Traian Cercega on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the
 Marcus Ulpius Trajanus was born on 18 September 53AD in the Roman province of Hispania BaeticaSyme, Tacitus, 30–44; PIR Vlpivs 575 (in what is now Andalusia in modern Spain), in the small roman '' municipium'' of Italica (now in the municipal area of Santiponce, in the outskirts of Seville). At the time of Trajan's birth, it was a small town, without baths, theatre and amphitheatre, and with a very narrow territory under its direct administration. His year of birth is not reliably attested and may have been 56 AD.
Some ancient authors, most notably Cassius Dio, claim that Trajan was the first emperor of non-Italic origins. However, Trajan's '' patria'' of Italica, in Spanish Baetica, was a Roman colony of Italic settlers founded in 206BC by
Marcus Ulpius Trajanus was born on 18 September 53AD in the Roman province of Hispania BaeticaSyme, Tacitus, 30–44; PIR Vlpivs 575 (in what is now Andalusia in modern Spain), in the small roman '' municipium'' of Italica (now in the municipal area of Santiponce, in the outskirts of Seville). At the time of Trajan's birth, it was a small town, without baths, theatre and amphitheatre, and with a very narrow territory under its direct administration. His year of birth is not reliably attested and may have been 56 AD.
Some ancient authors, most notably Cassius Dio, claim that Trajan was the first emperor of non-Italic origins. However, Trajan's '' patria'' of Italica, in Spanish Baetica, was a Roman colony of Italic settlers founded in 206BC by
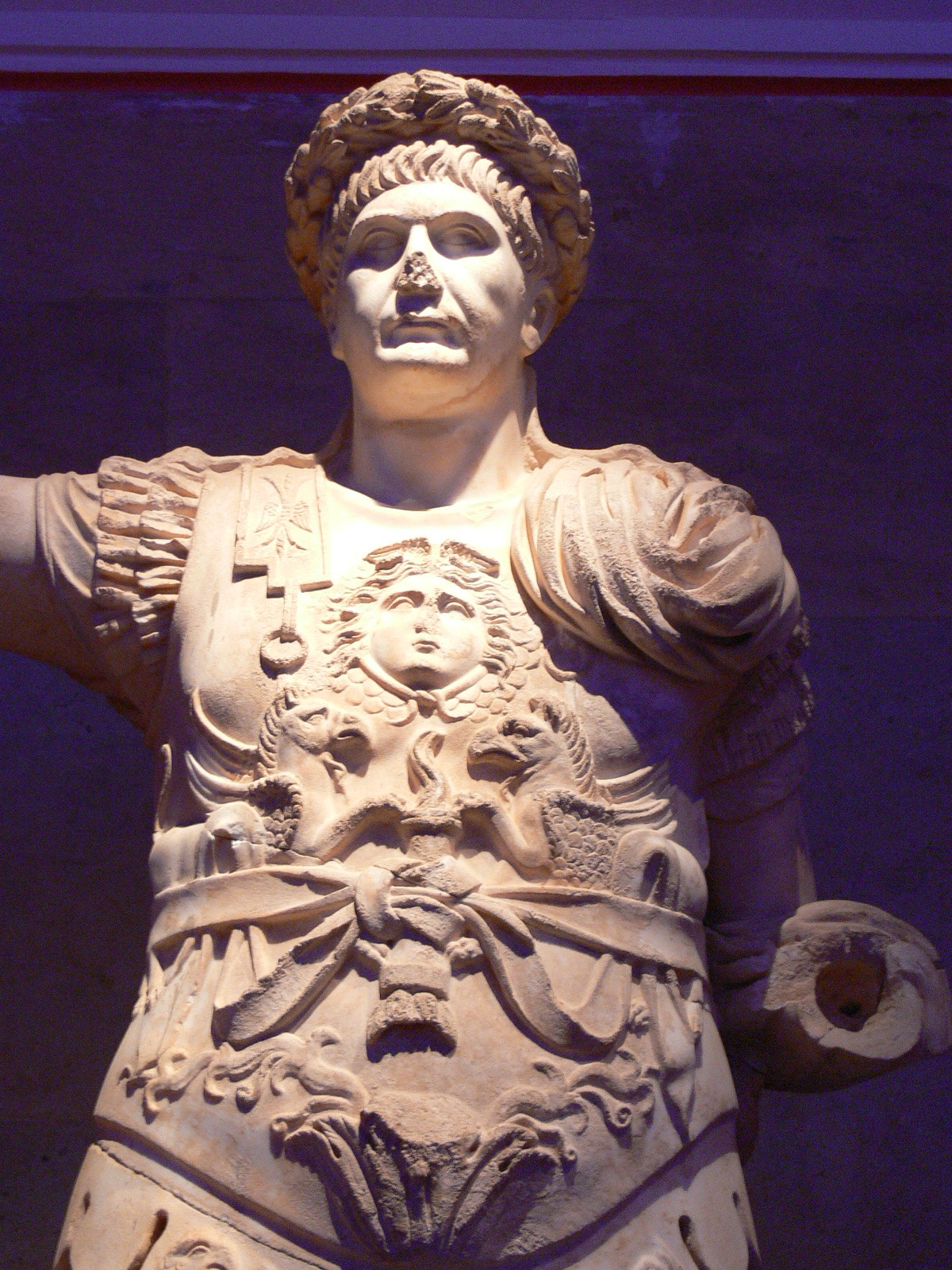 As a young man, Trajan rose through the ranks of the
As a young man, Trajan rose through the ranks of the
2.5–6
/ref> and married Pompeia Plotina, a noblewoman from the Roman settlement at
 In the formula developed by Pliny, however, Trajan was a "good" emperor in that, by himself, he approved or blamed the same things that the Senate would have approved or blamed. If in reality Trajan was an autocrat, his deferential behavior towards his peers qualified him to be viewed as a virtuous monarch. The idea is that Trajan wielded autocratic power through ''moderatio'' instead of ''contumacia''moderation instead of insolence. In short, according to the ethics for autocracy developed by most political writers of the Imperial Roman Age, Trajan was a good ruler in that he ruled less by fear, and more by acting as a role model, for, according to Pliny, "men learn better from examples". Eventually, Trajan's popularity among his peers was such that the Roman Senate bestowed upon him the honorific of ''optimus'', meaning "the best", which appears on coins from 105 on. This title had mostly to do with Trajan's role as benefactor, such as in the case of him returning confiscated property.
Pliny states that Trajan's ideal role was a conservative one, argued as well by the orations of Dio Chrysostom—in particular his four ''Orations on Kingship'', composed early during Trajan's reign. Dio, as a Greek notable and intellectual with friends in high places, and possibly an official friend to the emperor (''amicus caesaris''), saw Trajan as a defender of the ''status quo''. In his third kingship oration, Dio describes an ideal king ruling by means of "friendship"that is, through patronage and a network of local notables who act as mediators between the ruled and the ruler. Dio's notion of being "friend" to Trajan (or any other Roman emperor), however, was that of an ''informal'' arrangement, that involved no formal entry of such "friends" into the Roman administration. Trajan ingratiated himself with the Greek intellectual elite by recalling to Rome many (including Dio) who had been exiled by Domitian, and by returning (in a process begun by Nerva) a great deal of private property that Domitian had confiscated. He also had good dealings with Plutarch, who, as a notable of
In the formula developed by Pliny, however, Trajan was a "good" emperor in that, by himself, he approved or blamed the same things that the Senate would have approved or blamed. If in reality Trajan was an autocrat, his deferential behavior towards his peers qualified him to be viewed as a virtuous monarch. The idea is that Trajan wielded autocratic power through ''moderatio'' instead of ''contumacia''moderation instead of insolence. In short, according to the ethics for autocracy developed by most political writers of the Imperial Roman Age, Trajan was a good ruler in that he ruled less by fear, and more by acting as a role model, for, according to Pliny, "men learn better from examples". Eventually, Trajan's popularity among his peers was such that the Roman Senate bestowed upon him the honorific of ''optimus'', meaning "the best", which appears on coins from 105 on. This title had mostly to do with Trajan's role as benefactor, such as in the case of him returning confiscated property.
Pliny states that Trajan's ideal role was a conservative one, argued as well by the orations of Dio Chrysostom—in particular his four ''Orations on Kingship'', composed early during Trajan's reign. Dio, as a Greek notable and intellectual with friends in high places, and possibly an official friend to the emperor (''amicus caesaris''), saw Trajan as a defender of the ''status quo''. In his third kingship oration, Dio describes an ideal king ruling by means of "friendship"that is, through patronage and a network of local notables who act as mediators between the ruled and the ruler. Dio's notion of being "friend" to Trajan (or any other Roman emperor), however, was that of an ''informal'' arrangement, that involved no formal entry of such "friends" into the Roman administration. Trajan ingratiated himself with the Greek intellectual elite by recalling to Rome many (including Dio) who had been exiled by Domitian, and by returning (in a process begun by Nerva) a great deal of private property that Domitian had confiscated. He also had good dealings with Plutarch, who, as a notable of
 As a senatorial Emperor, Trajan was inclined to choose his local base of political support from among the members of the ruling urban oligarchies. In the West, that meant local senatorial families like his own. In the East, that meant the families of Greek notables. The Greeks, though, had their own memories of independenceand a commonly acknowledged sense of cultural superiorityand, instead of seeing themselves as Roman, disdained Roman rule. What the Greek oligarchies wanted from Rome was, above all, to be left in peace, to be allowed to exert their right to self-government (i.e., to be excluded from the provincial government, as was Italy) and to concentrate on their local interests. This was something the Romans were not disposed to do as from their perspective the Greek notables were shunning their responsibilities in regard to the management of Imperial affairsprimarily in failing to keep the common people under control, thus creating the need for the Roman governor to intervene. An excellent example of this Greek alienation was the personal role played by Dio of Prusa in his relationship with Trajan. Dio is described by Philostratus as Trajan's close friend, and Trajan as supposedly engaging publicly in conversations with Dio.
Nevertheless, as a Greek local magnate with a taste for costly building projects and pretensions of being an important political agent for Rome, Dio of Prusa was actually a target for one of Trajan's authoritarian innovations: the appointing of imperial ''correctores'' to audit the civic finances of the technically free Greek cities. The main goal was to curb the overenthusiastic spending on public works that served to channel ancient rivalries between neighbouring cities. As Pliny wrote to Trajan, this had as its most visible consequence a trail of unfinished or ill-kept public utilities. Competition among Greek cities and their ruling oligarchies was mainly for marks of pre-eminence, especially for titles bestowed by the Roman emperor. Such titles were ordered in a ranking system that determined how the cities were to be outwardly treated by Rome. The usual form that such rivalries took was that of grandiose building plans, giving the cities the opportunity to vie with each other over "extravagant, needless... structures that would make a show". A side effect of such extravagant spending was that junior and thus less wealthy members of the local oligarchies felt disinclined to present themselves to fill posts as local magistrates, positions that involved ever-increasing personal expense. Roman authorities liked to play the Greek cities against one anothersomething of which Dio of Prusa was fully aware:
These same Roman authorities had also an interest in assuring the cities' solvency and therefore ready collection of Imperial taxes. Last but not least, inordinate spending on civic buildings was not only a means to achieve local superiority, but also a means for the local Greek elites to maintain a separate cultural identitysomething expressed in the contemporary rise of the Second Sophistic; this "cultural patriotism" acted as a kind of substitute for the loss of political independence, and as such was shunned by Roman authorities. As Trajan himself wrote to Pliny: "These poor Greeks all love a gymnasium... they will have to content with one that suits their real needs". The first known ''corrector'' was charged with a commission "to deal with the situation of the free cities", as it was felt that the old method of ''ad hoc'' intervention by the Emperor and/or the proconsuls had not been enough to curb the pretensions of the Greek notables. It is noteworthy that an embassy from Dio's city of Prusa was not favourably received by Trajan, and that this had to do with Dio's chief objective, which was to elevate Prusa to the status of a free city, an "independent" city-state exempt from paying taxes to Rome. Eventually, Dio gained for Prusa the right to become the head of the assize-district, conventus (meaning that Prusans did not have to travel to be judged by the Roman governor), but ''eleutheria'' (freedom, in the sense of full political autonomy) was denied.
Eventually, it fell to Pliny, as imperial governor of Bithynia in 110AD, to deal with the consequences of the financial mess wrought by Dio and his fellow civic officials. "It's well established that
As a senatorial Emperor, Trajan was inclined to choose his local base of political support from among the members of the ruling urban oligarchies. In the West, that meant local senatorial families like his own. In the East, that meant the families of Greek notables. The Greeks, though, had their own memories of independenceand a commonly acknowledged sense of cultural superiorityand, instead of seeing themselves as Roman, disdained Roman rule. What the Greek oligarchies wanted from Rome was, above all, to be left in peace, to be allowed to exert their right to self-government (i.e., to be excluded from the provincial government, as was Italy) and to concentrate on their local interests. This was something the Romans were not disposed to do as from their perspective the Greek notables were shunning their responsibilities in regard to the management of Imperial affairsprimarily in failing to keep the common people under control, thus creating the need for the Roman governor to intervene. An excellent example of this Greek alienation was the personal role played by Dio of Prusa in his relationship with Trajan. Dio is described by Philostratus as Trajan's close friend, and Trajan as supposedly engaging publicly in conversations with Dio.
Nevertheless, as a Greek local magnate with a taste for costly building projects and pretensions of being an important political agent for Rome, Dio of Prusa was actually a target for one of Trajan's authoritarian innovations: the appointing of imperial ''correctores'' to audit the civic finances of the technically free Greek cities. The main goal was to curb the overenthusiastic spending on public works that served to channel ancient rivalries between neighbouring cities. As Pliny wrote to Trajan, this had as its most visible consequence a trail of unfinished or ill-kept public utilities. Competition among Greek cities and their ruling oligarchies was mainly for marks of pre-eminence, especially for titles bestowed by the Roman emperor. Such titles were ordered in a ranking system that determined how the cities were to be outwardly treated by Rome. The usual form that such rivalries took was that of grandiose building plans, giving the cities the opportunity to vie with each other over "extravagant, needless... structures that would make a show". A side effect of such extravagant spending was that junior and thus less wealthy members of the local oligarchies felt disinclined to present themselves to fill posts as local magistrates, positions that involved ever-increasing personal expense. Roman authorities liked to play the Greek cities against one anothersomething of which Dio of Prusa was fully aware:
These same Roman authorities had also an interest in assuring the cities' solvency and therefore ready collection of Imperial taxes. Last but not least, inordinate spending on civic buildings was not only a means to achieve local superiority, but also a means for the local Greek elites to maintain a separate cultural identitysomething expressed in the contemporary rise of the Second Sophistic; this "cultural patriotism" acted as a kind of substitute for the loss of political independence, and as such was shunned by Roman authorities. As Trajan himself wrote to Pliny: "These poor Greeks all love a gymnasium... they will have to content with one that suits their real needs". The first known ''corrector'' was charged with a commission "to deal with the situation of the free cities", as it was felt that the old method of ''ad hoc'' intervention by the Emperor and/or the proconsuls had not been enough to curb the pretensions of the Greek notables. It is noteworthy that an embassy from Dio's city of Prusa was not favourably received by Trajan, and that this had to do with Dio's chief objective, which was to elevate Prusa to the status of a free city, an "independent" city-state exempt from paying taxes to Rome. Eventually, Dio gained for Prusa the right to become the head of the assize-district, conventus (meaning that Prusans did not have to travel to be judged by the Roman governor), but ''eleutheria'' (freedom, in the sense of full political autonomy) was denied.
