Ultra Endurance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
adopted by British military intelligence in June 1941 for wartime


 Army- and Air Force-related intelligence derived from
Army- and Air Force-related intelligence derived from
 After encryption systems were "broken", there was a large volume of cryptologic work needed to recover daily key settings and keep up with changes in enemy security procedures, plus the more mundane work of processing, translating, indexing, analyzing and distributing tens of thousands of intercepted messages daily. The more successful the code breakers were, the more labor was required. Some 8,000 women worked at Bletchley Park, about three quarters of the work force. Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the US Navy sent letters to top women's colleges seeking introductions to their best seniors; the Army soon followed suit. By the end of the war, some 7000 workers in the Army Signal Intelligence service, out of a total 10,500, were female. By contrast, the Germans and Japanese had strong ideological objections to women engaging in war work. The Nazis even created a
After encryption systems were "broken", there was a large volume of cryptologic work needed to recover daily key settings and keep up with changes in enemy security procedures, plus the more mundane work of processing, translating, indexing, analyzing and distributing tens of thousands of intercepted messages daily. The more successful the code breakers were, the more labor was required. Some 8,000 women worked at Bletchley Park, about three quarters of the work force. Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the US Navy sent letters to top women's colleges seeking introductions to their best seniors; the Army soon followed suit. By the end of the war, some 7000 workers in the Army Signal Intelligence service, out of a total 10,500, were female. By contrast, the Germans and Japanese had strong ideological objections to women engaging in war work. The Nazis even created a
signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
obtained by breaking high-level encrypted enemy radio and teleprinter communications at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. ''Ultra'' eventually became the standard designation among the western Allies for all such intelligence. The name arose because the intelligence obtained was considered more important than that designated by the highest British security classification then used (''Most Secret'') and so was regarded as being ''Ultra Secret''. Several other cryptonyms had been used for such intelligence.
The code name ''Boniface'' was used as a cover name for ''Ultra''. In order to ensure that the successful code-breaking did not become apparent to the Germans, British intelligence created a fictional MI6 master spy, Boniface, who controlled a fictional series of agents throughout Germany. Information obtained through code-breaking was often attributed to the human intelligence from the Boniface network. The U.S. used the codename '' Magic'' for its decrypts from Japanese sources, including the " Purple" cipher.
Much of the German cipher traffic was encrypted on the Enigma machine. Used properly, the German military Enigma would have been virtually unbreakable; in practice, shortcomings in operation allowed it to be broken. The term "Ultra" has often been used almost synonymously with " Enigma decrypts". However, Ultra also encompassed decrypts of the German Lorenz SZ 40/42 machines that were used by the German High Command, and the Hagelin machine.
Many observers, at the time and later, regarded Ultra as immensely valuable to the Allies. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
was reported to have told King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of Ind ...
, when presenting to him Stewart Menzies (head of the Secret Intelligence Service
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6 ( Military Intelligence, Section 6), is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligenc ...
and the person who controlled distribution of Ultra decrypts to the government): "It is thanks to the secret weapon of General Menzies, put into use on all the fronts, that we won the war!" F. W. Winterbotham
Frederick William Winterbotham (16 April 1897 – 28 January 1990) was a British Royal Air Force officer (latterly a Group Captain) who during World War II supervised the distribution of Ultra intelligence. His book ''The Ultra Secret'' was t ...
quoted the western Supreme Allied Commander, Dwight D. Eisenhower, at war's end describing Ultra as having been "decisive" to Allied victory. Sir Harry Hinsley, Bletchley Park veteran and official historian of British Intelligence in World War II, made a similar assessment of Ultra, saying that while the Allies would have won the war without it, "the war would have been something like two years longer, perhaps three years longer, possibly four years longer than it was." However, Hinsley and others have emphasized the difficulties of counterfactual history in attempting such conclusions, and some historians, such as Keegan, have said the shortening might have been as little as the three months it took the United States to deploy the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
.
The existence of Ultra was kept secret for many years after the war. Since the Ultra story was widely disseminated by Winterbotham in 1974, historians have altered the historiography of World War II. For example, Andrew Roberts, writing in the 21st century, states, "Because he had the invaluable advantage of being able to read Field Marshal Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel () (15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944) was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox (, ), he served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as servi ...
's Enigma communications, General Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and t ...
knew how short the Germans were of men, ammunition, food and above all fuel. When he put Rommel's picture up in his caravan he wanted to be seen to be almost reading his opponent's mind. In fact he was reading his mail." Over time, Ultra has become embedded in the public consciousness and Bletchley Park has become a significant visitor attraction. As stated by historian Thomas Haigh
Thomas Haigh (1769 – 1808), was an English violinist, pianist, and composer.
Haigh was born in London in 1769, and studied composition under Haydn in 1791 and 1792. Haigh's numerous compositions include sonatas for pianoforte solo and fo ...
, "The British code-breaking effort of the Second World War, formerly secret, is now one of the most celebrated aspects of modern British history, an inspiring story in which a free society mobilized its intellectual resources against a terrible enemy."
Sources of intelligence
Most Ultra intelligence was derived from reading radio messages that had been encrypted with cipher machines, complemented by material from radio communications using traffic analysis and direction finding. In the early phases of the war, particularly during the eight-month Phoney War, the Germans could transmit most of their messages using land lines and so had no need to use radio. This meant that those at Bletchley Park had some time to build up experience of collecting and starting to decrypt messages on the various radio networks. German Enigma messages were the main source, with those of the Luftwaffe predominating, as they used radio more and their operators were particularly ill-disciplined.German


Enigma
" Enigma" refers to a family of electro-mechanical rotor cipher machines. These produced a polyalphabetic substitution cipher and were widely thought to be unbreakable in the 1920s, when a variant of the commercial Model D was first used by the Reichswehr. TheGerman Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
, Navy, Air Force, Nazi party, Gestapo and German diplomats used Enigma machines in several variants. Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' (German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the ''Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. A ...
