Tracheal Fracture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tracheobronchial injury is damage to the
 Signs and symptoms vary depending on what part of the tracheobronchial tree is injured and how severely it is damaged. There are no direct signs of TBI, but certain signs suggest the injury and raise a clinician's suspicion that it has occurred. Many of the signs and symptoms are also present in injuries with similar injury mechanisms such as pneumothorax. Dyspnea and
Signs and symptoms vary depending on what part of the tracheobronchial tree is injured and how severely it is damaged. There are no direct signs of TBI, but certain signs suggest the injury and raise a clinician's suspicion that it has occurred. Many of the signs and symptoms are also present in injuries with similar injury mechanisms such as pneumothorax. Dyspnea and
 The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. The trachea is situated between the lower end of the larynx and the center of the chest, where it splits into the two bronchi at a ridge called the
The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. The trachea is situated between the lower end of the larynx and the center of the chest, where it splits into the two bronchi at a ridge called the
 Rapid diagnosis and treatment are important in the care of TBI; if the injury is not diagnosed shortly after the injury, the risk of complications is higher. Bronchoscopy is the most effective method to diagnose, locate, and determine the severity of TBI, and it is usually the only method that allows a definitive diagnosis. Diagnosis with a flexible bronchoscope, which allows the injury to be visualized directly, is the fastest and most reliable technique. In people with TBI, bronchoscopy may reveal that the airway is torn, or that the airways are blocked by blood, or that a bronchus has collapsed, obscuring more distal (lower) bronchi from view.
Chest x-ray is the initial imaging technique used to diagnose TBI. The film may not have any signs in an otherwise asymptomatic patient. Indications of TBI seen on radiographs include deformity in the trachea or a defect in the tracheal wall. Radiography may also show cervical emphysema, air in the tissues of the neck. X-rays may also show accompanying injuries and signs such as fractures and subcutaneous emphysema. If subcutaneous emphysema occurs and the hyoid bone appears in an X-ray to be sitting unusually high in the throat, it may be an indication that the trachea has been severed. TBI is also suspected if an endotracheal tube appears in an X-ray to be out of place, or if its cuff appears to be more full than normal or to protrude through a tear in the airway. If a bronchus is torn all the way around, the lung may collapse outward toward the chest wall (rather than inward, as it usually does in pneumothorax) because it loses the attachment to the bronchus which normally holds it toward the center. In a person lying face-up, the lung collapses toward the diaphragm and the back. This sign, described in 1969, is called fallen lung sign and is
Rapid diagnosis and treatment are important in the care of TBI; if the injury is not diagnosed shortly after the injury, the risk of complications is higher. Bronchoscopy is the most effective method to diagnose, locate, and determine the severity of TBI, and it is usually the only method that allows a definitive diagnosis. Diagnosis with a flexible bronchoscope, which allows the injury to be visualized directly, is the fastest and most reliable technique. In people with TBI, bronchoscopy may reveal that the airway is torn, or that the airways are blocked by blood, or that a bronchus has collapsed, obscuring more distal (lower) bronchi from view.
Chest x-ray is the initial imaging technique used to diagnose TBI. The film may not have any signs in an otherwise asymptomatic patient. Indications of TBI seen on radiographs include deformity in the trachea or a defect in the tracheal wall. Radiography may also show cervical emphysema, air in the tissues of the neck. X-rays may also show accompanying injuries and signs such as fractures and subcutaneous emphysema. If subcutaneous emphysema occurs and the hyoid bone appears in an X-ray to be sitting unusually high in the throat, it may be an indication that the trachea has been severed. TBI is also suspected if an endotracheal tube appears in an X-ray to be out of place, or if its cuff appears to be more full than normal or to protrude through a tear in the airway. If a bronchus is torn all the way around, the lung may collapse outward toward the chest wall (rather than inward, as it usually does in pneumothorax) because it loses the attachment to the bronchus which normally holds it toward the center. In a person lying face-up, the lung collapses toward the diaphragm and the back. This sign, described in 1969, is called fallen lung sign and is