Eventually, it fell to Pliny, as imperial governor of Bithynia in 110AD, to deal with the consequences of the financial mess wrought by Dio and his fellow civic officials. "It's well established that
 Some historians attribute the construction or reconstruction of
Some historians attribute the construction or reconstruction of
 Trajan took the Roman empire to its greatest expanse. The earliest conquests were Rome's two wars against Dacia, an area that had troubled Roman politics for over a decade in regard to the unstable peace negotiated by Domitian's ministers with the powerful Dacian king Decebalus. Dacia would be reduced by Trajan's Rome to a
Trajan took the Roman empire to its greatest expanse. The earliest conquests were Rome's two wars against Dacia, an area that had troubled Roman politics for over a decade in regard to the unstable peace negotiated by Domitian's ministers with the powerful Dacian king Decebalus. Dacia would be reduced by Trajan's Rome to a  Prior to the campaign, Trajan had raised two entirely new legions: II Traianawhich, however, may have been posted in the East, at the Syrian port of Laodiceaand XXX Ulpia Victrix, which was posted to Brigetio, in
Prior to the campaign, Trajan had raised two entirely new legions: II Traianawhich, however, may have been posted in the East, at the Syrian port of Laodiceaand XXX Ulpia Victrix, which was posted to Brigetio, in  Trajan built a new city, Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa, on another site (north of the hill citadel holding the previous Dacian capital), although bearing the same full name, Sarmizegetusa. This capital city was conceived as a purely civilian administrative centre and was provided the usual Romanized administrative apparatus ( decurions, aediles, etc.). Urban life in Roman Dacia seems to have been restricted to Roman colonists, mostly military veterans; there is no extant evidence for the existence in the province of peregrine cities. Native Dacians continued to live in scattered rural settlements, according to their own ways. In another arrangement with no parallels in any other Roman province, the existing quasi-urban Dacian settlements disappeared after the Roman conquest.
A number of unorganized urban settlements ( ''vici'') developed around military encampments in Dacia proper – the most important being Apulum – but were only acknowledged as cities proper well after Trajan's reign. The main regional effort of urbanization was concentrated by Trajan at the rearguard, in Moesia, where he created the new cities of Nicopolis ad Istrum and Marcianopolis. A vicus was also created around the Tropaeum Traianum. The garrison city of Oescus received the status of Roman colony after its
Trajan built a new city, Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa, on another site (north of the hill citadel holding the previous Dacian capital), although bearing the same full name, Sarmizegetusa. This capital city was conceived as a purely civilian administrative centre and was provided the usual Romanized administrative apparatus ( decurions, aediles, etc.). Urban life in Roman Dacia seems to have been restricted to Roman colonists, mostly military veterans; there is no extant evidence for the existence in the province of peregrine cities. Native Dacians continued to live in scattered rural settlements, according to their own ways. In another arrangement with no parallels in any other Roman province, the existing quasi-urban Dacian settlements disappeared after the Roman conquest.
A number of unorganized urban settlements ( ''vici'') developed around military encampments in Dacia proper – the most important being Apulum – but were only acknowledged as cities proper well after Trajan's reign. The main regional effort of urbanization was concentrated by Trajan at the rearguard, in Moesia, where he created the new cities of Nicopolis ad Istrum and Marcianopolis. A vicus was also created around the Tropaeum Traianum. The garrison city of Oescus received the status of Roman colony after its  Defence of the province was entrusted to a single legion, the XIII Gemina, stationed at Apulum, which functioned as an advance guard that could, in case of need, strike either west or east at the Sarmatians living at the borders. Therefore, the indefensible character of the province did not appear to be a problem for Trajan, as the province was conceived more as a sally-base for further attacks. Even in the absence of further Roman expansion, the value of the province depended on Roman overall strength: while Rome was strong, the Dacian salient was an instrument of military and diplomatic control over the Danubian lands; when Rome was weak, as during the Crisis of the Third Century, the province became a liability and was eventually abandoned. Trajan resettled Dacia with Romans and annexed it as a province of the Roman Empire. Aside from their enormous booty (over half a million slaves, according to John Lydus), Trajan's Dacian campaigns benefited the Empire's finances through the acquisition of Dacia's gold mines, managed by an imperial procurator of equestrian rank (''procurator aurariarum''). On the other hand, commercial agricultural exploitation on the villa model, based on the centralized management of a huge landed estate by a single owner (''fundus'') was poorly developed. Therefore, use of slave labor in the province itself seems to have been relatively undeveloped, and epigraphic evidence points to work in the gold mines being conducted by means of labor contracts (''locatio conductio rei'') and seasonal wage-earning. The victory was commemorated by the construction both of the 102 cenotaph generally known as the Tropaeum Traiani in Moesia, as well of the much later (113) Trajan's Column in Rome, the latter depicting in stone carved bas-reliefs the Dacian Wars' most important moments.
Defence of the province was entrusted to a single legion, the XIII Gemina, stationed at Apulum, which functioned as an advance guard that could, in case of need, strike either west or east at the Sarmatians living at the borders. Therefore, the indefensible character of the province did not appear to be a problem for Trajan, as the province was conceived more as a sally-base for further attacks. Even in the absence of further Roman expansion, the value of the province depended on Roman overall strength: while Rome was strong, the Dacian salient was an instrument of military and diplomatic control over the Danubian lands; when Rome was weak, as during the Crisis of the Third Century, the province became a liability and was eventually abandoned. Trajan resettled Dacia with Romans and annexed it as a province of the Roman Empire. Aside from their enormous booty (over half a million slaves, according to John Lydus), Trajan's Dacian campaigns benefited the Empire's finances through the acquisition of Dacia's gold mines, managed by an imperial procurator of equestrian rank (''procurator aurariarum''). On the other hand, commercial agricultural exploitation on the villa model, based on the centralized management of a huge landed estate by a single owner (''fundus'') was poorly developed. Therefore, use of slave labor in the province itself seems to have been relatively undeveloped, and epigraphic evidence points to work in the gold mines being conducted by means of labor contracts (''locatio conductio rei'') and seasonal wage-earning. The victory was commemorated by the construction both of the 102 cenotaph generally known as the Tropaeum Traiani in Moesia, as well of the much later (113) Trajan's Column in Rome, the latter depicting in stone carved bas-reliefs the Dacian Wars' most important moments.
 In 113, Trajan embarked on his last campaign, provoked by Parthia's decision to put an unacceptable king on the throne of Armenia, a kingdom over which the two great empires had shared hegemony since the time of Nero some fifty years earlier. Trajan, already in Syria early in 113, consistently refused to accept diplomatic approaches from the Parthians intended to settle the Armenian imbroglio peacefully. As the surviving literary accounts of Trajan's Parthian War are fragmentary and scattered, it is difficult to assign them a proper context, something that has led to a long-running controversy about its precise happenings and ultimate aims.
In 113, Trajan embarked on his last campaign, provoked by Parthia's decision to put an unacceptable king on the throne of Armenia, a kingdom over which the two great empires had shared hegemony since the time of Nero some fifty years earlier. Trajan, already in Syria early in 113, consistently refused to accept diplomatic approaches from the Parthians intended to settle the Armenian imbroglio peacefully. As the surviving literary accounts of Trajan's Parthian War are fragmentary and scattered, it is difficult to assign them a proper context, something that has led to a long-running controversy about its precise happenings and ultimate aims.
 In his Dacian conquests, Trajan had already resorted to Syrian auxiliary units, whose veterans, along with Syrian traders, had an important role in the subsequent colonization of Dacia. He had recruited Palmyrene units into his army, including a camel unit, therefore apparently procuring Palmyrene support to his ultimate goal of annexing Charax. It has even been ventured that, when earlier in his campaign Trajan annexed Armenia, he was bound to annex the whole of Mesopotamia lest the Parthians interrupt the flux of trade from the Persian Gulf and/or foment trouble at the Roman frontier on the Danube. Other historians reject these motives, as the supposed Parthian "control" over the maritime Far Eastern trade route was, at best, conjectural and based on a selective reading of Chinese sourcestrade by land through Parthia seems to have been unhampered by Parthian authorities and left solely to the devices of private enterprise. Commercial activity in second century Mesopotamia seems to have been a general phenomenon, shared by many peoples within and without the Roman Empire, with no sign of a concerted Imperial policy towards it.
As in the case of the ''alimenta'', scholars like Moses Finley and Paul Veyne have considered the whole idea of a foreign trade "policy" behind Trajan's war anachronistic: according to them, the sole Roman concern with the Far Eastern luxuries tradebesides collecting toll taxes and customswas moral and involved frowning upon the "softness" of luxuries, but no economic policy. In the absence of conclusive evidence, trade between Rome and India might have been far more balanced, in terms of quantities of precious metals exchanged: one of our sources for the notion of the Roman gold drainPliny's the Younger's uncle Pliny the Elderhad earlier described the
In his Dacian conquests, Trajan had already resorted to Syrian auxiliary units, whose veterans, along with Syrian traders, had an important role in the subsequent colonization of Dacia. He had recruited Palmyrene units into his army, including a camel unit, therefore apparently procuring Palmyrene support to his ultimate goal of annexing Charax. It has even been ventured that, when earlier in his campaign Trajan annexed Armenia, he was bound to annex the whole of Mesopotamia lest the Parthians interrupt the flux of trade from the Persian Gulf and/or foment trouble at the Roman frontier on the Danube. Other historians reject these motives, as the supposed Parthian "control" over the maritime Far Eastern trade route was, at best, conjectural and based on a selective reading of Chinese sourcestrade by land through Parthia seems to have been unhampered by Parthian authorities and left solely to the devices of private enterprise. Commercial activity in second century Mesopotamia seems to have been a general phenomenon, shared by many peoples within and without the Roman Empire, with no sign of a concerted Imperial policy towards it.
As in the case of the ''alimenta'', scholars like Moses Finley and Paul Veyne have considered the whole idea of a foreign trade "policy" behind Trajan's war anachronistic: according to them, the sole Roman concern with the Far Eastern luxuries tradebesides collecting toll taxes and customswas moral and involved frowning upon the "softness" of luxuries, but no economic policy. In the absence of conclusive evidence, trade between Rome and India might have been far more balanced, in terms of quantities of precious metals exchanged: one of our sources for the notion of the Roman gold drainPliny's the Younger's uncle Pliny the Elderhad earlier described the  The alternative view is to see the campaign as triggered by the lure of territorial annexation and prestige, the sole motive ascribed by Cassius Dio. As far as territorial conquest involved tax-collecting, especially of the 25% tax levied on all goods entering the Roman Empire, the ''tetarte'', one can say that Trajan's Parthian War had an "economic" motive. Also, there was the propaganda value of an Eastern conquest that would emulate, in Roman fashion, those of Alexander the Great. The fact that emissaries from the
The alternative view is to see the campaign as triggered by the lure of territorial annexation and prestige, the sole motive ascribed by Cassius Dio. As far as territorial conquest involved tax-collecting, especially of the 25% tax levied on all goods entering the Roman Empire, the ''tetarte'', one can say that Trajan's Parthian War had an "economic" motive. Also, there was the propaganda value of an Eastern conquest that would emulate, in Roman fashion, those of Alexander the Great. The fact that emissaries from the
 The chronology of subsequent events is uncertain, but it is generally believed that early in 115 Trajan launched a Mesopotamian campaign, marching down towards the Taurus mountains in order to consolidate territory between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. He placed permanent garrisons along the way to secure the territory. While Trajan moved from west to east, Lusius Quietus moved with his army from the Caspian Sea towards the west, both armies performing a successful pincer movement, whose apparent result was to establish a Roman presence into the Parthian Empire proper, with Trajan taking the northern Mesopotamian cities of Nisibis and Batnae and organizing a province of Mesopotamia, including the Kingdom of Osrhoenewhere King Abgar VII submitted to Trajan publiclyas a Roman protectorate. This process seems to have been completed at the beginning of 116, when coins were issued announcing that Armenia and Mesopotamia had been put under the authority of the Roman people. The area between the Khabur River and the mountains around Singara seems to have been considered as the new frontier, and as such received a road surrounded by fortresses.
After wintering in Antioch during 115/116 and, according to literary sources, barely escaping from a violent earthquake that claimed the life of one of the consuls, Marcus Pedo VirgilianusTrajan again took to the field in 116, with a view to the conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia, an overambitious goal that eventually backfired on the results of his entire campaign. According to some modern historians, the aim of the campaign of 116 was to achieve a "pre-emptive demonstration" aiming not toward the conquest of Parthia, but for tighter Roman control over the Eastern trade route. However, the overall scarcity of manpower for the Roman military establishment meant that the campaign was doomed from the start. It is noteworthy that no new legions were raised by Trajan before the Parthian campaign, maybe because the sources of new citizen recruits were already over-exploited.
As far as the sources allow a description of this campaign, it seems that one Roman division crossed the Tigris into Adiabene, sweeping south and capturing Adenystrae; a second followed the river south, capturing
The chronology of subsequent events is uncertain, but it is generally believed that early in 115 Trajan launched a Mesopotamian campaign, marching down towards the Taurus mountains in order to consolidate territory between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. He placed permanent garrisons along the way to secure the territory. While Trajan moved from west to east, Lusius Quietus moved with his army from the Caspian Sea towards the west, both armies performing a successful pincer movement, whose apparent result was to establish a Roman presence into the Parthian Empire proper, with Trajan taking the northern Mesopotamian cities of Nisibis and Batnae and organizing a province of Mesopotamia, including the Kingdom of Osrhoenewhere King Abgar VII submitted to Trajan publiclyas a Roman protectorate. This process seems to have been completed at the beginning of 116, when coins were issued announcing that Armenia and Mesopotamia had been put under the authority of the Roman people. The area between the Khabur River and the mountains around Singara seems to have been considered as the new frontier, and as such received a road surrounded by fortresses.
After wintering in Antioch during 115/116 and, according to literary sources, barely escaping from a violent earthquake that claimed the life of one of the consuls, Marcus Pedo VirgilianusTrajan again took to the field in 116, with a view to the conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia, an overambitious goal that eventually backfired on the results of his entire campaign. According to some modern historians, the aim of the campaign of 116 was to achieve a "pre-emptive demonstration" aiming not toward the conquest of Parthia, but for tighter Roman control over the Eastern trade route. However, the overall scarcity of manpower for the Roman military establishment meant that the campaign was doomed from the start. It is noteworthy that no new legions were raised by Trajan before the Parthian campaign, maybe because the sources of new citizen recruits were already over-exploited.
As far as the sources allow a description of this campaign, it seems that one Roman division crossed the Tigris into Adiabene, sweeping south and capturing Adenystrae; a second followed the river south, capturing  According to late literary sources (not backed by numismatic or inscriptional evidence) a province of Assyria was also proclaimed, apparently covering the territory of Adiabene. Some measures seem to have been considered regarding the fiscal administration of Indian tradeor simply about the payment of customs (''portoria'') on goods traded on the Euphrates and Tigris. It is possible that it was this "streamlining" of the administration of the newly conquered lands according to the standard pattern of Roman provincial administration in tax collecting, requisitions and the handling of local potentates' prerogatives, that triggered later resistance against Trajan. According to some modern historians, Trajan might have busied himself during his stay on the Persian Gulf with ordering raids on the Parthian coasts, as well as probing into extending Roman suzerainty over the mountaineer tribes holding the passes across the Zagros Mountains into the Iranian plateau eastward, as well as establishing some sort of direct contact between Rome and the Kushan Empire. No attempt was made to expand into the Iranian Plateau itself, where the Roman army, with its relative weakness in cavalry, would have been at a disadvantage.
