UK garage duos on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a
 In 1066, the
In 1066, the
 On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706
 After the defeat of France at the end of the
After the defeat of France at the end of the
 Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the
Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the  Nonetheless, "Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system."; After
Nonetheless, "Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system."; After
 During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world; it was an original signatory to the
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world; it was an original signatory to the  In the decades-long process of
In the decades-long process of
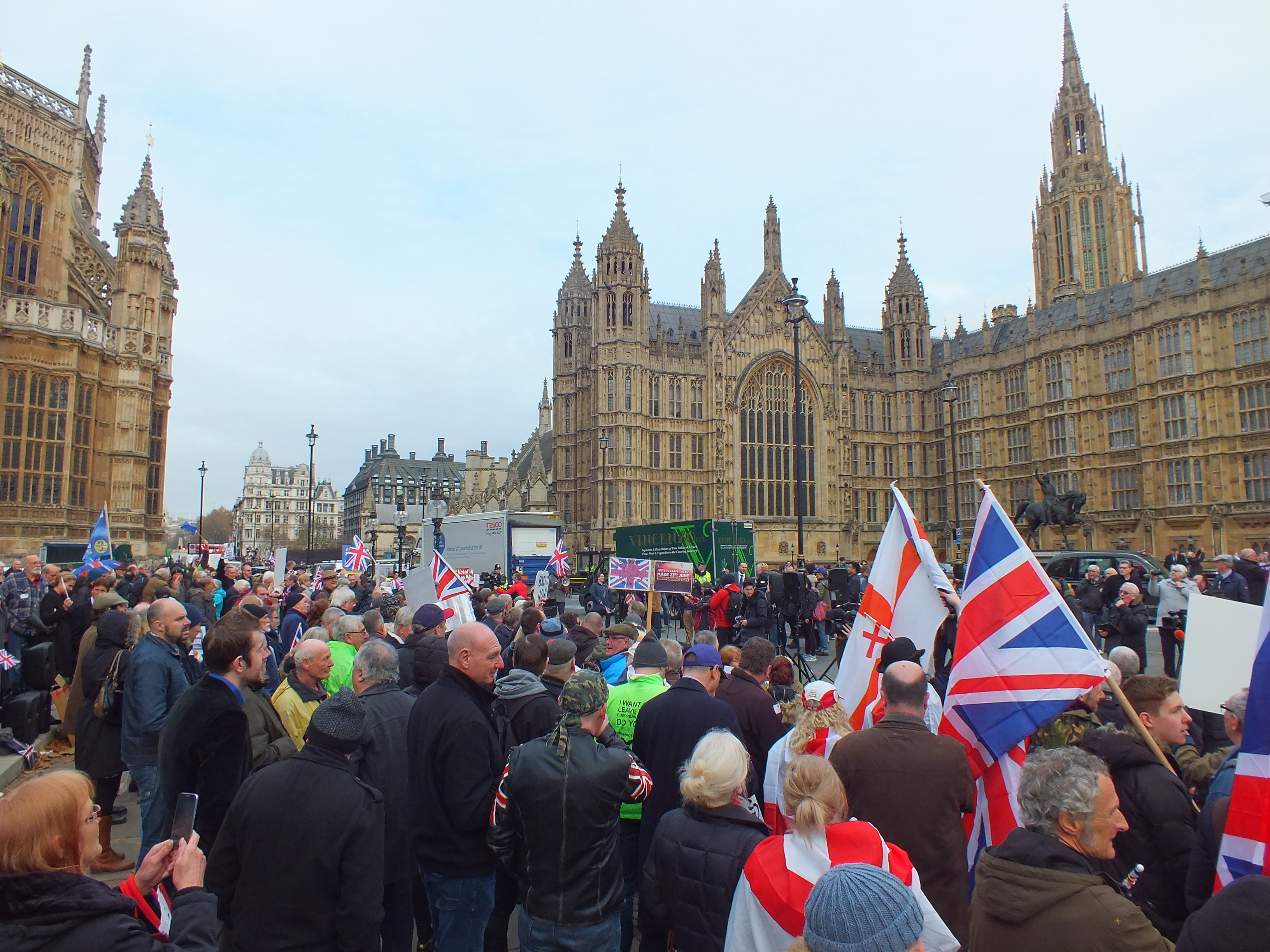 The UK broadly supported the United States' approach to the
The UK broadly supported the United States' approach to the
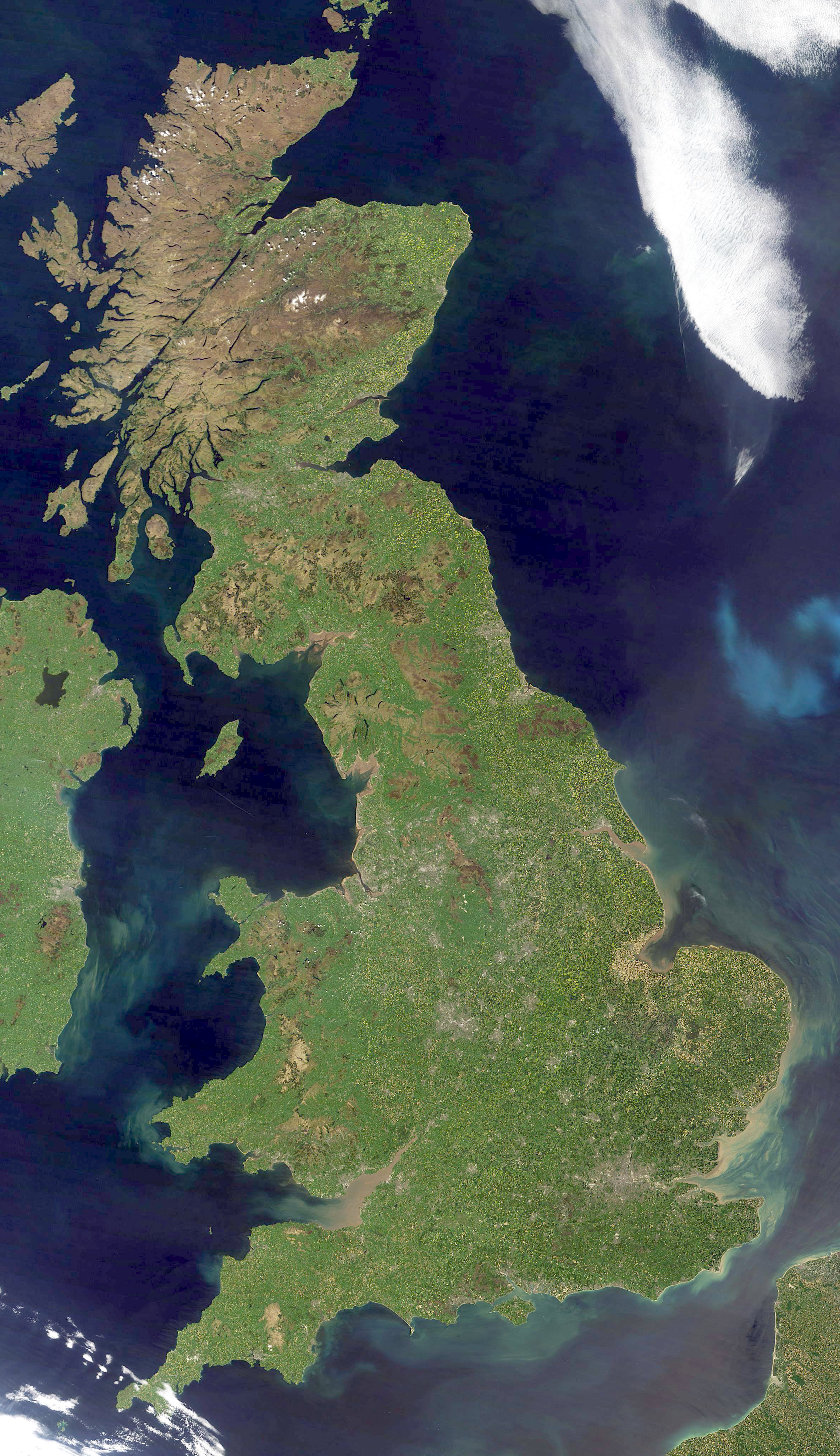 The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately . The country occupies the major part of the
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately . The country occupies the major part of the
 Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round. The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below or rising above . Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a
Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round. The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below or rising above . Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a
 The UK is a
The UK is a
 Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a  The
The
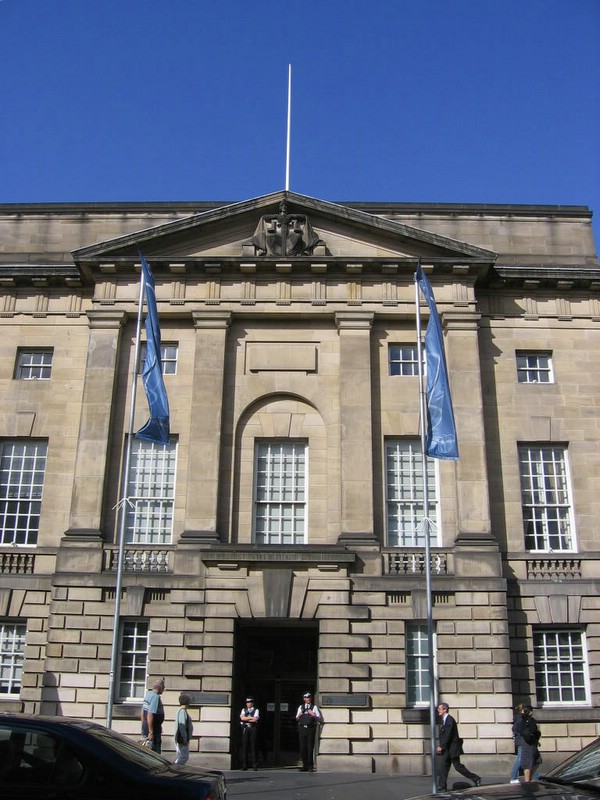 The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland's separate legal system. Today the UK has three distinct
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland's separate legal system. Today the UK has three distinct  Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the
 The UK has a partially regulated
The UK has a partially regulated  The
The
 England and Scotland were leading centres of the
England and Scotland were leading centres of the
 A radial road network totals of main roads, of motorways and of paved roads. The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world. In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the
A radial road network totals of main roads, of motorways and of paved roads. The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world. In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the

 In 2006, the UK was the world's ninth-largest consumer of energy and the 15th-largest producer. The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six oil and gas "
In 2006, the UK was the world's ninth-largest consumer of energy and the 15th-largest producer. The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six oil and gas "
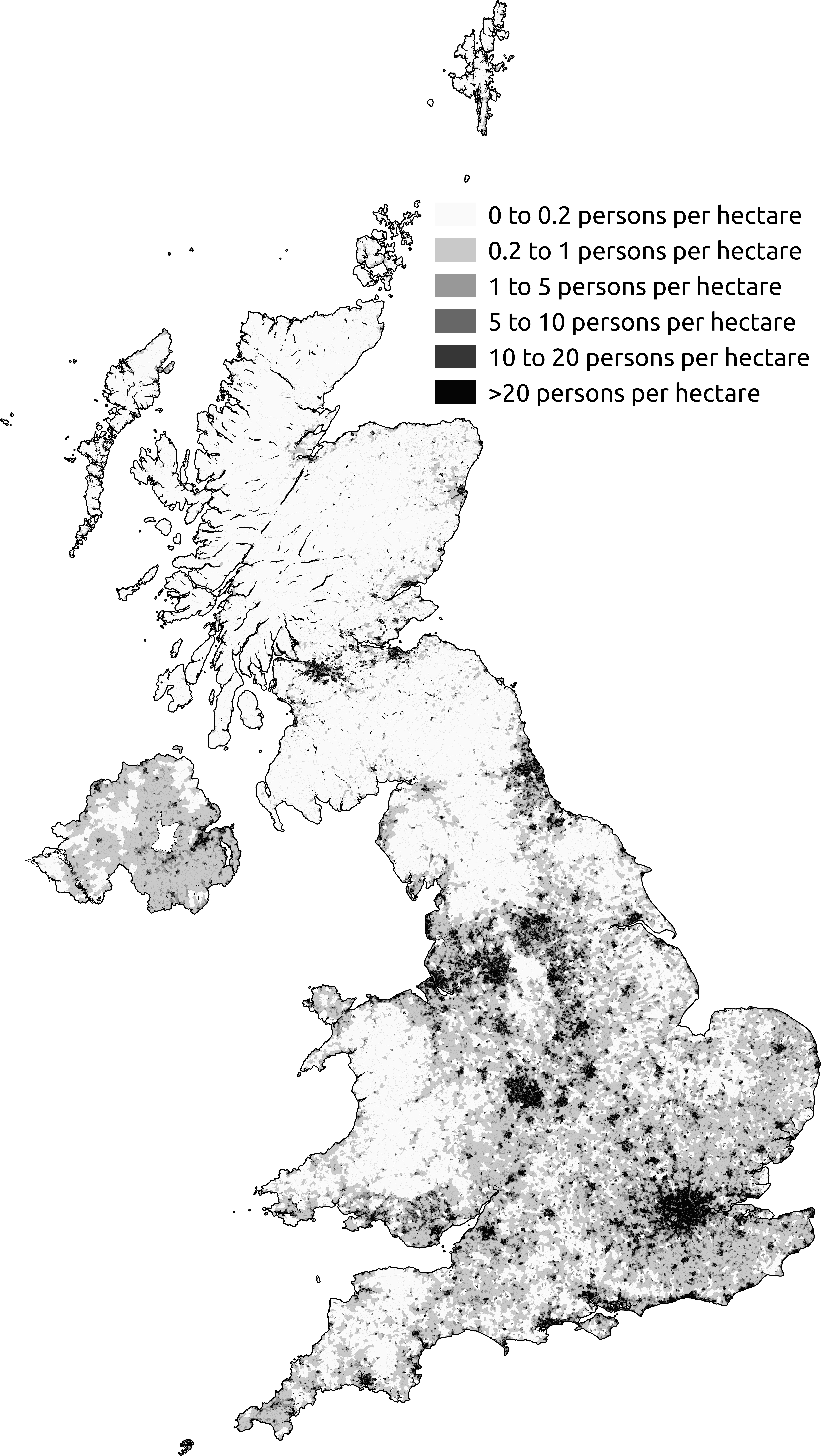 A
A
 The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain. Throughout the 19th century a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The Germans in the United Kingdom, German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to History of the Jews in Russia, Russian Jews. After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2,000,000 left the
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain. Throughout the 19th century a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The Germans in the United Kingdom, German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to History of the Jews in Russia, Russian Jews. After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2,000,000 left the  In 2008, the British Government introduced a Points-based immigration system (United Kingdom), points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government's Fresh Talent Initiative. In June 2010 a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe. Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad, mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.
In 2008, the British Government introduced a Points-based immigration system (United Kingdom), points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government's Fresh Talent Initiative. In June 2010 a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe. Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad, mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.
 Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of Local education authority, local authorities. Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944. Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18. In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science. The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools, while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of Local education authority, local authorities. Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944. Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18. In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science. The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools, while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.