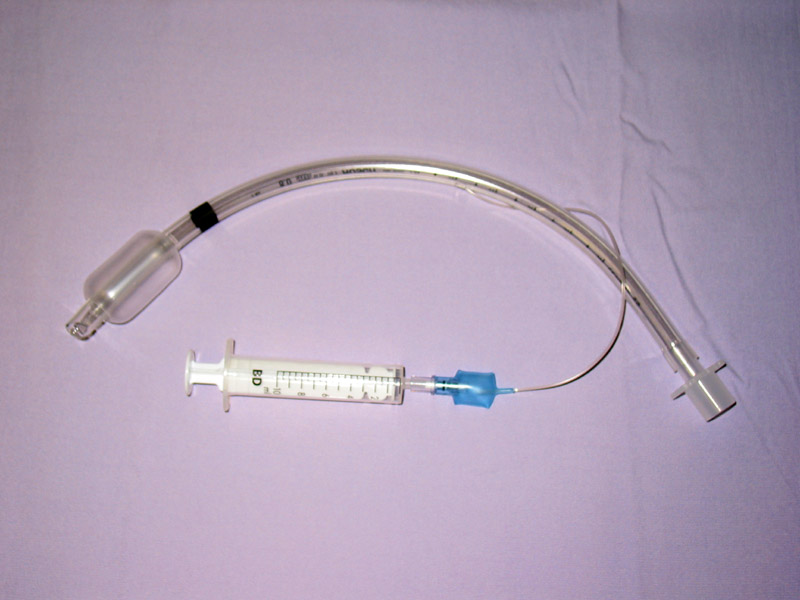 Treatment of TBI varies based on the location and severity of injury and whether the patient is stable or having trouble breathing, but ensuring that the airway is patent so that the patient can breathe is always of paramount importance. Ensuring an open airway and adequate ventilation may be difficult in people with TBI. Intubation, one method to secure the airway, may be used to bypass a disruption in the airway in order to send air to the lungs. If necessary, a tube can be placed into the uninjured bronchus, and a single lung can be ventilated. If there is a penetrating injury to the neck through which air is escaping, the trachea may be intubated through the wound. Multiple unsuccessful attempts at conventional (direct)
Treatment of TBI varies based on the location and severity of injury and whether the patient is stable or having trouble breathing, but ensuring that the airway is patent so that the patient can breathe is always of paramount importance. Ensuring an open airway and adequate ventilation may be difficult in people with TBI. Intubation, one method to secure the airway, may be used to bypass a disruption in the airway in order to send air to the lungs. If necessary, a tube can be placed into the uninjured bronchus, and a single lung can be ventilated. If there is a penetrating injury to the neck through which air is escaping, the trachea may be intubated through the wound. Multiple unsuccessful attempts at conventional (direct)  People with TBI are provided with supplemental oxygen and may need
People with TBI are provided with supplemental oxygen and may need
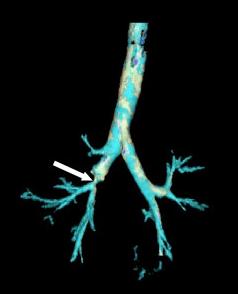 Most people with TBI who die do so within minutes of the injury, due to complications such as pneumothorax and insufficient airway and to other injuries that occurred at the same time. Most late deaths that occur in TBI are attributed to
Most people with TBI who die do so within minutes of the injury, due to complications such as pneumothorax and insufficient airway and to other injuries that occurred at the same time. Most late deaths that occur in TBI are attributed to
tracheobronchial tree
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
(the airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
structure involving the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
and bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
). It can result from blunt
Blunt may refer to:
* Blunt (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name)
* Blunt (cigar), a term used in the cigar industry to designate blunt-tipped, usually factory-rolled cigars
* Blunt (cannabis), a slang term used in cannabis cult ...
or penetrating trauma to the neck or chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
, inhalation of harmful fumes or smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-produc ...
, or aspiration of liquids or objects.
Though rare, TBI is a serious condition; it may cause obstruction of the airway with resulting life-threatening respiratory insufficiency
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
. Other injuries accompany TBI in about half of cases. Of those people with TBI who die, most do so before receiving emergency care, either from airway obstruction, exsanguination
Exsanguination is death caused by loss of blood. Depending upon the health of the individual, people usually die from losing half to two-thirds of their blood; a loss of roughly one-third of the blood volume is considered very serious. Even a sin ...
, or from injuries to other vital organs. Of those who do reach a hospital, the mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
may be as high as 30%.
TBI is frequently difficult to diagnose
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
and treat. Early diagnosis is important to prevent complications, which include stenosis (narrowing) of the airway, respiratory tract infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infectious diseases involving the respiratory tract. An infection of this type usually is further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection (URI or URTI) or a lower respiratory tract infection (LRI ...
, and damage to the lung tissue. Diagnosis involves procedures such as bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a trac ...
, radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
, and x-ray computed tomography
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
to visualize the tracheobronchial tree. Signs and symptoms vary based on the location and severity of the injury; they commonly include dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
(difficulty breathing), dysphonia
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice, can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
(a condition where the voice can be hoarse, weak, or excessively breathy), coughing, and abnormal breath sounds. In the emergency setting, tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
can be used to ensure that the airway remains open. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a TBI.
Signs and symptoms
 Signs and symptoms vary depending on what part of the tracheobronchial tree is injured and how severely it is damaged. There are no direct signs of TBI, but certain signs suggest the injury and raise a clinician's suspicion that it has occurred. Many of the signs and symptoms are also present in injuries with similar injury mechanisms such as pneumothorax. Dyspnea and
Signs and symptoms vary depending on what part of the tracheobronchial tree is injured and how severely it is damaged. There are no direct signs of TBI, but certain signs suggest the injury and raise a clinician's suspicion that it has occurred. Many of the signs and symptoms are also present in injuries with similar injury mechanisms such as pneumothorax. Dyspnea and respiratory distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
are found in 76–100% of people with TBI, and coughing up blood has been found in up to 25%. However, isolated TBI does not usually cause profuse bleeding; if such bleeding is observed it is likely to be due to another injury such as a ruptured large blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
. The patient may exhibit dysphonia or have diminished breath sounds, and rapid breathing is common. Coughing may be present, and stridor, an abnormal, high-pitched breath sound indicating obstruction of the upper airway can also occur.
Damage to the airways can cause subcutaneous emphysema (air trapped in the subcutaneous tissue of the skin) in the abdomen, chest, neck, and head. Subcutaneous emphysema, present in up to 85% of people with TBI, is particularly indicative of the injury when it is only in the neck.Paidas CN. (September 15, 2006) Thoracic Trauma. Retrieved on June 13, 2007. Air is trapped in the chest cavity outside the lungs (pneumothorax) in about 70% of TBI. Especially strong evidence that TBI has occurred is failure of a pneumothorax to resolve even when a chest tube
A chest tube (also chest drain, thoracic catheter, tube thoracostomy or intercostal drain) is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum in order to remove clinically undesired substance ...
is placed to rid the chest cavity of the air; it shows that air is continually leaking into the chest cavity from the site of the tear. Air can also be trapped in the mediastinum, the center of the chest cavity (pneumomediastinum
Pneumomediastinum (from Greek ''pneuma'' – "air", also known as mediastinal emphysema) is pneumatosis (abnormal presence of air or other gas) in the mediastinum, the central part of the chest cavity. First described in 1819 by René Laennec, ...
). If air escapes from a penetrating injury to the neck, a definite diagnosis of TBI can be made. Hamman's sign
Hamman's sign (rarely, Hammond's sign or Hammond's crunch) is a crunching, rasping sound, synchronous with the heartbeat, heard over the precordium in spontaneous mediastinal emphysema. It is felt to result from the heart beating against air-fille ...
, a sound of crackling that occurs in time with the heartbeat, may also accompany TBI.
Causes
Injuries to the tracheobronchial tree within the chest may occur due to penetrating forces such asgunshot wounds
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating injury caused by a projectile (e.g. a bullet) from a gun (typically firearm or air gun). Damages may include bleeding, bone fractures, organ damage, wound infection, loss of the ability to move part ...
, but are more often the result of blunt trauma. TBI due blunt forces usually results from high-energy impacts such as falls from height and motor vehicle accidents; the injury is rare in low-impact mechanisms. Injuries of the trachea cause about 1% of traffic-related deaths. Other potential causes are falls from high places and injuries in which the chest is crushed. Explosions are another cause.
Gunshot wounds are the commonest form of penetrating trauma that cause TBI. Less commonly, knife wounds and shrapnel from motor vehicle accidents can also penetrate the airways. Most injuries to the trachea occur in the neck, because the airways within the chest are deep and therefore well protected; however, up to a quarter of TBI resulting from penetrating trauma occurs within the chest. Injury to the cervical trachea usually affects the anterior (front) part of the trachea.
Certain medical procedures can also injure the airways; these include tracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, and tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The r ...
