Trianon Peace Treaty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the
''Defeat and Disarmament, Allied Diplomacy and Politics of Military Affairs in Austria, 1918–1922''
Associated University Presses 1986. p. 34.Sharp A
''The Versailles Settlement: Peacemaking after the First World War, 1919–1923''
Palgrave Macmillan 2008. p. 156. . When
''Dreamland: Europeans and Jews in the Aftermath of the Great War.''
''World War I: the Definitive Encyclopedia and Document Collection''
ABC-CLIO 2014. p. 867. . Kun formed a
''A Shattered Peace: Versailles 1919 and the Price We Pay Today.''
John Wiley and Sons. p. 193 . The Hungarian Soviet Republic was a small communist
 The Hungarian "Conditions of Peace" were dated 15 January 1920, and their "Observations" handed in on 20 February. French diplomats played the major role in the drafting, and Hungarians were kept in the dark. Their long-term goal was to build a coalition of small new nations led by France and capable of standing up to Russia or Germany. This led to the "
The Hungarian "Conditions of Peace" were dated 15 January 1920, and their "Observations" handed in on 20 February. French diplomats played the major role in the drafting, and Hungarians were kept in the dark. Their long-term goal was to build a coalition of small new nations led by France and capable of standing up to Russia or Germany. This led to the "
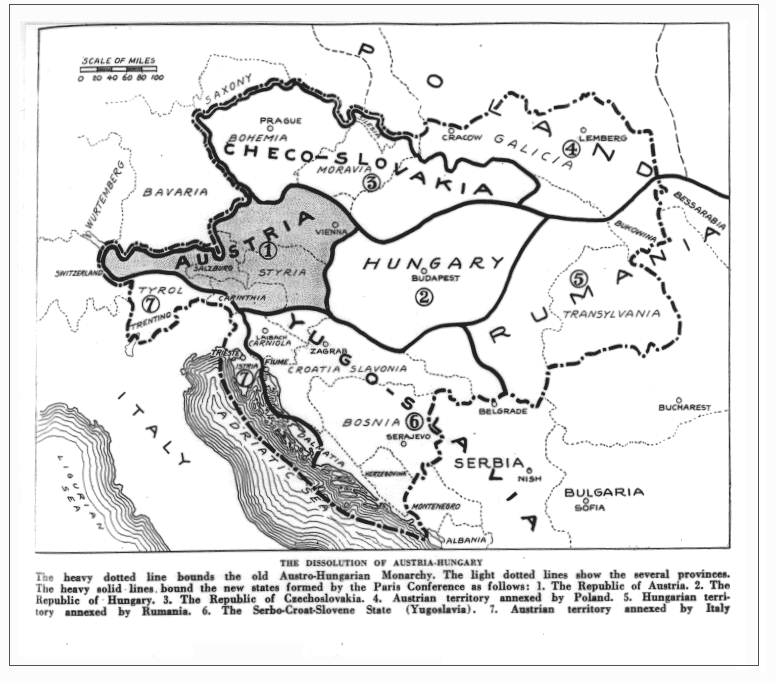 The Hungarian government terminated its union with Austria on 31 October 1918, officially dissolving the Austro-Hungarian state. The ''de facto'' temporary borders of independent Hungary were defined by the ceasefire lines in November–December 1918. Compared with the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, these temporary borders did not include:
* Part of
The Hungarian government terminated its union with Austria on 31 October 1918, officially dissolving the Austro-Hungarian state. The ''de facto'' temporary borders of independent Hungary were defined by the ceasefire lines in November–December 1918. Compared with the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, these temporary borders did not include:
* Part of  Representatives of small nations living in the former Austria-Hungary and active in the Congress of Oppressed Nations regarded the treaty of Trianon for being an act of historical righteousness because a better future for their nations was "to be founded and durably assured on the firm basis of world democracy, real and sovereign government by the people, and a universal alliance of the nations vested with the authority of arbitration" while at the same time making a call for putting an end to "the existing unbearable domination of one nation over the other" and making it possible "for nations to organize their relations to each other on the basis of equal rights and free conventions". Furthermore, they believed the treaty would help toward a new era of dependence on international law, the fraternity of nations, equal rights, and human liberty as well as aid civilisation in the effort to free humanity from international violence.
Representatives of small nations living in the former Austria-Hungary and active in the Congress of Oppressed Nations regarded the treaty of Trianon for being an act of historical righteousness because a better future for their nations was "to be founded and durably assured on the firm basis of world democracy, real and sovereign government by the people, and a universal alliance of the nations vested with the authority of arbitration" while at the same time making a call for putting an end to "the existing unbearable domination of one nation over the other" and making it possible "for nations to organize their relations to each other on the basis of equal rights and free conventions". Furthermore, they believed the treaty would help toward a new era of dependence on international law, the fraternity of nations, equal rights, and human liberty as well as aid civilisation in the effort to free humanity from international violence.
 Irredentism—the demand for reunification of Hungarian peoples—became a central theme of Hungarian politics and diplomacy.
Irredentism—the demand for reunification of Hungarian peoples—became a central theme of Hungarian politics and diplomacy.
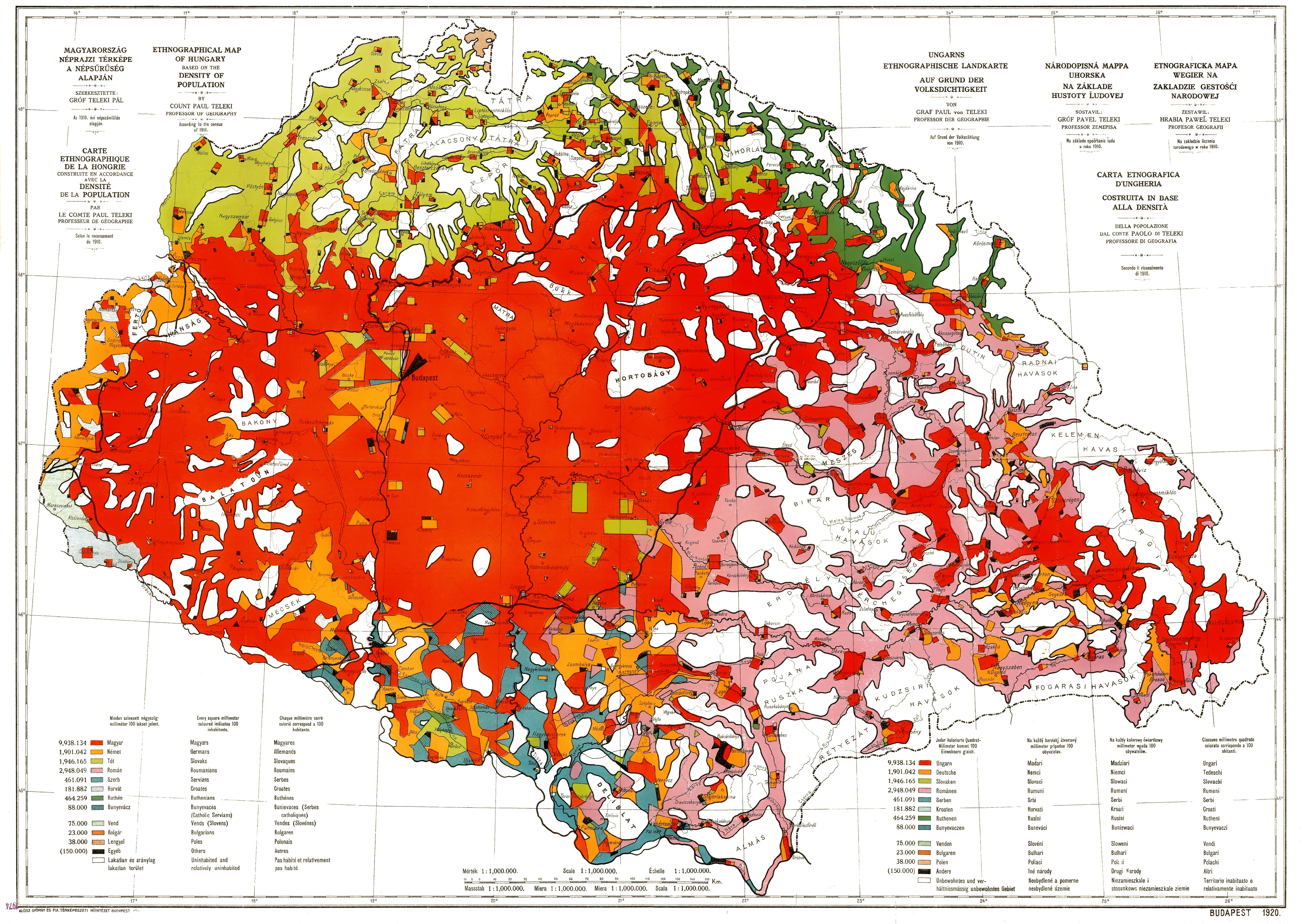
 The territories of the former Hungarian Kingdom that were ceded by the treaty to neighbouring countries in total (and each of them separately) had a majority of non-Hungarian nationals; however, the Hungarian ethnic area was much larger than the newly established territory of Hungary,Eberhardt, Piotr (2003
The territories of the former Hungarian Kingdom that were ceded by the treaty to neighbouring countries in total (and each of them separately) had a majority of non-Hungarian nationals; however, the Hungarian ethnic area was much larger than the newly established territory of Hungary,Eberhardt, Piotr (2003
''Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, and Analysis''
M.E. Sharpe. pp. 290–299. therefore 30% of the ethnic Hungarians were under foreign authority. After the treaty, the percentage and the absolute number of all Hungarian populations outside of Hungary decreased in the next decades (although, some of these populations also recorded temporary increase of the absolute population number). There are several reasons for this population decrease, some of which were spontaneous assimilation and certain state policies, like Slovakization, Romanianization, Serbianisation. Other important factors were the Hungarian migration from the neighbouring states to Hungary or to some western countries as well as decreased birth rate of Hungarian populations. According to the National Office for Refugees, the number of Hungarians who immigrated to Hungary from neighbouring countries was about 350,000 between 1918 and 1924.

 Officially the treaty was intended to be a confirmation of the right of self-determination for nations and of the concept of nation-states replacing the old multinational Austro-Hungarian empire. Although the treaty addressed some nationality issues, it also sparked some new ones.
The minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom were the major beneficiaries. The Allies had explicitly committed themselves to the causes of the minority peoples of Austria-Hungary late in World War I. For all intents and purposes, the death knell of the Austro-Hungarian empire sounded on 14 October 1918, when United States Secretary of State Robert Lansing informed Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Stephan Burián von Rajecz, István Burián that autonomy for the nationalities was no longer enough. Accordingly, the Allies assumed without question that the minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom wanted to leave Hungary. The Romanians joined their ethnic brethren in Romania, while the Slovaks, Serbs and Croats helped establish states of their own (Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia). However, these new or enlarged countries also absorbed large slices of territory with a majority of ethnic Hungarians or Hungarian speaking population. As a result, as many as a third of Hungarian language-speakers found themselves outside the borders of the post-Trianon Hungary.
While the territories that were now outside Hungary's borders had non-Hungarian majorities overall, there also existed some sizeable areas with a majority of Hungarians, largely near the newly defined borders. Over the last century, concerns have occasionally been raised about the treatment of these ethnic Hungarian communities in the neighbouring states. Areas with significant Hungarian populations included the
Officially the treaty was intended to be a confirmation of the right of self-determination for nations and of the concept of nation-states replacing the old multinational Austro-Hungarian empire. Although the treaty addressed some nationality issues, it also sparked some new ones.
The minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom were the major beneficiaries. The Allies had explicitly committed themselves to the causes of the minority peoples of Austria-Hungary late in World War I. For all intents and purposes, the death knell of the Austro-Hungarian empire sounded on 14 October 1918, when United States Secretary of State Robert Lansing informed Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Stephan Burián von Rajecz, István Burián that autonomy for the nationalities was no longer enough. Accordingly, the Allies assumed without question that the minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom wanted to leave Hungary. The Romanians joined their ethnic brethren in Romania, while the Slovaks, Serbs and Croats helped establish states of their own (Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia). However, these new or enlarged countries also absorbed large slices of territory with a majority of ethnic Hungarians or Hungarian speaking population. As a result, as many as a third of Hungarian language-speakers found themselves outside the borders of the post-Trianon Hungary.
While the territories that were now outside Hungary's borders had non-Hungarian majorities overall, there also existed some sizeable areas with a majority of Hungarians, largely near the newly defined borders. Over the last century, concerns have occasionally been raised about the treatment of these ethnic Hungarian communities in the neighbouring states. Areas with significant Hungarian populations included the
– population of Transylvania or France so it was considered that the Western powers had a moral debt to repay. In ''absolute'' terms, Romanian troops had considerably fewer casualties than either Britain or France, however. The underlying reason for the decision was a Secret treaty, secret pact between The Entente and Romania. In the Treaty of Bucharest (1916) Romania was promised Transylvania and some other territories to the east of river Tisza, provided that she attacked Austria-Hungary from the south-east, where defences were weak. However, after the Central Powers had noticed the military manoeuvre, the attempt was quickly choked off and Bucharest fell in the same year. By the time the victorious Allies arrived in France, the treaty was already settled, which made the outcome inevitable. At the heart of the dispute lay fundamentally different views on the nature of the Hungarian presence in the disputed territories. For Hungarians, the outer territories were not seen as colonial territories but rather part of the core national territory. The non-Hungarians that lived in the Pannonian Basin saw the Hungarians as colonial-style rulers who had oppressed the Slavs and Romanians since 1848, when they introduced laws that the language used in education and in local offices was to be Hungarian. For non-Hungarians from the Pannonian Basin it was a process of decolonisation instead of a punitive dismemberment (as was seen by the Hungarians). The Hungarians did not see it this way because the newly defined borders did not fully respect territorial distribution of ethnic groups,:File:Redmap.jpg, Ethnic map of Kingdom of Hungary without Croatia-Slavonia with areas where there were Hungarian majorities outside the new borders. The French sided with their allies the Romanians who had a long policy of cultural ties to France since the country broke from the
By the time the victorious Allies arrived in France, the treaty was already settled, which made the outcome inevitable. At the heart of the dispute lay fundamentally different views on the nature of the Hungarian presence in the disputed territories. For Hungarians, the outer territories were not seen as colonial territories but rather part of the core national territory. The non-Hungarians that lived in the Pannonian Basin saw the Hungarians as colonial-style rulers who had oppressed the Slavs and Romanians since 1848, when they introduced laws that the language used in education and in local offices was to be Hungarian. For non-Hungarians from the Pannonian Basin it was a process of decolonisation instead of a punitive dismemberment (as was seen by the Hungarians). The Hungarians did not see it this way because the newly defined borders did not fully respect territorial distribution of ethnic groups,:File:Redmap.jpg, Ethnic map of Kingdom of Hungary without Croatia-Slavonia with areas where there were Hungarian majorities outside the new borders. The French sided with their allies the Romanians who had a long policy of cultural ties to France since the country broke from the
 The Austro-Hungarian Empire was economic and monetary union, one economic unit with autarky, autarkic characteristics during its golden age and therefore achieved rapid growth, especially in the early 20th century when Gross national income, GNP grew by 1.46%. This level of growth compared very favourably to that of other European states such as Britain (1.00%), France (1.06%), and Germany (1.51%). There was also a division of labour present throughout the empire: that is, in the Austrian part of the monarchy manufacturing industries were highly advanced, while in the Kingdom of Hungary an agro-industrial economy had emerged. By the late 19th century, economic growth of the eastern regions consistently surpassed that of western, thus discrepancies eventually began to diminish. The key success of fast development was specialisation of each region in fields that they were best.
The Kingdom of Hungary was the main supplier of wheat, rye, barley and other various goods in the empire, and these comprised a large portion of the empire's exports. Meanwhile, the territory of present-day Czech Republic (Kingdom of Bohemia) owned 75% of the whole industrial capacity of former Austria-Hungary. This shows that the various parts of the former monarchy were economically interdependent. As a further illustration of this issue, post-Trianon Hungary produced 5 times more agricultural goods than it needed for itself, and mills around Budapest (some of the largest ones in Europe at the time) operated at 20% capacity. As a consequence of the treaty, all the Competition (economics), competitive industries of the former empire were compelled to close doors, as great capacity was met by negligible demand owing to economic barriers presented in the form of the newly defined borders.
The Austro-Hungarian Empire was economic and monetary union, one economic unit with autarky, autarkic characteristics during its golden age and therefore achieved rapid growth, especially in the early 20th century when Gross national income, GNP grew by 1.46%. This level of growth compared very favourably to that of other European states such as Britain (1.00%), France (1.06%), and Germany (1.51%). There was also a division of labour present throughout the empire: that is, in the Austrian part of the monarchy manufacturing industries were highly advanced, while in the Kingdom of Hungary an agro-industrial economy had emerged. By the late 19th century, economic growth of the eastern regions consistently surpassed that of western, thus discrepancies eventually began to diminish. The key success of fast development was specialisation of each region in fields that they were best.
The Kingdom of Hungary was the main supplier of wheat, rye, barley and other various goods in the empire, and these comprised a large portion of the empire's exports. Meanwhile, the territory of present-day Czech Republic (Kingdom of Bohemia) owned 75% of the whole industrial capacity of former Austria-Hungary. This shows that the various parts of the former monarchy were economically interdependent. As a further illustration of this issue, post-Trianon Hungary produced 5 times more agricultural goods than it needed for itself, and mills around Budapest (some of the largest ones in Europe at the time) operated at 20% capacity. As a consequence of the treaty, all the Competition (economics), competitive industries of the former empire were compelled to close doors, as great capacity was met by negligible demand owing to economic barriers presented in the form of the newly defined borders.
 Post-Trianon Hungary possessed 90% of the engineering and printing industry of the pre-war kingdom, while only 11% of timber and 16% of iron was retained. In addition, 61% of arable land, 74% of public roads, 65% of canals, 62% of railroads, 64% of hard surface roads, 83% of pig iron output, 55% of industrial plants, and 67% of credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary lay within the territory of Hungary's neighbours. These statistics correspond to post-Trianon Hungary retaining only around a third of the kingdom's territory before the war and around 60% of its population. The new borders also bisected transport links – in the Kingdom of Hungary the road and railway network had a radial structure, with Budapest in the centre. Many roads and railways, running along the newly defined borders and interlinking radial transport lines, ended up in different, highly introvert countries. Hence, much of the rail cargo traffic of the emergent states was virtually paralysed. These factors all combined created some imbalances in the now separated economic regions of the former monarchy.
Post-Trianon Hungary possessed 90% of the engineering and printing industry of the pre-war kingdom, while only 11% of timber and 16% of iron was retained. In addition, 61% of arable land, 74% of public roads, 65% of canals, 62% of railroads, 64% of hard surface roads, 83% of pig iron output, 55% of industrial plants, and 67% of credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary lay within the territory of Hungary's neighbours. These statistics correspond to post-Trianon Hungary retaining only around a third of the kingdom's territory before the war and around 60% of its population. The new borders also bisected transport links – in the Kingdom of Hungary the road and railway network had a radial structure, with Budapest in the centre. Many roads and railways, running along the newly defined borders and interlinking radial transport lines, ended up in different, highly introvert countries. Hence, much of the rail cargo traffic of the emergent states was virtually paralysed. These factors all combined created some imbalances in the now separated economic regions of the former monarchy.
 The disseminating economic problems had been also noted in the ''Coolidge Report'' as a serious potential aftermath of the treaty. This opinion was not taken into account during the negotiations. Thus, the resulting uneasiness and despondency of one part of the concerned population was later one of the main antecedents of World War II. Unemployment levels in Austria, as well as in Hungary, were dangerously high, and industrial output dropped by 65%. What happened to Austria in industry happened to Hungary in agriculture where production of grain declined by more than 70%. Austria, especially the imperial capital Vienna, was a leading investor of development projects throughout the empire with more than 2.2 billion crown capital. This sum sunk to a mere 8.6 million crowns after the treaty took effect and resulted in a starving of capital in other regions of the former empire.
The disintegration of the multinational state conversely impacted neighbouring countries, too: In Poland, Romania, Yugoslavia, and Bulgaria a fifth to a third of the rural population could find no work, and industry was in no position to absorb them. In comparison, by 1921 the new Czechoslovak state reached 75% of its pre-war production owing to their favourable position among the victors and greater associated access to international rehabilitation resources.
With the creation of customs barriers and Protectionism, fragmented protective economies, the economic growth and outlook in the region sharply declined, ultimately culminating in a deep recession. It proved to be immensely challenging for the successor states to successfully transform their economies to adapt to the new circumstances. All the formal districts of Austria-Hungary used to rely on each other's exports for growth and welfare; by contrast, 5 years after the treaty, traffic of goods between the countries dropped to less than 5% of its former value. This could be attributed to the introduction of aggressive nationalistic policies by local political leaders.
The drastic shift in economic climate forced the countries to re-evaluate their situation and to promote industries where they had fallen short. Austria and Czechoslovakia subsidised the mill, sugar and brewing industries, while Hungary attempted to increase the efficiency of iron, steel, glass and chemical industries. The stated objective was that all countries should become self-sufficient. This tendency, however, led to uniform economies and competitive economic advantage of long well-established industries and research fields evaporated. The lack of specialisation adversely affected the whole Danube-Carpathian region and caused a distinct setback of growth and development compared to western and northern European regions as well as high financial vulnerability and instability.
The disseminating economic problems had been also noted in the ''Coolidge Report'' as a serious potential aftermath of the treaty. This opinion was not taken into account during the negotiations. Thus, the resulting uneasiness and despondency of one part of the concerned population was later one of the main antecedents of World War II. Unemployment levels in Austria, as well as in Hungary, were dangerously high, and industrial output dropped by 65%. What happened to Austria in industry happened to Hungary in agriculture where production of grain declined by more than 70%. Austria, especially the imperial capital Vienna, was a leading investor of development projects throughout the empire with more than 2.2 billion crown capital. This sum sunk to a mere 8.6 million crowns after the treaty took effect and resulted in a starving of capital in other regions of the former empire.
The disintegration of the multinational state conversely impacted neighbouring countries, too: In Poland, Romania, Yugoslavia, and Bulgaria a fifth to a third of the rural population could find no work, and industry was in no position to absorb them. In comparison, by 1921 the new Czechoslovak state reached 75% of its pre-war production owing to their favourable position among the victors and greater associated access to international rehabilitation resources.
With the creation of customs barriers and Protectionism, fragmented protective economies, the economic growth and outlook in the region sharply declined, ultimately culminating in a deep recession. It proved to be immensely challenging for the successor states to successfully transform their economies to adapt to the new circumstances. All the formal districts of Austria-Hungary used to rely on each other's exports for growth and welfare; by contrast, 5 years after the treaty, traffic of goods between the countries dropped to less than 5% of its former value. This could be attributed to the introduction of aggressive nationalistic policies by local political leaders.