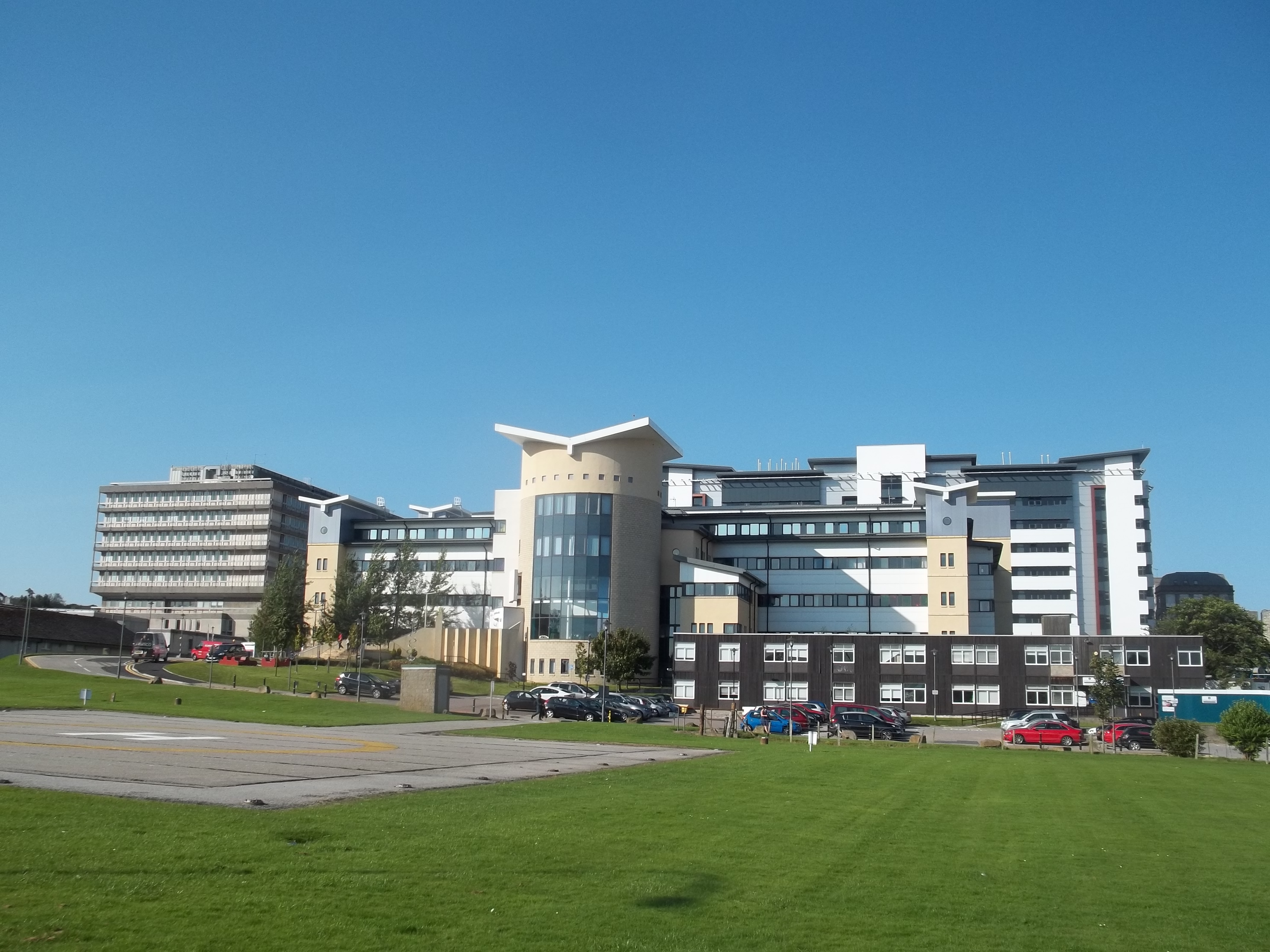
 Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a Devolution, devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all British nationality law, UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from Taxation in the United Kingdom, general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly. The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head. In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the
Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a Devolution, devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all British nationality law, UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from Taxation in the United Kingdom, general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly. The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head. In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the
. Journal of the British Politics Society, Norway. Volume 6. No. 1. Winter 2011 A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.
 "British literature" refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the
"British literature" refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the
 The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of 'British Empiricism', a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and 'Scottish Philosophy', sometimes referred to as the 'Scottish School of Common Sense'. The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet, William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish "common sense" school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work ''Utilitarianism (book), Utilitarianism''.
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of 'British Empiricism', a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and 'Scottish Philosophy', sometimes referred to as the 'Scottish School of Common Sense'. The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet, William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish "common sense" school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work ''Utilitarianism (book), Utilitarianism''.
 According to the website of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', the term "pop music" originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll's fusion with the "new youth music". ''The Oxford Dictionary of Music'' states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s. In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock; raga rock; Heavy metal music, heavy metal; space rock; glam rock; Gothic rock, and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock; and punk rock. Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep. Pop music, Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of Single (music), singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by Hip hop music, hip-hop and Rhythm and blues, R&B at 24.5 per cent. Rock music, Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent. The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano (rapper), Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz (rapper), Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the List of best-selling music artists, biggest-selling and Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band in the history of popular music. Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen (band), Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more. The Brit Awards are the British Phonographic Industry, BPI's annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Brit Award for Outstanding Contribution to Music, Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band). More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis (band), Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide. Glasgow's contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music (UNESCO), City of Music. Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop. Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal music, heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.
According to the website of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', the term "pop music" originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll's fusion with the "new youth music". ''The Oxford Dictionary of Music'' states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s. In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock; raga rock; Heavy metal music, heavy metal; space rock; glam rock; Gothic rock, and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock; and punk rock. Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep. Pop music, Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of Single (music), singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by Hip hop music, hip-hop and Rhythm and blues, R&B at 24.5 per cent. Rock music, Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent. The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano (rapper), Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz (rapper), Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the List of best-selling music artists, biggest-selling and Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band in the history of popular music. Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen (band), Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more. The Brit Awards are the British Phonographic Industry, BPI's annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Brit Award for Outstanding Contribution to Music, Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band). More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis (band), Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide. Glasgow's contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music (UNESCO), City of Music. Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop. Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal music, heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.
 The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romanticism, Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Joshua Reynolds, Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon (artist), Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language; the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the Abstract art, abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the "Young British Artists": Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen (director), Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Jake and Dinos Chapman, Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery (London), National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romanticism, Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Joshua Reynolds, Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon (artist), Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language; the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the Abstract art, abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the "Young British Artists": Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen (director), Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Jake and Dinos Chapman, Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery (London), National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).
 The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film ''Vertigo (film), Vertigo'' is considered by some critics as the List of films considered the best, best film of all time, and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time. Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom. UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions. The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film ''Vertigo (film), Vertigo'' is considered by some critics as the List of films considered the best, best film of all time, and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time. Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom. UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions. The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.
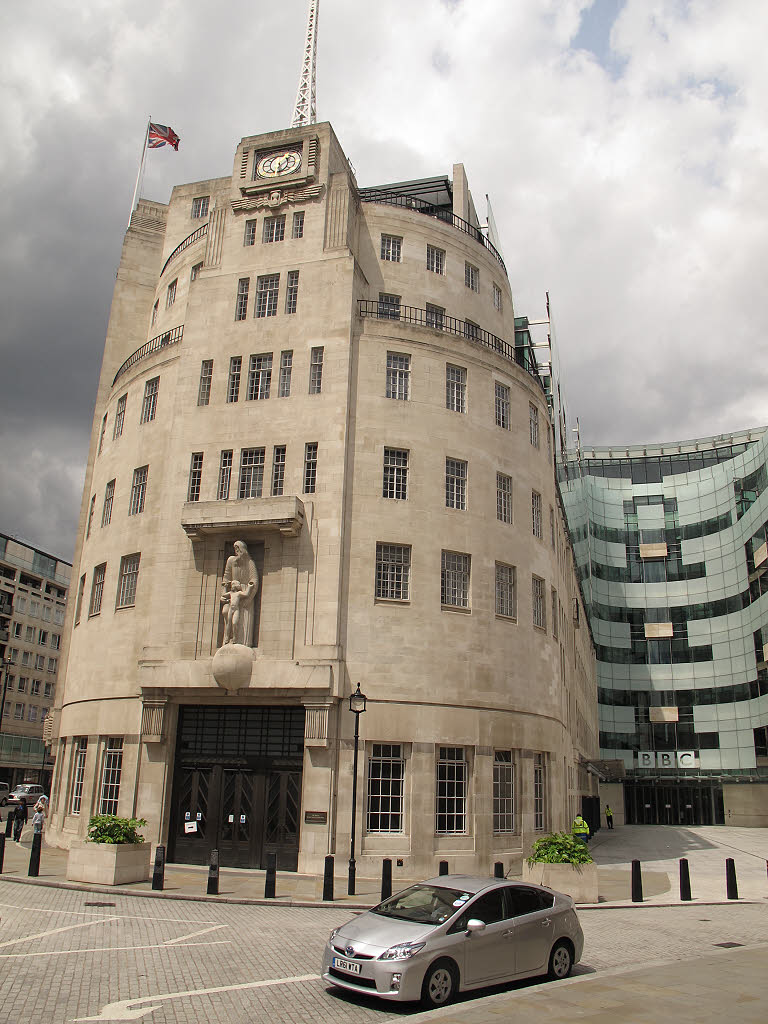 The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the Television licensing in the United Kingdom, television licence. The BBC World Service is an International broadcasting, international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV (TV network), ITV Network, and Sky UK, Sky. Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include ''The Times'', ''The Guardian'', ''The Observer,'' ''The Economist'', and the ''Financial Times''. Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include ''
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the Television licensing in the United Kingdom, television licence. The BBC World Service is an International broadcasting, international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV (TV network), ITV Network, and Sky UK, Sky. Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include ''The Times'', ''The Guardian'', ''The Observer,'' ''The Economist'', and the ''Financial Times''. Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include ''
 The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack). It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick's Flag. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out. The national anthem of the United Kingdom is "God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside The Lion and the Unicorn, the lion and the unicorn and the Welsh Dragon, dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack). It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick's Flag. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out. The national anthem of the United Kingdom is "God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside The Lion and the Unicorn, the lion and the unicorn and the Welsh Dragon, dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of
 Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, English billiards, billiards, darts, Rowing (sport), rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in the late 19th century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, "This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum".
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the United Kingdom. England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and The Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. Each of the Home Nations has its own football association, national team and league system and individually are the governing members of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world. The first international football match was contested by England national football team, England and Scotland national football team, Scotland on 30 November 1872. England, Scotland, Wales national football team, Wales and Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, English billiards, billiards, darts, Rowing (sport), rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in the late 19th century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, "This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum".
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the United Kingdom. England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and The Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. Each of the Home Nations has its own football association, national team and league system and individually are the governing members of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world. The first international football match was contested by England national football team, England and Scotland national football team, Scotland on 30 November 1872. England, Scotland, Wales national football team, Wales and Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.
 In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK. The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship; the premier international tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sport governing body, Sport governing bodies in Rugby union in England, England, Rugby union in Scotland, Scotland, Rugby union in Wales, Wales and Rugby union in Ireland, Ireland organise and regulate the game separately. Every four years, England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions. The team tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its Laws of cricket, laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788. The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board, and the Irish cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test cricket, Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales had fielded its own team in the past. Cricket in Scotland, Scottish players have played for England because Scotland national cricket team, Scotland does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals. Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, with England winning the tournament in 2019. There is a professional County Championship, league championship in which clubs representing 17 English counties and 1 Welsh county compete.
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK. The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship; the premier international tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sport governing body, Sport governing bodies in Rugby union in England, England, Rugby union in Scotland, Scotland, Rugby union in Wales, Wales and Rugby union in Ireland, Ireland organise and regulate the game separately. Every four years, England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions. The team tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its Laws of cricket, laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788. The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board, and the Irish cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test cricket, Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales had fielded its own team in the past. Cricket in Scotland, Scottish players have played for England because Scotland national cricket team, Scotland does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals. Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, with England winning the tournament in 2019. There is a professional County Championship, league championship in which clubs representing 17 English counties and 1 Welsh county compete.
 The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s, before spreading around the world. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, drivers' and List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, constructors' Formula One World Championship, titles than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone, the location of the British Grand Prix held each year in July.
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s, before spreading around the world. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, drivers' and List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, constructors' Formula One World Championship, titles than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone, the location of the British Grand Prix held each year in July.
 Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport's home course, the world's oldest golf course is actually Musselburgh Links' Old Golf Course. In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes. The oldest golf tournament in the world, and the first major championship in golf, The Open Championship, is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England. A single 'Great Britain Lions' team had competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games, but this changed in 2008 when England national rugby league team, England, Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland and Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland competed as separate nations. Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.
The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing. Snooker is another of the UK's popular sporting exports, with the world championships held annually in Sheffield. In Northern Ireland, Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports, both in terms of participation and spectating. Irish expatriates in the UK and the US also play them. Shinty (or ''camanachd'') is popular in the Scottish Highlands. Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport's home course, the world's oldest golf course is actually Musselburgh Links' Old Golf Course. In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes. The oldest golf tournament in the world, and the first major championship in golf, The Open Championship, is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England. A single 'Great Britain Lions' team had competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games, but this changed in 2008 when England national rugby league team, England, Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland and Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland competed as separate nations. Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.
The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing. Snooker is another of the UK's popular sporting exports, with the world championships held annually in Sheffield. In Northern Ireland, Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports, both in terms of participation and spectating. Irish expatriates in the UK and the US also play them. Shinty (or ''camanachd'') is popular in the Scottish Highlands. Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands."Sport in Scotland"
Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
The United Kingdom has hosted the Summer Olympic Games on three occasions in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, 1948 Summer Olympics, 1948 and 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012, with London acting as the host city for all three games respectively. The 2022 Commonwealth Games were hosted in Birmingham, the seventh time the UK has hosted the Commonwealth Games.
Official website of HM Government
Official website of the British Monarchy
The official site of the British Prime Minister's Office
United Kingdom
from the BBC News
United Kingdom
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
United Kingdom
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
United Kingdom
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' entry * *
Key Development Forecasts for the United Kingdom
from International Futures
Official tourist guide to Britain
{{Coord, 55, N, 3, W, display=title, scale:10000000 United Kingdom, British Islands Countries in Europe English-speaking countries and territories G7 nations G20 nations Island countries Northwestern European countries Member states of NATO Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the United Nations OECD members
country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, whi ...
in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, and many smaller islands within the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. ...
; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
, the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
, the Celtic Sea
The Celtic Sea ; cy, Y Môr Celtaidd ; kw, An Mor Keltek ; br, Ar Mor Keltiek ; french: La mer Celtique is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits includ ...
and the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the C ...
. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.
The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
between the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
(which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
in 1707 formed the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
. Its union in 1801 with the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label= Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which formally adopted that name in 1927. The nearby Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
, Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency.
It is the second largest of the Channel Islands ...
and Jersey
Jersey ( , ; nrf, Jèrri, label= Jèrriais ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey (french: Bailliage de Jersey, links=no; Jèrriais: ), is an island country and self-governing Crown Dependency near the coast of north-west France. It is the ...
are not part of the UK, being Crown Dependencies with the British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
responsible for defence and international representation. There are also 14 British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
, the last remnants of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world's landmass and a third of the world's population, and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and the legal and political systems of many of its former colonies.
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
and parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
. The capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
is London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, a global city and financial centre with a metropolitan area population of over 14 million. Other major cities include Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
, Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
and Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by popul ...
. Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments, each with varying powers. The UK became the world's first industrialised
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
country and was the world's foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries. In the 21st century, the UK retains considerable economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
, cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
, military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
, scientific, technological and political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
influence. The United Kingdom has the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the eighth-largest by purchasing power parity. It has a high-income economy and a very high Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, w ...
rating, ranking 18th in the world. It also performs well in international rankings of education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
, healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health pro ...
, life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
and human development. It is a recognised nuclear state and is ranked fourth globally in military expenditure. It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, ...
since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, Five Eyes
The Five Eyes (FVEY) is an intelligence alliance comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These countries are parties to the multilateral UKUSA Agreement, a treaty for joint cooperation in sig ...
, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
, AUKUS
AUKUS (, ) is a trilateral security pact between Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States, announced on 15 September 2021 for the Indo-Pacific region. Under the pact, the US and the UK will help Australia to acquire nuclear-powered ...
, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
(OECD), Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cr ...
, and the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
(WTO). It was a member state of the European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
(EC) and its successor, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
(EU), from its accession in 1973 until its withdrawal in 2020 following a referendum held in 2016.
Etymology and terminology
In , ''Britannia'' referred to theRoman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
that encompassed modern day England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
. Great Britain encompassed the whole island, taking in the land north of the River Forth
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Gaelic name for the upper reach of t ...
known to the Romans as Caledonia
Caledonia (; ) was the Latin name used by the Roman Empire to refer to the part of Great Britain () that lies north of the River Forth, which includes most of the land area of Scotland. Today, it is used as a romantic or poetic name for all ...
in modern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
(i.e. "greater" Britain). In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the name "Britain" was also applied to a small part of France now known as Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
. As a result, Great Britain (likely from the French "") came into use to refer specifically to the island, with Brittany often referred to as "Little Britain". However, that name had no official significance until 1707, when the island's kingdoms of England and Scotland were united as the Kingdom of Great Britain.
The Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the t ...
declared that the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
and Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
were "United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
". The term "United Kingdom" has occasionally been used as a description for the former Kingdom of Great Britain, although its official name from 1707 to 1800 was simply "Great Britain". The Acts of Union 1800
The Acts of Union 1800 (sometimes incorrectly referred to as a single 'Act of Union 1801') were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ir ...
united the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
in 1801, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
. Following the partition of Ireland
The partition of Ireland ( ga, críochdheighilt na hÉireann) was the process by which the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland divided Ireland into two self-governing polities: Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland. ...
and the independence of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
in 1922, which left Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
as the only part of the island of Ireland within the United Kingdom, the name was changed to the "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland".
Although the United Kingdom is a sovereign country, England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are also widely referred to as countries. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as "regions". Northern Ireland is also referred to as a "province". With regard to Northern Ireland, the descriptive name used "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".
The term "Great Britain" conventionally refers to the island of Great Britain, or politically to England, Scotland and Wales in combination. It is sometimes used as a loose synonym for the United Kingdom as a whole. The word ''England'' is occasionally used incorrectly to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole, a mistake principally made by people from outside the UK.
The term "Britain" is used both as a synonym for Great Britain, and as a synonym for the United Kingdom. Usage is mixed: the UK Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
prefers to use the term "UK" rather than "Britain" or "British" on its own website (except when referring to embassies), while acknowledging that both terms refer to the United Kingdom and that elsewhere "British government" is used at least as frequently as "United Kingdom government". The UK Permanent Committee on Geographical Names recognises "United Kingdom", "UK" and "U.K." as shortened and abbreviated geopolitical terms for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in its toponymic guidelines; it does not list "Britain" but notes that "it is only the one specific nominal term 'Great Britain' which invariably excludes Northern Ireland". The BBC historically preferred to use "Britain" as shorthand only for Great Britain, though the present style guide does not take a position except that "Great Britain" excludes Northern Ireland.
The adjective "British" is commonly used to refer to matters relating to the United Kingdom and is used in law to refer to United Kingdom citizenship and matters to do with nationality. People of the United Kingdom use several different terms to describe their national identity and may identify themselves as being British, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, Scottish, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, Northern Irish
Northern Irish people is a demonym for all people born in Northern Ireland or people who are entitled to reside in Northern Ireland without any restriction on their period of residence. Most Northern Irish people either identify as Northern ...
, or Irish; or as having a combination of different national identities. The official designation for a citizen of the United Kingdom is "British citizen".
History
Prior to the Treaty of Union
Settlement byanatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish '' Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from exti ...
of what was to become the United Kingdom occurred in waves beginning by about 30,000 years ago. By the end of the region's prehistoric period, the population is thought to have belonged, in the main, to a culture termed Insular Celtic
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany, ...
, comprising Brittonic Britain and Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans c ...
.
The Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD, and the 400-year rule of southern Britain, was followed by an invasion by Germanic Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
settlers, reducing the Brittonic area mainly to what was to become Wales, Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a Historic counties of England, historic county and Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people ...
and, until the latter stages of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, the Hen Ogledd
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population sp ...
(northern England and parts of southern Scotland). Most of the region settled by the Anglo-Saxons became unified as the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
in the 10th century. Meanwhile, Gaelic-speakers in north-west Britain (with connections to the north-east of Ireland and traditionally supposed to have migrated from there in the 5th century) united with the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
to create the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
in the 9th century.
 In 1066, the
In 1066, the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
invaded England from northern France. After conquering England, they seized large parts of Wales, conquered much of Ireland and were invited to settle in Scotland, bringing to each country feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
on the Northern French model and Norman-French culture. The Anglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
*Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 ...
ruling class
In sociology, the ruling class of a society is the social class who set and decide the political and economic agenda of society. In Marxist philosophy, the ruling class are the capitalist social class who own the means of production and by ex ...
greatly influenced, but eventually assimilated with, each of the local cultures. Subsequent medieval English kings completed the conquest of Wales and made unsuccessful attempts to annex Scotland. Asserting its independence in the 1320 Declaration of Arbroath
The Declaration of Arbroath ( la, Declaratio Arbroathis; sco, Declaration o Aiberbrothock; gd, Tiomnadh Bhruis) is the name usually given to a letter, dated 6 April 1320 at Arbroath, written by Scottish barons and addressed to Pope John ...
, Scotland maintained its independence thereafter, albeit in near-constant conflict with England.
The English monarchs, through inheritance of substantial territories in France and claims to the French crown, were also heavily involved in conflicts in France, most notably the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
, while the Kings of Scots
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have grown ...
were in an alliance with the French during this period.
Early modern Britain
Early modern Britain is the history of the island of Great Britain roughly corresponding to the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries. Major historical events in early modern British history include numerous wars, especially with France, along with the E ...
saw religious conflict resulting from the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and the introduction of Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
state churches in each country. Wales was fully incorporated into the Kingdom of England, and Ireland was constituted as a kingdom in personal union with the English crown. In what was to become Northern Ireland, the lands of the independent Catholic Gaelic nobility were confiscated and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland were united in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
when James VI, King of Scots, inherited the crowns of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
to London; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal, and religious institutions.
In the mid-17th century, all three kingdoms were involved in a series of connected wars (including the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
) which led to the temporary overthrow of the monarchy, with the execution of King Charles I
The execution of Charles I by beheading occurred on Tuesday, 30 January 1649 outside the Banqueting House on Whitehall. The execution was the culmination of political and military conflicts between the royalists and the parliamentarians in E ...
, and the establishment of the short-lived unitary republic
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only t ...
of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
. During the 17th and 18th centuries, British sailors were involved in acts of piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
( privateering), attacking and stealing from ships off the coast of Europe and the Caribbean.
Although the monarchy was restored, the Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
along with the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
of 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689
The Bill of Rights 1689 is an Act of the Parliament of England, which sets out certain basic civil rights and clarifies who would be next to inherit the Crown, and is seen as a crucial landmark in English constitutional law. It received Royal ...
in England and Claim of Right Act 1689
The Claim of Right (c. 28) is an Act passed by the Convention of the Estates, a sister body to the Parliament of Scotland (or Three Estates), in April 1689. It is one of the key documents of United Kingdom constitutional law and Scottish con ...
in Scotland ensured that, unlike much of the rest of Europe, royal absolutism
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitut ...
would not prevail, and a professed Catholic could never accede to the throne. The British constitution
The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland as a political body. Unlike in most countries, no attempt ...
would develop on the basis of constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
and the parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of th ...
. With the founding of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in 1660, science was greatly encouraged. During this period, particularly in England, the development of naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.
Though previous attempts at uniting the two kingdoms within Great Britain in 1606, 1667, and 1689 had proved unsuccessful, the attempt initiated in 1705 led to the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
of 1706 being agreed and ratified by both parliaments.
Kingdom of Great Britain
 On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
and so unite the two kingdoms.
In the 18th century, cabinet government developed under Robert Walpole
Robert Walpole, 1st Earl of Orford, (26 August 1676 – 18 March 1745; known between 1725 and 1742 as Sir Robert Walpole) was a British statesman and Whig politician who, as First Lord of the Treasury, Chancellor of the Exchequer, and Lea ...
, in practice the first prime minister (1721–1742). A series of Jacobite Uprisings sought to remove the Protestant House of Hanover
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house or ...
from the British throne and restore the Catholic House of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fi ...
. The Jacobites were finally defeated at the Battle of Culloden
The Battle of Culloden (; gd, Blàr Chùil Lodair) was the final confrontation of the Jacobite rising of 1745. On 16 April 1746, the Jacobite army of Charles Edward Stuart was decisively defeated by a British government force under Prince Wi ...
in 1746, after which the Scottish Highlanders
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sc ...
were brutally suppressed. The British colonies in North America that broke away from Britain in the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
became the United States of America, recognised by Britain in 1783. British imperial ambition turned towards Asia, particularly to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Britain played a leading part in the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and ...
, mainly between 1662 and 1807 when British or British-colonial Slave ships transported nearly 3.3 million slaves from Africa. The slaves were taken to work on plantations
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
in British possessions, principally in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
but also North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
. Slavery coupled with the Caribbean sugar industry had a significant role in strengthening and developing the British economy in the 18th century. However, Parliament banned the trade in 1807, banned slavery in the British Empire in 1833, and Britain took a role in the movement to abolish slavery worldwide through the blockade of Africa
The Blockade of Africa began in 1808 after the United Kingdom outlawed the Atlantic slave trade, making it illegal for British ships to transport slaves. The Royal Navy immediately established a presence off Africa to enforce the ban, called ...
and pressing other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties.
Union with Ireland
The term "United Kingdom" became official in 1801 when the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland each passed an Act of Union, uniting the two kingdoms and creating theUnited Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
.
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Pruss ...
and Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
(1792–1815), the United Kingdom emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century (with London the largest city in the world from about 1830). Unchallenged at sea, British dominance was later described as ''Pax Britannica
''Pax Britannica'' (Latin for "British Peace", modelled after '' Pax Romana'') was the period of relative peace between the great powers during which the British Empire became the global hegemonic power and adopted the role of a "global poli ...
'' ("British Peace"), a period of relative peace among the Great Powers (1815–1914) during which the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
became the global hegemon
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over other city-states. ...
and adopted the role of global policeman. By the time of the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
of 1851, Britain was described as the "workshop of the world". From 1853 to 1856, Britain took part in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
, allied with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in the fight against the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, participating in the naval battles of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
known as the Åland War
The Åland War ( fi, Oolannin sota, sv, Åländska kriget) is the Finnish term for the operations of a British-French naval force against military and civilian facilities on the coast of the Grand Duchy of Finland in 1854–1856, during the Crime ...
in the Gulf of Bothnia
The Gulf of Bothnia (; fi, Pohjanlahti; sv, Bottniska viken) is divided into the Bothnian Bay and Bothnian Sea, and it is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast ( East Bothnia) and the Sweden's east coast ( We ...
and the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and ...
, among others. The British Empire was expanded to include India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, large parts of Africa and many other territories throughout the world. Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, British dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and Latin America.
Domestically, political attitudes favoured free trade and laissez-faire policies and a gradual widening of the voting franchise. During the century, the population increased at a dramatic rate, accompanied by rapid urbanisation, causing significant social and economic stresses. To seek new markets and sources of raw materials, the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
under Disraeli launched a period of imperialist expansion in Egypt, South Africa, and elsewhere. Canada, Australia and New Zealand became self-governing dominions. After the turn of the century, Britain's industrial dominance was challenged by Germany and the United States. Social reform and home rule for Ireland were important domestic issues after 1900. The Labour Party emerged from an alliance of trade unions and small socialist groups in 1900, and suffragettes
A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to member ...
campaigned from before 1914 for women's right to vote.
World Wars and Partition of Ireland
 Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the
Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
(1914–1918). British armed forces were engaged across much of the British Empire and in several regions of Europe, particularly on the Western front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
. The high fatalities of trench warfare caused the loss of much of a generation of men, with lasting social effects in the nation and a great disruption in the social order. After the war, Britain received the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
mandate over a number of former German and Ottoman colonies. The British Empire reached its greatest extent, covering a fifth of the world's land surface and a quarter of its population. Britain had suffered 2.5 million casualties and finished the war with a huge national debt.Westwell, I.; Cove, D. (eds) (2002). ''History of World War I, Volume 3''. London: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 698 and 705. .
By the mid-1920s most of the British population could listen to BBC radio programmes. Experimental television broadcasts began in 1929 and the first scheduled BBC Television Service commenced in 1936. The rise of Irish nationalism
Irish nationalism is a nationalist political movement which, in its broadest sense, asserts that the people of Ireland should govern Ireland as a sovereign state. Since the mid-19th century, Irish nationalism has largely taken the form of c ...
, and disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule
The Irish Home Rule movement was a movement that campaigned for self-government (or "home rule") for Ireland within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was the dominant political movement of Irish nationalism from 1870 to the ...
, led eventually to the partition of the island in 1921. The Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
became independent, initially with Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
status in 1922, and unambiguously independent in 1931. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom. The 1928 Act widened suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
by giving women electoral equality with men. A wave of strikes in the mid-1920s culminated in the General Strike of 1926. Britain had still not recovered from the effects of the war when the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
(1929–1932) occurred. This led to considerable unemployment and hardship in the old industrial areas, as well as political and social unrest in the 1930s, with rising membership in communist and socialist parties. A coalition government was formed in 1931.
 Nonetheless, "Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system."; After
Nonetheless, "Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system."; After Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
invaded Poland, Britain entered the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
by declaring war on Germany in 1939. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
became prime minister and head of a coalition government in 1940. Despite the defeat of its European allies in the first year of the war, Britain and its Empire continued the fight alone against Germany. Churchill engaged industry, scientists, and engineers to advise and support the government and the military in the prosecution of the war effort. In 1940, the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
defeated the German Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
in a struggle for control of the skies in the Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
. Urban areas suffered heavy bombing during the Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
. The Grand Alliance of Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
formed in 1941 leading the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
against the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
. There were eventual hard-fought victories in the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allies of World War II, ...
, the North Africa campaign and the Italian campaign. British forces played an important role in the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
of 1944 and the liberation of Europe
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst, Berlin. After German dictator Adolf ...
, achieved with its allies the United States, the Soviet Union and other Allied countries. The British Army led the Burma campaign against Japan and the British Pacific Fleet
The British Pacific Fleet (BPF) was a Royal Navy formation that saw action against Japan during the Second World War. The fleet was composed of empire naval vessels. The BPF formally came into being on 22 November 1944 from the remaining ships o ...
fought Japan at sea. British scientists contributed to the Manhattan Project which led to the surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Na ...
.
Postwar 20th century
 During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world; it was an original signatory to the
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world; it was an original signatory to the Declaration by United Nations
The Declaration by United Nations was the main treaty that formalized the Allies of World War II and was signed by 47 national governments between 1942 and 1945. On 1 January 1942, during the Arcadia Conference, the Allied " Big Four"—the Unite ...
. After the war, the UK became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, ...
and worked closely with the United States to establish the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glob ...
, World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
. The war left the UK severely weakened and financially dependent on the Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred over $13 billion (equivalent of about $ in ) in economic re ...
, but it was spared the total war that devastated eastern Europe. In the immediate post-war years, the Labour government initiated a radical programme of reforms, which had a significant effect on British society in the following decades. Major industries and public utilities were nationalised
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to p ...