. The back of the trachea may be damaged during tracheotomy. TBI resulting from tracheal intubation (insertion of a tube into the trachea) is rare, and the mechanism by which it occurs is unclear. However, one likely mechanism involves an endotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the Vertebrate trachea, trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate Gas exchange, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many diffe ...
catching in a fold of membrane and tearing it as it is advanced downward through the airway. When an endotracheal tube tears the trachea, it typically does so at the posterior (back) membranous wall. Unlike TBI that results from blunt trauma, most iatrogenic injuries to the airway involve longitudinal tears to the back of the trachea or tears on the side that pull the membranous part of the trachea away from the cartilage. Excessive pressure from the cuff of an endotracheal tube can reduce blood supply to the tissues of the trachea, leading to ischemia and potentially causing it to become ulcerated, infected, and, later, narrowed.
The mucosal lining of the trachea may also be injured by inhalation of hot gases or harmful fumes such as chlorine gas
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
. This can lead to edema (swelling), necrosis (death of the tissue), scar formation, and ultimately stenosis. However, TBI due to inhalation, foreign body aspiration, and medical procedures is uncommon.
Mechanism
The structures in the tracheobronchial tree are well protected, so it normally takes a large amount of force to injure them. In blunt trauma, TBI is usually the result of violent compression of the chest. Rapidhyperextension
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
of the neck, usually resulting from vehicle crashes, can also injure the trachea, and trauma to the neck can crush the trachea against the vertebrae. A crush injury of the larynx or cervical trachea can occur in head-on collisions when the neck is hyperextended and strikes the steering wheel or dashboard; this has been called a "dashboard injury". The larynx and cervical trachea may also be injured in front-on collisions by the seat belt.
Although the mechanism is not well understood, TBI due to blunt trauma is widely thought to be caused by any combination of three possible mechanisms: an increase in pressure within the airways, shearing
Sheep shearing is the process by which the woollen fleece of a sheep is cut off. The person who removes the sheep's wool is called a '' shearer''. Typically each adult sheep is shorn once each year (a sheep may be said to have been "shorn" or ...
, and pulling apart. The first type of injury, sometimes called an "explosive rupture", may occur when the chest is violently compressed, for example when a driver strikes the steering wheel in a vehicle accident or when the chest is crushed. The pressure in the airways, especially the larger airways (the trachea and bronchi), quickly rises as a result of the compression, because the glottis reflexively closes off the airways. When this pressure exceeds the elasticity of the tissues, they burst; thus the membranous part of the trachea is more commonly affected by this mechanism of injury than cartilaginous portions.
The second mechanism may occur when the chest is suddenly decelerated, as occurs in vehicle accidents, producing a shearing force. The lungs are mobile in the chest cavity but their movement is more restricted near the hilum. Areas near the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
and carina are fixed to the thyroid cartilage
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the ''laryngeal skeleton'', the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx (only the cricoid cartilage ...
and the pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made o ...
respectively; thus if the airways move, they can tear at these points of fixation.
The third mechanism occurs when the chest is compressed from front to back, causing it to widen from side to side. The lungs adhere to the chest wall because of the negative pressure between them and the pleural membranes lining the inside of the chest cavity; thus when the chest widens, they are pulled apart. This creates tension at the carina; the airway tears if this tensile force exceeds its elasticity. This mechanism may be the cause of injury when the chest is crushed. Most TBI are probably due to a combination of these three mechanisms.
When airways are damaged, air can escape from them and be trapped in the surrounding tissues in the neck (subcutaneous emphysema) and mediastinum (pneumomediastinum); if it builds up to high enough pressures there, it can compress the airways. Massive air leaks from a ruptured airway can also compromise the circulation by preventing blood from returning to the heart from the head and lower body; this causes a potentially deadly reduction in the amount of blood the heart is able to pump out. Blood and other fluids can build up in the airways, and the injury can interfere with the patency of the airway and interfere with its continuity. However, even if the trachea is completely transected, the tissues surrounding it may hold it together enough for adequate air exchange to occur, at least at first.
Anatomy
 The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. The trachea is situated between the lower end of the larynx and the center of the chest, where it splits into the two bronchi at a ridge called the
The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. The trachea is situated between the lower end of the larynx and the center of the chest, where it splits into the two bronchi at a ridge called the carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
. The trachea is stabilized and kept open by rings made of cartilage that surround the front and sides of the structure; these rings are not closed and do not surround the back, which is made of membrane. The bronchi split into smaller branches and then to bronchioles that supply air to the alveoli, the tiny air-filled sacs in the lungs responsible for absorbing oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
. An arbitrary division can be made between the intrathoracic
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There a ...
and cervical
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings:
# of or pertaining to any neck.
# of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus.
*Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are
**cervical collar
**cerv ...
trachea at the thoracic inlet, an opening at the top of the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
. Anatomical structures that surround and protect the tracheobronchial tree include the lungs, the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
, large blood vessels, the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a sem ...