(German military intelligence) used a four-rotor machine without a plugboard and Naval Enigma used different key management from that of the army or air force, making its traffic far more difficult to cryptanalyse; each variant required different cryptanalytic treatment. The commercial versions were not as secure and Dilly Knox of GC&CS is said to have broken one before the war.
German military Enigma was first broken in December 1932 by the Polish Cipher Bureau
The Cipher Bureau, in Polish language, Polish: ''Biuro Szyfrów'' (), was the interwar Polish General Staff's Second Department of Polish General Staff, Second Department's unit charged with SIGINT and both cryptography (the ''use'' of ciphers an ...
, using a combination of brilliant mathematics, the services of a spy in the German office responsible for administering encrypted communications, and good luck. The Poles read Enigma to the outbreak of World War II and beyond, in France. At the turn of 1939, the Germans made the systems ten times more complex, which required a tenfold increase in Polish decryption equipment, which they could not meet. On 25 July 1939, the Polish Cipher Bureau handed reconstructed Enigma machines and their techniques for decrypting ciphers to the French and British. Gordon Welchman wrote,
At Bletchley Park, some of the key people responsible for success against Enigma included mathematicians Alan Turing and Hugh Alexander and, at the British Tabulating Machine Company, chief engineer Harold Keen.
After the war, interrogation of German cryptographic personnel led to the conclusion that German cryptanalysts understood that cryptanalytic attacks against Enigma were possible but were thought to require impracticable amounts of effort and investment. The Poles' early start at breaking Enigma and the continuity of their success gave the Allies an advantage when World War II began.
Lorenz cipher
In June 1941, the Germans started to introduce on-linestream cipher
stream cipher is a symmetric key cipher where plaintext digits are combined with a pseudorandom cipher digit stream (keystream). In a stream cipher, each plaintext digit is encrypted one at a time with the corresponding digit of the keystream ...
teleprinter systems for strategic point-to-point radio links, to which the British gave the code-name Fish. Several systems were used, principally the Lorenz SZ 40/42 (Tunny) and Geheimfernschreiber
The Siemens & Halske T52, also known as the Geheimschreiber ("secret teleprinter"), or ''Schlüsselfernschreibmaschine'' (SFM), was a World War II German cipher machine and teleprinter produced by the electrical engineering firm Siemens & Halske. ...
(Sturgeon
Sturgeon is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretace ...
). These cipher systems were cryptanalysed, particularly Tunny, which the British thoroughly penetrated. It was eventually attacked using Colossus machines, which were the first digital programme-controlled electronic computers. In many respects the Tunny work was more difficult than for the Enigma, since the British codebreakers had no knowledge of the machine producing it and no head-start such as that the Poles had given them against Enigma.
Although the volume of intelligence derived from this system was much smaller than that from Enigma, its importance was often far higher because it produced primarily high-level, strategic intelligence that was sent between Wehrmacht High Command (OKW). The eventual bulk decryption of Lorenz-enciphered messages contributed significantly, and perhaps decisively, to the defeat of Nazi Germany. Nevertheless, the Tunny story has become much less well known among the public than the Enigma one. At Bletchley Park, some of the key people responsible for success in the Tunny effort included mathematicians W. T. "Bill" Tutte and Max Newman and electrical engineer Tommy Flowers.
Italian
In June 1940, the Italians were using book codes for most of their military messages, except for the Italian Navy, which in early 1941 had started using a version of the Hagelin rotor-based cipher machine C-38. This was broken from June 1941 onwards by the Italian subsection of GC&CS at Bletchley Park.Japanese
In the Pacific theatre, a Japanese cipher machine, called " Purple" by the Americans, was used for highest-level Japanese diplomatic traffic. It produced a polyalphabetic substitution cipher, but unlike Enigma, was not a rotor machine, being built around electrical stepping switches. It was broken by the US Army Signal Intelligence Service and disseminated as '' Magic''. Detailed reports by the Japanese ambassador to Germany were encrypted on the Purple machine. His reports included reviews of German assessments of the military situation, reviews of strategy and intentions, reports on direct inspections by the ambassador (in one case, of Normandy beach defences), and reports of long interviews with Hitler. The Japanese are said to have obtained an Enigma machine in 1937, although it is debated whether they were given it by the Germans or bought a commercial version, which, apart from the plugboard and internal wiring, was the German ''Heer/Luftwaffe'' machine. Having developed a similar machine, the Japanese did not use the Enigma machine for their most secret communications. The chief fleet communications code system used by the Imperial Japanese Navy was called JN-25 by the Americans, and by early 1942 the US Navy had made considerable progress in decrypting Japanese naval messages. The US Army also made progress on the Japanese Army's codes in 1943, including codes used by supply ships, resulting in heavy losses to their shipping.Distribution
 Army- and Air Force-related intelligence derived from
Army- and Air Force-related intelligence derived from signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
(SIGINT) sources—mainly Enigma decrypts in Hut 6—was compiled in summaries at GC&CS ( Bletchley Park) Hut 3 and distributed initially under the codeword "BONIFACE", implying that it was acquired from a well placed agent in Berlin. The volume of the intelligence reports going out to commanders in the field built up gradually.
Naval Enigma decrypted in Hut 8 was forwarded from Hut 4 to the Admiralty's Operational Intelligence Centre (OIC), which distributed it initially under the codeword "HYDRO".
The codeword "ULTRA" was adopted in June 1941. This codeword was reportedly suggested by Commander Geoffrey Colpoys, RN, who served in the Royal Navy's OIC.
Army and Air Force
The distribution of Ultra information to Allied commanders and units in the field involved considerable risk of discovery by the Germans, and great care was taken to control both the information and knowledge of how it was obtained. Liaison officers were appointed for each field command to manage and control dissemination. Dissemination of Ultra intelligence to field commanders was carried out by MI6, which operated Special Liaison Units (SLU) attached to major army and air force commands. The activity was organized and supervised on behalf of MI6 byGroup Captain
Group captain is a senior commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force, where it originated, as well as the air forces of many countries that have historical British influence. It is sometimes used as the English translation of an equivalent rank i ...