, a welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equita ...
was established, and a comprehensive, publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
, was created. The rise of nationalism in the colonies coincided with Britain's now much-diminished economic position, so that a policy of decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence ...
was unavoidable. Independence was granted to India and Pakistan in 1947. Over the next three decades, most colonies of the British Empire gained their independence, with all those that sought independence supported by the UK, during both the transition period and afterwards. Many became members of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
.
The UK was the third country to develop a nuclear weapons arsenal (with its first atomic bomb test, Operation Hurricane
Operation Hurricane was the first test of a British atomic device. A plutonium implosion device was detonated on 3 October 1952 in Main Bay, Trimouille Island, in the Montebello Islands in Western Australia. With the success of Operation ...
, in 1952), but the new post-war limits of Britain's international role were illustrated by the Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
of 1956. The international spread of the English language ensured the continuing international influence of its literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
. As a result of a shortage of workers in the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries
The Commonwealth of Nations is a voluntary association of 56 sovereign states. Most of them were British colonies or dependencies of those colonies.
No one government in the Commonwealth exercises power over the others, as is the case in a p ...
. In the following decades, the UK became a more multi-ethnic society than before. Despite rising living standards in the late 1950s and 1960s, the UK's economic performance was less successful than many of its main competitors such as France, West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
and Japan.
 In the decades-long process of
In the decades-long process of European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integration has primarily come about through the European Union and its ...
, the UK was a founding member of the alliance called the Western European Union
The Western European Union (WEU; french: Union de l'Europe occidentale, UEO; german: Westeuropäische Union, WEU) was the international organisation and military alliance that succeeded the Western Union (WU) after the 1954 amendment of the 1948 ...
, established with the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. In 1960 the UK was one of the seven founding members of the European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European U ...
(EFTA), but in 1973 it left to join the European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
(EC). When the EC became the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
(EU) in 1992, the UK was one of the 12 founding member states. The Treaty of Lisbon
The Treaty of Lisbon (initially known as the Reform Treaty) is an international agreement that amends the two treaties which form the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU). The Treaty of Lisbon, which was signed by the EU member s ...
, signed in 2007, forms the constitutional basis of the European Union since then.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland suffered communal and paramilitary violence (sometimes affecting other parts of the UK) conventionally known as the Troubles
The Troubles ( ga, Na Trioblóidí) were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it is sometimes described as an "i ...
. It is usually considered to have ended with the Belfast "Good Friday" Agreement of 1998.
Following a period of widespread economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the Conservative government of the 1980s under Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. She was the first female British prime ...
initiated a radical policy of monetarism
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on nati ...
, deregulation, particularly of the financial sector (for example, the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
in 1986) and labour markets, the sale of state-owned companies (privatisation), and the withdrawal of subsidies to others. From 1984, the economy was helped by the inflow of substantial North Sea oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
In the petroleum industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Se ...
revenues.
Around the end of the 20th century, there were major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The statutory incorporation followed acceptance of the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
. The UK is still a key global player diplomatically and militarily. It plays leading roles in the UN and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
.
21st century
 The UK broadly supported the United States' approach to the
The UK broadly supported the United States' approach to the War on Terror
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campaign are militant ...
in the early years of the 21st century. Controversy surrounded some of Britain's overseas military deployments, particularly in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
.
The 2008 global financial crisis severely affected the UK economy. The Cameron–Clegg coalition
The Cameron–Clegg coalition was formed by David Cameron and Nick Clegg when Cameron was invited by Queen Elizabeth II to form a new administration, following the resignation of Prime Minister Gordon Brown on 11 May 2010, after the gene ...
government of 2010 introduced austerity
Austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. There are three primary types of austerity measures: higher taxes to fund spend ...
measures intended to tackle the substantial public deficits which resulted. The devolved Scottish Government and UK government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
agreed for a referendum to be held on Scottish independence
Scottish independence ( gd, Neo-eisimeileachd na h-Alba; sco, Scots unthirldom) is the idea of Scotland as a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom, and refers to the political movement that is campaigning to bring it about.
...
in 2014. This referendum resulted in the electorate in Scotland voting by 55.3 to 44.7% for Scotland to remain part of the United Kingdom.
In 2016, 51.9 per cent of voters in the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union. The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 and completed its withdrawal in full at the end of that year.
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
had a severe impact on the UK's economy, caused major disruptions to education and had far-reaching impacts on society and politics in 2020 and 2021.
On 8 September 2022, Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
, the longest-living and longest-reigning British monarch, died at the age of 96. Upon the Queen's death, her eldest child Charles, Prince of Wales, immediately acceded to the British throne as King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person ...
.
Geography
 The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately . The country occupies the major part of the
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately . The country occupies the major part of the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and some smaller surrounding islands. It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea with the southeast coast coming within of the coast of northern France, from which it is separated by the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
. In 1993 10 per cent of the UK was forested, 46 per cent used for pastures and 25 per cent cultivated for agriculture. The Royal Greenwich Observatory
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich (ROG; known as the Old Royal Observatory from 1957 to 1998, when the working Royal Greenwich Observatory, RGO, temporarily moved south from Greenwich to Herstmonceux) is an observatory situated on a hill in ...
in London was chosen as the defining point of the Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great ...
in Washington, DC, in 1884, although due to more accurate modern measurement the meridian actually lies 100 metres to the east of the observatory.
The United Kingdom lies between latitudes 49° and 61° N, and longitudes 9° W and 2° E. Northern Ireland shares a land boundary with the Republic of Ireland. The coastline of Great Britain is long. It is connected to continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover ...
, which at ( underwater) is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.
The UK contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Celtic broadleaf forests
The Celtic broadleaf forests are a terrestrial ecoregion that covers most of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland.
Geography
The Celtic broadleaf forests occupy most of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, including the Republic of Irel ...
, English Lowlands beech forests, North Atlantic moist mixed forests, and Caledon conifer forests. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 1.65/10, ranking it 161th globally out of 172 countries.
Climate
subpolar oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
(''Cfc''). Higher elevations in Scotland experience a continental subarctic climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ...
(''Dfc'') and the mountains experience a tundra climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. undra climate https://www.britannica.com/science/tundra-climateThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2019 It is classified as ET according to Köppen ...
(''ET'').
The prevailing wind is from the southwest and bears frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean, although the eastern parts are mostly sheltered from this wind since the majority of the rain falls over the western regions the eastern parts are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ...
, bring mild winters; especially in the west where winters are wet and even more so over high ground. Summers are warmest in the southeast of England and coolest in the north. Heavy snowfall can occur in winter and early spring on high ground, and occasionally settles to great depth away from the hills.
United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scal ...
. A law has been passed that UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the " ...
by 2050.
Topography
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
accounts for just over half (53 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering . Most of the country consists of lowland terrain, with more upland and some mountainous terrain northwest of the Tees–Exe line
The Tees–Exe line is an imaginary northeast-southwest line that can be drawn on a map of Great Britain which roughly divides the island into lowland and upland regions.
The line links the mouth of the River Tees between Redcar and Hartlepool i ...
; including the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or '' fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
, the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Common ...
, Exmoor
Exmoor is loosely defined as an area of hilly open moorland in west Somerset and north Devon in South West England. It is named after the River Exe, the source of which is situated in the centre of the area, two miles north-west of Simonsbath ...
and Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous P ...
. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
, Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
and the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between ...
. England's highest mountain is Scafell Pike
Scafell Pike () is the highest and the most prominent mountain in England, at an elevation of above sea level. It is located in the Lake District National Park, in Cumbria, and is part of the Southern Fells and the Scafell massif.
Scafell P ...
() in the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or '' fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
.
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
accounts for just under one-third (32 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering . This includes nearly 800 islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
, predominantly west and north of the mainland; notably the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
, Orkney Islands
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) no ...
and Shetland Islands
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its topography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses Scotland from Arran in the west to Stonehaven
Stonehaven ( , ) is a town in Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 11,602 at the 2011 Census.
After the demise of the town of Kincardine, which was gradually abandoned after the destruction of its royal cast ...
in the east. The fault separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland's mountainous land, including Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; gd, Beinn Nibheis ) is the highest mountain in Scotland, the United Kingdom and the British Isles. The summit is above sea level and is the highest land in any direction for . Ben Nevis stands at the western end of the Grampian ...
which at is the highest point in the British Isles. Lowland areas – especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
and the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
known as the Central Belt
The Central Belt of Scotland is the area of highest population density within Scotland. Depending on the definition used, it has a population of between 2.4 and 4.2 million (the country's total was around 5.4 million in 2019), including Gre ...
– are flatter and home to most of the population including Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
, Scotland's largest city, and Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
, its capital and political centre, although upland and mountainous terrain lies within the Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands ( gd, Na Monaidhean a Deas) are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas (the other two being the Central Lowlands and the Grampian Mountains and the Highlands, as illustrate ...
.
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
accounts for less than one-tenth (9 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering . Wales is mostly mountainous, though South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
is less mountainous than North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and mid Wales
Mid Wales ( cy, Canolbarth Cymru or simply ''Y Canolbarth'', meaning "the midlands") or Central Wales refers to a region of Wales, encompassing its midlands, in-between North Wales and South Wales. The Mid Wales Regional Committee of the Senedd ...
. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the coastal cities of Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. It forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a ...
, Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the C ...
and Newport, and the South Wales Valleys to their north. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia
Snowdonia or Eryri (), is a mountainous region in northwestern Wales and a national park of in area. It was the first to be designated of the three national parks in Wales, in 1951.
Name and extent
It was a commonly held belief that the na ...
and include Snowdon
Snowdon () or (), is the highest mountain in Wales, at an elevation of above sea level, and the highest point in the British Isles outside the Scottish Highlands. It is located in Snowdonia National Park (') in Gwynedd (histori ...
() which, at , is the highest peak in Wales. Wales has over of coastline. Several islands lie off the Welsh mainland, the largest of which is Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
(''Ynys Môn'') in the north-west.
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the C ...
and North Channel, has an area of and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh
Lough Neagh ( ) is a freshwater lake in Northern Ireland and is the largest lake in the island of Ireland, the United Kingdom and the British Isles. It has a surface area of and supplies 40% of Northern Ireland's water. Its main inflows come ...
which, at , is the largest lake in the British Isles by area. The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard
Slieve Donard ( ; ) is the highest mountain in Northern Ireland and the wider province of Ulster, with a height of . The highest of the Mourne Mountains, it is near the town of Newcastle on the eastern coast of County Down, overlooking the Iri ...
in the Mourne Mountains
The Mourne Mountains ( ; ga, Beanna Boirche), also called the Mournes or Mountains of Mourne, are a granite mountain range in County Down in the south-east of Northern Ireland. They include the highest mountains in Northern Ireland, the hig ...
at .
Government and politics
The United Kingdom is aunitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
under a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
. King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to a ...
is the monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
and head of state of the UK, as well as 14 other independent countries. These 15 countries are sometimes referred to as "Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s". The monarch has "the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn". The Constitution of the United Kingdom
The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland as a political body. Unlike in most countries, no attemp ...
is uncodified and consists mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by ...
s, judge-made case law
Case law, also used interchangeably with common law, is law that is based on precedents, that is the judicial decisions from previous cases, rather than law based on constitutions, statutes, or regulations. Case law uses the detailed facts of ...
and international treaties, together with constitutional conventions. The UK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
can carry out constitutional reform by passing acts of parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament be ...
, and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. No sitting parliament can pass laws that future parliaments cannot change.
 The UK is a
The UK is a parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
and a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
. The Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
is sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
. It is made up of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
and the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
. The main business of parliament takes place in the two houses, but royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
is required for a bill to become an act of parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliame ...
(law).
For general elections (elections to the House of Commons), the UK is divided into 650 constituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
, each of which is represented by a member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
(MP). MPs hold office for up to five years and are always up for re-election in general elections. The Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
, Labour Party and Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from th ...
are, respectively, the current first, second and third largest parties (by number of MPs) in the House of Commons.
The prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
is the head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a ...
in the United Kingdom. Nearly all prime ministers have served as First Lord of the Treasury
The first lord of the Treasury is the head of the Lords Commissioners of the Treasury exercising the ancient office of Lord High Treasurer in the United Kingdom, and is by convention also the prime minister. This office is not equivalent to the ...
and all prime ministers have continuously served as First Lord of the Treasury since 1905, Minister for the Civil Service
In the Government of the United Kingdom, the minister for the Civil Service is responsible for regulations regarding His Majesty's Civil Service, the role of which is to assist the governments of the United Kingdom in formulating and implementin ...
since 1968 and Minister for the Union since 2019. In modern times, the prime minister is, by constitutional convention, an MP. The prime minister is appointed by the monarch and their appointment is governed by constitutional conventions. However, they are normally the leader of the political party
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular country's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
with the most seats in the House of Commons and hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons.
The prime minister not only has statutory functions (alongside other ministers), but is the monarch's principal adviser and it is for them to advise the monarch on the exercise of the royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
in relation to government. In particular, the prime minister recommends the appointment of ministers and chairs the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
.
Administrative divisions
The geographical division of the United Kingdom intocounties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
or shires began in England and Scotland in the early Middle Ages and was complete throughout Great Britain and Ireland by the early Modern Period. Administrative arrangements were developed separately in each country of the United Kingdom, with origins which often predated the formation of the United Kingdom. Modern local government by elected councils, partly based on the ancient counties, was introduced separately: in England and Wales in a 1888 act, Scotland in a 1889 act and Ireland in a 1898 act, meaning there is no consistent system of administrative or geographic demarcation across the United Kingdom.
Until the 19th century there was little change to those arrangements, but there has since been a constant evolution of role and function.
The organisation of local government in England
Local government in England broadly consists of three layers: regional authorities, local authorities and parish councils. Legislation concerning English local government is passed by Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament, as England does n ...
is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to local arrangements. The upper-tier subdivisions of England
The subdivisions of England constitute a hierarchy of administrative divisions and non-administrative ceremonial areas.
Overall, England is divided into nine regions and 48 ceremonial counties, although these have only a limited role in publ ...
are the nine regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, now used primarily for statistical purposes. One region, Greater London
Greater may refer to:
*Greatness
Greatness is a concept of a state of superiority affecting a person or object in a particular place or area. Greatness can also be attributed to individuals who possess a natural ability to be better than al ...
, has had a directly elected assembly and mayor since 2000 following popular support for the proposal in a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
. It was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies, but a proposed assembly in the North East
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
region was rejected by a referendum in 2004. Since 2011, ten combined authorities
A combined authority is a type of local government institution introduced in England outside Greater London by the Local Democracy, Economic Development and Construction Act 2009. Combined authorities are created voluntarily and allow a grou ...
have been established in England. Eight of these have elected mayors, the first elections for which took place on 4 May 2017. Below the regional tier, some parts of England have county councils
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
and district councils and others have unitary authorities
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
, while London consists of 32 London borough
The London boroughs are the 32 local authority districts that together with the City of London make up the administrative area of Greater London; each is governed by a London borough council. The present London boroughs were all created at ...
s and the City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
. Councillors are elected by the first-past-the-post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast the ...
system in single-member wards or by the multi-member plurality system
Plurality block voting, also known as plurality-at-large voting, block vote or block voting (BV) is a non- proportional voting system for electing representatives in multi-winner elections. Each voter may cast as many votes as the number of sea ...
in multi-member wards.
