|
Monopropellant
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipropellants that release energy through the chemical reaction between an oxidizer and a fuel. While stable under defined storage conditions, monopropellants decompose very rapidly under certain other conditions to produce a large volume of its own energetic (hot) gases for the performance of mechanical work. Although solid deflagrants such as nitrocellulose, the most commonly used propellant in firearms, could be thought of as monopropellants, the term is usually reserved for liquids in engineering literature. Uses The most common use of monopropellants is in low-impulse monopropellant rocket motors, such as reaction control thrusters, the usual propellant being hydrazine, p. 230 which is generally decomposed by exposure to an irid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monopropellant Rocket
A monopropellant rocket (or "monochemical rocket") is a rocket that uses a single chemical as its propellant. Monopropellant rockets are commonly used as small attitude and trajectory control rockets in satellites, rocket upper stages, crewed spacecraft, and spaceplanes. Chemical-reaction based monopropellant rockets The simplest monopropellant rockets depend on the chemical decomposition of a storable propellant after passing it over a catalyst bed. The power for the thruster comes from the high pressure gas created during the decomposition reaction that allows a Rocket engine nozzle, rocket nozzle to speed up the gas to create thrust. The most commonly used monopropellant is hydrazine (), a compound unstable in the presence of a Catalysis, catalyst and which is also a strong reducing agent. The most common catalyst is granular alumina (aluminum oxide, ) coated with iridium. These coated granules are usually under the commercial labels Aerojet S-405 (previously made by Shell plc, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly into water and elemental oxygen when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in an opaque bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
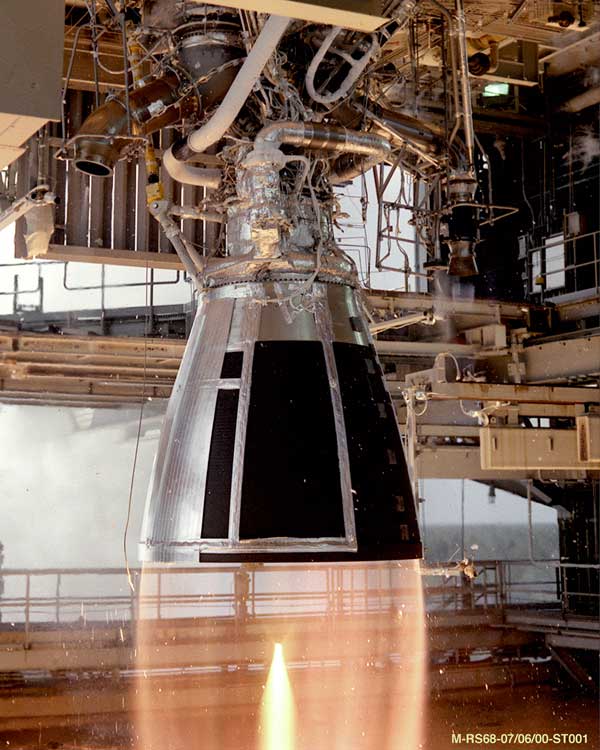
Rocket Motor
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny fireworks to man-sized weapons to huge spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal exhaust is hydrogen, the lightest of all elements, but chemical rockets produce a mix o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
High-test Peroxide
High-test peroxide (HTP) is a highly concentrated (85 to 98%) solution of hydrogen peroxide, with the remainder consisting predominantly of water. In contact with a catalyst, it decomposes into a high-temperature mixture of steam and oxygen, with no remaining liquid water. It was used as a propellant of HTP rockets and torpedoes, and has been used for high-performance vernier engines. Properties Hydrogen peroxide works best as a propellant in extremely high concentrations (roughly over 70%). Although any concentration of peroxide will generate some hot gas (oxygen plus some steam), at concentrations above approximately 67%, the heat of decomposing hydrogen peroxide becomes large enough to completely vaporize all the liquid at standard pressure. This represents a safety and utilization turning point, since decomposition of any concentration above this amount is capable of transforming the liquid entirely to heated gas (the higher the concentration, the hotter the resulting gas). Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Propellants
A propellant (or propellent) is a reaction mass, mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another Net force, motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in Rocket engine, chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
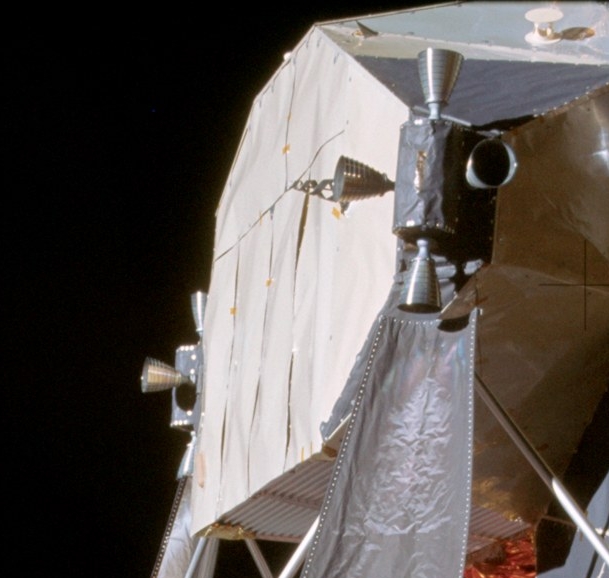
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses Thrusters (spacecraft), thrusters to provide Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control and translation (physics), translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels can be used for attitude control, rather than RCS. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a V/STOL, short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Hawker Siddeley Harrier#Controls and handling, Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation (aircraft principal axes, roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small (vernier thruster, vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Otto Fuel II
Otto fuel II is a monopropellant mixture of chiefly propylene glycol dinitrate (an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol, and structurally similar to nitroglycerin) that is used to drive torpedoes and other weapon systems. It was invented by Otto Reitlinger in 1963 (although tests with the substance had taken place before, for example in 1960). Otto fuel II, sometimes known simply as Otto fuel, is not related to the Otto cycle; it is named after Reitlinger and for being the second iteration of the fuel. It was developed by the US Navy and the first torpedo to use it was the Mark 48 torpedo in the 1960s. Properties Otto fuel II is a distinct-smelling (described by submariners as being similar in smell to methyl salicylate, wintergreen oil; i.e. sweet, fruity and minty), reddish-orange, oily liquid that is a mixture of three synthetic substances: propylene glycol dinitrate (the major component), 2-Nitrodiphenylamine, 2-nitrodiphenylamine, and dibutyl sebacate. It does not need e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Propylene Glycol Dinitrate
Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas. :C3H6(ONO2)2 → 3 CO + 3 H2O + N2 The principal current use of propylene glycol dinitrate is as a propellant in Otto Fuel II, together with 2-nitrodiphenylamine and dibutyl sebacate. Otto Fuel II is used in some torpedoes as a propellant. Nitrates of polyhydric alcohols, of which propylene glycol dinitrate is an example, have been used in medicine for the treatment of angina pectoris, and as explosives since the mid-nineteenth century. PGDN affects blood pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Specific Gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest (at ); for gases, the reference is air at room temperature (). The term "relative density" (abbreviated r.d. or RD) is preferred in SI, whereas the term "specific gravity" is gradually being abandoned. If a substance's relative density is less than 1 then it is less dense than the reference; if greater than 1 then it is denser than the reference. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal; that is, equal volumes of the two substances have the same mass. If the reference material is water, then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |