History
On March 18, 1970, postal workers in New York City—upset over low wages and poor working conditions, and emboldened by the Civil Rights Movement— organized a strike against the United States government. The strike initially involved postal workers in only New York City, but it eventually gained support of over 210,000 U.S. Post Office Department workers across the nation. While the strike ended without any concessions from the Federal government, it did ultimately allow for postal worker unions and the government to negotiate a contract which gave the unions most of what they wanted, as well as the signing of theCurrent operations
Deliveries
 The USPS is by geography and volume the globe's largest postal system, delivering 47% of the world's mail. As of 2021, the USPS operates 31,330 post offices and locations in the U.S., and delivers 128.8 billion pieces of mail annually, to 163 million delivery points (as of 2022).
USPS delivers mail and packages Monday through Saturday as required by the Postal Service Reform Act of 2022; on Sundays only Priority Express and packages for Amazon.com are delivered. During the four weeks preceding Christmas since 2013, packages from all mail classes and senders were delivered on Sunday in some areas.
Parcels are also delivered on holidays, with the exception of Thanksgiving and Christmas.
The period between Thanksgiving and Christmas is the busiest time of the year for the USPS with the agency delivering an estimated 900 million packages during the period of 2018.
The USPS is by geography and volume the globe's largest postal system, delivering 47% of the world's mail. As of 2021, the USPS operates 31,330 post offices and locations in the U.S., and delivers 128.8 billion pieces of mail annually, to 163 million delivery points (as of 2022).
USPS delivers mail and packages Monday through Saturday as required by the Postal Service Reform Act of 2022; on Sundays only Priority Express and packages for Amazon.com are delivered. During the four weeks preceding Christmas since 2013, packages from all mail classes and senders were delivered on Sunday in some areas.
Parcels are also delivered on holidays, with the exception of Thanksgiving and Christmas.
The period between Thanksgiving and Christmas is the busiest time of the year for the USPS with the agency delivering an estimated 900 million packages during the period of 2018.
Fleet
 The USPS operates one of the largest civilian
The USPS operates one of the largest civilian /ref> partly in response to criticism from the
Military mail
The Department of Defense and the USPS jointly operate a postal system to deliver mail for the military; this is known as the Army Post Office (for Army and Air Force postal facilities) and the Fleet Post Office (for Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard postal facilities).Operation and budget
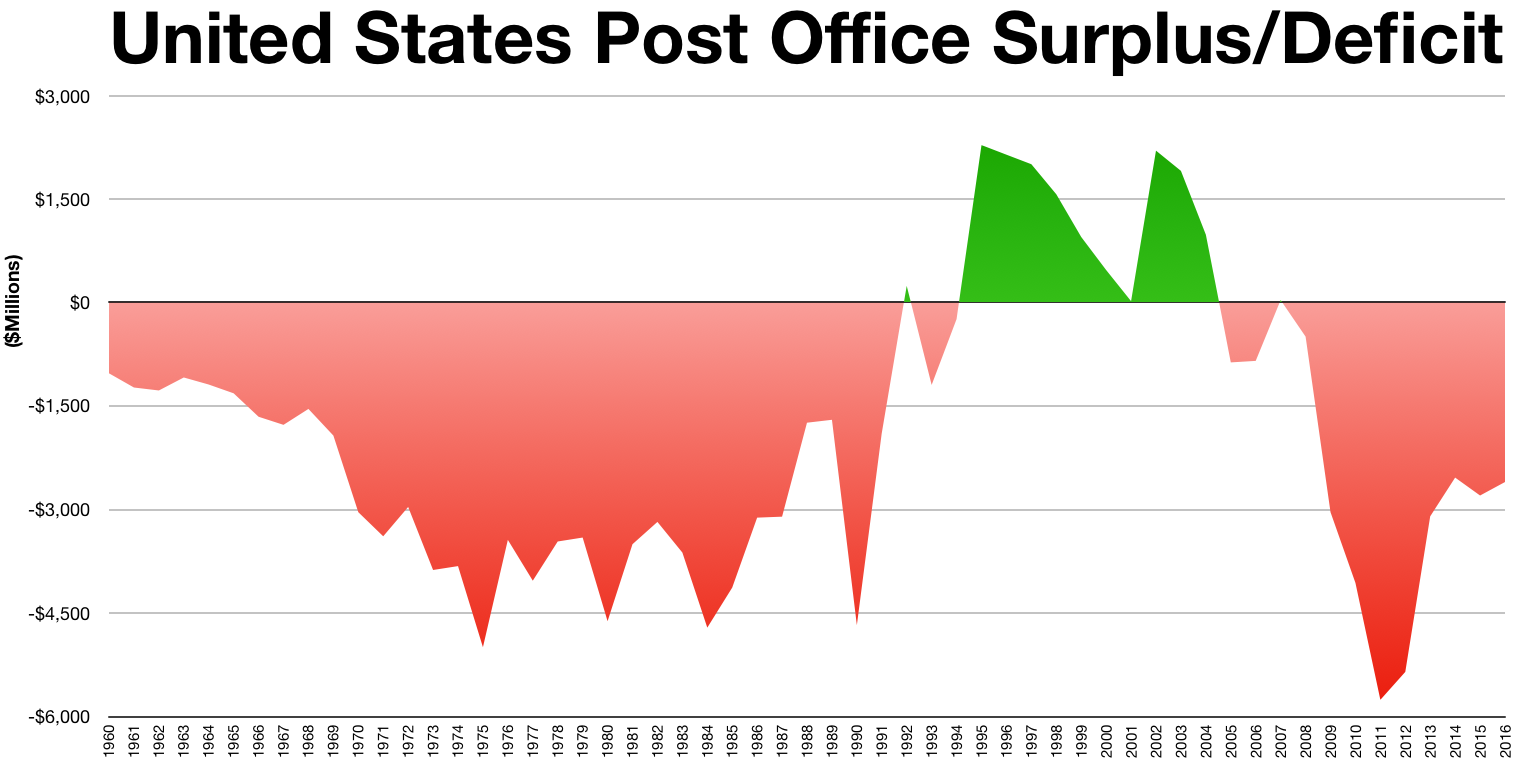 In Fiscal Year 2021, the Postal Service had $77.06 billion in revenue and expenses of $81.99 billion with a net loss of $4.93 billion.
In Fiscal Year 2021, the Postal Service had $77.06 billion in revenue and expenses of $81.99 billion with a net loss of $4.93 billion.