, the thoracic spine
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
, and the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sha ...
. Children have softer tracheas and a more elastic tracheobronchial trees than adults; this elasticity, which helps protect the structures from injury when they are compressed, may contribute to the lower incidence of TBI in children.
Diagnosis
 Rapid diagnosis and treatment are important in the care of TBI; if the injury is not diagnosed shortly after the injury, the risk of complications is higher. Bronchoscopy is the most effective method to diagnose, locate, and determine the severity of TBI, and it is usually the only method that allows a definitive diagnosis. Diagnosis with a flexible bronchoscope, which allows the injury to be visualized directly, is the fastest and most reliable technique. In people with TBI, bronchoscopy may reveal that the airway is torn, or that the airways are blocked by blood, or that a bronchus has collapsed, obscuring more distal (lower) bronchi from view.
Chest x-ray is the initial imaging technique used to diagnose TBI. The film may not have any signs in an otherwise asymptomatic patient. Indications of TBI seen on radiographs include deformity in the trachea or a defect in the tracheal wall. Radiography may also show cervical emphysema, air in the tissues of the neck. X-rays may also show accompanying injuries and signs such as fractures and subcutaneous emphysema. If subcutaneous emphysema occurs and the hyoid bone appears in an X-ray to be sitting unusually high in the throat, it may be an indication that the trachea has been severed. TBI is also suspected if an endotracheal tube appears in an X-ray to be out of place, or if its cuff appears to be more full than normal or to protrude through a tear in the airway. If a bronchus is torn all the way around, the lung may collapse outward toward the chest wall (rather than inward, as it usually does in pneumothorax) because it loses the attachment to the bronchus which normally holds it toward the center. In a person lying face-up, the lung collapses toward the diaphragm and the back. This sign, described in 1969, is called fallen lung sign and is
Rapid diagnosis and treatment are important in the care of TBI; if the injury is not diagnosed shortly after the injury, the risk of complications is higher. Bronchoscopy is the most effective method to diagnose, locate, and determine the severity of TBI, and it is usually the only method that allows a definitive diagnosis. Diagnosis with a flexible bronchoscope, which allows the injury to be visualized directly, is the fastest and most reliable technique. In people with TBI, bronchoscopy may reveal that the airway is torn, or that the airways are blocked by blood, or that a bronchus has collapsed, obscuring more distal (lower) bronchi from view.
Chest x-ray is the initial imaging technique used to diagnose TBI. The film may not have any signs in an otherwise asymptomatic patient. Indications of TBI seen on radiographs include deformity in the trachea or a defect in the tracheal wall. Radiography may also show cervical emphysema, air in the tissues of the neck. X-rays may also show accompanying injuries and signs such as fractures and subcutaneous emphysema. If subcutaneous emphysema occurs and the hyoid bone appears in an X-ray to be sitting unusually high in the throat, it may be an indication that the trachea has been severed. TBI is also suspected if an endotracheal tube appears in an X-ray to be out of place, or if its cuff appears to be more full than normal or to protrude through a tear in the airway. If a bronchus is torn all the way around, the lung may collapse outward toward the chest wall (rather than inward, as it usually does in pneumothorax) because it loses the attachment to the bronchus which normally holds it toward the center. In a person lying face-up, the lung collapses toward the diaphragm and the back. This sign, described in 1969, is called fallen lung sign and is pathognomonic Pathognomonic (rare synonym ''pathognomic'') is a term, often used in medicine, that means "characteristic for a particular disease". A pathognomonic sign is a particular sign whose presence means that a particular disease is present beyond any doub ...
of TBI (that is, it is diagnostic for TBI because it does not occur in other conditions); however it occurs only rarely. In as many as one in five cases, people with blunt trauma and TBI have no signs of the injury on chest X-ray. CT scanning detects over 90% of TBI resulting from blunt trauma, but neither X-ray nor CT are a replacement for bronchoscopy.
At least 30% of TBI are not discovered at first; this number may be as high as 50%. In about 10% of cases, TBI has no specific signs either clinically or on chest radiography, and its detection may be further complicated by concurrent injuries, since TBI tends to occur after high-energy accidents. Weeks or months may go by before the injury is diagnosed, even though the injury is better known than it was in the past.