F. W. Winterbotham
Frederick William Winterbotham (16 April 1897 – 28 January 1990) was a British Royal Air Force officer (latterly a Group Captain) who during World War II supervised the distribution of Ultra intelligence. His book ''The Ultra Secret'' was t ...
. Each SLU included intelligence, communications, and cryptographic elements. It was headed by a British Army or RAF officer, usually a major, known as "Special Liaison Officer". The main function of the liaison officer or his deputy was to pass Ultra intelligence bulletins to the commander of the command he was attached to, or to other indoctrinated staff officers. In order to safeguard Ultra, special precautions were taken. The standard procedure was for the liaison officer to present the intelligence summary to the recipient, stay with him while he studied it, then take it back and destroy it.
By the end of the war, there were about 40 SLUs serving commands around the world. Fixed SLUs existed at the Admiralty, the War Office, the Air Ministry, RAF Fighter Command, the US Strategic Air Forces in Europe (Wycombe Abbey) and other fixed headquarters in the UK. An SLU was operating at the War HQ in Valletta, Malta. These units had permanent teleprinter links to Bletchley Park.
Mobile SLUs were attached to field army and air force headquarters and depended on radio communications to receive intelligence summaries. The first mobile SLUs appeared during the French campaign of 1940. An SLU supported the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) headed by General Lord Gort. The first liaison officers were Robert Gore-Browne and Humphrey Plowden. A second SLU of the 1940 period was attached to the RAF Advanced Air Striking Force at Meaux commanded by Air Vice-Marshal P H Lyon Playfair. This SLU was commanded by Squadron Leader F.W. "Tubby" Long.
Intelligence agencies
In 1940, special arrangements were made within the British intelligence services for handling BONIFACE and later Ultra intelligence. The Security Service started "Special Research Unit B1(b)" under Herbert Hart. In the SIS this intelligence was handled by "Section V" based atSt Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major ...
.
Radio and cryptography
The communications system was founded by Brigadier SirRichard Gambier-Parry
Brigadier Sir Richard Gambier-Parry, (20 January 1894 – 19 June 1965) was a British military officer who served in both the army and the air force during World War I. He remained in military service post-war, but then entered into civilian lif ...
, who from 1938 to 1946 was head of MI6 Section VIII, based at Whaddon Hall in Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (), abbreviated Bucks, is a ceremonial county in South East England that borders Greater London to the south-east, Berkshire to the south, Oxfordshire to the west, Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-ea ...
, UK. Ultra summaries from Bletchley Park were sent over landline to the Section VIII radio transmitter at Windy Ridge. From there they were transmitted to the destination SLUs.
The communications element of each SLU was called a "Special Communications Unit" or SCU. Radio transmitters were constructed at Whaddon Hall workshops, while receivers were the National HRO, made in the USA. The SCUs were highly mobile and the first such units used civilian Packard
Packard or Packard Motor Car Company was an American luxury automobile company located in Detroit, Michigan. The first Packard automobiles were produced in 1899, and the last Packards were built in South Bend, Indiana in 1958.
One of the "Thr ...
cars. The following SCUs are listed: SCU1 (Whaddon Hall), SCU2 (France before 1940, India), SCU3 (RSS Hanslope Park), SCU5, SCU6 (possibly Algiers and Italy), SCU7 (training unit in the UK), SCU8 (Europe after D-day), SCU9 (Europe after D-day), SCU11 (Palestine and India), SCU12 (India), SCU13 and SCU14.
The cryptographic element of each SLU was supplied by the RAF and was based on the TYPEX cryptographic machine and one-time pad systems.
RN Ultra messages from the OIC to ships at sea were necessarily transmitted over normal naval radio circuits and were protected by one-time pad encryption.
Lucy
An intriguing question concerns the alleged use of Ultra information by the "Lucy" spy ring, headquartered inSwitzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and apparently operated by one man, Rudolf Roessler
Rudolf Roessler (German: ''Rößler''; 22 November 1897 – 11 December 1958) was a Protestant Germany, German and dedicated anti-Nazi. During the interwar period, Roessler was a lively cultural journalist, with a focus on theatre. In 1933 while ...
. This was an extremely well informed, responsive ring that was able to get information "directly from German General Staff Headquarters" – often on specific request. It has been alleged that "Lucy" was in major part a conduit for the British to feed Ultra intelligence to the Soviets in a way that made it appear to have come from highly placed espionage rather than from cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic sec ...
of German radio traffic. The Soviets, however, through an agent at Bletchley, John Cairncross, knew that Britain had broken Enigma. The "Lucy" ring was initially treated with suspicion by the Soviets. The information it provided was accurate and timely, however, and Soviet agents in Switzerland (including their chief, Alexander Radó) eventually learned to take it seriously. However, the theory that the Lucy ring was a cover for Britain to pass Enigma intelligence to the Soviets has not gained traction. Among others who have rejected the theory, Harry Hinsley, the official historian for the British Secret Services in World War II, stated that "there is no truth in the much-publicized claim that the British authorities made use of the ‘Lucy’ ring..to forward intelligence to Moscow".
Use of intelligence
Most deciphered messages, often about relative trivia, were insufficient as intelligence reports for military strategists or field commanders. The organisation, interpretation and distribution of decrypted Enigma message traffic and other sources into usable intelligence was a subtle task. At Bletchley Park, extensive indices were kept of the information in the messages decrypted. For each message the traffic analysis recorded the radio frequency, the date and time of intercept, and the preamble—which contained the network-identifying discriminant, the time of origin of the message, the callsign of the originating and receiving stations, and the indicator setting. This allowed cross referencing of a new message with a previous one. The indices included message preambles, every person, every ship, every unit, every weapon, every technical term and of repeated phrases such as forms of address and other German military jargon that might be usable as '' cribs''. The first decryption of a wartime Enigma message, albeit one that had been transmitted three months earlier, was achieved by the Poles at PC Bruno on 17 January 1940. Little had been achieved by the start of the Allied campaign in Norway in April. At the start of theBattle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
on 10 May 1940, the Germans made a very significant change in the indicator procedures for Enigma messages. However, the Bletchley Park cryptanalysts had anticipated this, and were able — jointly with PC Bruno — to resume breaking messages from 22 May, although often with some delay. The intelligence that these messages yielded was of little operational use in the fast-moving situation of the German advance.
