Trace Italienne on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
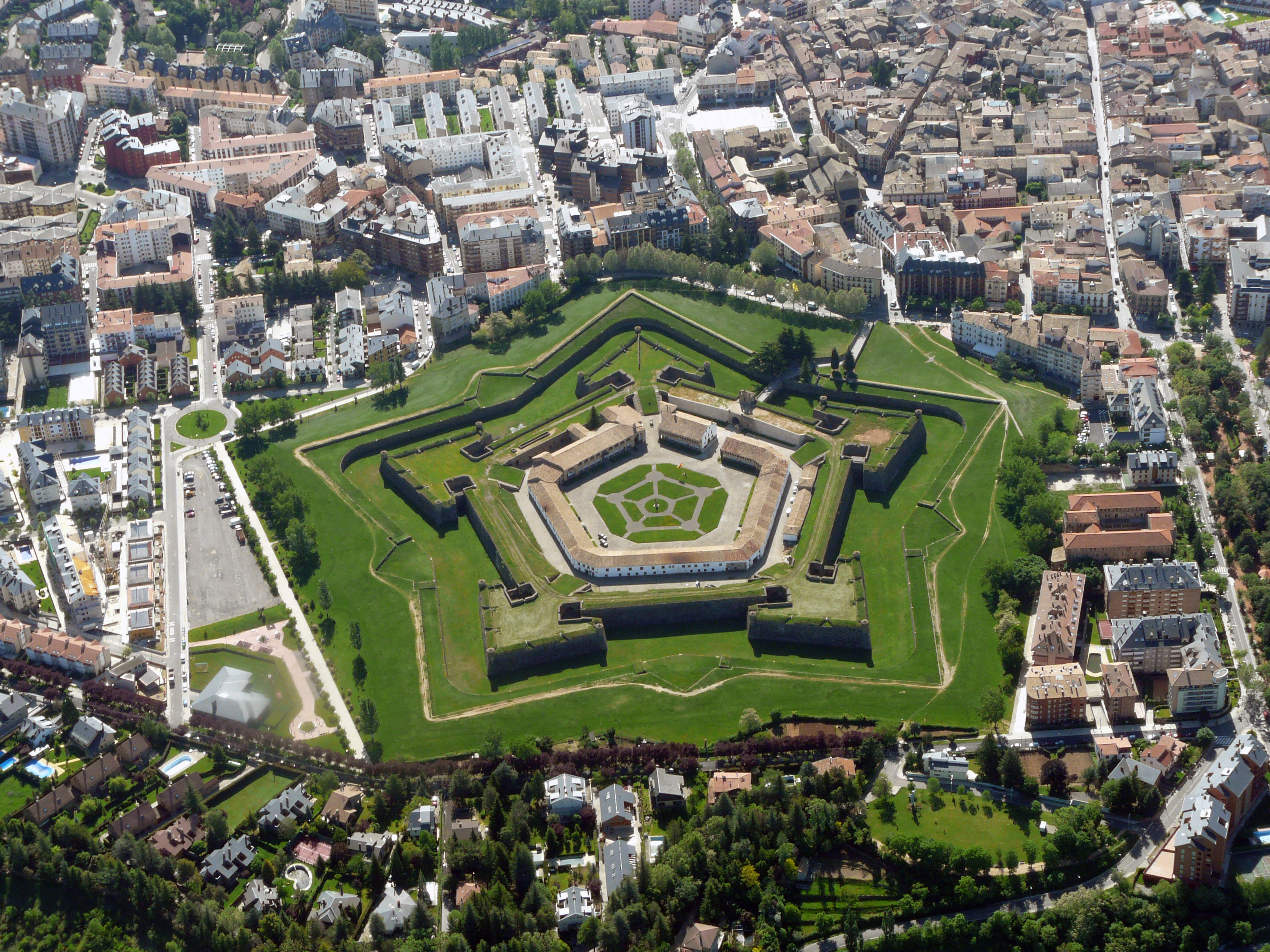
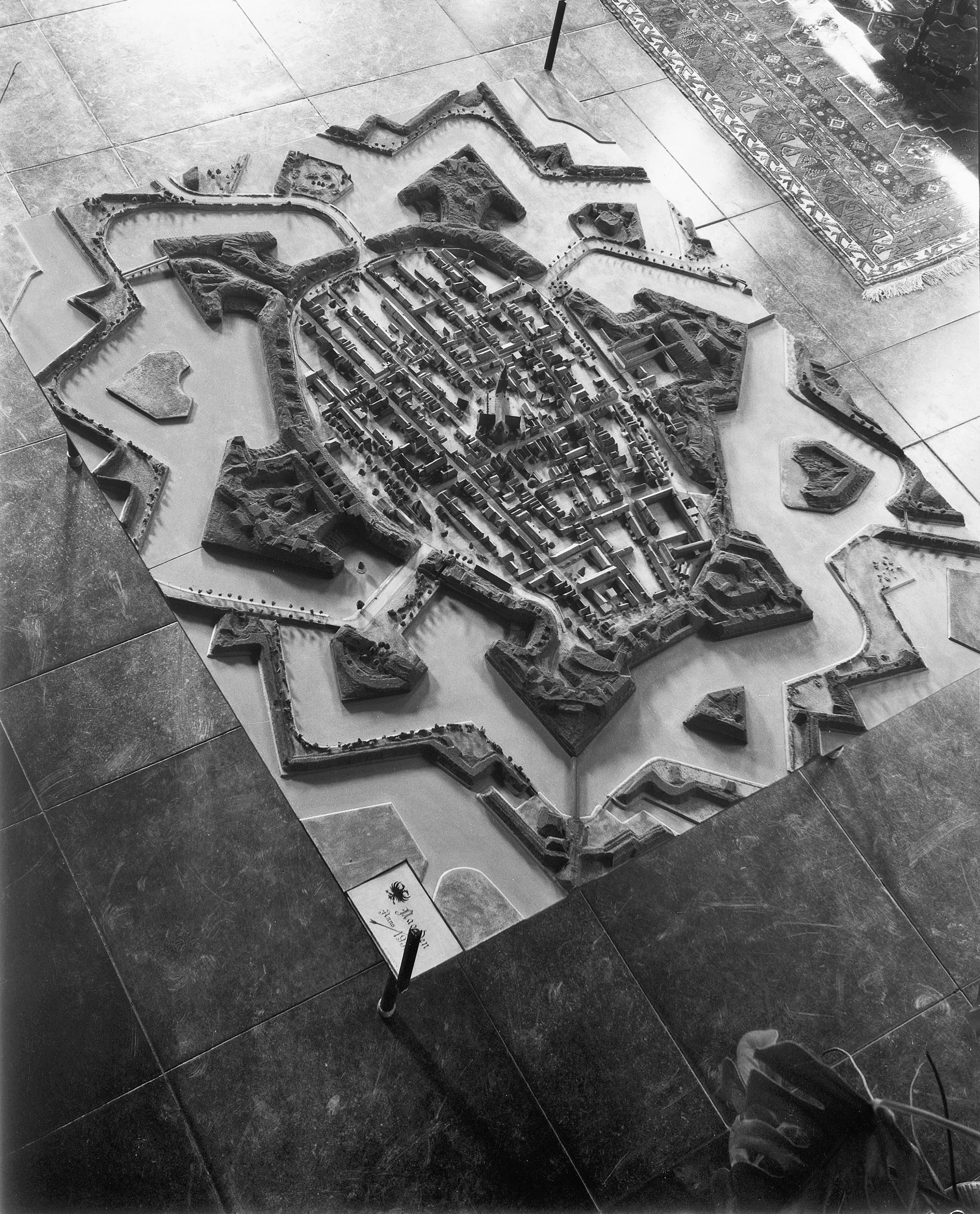

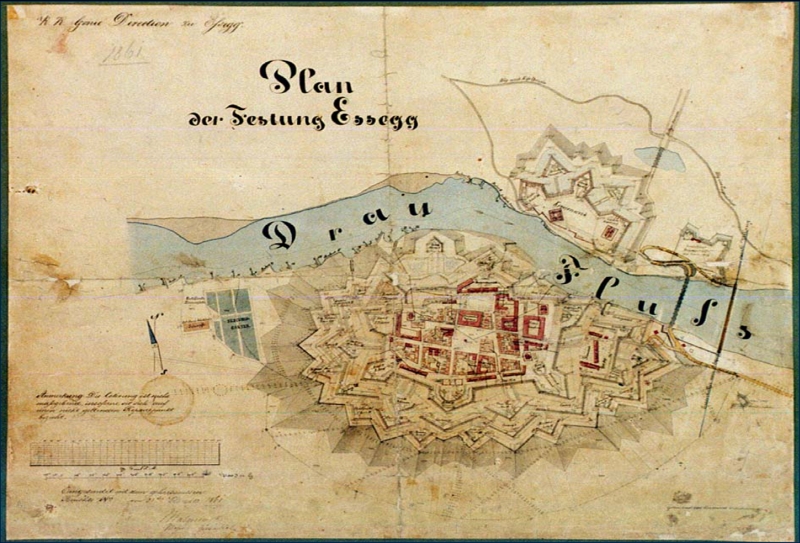
 A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a
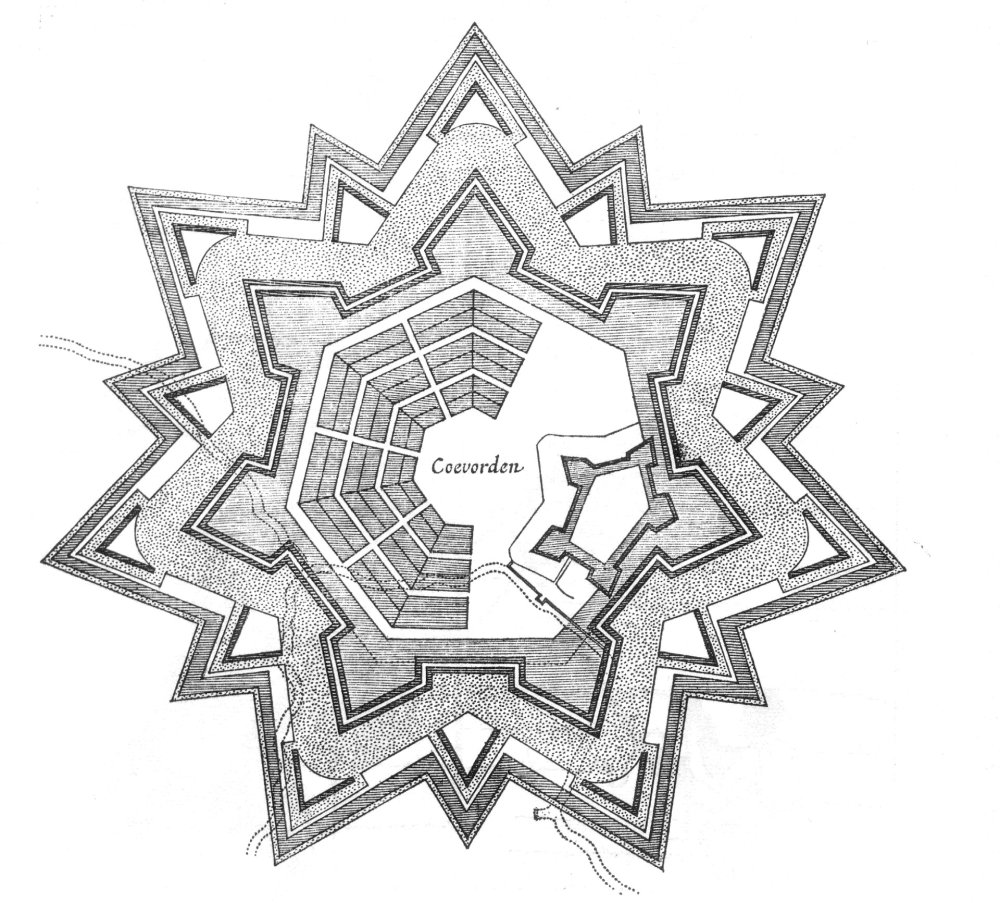 Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high
Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high
 Thus forts evolved complex shapes that allowed defensive batteries of cannon to command interlocking