Classification
Lesions can betransverse
Transverse may refer to:
*Transverse engine, an engine in which the crankshaft is oriented side-to-side relative to the wheels of the vehicle
*Transverse flute, a flute that is held horizontally
* Transverse force (or ''Euler force''), the tangen ...
, occurring between the rings of the trachea, longitudinal or spiral. They may occur along the membranous part of the trachea, the main bronchi, or both. In 8% of ruptures, lesions are complex, occurring in more than one location, with more than one type of lesion, or on both of the main bronchi and the trachea. Transverse tears are more common than longitudinal or complex ones. The laceration may completely transect the airway or it may go only partway around. Partial tears that do not go all the way around the circumference of the airway do not allow a lacerated airway to become completely detached; tears that encircle the whole airway can allow separation to occur. Lacerations may also be classified as complete or incomplete. In an incomplete lesion, a layer of tissue surrounding the bronchus remains intact and can keep the air in the airway, preventing it from leaking into the areas surrounding the airways. Incomplete lacerations may require closer scrutiny to detect and may not be diagnosed right away.
Bronchial injuries are divided into those that are accompanied by a disruption of the pleura
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls.
The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips b ...
and those that are not; in the former, air can leak from the hole in the airway and a pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
can form. The latter type is associated with more minor signs; pneumothorax is small if it occurs at all, and although function is lost in the part of the lung supplied by the injured bronchus, unaffected parts of the lungs may be able to compensate.
Most TBI that results from blunt trauma occurs within the chest. The most common tracheal injury is a tear near the carina or in the membranous wall of the trachea. In blunt chest trauma, TBI occurs within 2.5 cm of the carina 40–80% of the time. The injury is more common in the right main bronchus than the left, possibly because the former is near vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
, which may injure it. Also, the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
and other tissues in the mid chest that surround the left main bronchus may protect it. Another possibility is that people with left main bronchus injuries are more likely to also have other deadly injuries and therefore die before reaching hospital, making them less likely to be included in studies that determine rates of injuries.
Prevention
Vehicle occupants who wear seat belts have a lower incidence of TBI after a motor vehicle accident. However, if the strap is situated across the front of the neck (instead of the chest), this increases the risk of tracheal injury. Design of medical instruments can be modified to prevent iatrogenic TBI, and medical practitioners can use techniques that reduce the risk of injury with procedures such as tracheotomy.Treatment
 Treatment of TBI varies based on the location and severity of injury and whether the patient is stable or having trouble breathing, but ensuring that the airway is patent so that the patient can breathe is always of paramount importance. Ensuring an open airway and adequate ventilation may be difficult in people with TBI. Intubation, one method to secure the airway, may be used to bypass a disruption in the airway in order to send air to the lungs. If necessary, a tube can be placed into the uninjured bronchus, and a single lung can be ventilated. If there is a penetrating injury to the neck through which air is escaping, the trachea may be intubated through the wound. Multiple unsuccessful attempts at conventional (direct)
Treatment of TBI varies based on the location and severity of injury and whether the patient is stable or having trouble breathing, but ensuring that the airway is patent so that the patient can breathe is always of paramount importance. Ensuring an open airway and adequate ventilation may be difficult in people with TBI. Intubation, one method to secure the airway, may be used to bypass a disruption in the airway in order to send air to the lungs. If necessary, a tube can be placed into the uninjured bronchus, and a single lung can be ventilated. If there is a penetrating injury to the neck through which air is escaping, the trachea may be intubated through the wound. Multiple unsuccessful attempts at conventional (direct) laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ...
may threaten the airway, so alternative techniques to visualize the airway, such as fiberoptic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
or video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) syst ...
laryngoscopy, may be employed to facilitate tracheal intubation. If the upper trachea is injured, an incision can be made in the trachea (tracheotomy) or the cricothyroid membrane
The cricothyroid ligament (also known as the cricothyroid membrane or cricovocal membrane) is a ligament in the neck. It connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. It prevents these cartilages from moving too far apart. It is cut dur ...
(cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, o ...
, or cricothyroidotomy) in order to ensure an open airway. However, cricothyrotomy may not be useful if the trachea is lacerated below the site of the artificial airway. Tracheotomy is used sparingly because it can cause complications such as infections and narrowing of the trachea and larynx. When it is impossible to establish a sufficient airway, or when complicated surgery must be performed, cardiopulmonary bypass
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen to the body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a ...
may be used—blood is pumped out of the body, oxygenated by a machine, and pumped back in. If a pneumothorax occurs, a chest tube may be inserted into the pleural cavity to remove the air.