Decryption of Enigma traffic built up gradually during 1940, with the first two prototype bombes being delivered in March and August. The traffic was almost entirely limited to ''Luftwaffe'' messages. By the peak of the Battle of the Mediterranean
The Battle of the Mediterranean was the name given to the naval campaign fought in the Mediterranean Sea during World War II, from 10 June 1940 to 2 May 1945.
For the most part, the campaign was fought between the Italian Royal Navy (''Regia ...
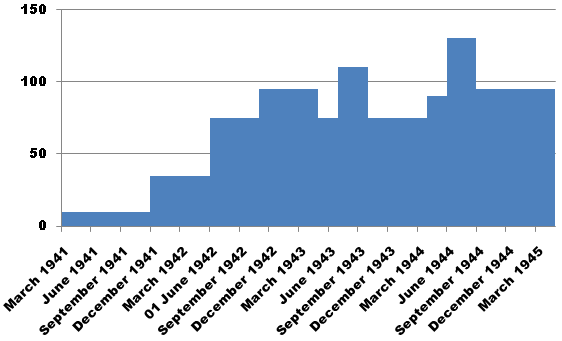
in 1941, however, Bletchley Park was deciphering daily 2,000 Italian Hagelin messages. By the second half of 1941 30,000 Enigma messages a month were being deciphered, rising to 90,000 a month of Enigma and Fish decrypts combined later in the war.
Some of the contributions that Ultra intelligence made to the Allied successes are given below.
* In April 1940, Ultra information provided a detailed picture of the disposition of the German forces, and then their movement orders for the attack on the Low Countries prior to the Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
in May.
* An Ultra decrypt of June 1940 read '' KNICKEBEIN KLEVE IST AUF PUNKT 53 GRAD 24 MINUTEN NORD UND EIN GRAD WEST EINGERICHTET'' ("The Cleves ''Knickebein'' is directed at position 53 degrees 24 minutes north and 1 degree west"). This was the definitive piece of evidence that Dr R V Jones of scientific intelligence in the Air Ministry needed to show that the Germans were developing a radio guidance system for their bombers. Ultra intelligence then continued to play a vital role in the so-called Battle of the Beams.
* During the Battle of Britain, Air Chief Marshal Sir Hugh Dowding
Air Chief Marshal Hugh Caswall Tremenheere Dowding, 1st Baron Dowding, (24 April 1882 – 15 February 1970) was an officer in the Royal Air Force. He was Air Officer Commanding RAF Fighter Command during the Battle of Britain and is generally c ...
, Commander-in-Chief of RAF Fighter Command, had a teleprinter link from Bletchley Park to his headquarters at RAF Bentley Priory, for Ultra reports. Ultra intelligence kept him informed of German strategy, and of the strength and location of various ''Luftwaffe'' units, and often provided advance warning of bombing raids (but not of their specific targets). These contributed to the British success. Dowding was bitterly and sometimes unfairly criticized by others who did not see Ultra, but he did not disclose his source.
* Decryption of traffic from ''Luftwaffe'' radio networks provided a great deal of indirect intelligence about the Germans' planned Operation Sea Lion to invade England in 1940.
* On 17 September 1940 an Ultra message reported that equipment at German airfields in Belgium for loading planes with paratroops and their gear, was to be dismantled. This was taken as a clear signal that Sea Lion had been cancelled.
* Ultra revealed that a major German air raid was planned for the night of 14 November 1940, and indicated three possible targets, including London and Coventry. However, the specific target was not determined until late on the afternoon of 14 November, by detection of the German radio guidance signals. Unfortunately, countermeasures failed to prevent the devastating Coventry Blitz. F. W. Winterbotham claimed that Churchill had advance warning, but intentionally did nothing about the raid, to safeguard Ultra. This claim has been comprehensively refuted by R V Jones, Sir David Hunt, Ralph Bennett and Peter Calvocoressi. Ultra warned of a raid but did not reveal the target. Churchill, who had been ''en route'' to Ditchley Park, was told that London might be bombed and returned to 10 Downing Street
10 Downing Street in London, also known colloquially in the United Kingdom as Number 10, is the official residence and executive office of the first lord of the treasury, usually, by convention, the prime minister of the United Kingdom. Along wi ...
so that he could observe the raid from the Air Ministry roof.
* Ultra intelligence considerably aided the British Army's Operation Compass victory over the much larger Italian army in Libya in December 1940 – February 1941.
* Ultra intelligence greatly aided the Royal Navy's victory over the Italian navy in the Battle of Cape Matapan in March 1941.
* Although the Allies lost the Battle of Crete in May 1941, the Ultra intelligence that a parachute landing was planned, and the exact day of the invasion, meant that heavy losses were inflicted on the Germans and that fewer British troops were captured.
* Ultra intelligence fully revealed the preparations for Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the USSR. Although this information was passed to the Soviet government, Stalin refused to believe it. The information did, however, help British planning, knowing that substantial German forces were to be deployed to the East.
* Ultra intelligence made a very significant contribution in the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade ...