Revenue decline and planned cuts
In 2016, the USPS had its fifth straight annual operating loss, in the amount of $5.6 billion, of which $5.8 billion was the accrual of unpaid mandatory retiree health payments.Declining mail volume
First-class mail volume peaked in 2001 to 103.65 billion declining to 52.62 billion by 2020 due to the increasing use of email and the World Wide Web for correspondence and business transactions. USPS also almost delivered the first email but did not do so. Private courier services, such asInternal streamlining and delivery slowdown
In response, the USPS has increased productivity each year from 2000 to 2007, through increased automation, route re-optimization, and facility consolidation. Despite these efforts, the organization saw an $8.5 billion budget shortfall in 2010, and was losing money at a rate of about $3 billion per quarter in 2011. On December 5, 2011, the USPS announced it would close more than half of its mail processing centers, eliminate 28,000 jobs and reduce overnight delivery of First-Class Mail. This will close down 252 of its 461 processing centers. (At peak mail volume in 2006, the USPS operated 673 facilities.) As of May 2012, the plan was to start the first round of consolidation in summer 2012, pause from September to December, and begin a second round in February 2014; 80% of first-class mail would still be delivered overnight through the end of 2013. New delivery standards were issued in January 2015, and the majority of single-piece (not presorted) first-class mail is now being delivered in two days instead of one. Large commercial mailers can still have first-class mail delivered overnight if delivered directly to a processing center in the early morning, though as of 2014 this represented only 11% of first-class mail. Unsorted first-class mail will continue to be delivered anywhere in the contiguous United States within three days.Post office closures
In July 2011, the USPS announced a plan to close about 3,700 small post offices. Various representatives in Congress protested, and the Senate passed a bill that would have kept open all post offices farther than from the next office. In May 2012, the service announced it had modified its plan. Instead, rural post offices would remain open with reduced retail hours (some as little as two hours per day) unless there was a community preference for a different option. In a survey of rural customers, 54% preferred the new plan of retaining rural post offices with reduced hours, 20% preferred the "Village Post Office" replacement (where a nearby private retail store would provide basic mail services with expanded hours), 15% preferred merger with another Post Office, and 11% preferred expanded rural delivery services. Approximately 40% of postal revenue already comes from online purchases or private retail partners including Walmart, Staples,Elimination of Saturday delivery averted
On January 28, 2009, Postmaster GeneralRetirement funding and payment defaults
The Postal Accountability and Enhancement Act of 2006 (PAEA) obligated the USPS to fund the present value of earned retirement obligations (essentially past promises which have not yet come due) within a ten-year time span. The U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) is the main bureaucratic organization responsible for the human resources aspect of many federal agencies and their employees. The PAEA created the Postal Service Retiree Health Benefit Fund (PSRHB) after Congress removed the Postal Service contribution to the Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS). Most other employees that contribute to the CSRS have 7% deducted from their wages. Currently, all new employees contribute into Federal Employee Retirement System (FERS) once they become a full-time regular employees. Running low on cash, in order to continue operations unaffected and continue to meet payroll, the USPS defaulted for the first time on a $5.5 billion retirement benefits payment due August 1, 2012, and a $5.6 billion payment due September 30, 2012. On September 30, 2014, the USPS failed to make a $5.7 billion payment on this debt, the fourth such default. In 2017, the USPS defaulted on some of the last lump-sum payments required by the 2006 law, though other payments were also still required. Proposals to cancel the funding obligation and plan a new schedule for the debt were introduced in Congress as early as 2016. A 2019 bill entitled the "USPS Fairness Act", which would have eliminated the pension funding obligation, passed the House but did not proceed further. As of March 8, 2022, the Postal Service Reform Act of 2022, which includes a section entitled "USPS Fairness Act" cancelling the obligation, has passed both the House and the Senate; President Joe Biden signed the bill into law on April 6, 2022.Rate increases
Congress has limited rate increases for First-Class Mail to the cost of inflation, unless approved by the Postal Regulatory Commission. A three-cent surcharge above inflation increased the rate to 49¢ in January 2014, but this was approved by the commission for two years only. As of July 10, 2022, first-class postage for up to 1 ounce is $0.60.Reform proposals and delivery changes
Robert Reisner - Digital - Email
Robert Reisner, an undergraduate degree holder from Yale and an MBA degree holder from Harvard, was the agency’s first chief president of technology applications in 1993. He helped USPS launch its first website in 1994. He tried to bring USPS into the digital age. He brought a new digital postmark which allowed email to be certified just as the traditional postmark did paper envelopes. Another improvement he did allowed customers to create fliers and catalogs on their home computers and e-mail them to the USPS that delivered them as hard copies. Reisner wanted to bring email service to the USPS. William Henderson, a past Postmaster General, was also interested. Henderson had a plan for every American to get a free email address. He says now, “If we could control millions of mailboxes in the United States effectively, we can certainly control e-mail addresses.” Reisner, tried but was unsuccessful to bring the USPS into the digital age with an email service for the public. Bloomberg Businessweek''’s Devin Leonard wrote in his book,'' Neither Snow nor Rain: A History of the United States Postal Service, that if things had gone differently, the first email would have been delivered by your USPS mailman. On the whole there were a failed visionaries, such as Robert Reisner, who tried to turn the United States Postal Service into an internet pioneer but ultimately could not due to it being a bureaucracy that was not willing to adapt.During the Obama administration
 Comprehensive reform packages considered in the
Comprehensive reform packages considered in the During the Trump administration
As part of a June 2018 governmental reorganization plan, the Donald Trump administration proposed turning USPS into "a private postal operator" which could save costs through measures like delivering mail fewer days per week, or delivering to central locations instead of door to door. There was strong bipartisan opposition to the idea in Congress. In April 2020, Congress approved a $10 billion loan from the Treasury to the post office. According to ''The Washington Post'', officials under Treasury SecretaryCoronavirus pandemic and voting by mail
Voting by mail has become an increasingly common practice in the United States, with 25% of voters nationwide mailing their ballots in 2016 and 2018. The coronavirus pandemic of 2020 was predicted to cause a large increase in mail voting because of the possible danger of congregating at polling places. For the 2020 election, a state-by-state analysis concluded that 76% of Americans were eligible to vote by mail in 2020, a record number. The analysis predicted that 80 million ballots could be cast by mail in 2020 – more than double the number in 2016. The Postal Service sent a letter to 46 states in July 2020, warning that the service might not be able to meet the state's deadlines for requesting and casting last-minute absentee ballots. The House of Representatives voted to include an emergency grant of $25 billion to the post office to facilitate the predicted flood of mail ballots. Trump conceded that the post office would need additional funds to handle the additional mail-in voting, but said he would oppose any additional funding so that "universal mail-in voting" would not be possible. On August 14, 2020, President Trump said he was willing to approve USPS funding if concessions were made to some funding asks in coronavirus relief package.Governance and organization
ThePrivatization proposals
Since the 1990s, Republicans have been discussing the idea of privatizing the U.S. Postal Service. President Trump's administration proposed turning USPS into "a private postal operator" as part of a June 2018 governmental reorganization plan, although there was strong bipartisan opposition to the idea in Congress. On December 17, 2017, President Trump criticized the postal service's relationship with Amazon. In a post on Twitter, he stated: "Why is the United States Post Office, which is losing many billions of dollars a year, while charging Amazon and others so little to deliver their packages, making Amazon richer and the Post Office dumber and poorer? Should be charging MUCH MORE!" Amazon maintains that the Postal Service makes a profit from its contract with the company.Gold, Michael, and Katie Rogers (March 29, 2018)."The Facts Behind Trump's Tweets on Amazon, Taxes and the Postal Service."