Thus forts evolved complex shapes that allowed defensive batteries of cannon to command interlocking 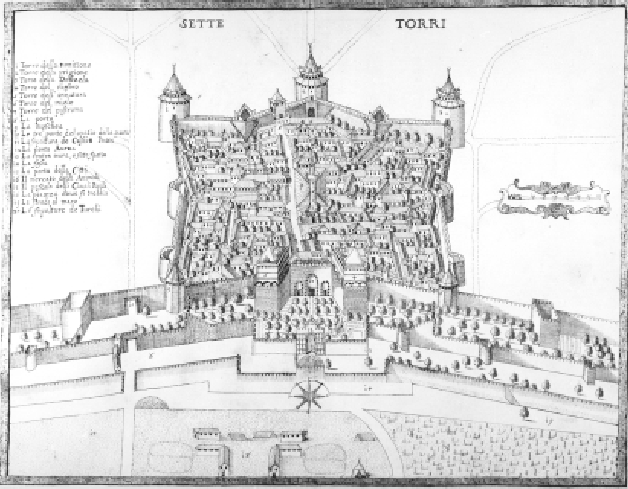 Fortifications of this type continued to be effective while the attackers were armed only with cannon, where the majority of the damage inflicted was caused by momentum from the impact of solid shot. Because only low explosives such as black powder were available, explosive shells were largely ineffective against such fortifications. The development of mortars, high explosives, and the consequent large increase in the destructive power of explosive shells and thus plunging fire rendered the intricate geometry of such fortifications