. Winston Churchill wrote "The only thing that ever really frightened me during the war was the U-boat peril." The decryption of Enigma signals to the U-boats was much more difficult than those of the ''Luftwaffe''. It was not until June 1941 that Bletchley Park was able to read a significant amount of this traffic currently. Transatlantic convoys were then diverted away from the U-boat "wolfpacks", and the U-boat supply vessels were sunk. On 1 February 1942, Enigma U-boat traffic became unreadable because of the introduction of a different 4-rotor Enigma machine. This situation persisted until December 1942, although other German naval Enigma messages were still being deciphered, such as those of the U-boat training command at Kiel. From December 1942 to the end of the war, Ultra allowed Allied convoys to evade U-boat patrol lines, and guided Allied anti-submarine forces to the location of U-boats at sea.
* In the Western Desert Campaign, Ultra intelligence helped Wavell and Auchinleck to prevent Rommel's forces from reaching Cairo in the autumn of 1941.
* Ultra intelligence from Hagelin decrypts, and from ''Luftwaffe'' and German naval Enigma decrypts, helped sink about half of the ships supplying the Axis forces in North Africa.
* Ultra intelligence from ''Abwehr'' transmissions confirmed that Britain's Security Service ( MI5) had captured all of the German agents in Britain, and that the ''Abwehr'' still believed in the many double agents which MI5 controlled under the Double Cross System
The Double-Cross System or XX System was a World War II counter-espionage and deception operation of the British Security Service (a civilian organisation usually referred to by its cover title MI5). Nazi agents in Britain – real and false – w ...
. This enabled major deception operations.
* Deciphered JN-25 messages allowed the U.S. to turn back a Japanese offensive in the Battle of the Coral Sea
The Battle of the Coral Sea, from 4 to 8 May 1942, was a major naval battle between the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and naval and air forces of the United States and Australia. Taking place in the Pacific Theatre of World War II, the batt ...
in April 1942 and set up the decisive American victory at the Battle of Midway in June 1942.
* Ultra contributed very significantly to the monitoring of German developments at Peenemünde and the collection of V-1 and V-2 Intelligence
Military intelligence on the V-1 flying bomb, V-1 and V-2 rocket, V-2 weapons developed by the Germans for attacks on the United Kingdom during the Second World War was important to countering them. Intelligence came from a number of sources and ...
from 1942 onwards.
* Ultra contributed to Montgomery's victory at the Battle of Alam el Halfa by providing warning of Rommel's planned attack.
* Ultra also contributed to the success of Montgomery's offensive in the Second Battle of El Alamein, by providing him (before the battle) with a complete picture of Axis forces, and (during the battle) with Rommel's own action reports to Germany.
* Ultra provided evidence that the Allied landings in French North Africa (Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of secu ...
) were not anticipated.
* A JN-25 decrypt of 14 April 1943 provided details of Admiral Yamamoto's forthcoming visit to Balalae Island, and on 18 April, a year to the day following the Doolittle Raid, his aircraft was shot down, killing this man who was regarded as irreplaceable.
* Ship position reports in the Japanese Army’s "2468" water transport code, decrypted by the SIS starting in July 1943, helped U.S. submarines and aircraft sink two-thirds of the Japanese merchant marine.
* The part played by Ultra intelligence in the preparation for the Allied invasion of Sicily was of unprecedented importance. It provided information as to where the enemy's forces were strongest and that the elaborate strategic deceptions had convinced Hitler and the German high command.
* The success of the Battle of North Cape, in which HMS ''Duke of York'' sank the German battleship ''Scharnhorst'', was entirely built on prompt deciphering of German naval signals.
* US Army Lieutenant Arthur J Levenson who worked on both Enigma and Tunny at Bletchley Park, said in a 1980 interview of intelligence from Tunny
* Both Enigma and Tunny decrypts showed Germany had been taken in by Operation Bodyguard, the deception operation to protect Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operat ...
. They revealed the Germans did not anticipate the Normandy landings and even after D-Day still believed Normandy was only a feint, with the main invasion to be in the Pas de Calais.
* Information that there was German '' Panzergrenadier'' division in the planned dropping zone for the US 101st Airborne Division
The 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault) ("Screaming Eagles") is a light infantry division of the United States Army that specializes in air assault operations. It can plan, coordinate, and execute multiple battalion-size air assault operati ...
in Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operat ...
led to a change of location.
* It assisted greatly in Operation Cobra.
* It warned of the major German counterattack at Mortain, and allowed the Allies to surround the forces at Falaise.
* During the Allied advance to Germany, Ultra often provided detailed tactical information, and showed how Hitler ignored the advice of his generals and insisted on German troops fighting in place "to the last man".
* Arthur "Bomber" Harris, officer commanding RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bo ...
, was not cleared for Ultra. After D-Day, with the resumption of the strategic bomber campaign over Germany, Harris remained wedded to area bombardment. Historian Frederick Taylor argues that, as Harris was not cleared for access to Ultra, he was given some information gleaned from Enigma but not the information's source. This affected his attitude about post-D-Day directives to target oil installations, since he did not know that senior Allied commanders were using high-level German sources to assess just how much this was hurting the German war effort; thus Harris tended to see the directives to bomb specific oil and munitions targets as a "panacea" (his word) and a distraction from the real task of making the rubble bounce.
