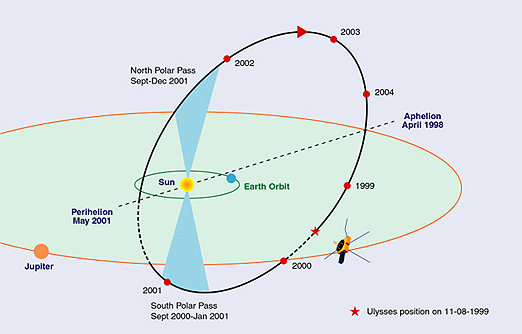
that increased its inclination to the ecliptic by 80.2°. The giant planet's gravity bent the spacecraft's flight path southward and away from the ecliptic plane. This put it into a final orbit around the Sun that would take it past the Sun's north and south poles. The size and shape of the orbit were adjusted to a much smaller degree so that aphelion remained at approximately 5 AU, Jupiter's distance from the Sun, and perihelion was somewhat greater than 1 AU, the Earth's distance from the Sun. The orbital period is approximately six years.
Polar regions of the Sun
Between 1994 and 1995 it explored both the southern and northern polar regions of the Sun, respectively.Comet C/1996 B2 (Hyakutake)
On 1 May 1996, the spacecraft unexpectedly crossed the ion tail of Comet Hyakutake (C/1996 B2), revealing the tail to be at least 3.8 AU in length.Comet C/1999 T1 (McNaught–Hartley)
An encounter with a comet tail happened again in 2004 when ''Ulysses'' flew through the ion tailings of C/1999 T1 (McNaught-Hartley). A coronal mass ejection carried the cometary material to ''Ulysses''.Ulysses Catches Another Comet by the Tail/ref>
/ref>
Second Jupiter encounter
''Ulysses'' approached aphelion in 2003/2004 and made further distant observations of Jupiter.Comet C/2006 P1 (McNaught)
In 2007, ''Ulysses'' passed through the tail of comet C/2006 P1 (McNaught). The results were surprisingly different from its pass through Hyakutake's tail, with the measured solar wind velocity dropping from approximately 700 kilometers per second (1,566,000 mph) to less than 400 kilometers per second (895,000 mph).Extended mission
 ESA's Science Program Committee approved the fourth extension of the ''Ulysses'' mission to March 2004 thereby allowing it to operate over the Sun's poles for the third time in 2007 and 2008. After it became clear that the power output from the spacecraft's RTG would be insufficient to operate science instruments and keep the attitude control fuel,
ESA's Science Program Committee approved the fourth extension of the ''Ulysses'' mission to March 2004 thereby allowing it to operate over the Sun's poles for the third time in 2007 and 2008. After it became clear that the power output from the spacecraft's RTG would be insufficient to operate science instruments and keep the attitude control fuel, hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
, from freezing, instrument power sharing was initiated. Up until then, the most important instruments had been kept online constantly, whilst others were deactivated. When the probe neared the Sun, its power-hungry heaters were turned off and all instruments were turned on.
On 22 February 2008, 17 years and 4 months after the launch of the spacecraft, ESA and NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
announced that the mission operations for ''Ulysses'' would likely cease within a few months. On 12 April 2008, NASA announced that the end date will be 1 July 2008.
The spacecraft operated successfully for over four times its design life. A component within the last remaining working chain of X-band downlink subsystem failed on 15 January 2008. The other chain in the X-band subsystem had previously failed in 2003.
Downlink to Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
resumed on S-band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional ...
, but the beamwidth of the high gain antenna in the S-band was not as narrow as in the X–band, so that the received downlink signal was much weaker, hence reducing the achievable data rate Data rate and data transfer rate can refer to several related and overlapping concepts in communications networks:
Achieved rate
* Bit rate, the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time
** Data signaling rate or gross bit rate ...
. As the spacecraft traveled on its outbound trajectory to the orbit of Jupiter, the downlink signal would have eventually fallen below the receiving capability of even the largest antennas (70 meters - 229.7 feet - in diameter) of the Deep Space Network.
Even before the downlink signal was lost due to distance, the hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
attitude control fuel on board the spacecraft was considered likely to freeze, as the radioisotope thermal generators (RTGs) failed to generate enough power for the heaters to overcome radiative heat loss into space. Once the hydrazine froze, the spacecraft would no longer be able to maneuver to keep its high gain antenna pointing towards Earth, and the downlink signal would then be lost in a matter of days. The failure of the X-band communications subsystem hastened this, because the coldest part of the fuel pipework was routed over the X-band traveling-wave tube amplifier
A traveling-wave tube (TWT, pronounced "twit") or traveling-wave tube amplifier (TWTA, pronounced "tweeta") is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. The TWT belongs t ...
s, because they generated enough heat during operation to keep the propellant plumbing warm.