Trajan left the Persian Gulf for Babylonwhere he intended to offer sacrifice to Alexander in the house where he had died in 323BCBennett, Trajan, 199 But a revolt led by Sanatruces, a nephew of the Parthian king Osroes I who had retained a cavalry force, possibly strengthened by the addition of Saka archers, imperilled Roman positions in Mesopotamia and Armenia. Trajan sought to deal with this by forsaking direct Roman rule in Parthia proper, at least partially. Trajan sent two armies towards Northern Mesopotamia: the first, under Lusius Quietus, recovered Nisibis and
According to late literary sources (not backed by numismatic or inscriptional evidence) a province of Assyria was also proclaimed, apparently covering the territory of Adiabene. Some measures seem to have been considered regarding the fiscal administration of Indian tradeor simply about the payment of customs (''portoria'') on goods traded on the Euphrates and Tigris. It is possible that it was this "streamlining" of the administration of the newly conquered lands according to the standard pattern of Roman provincial administration in tax collecting, requisitions and the handling of local potentates' prerogatives, that triggered later resistance against Trajan. According to some modern historians, Trajan might have busied himself during his stay on the Persian Gulf with ordering raids on the Parthian coasts, as well as probing into extending Roman suzerainty over the mountaineer tribes holding the passes across the Zagros Mountains into the Iranian plateau eastward, as well as establishing some sort of direct contact between Rome and the Kushan Empire. No attempt was made to expand into the Iranian Plateau itself, where the Roman army, with its relative weakness in cavalry, would have been at a disadvantage.
Trajan left the Persian Gulf for Babylonwhere he intended to offer sacrifice to Alexander in the house where he had died in 323BCBennett, Trajan, 199 But a revolt led by Sanatruces, a nephew of the Parthian king Osroes I who had retained a cavalry force, possibly strengthened by the addition of Saka archers, imperilled Roman positions in Mesopotamia and Armenia. Trajan sought to deal with this by forsaking direct Roman rule in Parthia proper, at least partially. Trajan sent two armies towards Northern Mesopotamia: the first, under Lusius Quietus, recovered Nisibis and
 Shortly afterwards, the Jews inside the Eastern Roman Empire, in Egypt, Cyprus, and Cyrenethis last province being probably the original trouble hotspotrose up in what probably was an outburst of religious rebellion against the local pagans, this widespread rebellion being afterwards named the Kitos War. Another rebellion flared up among the Jewish communities of Northern Mesopotamia, probably part of a general reaction against Roman occupation. Trajan was forced to withdraw his army in order to put down the revolts. He saw this withdrawal as simply a temporary setback, but he was destined never to command an army in the field again, turning his Eastern armies over to Lusius Quietus, who meanwhile (early 117) had been made governor of Judaea and might have had to deal earlier with some kind of Jewish unrest in the province. Quietus discharged his commissions successfully, so much that the war was afterward named after him''Kitus'' being a corruption of ''Quietus''. Whether or not the Kitos War theatre included Judea proper, or only the Jewish Eastern diaspora, remains doubtful in the absence of clear epigraphic and archaeological evidence. What is certain is that there was an increased Roman military presence in Judea at the time.
Quietus was promised a consulate in the following year (118) for his victories, but he was killed before this could occur, during the bloody purge that opened Hadrian's reign, in which Quietus and three other former consuls were sentenced to death after being tried on a vague charge of conspiracy by the (secret) court of the Praetorian Prefect Attianus. It has been thought that Quietus and his colleagues were executed on Hadrian's direct orders, for fear of their popular standing with the army and their close connections to Trajan. In contrast, the next prominent Roman figure in charge of the repression of the Jewish revolt, the equestrian Quintus Marcius Turbo, who had dealt with the rebel leader from Cyrene, Loukuas, retained Hadrian's trust, eventually becoming his
Shortly afterwards, the Jews inside the Eastern Roman Empire, in Egypt, Cyprus, and Cyrenethis last province being probably the original trouble hotspotrose up in what probably was an outburst of religious rebellion against the local pagans, this widespread rebellion being afterwards named the Kitos War. Another rebellion flared up among the Jewish communities of Northern Mesopotamia, probably part of a general reaction against Roman occupation. Trajan was forced to withdraw his army in order to put down the revolts. He saw this withdrawal as simply a temporary setback, but he was destined never to command an army in the field again, turning his Eastern armies over to Lusius Quietus, who meanwhile (early 117) had been made governor of Judaea and might have had to deal earlier with some kind of Jewish unrest in the province. Quietus discharged his commissions successfully, so much that the war was afterward named after him''Kitus'' being a corruption of ''Quietus''. Whether or not the Kitos War theatre included Judea proper, or only the Jewish Eastern diaspora, remains doubtful in the absence of clear epigraphic and archaeological evidence. What is certain is that there was an increased Roman military presence in Judea at the time.
Quietus was promised a consulate in the following year (118) for his victories, but he was killed before this could occur, during the bloody purge that opened Hadrian's reign, in which Quietus and three other former consuls were sentenced to death after being tried on a vague charge of conspiracy by the (secret) court of the Praetorian Prefect Attianus. It has been thought that Quietus and his colleagues were executed on Hadrian's direct orders, for fear of their popular standing with the army and their close connections to Trajan. In contrast, the next prominent Roman figure in charge of the repression of the Jewish revolt, the equestrian Quintus Marcius Turbo, who had dealt with the rebel leader from Cyrene, Loukuas, retained Hadrian's trust, eventually becoming his
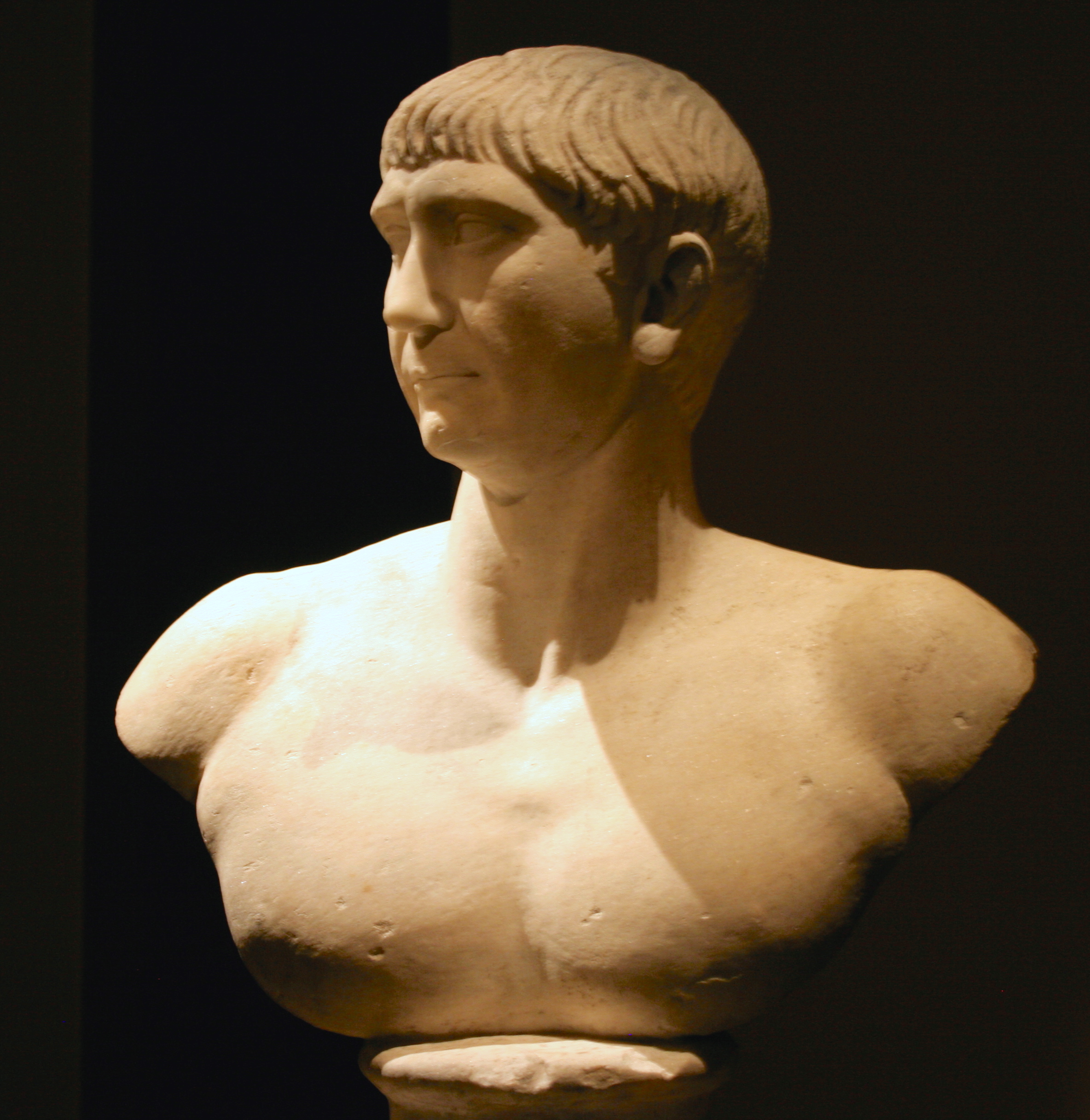 Ancient sources on Trajan's personality and accomplishments are unanimously positive. Pliny the Younger, for example, celebrates Trajan in his panegyric as a wise and just emperor and a moral man. Cassius Dio added that he always remained dignified and fair.Dio Cassius, Epitome of Book 6; 21.2–3 A third-century emperor, Decius, even received from the Senate the name Trajan as a decoration. After the setbacks of the
Ancient sources on Trajan's personality and accomplishments are unanimously positive. Pliny the Younger, for example, celebrates Trajan in his panegyric as a wise and just emperor and a moral man. Cassius Dio added that he always remained dignified and fair.Dio Cassius, Epitome of Book 6; 21.2–3 A third-century emperor, Decius, even received from the Senate the name Trajan as a decoration. After the setbacks of the
Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'' Book 68
English translation
English translation
English translation
senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history
The history of Rome includes the history of the city of Rome as well as the civilisation of ancient Rome. Roman history has been influential on the modern world, especially in the history of the Catholic Church, and Roman law has influenced ma ...
and led the empire to attain its greatest territorial extent by the time of his death. He is also known for his philanthropic rule, overseeing extensive public building programs and implementing social welfare policies, which earned him his enduring reputation as the second of the Five Good Emperors who presided over an era of peace within the Empire and prosperity in the Mediterranean world.
Trajan was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in present-day Spain, a small Roman '' municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in the province of Hispania Baetica. He came from a branch of the gens Ulpia, the ''Ulpi Traiani'', that originated in the Umbrian town of Tuder. His father Marcus Ulpius Traianus
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, also born in Italica, was a senator, and therefore Trajan was born into a senatorial family.
Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
, in 89 Trajan supported Domitian against a revolt on the Rhine led by Antonius Saturninus. In September 96, Domitian was succeeded by the old and childless Nerva
Nerva (; originally Marcus Cocceius Nerva; 8 November 30 – 27 January 98) was Roman emperor from 96 to 98. Nerva became emperor when aged almost 66, after a lifetime of imperial service under Nero and the succeeding rulers of the Flavian dy ...
, who proved to be unpopular with the army. After a brief and tumultuous year in power, culminating in a revolt by members of the Praetorian Guard, he decided to adopt the more popular Trajan as his heir and successor. Nerva died in 98 and was succeeded by his adopted son without incident.
Trajan's extensive public building program reshaped the city of Rome and left numerous enduring landmarks such as Trajan's Forum, Trajan's Market, and Trajan's Column. Early in his reign, he annexed the Nabataean Kingdom, creating the province of Arabia Petraea. His conquest of Dacia enriched the empire greatly, as the new province possessed many valuable gold mines. Trajan's war against the Parthian Empire ended with the sack of its capital Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
and the annexation of Armenia, Mesopotamia, and (possibly) Assyria. In late 117, while sailing back to Rome, Trajan fell ill and died of a stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
in the city of Selinus. He was deified by the Senate and his cousin and successor, Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
, whom Trajan had supposedly adopted while on his deathbed. According to historical tradition, Trajan's ashes were entombed in a small room beneath Trajan's Column.
Sources
As an emperor, Trajan's reputation has enduredhe is one of the few rulers whose reputation has survived nineteen centuries. Every new emperor after him was honoured by the Senate with the wish '' felicior Augusto, melior Traiano'' (that he be "luckier than Augustus and better than Trajan"). Among medieval Christian theologians, Trajan was considered a virtuous pagan. In the Renaissance, Machiavelli, speaking on the advantages of adoptive succession over heredity, mentioned the five successive good emperors "from Nerva toMarcus Marcus, Markus, Márkus or Mărcuș may refer to:
* Marcus (name), a masculine given name
* Marcus (praenomen), a Roman personal name
Places
* Marcus, a main belt asteroid, also known as (369088) Marcus 2008 GG44
* Mărcuş, a village in Dobârl� ...
"a trope out of which the 18th-century historian Edward Gibbon popularized the notion of the Five Good Emperors, of whom Trajan was the second.
An account of the Dacian Wars, the '' Commentarii de bellis Dacicis'', written by Trajan himself or a ghostwriter and modelled after Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
's '' Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', is lost with the exception of one sentence. Only fragments remain of the ''Getica'', a book by Trajan's personal physician Titus Statilius Criton
Criton of Heraclea ( el, Κρίτων, la, Titus Statilius Crito) was a 2nd-century (c. 100 AD) Greek chief physician and procurator of Roman Emperor Trajan (98–117) in the campaign in Dacia. He is perhaps the Criton mentioned in Martial's ''E ...
. The ''Parthica'', a 17-volume account of the Parthian Wars written by Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period.
''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ...
, has met a similar fate. Book68 in Cassius Dio's ''Roman History'', which survives mostly as Byzantine abridgements and epitome
An epitome (; gr, ἐπιτομή, from ἐπιτέμνειν ''epitemnein'' meaning "to cut short") is a summary or miniature form, or an instance that represents a larger reality, also used as a synonym for embodiment. Epitomacy represents "t ...
s, is the main source for the political history of Trajan's rule. Besides this, Pliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate ...
's ''Panegyricus'' and Dio Chrysostom's orations are the best surviving contemporary sources. Both are adulatory perorations, typical of the High Imperial period, that describe an idealized monarch and an equally idealized view of Trajan's rule, and concern themselves more with ideology than with fact.
The tenth volume of Pliny's letters contains his correspondence with Trajan, which deals with various aspects of imperial Roman government, but this correspondence is neither intimate nor candid: it is an exchange of official mail, in which Pliny's stance borders on the servile. It is certain that much of the text of the letters that appear in this collection over Trajan's signature was written and/or edited by Trajan's Imperial secretary, his '' ab epistulis''. Therefore, discussion of Trajan and his rule in modern historiography cannot avoid speculation. Non-literary sources such as archaeology, epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
, and numismatics are also useful for reconstructing his reign.
Early life
 Marcus Ulpius Trajanus was born on 18 September 53AD in the Roman province of Hispania BaeticaSyme, Tacitus, 30–44; PIR Vlpivs 575 (in what is now Andalusia in modern Spain), in the small roman '' municipium'' of Italica (now in the municipal area of Santiponce, in the outskirts of Seville). At the time of Trajan's birth, it was a small town, without baths, theatre and amphitheatre, and with a very narrow territory under its direct administration. His year of birth is not reliably attested and may have been 56 AD.