The drastic shift in economic climate forced the countries to re-evaluate their situation and to promote industries where they had fallen short. Austria and Czechoslovakia subsidised the mill, sugar and brewing industries, while Hungary attempted to increase the efficiency of iron, steel, glass and chemical industries. The stated objective was that all countries should become self-sufficient. This tendency, however, led to uniform economies and competitive economic advantage of long well-established industries and research fields evaporated. The lack of specialisation adversely affected the whole Danube-Carpathian region and caused a distinct setback of growth and development compared to western and northern European regions as well as high financial vulnerability and instability.
 Romania, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia had to assume part of the financial obligations of the former Kingdom of Hungary on account of the parts of its former territory that were assigned under their sovereignty. Some conditions of the treaty were similar to those imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles. After the war, the Austro-Hungarian navy, Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops, air force and army were disbanded. The army of post-Trianon Hungary was to be restricted to 35,000 men, and there was to be no conscription. Heavy artillery, tanks and air force were prohibited. No railway was to be built with more than one track, because at that time railways held substantial strategic importance economically and militarily.
Articles 54–60 of the treaty required Hungary to recognise various rights of national minorities within its borders. Articles 61–66 state that all former citizens of the Kingdom of Hungary living outside the newly defined frontiers of Hungary were to ''ipso facto'' lose their Hungarian citizenship in one year. Under articles 79 to 101 Hungary renounced all privileges of the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy in territories outside Europe, including Morocco, Egypt, Siam and China.s:Treaty of Trianon/Part IV, Wikisource: Hungarian Interests outside Europe
Romania, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia had to assume part of the financial obligations of the former Kingdom of Hungary on account of the parts of its former territory that were assigned under their sovereignty. Some conditions of the treaty were similar to those imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles. After the war, the Austro-Hungarian navy, Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops, air force and army were disbanded. The army of post-Trianon Hungary was to be restricted to 35,000 men, and there was to be no conscription. Heavy artillery, tanks and air force were prohibited. No railway was to be built with more than one track, because at that time railways held substantial strategic importance economically and militarily.
Articles 54–60 of the treaty required Hungary to recognise various rights of national minorities within its borders. Articles 61–66 state that all former citizens of the Kingdom of Hungary living outside the newly defined frontiers of Hungary were to ''ipso facto'' lose their Hungarian citizenship in one year. Under articles 79 to 101 Hungary renounced all privileges of the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy in territories outside Europe, including Morocco, Egypt, Siam and China.s:Treaty of Trianon/Part IV, Wikisource: Hungarian Interests outside Europe
online
* Balogh, Eva S. "Peaceful Revision: The Diplomatic Road to War." ''Hungarian Studies Review'' 10.1 (1983): 43- 51
online
* Bandholtz, H.H. ''An Undiplomatic Diary by the American Member of the Inter-Allied Military Mission to Hungary: 1919–1920.'' (1933
* Bartha, Dezso. "Trianon and the Predestination of Hungarian Politics: A Historiography of Hungarian Revisionism, 1918–1944." (Thesis, University of Central Florida, 2006
online
* Bihari, Peter. "Images of defeat: Hungary after the lost war, the revolutions and the Peace Treaty of Trianon." ''Crossroads of European histories: multiple outlooks on five key moments in the history of Europe'' (2006) pp: 165–171. * Hanák, Peter. "Hungary on a fixed course: An outline of Hungarian history, 1918–1945." in Joseph Held, ed., ''Columbia history of Eastern Europe in the Twentieth Century'' (1992) pp: 164–204. * Jeszenszky, Géza. "The Afterlife of the Treaty of Trianon." ''The Hungarian Quarterly'' 184 (2006): 101–111. * Király, Béla K. and László Veszprémy, eds. ''Trianon and East Central Europe: Antecedents and Repercussions'' (Columbia University Press, 1995). * Macartney, Carlile Aylmer ''Hungary and Her Successors: The Treaty of Trianon and Its Consequences 1919–1937'' (1937) * Macartney, Carlile Aylmer'' October Fifteenth – A History of Modern Hungary 1929–1945''. Edinburgh University Press (1956) * Aliaksandr Piahanau, ''Hungary's Policy Towards Czechoslovakia, 1918–36''. PhD dissertation. Toulouse University, 201
Hungary's Policy Towards Czechoslovakia in 1918 - 36
* Romsics, Ignác. ''The Dismantling of Historic Hungary: The Peace Treaty of Trianon, 1920'' (Boulder, CO: Social Science Monographs, 2002). * Romsics, Ignác. "The Trianon Peace Treaty in Hungarian Historiography and Political Thinking." ''East European Monographs'' (2000): 89–105. * Romsics, Ignác. "Hungarian Revisionism in Thought and Action, 1920–1941: Plans, Expectations, Reality" in Marina Cattaruzza ed., ''Territorial Revisionism and the Allies of Germany in the Second World War: Goals, Expectations, Practices'' (2013) pp. 92–10
online
* Steiner, Zara S. ''The lights that failed: European international history, 1919–1933'' (2007) Trianon in relation to powers and nearby countries. ** Steiner, Zara. ''The triumph of the dark: European international history 1933–1939'' (2011), continued, * Várdy, Steven Béla. "The Impact of Trianon upon Hungary and the Hungarian Mind: The Nature of Interwar Hungarian Irredentism." ''Hungarian Studies Review'' 10.1 (1983): 21+
online
* Wojatsek, Charles. ''From Trianon to the First Vienna Arbitral Award: The Hungarian Minority in the First Czechoslovak Republic, 1918–1938'' (Montreal: Institute of Comparative Civilizations, 1980).
Treaty of Trianon
in
* Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
* [https://wwi.lib.byu.edu/index.php/Treaty_of_Trianon Trianon Treaty text (in English)]
Map of Hungarian borders in November–December 1918
Map of Europe and Treaty of Trianon
at omniatlas.com {{Authority control Borders of Hungary Boundary treaties, Trianon History of Austria-Hungary 1920 in Austria 1920 in Czechoslovakia 1920 in Hungary 1920 in Romania 1920 in Slovakia 1920 in Ukraine 20th century in Transylvania 20th century in Vojvodina Interwar-period treaties Military history of Austria-Hungary Modern history of Slovenia Peace treaties of France Peace treaties of Hungary, Trianon Peace treaties of Italy Peace treaties of Japan Peace treaties of the United Kingdom, Trianon Peace treaties of the United States, Trianon Treaties concluded in 1920 Treaties entered into force in 1921 Treaties of Belgium Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of Nicaragua Treaties of Panama Treaties of Thailand Treaties of the Empire of Japan Treaties of the French Third Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece Treaties of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946) Treaties of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946) Treaties of the Kingdom of Romania Great Union (Romania) Treaties of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia Treaties of the Portuguese First Republic Treaties of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Treaties of the Second Polish Republic Treaties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922) World War I treaties, Trianon Yugoslav Croatia Yugoslav Serbia Greater Romania Territorial evolution of Hungary Territorial evolution of Romania Dissolution of Austria-Hungary Hungary–Romania relations Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920) Partition (politics)
Grand Trianon
The Grand Trianon () is a French Baroque style château situated in the northwestern part of the Domain of Versailles in Versailles, France. It was built at the request of King Louis XIV of France as a retreat for himself and his '' maîtresse- ...
château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally ended World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
between most of the Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Em ...
and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. French diplomats played the major role in designing the treaty, with a view to establishing a French-led coalition of the newly formed states. It regulated the status of the Kingdom of Hungary and defined its borders generally within the ceasefire lines established in November–December 1918 and left Hungary as a landlocked state that included , 28% of the that had constituted the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(the Hungarian half of the Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
monarchy). The truncated kingdom had a population of 7.6 million, 36% compared to the pre-war kingdom's population of 20.9 million. Though the areas that were allocated to neighbouring countries had a majority of non-Hungarians, in them lived 3.3 million Hungarians – 31% of the Hungarians – who then became minorities. The treaty limited Hungary's army to 35,000 officers and men, and the Austro-Hungarian Navy
The Austro-Hungarian Navy or Imperial and Royal War Navy (german: kaiserliche und königliche Kriegsmarine, in short ''k.u.k. Kriegsmarine'', hu, Császári és Királyi Haditengerészet) was the naval force of Austria-Hungary. Ships of the A ...
ceased to exist. These decisions and their consequences have been the cause of deep resentment in Hungary ever since.
The principal beneficiaries were the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
, the Czechoslovak Republic
Czechoslovak Republic (Czech and Slovak: ''Československá republika, ČSR''), was the official name of Czechoslovakia between 1918 and 1939 and between 1945 and 1960. See:
*First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–1938)
*Second Czechoslovak Republic ...
, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(later Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
), and the First Austrian Republic
The First Austrian Republic (german: Erste Österreichische Republik), officially the Republic of Austria, was created after the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye on 10 September 1919—the settlement after the end of World War I w ...
. One of the main elements of the treaty was the doctrine of "self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
of peoples", and it was an attempt to give the non-Hungarians their own national states. In addition, Hungary had to pay war reparations
War reparations are compensation payments made after a war by one side to the other. They are intended to cover damage or injury inflicted during a war.
History
Making one party pay a war indemnity is a common practice with a long history.
R ...
to its neighbours. The treaty was dictated by the Allies rather than negotiated, and the Hungarians had no option but to accept its terms. The Hungarian delegation signed the treaty under protest, and agitation for its revision began immediately.
The current boundaries of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
are for the most part the same as those defined by the Treaty of Trianon, with minor modifications until 1924 regarding the Hungarian-Austrian border and the transfer of three villages to Czechoslovakia in 1947.
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, despite of the "self-determination of peoples" idea of the Allied Powers, only one plebiscite was permitted (later known as the Sopron plebiscite) to settle disputed borders on the former territory of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, settling a smaller territorial dispute between the First Austrian Republic
The First Austrian Republic (german: Erste Österreichische Republik), officially the Republic of Austria, was created after the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye on 10 September 1919—the settlement after the end of World War I w ...
and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, because some months earlier, the Rongyos Gárda launched a series of attacks to oust the Austrian forces that entered the area. During the plebiscite in late 1921, the polling stations were supervised by British, French, and Italian army officers of the Allied Powers.
Background
First World War and Austro-Hungarian Armistice
On 28 June 1914, the heir to the throne ofAustria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, the Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
, was assassinated by a Serbian nationalist
Serbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, und ...
. This caused a rapidly escalating July Crisis
The July Crisis was a series of interrelated diplomatic and military escalations among the major powers of Europe in the summer of 1914, Causes of World War I, which led to the outbreak of World War I (1914–1918). The crisis began on 28 June 1 ...
resulting in Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia, followed quickly by the entry of most European powers into the First World War. Two alliances faced off, the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
(led by Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
) and the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
(led by Britain, France and Russia). In 1918 Germany tried to overwhelm the Allies on the Western Front but failed. Instead the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
began a successful counteroffensive and forced the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
that resembled a surrender by the Central Powers.
On 6 April 1917, the United States entered the war against Germany and in December 1917 against Austria-Hungary. The American war aim was to end aggressive militarism as shown by Berlin and Vienna. The United States never formally joined the Allies. President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
acted as an independent force, and his Fourteen Points
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms ...
was accepted by Germany as a basis for the armistice of November 1918. It outlined a policy of free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econo ...