'' The New York Times''. Retrieved November 9, 2019. On June 21, 2018, Trump proposed a sweeping reorganization but Congress did not act. Lisa Graves has documented decades-long efforts to privatize the U.S. Postal Service through driving the public service to financial collapse. The Council on Foreign Relations brings up the idea of bringing USPS online with a digital identity via an email address. USPS explored a digital identity using an email address in its "Digital Identity – Opportunities for the Postal Service" report in 2012.
Universal service obligation and monopoly status
Legal basis and rationale
Article I, section 8, Clause 7 of the U.S. Constitution grants Congress the power to establish post offices and post roads, which has been interpreted as a de facto Congressional monopoly over the delivery of first-class residential mail—which has been defined as non-urgent residential letters (not packages). Accordingly, no other system for delivering first-class residential mail—public or private—has been tolerated, absent Congress's consent. The mission of the Postal Service is to provide the American public with trusted universal postal service. While not explicitly defined, the Postal Service's universal service obligation (USO) is broadly outlined in statute and includes multiple dimensions: geographic scope, range of products, access to services and facilities, delivery frequency, affordable and uniform pricing, service quality, and security of the mail. While other carriers may claim to voluntarily provide delivery on a broad basis, the Postal Service is the only carrier with a ''legal obligation'' to provide all the various aspects of universal service. Proponents of universal service principles claim that since any obligation must be matched by the financial capability to meet that obligation, the postal monopoly was put in place as a funding mechanism for the USO, and it has been in place for over a hundred years. It consists of two parts: the Private Express Statutes (PES) and the mailbox access rule. The PES refer to the Postal Service's monopoly on the delivery of letters, and the mailbox rule refers to the Postal Service's exclusive access to customer mailboxes. Proponents of universal service principles further claim that eliminating or reducing the PES or mailbox rule would affect the ability of the Postal Service to provide affordable universal service. If, for example, the PES and the mailbox rule were to be eliminated, and the USO maintained, then either billions of dollars in tax revenues or some other source of funding would have to be found. Some proponents of universal service principles suggest that private communications that are protected by the veil of government promote the exchange of free ideas and communications. This separates private communications from the ability of a private for-profit or non-profit organization to corrupt. Security for the individual is in this way protected by the United States Post Office, maintaining confidentiality and anonymity, as well as government employees being much less likely to be instructed by superiors to engage in nefarious spying. It is seen by some as a dangerous step to extract the universal service principle from the post office, as the untainted nature of private communications is preserved as assurance of the protection of individual freedom of privacy. However, as the recent notice of a termination of mail service to residents of the2008 report on universal postal service and the postal monopoly
The Postal Act of 2006 required the Postal Regulatory Commission (PRC) to submit a report to the president and Congress on universal postal service and the postal monopoly in December 2008. The report must include any recommended changes. The Postal Service report supports the requirement that the PRC is to consult with and solicit written comments from the Postal Service. In addition, the Government Accountability Office was required to evaluate broader business model issues by 2011. On October 15, 2008, the Postal Service submitted a report to the PRC on its position related to the Universal Service Obligation (USO). It said no changes to the USO and restriction on mailbox access were necessary at that time, but increased regulatory flexibility was required to ensure affordable universal service in the future. In February 2013, the Postal Service announced that starting August 2013, Saturday delivery would be discontinued. Congress traditionally includes a provision in an annual continuing resolution that requires six-day delivery; it did so again in March 2013, and the Postal Service was forced to continue Saturday delivery. Obligations of the USO include uniform prices, quality of service, access to services, and six-day delivery to every part of the country. To assure financial support for these obligations, the postal monopoly provides the Postal Service the exclusive right to deliver letters and restricts mailbox access solely for mail. The report argued that eliminating or reducing either aspect of the monopoly "would have a devastating impact on the ability ... to provide the affordable universal service that the country values so highly". Relaxing access to the mailbox would also pose security concerns, increase delivery costs, and hurt customer service, according to the Post Office. The report notes:It is somewhat misleading to characterize the mailbox rule as a "monopoly," because the enforcement of leaves customers with ample alternative means of delivering their messages. Customers can deliver their messages either by paying postage, by placing messages on or under a door or a doormat, by using newspaper or non-postal boxes, by telephoning or emailing, by engaging in person-to-person delivery in public areas, by tacking or taping their notices on a door post, or by placing advertisements in local newspapers. These methods are comparable in efficacy to communication via the mailbox.Most of these alternatives are not actually free in some communities. For example, in the Chicago metropolitan area and many other major metros one must get a background check from police and pay a daily fee for the right to solicit or post commercial messages on
Competitors

Alternative transmission methods
The Post Office Department owned and operated the first public telegraph lines in the United States, starting in 1844 from Washington to Baltimore, and eventually extending to New York, Boston, Buffalo, and Philadelphia. In 1847, the telegraph system was privatized, except for a period during World War I, when it was used to accelerate the delivery of letters arriving at night. Between 1942 and 1945, " V-Mail" (for "Victory Mail") service was available for military mail. Letters were converted into microfilm and reprinted near the destination, to save room on transport vehicles for military cargo. In 1970, Western Union in co-operation with the Postal Service introduced the " Mailgram", a special type of telegram offered by Western Union intended for bulk mailing to multiple addressees. The sender would contact WU and submit to them the message to be sent and a list of addressees to mail the requested Mailgrams to. The message and address data were then sent electronically over Western Union's terrestrial network normally used for standard telegrams, with WU's Westar 1 satellite used instead starting in 1974 with its launch, for Mailgram transmission to participating Postal Service centers, who would then print and mail the Mailgrams to the requested addressees. Similar to WU's Mailgrams was Electronic Computer Originated Mail, offered by the Postal Service from 1982 to 1985. Also known as E-COM, it too was used for bulk mailings. Text was transmitted electronically to one of 25 post offices nationwide. The Postal Service would print the mail and put it in special envelopes bearing a blue E-COM logo. Delivery was assured within 2 days. To improve accuracy and efficiency, the Postal Service introduced the Intelligent Mail program to complement the ZIP code system. This system, which was intended to replace the deprecated POSTNET system, allows bulk mailers to use pre-printed bar codes to assist in mail delivery and sorting. Additional features, called Enhanced, or Full-Service, Intelligent Mail Barcodes allow for mail tracking of bulk mail through the postal system up to the final delivery Post Office.Criticism of the universal service requirement and the postal monopoly