Some ancient authors, most notably Cassius Dio, claim that Trajan was the first emperor of non-Italic origins. However, Trajan's '' patria'' of Italica, in Spanish Baetica, was a Roman colony of Italic settlers founded in 206BC by
Marcus Ulpius Trajanus was born on 18 September 53AD in the Roman province of Hispania BaeticaSyme, Tacitus, 30–44; PIR Vlpivs 575 (in what is now Andalusia in modern Spain), in the small roman '' municipium'' of Italica (now in the municipal area of Santiponce, in the outskirts of Seville). At the time of Trajan's birth, it was a small town, without baths, theatre and amphitheatre, and with a very narrow territory under its direct administration. His year of birth is not reliably attested and may have been 56 AD.
Some ancient authors, most notably Cassius Dio, claim that Trajan was the first emperor of non-Italic origins. However, Trajan's '' patria'' of Italica, in Spanish Baetica, was a Roman colony of Italic settlers founded in 206BC by Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–183 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the best military com ...
. Trajan's paternal branch of the gens Ulpia came from Umbria, particularly from the city of ''Tuder'' ( Todi), and was either among the original settlers of the town or arrived there at an unknown time, and his maternal gens Marcia was of Sabine origin. For this reason, modern historians, such as Julian Bennett, reject Dio's claim. It is possible, but cannot be substantiated, that Trajan's ancestors married locals and lost their citizenship at some point, but they would have certainly recovered their status when the city became a municipium with Latin citizenship
Latin rights (also Latin citizenship, Latin: ''ius Latii'' or ''ius latinum'') were a set of legal rights that were originally granted to the Latins (Latin: "Latini", the People of Latium, the land of the Latins) under Roman law in their origi ...
in the mid-1st century BC. Trajan was the son of Marcia, a Roman noblewoman and sister-in-law of the second Flavian Emperor Titus, and Marcus Ulpius Trajanus, a prominent senator and general from the '' gens Ulpia''. Marcus Ulpius Trajanus the elder served Vespasian in the First Jewish-Roman War, commanding the '' Legio X ''Fretensis''''.
Trajan himself was just one of many well-known Ulpii in a line that continued long after his own death. His elder sister was Ulpia Marciana, and his niece was Salonia Matidia
Salonia Matidia (4 July 68 – 23 December 119) was the daughter and only child of Ulpia Marciana and wealthy praetor Gaius Salonius Matidius Patruinus. Her maternal uncle was the Roman emperor Trajan. Trajan had no children and treated her like ...
. Very little is known about Trajan's early formative years, but it is thought likely that he spent his first months or years in Italica before moving to Rome and then, perhaps at around eight or nine years of age, he almost certainly would have returned temporarily to Italica with his father during Trajanus’ governorship of Baetica (ca. 64–65). The lack of a strong local power base caused by the size of the town from which they came, made it necessary for the Ulpii (and for the Aelii, the other important senatorial family of Italica with whom they were allied) to weave local alliances, in the Baetica (with the Annii, the Ucubi and perhaps the Dasumii from Corduba), the Tarraconense and the Narbonense, here above all through Pompeia Plotina, Trajan's wife. Many of these alliances were made not in Spain, but in Rome.
The family home in Rome, the Domus Traiana, was on the Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill (; la, Collis Aventinus; it, Aventino ) is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth ''rione'', or ward, of Rome.
Location and boundaries
The Aventine Hill is the sou ...
, and excavation findings under a car park in the Piazza del Tempio di Diana are thought to be the family's large suburban villa with exquisitely decorated rooms.
Military career
 As a young man, Trajan rose through the ranks of the
As a young man, Trajan rose through the ranks of the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval continu ...
, serving in some of the most contested parts of the Empire's frontier. In 7677, his father was Governor of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
('' Legatus pro praetore Syriae''), where Trajan himself remained as '' Tribunus legionis''. From there, after his father's replacement, he seems to have been transferred to an unspecified Rhine province, and Pliny implies that he engaged in active combat duty during both commissions. In about 86, Trajan's cousin Aelius Afer died, leaving his young children Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
and Paulina
Paulina or Paullina (, ) was a name shared by three relatives of the Roman Emperor Hadrian: his mother, his elder sister and his niece.
Mother of Hadrian
Domitia Paulina or Paullina, Domitia Paulina Major or Paulina Major, (''Major'' Latin fo ...
orphans. Trajan and his colleague Publius Acilius Attianus became co-guardians of the two children. Trajan, in his late thirties, was created ordinary Consul for the year 91. The minimum legal age for that position was 32. This early appointment may reflect the prominence of his father's career, as his father had been instrumental to the ascent of the ruling Flavian dynasty, held consular rank himself and had just been made a patrician. Around this time Trajan brought the architect and engineer Apollodorus of Damascus with him to Rome,Augustan History, ''Life of Hadrian'2.5–6
/ref> and married Pompeia Plotina, a noblewoman from the Roman settlement at
Nîmes
Nîmes ( , ; oc, Nimes ; Latin: ''Nemausus'') is the prefecture of the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and Cévennes, the commune of Nîmes has an estimated population of 148,5 ...
; the marriage ultimately remained childless.
Dio Cassius later noted that Trajan was a lover of young men, in contrast to the usual bisexual
Bisexuality is a romantic or sexual attraction or behavior toward both males and females, or to more than one gender. It may also be defined to include romantic or sexual attraction to people regardless of their sex or gender identity, whi ...
activity that was common among upper class Roman men of the period. The Emperor Julian also made a sardonic reference to his predecessor's sexual preference, stating that Zeus himself would have had to be on guard had his Ganymede come within Trajan's vicinity. This distaste reflected a change of mores that began with the Severan dynasty, Trajan's putative lovers included the future emperor Hadrian, pages of the imperial household, the actor Pylades, a dancer called Apolaustus, Lucius Licinius Sura, and Trajan's predecessor Nerva. Cassius Dio also relates that Trajan made an ally out of Abgar VII on account of the latter's beautiful son, Arbandes, who would then dance for Trajan at a banquet. The details of Trajan's early military career are obscure, save for the fact that in 89, as legate of Legio VII Gemina in Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
, he supported Domitian against an attempted ''coup'' by Lucius Antonius Saturninus, the governor of Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio' ...
. Trajan probably remained in the region after the revolt was quashed, to engage with the Chatti who had sided with Saturninus, before returning the VII Gemina legion to Legio in Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
. In 91 he held a consulate with Acilius Glabrio Acilius Glabrio may refer to:
* Manius Acilius Glabrio (disambiguation)
* Marcus Acilius Glabrio (consul 33 BC)
* Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus, Roman senator
See also
*
* Acilia gens
The gens Acilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, t ...
, a rarity in that neither consul was a member of the ruling dynasty. He held an unspecified consular commission as governor of either Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
or Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio' ...
, or possibly both. Plinywho seems to deliberately avoid offering details that would stress personal attachment between Trajan and the "tyrant" Domitianattributes to him, at the time, various (and unspecified) feats of arms.
Rise to power
Domitian's successor,Nerva
Nerva (; originally Marcus Cocceius Nerva; 8 November 30 – 27 January 98) was Roman emperor from 96 to 98. Nerva became emperor when aged almost 66, after a lifetime of imperial service under Nero and the succeeding rulers of the Flavian dy ...
, was unpopular with the army, and had been forced by his Praetorian Prefect Casperius Aelianus to execute Domitian's killers. Nerva needed the army's support to avoid being ousted. He accomplished this in the summer of 97 by naming Trajan as his adoptive son and successor, claiming that this was entirely due to Trajan's outstanding military merits. There are hints, however, in contemporary literary sources that Trajan's adoption was imposed on Nerva. Pliny implied as much when he wrote that, although an emperor could not be coerced into doing something, if this was the way in which Trajan was raised to power, then it was worth it. Alice König argues that the notion of a natural continuity between Nerva's and Trajan's reigns was an ''ex post facto'' fiction developed by authors writing under Trajan, including Tacitus and Pliny.
According to the ''Augustan History
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
'', the future Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
brought word to Trajan of his adoption. Trajan retained Hadrian on the Rhine frontier as a military tribune, and Hadrian thus became privy to the circle of friends and relations with whom Trajan surrounded himself. Among them was the governor of Germania Inferior, the Spaniard Lucius Licinius Sura, who became Trajan's chief personal adviser and official friend. Sura was highly influential, and was appointed consul for third term in 107. Some senators may have resented Sura's activities as a kingmaker
A kingmaker is a person or group that has great influence on a royal or political succession, without themselves being a viable candidate. Kingmakers may use political, monetary, religious and military means to influence the succession. Origina ...
and éminence grise, among them the historian Tacitus, who acknowledged Sura's military and oratorical talents, but compared his rapacity and devious ways to those of Vespasian's éminence grise Licinius Mucianus. Sura is said to have informed Hadrian in 108 that he had been chosen as Trajan's imperial heir.
As governor of Upper Germany (Germania Superior) during Nerva's reign, Trajan received the impressive title of ''Germanicus'' for his skilful management and rule of the volatile Imperial province. When Nerva died on 28 January 98, Trajan succeeded to the role of emperor without any outward adverse incident. The fact that he chose not to hasten towards Rome, but made a lengthy tour of inspection on the Rhine and Danube frontiers, may suggest that he was unsure of his position, both in Rome and with the armies at the front. Alternatively, Trajan's keen military mind understood the importance of strengthening the empire's frontiers. His vision for future conquests required the diligent improvement of surveillance networks, defences and transport along the Danube. Prior to his frontier tours, Trajan ordered his Prefect Aelianus to attend him in Germany, where he was apparently executed forthwith ("put out of the way"), and his now-vacant post taken by Attius Suburanus. Trajan's accession, therefore, could qualify more as a successful ''coup'' than an orderly succession.
Roman emperor
On his entry to Rome, Trajan granted theplebs
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizenship, Roman citizens who were not Patrician (ancient Rome), patricians, as determined by the capite censi, census, or in other words "commoners". Both ...
a direct gift of money. The traditional donative to the troops, however, was reduced by half. There remained the issue of the strained relations between the emperor and the Senate, especially after the supposed bloodiness that had marked Domitian's reign and his dealings with the Curia. By feigning reluctance to hold power, Trajan was able to start building a consensus around him in the Senate. His belated ceremonial entry into Rome in 99 was notably understated, something on which Pliny the Younger elaborated. By not openly supporting Domitian's preference for equestrian officers, Trajan appeared to conform to the idea (developed by Pliny) that an emperor derived his legitimacy from his adherence to traditional hierarchies and senatorial morals. Therefore, he could point to the allegedly republican character of his rule.
In a speech at the inauguration of his third consulship, on 1January 100, Trajan exhorted the Senate to share the care-taking of the Empire with himan event later celebrated on a coin. In reality, Trajan did not share power in any meaningful way with the Senate, something that Pliny admits candidly: " erything depends on the whims of a single man who, on behalf of the common welfare, has taken upon himself all functions and all tasks". One of the most significant trends of his reign was his encroachment on the Senate's sphere of authority, such as his decision to make the senatorial provinces of Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaïa'' ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. The ...
and Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Pa ...
into imperial ones in order to deal with the inordinate spending on public works by local magnates and the general mismanagement of provincial affairs by various proconsuls appointed by the Senate.
''Optimus princeps''
 In the formula developed by Pliny, however, Trajan was a "good" emperor in that, by himself, he approved or blamed the same things that the Senate would have approved or blamed. If in reality Trajan was an autocrat, his deferential behavior towards his peers qualified him to be viewed as a virtuous monarch. The idea is that Trajan wielded autocratic power through ''moderatio'' instead of ''contumacia''moderation instead of insolence. In short, according to the ethics for autocracy developed by most political writers of the Imperial Roman Age, Trajan was a good ruler in that he ruled less by fear, and more by acting as a role model, for, according to Pliny, "men learn better from examples". Eventually, Trajan's popularity among his peers was such that the Roman Senate bestowed upon him the honorific of ''optimus'', meaning "the best", which appears on coins from 105 on. This title had mostly to do with Trajan's role as benefactor, such as in the case of him returning confiscated property.
Pliny states that Trajan's ideal role was a conservative one, argued as well by the orations of Dio Chrysostom—in particular his four ''Orations on Kingship'', composed early during Trajan's reign. Dio, as a Greek notable and intellectual with friends in high places, and possibly an official friend to the emperor (''amicus caesaris''), saw Trajan as a defender of the ''status quo''. In his third kingship oration, Dio describes an ideal king ruling by means of "friendship"that is, through patronage and a network of local notables who act as mediators between the ruled and the ruler. Dio's notion of being "friend" to Trajan (or any other Roman emperor), however, was that of an ''informal'' arrangement, that involved no formal entry of such "friends" into the Roman administration. Trajan ingratiated himself with the Greek intellectual elite by recalling to Rome many (including Dio) who had been exiled by Domitian, and by returning (in a process begun by Nerva) a great deal of private property that Domitian had confiscated. He also had good dealings with Plutarch, who, as a notable of
In the formula developed by Pliny, however, Trajan was a "good" emperor in that, by himself, he approved or blamed the same things that the Senate would have approved or blamed. If in reality Trajan was an autocrat, his deferential behavior towards his peers qualified him to be viewed as a virtuous monarch. The idea is that Trajan wielded autocratic power through ''moderatio'' instead of ''contumacia''moderation instead of insolence. In short, according to the ethics for autocracy developed by most political writers of the Imperial Roman Age, Trajan was a good ruler in that he ruled less by fear, and more by acting as a role model, for, according to Pliny, "men learn better from examples". Eventually, Trajan's popularity among his peers was such that the Roman Senate bestowed upon him the honorific of ''optimus'', meaning "the best", which appears on coins from 105 on. This title had mostly to do with Trajan's role as benefactor, such as in the case of him returning confiscated property.
Pliny states that Trajan's ideal role was a conservative one, argued as well by the orations of Dio Chrysostom—in particular his four ''Orations on Kingship'', composed early during Trajan's reign. Dio, as a Greek notable and intellectual with friends in high places, and possibly an official friend to the emperor (''amicus caesaris''), saw Trajan as a defender of the ''status quo''. In his third kingship oration, Dio describes an ideal king ruling by means of "friendship"that is, through patronage and a network of local notables who act as mediators between the ruled and the ruler. Dio's notion of being "friend" to Trajan (or any other Roman emperor), however, was that of an ''informal'' arrangement, that involved no formal entry of such "friends" into the Roman administration. Trajan ingratiated himself with the Greek intellectual elite by recalling to Rome many (including Dio) who had been exiled by Domitian, and by returning (in a process begun by Nerva) a great deal of private property that Domitian had confiscated. He also had good dealings with Plutarch, who, as a notable of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
, seems to have been favoured by the decisions taken on behalf of his home-place by one of Trajan's legates, who had arbitrated a boundary dispute between Delphi and its neighbouring cities.
However, it was clear to Trajan that Greek intellectuals and notables were to be regarded as tools for local administration, and not be allowed to fancy themselves in a privileged position. As Pliny said in one of his letters at the time, it was official policy that Greek civic elites be treated according to their status as notionally free but not put on an equal footing with their Roman rulers. When the city of Apamea complained of an audit of its accounts by Pliny, alleging its "free" status as a Roman colony, Trajan replied by writing that it was by his own wish that such inspections had been ordered. Concern about independent local political activity is seen in Trajan's decision to forbid Nicomedia from having a corps of firemen ("If people assemble for a common purpose... they soon turn it into a political society", Trajan wrote to Pliny) as well as in his and Pliny's fears about excessive civic generosities by local notables such as distribution of money or gifts.