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 council areas, with wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
, Edinburgh, Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), a ...
and Dundee
Dundee (; sco, Dundee; gd, Dùn Dè or ) is Scotland's fourth-largest city and the 51st-most-populous built-up area in the United Kingdom. The mid-year population estimate for 2016 was , giving Dundee a population density of 2,478/km2 or ...
are separate council areas, as is the Highland Council
The Highland Council (' ), the political body covering the Highland local authority created in 1995, comprises 21 wards, each electing three or four councillors by the single transferable vote system, which creates a form of proportional represe ...
, which includes a third of Scotland's area but only just over 200,000 people. Local councils are made up of elected councillors, of whom there are 1,223; they are paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by single transferable vote
Single transferable vote (STV) is a multi-winner electoral system in which voters cast a single vote in the form of a ranked-choice ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternate p ...
in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost, or Convenor
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the group ...
, to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales
Since 1 April 1996, Wales has been divided into 22 unitary authority, single-tier principal areas ( cy, Awdurdodau unedol), styled as counties or county boroughs ( or ) for local government purposes. The elected councils of these areas are resp ...
consists of 22 unitary authorities. All unitary authorities are led by a leader and cabinet elected by the council itself. These include the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, which are unitary authorities in their own right. Elections are held every four years under the first-past-the-post system.
Local government in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is divided into 11 districts for local government purposes. In Northern Ireland, local councils do not carry out the same range of functions as those in the rest of the United Kingdom; for example they have no responsibility f ...
has since 1973 been organised into 26 district councils, each elected by single transferable vote. Their powers are limited to services such as collecting waste, controlling dogs and maintaining parks and cemeteries. In 2008 the executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils and replace the present system.
Devolved governments
 Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a first minister
A first minister is any of a variety of leaders of government cabinets. The term literally has the same meaning as "prime minister" but is typically chosen to distinguish the office-holder from a superior prime minister. Currently the title of '' ...
(or, in the case of Northern Ireland, a diarchal first minister and deputy first minister
The First Minister and deputy First Minister of Northern Ireland are the joint heads of government of the Northern Ireland Executive and have overall responsibility for the running of the Executive Office. Despite the different titles for the two ...
), and a devolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories h ...
unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
legislature. England, the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is administered and legislated for directly by the UK's government and parliament on all issues. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question
The West Lothian question, also known as the English question, is a political issue in the United Kingdom. It concerns the question of whether MPs from Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales who sit in the House of Commons should be able to vote ...
, which concerns the fact that members of parliament from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can vote, sometimes decisively, on matters that affect only England. The 2013 McKay Commission
The Commission on the consequences of devolution for the House of Commons, also known as the McKay Commission, was an independent commission established in the United Kingdom to consider issues arising from devolution in the United Kingdom and ...
on this recommended that laws affecting only England should need support from a majority of English members of parliament.
The Scottish Government and Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
have wide-ranging powers over any matter that has not been specifically reserved
Reserved is a Polish apparel retailer headquartered in Gdańsk, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomerania, Poland. It was founded in 1999 and remains the largest company of the LPP (company), LPP group, which has more than 1,700 retail stores located in ...
to the UK Parliament, including education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
, healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
, Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
and local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
. Their power over economic issues is significantly constrained by an act of the UK parliament passed in 2020.
 The
The Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( cy, Llywodraeth Cymru) is the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of ministers and Minister (government), deputy ministers, and also of a Counsel General for Wales, counsel general. Minist ...
and the Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
(Welsh Parliament; formerly the National Assembly for Wales) have more limited powers than those devolved to Scotland. The Senedd is able to legislate on any matter not specifically reserved to the UK Parliament through Acts of Senedd Cymru
An Act of Senedd Cymru ( cy, Deddf gan Senedd Cymru), or informally an Act of the Senedd, is primary legislation that can be made by the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ) under part 4 of the Government of Wales Act 2006 (as amended by the Wales Act ...
.
The Northern Ireland Executive
The Northern Ireland Executive is the devolved government of Northern Ireland, an administrative branch of the legislature – the Northern Ireland Assembly. It is answerable to the assembly and was initially established according to the ter ...
and Assembly
Assembly may refer to:
Organisations and meetings
* Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions
* General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa ...
have powers similar to those devolved to Scotland. The Executive is led by a diarchy
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', "the office of ...
representing unionist and nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
members of the Assembly. Devolution to Northern Ireland is contingent on participation by the Northern Ireland administration in the North-South Ministerial Council
The North/South Ministerial Council (NSMC) ( ga, An Chomhairle Aireachta Thuaidh-Theas, Ulster-Scots: ) is a body established under the Good Friday Agreement to co-ordinate activity and exercise certain governmental powers across the whole island ...
, where the Northern Ireland Executive cooperates and develops joint and shared policies with the Government of Ireland
The Government of Ireland ( ga, Rialtas na hÉireann) is the cabinet that exercises executive authority in Ireland.
The Constitution of Ireland vests executive authority in a government which is headed by the , the head of government. The governm ...
. The British and Irish governments co-operate on non-devolved matters affecting Northern Ireland through the British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference
The British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference (BIIGC) is an intergovernmental organisation established by the Governments of Ireland and the United Kingdom under the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. It first met in London in 1999, and the la ...
, which assumes the responsibilities of the Northern Ireland administration in the event of its non-operation.
The UK does not have a codified constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princi ...
and constitutional matters are not among the powers devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. Under the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over all ...
, the UK Parliament could, in theory, therefore, abolish the Scottish Parliament, Senedd or Northern Ireland Assembly. Indeed, in 1972, the UK Parliament unilaterally prorogued the Parliament of Northern Ireland
The Parliament of Northern Ireland was the home rule legislature of Northern Ireland, created under the Government of Ireland Act 1920, which sat from 7 June 1921 to 30 March 1972, when it was suspended because of its inability to restore ord ...
, setting a precedent relevant to contemporary devolved institutions. In practice, it would be politically difficult for the UK Parliament to abolish devolution to the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd, given the political entrenchment created by referendum decisions. The political constraints placed upon the UK Parliament's power to interfere with devolution in Northern Ireland are even greater than in relation to Scotland and Wales, given that devolution in Northern Ireland rests upon an international agreement with the Government of Ireland
The Government of Ireland ( ga, Rialtas na hÉireann) is the cabinet that exercises executive authority in Ireland.
The Constitution of Ireland vests executive authority in a government which is headed by the , the head of government. The governm ...
. The UK Parliament restricts the three devolved parliaments' legislative competence in economic areas through an Act passed in 2020.
Dependencies
The United Kingdom has responsibility for 17 territories that do not form part of the United Kingdom itself: 14 British Overseas Territories and three Crown Dependencies. The 14 British Overseas Territories are remnants of the British Empire:Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territo ...
; Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
; the British Antarctic Territory
The British Antarctic Territory (BAT) is a sector of Antarctica claimed by the United Kingdom as one of its 14 British Overseas Territories, of which it is by far the largest by area. It comprises the region south of 60°S latitude and between ...
; the British Indian Ocean Territory
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 ...
; the British Virgin Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = Territorial song
, song = "Oh, Beautiful Virgin Islands"
, image_map = File:British Virgin Islands on the globe (Americas centered).svg
, map_caption =
, mapsize = 290px
, image_map2 = Brit ...
; the Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
; the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
; Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
; Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
; the Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and n ...
; the Pitcairn Islands
The Pitcairn Islands (; Pitkern: '), officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four isl ...
; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in United Kingdom.svg
, map_caption = Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Oce ...
; and Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory o ...
on the island of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
. British claims in Antarctica have limited international recognition. Collectively Britain's overseas territories encompass an approximate land area of , with a total population of approximately 250,000. The overseas territories also give the UK the world's fifth largest exclusive economic zone at . A 1999 UK government white paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper ...
stated that: " heOverseas Territories are British for as long as they wish to remain British. Britain has willingly granted independence where it has been requested; and we will continue to do so where this is an option." Self-determination is also enshrined in the constitutions of several overseas territories and three have specifically voted to remain under British sovereignty (Bermuda in 1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is O. J. Simpson murder case, acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the 1994, year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The ...
, Gibraltar in 2002
File:2002 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 2002 Winter Olympics are held in Salt Lake City; Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother and her daughter Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon die; East Timor gains East Timor independence, indepe ...
and the Falkland Islands in 2013
File:2013 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: Edward Snowden becomes internationally famous for leaking classified NSA wiretapping information; Typhoon Haiyan kills over 6,000 in the Philippines and Southeast Asia; The Dhaka garment fact ...
).
The Crown dependencies are possessions of the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
, as opposed to overseas territories of the UK. They comprise three independently administered jurisdictions: the Channel Island
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
s of Jersey
Jersey ( , ; nrf, Jèrri, label= Jèrriais ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey (french: Bailliage de Jersey, links=no; Jèrriais: ), is an island country and self-governing Crown Dependency near the coast of north-west France. It is the ...
and Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency.
It is the second largest of the Channel Islands ...
in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
in the Irish Sea. By mutual agreement, the British Government manages the islands' foreign affairs and defence and the UK Parliament has the authority to legislate on their behalf. Internationally, they are regarded as "territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible". The power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with their own respective legislative assemblies, with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
or, in the case of the Isle of Man, in certain circumstances the Lieutenant-Governor). Since 2005 each Crown dependency has had a Chief Minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union terri ...
as its head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a ...
.
Law and criminal justice
 The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland's separate legal system. Today the UK has three distinct
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland's separate legal system. Today the UK has three distinct systems of law
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four basic systems: civil law, common law, statutory law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country is shaped by its unique history an ...
: English law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, be ...
, Northern Ireland law
The law of Northern Ireland is the legal system of statute and common law operating in Northern Ireland since the partition of Ireland established Northern Ireland as a distinct jurisdiction in 1921. Prior to 1921, Northern Ireland was part of ...
and Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
. A new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
came into being in October 2009 to replace the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords
Whilst the House of Lords of the United Kingdom is the upper chamber of Parliament and has government ministers, it for many centuries had a judicial function. It functioned as a court of first instance for the trials of peers, for impeachments, ...
. The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the highest court of appeal for the Crown Dependencies, the British Overseas Territories, some Commonwealth countries and a few institutions in the United Kingdom. Established on 14 Augus ...
, including the same members as the Supreme Court, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
and the Crown Dependencies.
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
, and Northern Ireland law
The law of Northern Ireland is the legal system of statute and common law operating in Northern Ireland since the partition of Ireland established Northern Ireland as a distinct jurisdiction in 1921. Prior to 1921, Northern Ireland was part of ...
are based on common-law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
principles. The essence of common law is that, subject to statute, the law is developed by judges in courts, applying statute, precedent
A precedent is a principle or rule established in a previous legal case that is either binding on or persuasive for a court or other tribunal when deciding subsequent cases with similar issues or facts. Common-law legal systems place great valu ...
and common sense to the facts before them to give explanatory judgements of the relevant legal principles, which are reported and binding in future similar cases (''stare decisis
A precedent is a principle or rule established in a previous legal case that is either binding on or persuasive for a court or other tribunal when deciding subsequent cases with similar issues or facts. Common-law legal systems place great valu ...
''). The courts of England and Wales
The courts of England and Wales, supported administratively by His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service, are the civil and criminal courts responsible for the administration of justice in England and Wales.
The United Kingdom does not have a ...
are headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales
The courts of England and Wales, supported administratively by His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service, are the civil and criminal courts responsible for the administration of justice in England and Wales.
The United Kingdom does not have a ...
, consisting of the Court of Appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of t ...
, the High Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal of England and Wales, Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Cou ...
(for civil cases) and the Crown Court
The Crown Court is the court of first instance of England and Wales responsible for hearing all Indictable offence, indictable offences, some Hybrid offence, either way offences and appeals lied to it by the Magistrates' court, magistrates' court ...
(for criminal cases). The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil appeal cases in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the same jurisdiction, often having a persuasive effect in other jurisdictions.
 Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the Court of Session
The Court of Session is the supreme civil court of Scotland and constitutes part of the College of Justice; the supreme criminal court of Scotland is the High Court of Justiciary. The Court of Session sits in Parliament House in Edinburgh ...
, for civil cases, and the High Court of Justiciary
The High Court of Justiciary is the supreme criminal court in Scotland. The High Court is both a trial court and a court of appeal. As a trial court, the High Court sits on circuit at Parliament House or in the adjacent former Sheriff Cou ...
, for criminal cases. The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law. Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as sheriff solemn court, or with a sheriff and no jury, known as sheriff summary Court. The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdict
In law, a verdict is the formal trier of fact, finding of fact made by a jury on matters or questions submitted to the jury by a judge. In a bench trial, the judge's decision near the end of the trial is simply referred to as a finding. In Engl ...
s for a criminal trial: "guilty
Guilty or The Guilty may refer to:
* Guilt (emotion), an experience that occurs when a person believes they have violated a moral standard
Law
*Culpability, the degree to which an agent can be held responsible for action or inaction
*Guilt (law) ...
", " not guilty" and "not proven
Not proven (, ) is a verdict available to a Courts of Scotland, court of law in Scotland. Under Scots law, a Criminal procedure, criminal trial may end in one of three verdicts, one of conviction ("guilty") and two of acquittal ("not proven" and ...
". Both "not guilty" and "not proven" result in an acquittal.
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995, though since that peak there has been an overall fall of 66 per cent in recorded crime from 1995 to 2015, according to crime statistics
Crime statistics refer to systematic, quantitative results about crime, as opposed to crime news or anecdotes. Notably, crime statistics can be the result of two rather different processes:
* scientific research, such as criminological studies, vi ...
. The prison population of England and Wales
The United Kingdom has three distinct legal systems with a separate prison system in each: one for both England and Wales, one for Scotland, and one for Northern Ireland.
Numbers of prisoners
The total UK prison population was 83,618 (0.088% of th ...
has increased to 86,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 148 per 100,000. His Majesty's Prison Service
His Majesty's Prison Service (HMPS) is a part of HM Prison and Probation Service (formerly the National Offender Management Service), which is the part of His Majesty's Government charged with managing most of the prisons within England and Wale ...
, which reports to the Ministry of Justice A Ministry of Justice is a common type of government department that serves as a justice ministry.
Lists of current ministries of justice
Named "Ministry"
* Ministry of Justice (Abkhazia)
* Ministry of Justice (Afghanistan)
* Ministry of Just ...
, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales. The murder rate in England and Wales has stabilised in the first half of the 2010s with a murder rate around 1 per 100,000 which is half the peak in 2002 and similar to the rate in the 1980s Crime in Scotland fell slightly in 2014–2015 to its lowest level in 39 years in with 59 killings for a murder rate of 1.1 per 100,000. Scotland's prisons are overcrowded but the prison population is shrinking.
Foreign relations
The UK is a permanent member of theUnited Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, ...
, a member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
, AUKUS
AUKUS (, ) is a trilateral security pact between Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States, announced on 15 September 2021 for the Indo-Pacific region. Under the pact, the US and the UK will help Australia to acquire nuclear-powered ...
, the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
, the G7 finance ministers
The Group of Seven (G7) is an inter-governmental, intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated membe ...
, the G7 forum
The Group of Seven (G7) is an inter-governmental, intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated membe ...
, the G20, the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
, the WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
and the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
. The UK is said to have a "Special Relationship
The Special Relationship is a term that is often used to describe the politics, political, social, diplomacy, diplomatic, culture, cultural, economics, economic, law, legal, Biophysical environment, environmental, religion, religious, military ...
" with the United States and a close partnership with France – the "Entente cordiale
The Entente Cordiale (; ) comprised a series of agreements signed on 8 April 1904 between the United Kingdom and the French Republic which saw a significant improvement in Anglo-French relations. Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial de ...