Critics of the universal service requirement and the statutory postal monopoly include several professional economists advocating for the privatization of the mail delivery system, or at least a relaxation of the universal service model that currently exists. Rick Geddes argued in 2000: Furthermore, some economists have argued that because public enterprises may pursue objectives different thanLaw enforcement agencies
Under the Mail Cover Program USPS photographs the front and back of every piece of U.S. mail as part of the sorting process, enabling law enforcement to obtain address information and images of the outsides of mail as part of an investigation without the need for a warrant.Postal Inspection Service
The United States Postal Inspection Service (USPIS) is one of the oldest law enforcement agencies in the U.S. Founded by Benjamin Franklin on August 7, 1775, its mission is to protect the Postal Service, its employees, and its customers from crime and protect the nation's mail system from criminal misuse. Postal Inspectors enforce over 200 federal laws providing for the protection of mail in investigations of crimes that may adversely affect or fraudulently use the U.S. Mail, the postal system or postal employees. The USPIS has the power to enforce the USPS monopoly by conducting search and seizure raids on entities they suspect of sending non-urgent mail through overnight delivery competitors. According to the American Enterprise Institute, a private conservative think tank, the USPIS raidedOffice of Inspector General
The United States Postal Service Office of Inspector General (OIG) was authorized by law in 1996. Prior to the 1996 legislation, the Postal Inspection Service performed the duties of the OIG. The inspector general, who is independent of postal management, is appointed by and reports directly to the nine presidentially appointed,How delivery services work
Elements of addressing and preparing domestic mail
All mailable articles (e.g., letters, flats, machinable parcels, irregular parcels, etc.) shipped within the United States must comply with an array of standards published in the USPS Domestic Mail Manual (DMM). Before addressing the mailpiece, one must first comply with the various mailability standards relating to attributes of the actual mailpiece such as: minimum/maximum dimensions and weight, acceptable mailing containers, proper mailpiece sealing/closure, utilization of various markings, and restrictions relating to various hazardous (e.g., explosives, flammables, etc.) and restricted (e.g., cigarettes, smokeless tobacco, etc.) materials, as well as others articulated in § 601 of the DMM. The USPS specifies the following key elements when preparing the face of a mailpiece: # Proper Placement: The Delivery Address should be left-justified and located roughly in the center of mailpiece's largest side. More precisely, on a letter-size piece, the recommended address placement is within the optical character reader (OCR) read area, which is a space on the address side of the mailpiece defined by these boundaries: Left: inch (13 mm) from the left edge of the piece; Right: inch (13 mm) from the right edge of the piece; Top: inches (70 mm) from the bottom edge of the piece; Bottom: inch (16 mm) from the bottom edge of the piece. Preferred placement of a return address is in the upper left portion of the mailpiece—on the side of the piece bearing postage. Finally, postage (e.g., stamps, meter imprints, information-based indicia (IBI), etc.) is to be affixed in the upper right corner of the address side of the mail cover. Any stamp/indicia partly concealed or otherwise obscured by an overlapping stamp/indicia may not be counted as valid postage. # Delivery Address (party receiving mail): The mail piece must have the address of the intended recipient, visible and legible, only on the side of the mail piece bearing postage. Generally, the name of the addressee should be included above the address itself. A ZIP+4 code will facilitate delivery. # Return Address (party sending mail): A return address tells the USPS where the sender wants the mail returned if it is undeliverable. Usage of a return address is required for some postal services (including Priority Mail, Express Mail, Periodicals in envelopes or wrappers, Insured Mail, Registered Mail, and parcel services). # Postage Payment: All mailpieces must include appropriate valid postage. Postage payment may be in the form of stamps, stamped stationery, precanceled stamps, postage meter imprints and PC Postage products ("Postage Evidencing Systems"), or permit imprint (indicia). Members of the U.S. Congress, among others, have franking privileges, which require only a signature. Domestic First-Class Mail costs 58¢ for envelopes (40 cents forDelivery Point Validation
Delivery Point Validation (DPV) provides the highest level of address accuracy checking. In a DPV process, the address is checked against the AMS data file to ensure that it exists as an active delivery point. 2004 Comprehensive Statement on Postal Operations Chapter 2 Postal Operations The USPS provides DPV on their website as part of the ZIP Code Lookup tool; there are also companies that offer services to perform DPV in bulk.Paying postage
The actual postage can be paid via: * Stamps purchased online at usps.com, at a post office, from a stamp vending machine or "Automated Postal Center" which can also handle packages, or from a third party (such as a grocery store) * Pre-cancelled stamps for bulk mailings * Postal meter * Prepaid envelope * Shipping label purchased online and printed by the customer on standard paper (e.g., with Click-N-Ship, or via a third-party such as PayPal or Amazon shipping) All unused U.S. postage stamps issued since 1861 are still valid as postage at their indicated value. Stamps with no value shown or denominated by a letter are also still valid, although the value depends upon the particular stamp. For some stamps issued without a printed value, the current value is the original value. But some stamps beginning in 1988 or earlier, including ''Forever Stamps'' (issued from April 2007) and all first-class, first-ounce stamps issued from January 21, 2011, the value is the current value of a first-class-mail first-ounce stamp. The USPS calls these Forever Stamps but the generic name is non-denominated postage. Forever stamps are sold at the First-Class Mail postage rate at the time of purchase, but will always be valid for First-Class Mail, up to , no matter how rates rise in the future. Britain has had a similar stamp since 1989. The cost of mailing a First-Class letter increased to 60 cents on July 10, 2022.Postage meters
A postage meter is a mechanical device used to create and apply physical evidence of postage (or franking) to mailed matter. Postage meters are regulated by a country's postal authority; for example, in the United States, the United States Postal Service specifies the rules for the creation, support, and use of postage meters. A postage meter imprints an amount of postage, functioning as a postage stamp, a cancellation and a dated postmark all in one. The meter stamp serves as proof of payment and eliminates the need for adhesive stamps.PC Postage