Pliny's letters suggest that Trajan and his aides were as much bored as they were alarmed by the claims of Dio and other Greek notables to political influence based on what they saw as their "special connection" to their Roman overlords. Pliny tells of Dio of Prusa placing a statue of Trajan in a building complex where Dio's wife and son were buried – therefore incurring a charge of treason for placing the Emperor's statue near a grave. Trajan, however, dropped the charge. Nevertheless, while the office of ''corrector'' was intended as a tool to curb any hint of independent political activity among local notables in the Greek cities, the ''correctores'' themselves were all men of the highest social standing entrusted with an exceptional commission. The post seems to have been conceived partly as a reward for senators who had chosen to make a career solely on the Emperor's behalf. Therefore, in reality the post was conceived as a means for "taming" both Greek notables and Roman senators. It must be added that, although Trajan was wary of the civic oligarchies in the Greek cities, he also admitted into the Senate a number of prominent Eastern notables already slated for promotion during Domitian's reign by reserving for them one of the twenty posts open each year for minor magistrates (the '' vigintiviri''). Such must be the case of the Galatian notable and "leading member of the Greek community" (according to one inscription) Gaius Julius Severus, who was a descendant of several Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
dynasts and client kings.
Severus was the grandfather of the prominent general Gaius Julius Quadratus Bassus, consul in 105. Other prominent Eastern senators included Gaius Julius Alexander Berenicianus, a descendant of Herod the Great, suffect consul in 116. Trajan created at least fourteen new senators from the Greek-speaking half of the Empire, an unprecedented recruitment number that opens to question the issue of the "traditionally Roman" character of his reign, as well as the "Hellenism" of his successor Hadrian. But then Trajan's new Eastern senators were mostly very powerful and very wealthy men with more than local influence and much interconnected by marriage, so that many of them were not altogether "new" to the Senate. On the local level, among the lower section of the Eastern propertied, the alienation of most Greek notables and intellectuals towards Roman rule, and the fact that the Romans were seen by most such Greek notables as aliens, persisted well after Trajan's reign. One of Trajan's senatorial creations from the East, the Athenian Gaius Julius Antiochus Epiphanes Philopappos, a member of the Royal House of Commagene, left behind him a funeral monument on the Mouseion Hill
The Musaeum or Mouseion of Alexandria ( grc, Μουσεῖον τῆς Ἀλεξανδρείας; ), which arguably included the Great Library of Alexandria, was an institution said to have been founded by Ptolemy I Soter and his son Ptolemy II Ph ...
that was later disparagingly described by Pausanias as "a monument built to a Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
man".
Greek-Roman relations
 As a senatorial Emperor, Trajan was inclined to choose his local base of political support from among the members of the ruling urban oligarchies. In the West, that meant local senatorial families like his own. In the East, that meant the families of Greek notables. The Greeks, though, had their own memories of independenceand a commonly acknowledged sense of cultural superiorityand, instead of seeing themselves as Roman, disdained Roman rule. What the Greek oligarchies wanted from Rome was, above all, to be left in peace, to be allowed to exert their right to self-government (i.e., to be excluded from the provincial government, as was Italy) and to concentrate on their local interests. This was something the Romans were not disposed to do as from their perspective the Greek notables were shunning their responsibilities in regard to the management of Imperial affairsprimarily in failing to keep the common people under control, thus creating the need for the Roman governor to intervene. An excellent example of this Greek alienation was the personal role played by Dio of Prusa in his relationship with Trajan. Dio is described by Philostratus as Trajan's close friend, and Trajan as supposedly engaging publicly in conversations with Dio.
Nevertheless, as a Greek local magnate with a taste for costly building projects and pretensions of being an important political agent for Rome, Dio of Prusa was actually a target for one of Trajan's authoritarian innovations: the appointing of imperial ''correctores'' to audit the civic finances of the technically free Greek cities. The main goal was to curb the overenthusiastic spending on public works that served to channel ancient rivalries between neighbouring cities. As Pliny wrote to Trajan, this had as its most visible consequence a trail of unfinished or ill-kept public utilities. Competition among Greek cities and their ruling oligarchies was mainly for marks of pre-eminence, especially for titles bestowed by the Roman emperor. Such titles were ordered in a ranking system that determined how the cities were to be outwardly treated by Rome. The usual form that such rivalries took was that of grandiose building plans, giving the cities the opportunity to vie with each other over "extravagant, needless... structures that would make a show". A side effect of such extravagant spending was that junior and thus less wealthy members of the local oligarchies felt disinclined to present themselves to fill posts as local magistrates, positions that involved ever-increasing personal expense. Roman authorities liked to play the Greek cities against one anothersomething of which Dio of Prusa was fully aware:
These same Roman authorities had also an interest in assuring the cities' solvency and therefore ready collection of Imperial taxes. Last but not least, inordinate spending on civic buildings was not only a means to achieve local superiority, but also a means for the local Greek elites to maintain a separate cultural identitysomething expressed in the contemporary rise of the Second Sophistic; this "cultural patriotism" acted as a kind of substitute for the loss of political independence, and as such was shunned by Roman authorities. As Trajan himself wrote to Pliny: "These poor Greeks all love a gymnasium... they will have to content with one that suits their real needs". The first known ''corrector'' was charged with a commission "to deal with the situation of the free cities", as it was felt that the old method of ''ad hoc'' intervention by the Emperor and/or the proconsuls had not been enough to curb the pretensions of the Greek notables. It is noteworthy that an embassy from Dio's city of Prusa was not favourably received by Trajan, and that this had to do with Dio's chief objective, which was to elevate Prusa to the status of a free city, an "independent" city-state exempt from paying taxes to Rome. Eventually, Dio gained for Prusa the right to become the head of the assize-district, conventus (meaning that Prusans did not have to travel to be judged by the Roman governor), but ''eleutheria'' (freedom, in the sense of full political autonomy) was denied.
Eventually, it fell to Pliny, as imperial governor of Bithynia in 110AD, to deal with the consequences of the financial mess wrought by Dio and his fellow civic officials. "It's well established that
As a senatorial Emperor, Trajan was inclined to choose his local base of political support from among the members of the ruling urban oligarchies. In the West, that meant local senatorial families like his own. In the East, that meant the families of Greek notables. The Greeks, though, had their own memories of independenceand a commonly acknowledged sense of cultural superiorityand, instead of seeing themselves as Roman, disdained Roman rule. What the Greek oligarchies wanted from Rome was, above all, to be left in peace, to be allowed to exert their right to self-government (i.e., to be excluded from the provincial government, as was Italy) and to concentrate on their local interests. This was something the Romans were not disposed to do as from their perspective the Greek notables were shunning their responsibilities in regard to the management of Imperial affairsprimarily in failing to keep the common people under control, thus creating the need for the Roman governor to intervene. An excellent example of this Greek alienation was the personal role played by Dio of Prusa in his relationship with Trajan. Dio is described by Philostratus as Trajan's close friend, and Trajan as supposedly engaging publicly in conversations with Dio.
Nevertheless, as a Greek local magnate with a taste for costly building projects and pretensions of being an important political agent for Rome, Dio of Prusa was actually a target for one of Trajan's authoritarian innovations: the appointing of imperial ''correctores'' to audit the civic finances of the technically free Greek cities. The main goal was to curb the overenthusiastic spending on public works that served to channel ancient rivalries between neighbouring cities. As Pliny wrote to Trajan, this had as its most visible consequence a trail of unfinished or ill-kept public utilities. Competition among Greek cities and their ruling oligarchies was mainly for marks of pre-eminence, especially for titles bestowed by the Roman emperor. Such titles were ordered in a ranking system that determined how the cities were to be outwardly treated by Rome. The usual form that such rivalries took was that of grandiose building plans, giving the cities the opportunity to vie with each other over "extravagant, needless... structures that would make a show". A side effect of such extravagant spending was that junior and thus less wealthy members of the local oligarchies felt disinclined to present themselves to fill posts as local magistrates, positions that involved ever-increasing personal expense. Roman authorities liked to play the Greek cities against one anothersomething of which Dio of Prusa was fully aware:
These same Roman authorities had also an interest in assuring the cities' solvency and therefore ready collection of Imperial taxes. Last but not least, inordinate spending on civic buildings was not only a means to achieve local superiority, but also a means for the local Greek elites to maintain a separate cultural identitysomething expressed in the contemporary rise of the Second Sophistic; this "cultural patriotism" acted as a kind of substitute for the loss of political independence, and as such was shunned by Roman authorities. As Trajan himself wrote to Pliny: "These poor Greeks all love a gymnasium... they will have to content with one that suits their real needs". The first known ''corrector'' was charged with a commission "to deal with the situation of the free cities", as it was felt that the old method of ''ad hoc'' intervention by the Emperor and/or the proconsuls had not been enough to curb the pretensions of the Greek notables. It is noteworthy that an embassy from Dio's city of Prusa was not favourably received by Trajan, and that this had to do with Dio's chief objective, which was to elevate Prusa to the status of a free city, an "independent" city-state exempt from paying taxes to Rome. Eventually, Dio gained for Prusa the right to become the head of the assize-district, conventus (meaning that Prusans did not have to travel to be judged by the Roman governor), but ''eleutheria'' (freedom, in the sense of full political autonomy) was denied.
Eventually, it fell to Pliny, as imperial governor of Bithynia in 110AD, to deal with the consequences of the financial mess wrought by Dio and his fellow civic officials. "It's well established that he cities' finances
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
are in a state of disorder", Pliny once wrote to Trajan, plans for unnecessary works made in collusion with local contractors being identified as one of the main problems. One of the compensatory measures proposed by Pliny expressed a thoroughly Roman conservative position: as the cities' financial solvency depended on the councilmen's purses, it was necessary to have more councilmen on the local city councils. According to Pliny, the best way to achieve this was to lower the minimum age for holding a seat on the council, making it possible for more sons of the established oligarchical families to join and thus contribute to civic spending; this was seen as preferable to enrolling non-noble wealthy upstarts. Such an increase in the number of council members was granted to Dio's city of Prusa, to the dismay of existing councilmen who felt their status lowered. A similar situation existed in Claudiopolis, where a public bath was built with the proceeds from the entrance fees paid by "supernumerary" members of the council, enrolled with Trajan's permission. According to the Digest
Digest may refer to:
Biology
*Digestion of food
*Restriction digest
Literature and publications
*''The Digest'', formerly the English and Empire Digest
*Digest size magazine format
* ''Digest'' (Roman law), also known as ''Pandects'', a digest ...
, Trajan decreed that when a city magistrate promised to achieve a particular public building, his heirs inherited responsibility for its completion.
Building projects
Trajan was a prolific builder. Many of his buildings were designed and erected by the gifted architect Apollodorus of Damascus, including a massive bridge over the Danube, which the Roman army and its reinforcements could use regardless of weather; the Danube sometimes froze over in winter, but seldom enough to bear the passage of a party of soldiers. Trajan's works at theIron Gates
The Iron Gates ( ro, Porțile de Fier; sr, / or / ; Hungarian: ''Vaskapu-szoros'') is a gorge on the river Danube. It forms part of the boundary between Serbia (to the south) and Romania (north). In the broad sense it encompasses a rou ...
region of the Danube created or enlarged the boardwalk road cut into the cliff-face along the Iron Gate's gorge. A canal was built between the Danube's Kasajna tributary and Ducis Pratum Ducis may refer to:
* The genitive case of dux, the Latin word "leader" and for the title of "duke"
* Collingbourne Ducis, a small village in the English countryside
* The Duke University Center for International Studies
People:
* Jean-François D ...
, circumventing rapids and cataracts.
Trajan's Forum Traiani
Trajan's Forum ( la, Forum Traiani; it, Foro di Traiano) was the last of the Imperial fora to be constructed in ancient Rome. The architect Apollodorus of Damascus oversaw its construction.
History
This forum was built on the order of the empe ...
was Rome's largest forum. It was built to commemorate his victories in Dacia, and was largely financed from that campaign's loot. To accommodate it, parts of the Capitoline and Quirinal Hills had to be removed, the latter enlarging a clear area first established by Domitian. Apollodorus of Damascus' "magnificent" design incorporated a Triumphal arch entrance, a forum space approximately 120 m long and 90m wide, surrounded by peristyles: a monumentally sized basilica: and later, Trajan's Column and libraries. It was started in 107 AD, dedicated on 1 January 112, and remained in use for at least 500 years. It still drew admiration when Emperor Constantius II visited Rome in the fourth century. It accommodated Trajan's Market, and an adjacent brick market.
Trajan was also a prolific builder of triumphal arches, many of which survive. He built roads, such as the Via Traiana, an extension of the Via Appia from Beneventum to Brundisium and the Via Traiana Nova, a mostly military road between Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
and Aila, which Rome employed in its annexation of Nabataea and founding of Arabia Province.
 Some historians attribute the construction or reconstruction of
Some historians attribute the construction or reconstruction of Old Cairo
Old Cairo (Arabic: مصر القديمة , Miṣr al-Qadīma, Egyptian pronunciation: Maṣr El-ʾAdīma) is a historic area in Cairo, Egypt, which includes the site of a Roman-era fortress and of Islamic-era settlements pre-dating the founding of ...
's Roman fortress (also known as "Babylon Fort") to Trajan, and the building of a canal between the River Nile and the Red Sea. In Egypt, Trajan was "quite active" in constructing and embellishing buildings. He is portrayed, together with Domitian, on the propylon of the Temple of Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky g ...
at Dendera. His cartouche also appears in the column shafts of the Temple of Khnum at Esna."Trajan was, in fact, quite active in Egypt. Separate scenes of Domitian and Trajan making offerings to the gods appear on reliefs on the propylon of the Temple of Hathor at Dendera. There are cartouches of Domitian and Trajan on the column shafts of the Temple of Knum at Esna, and on the exterior a frieze text mentions Domitian, Trajan, and Hadrian"
Games
Trajan invested heavily in the provision of popular amusements. He carried out a "massive reconstruction" of the Circus Maximus, which was already the Empire's biggest and best appointed circuit for the immensely popular sport of chariot racing. The Circus also hosted religious theatrical spectacles and games, and public processions on the grandest possible scale. Trajan's reconstruction, completed by 103, was modestly described by Trajan himself as "adequate" for the Roman people. It replaced flammable wooden seating tiers with stone, and increased the Circus' already vast capacity by about 5,000 seats. Its lofty, elevated Imperial viewing box was rebuilt among the seating tiers, so that spectators could see their emperor sharing their enjoyment of the races, alongside his family and images of the gods, At some time during 108 or 109, Trajan held 123 days of games to celebrate his Dacian victory. They involved "fully 10,000"gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s, and the slaughter of thousands, "possibly tens of thousands" of animals, both wild and domestic. Trajan's careful management of public spectacles led the orator Fronto to congratulate him for paying equal attention to public entertainments and more serious issues, acknowledging that "neglect of serious matters can cause greater damage, but neglect of amusements greater discontent". State-funded public entertainments helped to maintain contentment among the populace; the more "serious matter" of the corn dole aimed to satisfy individuals.
Christians
During the period of peace that followed the Dacian war, Trajan exchanged letters with Pliny the Younger on how best to deal with the Christians of Pontus. Trajan told Pliny to continue prosecutions of Christians if they merited that, but not to accept anonymous or malicious denunciations. He considered this to be in the interests of justice, and to reflect "the spirit of the age". Non-citizens who admitted to being Christians and refused to recant were to be executed "for obstinacy". Citizens were sent to Rome for trial.Currency and welfare
In 107, Trajan devalued theRoman currency
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denomi ...