" – and shares nuclear weapons technology with both countries; the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance
The Anglo-Portuguese Alliance (or , "Luso-English Alliance") is the oldest alliance based on known history in the world that is still in force by politics. It was established by the Treaty of Windsor in 1386, between the Kingdom of England ( ...
is considered to be the oldest binding military alliance in the world. The UK is also closely linked with the Republic of Ireland; the two countries share a Common Travel Area
The Common Travel Area (CTA; ga, Comhlimistéar Taistil, ) is an open borders area comprising the United Kingdom, Ireland, Isle of Man, and the Channel Islands. The British Overseas Territories are not included. Based on agreements that are not ...
and co-operate through the British-Irish Intergovernmental Conference and the British-Irish Council. Britain's global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations, foreign investments, official development assistance
Official development assistance (ODA) is a category used by the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the OECD, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to measure aid, foreign aid. The DAC first adopted the concept in ...
and military engagements. Canada, Australia and New Zealand, all of which are former colonies of the British Empire which share King Charles as their head of state, are the most favourably viewed countries in the world by British people
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mo ...
.
Military
''His Majesty's Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military, military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its British Overseas Territories, Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They al ...
'' consist of three professional service branches: the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
and Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
(forming the Naval Service Naval Service may refer to either:
* His Majesty's Naval Service, Britain's Royal Navy plus additional services
* Naval Service (Ireland), a branch of the Irish Defence Forces
* United States Department of the Navy, United States military department ...
), the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
and the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
. The armed forces of the United Kingdom are managed by the Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
and controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Secretary of State for Defence
The secretary of state for defence, also referred to as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for the business of the Ministry of Defence. The incumbent is a membe ...
. The Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwi ...
, to whom members of the forces swear an oath of allegiance. The Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK's global security interests and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps
The Allied Rapid Reaction Corps (ARRC) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization High Readiness Force (Land) Headquarters ready for deployment worldwide.
History
The ARRC was created on 1 October 1992 in Bielefeld based on the former I (Britis ...
, the Five Power Defence Arrangements
The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA) are a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom, all of which are Commonwe ...
, RIMPAC
RIMPAC, the Rim of the Pacific Exercise, is the world's largest international maritime warfare exercise. RIMPAC is held biennially during June and July of even-numbered years from Honolulu, Hawaii, with the exception of 2020 where it was held i ...
and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained in Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory o ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia is an island of the British Indian Ocean Territory, a disputed overseas territory of the United Kingdom. It is a militarised atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of the 60 small islands o ...
, the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
, Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
.
The British armed forces played a key role in establishing the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
as the dominant world power in the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. By emerging victorious from conflicts, Britain has often been able to decisively influence world events. Since the end of the British Empire, the UK has remained a major military power. Following the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, defence policy has a stated assumption that "the most demanding operations" will be undertaken as part of a coalition.
According to sources which include the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is an international institute based in Stockholm. It was founded in 1966 and provides data, analysis and recommendations for armed conflict, military expenditure and arms trade as well a ...
and the International Institute for Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is a British research institute or think tank in the area of international affairs. Since 1997, its headquarters have been Arundel House in London, England.
The 2017 Global Go To Think T ...
, the UK has either the fourth- or the fifth-highest military expenditure
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing milit ...
. Total defence spending amounts to 2.0 per cent of national GDP.
Economy
Overview
 The UK has a partially regulated
The UK has a partially regulated market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
. Based on market exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
s, the UK is today the fifth-largest economy in the world and the second-largest in Europe after Germany. HM Treasury
His Majesty's Treasury (HM Treasury), occasionally referred to as the Exchequer, or more informally the Treasury, is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and ec ...
, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
, is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance
Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achie ...
policy and economic policy
The economy of governments covers the systems for setting levels of taxation, government budgets, the money supply and interest rates as well as the labour market, national ownership, and many other areas of government interventions into the e ...
. The Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
is the UK's central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
and is responsible for issuing notes and coins in the nation's currency, the pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover their issue. The pound sterling is the world's fourth-largest reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
(after the US dollar, euro, and Japanese Yen). Since 1997 the Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) may refer to:
* Monetary Policy Committee (India)
The Monetary Policy Committee is responsible for fixing the benchmark interest rate in India. The meetings of the Monetary Policy Committee are held at least fo ...
, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England
The governor of the Bank of England is the most senior position in the Bank of England. It is nominally a civil service post, but the appointment tends to be from within the bank, with the incumbent grooming their successor. The governor of the Ba ...
, has been responsible for setting interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year.
The UK service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
makes up around 79 per cent of GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often ...
. London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
is one of the world's largest financial centres, ranking second in the world, behind New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, in the Global Financial Centres Index
The Global Financial Centres Index (GFCI) is a ranking of the competitiveness of financial centres based on over 29,000 financial centre assessments from an online questionnaire together with over 100 indices from organisations such as the World ...
in 2020. London also has the largest city GDP in Europe. Edinburgh ranks 17th in the world, and sixth in Western Europe in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020. Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
is very important to the British economy; with over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world and London has the most international visitors of any city in the world. The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.
Following the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union, the functioning of the UK internal economic market is enshrined by the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020
The United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom passed in December 2020. It is concerned with trade within the UK, as the UK is no longer subject to EU law. The act seeks to prevent internal trade b ...
which ensures trade in goods and services continues without internal barriers across the four countries of the United Kingdom.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
started in Britain with an initial concentration on the textile industry, followed by other heavy industries such as shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
, coal mining and steelmaking
Steelmaking is the process of producing steel from iron ore and carbon/or scrap. In steelmaking, impurities such as nitrogen, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and excess carbon (the most important impurity) are removed from the sourced iron, and all ...
. British merchants, shippers and bankers developed overwhelming advantage over those of other nations allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century. As other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy but accounted for only 16.7 per cent of national output in 2003.
 The
The automotive industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of company, companies and organizations involved in the design, Business development, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industry ...
employs around 800,000 people, with a turnover in 2015 of £70 billion, generating £34.6 billion of exports (11.8 per cent of the UK's total export goods). In 2015, the UK produced around 1.6 million passenger vehicles and 94,500 commercial vehicles. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing: in 2015 around 2.4 million engines were produced. The UK motorsport
Motorsport, motorsports or motor sport is a global term used to encompass the group of competitive sporting events which primarily involve the use of motorized vehicles. The terminology can also be used to describe forms of competition of two ...
industry employs around 41,000 people, comprises around 4,500 companies and has an annual turnover of around £6 billion.
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry in the world depending upon the method of measurement and has an annual turnover of around £30 billion.
BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
plays a critical role in some of the world's biggest defence aerospace projects. In the UK, the company makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter
The Eurofighter Typhoon is a European multinational twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter. The Typhoon was designed originally as an air-superiority fighter and is manufactured by a consortium of Airbus, BAE Systems and Leonardo ...
and assembles the aircraft for the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Joint Strike Fighter – the world's largest single defence project – for which it designs and manufactures a range of components. It also manufactures the Hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
, the world's most successful jet training aircraft. Airbus UK
Airbus UK is a wholly owned subsidiary of Airbus which produces wings for Airbus aircraft. When Airbus was incorporated as a joint-stock company in 2001, BAE Systems transferred its UK Airbus facilities in return for a 20% share of the new compa ...
also manufactures the wings for the A400M
The Airbus A400M AtlasNamed after the Greek mythological figure. is a European four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft. It was designed by Airbus Military (now Airbus Defence and Space) as a tactical airlifter with strategic capabil ...
military transporter. Rolls-Royce is the world's second-largest aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ai ...
and it has more than 30,000 engines in service in the civil and defence sectors.
The UK space industry was worth £9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency
The United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA) is an executive agency of the Government of the United Kingdom, responsible for the United Kingdom's civil space programme. It was established on 1 April 2010 to replace the British National Space Centre ...
. In 2013, the British Government pledged £60 m to the Skylon Skylon may refer to:
* Skylon (Festival of Britain), a landmark structure of the 1951 Festival of Britain
* Skylon (spacecraft), a proposed orbital spaceplane
* Skylon Tower, an observation tower in Niagara Falls, Ontario
* ''Skylon'' (album), a 20 ...
project: this investment will provide support at a "crucial stage" to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE
A sabre ( French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as th ...
engine to be built.
The pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing about 60 per cent of food needs with less than 1.6 per cent of the labour force (535,000 workers). Around two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The UK retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. It is also rich in a variety of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land. In 2020, coronavirus lockdown measures caused the UK economy to suffer its biggest slump on record, shrinking by 20.4 per cent between April and June compared to the first three months of the year, to push it officially into recession for the first time in 11 years.
The UK has an external debt of $9.6 trillion
''Trillion'' is a number with two distinct definitions:
* 1,000,000,000,000, i.e. one million million, or (ten to the twelfth power), as defined on the short scale. This is now the meaning in both American and British English.
* 1,000,000,000,0 ...
dollars, which is the second-highest in the world after the US. As a percentage of GDP, external debt is 408 per cent, which is the third-highest in the world after Luxembourg and Iceland.
Science and technology
 England and Scotland were leading centres of the
England and Scotland were leading centres of the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
from the 17th century. The United Kingdom led the Industrial Revolution from the 18th century, and has continued to produce scientists and engineers credited with important advances. Major theorists from the 17th and 18th centuries include Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
, whose laws of motion and illumination of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
have been seen as a keystone of modern science; from the 19th century Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
, whose theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charle ...
was fundamental to the development of modern biology, and James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and ligh ...
, who formulated classical electromagnetic theory
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of a ...
; and more recently Stephen Hawking, who advanced major theories in the fields of cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount (lexicographer), Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in ...
, quantum gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vi ...
and the investigation of black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
.
Major scientific discoveries from the 18th century include hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
by Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English natural philosopher and scientist who was an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "infl ...
; from the 20th century penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
by Alexander Fleming
Sir Alexander Fleming (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in 1928 of w ...
, and the structure of DNA, by Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
and others. Famous British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fun ...
, George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for ...
, Richard Arkwright
Sir Richard Arkwright (23 December 1732 – 3 August 1792) was an English inventor and a leading entrepreneur during the early Industrial Revolution. He is credited as the driving force behind the development of the spinning frame, known as t ...
, Robert Stephenson
Robert Stephenson Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS HFRSE FRSA Doctor of Civil Law, DCL (16 October 1803 – 12 October 1859) was an English civil engineer and designer of locomotives. The only son of George Stephenson, the "Father of Railway ...
and Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
. Other major engineering projects and applications by people from the UK include the steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
, developed by Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
and Andrew Vivian
Andrew Vivian (1759–1842) was a British mechanical engineer, inventor, and mine captain of the Dolcoath mine in Cornwall, England.
In partnership with his cousin Richard Trevithick, the inventor of the "high pressure" steam engine, and the e ...
; from the 19th century the electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
by Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, the first computer designed by Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered ...
, the first commercial electrical telegraph
Electrical telegraphs were point-to-point text messaging systems, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems ...
by William Fothergill Cooke
Sir William Fothergill Cooke (4 May 1806 – 25 June 1879) was an English inventor. He was, with Charles Wheatstone, the co-inventor of the Cooke-Wheatstone electrical telegraph, which was patented in May 1837. Together with John Ricardo he fo ...
and Charles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS FRSE DCL LLD (6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875), was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope (a device for di ...
, the incandescent light bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
by Joseph Swan
Sir Joseph Wilson Swan FRS (31 October 1828 – 27 May 1914) was an English physicist, chemist, and inventor. He is known as an independent early developer of a successful incandescent light bulb, and is the person responsible for develop ...
, and the first practical telephone, patented by Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell (, born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Te ...
; and in the 20th century the world's first working television system by John Logie Baird
John Logie Baird FRSE (; 13 August 188814 June 1946) was a Scottish inventor, electrical engineer, and innovator who demonstrated the world's first live working television system on 26 January 1926. He went on to invent the first publicly demo ...
and others, the jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
by Frank Whittle
Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, (1 June 1907 – 8 August 1996) was an English engineer, inventor and Royal Air Force (RAF) air officer. He is credited with inventing the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 for ...
, the basis of the modern computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These pr ...
by Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical com ...
, and the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web se ...
by Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. He is a Professorial Fellow of Computer Science at the University of Oxford and a profess ...
.
Scientific research and development remains important in British universities, with many establishing science park
A science park (also called a "university research park", "technology park”, "technopark", “technopole", or a "science and technology park" (STP)) is defined as being a property-based development that accommodates and fosters the growt ...
s to facilitate production and co-operation with industry. Between 2004 and 2008 the UK produced 7 per cent of the world's scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively). Scientific journals produced in the UK include ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
'', the ''British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origi ...
'' and ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles, ...
''. The United Kingdom was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British maga ...
2020, 2021 and 2022.
Transport
 A radial road network totals of main roads, of motorways and of paved roads. The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world. In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the
A radial road network totals of main roads, of motorways and of paved roads. The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world. In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
, East Coast
East Coast may refer to:
Entertainment
* East Coast hip hop, a subgenre of hip hop
* East Coast (ASAP Ferg song), "East Coast" (ASAP Ferg song), 2017
* East Coast (Saves the Day song), "East Coast" (Saves the Day song), 2004
* East Coast FM, a ra ...
, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1
High Speed 1 (HS1), legally the Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL), is a high-speed railway linking London with the Channel Tunnel.
It is part of a line carrying international passenger traffic between the United Kingdom and mainland Europe; ...
is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world's first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darl ...
, opened in 1825. Just under five years later the world's first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively ...
, designed by George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for ...
. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
.
The UK has a railway network of in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways
NI Railways, also known as Northern Ireland Railways (NIR) ( ga, Iarnród Thuaisceart Éireann); and for a brief period Ulster Transport Railways (UTR), is the railway operator in Northern Ireland. NIR is a subsidiary of Translink, whose parent ...
, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink Translink (or TransLink) may refer to:
* TransLink (British Columbia), the public transport operator in Vancouver, Canada
* Translink (Northern Ireland)
Translink is the brand name of the Northern Ireland Transport Holding Company (NITHCo), a ...
. In Great Britain, the British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
network was privatised
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety. HS2
High Speed 2 (HS2) is a planned high-speed railway line in England, the first phase of which is under construction in stages and due for completion between 2029 and 2033, depending on approval for later stages. The new line will run from its m ...
is a new high speed railway under construction linking up London, the Midlands, the North and Scotland serving over 25 stations, including eight of Britain's 10 largest cities and connecting around 30 million. Crossrail
Crossrail is a railway construction project mainly in central London. Its aim is to provide a high-frequency hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system crossing the capital from suburbs on the west to east, by connecting two major railway ...
, opened in 2022, was Europe's largest construction project with a £15 billion projected cost.
Great British Railways
Great British Railways (GBR) is a planned state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2024, with the exception of Transport for London, Merseytravel services, and light rail and trams elsewhere in England. I ...
is a planned state-owned
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownersh ...
public body
A statutory corporation is a government entity created as a statutory body by statute. Their precise nature varies by jurisdiction, thus, they are statutes owned by a government or controlled by national or sub-national government to the (in ...
that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain
The railway system in Great Britain is the oldest railway system in the world. The first locomotive-hauled public railway opened in 1825, which was followed by an era of rapid expansion. Most of the track is managed by Network Rail, which in ...
from 2023. In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK, 2.4 billion of which were in London. The red double-decker bus has entered popular culture as an internationally recognised icon of England. The London bus network is extensive, with over 6,800 scheduled services every weekday carrying about six million passengers on over 700 different routes making it one of the most extensive bus systems in the world and the largest in Europe.
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers. In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the Airports of London, London airport sys ...
(65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after H ...
(31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport
London Stansted Airport is a tertiary international airport serving London, England, United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, northeast of Central London.