In addition to using standard stamps, postage can now be printed in the form of an electronic stamp, or e-stamp, from a personal computer using a system called Information Based Indicia. This online PC Postage method relies upon application software on the customer's computer contacting a postal security device at the office of the postal service. PC Postage providers include: *Other electronic postage payment methods
Electronic Verification System (eVS) is the Postal Service's integrated mail management technology that centralizes payment processing and electronic postage reports. Part of an evolving suite of USPS electronic payment services called PostalOne!, eVS allows mailers shipping large volumes of parcels through the Postal Service a way to circumvent use of hard-copy manifests, postage statements and drop-shipment verification forms. Instead, mailers can pay postage automatically through a centralized account and track payments online. Beginning in August 2007, the Postal Service began requiring mailers shipping Parcel Select packages using a permit imprint to use eVS for manifesting their packages.Stamp copyright and reproduction
All U.S. postage stamps issued under the former United States Post Office Department and other postage items that were released before 1978 are not subject to copyright, but stamp designs since 1978 are copyrighted. TheService level choices
General domestic services
As of April 2011, domestic postage levels for low-volume mailers include: * Priority Mail Express (formerly Express Mail): Overnight delivery guaranteed to most locationsUSPS FAQ – Domestic Classes of Mail Estimated Delivery Time**1 or 2 day delivery guarantee **Delivery guaranteed by 6 PM () ** $100 insurance included. ** Tracking included. ** Flat Rate envelopes are available $26.35 postage. Otherwise, pricing varies by weight and distance. * Priority Mail: Day specific delivery service ranging from 1 to 3 days depending on origin of shipment (not guaranteed) ** As of January 27, 2013, tracking via Delivery Confirmation is now included on all Priority Mail shipments. ** Flat Rate envelopes and boxes (various sizes) are available free from the Postal Store. Otherwise, pricing varies by weight, size and distance. ** $50 insurance for retail/$100 insurance for commercial starting on July 28, 2013. ** Tracking Included * First-Class Mail ** 2- to 3-day delivery. *** In most cases for letters and small packages. ** Rate varies by size and weight, but not distance. *** Postcards (5″ × 3.5″ × 0.007 to 6″ × 4.25″ × 0.016″ × 27 × 89 × 0.18 to 152 × 108 × 0.4 mm: 40¢ *** Letters (up to 11.5″ × 6.125″ × 0.25″ ×, 3.5 oz 92 × 156 × 6.4 mm, 100 g: 58¢ + 20¢ for each additional ounce stamped, 53¢ + 20¢ for each additional ounce metered *** Large Envelope or Flat (up to 15″ × 12″ × 0.75″ ×, 13 oz 81 × 305 × 19 mm, 370 g: $1.16 + 20¢ each additional ounce (28 g). Must be rectangular, uniformly thick, and not too rigid. * First class package service ** Rate varies by weight and distance. *** Package/Parcel (Up to length plus girth, : $3.80-$4.20 up to 4 ounces, $4.60-$5.00 up to 8 ounces, $5.90-$6.50 up to 13 ounces * USPS Retail Ground (formerly Parcel Post) ** Slowest but cheapest service for packages too large or heavy for First Class—uses
Bulk mail
 Discounts are available for large volumes of mail. Depending on the postage level, certain conditions might be required or optional for an additional discount:
* Minimum number of pieces
* Weight limits
* Ability for the USPS to process by machine
* Addresses formatting standardized
* USPS-readable barcode
* Sorted by three-digit ZIP code prefix, five-digit ZIP code, ZIP+4, or 11-digit delivery point
* Delivered in trays, bundles, or pallets partitioned by destination
* Delivered directly to a regional Bulk Mail Center, destination SCF, or destination Post Office
* Certification of mailing list accuracy and freshness (e.g., correct ZIP codes, purging of stale addresses, processing of change-of-address notifications)
In addition to bulk discounts on Express, Priority, and First-Class Mail, the following postage levels are available for bulk mailers:
* Periodicals
* Standard Mail (A)
** Automation
** Enhanced Carrier Route
** Regular
* Standard Mail (B)
** Parcel Post
** Bound Printed Matter – Cheaper than Media Mail, for advertising catalogs, phone books, etc. up to 15 lb
** Special Standard Mail
** Library Mail
** Nonprofit
Discounts are available for large volumes of mail. Depending on the postage level, certain conditions might be required or optional for an additional discount:
* Minimum number of pieces
* Weight limits
* Ability for the USPS to process by machine
* Addresses formatting standardized
* USPS-readable barcode
* Sorted by three-digit ZIP code prefix, five-digit ZIP code, ZIP+4, or 11-digit delivery point
* Delivered in trays, bundles, or pallets partitioned by destination
* Delivered directly to a regional Bulk Mail Center, destination SCF, or destination Post Office
* Certification of mailing list accuracy and freshness (e.g., correct ZIP codes, purging of stale addresses, processing of change-of-address notifications)
In addition to bulk discounts on Express, Priority, and First-Class Mail, the following postage levels are available for bulk mailers:
* Periodicals
* Standard Mail (A)
** Automation
** Enhanced Carrier Route
** Regular
* Standard Mail (B)
** Parcel Post
** Bound Printed Matter – Cheaper than Media Mail, for advertising catalogs, phone books, etc. up to 15 lb
** Special Standard Mail
** Library Mail
** Nonprofit
Extra services
 Depending on the type of mail, additional services are available for an additional fee:
* Certificate of Mailing provides proof of the date a package was mailed.
* Certified Mail provides proof of mailing, and a delivery record. Used for serving legal documents and for sending U.S. Government classified information, up to the "confidential" level.
* Collect on Delivery (C.O.D.) allows merchants to offer customers an option to pay upon delivery, up to $1,000. Includes insurance.
* USPS Tracking provides proof of delivery to sorting facilities, local post office and destination, but no signature is required.
* Insurance is shipping insurance against loss or damage for the value of the goods mailed. Amount of coverage can be specified, up to $5,000.
* Registered Mail is used for highly valuable or irreplaceable items, and classified information up to the "secret" level. Registered mail is transported separately from other mail, in locked containers. Tracking is included and insurance up to $25,000 is available.
* Restricted Delivery requires delivery to a specific person or their authorized agent, not just to a mailbox.
* Return Receipt actively sends signature confirmation back to the sender by postcard or emailed PDF (as opposed to merely putting this information into the online tracking system).
* Signature Confirmation requires a delivery signature, which is kept on file. The online tracking system displays the first initial and last name of the signatory.
* Special Handling is for unusual items, like live animals.
Depending on the type of mail, additional services are available for an additional fee:
* Certificate of Mailing provides proof of the date a package was mailed.
* Certified Mail provides proof of mailing, and a delivery record. Used for serving legal documents and for sending U.S. Government classified information, up to the "confidential" level.
* Collect on Delivery (C.O.D.) allows merchants to offer customers an option to pay upon delivery, up to $1,000. Includes insurance.
* USPS Tracking provides proof of delivery to sorting facilities, local post office and destination, but no signature is required.