Safeguarding of sources
The Allies were seriously concerned with the prospect of the Axis command finding out that they had broken into the Enigma traffic. The British were more disciplined about such measures than the Americans, and this difference was a source of friction between them. To disguise the source of the intelligence for the Allied attacks on Axis supply ships bound for North Africa, "spotter" submarines and aircraft were sent to search for Axis ships. These searchers or their radio transmissions were observed by the Axis forces, who concluded their ships were being found by conventional reconnaissance. They suspected that there were some 400 Allied submarines in the Mediterranean and a huge fleet of reconnaissance aircraft on Malta. In fact, there were only 25 submarines and at times as few as three aircraft. This procedure also helped conceal the intelligence source from Allied personnel, who might give away the secret by careless talk, or under interrogation if captured. Along with the search mission that would find the Axis ships, two or three additional search missions would be sent out to other areas, so that crews would not begin to wonder why a single mission found the Axis ships every time. Other deceptive means were used. On one occasion, a convoy of five ships sailed from Naples to North Africa with essential supplies at a critical moment in the North African fighting. There was no time to have the ships properly spotted beforehand. The decision to attack solely on Ultra intelligence went directly to Churchill. The ships were all sunk by an attack "out of the blue", arousing German suspicions of a security breach. To distract the Germans from the idea of a signals breach (such as Ultra), the Allies sent a radio message to a fictitious spy in Naples, congratulating him for this success. According to some sources the Germans decrypted this message and believed it. In the Battle of the Atlantic, the precautions were taken to the extreme. In most cases where the Allies knew from intercepts the location of a U-boat in mid-Atlantic, the U-boat was not attacked immediately, until a "cover story" could be arranged. For example, a search plane might be "fortunate enough" to sight the U-boat, thus explaining the Allied attack. Some Germans had suspicions that all was not right with Enigma. AdmiralKarl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
received reports of "impossible" encounters between U-boats and enemy vessels which made him suspect some compromise of his communications. In one instance, three U-boats met at a tiny island in the Caribbean Sea, and a British destroyer promptly showed up. The U-boats escaped and reported what had happened. Dönitz immediately asked for a review of Enigma's security. The analysis suggested that the signals problem, if there was one, was not due to the Enigma itself. Dönitz had the settings book changed anyway, blacking out Bletchley Park for a period. However, the evidence was never enough to truly convince him that Naval Enigma was being read by the Allies. The more so, since ''B-Dienst
The ''B-Dienst'' (german: Beobachtungsdienst, observation service), also called x''B-Dienst'', X-''B-Dienst'' and χ''B-Dienst'', was a Department of the German Naval Intelligence Service (german: Marinenachrichtendienst, MND III) of the OKM, t ...
'', his own codebreaking group, had partially broken Royal Navy traffic (including its convoy codes early in the war), and supplied enough information to support the idea that the Allies were unable to read Naval Enigma.
By 1945, most German Enigma traffic could be decrypted within a day or two, yet the Germans remained confident of its security.
Role of women in Allied codebreaking
 After encryption systems were "broken", there was a large volume of cryptologic work needed to recover daily key settings and keep up with changes in enemy security procedures, plus the more mundane work of processing, translating, indexing, analyzing and distributing tens of thousands of intercepted messages daily. The more successful the code breakers were, the more labor was required. Some 8,000 women worked at Bletchley Park, about three quarters of the work force. Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the US Navy sent letters to top women's colleges seeking introductions to their best seniors; the Army soon followed suit. By the end of the war, some 7000 workers in the Army Signal Intelligence service, out of a total 10,500, were female. By contrast, the Germans and Japanese had strong ideological objections to women engaging in war work. The Nazis even created a
After encryption systems were "broken", there was a large volume of cryptologic work needed to recover daily key settings and keep up with changes in enemy security procedures, plus the more mundane work of processing, translating, indexing, analyzing and distributing tens of thousands of intercepted messages daily. The more successful the code breakers were, the more labor was required. Some 8,000 women worked at Bletchley Park, about three quarters of the work force. Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the US Navy sent letters to top women's colleges seeking introductions to their best seniors; the Army soon followed suit. By the end of the war, some 7000 workers in the Army Signal Intelligence service, out of a total 10,500, were female. By contrast, the Germans and Japanese had strong ideological objections to women engaging in war work. The Nazis even created a Cross of Honour of the German Mother
The Cross of Honour of the German Mother (), referred to colloquially as the ''Mutterehrenkreuz'' (Mother's Cross of Honour) or simply ''Mutterkreuz'' (Mother's Cross), was a state decoration conferred by the government of the German ReichStat ...
to encourage women to stay at home and have babies.
Effect on the war
The exact influence of Ultra on the course of the war is debated; an oft-repeated assessment is that decryption of German ciphers advanced the end of the European war by no less than two years. Hinsley, who first made this claim, is typically cited as an authority for the two-year estimate. Winterbotham's quoting of Eisenhower's "decisive" verdict is part of a letter sent by Eisenhower to Menzies after the conclusion of the European war and later found among his papers at the Eisenhower Presidential Library. It allows a contemporary, documentary view of a leader on Ultra's importance: There is wide disagreement about the importance of codebreaking in winning the crucialBattle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade ...
. To cite just one example, the historian Max Hastings states that "In 1941 alone, Ultra saved between 1.5 and two million tons of Allied ships from destruction." This would represent a 40 percent to 53 percent reduction, though it is not clear how this extrapolation was made.
Another view is from a history based on the German naval archives written after the war for the British Admiralty by a former U-boat commander and son-in-law of his commander, Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
. His book reports that several times during the war they undertook detailed investigations to see whether their operations were being compromised by broken Enigma ciphers. These investigations were spurred because the Germans had broken the British naval code and found the information useful. Their investigations were negative, and the conclusion was that their defeat "was due firstly to outstanding developments in enemy radar..." The great advance was centimetric radar, developed in a joint British-American venture, which became operational in the spring of 1943. Earlier radar was unable to distinguish U-boat conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
s from the surface of the sea, so it could not even locate U-boats attacking convoys on the surface on moonless nights; thus the surfaced U-boats were almost invisible, while having the additional advantage of being swifter than their prey. The new higher-frequency radar could spot conning towers, and periscopes could even be detected from airplanes. Some idea of the relative effect of cipher-breaking and radar improvement can be obtained from graphs showing the tonnage of merchantmen sunk and the number of U-boats sunk in each month of the Battle of the Atlantic. The graphs cannot be interpreted unambiguously, because it is challenging to factor in many variables such as improvements in cipher-breaking and the numerous other advances in equipment and techniques used to combat U-boats. Nonetheless, the data seem to favor the view of the former U-boat commander—that radar was crucial.