 People with TBI are provided with supplemental oxygen and may need
People with TBI are provided with supplemental oxygen and may need mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
. Employment of certain measures such as Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and ventilation at higher-than-normal pressures may be helpful in maintaining adequate oxygenation. However, such measures can also increase leakage of air through a tear, and can stress the sutures in a tear that has been surgically repaired; therefore the lowest possible airway pressures that still maintain oxygenation are typically used. The use of high frequency ventilation has been reported. Mechanical ventilation can also cause pulmonary barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in tensi ...
when high pressure is required to ventilate the lungs. Techniques such as pulmonary toilet (removal of secretions), fluid management, and treatment of pneumonia are employed to improve pulmonary compliance
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the vertebral column, backbone o ...
(the elasticity of the lungs).
While TBI may be managed without surgery, surgical repair of the tear is considered standard in the treatment of most TBI. It is required if a tear interferes with ventilation; if mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies:
* direct contamination
* hematogenous or lymphatic spread
* extension of infe ...
(inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest) occurs; or if subcutaneous or mediastinal emphysema progresses rapidly; or if air leak or large pneumothorax is persistent despite chest tube placement. Other indications for surgery are a tear more than one third the circumference of the airway, tears with loss of tissue, and a need for positive pressure ventilation.Riley ''et al.'' (2004). pp. 548–9. Damaged tissue around a rupture (e.g. torn or scarred tissue) may be removed in order to obtain clean edges that can be surgically repaired. Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
of damaged tissue can shorten the trachea by as much as 50%.Riley ''et al.'' (2004). pp. 550–51. Repair of extensive tears can include sewing a flap of tissue taken from the membranes surrounding the heart or lungs (the pericardium and pleura, respectively) over the sutures to protect them. When lung tissue is destroyed as a result of TBI complications, pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy (or pneumectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove a lung first successfully done in 1933 by Dr. Evarts Graham. This is not to be confused with a lobectomy or segmentectomy, which only removes one part of the lung.
There are two ...
or lobectomy
Lobectomy means ''surgical excision of a lobe''. This may refer to a lobe of the lung (also simply called a lobectomy), a lobe of the thyroid ( hemithyroidectomy), a lobe of the brain (as in anterior temporal lobectomy), or a lobe of the liver ...
(removal of a lung or of one lobe, respectively) may be required. Pneumonectomy is avoided whenever possible due to the high rate of death associated with the procedure. Surgery to repair a tear in the tracheobronchial tree can be successful even when it is performed months after the trauma, as can occur if the diagnosis of TBI is delayed. When airway stenosis results after delayed diagnosis, surgery is similar to that performed after early diagnosis: the stenotic section is removed and the cut airway is repaired.
Prognosis and complications
sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
or multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
(MODS). If the condition is not recognized and treated early, serious complications are more likely to occur; for example, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
and bronchiectasis may occur as late complications. Years can pass before the condition is recognized. Some TBI are so small that they do not have significant clinical manifestations; they may never be noticed or diagnosed and may heal without intervention.
If granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any siz ...
grows over the injured site, it can cause stenosis of the airway, after a week to a month. The granulation tissue must be surgically excised. Delayed diagnosis of a bronchial rupture increases risk of infection and lengthens hospital stay. People with a narrowed airway may develop dyspnea, coughing, wheezing
A wheeze is a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, some part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower respiratory tract ...
, respiratory tract infection, and difficulty with clearing secretions. If the bronchiole is completely obstructed, atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct ...
occurs: the alveoli of the lung collapse. Lung tissue distal to a completely obstructed bronchiole often does not become infected. Because it is filled with mucus, this tissue remains functional. When the secretions are removed, the affected portion of the lung is commonly able to function almost normally. However, infection is common in lungs distal to a partially obstructed bronchiole. Infected lung tissue distal to a stricture can be damaged, and wheezing and coughing may develop due to the narrowing. In addition to pneumonia, the stenosis may cause bronchiectasis, in which bronchi are dilated, to develop. Even after an airway with a stricture is restored to normal, the resulting loss of lung function may be permanent.