* Insurance is shipping insurance against loss or damage for the value of the goods mailed. Amount of coverage can be specified, up to $5,000.
* Registered Mail is used for highly valuable or irreplaceable items, and classified information up to the "secret" level. Registered mail is transported separately from other mail, in locked containers. Tracking is included and insurance up to $25,000 is available.
* Restricted Delivery requires delivery to a specific person or their authorized agent, not just to a mailbox.
* Return Receipt actively sends signature confirmation back to the sender by postcard or emailed PDF (as opposed to merely putting this information into the online tracking system).
* Signature Confirmation requires a delivery signature, which is kept on file. The online tracking system displays the first initial and last name of the signatory.
* Special Handling is for unusual items, like live animals.
International services
In May 2007, the USPS restructured international service names to correspond with domestic shipping options. Formerly, USPS International services were categorized as Airmail (Letter Post), Economy (Surface) Parcel Post, Airmail Parcel Post, Global Priority, Global Express, and Global Express Guaranteed Mail. The former Airmail (Letter Post) is now First-Class Mail International, and includes small packages weighing up to four pounds (1.8 kg). Economy Parcel Post was discontinued for international service, while Airmail Parcel Post was replaced by Priority Mail International. Priority Mail International Flat-Rate packaging in various sizes was introduced, with the same conditions of service previously used for Global Priority. Global Express is now Express Mail International, while Global Express Guaranteed is unchanged. The international mailing classes with a tracking ability are Express, Express Guaranteed, and Priority (except that tracking is not available for Priority Mail International Flat Rate Envelopes or Priority Mail International Small Flat Rate Boxes). One of the major changes in the new naming and services definitions is that USPS-supplied mailing boxes for Priority and Express mail are now allowed for international use. These services are offered to ship letters and packages to almost every country and territory on the globe. The USPS provides much of this service by contracting with a private parcel service, The USPS provides an service for international shipment of printed matter;Postal Explorer>IMM Issue 37 – International Mail Manual > 2 Conditions for Mailing
The USPS provides an service for international shipment of printed matter;Postal Explorer>IMM Issue 37 – International Mail Manual > 2 Conditions for Mailing 260 Direct Sacks of Printed Matter to One Addressee (M–bags)
previously surface M-bags existed, but with the 2007 elimination of surface mail, only airmail M-bags remain. The term "M-bag" is not expanded in USPS publications; M-bags are simply defined as "direct sacks of printed matter ... sent to a single foreign addressee at a single address"; however, the term is sometimes referred to informally as "media bag", as the bag can also contain "discs, tapes, and cassettes", in addition to books, for which the usual umbrella term is "media"; some also refer to them as "mail bags". Military mail is billed at domestic rates when being sent from the United States to a military outpost, and is free when sent by deployed military personnel. The overseas logistics are handled by the
The discontinuation of international surface mail
Sorting and delivery process
Types of postal facilities

 Although its retail postal facilities are called post offices in regular speech, the USPS recognizes several types of postal facilities, including the following:
* A main post office (formerly known as a general post office) is the primary postal facility in a community.
* A station or post office station is a postal facility that is not the main post office, but that is within the corporate limits of the community.
* A branch or post office branch is a postal facility that is not the main post office and that is outside the corporate limits of the community.
* A classified unit is a station or branch operated by USPS employees in a facility owned or leased by the USPS.
* A contract postal unit (or CPU) is a station or branch operated by a contractor, typically in a store or other place of business.
* A community post office (or CPO) is a contract postal unit providing services in a small community in which other types of post office facilities have been discontinued.
* An approved shipper is an independent shipping business licensed to use certain USPS branding and signage, but which does not receive any financial compensation from USPS and may opt to charge higher rates for postage. Approved Shippers may also accept packages for other carriers such as UPS or FedEx.
* A finance unit is a station or branch that provides window services and accepts mail, but does not provide delivery.
* A village post office (VPO) is an entity such as a local business or government center that provides postal services through a contract with the USPS. First introduced in 2011 as an integral part of the USPS plan to close low volume post offices, village post offices will fill the role of the post office within a ZIP Code.
* A processing and distribution center (P&DC, or processing and distribution facility, formerly known as a General Mail Facility) is a central mail facility that processes and dispatches incoming and outgoing mail to and from a designated service area (251 nationwide).
* A sectional center facility (SCF) is a P&DC for a designated geographical area defined by one or more three-digit ZIP Code prefixes.
* An international service center (ISC) is an international mail processing facility. There are only five such USPS facilities in the continental United States, located in Chicago, New York, Miami, Los Angeles and San Francisco.
* A network distribution center, formerly known as a bulk mail center (BMC), is a central mail facility that processes bulk rate parcels as the hub in a
Although its retail postal facilities are called post offices in regular speech, the USPS recognizes several types of postal facilities, including the following:
* A main post office (formerly known as a general post office) is the primary postal facility in a community.
* A station or post office station is a postal facility that is not the main post office, but that is within the corporate limits of the community.
* A branch or post office branch is a postal facility that is not the main post office and that is outside the corporate limits of the community.
* A classified unit is a station or branch operated by USPS employees in a facility owned or leased by the USPS.
* A contract postal unit (or CPU) is a station or branch operated by a contractor, typically in a store or other place of business.
* A community post office (or CPO) is a contract postal unit providing services in a small community in which other types of post office facilities have been discontinued.
* An approved shipper is an independent shipping business licensed to use certain USPS branding and signage, but which does not receive any financial compensation from USPS and may opt to charge higher rates for postage. Approved Shippers may also accept packages for other carriers such as UPS or FedEx.
* A finance unit is a station or branch that provides window services and accepts mail, but does not provide delivery.
* A village post office (VPO) is an entity such as a local business or government center that provides postal services through a contract with the USPS. First introduced in 2011 as an integral part of the USPS plan to close low volume post offices, village post offices will fill the role of the post office within a ZIP Code.
* A processing and distribution center (P&DC, or processing and distribution facility, formerly known as a General Mail Facility) is a central mail facility that processes and dispatches incoming and outgoing mail to and from a designated service area (251 nationwide).
* A sectional center facility (SCF) is a P&DC for a designated geographical area defined by one or more three-digit ZIP Code prefixes.
* An international service center (ISC) is an international mail processing facility. There are only five such USPS facilities in the continental United States, located in Chicago, New York, Miami, Los Angeles and San Francisco.
* A network distribution center, formerly known as a bulk mail center (BMC), is a central mail facility that processes bulk rate parcels as the hub in a . (PDF) . Retrieved on July 8, 2011. Post Offices often share facilities with other governmental organizations located within a city's central business district. In those locations, often Courthouses and Federal Buildings, the building is owned by the General Services Administration while the U.S. Postal Services operates as a tenant. The USPS retail system has approximately 36,000 post offices, stations, and branches.