, decreasing the silver content of the denarius from 93.5% to 89.0%the actual silver weight dropping from 3.04grams to 2.88grams. This devaluation, along with the massive amounts of gold and silver acquired through his Dacian wars, allowed Trajan to mint many more denarii than his predecessors. He also withdrew from circulation silver denarii minted before Nero's devaluation. Trajan's devaluation may have had a political intent, enabling planned increases in civil and military spending. Trajan formalised the alimenta, a welfare program that helped orphans and poor children throughout Italy by providing cash, food and subsidized education. The program was supported out of Dacian War booty, estate taxes and philanthropy. The alimenta also relied indirectly on mortgages secured against Italian farms (''fundi''). Registered landowners received a lump sum from the imperial treasury, and in return were expected to repay an annual sum to support the alimentary fund.
Military campaigns
Conquest of Dacia
 Trajan took the Roman empire to its greatest expanse. The earliest conquests were Rome's two wars against Dacia, an area that had troubled Roman politics for over a decade in regard to the unstable peace negotiated by Domitian's ministers with the powerful Dacian king Decebalus. Dacia would be reduced by Trajan's Rome to a
Trajan took the Roman empire to its greatest expanse. The earliest conquests were Rome's two wars against Dacia, an area that had troubled Roman politics for over a decade in regard to the unstable peace negotiated by Domitian's ministers with the powerful Dacian king Decebalus. Dacia would be reduced by Trajan's Rome to a client kingdom
A client state, in international relations, is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as ...
in the first war (101102), followed by a second war that ended in actual incorporation into the Empire of the trans-Danube border group of Dacia. According to the provisions of Decebalus's earlier treaty with Rome, made in the time of Domitian, Decebalus was acknowledged as ''rex amicus'', that is, client king; in exchange for accepting client status, he received from Rome both a generous stipend and a steady supply of technical experts. The treaty seems to have allowed Roman troops the right of passage through the Dacian kingdom in order to attack the Marcomanni, Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
and Sarmatians. However, senatorial opinion never forgave Domitian for paying what was seen as tribute to a barbarian king. Unlike the Germanic tribes, the Dacian kingdom was an organized state capable of developing alliances of its own, thus making it a strategic threat and giving Trajan a strong motive to attack it.
In May of 101, Trajan launched his first campaign into the Dacian kingdom, crossing to the northern bank of the Danube and defeating the Dacian army at Tapae (see Second Battle of Tapae
The Second Battle of Tapae (101) was the decisive battle of the first Dacian War, in which Roman Emperor Trajan defeated the Dacian King Decebalus's army. Other setbacks in the campaign delayed its completion until 102. The battle is most lik ...
), near the Iron Gates of Transylvania. It was not a decisive victory, however. Trajan's troops took heavy losses in the encounter, and he put off further campaigning for the year in order to regroup and reinforce his army. Nevertheless, the battle was considered a Roman victory and Trajan strived to ultimately consolidate his position, including other major engagements, as well as the capture of Decebalus' sister as depicted on Trajan's Column.
The following winter, Decebalus took the initiative by launching a counter-attack across the Danube further downstream, supported by Sarmatian cavalry, forcing Trajan to come to the aid of the troops in his rearguard. The Dacians and their allies were repulsed after two battles in Moesia, at Nicopolis ad Istrum and Adamclisi. Trajan's army then advanced further into Dacian territory, and, a year later, forced Decebalus to submit. He had to renounce claim to some regions of his kingdom, return runaways from Rome then under his protection (most of them technical experts), and surrender all his war machines. Trajan returned to Rome in triumph and was granted the title ''Dacicus''. The peace of 102 had returned Decebalus to the condition of more or less harmless client king; however, he soon began to rearm, to again harbour Roman runaways, and to pressure his Western neighbours, the Iazyges Sarmatians, into allying themselves with him. Through his efforts to develop an anti-Roman bloc, Decebalus prevented Trajan from treating Dacia as a protectorate instead of an outright conquest.Christol & Nony, 171 In 104, Decebalus devised an attempt on Trajan's life by means of some Roman deserters, a plan that failed. Decebalus also took prisoner Trajan's legate Longinus, who eventually poisoned himself while in custody. Finally, in 105, Decebalus undertook an invasion of Roman-occupied territory north of the Danube.
 Prior to the campaign, Trajan had raised two entirely new legions: II Traianawhich, however, may have been posted in the East, at the Syrian port of Laodiceaand XXX Ulpia Victrix, which was posted to Brigetio, in
Prior to the campaign, Trajan had raised two entirely new legions: II Traianawhich, however, may have been posted in the East, at the Syrian port of Laodiceaand XXX Ulpia Victrix, which was posted to Brigetio, in Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
. By 105, the concentration of Roman troops assembled in the middle and lower Danube amounted to fourteen legions (up from nine in 101)about half of the entire Roman army. Even after the Dacian wars, the Danube frontier would permanently replace the Rhine as the main military axis of the Roman Empire. Including auxilia
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of inf ...
ries, the number of Roman troops engaged on both campaigns was between 150,000 and 175,000, while Decebalus could dispose of up to 200,000. Other estimates for the Roman forces involved in Trajan's second Dacian War cite around 86,000 for active campaigning with large reserves retained in the proximal provinces, and potentially much lower numbers around 50,000 for Decebalus' depleted forces and absent allies.
In a fierce campaign that seems to have consisted mostly of static warfare, the Dacians, devoid of manoeuvring room, kept to their network of fortresses, which the Romans sought systematically to storm (see also Second Dacian War). The Romans gradually tightened their grip around Decebalus' stronghold in Sarmizegetusa Regia, which they finally took and destroyed. A controversial scene on Trajan's column just before the fall of Sarmizegetusa Regia suggests that Decebalus may have offered poison to his remaining men as an alternative option to capture or death while trying to flee the besieged capital with him. Decebalus fled but, when later cornered by Roman cavalry, committed suicide. His severed head, brought to Trajan by the cavalryman Tiberius Claudius Maximus, was later exhibited in Rome on the steps leading up to the Capitol and thrown on the Gemonian stairs. The famous Dacian treasures were not found in the captured capital and their whereabouts were only revealed when a Dacian nobleman called Bikilis was captured. Decebalus’ treasures had been buried under a temporarily diverted river and the captive workers executed to retain the secret. Staggering amounts of gold and silver were found and packed off to fill Rome's coffers.
 Trajan built a new city, Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa, on another site (north of the hill citadel holding the previous Dacian capital), although bearing the same full name, Sarmizegetusa. This capital city was conceived as a purely civilian administrative centre and was provided the usual Romanized administrative apparatus ( decurions, aediles, etc.). Urban life in Roman Dacia seems to have been restricted to Roman colonists, mostly military veterans; there is no extant evidence for the existence in the province of peregrine cities. Native Dacians continued to live in scattered rural settlements, according to their own ways. In another arrangement with no parallels in any other Roman province, the existing quasi-urban Dacian settlements disappeared after the Roman conquest.
A number of unorganized urban settlements ( ''vici'') developed around military encampments in Dacia proper – the most important being Apulum – but were only acknowledged as cities proper well after Trajan's reign. The main regional effort of urbanization was concentrated by Trajan at the rearguard, in Moesia, where he created the new cities of Nicopolis ad Istrum and Marcianopolis. A vicus was also created around the Tropaeum Traianum. The garrison city of Oescus received the status of Roman colony after its
Trajan built a new city, Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa, on another site (north of the hill citadel holding the previous Dacian capital), although bearing the same full name, Sarmizegetusa. This capital city was conceived as a purely civilian administrative centre and was provided the usual Romanized administrative apparatus ( decurions, aediles, etc.). Urban life in Roman Dacia seems to have been restricted to Roman colonists, mostly military veterans; there is no extant evidence for the existence in the province of peregrine cities. Native Dacians continued to live in scattered rural settlements, according to their own ways. In another arrangement with no parallels in any other Roman province, the existing quasi-urban Dacian settlements disappeared after the Roman conquest.
A number of unorganized urban settlements ( ''vici'') developed around military encampments in Dacia proper – the most important being Apulum – but were only acknowledged as cities proper well after Trajan's reign. The main regional effort of urbanization was concentrated by Trajan at the rearguard, in Moesia, where he created the new cities of Nicopolis ad Istrum and Marcianopolis. A vicus was also created around the Tropaeum Traianum. The garrison city of Oescus received the status of Roman colony after its legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republi ...
garrison was redeployed. The fact that these former Danubian outposts had ceased to be frontier bases and were now in the deep rear acted as an inducement to their urbanization and development. Not all of Dacia was permanently occupied. After the post-Trajanic evacuation of lands across the lower Danube, land extending from the Danube to the inner arch of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
, including Transylvania, the Metaliferi Mountains and Oltenia was absorbed into the Roman province, which eventually took the form of an "excrescence" with ill-defined limits, stretching from the Danube northwards to the Carpathians. This may have been intended as a basis for further expansion within Eastern Europe, as the Romans believed the region to be much more geographically "flattened", and thus easier to traverse, than it actually was; they also underestimated the distance from those vaguely defined borders to the ocean.
 Defence of the province was entrusted to a single legion, the XIII Gemina, stationed at Apulum, which functioned as an advance guard that could, in case of need, strike either west or east at the Sarmatians living at the borders. Therefore, the indefensible character of the province did not appear to be a problem for Trajan, as the province was conceived more as a sally-base for further attacks. Even in the absence of further Roman expansion, the value of the province depended on Roman overall strength: while Rome was strong, the Dacian salient was an instrument of military and diplomatic control over the Danubian lands; when Rome was weak, as during the Crisis of the Third Century, the province became a liability and was eventually abandoned. Trajan resettled Dacia with Romans and annexed it as a province of the Roman Empire. Aside from their enormous booty (over half a million slaves, according to John Lydus), Trajan's Dacian campaigns benefited the Empire's finances through the acquisition of Dacia's gold mines, managed by an imperial procurator of equestrian rank (''procurator aurariarum''). On the other hand, commercial agricultural exploitation on the villa model, based on the centralized management of a huge landed estate by a single owner (''fundus'') was poorly developed. Therefore, use of slave labor in the province itself seems to have been relatively undeveloped, and epigraphic evidence points to work in the gold mines being conducted by means of labor contracts (''locatio conductio rei'') and seasonal wage-earning. The victory was commemorated by the construction both of the 102 cenotaph generally known as the Tropaeum Traiani in Moesia, as well of the much later (113) Trajan's Column in Rome, the latter depicting in stone carved bas-reliefs the Dacian Wars' most important moments.
Defence of the province was entrusted to a single legion, the XIII Gemina, stationed at Apulum, which functioned as an advance guard that could, in case of need, strike either west or east at the Sarmatians living at the borders. Therefore, the indefensible character of the province did not appear to be a problem for Trajan, as the province was conceived more as a sally-base for further attacks. Even in the absence of further Roman expansion, the value of the province depended on Roman overall strength: while Rome was strong, the Dacian salient was an instrument of military and diplomatic control over the Danubian lands; when Rome was weak, as during the Crisis of the Third Century, the province became a liability and was eventually abandoned. Trajan resettled Dacia with Romans and annexed it as a province of the Roman Empire. Aside from their enormous booty (over half a million slaves, according to John Lydus), Trajan's Dacian campaigns benefited the Empire's finances through the acquisition of Dacia's gold mines, managed by an imperial procurator of equestrian rank (''procurator aurariarum''). On the other hand, commercial agricultural exploitation on the villa model, based on the centralized management of a huge landed estate by a single owner (''fundus'') was poorly developed. Therefore, use of slave labor in the province itself seems to have been relatively undeveloped, and epigraphic evidence points to work in the gold mines being conducted by means of labor contracts (''locatio conductio rei'') and seasonal wage-earning. The victory was commemorated by the construction both of the 102 cenotaph generally known as the Tropaeum Traiani in Moesia, as well of the much later (113) Trajan's Column in Rome, the latter depicting in stone carved bas-reliefs the Dacian Wars' most important moments.
Nabataean annexation
In 106, Rabbel II Soter, one of Rome's client kings, died. This event might have prompted the annexation of the Nabataean Kingdom, but the manner and the formal reasons for the annexation are unclear. Some epigraphic evidence suggests a military operation, with forces from Syria and Egypt. What is known is that by 107, Roman legions were stationed in the area aroundPetra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to t ...
and Bosra, as is shown by a papyrus found in Egypt. The furthest south the Romans occupied (or, better, garrisoned, adopting a policy of having garrisons at key points in the desert) was Hegra, over south-west of Petra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to t ...
. The empire gained what became the province of Arabia Petraea (modern southern Jordan and northwest Saudi Arabia). At this time, a Roman road ('' Via Traiana Nova'') was built from Aila (now Aqaba) in Limes Arabicus
The ''Limes Arabicus'' was a desert frontier of the Roman Empire, running north from its start in the province of Arabia Petraea. It ran northeast from the Gulf of Aqaba for about at its greatest extent, reaching northern Syria and forming part ...
to Bosrah. As Nabataea was the last client kingdom in Asia west of the Euphrates, the annexation meant that the entire Roman East had been provincialized, completing a trend towards direct rule that had begun under the Flavians.
Parthian campaign
 In 113, Trajan embarked on his last campaign, provoked by Parthia's decision to put an unacceptable king on the throne of Armenia, a kingdom over which the two great empires had shared hegemony since the time of Nero some fifty years earlier. Trajan, already in Syria early in 113, consistently refused to accept diplomatic approaches from the Parthians intended to settle the Armenian imbroglio peacefully. As the surviving literary accounts of Trajan's Parthian War are fragmentary and scattered, it is difficult to assign them a proper context, something that has led to a long-running controversy about its precise happenings and ultimate aims.
In 113, Trajan embarked on his last campaign, provoked by Parthia's decision to put an unacceptable king on the throne of Armenia, a kingdom over which the two great empires had shared hegemony since the time of Nero some fifty years earlier. Trajan, already in Syria early in 113, consistently refused to accept diplomatic approaches from the Parthians intended to settle the Armenian imbroglio peacefully. As the surviving literary accounts of Trajan's Parthian War are fragmentary and scattered, it is difficult to assign them a proper context, something that has led to a long-running controversy about its precise happenings and ultimate aims.
Cause of the war
Modern historians advance the possibility that Trajan's decision to wage war against Parthia had economic motives: after Trajan's annexation of Arabia, he built a new road, Via Traiana Nova, that went from Bostra to Aila on the Red Sea. That meant that Charax on the Persian Gulf was the sole remaining western terminus of the Indian trade route outside direct Roman control,Christol & Nony, Rome, 171 and such control was important in order to lower import prices and to limit the supposed drain of precious metals created by the deficit in Roman trade with the Far East. That Charax traded with the Roman Empire, there can be no doubt, as its actual connections with merchants from Palmyra during the period are well documented in a contemporary Palmyrene epigraph, which tells of various Palmyrene citizens honoured for holding office in Charax. Also, Charax's rulers domains at the time possibly included the Bahrain islands, which offered the possibility of extending Roman hegemony into the Persian Gulf itself. (A Palmyrene citizen held office assatrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
over the islands shortly after Trajan's death, though the appointment was made by a Parthian king of Charax.) The rationale behind Trajan's campaign, in this case, was one of breaking down a system of Far Eastern trade through small Semitic ("Arab") cities under Parthia's control and to put it under Roman control instead.