While Ultra certainly affected the course of the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
during the war, two factors often argued against Ultra having shortened the overall war by a measure of years are the relatively small role it played in the Eastern Front conflict between Germany and the Soviet Union, and the completely independent development of the U.S.-led Manhattan Project to create the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
. Author Jeffrey T. Richelson Jeffrey Talbot Richelson (31 December 1949 – 11 November 2017) was an American author and academic researcher who studied the process of intelligence gathering and national security. He authored at least thirteen books and many articles about int ...
mentions Hinsley's estimate of at least two years, and concludes that "It might be more accurate to say that Ultra helped shorten the war by three months – the interval between the actual end of the war in Europe and the time the United States would have been able to drop an atomic bomb on Hamburg or Berlin – and might have shortened the war by as much as two years had the U.S. atomic bomb program been unsuccessful." Military historian Guy Hartcup analyzes aspects of the question but then simply says, "It is impossible to calculate in terms of months or years how much Ultra shortened the war."
Postwar disclosures
While it is obvious why Britain and the U.S. went to considerable pains to keep Ultra a secret until the end of the war, it has been a matter of some conjecture why Ultra was kept officially secret for 29 years thereafter, until 1974. During that period, the important contributions to the war effort of a great many people remained unknown, and they were unable to share in the glory of what is now recognised as one of the chief reasons the Allies won the war – or, at least, as quickly as they did. At least three versions exist as to why Ultra was kept secret so long. Each has plausibility, and all may be true. First, as David Kahn pointed out in his 1974 ''New York Times'' review of Winterbotham's ''The Ultra Secret'', after the war, surplus Enigmas and Enigma-like machines were sold to Third World countries, which remained convinced of the security of the remarkable cipher machines. Their traffic was not as secure as they believed, however, which is one reason the British made the machines available. By the 1970s, newer computer-based ciphers were becoming popular as the world increasingly turned to computerised communications, and the usefulness of Enigma copies (and rotor machines generally) rapidly decreased. Switzerland developed its own version of Enigma, known as NEMA, and used it into the late 1970s, while the United States National Security Agency (NSA) retired the last of its rotor-based encryption systems, theKL-7
The TSEC/KL-7, also known as Adonis was an off-line non-reciprocal rotor encryption machine.
series, in the 1980s.
A second explanation relates to a misadventure of Churchill's between the World Wars, when he publicly disclosed information from decrypted Soviet communications. This had prompted the Soviets to change their ciphers, leading to a blackout.
The third explanation is given by Winterbotham, who recounts that two weeks after V-E Day, on 25 May 1945, Churchill requested former recipients of Ultra intelligence not to divulge the source or the information that they had received from it, in order that there be neither damage to the future operations of the Secret Service nor any cause for the Axis to blame Ultra for their defeat.
Since it was British and, later, American message-breaking which had been the most extensive, the importance of Enigma decrypts to the prosecution of the war remained unknown despite revelations by the Poles and the French of their early work on breaking the Enigma cipher. This work, which was carried out in the 1930s and continued into the early part of the war, was necessarily uninformed regarding further breakthroughs achieved by the Allies during the balance of the war. In 1967, Polish military historian Władysław Kozaczuk in his book ''Bitwa o tajemnice'' ("Battle for Secrets") first revealed Enigma had been broken by Polish cryptologists before World War II. Later the 1973 public disclosure of Enigma decryption in the book ''Enigma'' by French intelligence officer Gustave Bertrand generated pressure to discuss the rest of the Enigma–Ultra story.
In 1967, David Kahn in '' The Codebreakers'' described the 1944 capture of a Naval Enigma machine from and gave the first published hint about the scale, mechanisation and operational importance of the Anglo-American Enigma-breaking operation:
Ladislas Farago's 1971 best-seller ''The Game of the Foxes'' gave an early garbled version of the myth of the purloined Enigma. According to Farago, it was thanks to a "Polish-Swedish ring hatthe British obtained a working model of the 'Enigma' machine, which the Germans used to encipher their top-secret messages." "It was to pick up one of these machines that Commander Denniston went clandestinely to a secluded Polish castle on the eve of the war. Dilly Knox later solved its keying, exposing all Abwehr signals encoded by this system." "In 1941 e brilliant cryptologist Dillwyn Knox, working at the Government Code & Cypher School at the Bletchley centre of British code-cracking, solved the keying of the Abwehr's Enigma machine."
The British ban was finally lifted in 1974, the year that a key participant on the distribution side of the Ultra project, F. W. Winterbotham, published ''The Ultra Secret''. A succession of books by former participants and others followed. The official history of British intelligence in World War II was published in five volumes from 1979 to 1988, and included further details from official sources concerning the availability and employment of Ultra intelligence. It was chiefly edited by Harry Hinsley, with one volume by Michael Howard. There is also a one-volume collection of reminiscences by Ultra veterans, ''Codebreakers'' (1993), edited by Hinsley and Alan Stripp.
A 2012 London Science Museum exhibit, "Code Breaker: Alan Turing's Life and Legacy", marking the centenary
{{other uses, Centennial (disambiguation), Centenary (disambiguation)
A centennial, or centenary in British English, is a 100th anniversary or otherwise relates to a century, a period of 100 years.
Notable events
Notable centennial events at ...
of his birth, includes a short film of statements by half a dozen participants and historians of the World War II Bletchley Park Ultra operations. John Agar, a historian of science and technology, states that by war's end 8,995 people worked at Bletchley Park. Iain Standen, Chief Executive of the Bletchley Park Trust, says of the work done there: "It was crucial to the survival of Britain, and indeed of the West." The Departmental Historian at GCHQ (the Government Communications Headquarters), who identifies himself only as "Tony" but seems to speak authoritatively, says that Ultra was a "major force multiplier
In military science, force multiplication or a force multiplier is a factor or a combination of factors that gives personnel or weapons (or other hardware) the ability to accomplish greater feats than without it. The expected size increase requ ...