= Automated Postal Centers
= In the year 2004, the USPS began deploying Automated Postal Centers (APCs). APCs are unattended kiosks that are capable of weighing, franking, and storing packages for later pickup as well as selling domestic and international postage stamps. Since its introduction, APCs do not take cash payments – they only accept credit or debit cards. Similarly, traditional vending machines are available at many post offices to purchase stamps, though these are being phased out in many areas. Due to increasing use of Internet services, as of June 2009, no retail post office windows are open 24 hours; overnight services are limited to those provided by an Automated Postal Center.
In the year 2004, the USPS began deploying Automated Postal Centers (APCs). APCs are unattended kiosks that are capable of weighing, franking, and storing packages for later pickup as well as selling domestic and international postage stamps. Since its introduction, APCs do not take cash payments – they only accept credit or debit cards. Similarly, traditional vending machines are available at many post offices to purchase stamps, though these are being phased out in many areas. Due to increasing use of Internet services, as of June 2009, no retail post office windows are open 24 hours; overnight services are limited to those provided by an Automated Postal Center.
Evolutionary Network Development (END) program
In February 2006, the USPS announced that they plan to replace the nine existing facility-types with five processing facility-types: * Regional Distribution Centers (RDCs), which will process all classes of parcels and bundles and serve as Surface Transfer Centers; * Local Processing Centers (LPCs), which will process single-piece letters and flats and cancel mail; * Destination Processing Centers (DPC), sort the mail for individual letter-carrier route; * Airport Transfer Centers (ATCs), which will serve as transfer points only; and * Remote Encoding Centers (RECs). Over a period of years, these facilities are expected to replace Processing & Distribution Centers, Customer Service Facilities, Bulk Mail Centers, Logistic and Distribution Centers, annexes, the Hub and Spoke Program, Air Mail Centers, and International Service Centers. The changes are a result of the declining volumes of single-piece First-Class Mail, population shifts, the increase in drop shipments by advertising mailers at destinating postal facilities, advancements in equipment and technology, redundancies in the existing network, and the need for operational flexibility. The program was ended in early 2007 after an analysis revealed that the significant amount of capital investment required to implement the END network concept would not generate the benefits originally anticipated.Airline and rail division
 The United States Postal Service does not directly own or operate any aircraft or trains, although both were formerly operated. The mail and packages are flown on airlines with which the Postal Service has a contractual agreement. The contracts change periodically. Contract airlines have included: UPS,
The United States Postal Service does not directly own or operate any aircraft or trains, although both were formerly operated. The mail and packages are flown on airlines with which the Postal Service has a contractual agreement. The contracts change periodically. Contract airlines have included: UPS, ' This decision has been reversed by the U.S. postmaster general.
Parcel forwarding and private interchange
Private US parcel forwarding or US mail forwarding companies focusing on personal shopper, relocation, Ex-pat and mail box services often interface with the United States Postal Service for transporting of mail and packages for their customers.Delivery timing


Delivery days
From 1810, mail was delivered seven days a week. In 1828, local religious leaders noticed a decline in Sunday-morning church attendance because of local post offices' doubling as gathering places. These leaders appealed to the government to intervene and close post offices on Sundays. The government, however, declined, and mail was delivered seven days a week until 1912.. Retrieved October 10, 2007."The Unlikely Alliance That Ended Sunday Mail Delivery ... in 1912"
Today, U.S. Mail (with the exception of Express Mail) is not delivered on Sunday. Saturday delivery was temporarily suspended in April 1957, because of lack of funds, but quickly restored. Budget problems prompted consideration of dropping Saturday delivery starting around 2009. This culminated in a 2013 announcement that regular mail services would be cut to five days a week, which was reversed by Congress before it could take effect. (See the section Revenue decline and planned cuts.)
Direct delivery vs. customer pickup
Originally, mail was not delivered to homes and businesses, but to post offices. In 1863, "city delivery" began in urban areas with enough customers to make this economical. This required streets to be named, houses to be numbered, with sidewalks and lighting provided, and these street addresses to be added to envelopes. The number of routes served expanded over time. In 1891, the first experiments with Rural Free Delivery began in less densely populated areas. There is currently an effort to reduce direct delivery in favor of mailbox clusters. To compensate for high mail volume and slow long-distance transportation which saw mail arrive at post offices throughout the day, deliveries were made multiple times a day. This ranged from twice for residential areas to up to seven times for the central business district of Brooklyn, New York.Deliveries per Day. (PDF) . Retrieved on July 8, 2011. In the late 19th century, mail boxes were encouraged, saving carriers the time it took to deliver directly to the addressee in person; in the 1910s and 1920s, they were phased in as a requirement for service. In the 1940s, multiple daily deliveries began to be reduced, especially on Saturdays. By 1990, the last twice-daily deliveries in New York City were eliminated. Today, mail is delivered once a day on-site to most private homes and businesses. The USPS still distinguishes between city delivery (where carriers generally walk and deliver to mailboxes hung on exterior walls or porches, or to commercial reception areas) and rural delivery (where carriers generally drive). With "curbside delivery", mailboxes are at the ends of driveways, on the nearest convenient road. "Central point delivery" is used in some locations, where several nearby residences share a "cluster" of individual mailboxes in a single housing. Some customers choose to use
Special delivery
From 1885 to 1997, a service called special delivery was available, which caused a separate delivery to the final location earlier in the day than the usual daily rounds.Same-day trials
In December 2012, the USPS began a limited one-year trial of same-day deliveries directly from retailers or distribution hubs to residential addresses in the same local area, a service it dubbed "Metro Post". The trial was initially limited to San Francisco and the only retailer to participate in the first few weeks wasForwarding and holds
Residential customers can fill out a form to forward mail to a new address, and can also send pre-printed forms to any of their frequent correspondents. They can also put their mail on "hold", for example, while on vacation. The Post Office will store mail during the hold, instead of letting it overflow in the mailbox. These services are not available to large buildings and customers of aFirst-class packages
In April 2022, the USPS announced it would slow deliveries of almost one third of first-class packages as it sought to rely less on air transportation and find cost savings.Financial services
PostalEmployment
 The Postal Service is the nation's second-largest civilian employer. – There is als
The Postal Service is the nation's second-largest civilian employer. – There is alsa web version of the content