 In his Dacian conquests, Trajan had already resorted to Syrian auxiliary units, whose veterans, along with Syrian traders, had an important role in the subsequent colonization of Dacia. He had recruited Palmyrene units into his army, including a camel unit, therefore apparently procuring Palmyrene support to his ultimate goal of annexing Charax. It has even been ventured that, when earlier in his campaign Trajan annexed Armenia, he was bound to annex the whole of Mesopotamia lest the Parthians interrupt the flux of trade from the Persian Gulf and/or foment trouble at the Roman frontier on the Danube. Other historians reject these motives, as the supposed Parthian "control" over the maritime Far Eastern trade route was, at best, conjectural and based on a selective reading of Chinese sourcestrade by land through Parthia seems to have been unhampered by Parthian authorities and left solely to the devices of private enterprise. Commercial activity in second century Mesopotamia seems to have been a general phenomenon, shared by many peoples within and without the Roman Empire, with no sign of a concerted Imperial policy towards it.
As in the case of the ''alimenta'', scholars like Moses Finley and Paul Veyne have considered the whole idea of a foreign trade "policy" behind Trajan's war anachronistic: according to them, the sole Roman concern with the Far Eastern luxuries tradebesides collecting toll taxes and customswas moral and involved frowning upon the "softness" of luxuries, but no economic policy. In the absence of conclusive evidence, trade between Rome and India might have been far more balanced, in terms of quantities of precious metals exchanged: one of our sources for the notion of the Roman gold drainPliny's the Younger's uncle Pliny the Elderhad earlier described the
In his Dacian conquests, Trajan had already resorted to Syrian auxiliary units, whose veterans, along with Syrian traders, had an important role in the subsequent colonization of Dacia. He had recruited Palmyrene units into his army, including a camel unit, therefore apparently procuring Palmyrene support to his ultimate goal of annexing Charax. It has even been ventured that, when earlier in his campaign Trajan annexed Armenia, he was bound to annex the whole of Mesopotamia lest the Parthians interrupt the flux of trade from the Persian Gulf and/or foment trouble at the Roman frontier on the Danube. Other historians reject these motives, as the supposed Parthian "control" over the maritime Far Eastern trade route was, at best, conjectural and based on a selective reading of Chinese sourcestrade by land through Parthia seems to have been unhampered by Parthian authorities and left solely to the devices of private enterprise. Commercial activity in second century Mesopotamia seems to have been a general phenomenon, shared by many peoples within and without the Roman Empire, with no sign of a concerted Imperial policy towards it.
As in the case of the ''alimenta'', scholars like Moses Finley and Paul Veyne have considered the whole idea of a foreign trade "policy" behind Trajan's war anachronistic: according to them, the sole Roman concern with the Far Eastern luxuries tradebesides collecting toll taxes and customswas moral and involved frowning upon the "softness" of luxuries, but no economic policy. In the absence of conclusive evidence, trade between Rome and India might have been far more balanced, in terms of quantities of precious metals exchanged: one of our sources for the notion of the Roman gold drainPliny's the Younger's uncle Pliny the Elderhad earlier described the Gangetic Plains
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
as one of the gold sources for the Roman Empire. Accordingly, in his controversial book on the Ancient economy, Finley considers Trajan's "badly miscalculated and expensive assault on Parthia" to be an example of the many Roman "commercial wars" that had in common the fact of existing only in the books of modern historians.
 The alternative view is to see the campaign as triggered by the lure of territorial annexation and prestige, the sole motive ascribed by Cassius Dio. As far as territorial conquest involved tax-collecting, especially of the 25% tax levied on all goods entering the Roman Empire, the ''tetarte'', one can say that Trajan's Parthian War had an "economic" motive. Also, there was the propaganda value of an Eastern conquest that would emulate, in Roman fashion, those of Alexander the Great. The fact that emissaries from the
The alternative view is to see the campaign as triggered by the lure of territorial annexation and prestige, the sole motive ascribed by Cassius Dio. As far as territorial conquest involved tax-collecting, especially of the 25% tax levied on all goods entering the Roman Empire, the ''tetarte'', one can say that Trajan's Parthian War had an "economic" motive. Also, there was the propaganda value of an Eastern conquest that would emulate, in Roman fashion, those of Alexander the Great. The fact that emissaries from the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
might have attended to the commemorative ceremonies for the Dacian War may have kindled in some Greco-Roman intellectuals like Plutarchwho wrote about only 70,000 Roman soldiers being necessary to a conquest of Indiaas well as in Trajan's closer associates, speculative dreams about the booty to be obtained by reproducing Macedonian Eastern conquests. There could also be Trajan's idea to use an ambitious blueprint of conquests as a way to emphasize quasi-divine status, such as with his cultivated association, in coins and monuments, to Hercules.
Also, it is possible that the attachment of Trajan to an expansionist policy was supported by a powerful circle of conservative senators from Hispania committed to a policy of imperial expansion, first among them being the all-powerful Licinius Sura. Alternatively, one can explain the campaign by the fact that, for the Romans, their empire was in principle unlimited, and that Trajan only took advantage of an opportunity to make idea and reality coincide. Finally, there are other modern historians who think that Trajan's original aims were purely military and strategic: to assure a more defensible Eastern frontier for the Roman Empire, crossing Northern Mesopotamia along the course of the Khabur River in order to offer cover to a Roman Armenia. This interpretation is backed by the fact that all subsequent Roman wars against Parthia would aim at establishing a Roman presence deep into Parthia itself. It is possible that during the onset of Trajan's military experience, as a young tribune, he had witnessed engagement with the Parthians; so any strategic vision was grounded in a tactical awareness of what was needed to tackle Parthia.
Course of the war
The campaign was carefully planned in advance: ten legions were concentrated in the Eastern theatre; since 111, the correspondence of Pliny the Younger witnesses to the fact that provincial authorities in Bithynia had to organize supplies for passing troops, and local city councils and their individual members had to shoulder part of the increased expenses by supplying troops themselves. The intended campaign, therefore, was immensely costly from its very beginning. Trajan marched first on Armenia, deposed the Parthian-appointed king, Parthamasiris (who was afterwards murdered while kept in the custody of Roman troops in an unclear incident, later described by Fronto as a breach of Roman good faith), and annexed it to the Roman Empire as a province, receiving in passing the acknowledgement of Roman hegemony by various tribes in the Caucasus and on the Eastern coast of the Black Seaa process that kept him busy until the end of 114. At the same time, a Roman column under the legate Lusius Quietusan outstanding cavalry general who had signalled himself during the Dacian Wars by commanding a unit from his nativeMauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
crossed the Araxes
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
river from Armenia into Media Atropatene and the land of the Mardians
The Amardian Achaemenid_Empire.html"_;"title="satrap_shown_within_a_map_of_the_Achaemenid_Empire">satrap_shown_within_a_map_of_the_Achaemenid_Empire_at_its_greatest_extent_(500_BC).
The_Amardians,_widely_referred_to_as_the_Amardi_(and_sometimes_ ...
(present-day Ghilan). It is possible that Quietus' campaign had as its goal the extending of the newer, more defensible Roman border eastwards towards the Caspian Sea and northwards to the foothills of the Caucasus. This newer, more "rational" frontier, depended, however, on an increased, permanent Roman presence east of the Euphrates.
 The chronology of subsequent events is uncertain, but it is generally believed that early in 115 Trajan launched a Mesopotamian campaign, marching down towards the Taurus mountains in order to consolidate territory between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. He placed permanent garrisons along the way to secure the territory. While Trajan moved from west to east, Lusius Quietus moved with his army from the Caspian Sea towards the west, both armies performing a successful pincer movement, whose apparent result was to establish a Roman presence into the Parthian Empire proper, with Trajan taking the northern Mesopotamian cities of Nisibis and Batnae and organizing a province of Mesopotamia, including the Kingdom of Osrhoenewhere King Abgar VII submitted to Trajan publiclyas a Roman protectorate. This process seems to have been completed at the beginning of 116, when coins were issued announcing that Armenia and Mesopotamia had been put under the authority of the Roman people. The area between the Khabur River and the mountains around Singara seems to have been considered as the new frontier, and as such received a road surrounded by fortresses.
After wintering in Antioch during 115/116 and, according to literary sources, barely escaping from a violent earthquake that claimed the life of one of the consuls, Marcus Pedo VirgilianusTrajan again took to the field in 116, with a view to the conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia, an overambitious goal that eventually backfired on the results of his entire campaign. According to some modern historians, the aim of the campaign of 116 was to achieve a "pre-emptive demonstration" aiming not toward the conquest of Parthia, but for tighter Roman control over the Eastern trade route. However, the overall scarcity of manpower for the Roman military establishment meant that the campaign was doomed from the start. It is noteworthy that no new legions were raised by Trajan before the Parthian campaign, maybe because the sources of new citizen recruits were already over-exploited.
As far as the sources allow a description of this campaign, it seems that one Roman division crossed the Tigris into Adiabene, sweeping south and capturing Adenystrae; a second followed the river south, capturing
The chronology of subsequent events is uncertain, but it is generally believed that early in 115 Trajan launched a Mesopotamian campaign, marching down towards the Taurus mountains in order to consolidate territory between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. He placed permanent garrisons along the way to secure the territory. While Trajan moved from west to east, Lusius Quietus moved with his army from the Caspian Sea towards the west, both armies performing a successful pincer movement, whose apparent result was to establish a Roman presence into the Parthian Empire proper, with Trajan taking the northern Mesopotamian cities of Nisibis and Batnae and organizing a province of Mesopotamia, including the Kingdom of Osrhoenewhere King Abgar VII submitted to Trajan publiclyas a Roman protectorate. This process seems to have been completed at the beginning of 116, when coins were issued announcing that Armenia and Mesopotamia had been put under the authority of the Roman people. The area between the Khabur River and the mountains around Singara seems to have been considered as the new frontier, and as such received a road surrounded by fortresses.
After wintering in Antioch during 115/116 and, according to literary sources, barely escaping from a violent earthquake that claimed the life of one of the consuls, Marcus Pedo VirgilianusTrajan again took to the field in 116, with a view to the conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia, an overambitious goal that eventually backfired on the results of his entire campaign. According to some modern historians, the aim of the campaign of 116 was to achieve a "pre-emptive demonstration" aiming not toward the conquest of Parthia, but for tighter Roman control over the Eastern trade route. However, the overall scarcity of manpower for the Roman military establishment meant that the campaign was doomed from the start. It is noteworthy that no new legions were raised by Trajan before the Parthian campaign, maybe because the sources of new citizen recruits were already over-exploited.
As far as the sources allow a description of this campaign, it seems that one Roman division crossed the Tigris into Adiabene, sweeping south and capturing Adenystrae; a second followed the river south, capturing Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
; Trajan himself sailed down the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
from Dura-Europoswhere a triumphal arch was erected in his honourthrough Ozogardana, where he erected a "tribunal" still to be seen at the time of Julian the Apostate's campaigns in the same area. Having come to the narrow strip of land between the Euphrates and the Tigris, he then dragged his fleet overland into the Tigris, capturing Seleucia
Seleucia (; grc-gre, Σελεύκεια), also known as or , was a major Mesopotamian city of the Seleucid empire. It stood on the west bank of the Tigris River, within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq.
Name
Seleucia ( grc-gre, Σ ...
and finally the Parthian capital of Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
. He continued southward to the Persian Gulf, when, after escaping with his fleet a tidal bore on the Tigris,Longden, "Notes on the Parthian Campaigns", 8 he received the submission of Athambelus, the ruler of Charax. He declared Babylon a new province of the Empire and had his statue erected on the shore of the Persian Gulf, after which he sent the Senate a laurelled letter declaring the war to be at a close and bemoaning that he was too old to go on any further and repeat the conquests of Alexander the Great. Since Charax was a ''de facto'' independent kingdom whose connections to Palmyra were described above, Trajan's bid for the Persian Gulf may have coincided with Palmyrene interests in the region. Another hypothesis is that the rulers of Charax had expansionist designs on Parthian Babylon, giving them a rationale for alliance with Trajan. The Parthian city of Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
was apparently also occupied by the Romans.
 According to late literary sources (not backed by numismatic or inscriptional evidence) a province of Assyria was also proclaimed, apparently covering the territory of Adiabene. Some measures seem to have been considered regarding the fiscal administration of Indian tradeor simply about the payment of customs (''portoria'') on goods traded on the Euphrates and Tigris. It is possible that it was this "streamlining" of the administration of the newly conquered lands according to the standard pattern of Roman provincial administration in tax collecting, requisitions and the handling of local potentates' prerogatives, that triggered later resistance against Trajan. According to some modern historians, Trajan might have busied himself during his stay on the Persian Gulf with ordering raids on the Parthian coasts, as well as probing into extending Roman suzerainty over the mountaineer tribes holding the passes across the Zagros Mountains into the Iranian plateau eastward, as well as establishing some sort of direct contact between Rome and the Kushan Empire. No attempt was made to expand into the Iranian Plateau itself, where the Roman army, with its relative weakness in cavalry, would have been at a disadvantage.
Trajan left the Persian Gulf for Babylonwhere he intended to offer sacrifice to Alexander in the house where he had died in 323BCBennett, Trajan, 199 But a revolt led by Sanatruces, a nephew of the Parthian king Osroes I who had retained a cavalry force, possibly strengthened by the addition of Saka archers, imperilled Roman positions in Mesopotamia and Armenia. Trajan sought to deal with this by forsaking direct Roman rule in Parthia proper, at least partially. Trajan sent two armies towards Northern Mesopotamia: the first, under Lusius Quietus, recovered Nisibis and
According to late literary sources (not backed by numismatic or inscriptional evidence) a province of Assyria was also proclaimed, apparently covering the territory of Adiabene. Some measures seem to have been considered regarding the fiscal administration of Indian tradeor simply about the payment of customs (''portoria'') on goods traded on the Euphrates and Tigris. It is possible that it was this "streamlining" of the administration of the newly conquered lands according to the standard pattern of Roman provincial administration in tax collecting, requisitions and the handling of local potentates' prerogatives, that triggered later resistance against Trajan. According to some modern historians, Trajan might have busied himself during his stay on the Persian Gulf with ordering raids on the Parthian coasts, as well as probing into extending Roman suzerainty over the mountaineer tribes holding the passes across the Zagros Mountains into the Iranian plateau eastward, as well as establishing some sort of direct contact between Rome and the Kushan Empire. No attempt was made to expand into the Iranian Plateau itself, where the Roman army, with its relative weakness in cavalry, would have been at a disadvantage.
Trajan left the Persian Gulf for Babylonwhere he intended to offer sacrifice to Alexander in the house where he had died in 323BCBennett, Trajan, 199 But a revolt led by Sanatruces, a nephew of the Parthian king Osroes I who had retained a cavalry force, possibly strengthened by the addition of Saka archers, imperilled Roman positions in Mesopotamia and Armenia. Trajan sought to deal with this by forsaking direct Roman rule in Parthia proper, at least partially. Trajan sent two armies towards Northern Mesopotamia: the first, under Lusius Quietus, recovered Nisibis and Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ...
from the rebels, probably having King Abgarus deposed and killed in the process, with Quietus probably earning the right to receive the honors of a senator of praetorian rank (''adlectus inter praetorios''). The second army, however, under Appius Maximus Santra (probably a governor of Macedonia) was defeated and Santra killed.Julián González, ed., ''Trajano Emperador De Roma'', 216
Later in 116, Trajan, with the assistance of Quietus and two other legates, Marcus Erucius Clarus
Marcus Erucius Clarus ( fl. 2nd century AD), was a suffect consul (AD 117) and an influential friend and supporter of the famous Silver Age author Pliny the Younger.