. It was the first time that quantities of real-time intelligence became available to the British military." He further states that it is only in 2012 that Alan Turing's last two papers on Enigma decryption have been released to Britain's National Archives; the seven decades' delay had been due to their "continuing sensitivity... It wouldn't have been safe to release hem earlier"
Holocaust intelligence
Historians and Holocaust researchers have tried to establish when the Allies realized the full extent of Nazi-era extermination of Jews, and specifically, the extermination-camp system. In 1999, the U.S. Government passed the Nazi War Crimes Disclosure Act ( P.L. 105-246), making it policy to declassify all Nazi war crime documents in their files; this was later amended to include the Japanese Imperial Government. As a result, more than 600 decrypts and translations of intercepted messages were disclosed; NSA historian Robert Hanyok would conclude that Allied communications intelligence, "by itself, could not have provided an early warning to Allied leaders regarding the nature and scope of the Holocaust." Following Operation Barbarossa, decrypts in August 1941 alerted British authorities to the many massacres in occupied zones of the Soviet Union, including those of Jews, but specifics were not made public for security reasons. Revelations about the concentration camps were gleaned from other sources, and were publicly reported by the Polish government-in-exile, Jan Karski and the WJC offices in Switzerland a year or more later. A decrypted message referring to "Einsatz Reinhard
or ''Einsatz Reinhard''
, location = Occupied Poland
, date = October 1941 – November 1943
, incident_type = Mass deportations to extermination camps
, perpetrators = Odilo Globočnik, Hermann Höfle, Richard Thomalla, Erwin L ...
" (the Höfle Telegram
The Höfle Telegram (or Hoefle Telegram) is a cryptic one-page document, discovered in 2000 among the declassified World War II archives of the Public Record Office in Kew, England. The document consists of several radio telegrams in translation ...
), from January 11, 1943, may have outlined the system and listed the number of Jews and others gassed at four death camps the previous year, but codebreakers did not understand the meaning of the message. In summer 1944, Arthur Schlesinger, an OSS
OSS or Oss may refer to:
Places
* Oss, a city and municipality in the Netherlands
* Osh Airport, IATA code OSS
People with the name
* Oss (surname), a surname
Arts and entertainment
* ''O.S.S.'' (film), a 1946 World War II spy film about ...
analyst, interpreted the intelligence as an "incremental increase in persecution rather than... extermination."
Postwar consequences
There has been controversy about the influence of Allied Enigma decryption on the course of World War II. It has also been suggested that the question should be broadened to include Ultra's influence not only on the war itself, but also on the post-war period.F. W. Winterbotham
Frederick William Winterbotham (16 April 1897 – 28 January 1990) was a British Royal Air Force officer (latterly a Group Captain) who during World War II supervised the distribution of Ultra intelligence. His book ''The Ultra Secret'' was t ...
, the first author to outline the influence of Enigma decryption on the course of World War II, likewise made the earliest contribution to an appreciation of Ultra's ''postwar'' influence, which now continues into the 21st century—and not only in the postwar establishment of Britain's GCHQ (Government Communication Headquarters) and America's NSA. "Let no one be fooled," Winterbotham admonishes in chapter 3, "by the spate of television films and propaganda which has made the war seem like some great triumphant epic. It was, in fact, a very narrow shave, and the reader may like to ponder ..whether ..we might have won ithoutUltra."
Debate continues on whether, had postwar political and military leaders been aware of Ultra's role in Allied victory in World War II, these leaders might have been less optimistic about post-World War II military involvements.
Knightley suggests that Ultra may have contributed to the development of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The Soviets received disguised Ultra information, but the existence of Ultra itself was not disclosed by the western Allies. The Soviets, who had clues to Ultra's existence, possibly through Kim Philby, John Cairncross and Anthony Blunt
Anthony Frederick Blunt (26 September 1907 – 26 March 1983), styled Sir Anthony Blunt KCVO from 1956 to November 1979, was a leading British art historian and Soviet spy.
Blunt was professor of art history at the University of London, dire ...
, may thus have felt still more distrustful of their wartime partners.
The mystery surrounding the discovery of the sunk off the coast of New Jersey by divers Richie Kohler and John Chatterton was unravelled in part through the analysis of Ultra intercepts, which demonstrated that, although ''U-869'' had been ordered by U-boat Command to change course and proceed to North Africa, near Rabat, the submarine had missed the messages changing her assignment and had continued to the eastern coast of the U.S., her original destination.
In 1953, the CIA's Project ARTICHOKE, a series of experiments on human subjects to develop drugs for use in interrogations, was renamed Project MKUltra. MK was the CIA's designation for its Technical Services Division and Ultra was in reference to the Ultra project.
See also
* Hut 6 * Hut 8 *Magic (cryptography)
Magic was an Allied cryptanalysis project during World War II. It involved the United States Army's Signals Intelligence Service (SIS) and the United States Navy's Communication Special Unit.
Codebreaking
Magic was set up to combine the US gover ...
* Military intelligence
* Signals intelligence in modern history
* '' The Imitation Game''
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * A short account of World War II cryptology which covers more than just the Enigma story. * * * * * * * * Has been criticised for inaccuracy and exaggeration * * * * * * * * Transcript of a lecture given on Tuesday 19 October 1993 at Cambridge University * * * * * * * This is the standard reference on the crucial foundations laid by the Poles for World War II Enigma decryption. * Focuses on the battle-field exploitation of Ultra material. * * * * Rejewski, Marian, wrote a number of papers on his 1932 break into Enigma and his subsequent work on the cipher, well into World War II, with his fellow mathematician-cryptologists, Jerzy Różycki and Henryk Zygalski. Most of Rejewski's papers appear in * * * * This provides a description of the Enigma, other ciphers, and codes. * * * * * An early publication containing several misapprehensions that are corrected in an ''addendum'' in the 1997 edition. * * * The first published account of the previously secret wartime operation, concentrating mainly on distribution of intelligence. It was written from memory and has been shown by subsequent authors, who had access to official records, to contain some inaccuracies. {{Authority control Telecommunications-related introductions in 1941 1941 establishments in the United Kingdom Military intelligence Signals intelligence of World War II Secret Intelligence Service Bletchley Park