, open agreements, and democracy. While the term was not used, self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
was assumed. It called for a negotiated end to the war, international disarmament, the withdrawal of the Central Powers from occupied territories, the creation of a Polish state
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, the redrawing of Europe's borders along ethnic lines, and the formation of a League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
to guarantee the political independence and territorial integrity of all states. It called for a just and democratic peace uncompromised by territorial annexation. Point ten announced Wilson's "wish" that the peoples of Austria-Hungary be given autonomy—a point that Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
rejected.
Germany, the major ally of Austria-Hungary in World War I, suffered numerous losses during the Hundred Days Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allies of World War I, Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (1918), Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Wester ...
between August and November 1918 and was in negotiation of armistice with Allied Powers from the beginning of October 1918. Between 15 and 29 September 1918, Franchet d'Espèrey, in command of a relative small army of Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
(9 divisions), French (6 divisions), Serb
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
s (6 divisions), British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
(4 divisions) and Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
(1 division), staged a successful Vardar offensive in Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia ( Macedonian and sr, Вардарска Македонија, ''Vardarska Makedonija'') was the name given to the territory of the Kingdom of Serbia (1912–1918) and Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–1941) roughly corresponding to t ...
that ended by taking Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
out of the war. That collapse of the Southern (Italian) Front was one of several developments that effectively triggered the November 1918 armistice. By the end of October 1918, the Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army (, literally "Ground Forces of the Austro-Hungarians"; , literally "Imperial and Royal Army") was the ground force of the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy from 1867 to 1918. It was composed of three parts: the joint arm ...
was so fatigued that its commanders were forced to seek a ceasefire
A ceasefire (also known as a truce or armistice), also spelled cease fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Ceasefires may be between state act ...
. Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( ...
were proclaimed, and troops started deserting, disobeying orders and retreating. Many Czechoslovak troops, in fact, started working for the Allied cause, and in September 1918, five Czechoslovak Regiments were formed in the Italian Army. The troops of Austria-Hungary started a chaotic withdrawal during the Battle of Vittorio Veneto
The Battle of Vittorio Veneto was fought from 24 October to 3 November 1918 (with an armistice taking effect 24 hours later) near Vittorio Veneto on the Italian Front during World War I. After having thoroughly defeated Austro-Hungarian troop ...
, and Austria-Hungary began to negotiate a truce on 28 October.
Aster Revolution and the First Hungarian Republic
During the war, CountMihály Károlyi
Count Mihály Ádám György Miklós Károlyi de Nagykároly ( hu, gróf nagykárolyi Károlyi Mihály Ádám György Miklós; archaically English: Michael Adam George Nicholas Károlyi, or in short simple form: Michael Károlyi; 4 March 1875 � ...
led a small but very active pacifist anti-war maverick faction in the Hungarian parliament. He even organized covert contacts with British and French diplomats in Switzerland. The Austro-Hungarian monarchy politically collapsed and disintegrated as a result of a defeat in the Italian front. On 31 October 1918, in the midst of armistice negotiations, the Aster Revolution
The Aster Revolution or Chrysanthemum Revolution ( hu, Őszirózsás forradalom) was a revolution in Hungary led by Count Mihály Károlyi in the aftermath of World War I which resulted in the foundation of the short-lived First Hungarian Peop ...
in Budapest brought liberal Hungarian aristocrat Count Mihály Károlyi
Count Mihály Ádám György Miklós Károlyi de Nagykároly ( hu, gróf nagykárolyi Károlyi Mihály Ádám György Miklós; archaically English: Michael Adam George Nicholas Károlyi, or in short simple form: Michael Károlyi; 4 March 1875 � ...
, a supporter of the Allies, to power. King Charles had no other option than the appointment of Károlyi as prime minister of Hungary. On 25 October 1918 Károlyi had formed the Hungarian National Council. The Hungarian Royal Honvéd army still had more than 1,400,000 soldiers when Károlyi was announced as prime minister. Károlyi yielded to President Wilson's demand for pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaign ...
by ordering the unilateral self-disarmament of the Hungarian army. This happened under the direction of Minister of War Béla Linder on 2 November 1918Dixon J. C''Defeat and Disarmament, Allied Diplomacy and Politics of Military Affairs in Austria, 1918–1922''
Associated University Presses 1986. p. 34.Sharp A
''The Versailles Settlement: Peacemaking after the First World War, 1919–1923''
Palgrave Macmillan 2008. p. 156. . When
Oszkár Jászi
Oszkár Jászi (born Oszkár Jakobuvits; 2 March 1875 – 13 February 1957), also known in English as Oscar Jászi, was a Hungarian social scientist, historian, and politician.
Early life
Oszkár Jászi was born in Nagykároly on March 2, 187 ...
became the new Minister for National Minorities of Hungary, he immediately offered democratic referendums about the disputed borders for minorities; however, the political leaders of those minorities refused the very idea of democratic referendums regarding disputed territories at the Paris peace conference. Disarmament of its army meant that Hungary was to remain without a national defence at a time of particular vulnerability. The unilateral self-disarmament made the occupation of Hungary directly possible for the relatively small armies of Romania, the Franco-Serbian army, and the armed forces of the newly established Czechoslovakia. After self-disarmament, Czech, Serbian, and Romanian political leaders chose to attack Hungary instead of holding democratic plebiscites concerning the disputed areas.
On the request of the Austro-Hungarian government, an armistice was granted to Austria-Hungary on 3 November 1918 by the Allies. Military and political events changed rapidly and drastically after the Hungarian unilateral disarmament:
* On 5 November 1918, the Serbian army, with the help of the French army, crossed the southern borders.
* On 8 November, the Czechoslovak army crossed the northern borders.
* On 10 November d'Espérey's army crossed the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
River and was poised to enter the Hungarian heartland.
* On 11 November Germany signed an armistice with Allies, under which they had to immediately withdraw all German troops in Romania and in the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
back to German territory and Allies to have access to these countries.
* On 13 November, the Romanian army crossed the eastern borders of the Kingdom of Hungary.
During the rule of Károlyi's pacifist cabinet, Hungary rapidly lost control over approximately 75% of its former pre-WWI territories () without a fight and was subject to foreign occupation. The Armistice of 3 November was completed as regards Hungary on 13 November, when Károlyi signed the Armistice of Belgrade with the Allied nations, in order that a Treaty of Peace might be concluded. It limited the size of the Hungarian army to six infantry and two cavalry divisions. Demarcation lines defining the territory to remain under Hungarian control were made. The lines would apply until definitive borders could be established. Under the terms of the armistice, Serbian and French troops advanced from the south, taking control of the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
and Croatia. Czechoslovakia took control of "Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary is the usual English translation of ''Felvidék'' (literally: "Upland"), the Hungarian term for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been ...
", consisting roughly of present day Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
and Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia ( rue, Карпатьска Русь, Karpat'ska Rus'; uk, Закарпаття, Zakarpattia; sk, Podkarpatská Rus; hu, Kárpátalja; ro, Transcarpatia; pl, Zakarpacie); cz, Podkarpatská Rus; german: Karpatenukrai ...
. Romanian forces were permitted to advance to the River Mureș (Maros). However, on 14 November, Serbia occupied Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
.Breit, J. (1929) "Hungarian Revolutionary Movements of 1918–19 and the History of the Red War" in ''Main Events of the Károlyi Era''. Budapest. pp. 115–116. General Franchet d'Espèrey followed up the victory by overrunning much of the Balkans, and by the war's end his troops had penetrated well into Hungary.
After King Charles's withdrawal from government on 16 November 1918, Károlyi proclaimed the First Hungarian Republic
The First Hungarian Republic ( hu, Első Magyar Köztársaság), until 21 March 1919 the Hungarian People's Republic (), was a short-lived unrecognized country, which quickly transformed into a small rump state due to the foreign and military p ...
, with himself as provisional president of the republic.
Fall of the liberal First Hungarian Republic and communist coup d'état
The Károlyi government failed to manage both domestic and military issues and lost popular support. On 20 March 1919,Béla Kun
Béla Kun (born Béla Kohn; 20 February 1886 – 29 August 1938) was a Hungarian communist revolutionary and politician who governed the Hungarian Soviet Republic in 1919. After attending Franz Joseph University at Kolozsvár (today Cluj-Napoc ...
, who had been imprisoned in the Markó Street prison, was released.Sachar, H. M. (2007''Dreamland: Europeans and Jews in the Aftermath of the Great War.''
Knopf Doubleday
Random House is an American book publisher and the largest general-interest paperback publisher in the world. The company has several independently managed subsidiaries around the world. It is part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by Germ ...
. p. 409. . On 21 March, he led a successful communist coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
; Károlyi was deposed and arrested.Tucker S''World War I: the Definitive Encyclopedia and Document Collection''
ABC-CLIO 2014. p. 867. . Kun formed a
social democratic
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote soci ...
, communist coalition government
A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election, an atypical outcome in ...
and proclaimed the Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Socialist Federative Republic of Councils in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Szocialista Szövetséges Tanácsköztársaság) (due to an early mistranslation, it became widely known as the Hungarian Soviet Republic in English-language sources ( ...
. Days later the communists purged the social democrats from the government.Andelman, D. A. (2009''A Shattered Peace: Versailles 1919 and the Price We Pay Today.''
John Wiley and Sons. p. 193 . The Hungarian Soviet Republic was a small communist
rump state
A rump state is the remnant of a once much larger state, left with a reduced territory in the wake of secession, annexation, occupation, decolonization, or a successful coup d'état or revolution on part of its former territory. In the last case, ...
. When the Republic of Councils in Hungary was established, it controlled only approximately 23% of Hungary's historic territory.
The communists remained bitterly unpopular in the Hungarian countryside, where the authority of that government was often nonexistent. Rather than divide the big estates among the peasants – which might have gained their support for the government, but would have created a class of small-holding farmers the communist government proclaimed the nationalization of the estates. But having no skilled people to manage the estates, the communists had no choice but to leave the existing estate managers in place. These, while formally accepting their new government bosses, in practice retained their loyalty to the deposed aristocratic owners. The peasants felt that the revolution had no real effect on their lives and thus had no reason to support it. The communist party and communist policies only had real popular support among the proletarian masses of large industrial centers—especially in Budapest—where the working class represented a high proportion of the inhabitants. The communist government followed the Soviet model: the party established its terror groups (like the infamous Lenin Boys) to "overcome the obstacles" in the Hungarian countryside. This was later known as the Red Terror in Hungary.
In late May, after the Entente military representative demanded more territorial concessions from Hungary, Kun attempted to "fulfill" his promise to adhere to Hungary's historical borders. The men of the Hungarian Red Army were recruited mainly from the volunteers of the Budapest proletariat. On 20 May 1919, a force under Colonel Aurél Stromfeld attacked and routed Czechoslovak troops from Miskolc
Miskolc ( , , ; Czech language, Czech and sk, Miškovec; german: Mischkolz; yi, script=Latn, Mishkoltz; ro, Mișcolț) is a city in northeastern Hungary, known for its heavy industry. With a population of 161,265 (1 Jan 2014) Miskolc is the ...
. The Romanian Army attacked the Hungarian flank with troops from the 16th Infantry Division and the Second Vânători Division, aiming to maintain contact with the Czechoslovak Army. Hungarian troops prevailed, and the Romanian Army retreated to its bridgehead at Tokaj
Tokaj () is a historical town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary, 54 kilometers from county capital Miskolc. It is the centre of the Tokaj-Hegyalja wine district where Tokaji wine is produced.