Clarus was described by Pliny as a man of honor, integrity and learning, as w ...
and Tiberius Julius Alexander Julianus, defeated a Parthian army in a battle where Sanatruces was killed (possibly with the assistance of Osroes' son and Sanatruces' cousin, Parthamaspates, whom Trajan wooed successfully). After re-taking and burning Seleucia, Trajan then formally deposed Osroes, putting Parthamaspates on the throne as client ruler. This event was commemorated in a coin as the reduction of Parthia to client kingdom status: REX PARTHIS DATUS, "a king is given to the Parthians". That done, Trajan retreated north in order to retain what he could of the new provinces of Armeniawhere he had already accepted an armistice in exchange for surrendering part of the territory to Sanatruces' son Vologesesand Mesopotamia. It was at this point that Trajan's health started to fail him. The fortress city of Hatra, on the Tigris in his rear, continued to hold out against repeated Roman assaults. He was personally present at the siege, and it is possible that he suffered a heat stroke while in the blazing heat.
Kitos War
 Shortly afterwards, the Jews inside the Eastern Roman Empire, in Egypt, Cyprus, and Cyrenethis last province being probably the original trouble hotspotrose up in what probably was an outburst of religious rebellion against the local pagans, this widespread rebellion being afterwards named the Kitos War. Another rebellion flared up among the Jewish communities of Northern Mesopotamia, probably part of a general reaction against Roman occupation. Trajan was forced to withdraw his army in order to put down the revolts. He saw this withdrawal as simply a temporary setback, but he was destined never to command an army in the field again, turning his Eastern armies over to Lusius Quietus, who meanwhile (early 117) had been made governor of Judaea and might have had to deal earlier with some kind of Jewish unrest in the province. Quietus discharged his commissions successfully, so much that the war was afterward named after him''Kitus'' being a corruption of ''Quietus''. Whether or not the Kitos War theatre included Judea proper, or only the Jewish Eastern diaspora, remains doubtful in the absence of clear epigraphic and archaeological evidence. What is certain is that there was an increased Roman military presence in Judea at the time.
Quietus was promised a consulate in the following year (118) for his victories, but he was killed before this could occur, during the bloody purge that opened Hadrian's reign, in which Quietus and three other former consuls were sentenced to death after being tried on a vague charge of conspiracy by the (secret) court of the Praetorian Prefect Attianus. It has been thought that Quietus and his colleagues were executed on Hadrian's direct orders, for fear of their popular standing with the army and their close connections to Trajan. In contrast, the next prominent Roman figure in charge of the repression of the Jewish revolt, the equestrian Quintus Marcius Turbo, who had dealt with the rebel leader from Cyrene, Loukuas, retained Hadrian's trust, eventually becoming his
Shortly afterwards, the Jews inside the Eastern Roman Empire, in Egypt, Cyprus, and Cyrenethis last province being probably the original trouble hotspotrose up in what probably was an outburst of religious rebellion against the local pagans, this widespread rebellion being afterwards named the Kitos War. Another rebellion flared up among the Jewish communities of Northern Mesopotamia, probably part of a general reaction against Roman occupation. Trajan was forced to withdraw his army in order to put down the revolts. He saw this withdrawal as simply a temporary setback, but he was destined never to command an army in the field again, turning his Eastern armies over to Lusius Quietus, who meanwhile (early 117) had been made governor of Judaea and might have had to deal earlier with some kind of Jewish unrest in the province. Quietus discharged his commissions successfully, so much that the war was afterward named after him''Kitus'' being a corruption of ''Quietus''. Whether or not the Kitos War theatre included Judea proper, or only the Jewish Eastern diaspora, remains doubtful in the absence of clear epigraphic and archaeological evidence. What is certain is that there was an increased Roman military presence in Judea at the time.
Quietus was promised a consulate in the following year (118) for his victories, but he was killed before this could occur, during the bloody purge that opened Hadrian's reign, in which Quietus and three other former consuls were sentenced to death after being tried on a vague charge of conspiracy by the (secret) court of the Praetorian Prefect Attianus. It has been thought that Quietus and his colleagues were executed on Hadrian's direct orders, for fear of their popular standing with the army and their close connections to Trajan. In contrast, the next prominent Roman figure in charge of the repression of the Jewish revolt, the equestrian Quintus Marcius Turbo, who had dealt with the rebel leader from Cyrene, Loukuas, retained Hadrian's trust, eventually becoming his Praetorian Prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
. As all four consulars were senators of the highest standing and as such generally regarded as able to take imperial power (''capaces imperii''), Hadrian seems to have decided to forestall these prospective rivals.
Death and succession
Early in 117, Trajan grew ill and set sail for Italy. His health declined throughout the spring and summer of 117, possibly acknowledged to the public by the display of a bronze portrait-bust at the public baths of Ancyra, showing an aged and emaciated man, though the identification with Trajan is disputed. He reached Selinus, where he suddenly died, probably on 11 August and apparently fromedema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
. Trajan in person could have lawfully nominated Hadrian as his successor, but Dio claims that Trajan's wife, Pompeia Plotina, assured Hadrian's succession by keeping Trajan's death a secret, long enough for her to produce and sign a document attesting to Hadrian's adoption as son and successor. Dio, who tells this narrative, offers his fatherthe governor of Cilicia Apronianusas a source, so his narrative may be based on contemporary rumour. It may also reflect male Roman displeasure that an empresslet alone any woman could presume to meddle in Rome's political affairs.
Hadrian held an ambiguous position during Trajan's reign. After commanding Legio I Minervia during the Dacian Wars, he had been relieved from front-line duties at the decisive stage of the Second Dacian War, being sent to govern the newly created province of Pannonia Inferior. He had pursued a senatorial career without particular distinction and had not been officially adopted by Trajan although he received from him decorations and other marks of distinction that made him hope for the succession. He received no post after his 108 consulate and no further honours other than being made Archon eponymos for Athens in 111/112. He probably did not take part in the Parthian War. Literary sources relate that Trajan had considered others, such as the jurist Lucius Neratius Priscus
Lucius Neratius Priscus was a Roman Senator and leading jurist, serving for a time as the head of the Proculeian school. He was suffect consul in the ''nundinium'' of May–June 97 as the colleague of Marcus Annius Verus.
Family
The origins o ...
, as heir. Hadrian, who was eventually entrusted with the governorship of Syria at the time of Trajan's death, was Trajan's cousin and was married to Trajan's grandniece, which all made him as good as heir designate. Hadrian seems to have been well connected to the powerful and influential coterie of Spanish senators at Trajan's court, through his ties to Plotina and the Prefect Attianus. His refusal to sustain Trajan's senatorial and expansionist policy during his own reign may account for the "crass hostility" shown him by literary sources.
Hadrian's first major act as emperor was to abandon Mesopotamia as too costly and distant to defend, and to restore Armenia and Osrhoene to Parthian hegemony, under Rome's suzerainty. The Parthian campaign had been an enormous setback to Trajan's policy, proof that Rome had overstretched its capacity to sustain an ambitious program of conquest. According to the ''Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
'', Hadrian claimed to follow the precedent set by Cato the Elder towards the Macedonians, who "were to be set free because they could not be protected" – something Birley sees as an unconvincing precedent. Other territories conquered by Trajan were retained. According to a well-established historical tradition, Trajan's ashes were placed within the small cella that still survives at the base of Trajan's column. In some modern scholarship, his ashes were more likely interred near his column, in a mausoleum, temple or tomb built for his cult as a ''divus'' of the Roman state.
Legacy
third century
The 3rd century was the period from 201 (Roman numerals, CCI) to 300 (Roman numerals, CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar..
In this century, the Roman Empire saw a Crisis of the Third Century, crisis, starting with ...
, Trajan, together with Augustus, became in the Later Roman Empire the paragon of the most positive traits of the Imperial order.
Some theologians such as Thomas Aquinas discussed Trajan as an example of a virtuous pagan. In the '' Divine Comedy'', Dante, following this legend, sees the spirit of Trajan in the Heaven of Jupiter with other historical and mythological persons noted for their justice. Also, a mural of Trajan stopping to provide justice for a poor widow is present in the first terrace of Purgatory as a lesson to those who are purged for being proud.
I noticed that the inner bank of the curve... Was of white marble, and so decorated With carvings that not only Polycletus But nature herself would there be put to shame... There was recorded the high glory Of that ruler of Rome whose worth Moved Gregory to his great victory; I mean by this the Emperor Trajan; And at his bridle a poor widow Whose attitude bespoke tears and grief... The wretched woman, in the midst of all this, Seemed to be saying: 'Lord, avenge my son, Who is dead, so that my heart is broken..' So he said: 'Now be comforted, for I must Carry out my duty before I go on: Justice requires it and pity holds me back.' ''Dante, The Divine Comedy, Purgatorio X, ll. 32 f. and 73 f.''
Iconography
After the despised Nero, Roman emperors until Trajan were depicted shaven. Trajan's successor Hadrian made beards fashionable again for emperors.Later Emperors
Many emperors after Trajan would, when they were sworn into office, be wished '' Felicior Augusto, Melior Traiano'' ("May you rule fortunate like Augustus and better than Trajan"). The fourth-century emperorConstantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea ...
is credited with calling him a "plant upon every wall" for the many buildings bearing inscriptions with his name.
After Rome
In the 18th century, KingCharles III of Spain
it, Carlo Sebastiano di Borbone e Farnese
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Philip V of Spain
, mother = Elisabeth Farnese
, birth_date = 20 January 1716
, birth_place = Royal Alcazar of Madrid, Spain
, death_d ...
commissioned Anton Raphael Mengs to paint ''The Triumph of Trajan'' on the ceiling of the banquet hall of the Royal Palace of Madridconsidered among the best works of this artist.
It was only during the Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
that this legacy began to be contested, when Edward Gibbon expressed doubts about the militarized character of Trajan's reign in contrast to the "moderate" practices of his immediate successors. Mommsen
Mommsen is a surname, and may refer to one of a family of German historians, see Mommsen family:
* Theodor Mommsen (1817–1903), classical scholar, winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature
* Hans Mommsen (1930–2015), historian known for arguing ...
adopted a divided stance towards Trajan, at some point of his posthumously published lectures even speaking about his "vainglory" (''Scheinglorie''). Mommsen also speaks of Trajan's "insatiable, unlimited lust for conquest". Although Mommsen had no liking for Trajan's successor Hadrian"a repellent manner, and a venomous, envious and malicious nature"he admitted that Hadrian, in renouncing Trajan's conquests, was "doing what the situation clearly required".
It was exactly this military character of Trajan's reign that attracted his early twentieth-century biographer, the Italian Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
historian Roberto Paribeni, who in his 1927 two-volume biography ''Optimus Princeps'' described Trajan's reign as the acme of the Roman principate, which he saw as Italy's patrimony. Following in Paribeni's footsteps, the German historian Alfred Heuss saw in Trajan "the accomplished human embodiment of the imperial title" (''die ideale Verkörperung des humanen Kaiserbegriffs''). Trajan's first English-language biography by Julian Bennett is also a positive one in that it assumes that Trajan was an active policy-maker concerned with the management of the empire as a wholesomething his reviewer Lendon considers an anachronistic outlook that sees in the Roman emperor a kind of modern administrator.
During the 1980s, the Romanian historian Eugen Cizek took a more nuanced view as he described the changes in the ''personal'' ideology of Trajan's reign, stressing the fact that it became ever more autocratic and militarized, especially after 112 and towards the Parthian War (as "only an universal monarch, a ''kosmocrator'', could dictate his law to the East"). The biography by the German historian Karl Strobel stresses the continuity between Domitian's and Trajan's reigns, saying that Trajan's rule followed the same autocratic and sacred character as Domitian's, culminating in a failed Parthian adventure intended as the crown of his personal achievement. It is in modern French historiography that Trajan's reputation becomes most markedly deflated: Paul Petit writes about Trajan's portraits as a "lowbrow boor with a taste for booze and boys". For Paul Veyne, what is to be retained from Trajan's "stylish" qualities was that he was the last Roman emperor to think of the empire as a purely Italian and Rome-centred hegemony of conquest. In contrast, his successor Hadrian would stress the notion of the empire as ecumenical and of the Emperor as universal benefactor and not ''kosmocrator''.
In Jewish legend
In the Jewish homiletical works, such as '' Esther Rabbah'', Trajan is described with the epitaph "may his bones be crushed" ( he, שְׁחִיק עֲצָמוֹת, ''sh'hik atzamot''). The same epitaph is also used for Hadrian.Pius, A., Italica, H., Sabina, V., Aelius, L., Hadrianus, P. A., Augustus, C. P. A. T. H., ... & Paulina, D. Roman imperial dynasties. Nerva, 96, 98.See also
* Felicior Augusto, melior Traiano * Justice of Trajan * Trajanic artNotes
References
Sources and further reading
* * * Ancel, R. Manning. "Soldiers." ''Military Heritage
''Military Heritage'' is an American glossy, bi-monthly military history magazine that was first published in August 1999 by Sovereign Media. It was founded by Carl A. Gnam, Jr., who also serves as the editorial director. The current magazine edi ...
.'' December 2001. Volume 3, No. 3: 12, 14, 16, 20 (Trajan, Emperor of Rome).
*
*
*
* Bowersock, G.W. ''Roman Arabia'', Harvard University Press, 1983
*
*
*
* Cizek, Eugen. ''L'époque de Trajan: circonstances politiques et problèmes idéologiques''. Bucharest, Editura Științifică și Enciclopedică, 1983,
*
*
*
* Fuller, J.F.C. ''A Military History of the Western World''. Three Volumes. New York: Da Capo Press, Inc., 1987 and 1988.
** v. 1. ''From the late times to the Battle of Lepanto''; . 255, 266, 269, 270, 273 (Trajan, Roman Emperor).
*
*
*
* Isaac, B. ''The Limits of Empire'', The Roman Army in the East, Revised Edition, Oxford University Press, 1990
* Jackson, N. ''Trajan: Rome's Last Conqueror'', 1st edition, GreenHill Books, 2022. ISBN 9781784387075
* Kennedy, D. ''The Roman Army in Jordan'', Revised Edition, Council for British Research in the Levant, 2004.
*
*
* Lepper, F.A. ''Trajan's Parthian War''. London: Oxford University Press, 1948. Also available online.
*
*
*
* Minaud, Gérard, ''Les vies de 12 femmes d'empereur romainDevoirs, Intrigues & Voluptés '', Paris, L'Harmattan, 2012, ch. 6, '' La vie de Plotine, femme de Trajan'', p.147–168. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Wildfeuer, C.R.H. ''Trajan, Lion of Rome: the Untold Story of Rome's Greatest Emperor'', Aquifer Publishing, 2009. Historical fiction.
Primary sources
Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'' Book 68
English translation
English translation
English translation
Secondary material
*External links
, - {{authority control 53 births 117 deaths 1st-century Roman emperors 2nd-century Roman emperors Adult adoptees Ancient Roman adoptees Ancient Roman military personnel Deaths from edema Deified Roman emperors LGBT Roman emperors Imperial Roman consuls Latin letter writers Leaders who took power by coup People from Seville (comarca) People of the Roman–Parthian Wars Roman governors of Germania Superior Roman governors of Pannonia Roman legates Romans from Hispania Ulpii Roman pharaohs