London Stansted serves over 160 destinations acro ...
(18.9 million passengers). London Heathrow Airport, located west of the capital, has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world and is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a populati ...
, as well as Virgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic, a trading name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited and Virgin Atlantic International Limited, is a British airline with its head office in Crawley, England. The airline was established in 1984 as British Atlantic Airways, and w ...
.
Energy
supermajor
Big Oil is a name used to describe the world's six or seven largest publicly traded and investor-owned oil and gas companies, also known as supermajors. The term, particularly in the United States, emphasizes their economic power and influence ...
s" – BP and Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard ou ...
.
In 2013, the UK produced 914 thousand barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil and consumed 1,507 thousand bbl/d. Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005. the UK had around 3.1 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves, the largest of any EU member state.
In 2009, the UK was the 13th-largest producer of natural gas in the world and the largest producer in the EU. Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004.
Coal production played a key role in the UK economy in the 19th and 20th centuries. In the mid-1970s, 130 million tonnes of coal were produced annually, not falling below 100 million tonnes until the early 1980s. During the 1980s and 1990s, the industry was scaled back considerably. In 2011, the UK produced 18.3 million tonnes of coal. In 2005 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 171 million tons. The UK Coal Authority
The Coal Authority is a non-departmental public body of the United Kingdom government sponsored by the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS). On behalf of the country, it owns the vast majority of unworked coal in Great Brit ...
has stated there is a potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG) or ' fracking', and that, based on current UK coal consumption, such reserves could last between 200 and 400 years. Environmental and social concerns have been raised over chemicals getting into the water table and minor earthquakes damaging homes.
In the late 1990s, nuclear power plants contributed around 25 per cent of total annual electricity generation in the UK, but this has gradually declined as old plants have been shut down and ageing-related problems affect plant availability. In 2012, the UK had 16 reactors normally generating about 19 per cent of its electricity. All but one of the reactors will be retired by 2023. Unlike Germany and Japan, the UK intends to build a new generation of nuclear plants from about 2018.
The total of all renewable electricity sources provided for 38.9 per cent of the electricity generated in the United Kingdom in the third quarter of 2019, producing 28.8TWh of electricity. The UK is one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is its fastest-growing supply, in 2019 it generated almost 20 per cent of the UK's total electricity.
Water supply and sanitation
Access to improved water supply and sanitation in the UK is universal. It is estimated that 96.7 per cent of households are connected to the sewer network. According to the Environment Agency, total water abstraction for public water supply in the UK was 16,406megalitre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). ...
s per day in 2007.
In England and Wales water and sewerage services are provided by 10 private regional water and sewerage companies and 13 mostly smaller private "water only" companies. In Scotland, water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water
Scottish Water is a statutory corporation that provides water and sewerage services across Scotland. It is accountable to the public through the Scottish Government.
Operations
Scottish Water provides drinking water to 2.46 million households ...
. In Northern Ireland water and sewerage services are also provided by a single public entity, Northern Ireland Water
Northern Ireland Water Limited ( ga, Uisce Thuaisceart Éireann; Ulster-Scots: ''Norlin Airlan Wattèr'') is a water company in Northern Ireland.
Formerly an executive agency within Northern Ireland Executive, it became a government-owned comp ...
.
Demographics
 A
A census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
is taken simultaneously in all parts of the UK every 10 years. In the 2011 census the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775. It is the fourth-largest in Europe (after Russia, Germany and France), the fifth-largest in the Commonwealth and the 22nd-largest in the world. In mid-2014 and mid-2015 net long-term international migration contributed more to population growth. In mid-2012 and mid-2013 natural change contributed the most to population growth. Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by an average annual rate of approximately 0.7 per cent. This compares to 0.3 per cent per year in the period 1991 to 2001 and 0.2 per cent in the decade 1981 to 1991. The 2011 census also showed that, over the previous 100 years, the proportion of the population aged 0–14 fell from 31 per cent to 18 per cent, and the proportion of people aged 65 and over rose from 5 to 16 per cent. In 2018 the median age of the UK population was 41.7 years.
England's population in 2011 was 53 million, representing some 84 per cent of the UK total. It is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with 420 people resident per square kilometre in mid-2015, with a particular concentration in London and the south-east. The 2011 census put Scotland's population at 5.3 million, Wales at 3.06 million and Northern Ireland at 1.81 million.
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.74 children born per woman. While a rising birth rate is contributing to population growth, it remains considerably below the baby boom peak of 2.95 children per woman in 1964, or the high of 6.02 children born per woman in 1815, below the replacement rate of 2.1, but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63. In 2011, 47.3 per cent of births in the UK were to unmarried women. The Office for National Statistics published a bulletin in 2015 showing that, out of the UK population aged 16 and over, 1.7 per cent identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual (2.0 per cent of males and 1.5 per cent of females); 4.5 per cent of respondents responded with "other", "I don't know", or did not respond. The number of LGBT rights in the United Kingdom, transgender people in the UK was estimated to be between 65,000 and 300,000 by research between 2001 and 2008.
Ethnic groups
Historically, indigenous British people were thought to be Genetic history of the British Isles, descended from the various ethnic groups that settled there before the 12th century: the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse and theNormans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
. Welsh people could be the oldest ethnic group in the UK. A 2006 genetic study shows that more than 50 per cent of England's gene pool contains Germanic Y chromosomes. Another 2005 genetic analysis indicates that "about 75 per cent of the traceable ancestors of the modern British population had arrived in the British isles by about 6,200 years ago, at the start of the British Neolithic or Stone Age", and that the British broadly share a common ancestry with the Basque people. The UK has a history of non-white immigration with Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
having the oldest Black population in the country dating back to at least the 1730s during the period of the African slave trade. During this period it is estimated the Afro-Caribbean population of Great Britain was 10,000 to 15,000 which later declined due to the abolition of slavery. The UK also has the oldest British Chinese, Chinese community in Europe, dating to the arrival of Chinese seamen in the 19th century. In 1950 there were probably fewer than 20,000 non-white residents in Britain, almost all born overseas. In 1951 there were an estimated 94,500 people living in Britain who had been born in South Asia, China, Africa and the Caribbean, just under 0.2 per cent of the UK population. By 1961 this number had more than quadrupled to 384,000, just over 0.7 per cent of the United Kingdom population.
Since 1948 substantial immigration from Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia has been a legacy of ties forged by the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
. Migration from new EU member states in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe since 2004 has resulted in growth in these population groups, although some of this migration has been temporary. Since the 1990s, there has been substantial diversification of the immigrant population, with migrants to the UK coming from a much wider range of countries than previous waves, which tended to involve larger numbers of migrants coming from a relatively small number of countries.
Academics have argued that the Classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom, ethnicity categories employed in British national statistics, which were first introduced in the 1991 UK census, 1991 census, involve confusion between the concepts of ethnicity and Race (human classification), race. , 87.2 per cent of the UK population identified themselves as white, meaning 12.8 per cent of the UK population identify themselves as of one of number of minority group, ethnic minority groups. In the 2001 census, this figure was 7.9 per cent of the UK population. Because of differences in the wording of the census forms used in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, data on the Other White group is not available for the UK as a whole, but in England and Wales this was the fastest-growing group between the 2001 and 2011 censuses, increasing by 1.1 million (1.8 percentage points). Amongst groups for which comparable data is available for all parts of the UK level, the Other Asian category increased from 0.4 per cent to 1.4 per cent of the population between 2001 and 2011, while the Mixed (United Kingdom ethnicity category), Mixed category rose from 1.2 per cent to 2 per cent.
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4 per cent of London's population and 37.4 per cent of Leicester's was estimated to be non-white , whereas less than 5 per cent of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West England, South West were from ethnic minorities, according to the 2001 census. , 31.4 per cent of primary and 27.9 per cent of secondary pupils at state schools in England were members of an ethnic minority. The 1991 census was the first UK census to have a question on ethnic group. In the 1991 UK census 94.1 per cent of people reported themselves as being White British, White Irish or White Other with 5.9 per cent of people reporting themselves as coming from other minority groups.
Languages
The UK's ''de facto'' official language is English. It is estimated that 95 per cent of the UK's population are monolingual English speakers. 5.5 per cent of the population are estimated to speak languages brought to the UK as a result of relatively recent immigration. South Asian languages are the largest grouping which includes Punjabi language, Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali language, Bengali, Sylheti language, Sylheti, Hindi and Gujarati language, Gujarati. According to the 2011 census, Polish language, Polish has become the second-largest language spoken in England and has 546,000 speakers. In 2019, some three quarters of a million people spoke little or no English. Three indigenous Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh language, Welsh, Irish language, Irish and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish language, Cornish, which became extinct as a first language in the late 18th century, is subject to revival efforts and has a small group of second language speakers. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 people (17.8 per cent). In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England. In the 2011 census in Northern Ireland 167,487 people (10.4 per cent) stated that they had "some knowledge of Irish" (see Irish language in Northern Ireland), almost exclusively in the Irish nationalism, nationalist (mainly Catholic) population. Over 92,000 people in Scotland (just under 2 per cent of the population) had some Gaelic language ability, including 72 per cent of those living in the Outer Hebrides. The number of children being taught either Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is increasing. Among emigrant-descended populations some Scottish Gaelic is still Canadian Gaelic, spoken in Canada (principally Nova Scotia and Cape Breton Island), and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina. Scots language, Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, has limited European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, recognition alongside its regional variant, Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots in Northern Ireland, without specific commitments to protection and promotion. As of April 2020, there are said to be around 151,000 users of British Sign Language (BSL), a sign language used by deaf people, in the UK. BSL was recognised as a language of England, Scotland and Wales in law in 2022. It is compulsory for pupils to study a second language from the age of seven in England. French and Spanish are the two most commonly taught second languages in the United Kingdom. All pupils in Wales are either taught Welsh as a second language up to age 16, or are Welsh medium education, taught in Welsh as a first language. Welsh was recognised as having official status in Wales in 2011. Irish was recognised as having official status in Northern Ireland in 2022.Religion
Forms of Christianity have dominated religious life in what is now the United Kingdom for over 1,400 years. Although a majority of citizens still identify with Christianity in many surveys, regular church attendance has fallen dramatically since the middle of the 20th century, while immigration and demographic change have contributed to the growth of other faiths, most notably Islam. This has led some commentators to variously describe the UK as a multi-faith, secularism, secularised, or post-Christian society. In the 2001 census, 71.6 per cent of all respondents indicated that they were Christians, with the next largest faiths being Islam (2.8 per cent), Hinduism (1.0 per cent), Sikhism (0.6 per cent), Judaism (0.5 per cent), Buddhism (0.3 per cent) and all other religions (0.3 per cent). 15 per cent of respondents stated that they had irreligion, no religion, with a further 7 per cent not stating a religious preference. A Tearfund survey in 2007 showed only one in 10 Britons actually attend church weekly. Between the 2001 and 2011 census there was a decrease in the number of people who identified as Christian by 12 per cent, whilst the percentage of those reporting no religious affiliation doubled. This contrasted with growth in the other main religious group categories, with the number of Muslims increasing by the most substantial margin to a total of about 5 per cent. The Islam in the United Kingdom, Muslim population has increased from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group in the United Kingdom. In a 2016 survey conducted by British Social Attitudes, BSA (British Social Attitudes) on religious affiliation; 53 per cent of respondents indicated 'irreligious, no religion', while 41 per cent indicated they were Christians, followed by 6 per cent who affiliated with other religions (e.g. Islam, Hinduism, Judaism, etc.). Among Christians, adherents to the Church of England constituted 15 per cent, Catholic Church 9 per cent, and other Christians (including Presbyterians, Methodists, other Protestants, as well as Eastern Orthodox), 17 per cent. 71 per cent of young people aged 18––24 said they had no religion. The Church of England is the State religion, established church in England. It retains a Lords Spiritual, representation in the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament and theBritish monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwi ...
is its Supreme Governor of the Church of England, Supreme Governor. In religion in Scotland, Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognised as the national church. It is not State religion, subject to state control, and the British monarch is an ordinary member, required to swear an oath to "maintain and preserve the Protestantism, Protestant Religion and Presbyterian polity, Presbyterian Church Government" upon his or her accession. The Church in Wales was disestablished in 1920 and, as the Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1870 before the partition of Ireland
The partition of Ireland ( ga, críochdheighilt na hÉireann) was the process by which the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland divided Ireland into two self-governing polities: Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland. ...
, there is no established church in Northern Ireland. Although there are no UK-wide data in the 2001 census on adherence to individual Christian denominations, it has been estimated that 62 per cent of Christians are Anglican, 13.5 per cent Catholic Church, Catholic, 6 per cent Presbyterian, and 3.4 per cent Methodist, with small numbers of other Protestant denominations such as Plymouth Brethren, and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox churches.
In the 2021 United Kingdom census, less than half the English and Welsh population were Christian. 46.2% of the people of England and Wales said they were Christian, 37.2% that they had no religion, and 6.5% said they were Muslim.
Migration
 The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain. Throughout the 19th century a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The Germans in the United Kingdom, German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to History of the Jews in Russia, Russian Jews. After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2,000,000 left the
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain. Throughout the 19th century a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The Germans in the United Kingdom, German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to History of the Jews in Russia, Russian Jews. After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2,000,000 left the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
by 1914. Around 120,000 settled permanently in Britain, becoming the largest ethnic minority from outside the British Isles; this population had increased to 370,000 by 1938. Unable to return to Poland at the end of World War II, over 120,000 Polish Armed Forces in the West, Polish veterans remained in the UK permanently. After the Second World War, many people immigrated from colonies and former-colonies in the Caribbean and Indian subcontinent, as a legacy of empire or driven by labour shortages. In 1841, 0.25 per cent of the population of England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
was born in a foreign country, increasing to 1.5 per cent by 1901, 2.6 per cent by 1931 and 4.4 per cent in 1951.
In 2014 the immigration Net migration rate, net increase was 318,000: Immigration was at 641,000, up from 526,000 in 2013, while the number of emigrants leaving for over a year was 323,000. A recent migration trend has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe, known as the A8 countries. In 2011, citizens of new EU member states made up 13 per cent of immigrants. The UK applied temporary restrictions to citizens of Romania and Bulgaria, which joined the EU in January 2007. Research conducted by the Migration Policy Institute for the Equality and Human Rights Commission suggests that, between May 2004 and September 2009, 1.5 million workers migrated from the new EU member states to the UK, most of them Polish. Many subsequently returned home, resulting in a net increase in the number of nationals of the new member states in the UK. The late-2000s recession in the UK reduced economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK, making migration temporary and circular. The proportion of foreign-born people in the UK remains slightly below that of many other European countries.
Immigration is now contributing to a rising population, with arrivals and UK-born children of migrants accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. 27 per cent of UK live births in 2014 were to mothers born outside the UK, according to official statistics released in 2015. The ONS reported that net migration rose from 2009 to 2010 by 21 per cent to 239,000.
In 2013, approximately 208,000 foreign nationals were naturalised as British citizens, the highest number since 1962. This figure fell to around 125,800 in 2014. Between 2009 and 2013, the average British citizenships granted annually was 195,800. The most common previous nationalities of those naturalised in 2014 were India, Pakistan, the Philippines, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Nepal, China, South Africa, Poland and Somalia. The total number of grants of settlement, which confer Permanent residency, permanent residence in the UK but not citizenship, was approximately 154,700 in 2013, higher than the previous two years.