History
The wine-growing area w ...
. There, between 25–30 May, Romanian forces were required to defend their position against Hungarian attacks. On 3 June, Romania was forced into further retreat but extended its line of defence along the Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
River and reinforced its position with the 8th Division, which had been moving forward from Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter BergerT ...
since 22 May. Hungary then controlled the territory almost to its old borders; regained control of industrial areas around Miskolc, Salgótarján
Salgótarján (; sk, Šalgotarján) is city with county rights in Hungary, the capital of Nógrád county, north-eastern Hungary, making it the third smallest county capital based on population. The nearby Salgó castle is a well-known tourist ...
, Selmecbánya (Banská Štiavnica), Kassa (Košice).
In June, the Hungarian Red Army invaded the eastern part of the so-called Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary is the usual English translation of ''Felvidék'' (literally: "Upland"), the Hungarian term for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been ...
, now claimed by the newly forming Czechoslovak state. The Hungarian Red Army achieved some military success early on: under the leadership of Colonel Aurél Stromfeld, it ousted Czechoslovak troops from the north and planned to march against the Romanian Army in the east. Kun ordered the preparation of an offensive against Czechoslovakia, which would increase his domestic support by making good on his promise to restore Hungary's borders. The Hungarian Red Army recruited men between 19–25 years of age. Industrial workers from Budapest volunteered. Many former Austro-Hungarian officers re-enlisted for patriotic reasons. The Hungarian Red Army moved its 1st and 5th artillery divisions—40 battalions—to Upper Hungary.
Despite promises for the restoration of the former borders of Hungary, the communists declared the establishment of the Slovak Soviet Republic
The Slovak Soviet Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika rád, hu, Szlovák Tanácsköztársaság, uk, Словацька Радянська Республіка, literally: 'Slovak Republic of Councils') was a short-lived Communist state in sout ...
in Prešov (Eperjes) on 16 June 1919. After the proclamation of the Slovak Soviet Republic
The Slovak Soviet Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika rád, hu, Szlovák Tanácsköztársaság, uk, Словацька Радянська Республіка, literally: 'Slovak Republic of Councils') was a short-lived Communist state in sout ...
, the Hungarian nationalists and patriots soon realized that the new communist government had no intentions to recapture the lost territories, only to spread communist ideology and establish other communist states in Europe, thus sacrificing Hungarian national interests. The Hungarian patriots and professional military officers in the Red Army saw the establishment of the Slovak Soviet Republic as a betrayal, and their support for the government began to erode (the communists and their government supported the establishment of the Slovak Communist state, while the Hungarian patriots wanted to keep the reoccupied territories for Hungary). Despite a series of military victories against the Czechoslovak army, the Hungarian Red Army started to disintegrate due to tension between nationalists and communists during the establishment of the Slovak Soviet Republic. The concession eroded support of the communist government among professional military officers and nationalists in the Hungarian Red Army; even the chief of the general staff The Chief of the General Staff (CGS) is a post in many armed forces (militaries), the head of the military staff.
List
* Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff ( United States)
* Chief of the General Staff (Abkhazia)
* Chief of General Staff (Af ...
Aurél Stromfeld, resigned his post in protest.
When the French promised the Hungarian government that Romanian forces would withdraw from the Tiszántúl
Tiszántúl or Transtisza (literal meaning: "beyond Tisza") is a geographical region of which lies between the Tisza river, Hungary and the Apuseni Mountains, Romania, bordered by the Mureș (river), Maros (Mureș) river. Alongside Kiskunság, it i ...
, Kun withdrew from Czechoslovakia his remaining military units who had remained loyal after the political fiasco with the Slovak Soviet Republic. Kun then unsuccessfully tried to turn the remaining units of the demoralized Hungarian Red Army on the Romanians.
Treaty preparation
Little Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (since 1929 Yugoslavia) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revanchism and the prospect of a Hab ...
" of Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. The lengthy negotiation process was recorded on a daily basis by , deputy first secretary of the Hungarian delegation. The treaty of peace in final form was submitted to the Hungarians on 6 May and signed by them in Grand Trianon on 4 June 1920, entering into force on 26 July 1921. The United States did not ratify the Treaty of Trianon. Instead it negotiated a separate peace treaty that did not contradict the terms of the Trianon treaty.
Borders of Hungary
 The Hungarian government terminated its union with Austria on 31 October 1918, officially dissolving the Austro-Hungarian state. The ''de facto'' temporary borders of independent Hungary were defined by the ceasefire lines in November–December 1918. Compared with the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, these temporary borders did not include:
* Part of
The Hungarian government terminated its union with Austria on 31 October 1918, officially dissolving the Austro-Hungarian state. The ''de facto'' temporary borders of independent Hungary were defined by the ceasefire lines in November–December 1918. Compared with the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, these temporary borders did not include:
* Part of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
south of the Mureș River Mureș may refer to:
* Mureș County, Romania
* Mureș (river) in Romania and Hungary (''Maros'')
* Mureș culture, a Bronze Age culture from Romania
See also
* Târgu Mureș, the capital of Mureș County
* Ocna Mureș
Ocna Mureș (; la, Sali ...
and east of the Someș
The Someș (; hu, Szamos; german: Somesch or ''Samosch'') is a left tributary of the Tisza in Hungary and Romania. It has a length of (including its source river Someșul Mare), of which 50 km are in Hungary.Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
signed on 13 November 1918).
* The General Council of the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
in Nagyszeben (now Sibiu
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Ci ...
in Romania) decided in question of Transylvania to choose clear neutrality, without committing themselves either to the Hungarian or the Romanian side on 25 November 1918.
* The Romanian Army occupied Marosvásárhely (now Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the List of cities and towns in Romania, 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 Romania ...
in Romania), the most important town of Székely Land
The Székely Land or Szeklerland ( hu, Székelyföld, ; ro, Ținutul Secuiesc and sometimes ; german: Szeklerland; la, Terra Siculorum) is a historic and ethnographic area in Romania, inhabited mainly by Székelys, a subgroup of Hungarians. ...
in Transylvania. On the same day the National Assembly of Székelys
The Székelys (, Székely runes: 𐳥𐳋𐳓𐳉𐳗), also referred to as Szeklers,; ro, secui; german: Szekler; la, Siculi; sr, Секељи, Sekelji; sk, Sikuli are a Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. ...
in Marosvásárhely reaffirms their support to the territorial integrity of Hungary on 25 November 1918.
* On 1 December 1918, the Great National Assembly of Alba Iulia Union of Transylvania with Romania, declared union with the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
.
* In response, a Hungarian General Assembly in Kolozsvár (now Cluj-Napoca, Cluj in Romania), the most important Hungarian town in Transylvania, reaffirms the loyalty of Hungarians from Transylvania to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
on 22 December 1918.
* Slovakia was proclaimed as part of Czechoslovakia (status quo set by the Czechoslovak Legion, Czechoslovak legions and accepted by the Entente on 25 November 1918). Afterwards, the Slovak politician Milan Hodža discussed with the Hungarian Minister of Defence, Albert Bartha, a temporary demarcation line that left between 650,000–886,000 Hungarians in the newly formed Czechoslovakia and between 142,000–399,000 Slovaks in the remainder of Hungary (the discrepancy was caused by the different way census was collected in Hungary and Czechoslovakia). That was signed on 6 December 1918.
* South Slavic lands, which, after the war, were organised into two political formations – the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( ...
and Banat, Bačka and Baranja, which both came under control of South Slavs, according to the ceasefire agreement of Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
signed on 13 November 1918. Previously, on 29 October 1918, the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia parliament, an autonomous kingdom within Transleithania, terminated the union with the Kingdom of Hungary and on 30 October 1918 the Hungarian diet adopted a motion declaring that the constitutional relations between the two states had ended. Croatia-Slavonia was included in a newly formed State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs (which also included some other South Slavic territories, formerly administered by Austria-Hungary) on 29 October 1918. This state and the Kingdom of Serbia formed the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia) on 1 December 1918.
The territories of Banat, Bačka and Baranja (which included most of the pre-war Hungarian counties of Baranya County (former), Baranya, Bács-Bodrog County, Bács-Bodrog, Torontál County, Torontál, and Temes County, Temes) came under military control by the Kingdom of Serbia and political control by local South Slavs. The Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, Bačka and Baranja declared union of this region with Serbia on 25 November 1918. The ceasefire line had the character of a temporary international border until the treaty. The central parts of Banat were later assigned to Romania, respecting the wishes of Romanians from this area, which, on 1 December 1918, were present in the National Assembly of Romanians in Alba Iulia, which Union of Transylvania with Romania, voted for union with the Kingdom of Romania.
* The city of Rijeka was occupied by the Italian nationalists group. Its affiliation was a matter of international dispute between the Kingdom of Italy and Yugoslavia.
* Croatian-populated territories in modern Međimurje County, Međimurje remained under Hungarian control after the Armistice of Belgrade of 13 November 1918. After the 1918 occupation of Međimurje, Međimurje was occupied by forces led by Slavko Kvaternik on 24 December 1918, this region declared separation from Hungary and entry into Yugoslavia at the popular assembly of 9 January 1919.
After the Romanian Army advanced beyond this cease-fire line, the Entente powers asked Hungary (Vix Note) to acknowledge the new Romanian territorial gains by a new line set along the Tisza river. Unable to reject these terms and unwilling to accept them, the leaders of the Hungarian Democratic Republic resigned and the Communists seized power. In spite of the country being under Allied blockade, the Hungarian Soviet Republic was formed and the Hungarian Red Army was rapidly set up. This army was initially successful against the Czechoslovak Legions, due to covert food and arms aid from Italy. This made it possible for Hungary to reach nearly the former Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, Galician (Polish) border, thus separating the Czechoslovak and Romanian troops from each other.
After a Hungarian-Czechoslovak cease-fire signed on 1 July 1919, the Hungarian Red Army left parts of Slovakia by 4 July, as the Entente powers promised to invite a Hungarian delegation to the Versailles Peace Conference. In the end, this particular invitation was not issued. Béla Kun
Béla Kun (born Béla Kohn; 20 February 1886 – 29 August 1938) was a Hungarian communist revolutionary and politician who governed the Hungarian Soviet Republic in 1919. After attending Franz Joseph University at Kolozsvár (today Cluj-Napoc ...
, leader of the Hungarian Soviet Republic, then turned the Hungarian Red Army on the Romanian Army and Hungarian–Romanian War, attacked at the Tisza river on 20 July 1919. After fierce fighting that lasted some five days, the Hungarian Red Army collapsed. The Royal Romanian Army marched into Budapest on 4 August 1919.
The Hungarian state was restored by the Entente powers, helping Admiral Miklós Horthy, Horthy into power in November 1919. On 1 December 1919, the Hungarian delegation was officially invited to the Versailles Peace Conference; however, the newly defined borders of Hungary were nearly concluded without the presence of the Hungarians.Mayer, Arno J. (1967). ''Politics and Diplomacy of Peacemaking. Containment and Counterrevolution at Versailles, 1918–1919''. New York: Knopf. p. 369 During prior negotiations, the Hungarian party, along with the Austrian, advocated the American principle of self-determination: that the population of disputed territories should decide by free plebiscite to which country they wished to belong. This view did not prevail for long, as it was disregarded by the decisive French and British delegates. According to some opinions, the Allies drafted the outline of the new frontiersMiller, Vol. IV, 209. Document 246. "Outline of Tentative Report and Recommendations Prepared by the Intelligence Section, in Accordance with Instructions, for the President and the Plenipotentiaries 21 January 1919." with little or no regard to the historical, cultural, ethnic, geographic, economic and strategic aspects of the region. The Allies assigned territories that were mostly populated by non-Hungarian ethnicities to successor states, but also allowed these states to absorb sizeable territories that were mainly inhabited by Hungarian-speaking populations. For instance, Romania gained all of Transylvania, which was home to 2,800,000 Romanians, but also contained a significant minority of 1,600,000 Hungarians and about 250,000 Germans. The intent of the Allies was principally to strengthen these successor states at the expense of Hungary. Although the countries that were the main beneficiaries of the treaty partially noted the issues, the Hungarian delegates tried to draw attention to them. Their views were disregarded by the Allied representatives.