irrelevant. Warfare was to become more mobile. It took, however, many years to abandon the old fortress thinking.
Fortifications of this type continued to be effective while the attackers were armed only with cannon, where the majority of the damage inflicted was caused by momentum from the impact of solid shot. Because only low explosives such as black powder were available, explosive shells were largely ineffective against such fortifications. The development of mortars, high explosives, and the consequent large increase in the destructive power of explosive shells and thus plunging fire rendered the intricate geometry of such fortifications irrelevant. Warfare was to become more mobile. It took, however, many years to abandon the old fortress thinking.


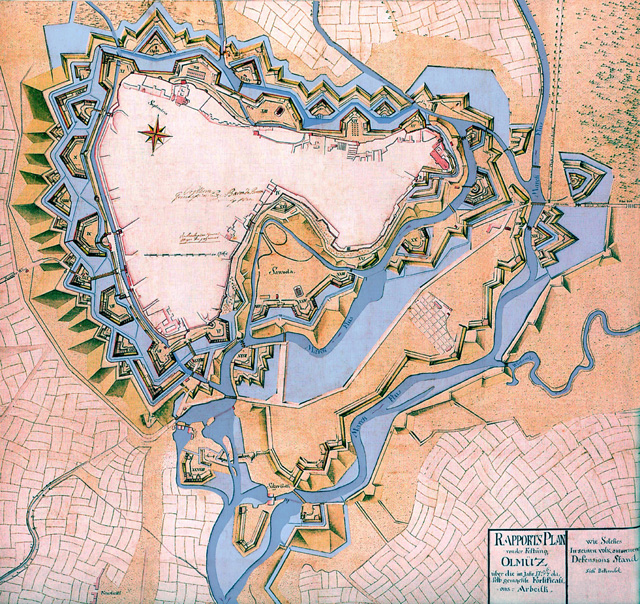 The first key instance of a ''trace Italianate'' was at the Papal port of Civitavecchia, where the original walls were lowered and thickened because the stone tended to shatter under bombardment.
The first key instance of a ''trace Italianate'' was at the Papal port of Civitavecchia, where the original walls were lowered and thickened because the stone tended to shatter under bombardment.