, it employed 495,941 career employees and 148,092 non-career personnel, divided among offices, processing centers, and actual post offices. The United States Postal Service would rank 44th on the 2019 Fortune 500 list, if considered a private company and ranks 136 on Global Fortune 500 list. Labor unions representing USPS employees include: The American Postal Workers Union (APWU), which represents postal clerks and maintenance, motor vehicle, mail equipment shops, material distribution centers, and operating services and facilities services employees, postal nurses, and IT and accounting; the National Association of Letter Carriers (NALC), which represents city letter carriers; the National Rural Letter Carriers' Association (NRLCA), which represents rural letter carriers; and the National Postal Mail Handlers Union (NPMHU). USPS employees are divided into major crafts according to the work they engage in: * Letter carriers, also referred to as mailmen or mail carriers, prepare and deliver mail and parcels. They are divided into two categories: City Letter Carriers, who are represented by the NALC, and Rural Letter Carriers, who are represented by the NRLCA. City Carriers are paid hourly with automatic overtime paid after 8 hours or 40 hours a week of duty. City Carriers are required to work in any kind of weather, daylight or dark and carry three bundles of mail (letters in one hand with magazines and other larger mail pieces) on the forearm carrying the mail. Advertisement mail, Every door direct (EDD) and smaller parcels all go in the carriers satchel). Larger parcels, up to a total of 70 lbs. may be delivered at various times of the day or with the mail. Mail routes are outfitted with a number of scanpoints (mailbox barcodes) on random streets every 30 to 40 minutes apart to keep track of the carriers whereabouts in real-time. * Rural carriers are under a form of salary called "evaluated hours", usually with overtime built into their pay. The evaluated hours are created by having all mail counted for a period of two or four weeks, and a formula used to create the set dollar amount they will be paid for each day worked until the next time the route is counted. * Mail handlers and processors, prepare, separate, load and unload mail and parcels, by delivery ZIP code and station, for the clerks. They work almost exclusively at the plants or larger mail facilities now after having their duties excessed and reassigned to clerks in Post Offices and Station branches. * Clerks, have a dual function by design of where their assignment is. Window clerks directly handle customer service needs at the counter, sort box mail and sort first-class letters, standard and bulk-rate mail for the carriers on the work floor. Clerks may also work alongside mail handlers in large sorting facilities, outside of the public view, sorting mail. Data Conversion Operators, who encode address information at Remote Encoding Centers, are also members of the clerk craft. Mail handlers and Clerks are represented by the NPMHU and the APWU, respectively. Other non-managerial positions in the USPS include: * Maintenance and custodians, who see to the overall operation and cleaning of mail sorting machines, work areas, public parking and general facility operations. * City Carrier Assistants. (CCAs) With the Das Arbitration award the designation of PTF City Carrier has been abolished. TE City Carriers will have the opportunity to become CCAs. A CCA is a non-career employee who is hired for a 360-day term, similar to what TEs had. CCAs earn annual leave. CCAs, unlike TEs do have a direct path to becoming career employees. When excess City Carrier positions exist the CCA in that work installation with the highest "relative standing" will be promoted to a career employee and be assigned to the vacant position. * Career, Part Time Flexible and Transitional employees (Career, PTF & TE) There are a variety of other non-managerial positions in such crafts as accounting, information technology, and the remote encoding center. These are under a different contract than plant workers or letter carriers. *Contractors are not USPS employees, but work for the USPS under a written contract and usually paid per mile. They do not get benefits including health insurance, leave, life insurance, and pension. They must use their own vehicle and pay any cost to maintain, insure, or replace. Contractors generally make less than employees. Just like regular carriers they deliver packages and letters to mailboxes and doors. Though the USPS employs many individuals, as more Americans send information via email, fewer postal workers are needed to work dwindling amounts of mail. Post offices and mail facilities are constantly downsizing, replacing craft positions with new machines and consolidating mail routes through the MIARAP (Modified Interim Alternate Route Adjustment Process) agreement. A major round of job cuts, early retirements, and a construction freeze were announced on March 20, 2009.
Workplace violence
In the early 1990s, widely publicizedIn fiction
* In the film '' Miracle on 34th Street'' (1947), the identity of Kris Kringle (played by Edmund Gwenn) as the one and only "See also
* List of U.S. state abbreviations * List of Zip Code Prefixes * United States Postal Service creed * USPS Post Office Box Lobby Recycling programHistory
* William Goddard (publisher) — Worked with Benjamin Franklin in establishing the U.S. postal system. * American Letter Mail Company * History of United States postage rates * Owney (dog) *International associations
*Key related, comparable, and competing entities
* Pony Express * Wells Fargo, particularly: :*Mail bag types
* Catcher pouch * Mail pouch * Mail sack * Mail satchel * Pony Express mochila * PortmanteauWorkplace violence
*References
Further reading
* Adelman, Joseph M. "'A Constitutional Conveyance of Intelligence, Public and Private': The Post Office, the Business of Printing, and the American Revolution," ''Enterprise & Society'' (2010) 11#4 pp 709–52in Project MUSE
* Carpenter, D. (2000). State Building through Reputation Building: Coalitions of Esteem and Program Innovation in the National Postal System, 1883–1913. ''Studies in American Political Development,'' ''14''(2), 121–155. * Fuller, Wayne. ''American Mail: Enlarger of the Common Life'' (1972) * Gallagher, Winifred. ''How the Post Office Created America'' (New York: Penguin, 2017). 326 pp * Henkin, David M. ''The Postal Age: The Emergence of Modern Communications in Nineteenth-Century America'' (2007
excerpt and text search
* John, Richard R. ''Spreading the News: The American Postal System From Franklin to Morse'' (1998
excerpt and text search
* Kielbowicz, R. (1994). Government Goes into Business: Parcel Post in the Nation's Political Economy, 1880–1915. ''Studies in American Political Development,'' ''8''(1), 150–172. * Kielbowicz, Richard. "The Press, Post Office, and Flow of News in the Early Republic," ''Journal of the Early Republic'' (1983) 3: 255–80. * Kielbowicz, Richard. ''News in the Mail: The Press, Post Office, and Public Information, 1700–1860s'' (1989)
excerpt and text search
* * * Musacco Ph.D., Stephen. "Beyond Going Postal: Shifting from Workplace Tragedies and Toxic Work Environments to a Safe and Healthy Organization", (2009) Booksurge Publishing
Book Trailer
* Rich, Wesley Everett. ''The History of the United States Post Office to the Year 1829'' (Harvard University Press, 1924) * * * White, Leonard D. ''The Federalists: A study in administrative history: 1789–1801'' (1948), pp 173–98 * White, Leonard D. ''The Jeffersonians: A study in administrative history: 1801–29'' (1950), pp 299–335 * White, Leonard D. ''The Jacksonians: A study in administrative history: 1829–61'' (1954), pp 251–83 * White, Leonard D. ''The Republican Era: A study in administrative history: 1869–1901'' (1963), pp 257–77
External links
*United States Postal Service
in the ''