The previously announced mission end date of 1 July 2008, came and went but mission operations continued albeit in a reduced capacity. The availability of science data gathering was limited to only when ''Ulysses'' was in contact with a ground station due to the deteriorating S-band downlink margin no longer being able to support simultaneous real-time data and tape recorder playback. When the spacecraft was out of contact with a ground station, the S-band transmitter was switched off and the power was diverted to the internal heaters to add to the warming of the hydrazine. On 30 June 2009, ground controllers sent commands to switch to the low gain antennas. This stopped communications with the spacecraft, in combination with previous commands to shut down its transmitter entirely.
Results
 During cruise phases, ''Ulysses'' provided unique data. As the only spacecraft out of the ecliptic with a gamma-ray instrument, ''Ulysses'' was an important part of the InterPlanetary Network (IPN). The IPN detects gamma ray bursts (GRBs); since gamma rays cannot be focused with mirrors, it was very difficult to locate GRBs with enough accuracy to study them further. Instead, several spacecraft can locate the burst through multilateration. Each spacecraft has a gamma-ray detector, with readouts noted in tiny fractions of a second. By comparing the arrival times of gamma showers with the separations of the spacecraft, a location can be determined, for follow-up with other telescopes. Because gamma rays travel at the speed of light, wide separations are needed. Typically, a determination came from comparing: one of several spacecraft orbiting the Earth, an inner-Solar-system probe (to Mars, Venus, or an
During cruise phases, ''Ulysses'' provided unique data. As the only spacecraft out of the ecliptic with a gamma-ray instrument, ''Ulysses'' was an important part of the InterPlanetary Network (IPN). The IPN detects gamma ray bursts (GRBs); since gamma rays cannot be focused with mirrors, it was very difficult to locate GRBs with enough accuracy to study them further. Instead, several spacecraft can locate the burst through multilateration. Each spacecraft has a gamma-ray detector, with readouts noted in tiny fractions of a second. By comparing the arrival times of gamma showers with the separations of the spacecraft, a location can be determined, for follow-up with other telescopes. Because gamma rays travel at the speed of light, wide separations are needed. Typically, a determination came from comparing: one of several spacecraft orbiting the Earth, an inner-Solar-system probe (to Mars, Venus, or an asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic o ...
), and ''Ulysses''. When ''Ulysses'' crossed the ecliptic twice per orbit, many GRB determinations lost accuracy.
Additional discoveries:
* Data provided by ''Ulysses'' led to the discovery that the Sun's magnetic field interacts with the Solar System in a more complex fashion than previously assumed.
* Data provided by ''Ulysses'' led to the discovery that dust coming into the Solar System from deep space was 30 times more abundant than previously expected.
* In 2007–2008 data provided by ''Ulysses'' led to the determination that the magnetic field emanating from the Sun's poles is much weaker than previously observed.
* That the solar wind has "grown progressively weaker during the mission and is currently at its weakest since the start of the Space Age".
Fate
Ulysses will most likely continue in heliocentric orbit around the Sun indefinitely. However, there is a chance that in one of its re-encounters with Jupiter, that a close fly-by with one of the Jovian moons would be enough to alter its course and so the probe would enter a hyperbolic trajectory around the Sun and leave the Solar System.See also
* * * * * * * * *References
External links
ESA ''Ulysses'' website
ESA ''Ulysses'' mission operations website
ESA ''Ulysses'' Home page
NASA/JPL ''Ulysses'' website
''Ulysses'' Measuring Mission Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060928042857/http://ulysses-ops.jpl.esa.int/ulsfct/rgpCafe/solsys/solsys.html Where is ''Ulysses' now!
Max Planck Institute ''Ulysses'' website
Interview with ''Ulysses'' Mission Operations Manager Nigel Angold on Planetary Radio
Interactive 3D visualisation of Ulysses Jupiter gravity assist and polar orbit around the Sun
{{Authority control European Space Agency space probes NASA space probes Missions to the Sun Missions to Jupiter Derelict satellites in heliocentric orbit Missions to comets Spacecraft launched by the Space Shuttle Derelict space probes Spacecraft launched in 1990 Spacecraft decommissioned in 2009 Solar space observatories