Some predominantly Hungarian settlements, consisting of more than two million people, were situated in a typically wide strip along the new borders in foreign territory. More concentrated groups were found in Czechoslovakia (parts of southern Slovakia), Yugoslavia (parts of northern Délvidék), and Romania (parts of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
).
The final borders of Hungary were defined by the Treaty of Trianon signed on 4 June 1920. Beside exclusion of the previously mentioned territories, they did not include:
* the rest of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, which together with some additional parts of the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary became part of Romania;
* Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia ( rue, Карпатьска Русь, Karpat'ska Rus'; uk, Закарпаття, Zakarpattia; sk, Podkarpatská Rus; hu, Kárpátalja; ro, Transcarpatia; pl, Zakarpacie); cz, Podkarpatská Rus; german: Karpatenukrai ...
, which became part of Czechoslovakia, pursuant to the Treaty of Saint-Germain in 1919;
* most of Burgenland, which became part of Austria, also pursuant to the Treaty of Saint-Germain (the district of Sopron opted to remain within Hungary after a plebiscite held in December 1921, the only place where a plebiscite was held and factored in the decision);
* Međimurje County, Međimurje and the 2/3 of the Slovene March (Kingdom of Hungary), Slovene March or ''Vendvidék'' (now Prekmurje), which became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
By the Treaty of Trianon, the cities of Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
, Mohács, Baja, Hungary, Baja and Szigetvár, which were under Serb-Croat-Slovene administration after November 1918, were assigned to Hungary. An arbitration committee in 1920 assigned small northern parts of the former Árva and Szepes counties of the Kingdom of Hungary with Polish majority population to Second Polish Republic, Poland. After 1918, Hungary did not have access to the sea, which pre-war Hungary formerly had directly through the Rijeka coastline and indirectly through Croatia-Slavonia.
 Representatives of small nations living in the former Austria-Hungary and active in the Congress of Oppressed Nations regarded the treaty of Trianon for being an act of historical righteousness because a better future for their nations was "to be founded and durably assured on the firm basis of world democracy, real and sovereign government by the people, and a universal alliance of the nations vested with the authority of arbitration" while at the same time making a call for putting an end to "the existing unbearable domination of one nation over the other" and making it possible "for nations to organize their relations to each other on the basis of equal rights and free conventions". Furthermore, they believed the treaty would help toward a new era of dependence on international law, the fraternity of nations, equal rights, and human liberty as well as aid civilisation in the effort to free humanity from international violence.
Representatives of small nations living in the former Austria-Hungary and active in the Congress of Oppressed Nations regarded the treaty of Trianon for being an act of historical righteousness because a better future for their nations was "to be founded and durably assured on the firm basis of world democracy, real and sovereign government by the people, and a universal alliance of the nations vested with the authority of arbitration" while at the same time making a call for putting an end to "the existing unbearable domination of one nation over the other" and making it possible "for nations to organize their relations to each other on the basis of equal rights and free conventions". Furthermore, they believed the treaty would help toward a new era of dependence on international law, the fraternity of nations, equal rights, and human liberty as well as aid civilisation in the effort to free humanity from international violence.
Results and consequences
 Irredentism—the demand for reunification of Hungarian peoples—became a central theme of Hungarian politics and diplomacy.
Irredentism—the demand for reunification of Hungarian peoples—became a central theme of Hungarian politics and diplomacy.
1910 census
The last census before the Treaty of Trianon was held in 1910. This census recorded population by language and religion but not by ethnicity. However, it is generally accepted that the largest ethnic group in the Kingdom of Hungary in this time were the Hungarians. According to the census, speakers of the Hungarian language included approximately 48% of the population of the kingdom and 54% of the population of the territory referred to as "Hungary proper", i.e. excluding Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, Croatia-Slavonia. Within the borders of "Hungary proper" numerous ethnic minorities were present: 16.1% Romanians, 10.5% Slovaks, 10.4% Germans, 2.5% Ruthenians, 2.5% Serbs and 8% others. 5% of the population of "Hungary proper" were History of the Jews in Hungary, Jews, who were included in speakers of the Hungarian language. The population of the autonomous Croatia-Slavonia was mostly composed of Croats and Serbs (who together counted 87% of population).Criticism of the 1910 census
The census of 1910 classified the residents of the Kingdom of Hungary by their native languages and religions, so it presents the preferred language of the individual, which may or may not correspond to the individual's ethnic identity. To make the situation even more complex, in the multilingual kingdom there were territories with ethnically mixed populations where people spoke two or even three languages natively. For example, in the territory what is today Slovakia (then part of Upper Hungary) 18% of the Slovaks, 33% of the Hungarians and 65% of the Germans were bilingual. In addition, 21% of the Germans spoke both Slovak and Hungarian beside German. These reasons are ground for debate about the accuracy of the census. While several demographers (David W. Paul, Peter Hanak, László Katus) state that the outcome of the census is reasonably accurate (assuming that it is also properly interpreted), others believe that the 1910 census was manipulated by exaggerating the percentage of the speakers of Hungarian, pointing to the discrepancy between an improbably high growth of the Hungarian-speaking population and the decrease of percentual participation of speakers of other languages through Magyarization in the late 19th century. For example, the 1921 census in Czechoslovakia (only one year after the Treaty of Trianon) shows 21% Hungarians in Slovakia, compared to 30% based on 1910 census. Some Slovak demographers (such as and Julius Mesaros) dispute the result of every pre-war census. Owen Johnson, an American historian, accepts the numbers of the earlier censuses up to the one in 1900, according to which the proportion of the Hungarians was 51.4%, but he neglects the 1910 census as he thinks the changes since the last census are too big. It is also argued that there were different results in previous censuses in the Kingdom of Hungary and subsequent censuses in the new states. Considering the size of discrepancies, some demographers are on the opinion that these censuses were somewhat biased in the favour of the respective ruling nation.Distribution of the non-Hungarian and Hungarian populations
The number of non-Hungarian and Hungarian communities in the different areas based on the census data of 1910 (in this, people were not directly asked about their ethnicity, but about their native language). The present day location of each area is given in parenthesis. According to another source, population distribution in 1910 looked as follows:Hungarians outside the newly defined borders
 The territories of the former Hungarian Kingdom that were ceded by the treaty to neighbouring countries in total (and each of them separately) had a majority of non-Hungarian nationals; however, the Hungarian ethnic area was much larger than the newly established territory of Hungary,Eberhardt, Piotr (2003
The territories of the former Hungarian Kingdom that were ceded by the treaty to neighbouring countries in total (and each of them separately) had a majority of non-Hungarian nationals; however, the Hungarian ethnic area was much larger than the newly established territory of Hungary,Eberhardt, Piotr (2003''Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, and Analysis''
M.E. Sharpe. pp. 290–299. therefore 30% of the ethnic Hungarians were under foreign authority. After the treaty, the percentage and the absolute number of all Hungarian populations outside of Hungary decreased in the next decades (although, some of these populations also recorded temporary increase of the absolute population number). There are several reasons for this population decrease, some of which were spontaneous assimilation and certain state policies, like Slovakization, Romanianization, Serbianisation. Other important factors were the Hungarian migration from the neighbouring states to Hungary or to some western countries as well as decreased birth rate of Hungarian populations. According to the National Office for Refugees, the number of Hungarians who immigrated to Hungary from neighbouring countries was about 350,000 between 1918 and 1924.
Minorities in post-Trianon Hungary
On the other hand, a considerable number of other nationalities remained within the frontiers of the independent Hungary: According to the 1920 census 10.4% of the population spoke one of the minority languages as mother language: * 551,212 German (6.9%) * 141,882 Slovak (1.8%) * 36,858 Croatian (0.5%) * 23,760 Romanian (0.3%) * 23,228 Bunjevac and Šokac (0.3%) * 17,131 Serbian (0.2%) * 7,000 Slovene (0.08%) The number of bilingual people was much higher, for example 1,398,729 people spoke German (17%), 399,176 people spoke Slovak (5%), 179,928 people spoke Croatian (2.2%) and 88,828 people spoke Romanian (1.1%). Hungarian was spoken by 96% of the total population and was the mother language of 89%.A népesség változó etnikai arculata Magyarország mai területén (map+data+essay) (Kocsis Károly, Bottlik Zsolt, Hungarian Academy of Sciences – Földrajztudományi Kutatóintézet, Budapest, 2009, ) The percentage and the absolute number of all non-Hungarian nationalities decreased in the next decades, although the total population of the country increased. Bilingualism was also disappearing. The main reasons of this process were both spontaneous assimilation and the deliberate Magyarization policy of the state. Minorities made up 8% of the total population in 1930 and 7% in 1941 (on the post-Trianon territory). After World War II approximately 200,000 Germans were deported to Germany, according to the decree of the Potsdam Conference. Under the forced exchange of population between Czechoslovakia and Hungary, approximately 73,000 Slovaks left Hungary and according to different estimations 120,500 or 45,000 Hungarians moved to present day Hungarian territory from Czechoslovakia. After these population movements, Hungary became a nearly ethnically homogeneous country.Political consequences

 Officially the treaty was intended to be a confirmation of the right of self-determination for nations and of the concept of nation-states replacing the old multinational Austro-Hungarian empire. Although the treaty addressed some nationality issues, it also sparked some new ones.
The minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom were the major beneficiaries. The Allies had explicitly committed themselves to the causes of the minority peoples of Austria-Hungary late in World War I. For all intents and purposes, the death knell of the Austro-Hungarian empire sounded on 14 October 1918, when United States Secretary of State Robert Lansing informed Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Stephan Burián von Rajecz, István Burián that autonomy for the nationalities was no longer enough. Accordingly, the Allies assumed without question that the minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom wanted to leave Hungary. The Romanians joined their ethnic brethren in Romania, while the Slovaks, Serbs and Croats helped establish states of their own (Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia). However, these new or enlarged countries also absorbed large slices of territory with a majority of ethnic Hungarians or Hungarian speaking population. As a result, as many as a third of Hungarian language-speakers found themselves outside the borders of the post-Trianon Hungary.
While the territories that were now outside Hungary's borders had non-Hungarian majorities overall, there also existed some sizeable areas with a majority of Hungarians, largely near the newly defined borders. Over the last century, concerns have occasionally been raised about the treatment of these ethnic Hungarian communities in the neighbouring states. Areas with significant Hungarian populations included the
Officially the treaty was intended to be a confirmation of the right of self-determination for nations and of the concept of nation-states replacing the old multinational Austro-Hungarian empire. Although the treaty addressed some nationality issues, it also sparked some new ones.
The minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom were the major beneficiaries. The Allies had explicitly committed themselves to the causes of the minority peoples of Austria-Hungary late in World War I. For all intents and purposes, the death knell of the Austro-Hungarian empire sounded on 14 October 1918, when United States Secretary of State Robert Lansing informed Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Stephan Burián von Rajecz, István Burián that autonomy for the nationalities was no longer enough. Accordingly, the Allies assumed without question that the minority ethnic groups of the pre-war kingdom wanted to leave Hungary. The Romanians joined their ethnic brethren in Romania, while the Slovaks, Serbs and Croats helped establish states of their own (Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia). However, these new or enlarged countries also absorbed large slices of territory with a majority of ethnic Hungarians or Hungarian speaking population. As a result, as many as a third of Hungarian language-speakers found themselves outside the borders of the post-Trianon Hungary.
While the territories that were now outside Hungary's borders had non-Hungarian majorities overall, there also existed some sizeable areas with a majority of Hungarians, largely near the newly defined borders. Over the last century, concerns have occasionally been raised about the treatment of these ethnic Hungarian communities in the neighbouring states. Areas with significant Hungarian populations included the Székely Land
The Székely Land or Szeklerland ( hu, Székelyföld, ; ro, Ținutul Secuiesc and sometimes ; german: Szeklerland; la, Terra Siculorum) is a historic and ethnographic area in Romania, inhabited mainly by Székelys, a subgroup of Hungarians. ...
in eastern Transylvania, the area along the newly defined Romanian-Hungarian border (cities of Arad, Romania, Arad, Oradea), the area north of the newly defined Czechoslovak–Hungarian border (Komárno, Csallóköz), southern parts of Subcarpathia and northern parts of Ethnic groups in Vojvodina, Vojvodina.
The Allies rejected the idea of referendum, plebiscites in the disputed areas with the exception of the city of Sopron, which voted in favour of Hungary. The Allies were indifferent as to the exact line of the newly defined border between Austria and Hungary. Furthermore, ethnically diverse Transylvania, with an overall Romanian majority (53.8% – 1910 census data or 57.1% – 1919 census data or 57.3% – 1920 census data), was treated as a single entity at the peace negotiations and was assigned in its entirety to Romania. The option of partition along ethnic lines as an alternative was rejected.
Another reason why the victorious Allies decided to dissolve the Austria-Hungary was to prevent Germany from acquiring substantial influence in the future, since Austria-Hungary was a strong German supporter and fast developing region.Duroselle, Jean-Baptiste (1968) ''From Wilson to Roosevelt''. Harper & Row Torchbooks The Western powers' main priority was to prevent a resurgence of the German Reich, and they therefore decided that her allies in the region should be "contained" by a ring of states friendly to the Allies, each of which would be bigger than either Austria or Hungary. Compared to the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary, post-Trianon Hungary had 60% less population, and its political and economic footprint in the region was significantly reduced. Hungary lost connection to strategic military and economic infrastructure because of the concentric layout of the railway and road network, which the borders bisected. In addition, the structure of its economy collapsed because it had relied on other parts of the pre-war kingdom. The country lost access to the Mediterranean and to the important sea port of Rijeka (Fiume) and became landlocked, which had a negative effect on sea trading and strategic naval operations. Many trading routes that went through the newly defined borders from various parts of the pre-war kingdom were abandoned.
With regard to the ethnic issues, the Western powers were aware of the problem posed by the presence of so many Hungarians (and Germans) living outside the newly formed states of Hungary and Austria. The Romanian delegation to Versailles feared in 1919 that the Allies were beginning to favour the partition of Transylvania along ethnic lines to reduce the potential exodus, and Prime Minister Ion I. C. Brătianu even summoned British-born Marie of Romania, Queen Marie to France to strengthen their case. The Romanians had suffered a higher ''relative'' casualty rate in the war than either BritainPresent Day Romania census 1912– population of Transylvania or France so it was considered that the Western powers had a moral debt to repay. In ''absolute'' terms, Romanian troops had considerably fewer casualties than either Britain or France, however. The underlying reason for the decision was a Secret treaty, secret pact between The Entente and Romania. In the Treaty of Bucharest (1916) Romania was promised Transylvania and some other territories to the east of river Tisza, provided that she attacked Austria-Hungary from the south-east, where defences were weak. However, after the Central Powers had noticed the military manoeuvre, the attempt was quickly choked off and Bucharest fell in the same year.
 By the time the victorious Allies arrived in France, the treaty was already settled, which made the outcome inevitable. At the heart of the dispute lay fundamentally different views on the nature of the Hungarian presence in the disputed territories. For Hungarians, the outer territories were not seen as colonial territories but rather part of the core national territory. The non-Hungarians that lived in the Pannonian Basin saw the Hungarians as colonial-style rulers who had oppressed the Slavs and Romanians since 1848, when they introduced laws that the language used in education and in local offices was to be Hungarian. For non-Hungarians from the Pannonian Basin it was a process of decolonisation instead of a punitive dismemberment (as was seen by the Hungarians). The Hungarians did not see it this way because the newly defined borders did not fully respect territorial distribution of ethnic groups,:File:Redmap.jpg, Ethnic map of Kingdom of Hungary without Croatia-Slavonia with areas where there were Hungarian majorities outside the new borders. The French sided with their allies the Romanians who had a long policy of cultural ties to France since the country broke from the
By the time the victorious Allies arrived in France, the treaty was already settled, which made the outcome inevitable. At the heart of the dispute lay fundamentally different views on the nature of the Hungarian presence in the disputed territories. For Hungarians, the outer territories were not seen as colonial territories but rather part of the core national territory. The non-Hungarians that lived in the Pannonian Basin saw the Hungarians as colonial-style rulers who had oppressed the Slavs and Romanians since 1848, when they introduced laws that the language used in education and in local offices was to be Hungarian. For non-Hungarians from the Pannonian Basin it was a process of decolonisation instead of a punitive dismemberment (as was seen by the Hungarians). The Hungarians did not see it this way because the newly defined borders did not fully respect territorial distribution of ethnic groups,:File:Redmap.jpg, Ethnic map of Kingdom of Hungary without Croatia-Slavonia with areas where there were Hungarian majorities outside the new borders. The French sided with their allies the Romanians who had a long policy of cultural ties to France since the country broke from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(partly because of the relative ease at which Romanians could learn French) although Georges Clemenceau, Clemenceau personally detested Ion C. Brătianu, Brătianu. President Wilson initially supported the outline of a border that would have more respect to ethnic distribution of population based on the ''Coolidge Report,'' led by Archibald Cary Coolidge, a Harvard professor, but later gave in because of changing international politics and as a courtesy to other allies.
For Hungarian public opinion, the fact that almost three-fourths of the pre-war kingdom's territory and a significant number of ethnic Hungarians were assigned to neighbouring countries triggered considerable bitterness. Most Hungarians preferred to maintain the territorial integrity of the pre-war kingdom. The Hungarian politicians claimed that they were ready to give the non-Hungarian ethnicities a great deal of autonomy. Most Hungarians regarded the treaty as an insult to the nation's honour. The Hungarian political attitude towards Trianon was summed up in the phrases ''Nem, nem, soha!'' ("No, no, never!") and ''Mindent vissza!'' ("Return everything!" or "Everything back!"). The perceived humiliation of the treaty became a dominant theme in inter-war Hungarian politics, analogous with the German reaction to the Treaty of Versailles.
By the arbitrations of Nazi Germany, Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Italy, Hungary Hungary in World War II, expanded its borders towards neighbouring countries before and during World War II. This started by the First Vienna Award, then was continued with the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1939 (annexation of the remainder of Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia ( rue, Карпатьска Русь, Karpat'ska Rus'; uk, Закарпаття, Zakarpattia; sk, Podkarpatská Rus; hu, Kárpátalja; ro, Transcarpatia; pl, Zakarpacie); cz, Podkarpatská Rus; german: Karpatenukrai ...
and a small strip from eastern Slovakia), afterwards by the Second Vienna Award in 1940, and finally by the Invasion of Yugoslavia, annexations of territories after the breakup of Yugoslavia. This territorial expansion was short-lived, since the post-war Hungarian boundaries in the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947 were nearly identical to those of 1920 (with three villages – Jarovce, Horvátjárfalu, Rusovce, Oroszvár, and Čunovo, Dunacsún – transferred to Czechoslovakia).
Legacy
Francesco Saverio Nitti served as Prime Minister of Italy between 1919 and 1920. Italy was a member of the Entente and participated in the treaty, he wrote in the Peaceless Europe in 1922:In modern historiography
The treaty's perceived disproportion has had a lasting impact on Hungarian politics and culture, with some commentators even likening it to a "collective pathology" that places Trianon into a much larger narrative of Hungarian victimhood at the hands of foreign powers. Within Hungary, Trianon is often referred to as a "diktat," "tragedy," and "trauma." According to a study, two-thirds of Hungarians agreed in 2020 that parts of neighbouring countries should belong to them, the highest percentage in any NATO country. Hungarian irredentism, Such irredentism was one of the main contributing factors to Hungary's decision to Hungary in World War II, enter World War II as an Axis powers, Axis power; Adolf Hitler had promised to intervene on Hungary's behalf to restore majority-ethnic Hungarian lands lost after Trianon. Hungarian bitterness at Trianon was also a source of regional tension after the Cold War ended in 1989. For example, Hungary attracted international media attention in 1999 for passing the "status law" concerning estimated three-million ethnic Hungarian minorities in neighbouring Romania, Slovakia, Serbia and Montenegro, Croatia, Slovenia and Ukraine. The law aimed to provide education, health benefits and employment rights to these minorities as a means of providing reparations for Trianon's negative consequences. Trianon's legacy is similarly implicated in the question of whether to grant extraterritorial ethnic Hungarians citizenship, an important issue in contemporary Hungarian politics. In 2004, a majority of voters approved extending citizenship to ethnic Hungarians in 2004 Hungarian dual citizenship referendum, a referendum, which nonetheless failed due to low turnout.Nohlen, Dieter and Stöver, Philip (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook''. p. 899 In 2011, Viktor Orbán's newly-formed government liberalized the nationality law by statute. Although Orbán depicted the new law as redressing Trianon, many commentators speculated about an additional political motivation; the law granted voting rights to extraterritorial Hungarians, who were seen as a reliable base of support for Orbán's national-conservative Fidesz party.Economic consequences
 Post-Trianon Hungary possessed 90% of the engineering and printing industry of the pre-war kingdom, while only 11% of timber and 16% of iron was retained. In addition, 61% of arable land, 74% of public roads, 65% of canals, 62% of railroads, 64% of hard surface roads, 83% of pig iron output, 55% of industrial plants, and 67% of credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary lay within the territory of Hungary's neighbours. These statistics correspond to post-Trianon Hungary retaining only around a third of the kingdom's territory before the war and around 60% of its population. The new borders also bisected transport links – in the Kingdom of Hungary the road and railway network had a radial structure, with Budapest in the centre. Many roads and railways, running along the newly defined borders and interlinking radial transport lines, ended up in different, highly introvert countries. Hence, much of the rail cargo traffic of the emergent states was virtually paralysed. These factors all combined created some imbalances in the now separated economic regions of the former monarchy.
Post-Trianon Hungary possessed 90% of the engineering and printing industry of the pre-war kingdom, while only 11% of timber and 16% of iron was retained. In addition, 61% of arable land, 74% of public roads, 65% of canals, 62% of railroads, 64% of hard surface roads, 83% of pig iron output, 55% of industrial plants, and 67% of credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary lay within the territory of Hungary's neighbours. These statistics correspond to post-Trianon Hungary retaining only around a third of the kingdom's territory before the war and around 60% of its population. The new borders also bisected transport links – in the Kingdom of Hungary the road and railway network had a radial structure, with Budapest in the centre. Many roads and railways, running along the newly defined borders and interlinking radial transport lines, ended up in different, highly introvert countries. Hence, much of the rail cargo traffic of the emergent states was virtually paralysed. These factors all combined created some imbalances in the now separated economic regions of the former monarchy.