Education
Education in the United Kingdom is a Devolution, devolved matter, with each country having a separate education system. Considering the four systems together, about 38 per cent of the United Kingdom population has a university or college degree, which is the highest percentage in Europe, and among the highest percentages in the world. The United Kingdom trails only the United States in terms of representation on lists of top 100 universities. A Social Mobility and Child Poverty Commission, government commission's report in 2014 found that privately educated people comprise 7 per cent of the general population of the UK but much larger percentages of the top professions, the most extreme case quoted being 71 per cent of senior judges.England
 Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of Local education authority, local authorities. Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944. Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18. In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science. The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools, while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of Local education authority, local authorities. Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944. Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18. In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science. The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools, while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.

Scotland
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day-to-day administration and funding of state schools the responsibility of Local Authorities. Two Scottish public bodies, non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education. The Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, Tertiary education, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centres. Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to education professionals. Scotland first legislated for compulsory education in 1496. The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4 per cent in 2016, but it has been falling slowly in recent years. Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges, as fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.Wales
TheWelsh Government
The Welsh Government ( cy, Llywodraeth Cymru) is the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of ministers and Minister (government), deputy ministers, and also of a Counsel General for Wales, counsel general. Minist ...
's Jeremy Miles, Minister for Education has responsibility for education in Wales. State funded education is available to children from the age of three whilst the legal obligation for parents to have their children educated, usually at school, begins at age five. A sizeable minority of pupils are educated in Welsh whilst the rest are obliged to study the language until the age of 16. Wales' performance in Pisa testing, which compares the academic performance of adolescents around the world, has improved in recent years but remains lower than other parts of the UK. In 2019, just under 60% of entrants passed their main English and math GCSEs. The obligation to receive education in Wales ends at the age of 16. In 2017 and 2018, just under 80% of 16 to 18 and just under 40% of 19 to 24-year-olds were in some kind of education or training.
Northern Ireland
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Department of Education (Northern Ireland), Minister of Education, although responsibility at a local level is administered by the Education Authority which is further sub-divided into five geographical areas. The Council for the Curriculum, Examinations & Assessment (CCEA) is the body responsible for advising the Northern Ireland Executive, government on what should be taught in Northern Ireland's schools, monitoring standards and awarding qualifications.Healthcare
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
.
Regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based, such as the Royal Colleges. Political and operational responsibility for healthcare lies with four national executive (government), executives; healthcare in England is the responsibility of the UK Government; healthcare in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Northern Ireland Executive
The Northern Ireland Executive is the devolved government of Northern Ireland, an administrative branch of the legislature – the Northern Ireland Assembly. It is answerable to the assembly and was initially established according to the ter ...
; healthcare in Scotland is the responsibility of the Scottish Government; and healthcare in Wales is the responsibility of the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( cy, Llywodraeth Cymru) is the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of ministers and Minister (government), deputy ministers, and also of a Counsel General for Wales, counsel general. Minist ...
. Each National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
has different policies and priorities, resulting in contrasts.
Culture
The culture of the United Kingdom has been influenced by many factors including: the nation's island status; its History of the United Kingdom, history as a western liberal democracy and a major power; as well as being a political union of four countries with each preserving elements of distinctive traditions, customs and symbolism. As a result of theBritish Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, British influence can be observed in the English language, language, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
and Common law, legal systems of many of its former colonies including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States; a common culture coined today as the Anglosphere. The substantial cultural influence of the United Kingdom has led it to be described as a "cultural superpower"."The cultural superpower: British cultural projection abroad". Journal of the British Politics Society, Norway. Volume 6. No. 1. Winter 2011 A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.
Literature
 "British literature" refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the
"British literature" refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
and the Channel Islands. Most British literature is in the English language. In 2005, some 206,000 books were published in the United Kingdom and in 2006 it was the books published per country per year, largest publisher of books in the world.
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time. The 20th-century English crime writer Agatha Christie is the List of best-selling fiction authors, best-selling novelist of all time. Twelve of the top 25 of 100 novels by British writers chosen by a BBC poll of global critics were written by women; these included works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, Charlotte Brontë, Charlotte and Emily Brontë, Mary Shelley, Jane Austen, Doris Lessing and Zadie Smith.
Scottish literature, Scotland's contributions include Arthur Conan Doyle (the creator of Sherlock Holmes), Walter Scott, Sir Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, Robert Louis Stevenson and the poet Robert Burns. More recently Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance, with grimmer works from Ian Rankin and Iain Banks. Scotland's capital, Edinburgh, was UNESCO's first worldwide City of Literature.
Britain's oldest known poem, ''Y Gododdin'', was composed most likely in the late 6th century. It was written in Cumbric language, Cumbric or Old Welsh and contains the earliest known reference to King Arthur. The Arthurian legend was further developed by Geoffrey of Monmouth. Poet Dafydd ap Gwilym (''fl.'' 1320–1370) is regarded as one of the greatest European poets of his age. Daniel Owen is credited as the first Welsh-language novelist, publishing ''Rhys Lewis (novel), Rhys Lewis'' in 1885. The best-known of the Anglo-Welsh poetry, Anglo-Welsh poets are Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas, the latter nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1996. Leading Welsh novelists of the twentieth century include Richard Llewellyn and Kate Roberts (author), Kate Roberts.
Irish writers, living at a time when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, include Oscar Wilde, Bram Stoker and George Bernard Shaw. There have been many authors whose origins were from outside the United Kingdom but who moved to the UK. These include Joseph Conrad, T. S. Eliot, Kazuo Ishiguro, Sir Salman Rushdie and Ezra Pound.
Philosophy
 The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of 'British Empiricism', a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and 'Scottish Philosophy', sometimes referred to as the 'Scottish School of Common Sense'. The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet, William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish "common sense" school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work ''Utilitarianism (book), Utilitarianism''.
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of 'British Empiricism', a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and 'Scottish Philosophy', sometimes referred to as the 'Scottish School of Common Sense'. The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet, William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish "common sense" school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work ''Utilitarianism (book), Utilitarianism''.
Music
Various styles of music have become popular in the UK, including the indigenous folk music of Folk music of England, England, Music of Wales#Folk music, Wales, Folk music of Scotland, Scotland and Folk music of Northern Ireland, Northern Ireland. Historically, there has been exceptional Renaissance music from the Tudor period, with masses, madrigals and lute music by Thomas Tallis, John Taverner, William Byrd, Orlando Gibbons and John Dowland. After the Stuart Restoration, an English tradition of dramatic masques, anthems and airs became established, led by Henry Purcell, followed by Thomas Arne and others. The German-born composer George Frideric Handel became a Naturalization, naturalised British nationality law, British citizen in 1727, when he composed the anthem ''Zadok the Priest'' for the coronation of George II of Great Britain, George II; it became the traditional ceremonial music for anointing all future monarchs. Handel's many oratorios, such as his famous ''Messiah (Handel), Messiah'', were written in the English language. Ceremonial music is also performed to mark Remembrance Sunday across the UK, including the National Service of Remembrance#Traditional music, Traditional Music played at the Cenotaph. In the second half of the 19th century, as Arthur Sullivan and his librettist W. S. Gilbert wrote their popular Savoy operas, Edward Elgar's wide range of music rivalled that of his contemporaries on the continent. Increasingly, however, composers became inspired by the English countryside and its folk music, notably Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, a pioneer of modern British opera. Among the many post-war composers, some of the most notable have made their own personal choice of musical identity: Peter Maxwell Davies (Orkney), Harrison Birtwistle (mythological), and John Tavener (religious).Visual art
 The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romanticism, Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Joshua Reynolds, Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon (artist), Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language; the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the Abstract art, abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the "Young British Artists": Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen (director), Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Jake and Dinos Chapman, Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery (London), National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romanticism, Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Joshua Reynolds, Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon (artist), Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language; the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the Abstract art, abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the "Young British Artists": Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen (director), Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Jake and Dinos Chapman, Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery (London), National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).
Cinema
 The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film ''Vertigo (film), Vertigo'' is considered by some critics as the List of films considered the best, best film of all time, and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time. Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom. UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions. The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film ''Vertigo (film), Vertigo'' is considered by some critics as the List of films considered the best, best film of all time, and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time. Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the List of highest-grossing film series, highest-grossing film franchises (''Harry Potter (film series), Harry Potter'' and ''James Bond (film series), James Bond''). Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom. UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions. The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.
Cuisine
British cuisine developed from various influences reflective of its land, settlements, arrivals of new settlers and immigrants, trade and colonialism. Celtic fields, Celtic agriculture and animal breeding produced a wide variety of foodstuffs for indigenous Celts and Britons (historic), Britons. Anglo-Saxon England developed meat and savoury herb stewing techniques before the practice became common in Europe. The Norman conquest introduced exotic spices into England in the Middle Ages. TheBritish Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
facilitated a knowledge of Indian cuisine with its "strong, penetrating spices and herbs". British cuisine has absorbed the cultural influence of those who have Immigration to the United Kingdom since 1922, settled in Britain, producing hybrid dishes, such as chicken tikka masala. Veganism, Vegan and Vegetarianism, vegetarian diets have increased in Britain in recent years. In 2021, a survey found that 8% of British respondents eat a plant-based diet and 36% of respondents have a favourable view of plant-based diets.
Media
 The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the Television licensing in the United Kingdom, television licence. The BBC World Service is an International broadcasting, international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV (TV network), ITV Network, and Sky UK, Sky. Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include ''The Times'', ''The Guardian'', ''The Observer,'' ''The Economist'', and the ''Financial Times''. Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include ''
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the Television licensing in the United Kingdom, television licence. The BBC World Service is an International broadcasting, international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV (TV network), ITV Network, and Sky UK, Sky. Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include ''The Times'', ''The Guardian'', ''The Observer,'' ''The Economist'', and the ''Financial Times''. Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
'', ''New Scientist'', ''The Spectator'', ''Prospect (magazine), Prospect'', ''NME'', ''Radio Times'', and ''The Economist''.
London dominates the media sector in the UK: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. Edinburgh and Glasgow, and Cardiff, are important centres of newspaper and broadcasting production in Scotland and Wales, respectively. The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around £20 billion and employs around 167,000 people. In 2015, the UK published 2,710 book titles per million inhabitants, more than any other country, much of this being exported to other Anglophone countries.
In 2009, it was estimated that individuals viewed a mean of 3.75 hours of television per day and 2.81 hours of radio. In that year the main BBC Public service broadcasting in the United Kingdom, public service broadcasting channels accounted for an estimated 28.4 per cent of all television viewing; the three main independent channels accounted for 29.5 per cent and the increasingly important other satellite and digital channels for the remaining 42.1 per cent. Sales of newspapers have fallen since the 1970s and in 2010 41 per cent of people reported reading a daily national newspaper. In 2010, 82.5 per cent of the UK population were Internet users, the highest proportion amongst the 20 countries with the largest total number of users in that year.
Symbols
 The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack). It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick's Flag. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out. The national anthem of the United Kingdom is "God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside The Lion and the Unicorn, the lion and the unicorn and the Welsh Dragon, dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack). It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick's Flag. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out. The national anthem of the United Kingdom is "God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside The Lion and the Unicorn, the lion and the unicorn and the Welsh Dragon, dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill's defiance of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. A now rare personification is a character originating in the 18th century, John Bull, a portly country gentleman dressed in a top hat and tailcoat with a Union Jack waistcoat, often accompanied by a bulldog.
The floral emblems of the three kingdoms are the Tudor rose for England, the thistle for Scotland and the shamrock for Northern Ireland; they are sometimes shown intertwined to represent unity. The daffodil and the leek are the symbols of Wales. Alternatives include the Royal Oak for England and the flax flower for Northern Ireland.
Sport
 Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, English billiards, billiards, darts, Rowing (sport), rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in the late 19th century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, "This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum".
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the United Kingdom. England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and The Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. Each of the Home Nations has its own football association, national team and league system and individually are the governing members of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world. The first international football match was contested by England national football team, England and Scotland national football team, Scotland on 30 November 1872. England, Scotland, Wales national football team, Wales and Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, English billiards, billiards, darts, Rowing (sport), rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in the late 19th century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, "This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum".
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the United Kingdom. England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and The Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. Each of the Home Nations has its own football association, national team and league system and individually are the governing members of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world. The first international football match was contested by England national football team, England and Scotland national football team, Scotland on 30 November 1872. England, Scotland, Wales national football team, Wales and Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.
 In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK. The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship; the premier international tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sport governing body, Sport governing bodies in Rugby union in England, England, Rugby union in Scotland, Scotland, Rugby union in Wales, Wales and Rugby union in Ireland, Ireland organise and regulate the game separately. Every four years, England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions. The team tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its Laws of cricket, laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788. The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board, and the Irish cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test cricket, Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales had fielded its own team in the past. Cricket in Scotland, Scottish players have played for England because Scotland national cricket team, Scotland does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals. Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, with England winning the tournament in 2019. There is a professional County Championship, league championship in which clubs representing 17 English counties and 1 Welsh county compete.
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK. The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship; the premier international tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sport governing body, Sport governing bodies in Rugby union in England, England, Rugby union in Scotland, Scotland, Rugby union in Wales, Wales and Rugby union in Ireland, Ireland organise and regulate the game separately. Every four years, England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions. The team tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its Laws of cricket, laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788. The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board, and the Irish cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test cricket, Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales had fielded its own team in the past. Cricket in Scotland, Scottish players have played for England because Scotland national cricket team, Scotland does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals. Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, with England winning the tournament in 2019. There is a professional County Championship, league championship in which clubs representing 17 English counties and 1 Welsh county compete.
 The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s, before spreading around the world. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, drivers' and List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, constructors' Formula One World Championship, titles than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone, the location of the British Grand Prix held each year in July.
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s, before spreading around the world. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, drivers' and List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, constructors' Formula One World Championship, titles than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone, the location of the British Grand Prix held each year in July.
 Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport's home course, the world's oldest golf course is actually Musselburgh Links' Old Golf Course. In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes. The oldest golf tournament in the world, and the first major championship in golf, The Open Championship, is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England. A single 'Great Britain Lions' team had competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games, but this changed in 2008 when England national rugby league team, England, Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland and Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland competed as separate nations. Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.
The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing. Snooker is another of the UK's popular sporting exports, with the world championships held annually in Sheffield. In Northern Ireland, Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports, both in terms of participation and spectating. Irish expatriates in the UK and the US also play them. Shinty (or ''camanachd'') is popular in the Scottish Highlands. Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport's home course, the world's oldest golf course is actually Musselburgh Links' Old Golf Course. In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes. The oldest golf tournament in the world, and the first major championship in golf, The Open Championship, is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England. A single 'Great Britain Lions' team had competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games, but this changed in 2008 when England national rugby league team, England, Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland and Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland competed as separate nations. Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.
The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing. Snooker is another of the UK's popular sporting exports, with the world championships held annually in Sheffield. In Northern Ireland, Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports, both in terms of participation and spectating. Irish expatriates in the UK and the US also play them. Shinty (or ''camanachd'') is popular in the Scottish Highlands. Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
See also
* Outline of the United Kingdom ** Outline of England ** Outline of Northern Ireland ** Outline of Scotland ** Outline of Wales * Index of United Kingdom-related articles * International rankings of the United Kingdom * Historiography of the United Kingdom * Historiography of the British Empire * United Kingdom–Crown Dependencies Customs UnionNotes
References
External links
Government
Official website of HM Government
Official website of the British Monarchy
The official site of the British Prime Minister's Office
General information
United Kingdom
from the BBC News
United Kingdom
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
United Kingdom
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
United Kingdom
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' entry * *
Key Development Forecasts for the United Kingdom
from International Futures
Travel
Official tourist guide to Britain
{{Coord, 55, N, 3, W, display=title, scale:10000000 United Kingdom, British Islands Countries in Europe English-speaking countries and territories G7 nations G20 nations Island countries Northwestern European countries Member states of NATO Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the United Nations OECD members