Complications may also occur with treatment; for example, a granuloma can form at the suture site. Also, the sutured wound can tear again, as occurs when there is excessive pressure in the airways from ventilation. However, for people who do receive surgery soon after the injury to repair the lesion, outcome is usually good; the long-term outcome is good for over 90% of people who have TBI surgically repaired early in treatment. Even when surgery is performed years after the injury, the outlook is good, with low rates of death and disability and good chances of preserving lung function.
Epidemiology
Rupture of the trachea or bronchus is the most common type of blunt injury to the airway. It is difficult to determine the incidence of TBI: in as many as 30–80% of cases, death occurs before the person reaches a hospital, and these people may not be included in studies. On the other hand, some TBI are so small that they do not cause significant symptoms and are therefore never noticed. In addition, the injury sometimes is not associated with symptoms until complications develop later, further hindering estimation of the true incidence. However, autopsy studies have revealed TBI in 2.5–3.2% of people who died after trauma. Of all neck and chest traumas, including people that died immediately, TBI is estimated to occur in 0.5–2%. An estimated 0.5% ofpolytrauma Polytrauma and multiple trauma are medical terms describing the condition of a person who has been subjected to multiple traumatic injuries, such as a serious head injury in addition to a serious burn. The term is defined via an Injury Severity Sc ...
patients treated in trauma center
A trauma center (or trauma centre) is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major traumatic injuries such as falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. A trauma center may also refer to an emergen ...
s have TBI. The incidence is estimated at 2% in blunt chest and neck trauma and 1–2% in penetrating chest trauma. Laryngotracheal injuries occur in 8% of patients with penetrating injury to the neck, and TBI occurs in 2.8% of blunt chest trauma deaths. In people with blunt trauma who do reach a hospital alive, reports have found incidences of 2.1% and 5.3%. Another study of blunt chest trauma revealed an incidence of only 0.3%, but a mortality rate of 67% (possibly due in part to associated injuries). The incidence of iatrogenic TBI (that caused by medical procedures) is rising, and the risk may be higher for women and the elderly. TBI results about once every 20,000 times someone is intubated through the mouth, but when intubation is performed emergently, the incidence may be as high as 15%.
The mortality rate for people who reach a hospital alive was estimated at 30% in 1966; more recent estimates place this number at 9%. The number of people reaching a hospital alive has increased, perhaps due to improved prehospital
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to definitive care. ...
care or specialized treatment centers. Of those who reach the hospital alive but then die, most do so within the first two hours of arrival. The sooner a TBI is diagnosed, the higher the mortality rate; this is likely due to other accompanying injuries that prove fatal.
Accompanying injuries often play a key role in the outcome. Injuries that may accompany TBI include pulmonary contusion
A pulmonary contusion, also known as lung contusion, is a bruise of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, po ...
and laceration
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epid ...
; and fractures of the sternum, ribs
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
and clavicles
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right ...
. Spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cor ...
, facial trauma
Facial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations and bruises, or fractures of the facial bones such as nasal fractures and fractures ...
, traumatic aortic rupture
Traumatic aortic rupture, also called traumatic aortic disruption or transection, is a condition in which the aorta, the largest artery in the body, is torn or ruptured as a result of trauma to the body. The condition is frequently fatal due to th ...
, injuries to the abdomen, lung, and head are present in 40–100%. The most common accompanying injury is esophageal perforation or rupture (known as Boerhaave syndrome
Esophageal rupture is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal surgery. In contrast, the term Boerh ...
), which occurs in as many as 43% of the penetrating injuries to the neck that cause tracheal injury.
History
Throughout most of history, the mortality rate of TBI was thought to be 100%. However, in 1871 a healed TBI was noted in a duck that had been killed by a hunter, thus demonstrating that the injury could be survived, at least in the general sense.Riley ''et al.'' (2004). pp. 544–7. This report, made by Winslow, was the first record in the medical literature of a bronchus injury. In 1873, Seuvre made one of the earliest reports of TBI in the medical literature: a 74-year-old woman whose chest was crushed by a wagon wheel was found on autopsy to have an avulsion of the right bronchus. Long-term survival of the injury was unknown in humans until a report was made of a person who survived in 1927. In 1931, a report made by Nissen described successful removal of a lung in a 12-year-old girl who had had narrowing of the bronchus due to the injury. Repair of TBI was probably first attempted in 1945, when the first documented case of a successful suturing of a lacerated bronchus was made. Prior to 1950, the mortality rate was 36%; it had fallen to 9% by 2001; this improvement was likely due to improvements in treatments and surgical techniques, including those for injuries commonly associated with TBI.Notes
References
*External links
{{good article Chest trauma