 The disseminating economic problems had been also noted in the ''Coolidge Report'' as a serious potential aftermath of the treaty. This opinion was not taken into account during the negotiations. Thus, the resulting uneasiness and despondency of one part of the concerned population was later one of the main antecedents of World War II. Unemployment levels in Austria, as well as in Hungary, were dangerously high, and industrial output dropped by 65%. What happened to Austria in industry happened to Hungary in agriculture where production of grain declined by more than 70%. Austria, especially the imperial capital Vienna, was a leading investor of development projects throughout the empire with more than 2.2 billion crown capital. This sum sunk to a mere 8.6 million crowns after the treaty took effect and resulted in a starving of capital in other regions of the former empire.
The disintegration of the multinational state conversely impacted neighbouring countries, too: In Poland, Romania, Yugoslavia, and Bulgaria a fifth to a third of the rural population could find no work, and industry was in no position to absorb them. In comparison, by 1921 the new Czechoslovak state reached 75% of its pre-war production owing to their favourable position among the victors and greater associated access to international rehabilitation resources.
With the creation of customs barriers and Protectionism, fragmented protective economies, the economic growth and outlook in the region sharply declined, ultimately culminating in a deep recession. It proved to be immensely challenging for the successor states to successfully transform their economies to adapt to the new circumstances. All the formal districts of Austria-Hungary used to rely on each other's exports for growth and welfare; by contrast, 5 years after the treaty, traffic of goods between the countries dropped to less than 5% of its former value. This could be attributed to the introduction of aggressive nationalistic policies by local political leaders.
The drastic shift in economic climate forced the countries to re-evaluate their situation and to promote industries where they had fallen short. Austria and Czechoslovakia subsidised the mill, sugar and brewing industries, while Hungary attempted to increase the efficiency of iron, steel, glass and chemical industries. The stated objective was that all countries should become self-sufficient. This tendency, however, led to uniform economies and competitive economic advantage of long well-established industries and research fields evaporated. The lack of specialisation adversely affected the whole Danube-Carpathian region and caused a distinct setback of growth and development compared to western and northern European regions as well as high financial vulnerability and instability.
The disseminating economic problems had been also noted in the ''Coolidge Report'' as a serious potential aftermath of the treaty. This opinion was not taken into account during the negotiations. Thus, the resulting uneasiness and despondency of one part of the concerned population was later one of the main antecedents of World War II. Unemployment levels in Austria, as well as in Hungary, were dangerously high, and industrial output dropped by 65%. What happened to Austria in industry happened to Hungary in agriculture where production of grain declined by more than 70%. Austria, especially the imperial capital Vienna, was a leading investor of development projects throughout the empire with more than 2.2 billion crown capital. This sum sunk to a mere 8.6 million crowns after the treaty took effect and resulted in a starving of capital in other regions of the former empire.
The disintegration of the multinational state conversely impacted neighbouring countries, too: In Poland, Romania, Yugoslavia, and Bulgaria a fifth to a third of the rural population could find no work, and industry was in no position to absorb them. In comparison, by 1921 the new Czechoslovak state reached 75% of its pre-war production owing to their favourable position among the victors and greater associated access to international rehabilitation resources.
With the creation of customs barriers and Protectionism, fragmented protective economies, the economic growth and outlook in the region sharply declined, ultimately culminating in a deep recession. It proved to be immensely challenging for the successor states to successfully transform their economies to adapt to the new circumstances. All the formal districts of Austria-Hungary used to rely on each other's exports for growth and welfare; by contrast, 5 years after the treaty, traffic of goods between the countries dropped to less than 5% of its former value. This could be attributed to the introduction of aggressive nationalistic policies by local political leaders.
The drastic shift in economic climate forced the countries to re-evaluate their situation and to promote industries where they had fallen short. Austria and Czechoslovakia subsidised the mill, sugar and brewing industries, while Hungary attempted to increase the efficiency of iron, steel, glass and chemical industries. The stated objective was that all countries should become self-sufficient. This tendency, however, led to uniform economies and competitive economic advantage of long well-established industries and research fields evaporated. The lack of specialisation adversely affected the whole Danube-Carpathian region and caused a distinct setback of growth and development compared to western and northern European regions as well as high financial vulnerability and instability.
Miscellaneous consequences
 Romania, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia had to assume part of the financial obligations of the former Kingdom of Hungary on account of the parts of its former territory that were assigned under their sovereignty. Some conditions of the treaty were similar to those imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles. After the war, the Austro-Hungarian navy, Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops, air force and army were disbanded. The army of post-Trianon Hungary was to be restricted to 35,000 men, and there was to be no conscription. Heavy artillery, tanks and air force were prohibited. No railway was to be built with more than one track, because at that time railways held substantial strategic importance economically and militarily.
Articles 54–60 of the treaty required Hungary to recognise various rights of national minorities within its borders. Articles 61–66 state that all former citizens of the Kingdom of Hungary living outside the newly defined frontiers of Hungary were to ''ipso facto'' lose their Hungarian citizenship in one year. Under articles 79 to 101 Hungary renounced all privileges of the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy in territories outside Europe, including Morocco, Egypt, Siam and China.s:Treaty of Trianon/Part IV, Wikisource: Hungarian Interests outside Europe
Romania, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia had to assume part of the financial obligations of the former Kingdom of Hungary on account of the parts of its former territory that were assigned under their sovereignty. Some conditions of the treaty were similar to those imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles. After the war, the Austro-Hungarian navy, Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops, air force and army were disbanded. The army of post-Trianon Hungary was to be restricted to 35,000 men, and there was to be no conscription. Heavy artillery, tanks and air force were prohibited. No railway was to be built with more than one track, because at that time railways held substantial strategic importance economically and militarily.
Articles 54–60 of the treaty required Hungary to recognise various rights of national minorities within its borders. Articles 61–66 state that all former citizens of the Kingdom of Hungary living outside the newly defined frontiers of Hungary were to ''ipso facto'' lose their Hungarian citizenship in one year. Under articles 79 to 101 Hungary renounced all privileges of the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy in territories outside Europe, including Morocco, Egypt, Siam and China.s:Treaty of Trianon/Part IV, Wikisource: Hungarian Interests outside Europe
See also
* Union of Hungary and Romania * Millerand letter * Aftermath of World War I * Minority Treaties * Banat Republic * Republic of Prekmurje * Serbian–Hungarian Baranya–Baja Republic * Trianon Syndrome * Trianon Treaty DayNotes
References
Cited sources
* * * * *Further reading
* Badescu, Ilie. "Peacebuilding in an Era of State-Nations: The Europe of Trianon." ''Romanian Journal of Sociological Studies'' 2 (2018): 87–100online
* Balogh, Eva S. "Peaceful Revision: The Diplomatic Road to War." ''Hungarian Studies Review'' 10.1 (1983): 43- 51
online
* Bandholtz, H.H. ''An Undiplomatic Diary by the American Member of the Inter-Allied Military Mission to Hungary: 1919–1920.'' (1933
* Bartha, Dezso. "Trianon and the Predestination of Hungarian Politics: A Historiography of Hungarian Revisionism, 1918–1944." (Thesis, University of Central Florida, 2006
online
* Bihari, Peter. "Images of defeat: Hungary after the lost war, the revolutions and the Peace Treaty of Trianon." ''Crossroads of European histories: multiple outlooks on five key moments in the history of Europe'' (2006) pp: 165–171. * Hanák, Peter. "Hungary on a fixed course: An outline of Hungarian history, 1918–1945." in Joseph Held, ed., ''Columbia history of Eastern Europe in the Twentieth Century'' (1992) pp: 164–204. * Jeszenszky, Géza. "The Afterlife of the Treaty of Trianon." ''The Hungarian Quarterly'' 184 (2006): 101–111. * Király, Béla K. and László Veszprémy, eds. ''Trianon and East Central Europe: Antecedents and Repercussions'' (Columbia University Press, 1995). * Macartney, Carlile Aylmer ''Hungary and Her Successors: The Treaty of Trianon and Its Consequences 1919–1937'' (1937) * Macartney, Carlile Aylmer'' October Fifteenth – A History of Modern Hungary 1929–1945''. Edinburgh University Press (1956) * Aliaksandr Piahanau, ''Hungary's Policy Towards Czechoslovakia, 1918–36''. PhD dissertation. Toulouse University, 201
Hungary's Policy Towards Czechoslovakia in 1918 - 36
* Romsics, Ignác. ''The Dismantling of Historic Hungary: The Peace Treaty of Trianon, 1920'' (Boulder, CO: Social Science Monographs, 2002). * Romsics, Ignác. "The Trianon Peace Treaty in Hungarian Historiography and Political Thinking." ''East European Monographs'' (2000): 89–105. * Romsics, Ignác. "Hungarian Revisionism in Thought and Action, 1920–1941: Plans, Expectations, Reality" in Marina Cattaruzza ed., ''Territorial Revisionism and the Allies of Germany in the Second World War: Goals, Expectations, Practices'' (2013) pp. 92–10
online
* Steiner, Zara S. ''The lights that failed: European international history, 1919–1933'' (2007) Trianon in relation to powers and nearby countries. ** Steiner, Zara. ''The triumph of the dark: European international history 1933–1939'' (2011), continued, * Várdy, Steven Béla. "The Impact of Trianon upon Hungary and the Hungarian Mind: The Nature of Interwar Hungarian Irredentism." ''Hungarian Studies Review'' 10.1 (1983): 21+
online
* Wojatsek, Charles. ''From Trianon to the First Vienna Arbitral Award: The Hungarian Minority in the First Czechoslovak Republic, 1918–1938'' (Montreal: Institute of Comparative Civilizations, 1980).
External links
* Zeidler, MiklósTreaty of Trianon
in
* Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
* [https://wwi.lib.byu.edu/index.php/Treaty_of_Trianon Trianon Treaty text (in English)]
Map of Hungarian borders in November–December 1918
Map of Europe and Treaty of Trianon
at omniatlas.com {{Authority control Borders of Hungary Boundary treaties, Trianon History of Austria-Hungary 1920 in Austria 1920 in Czechoslovakia 1920 in Hungary 1920 in Romania 1920 in Slovakia 1920 in Ukraine 20th century in Transylvania 20th century in Vojvodina Interwar-period treaties Military history of Austria-Hungary Modern history of Slovenia Peace treaties of France Peace treaties of Hungary, Trianon Peace treaties of Italy Peace treaties of Japan Peace treaties of the United Kingdom, Trianon Peace treaties of the United States, Trianon Treaties concluded in 1920 Treaties entered into force in 1921 Treaties of Belgium Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of Nicaragua Treaties of Panama Treaties of Thailand Treaties of the Empire of Japan Treaties of the French Third Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece Treaties of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946) Treaties of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946) Treaties of the Kingdom of Romania Great Union (Romania) Treaties of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia Treaties of the Portuguese First Republic Treaties of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Treaties of the Second Polish Republic Treaties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922) World War I treaties, Trianon Yugoslav Croatia Yugoslav Serbia Greater Romania Territorial evolution of Hungary Territorial evolution of Romania Dissolution of Austria-Hungary Hungary–Romania relations Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920) Partition (politics)