 Two star forts were built by the Order of Saint John on the island of Malta in 1552, Fort Saint Elmo and Fort Saint Michael. Fort Saint Elmo played a critical role in the Ottoman siege of 1565 when it managed to hold out heavy bombardment for over a month. Eventually it fell, but the Ottoman casualties were very high, and it bought time for the relief force which arrived from
Two star forts were built by the Order of Saint John on the island of Malta in 1552, Fort Saint Elmo and Fort Saint Michael. Fort Saint Elmo played a critical role in the Ottoman siege of 1565 when it managed to hold out heavy bombardment for over a month. Eventually it fell, but the Ottoman casualties were very high, and it bought time for the relief force which arrived from
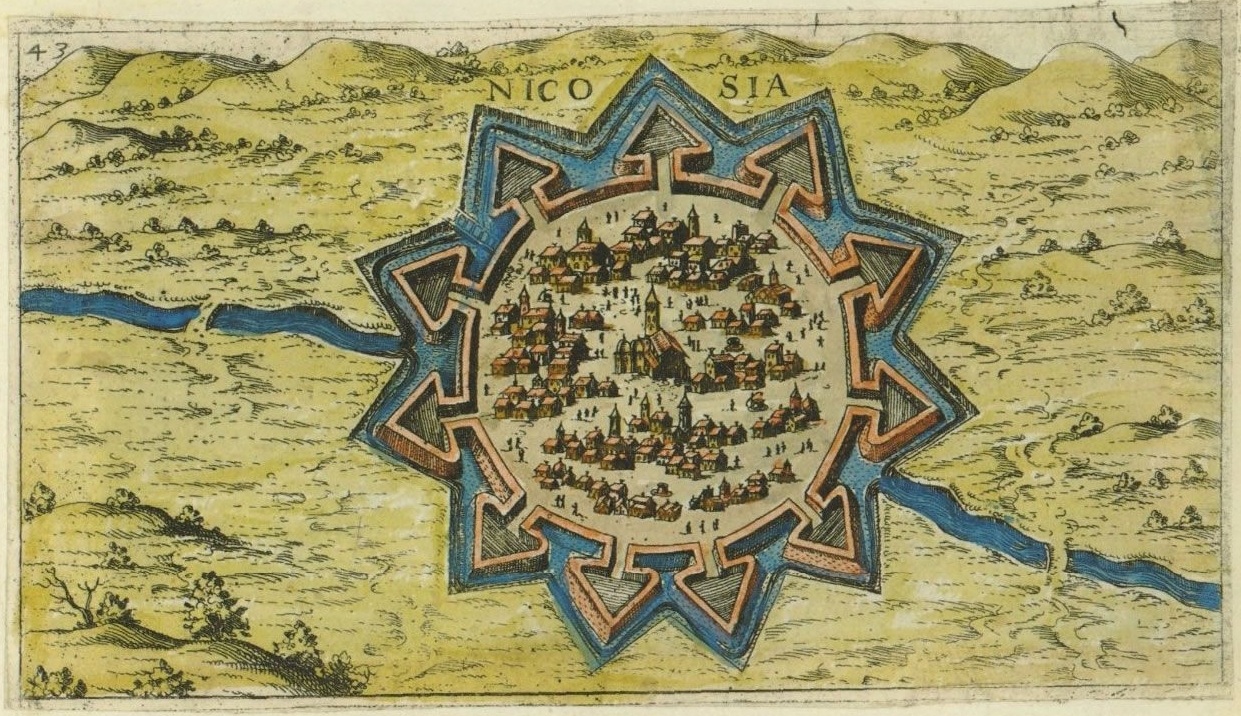 According to Geoffrey Parker in his article, ''The Military Revolution 1560–1660: A Myth?'', the appearance of the ''trace Italienne'' in early modern Europe, and the difficulty of taking such fortifications, resulted in a profound change in military strategy, most importantly, Parker argued, an increase in army sizes necessary to attack these forts. "Wars became a series of protracted sieges," Parker suggests, and open-pitch battles became "irrelevant" in regions where the ''trace Italienne'' existed. Ultimately, Parker argues, "military geography", in other words, the existence or absence of the ''trace Italienne'' in a given area, shaped military strategy in the early modern period. This is a profound alteration of the Military Revolution thesis originally proposed by Michael Roberts in 1955.
Parker's emphasis on the fortification as the key element has attracted substantial criticism from some academics, such as John A. Lynn and M. S. Kingra, particularly with respect to the claimed causal link between the new fortress design and increases in army sizes during this period.Kingra, Mahinder S. 'The Trace Italienne and the Military Revolution During the Eighty Years' War, 1567–1648.' The Journal of Military History 57, No. 3 (July, 1993): 431–446
According to Geoffrey Parker in his article, ''The Military Revolution 1560–1660: A Myth?'', the appearance of the ''trace Italienne'' in early modern Europe, and the difficulty of taking such fortifications, resulted in a profound change in military strategy, most importantly, Parker argued, an increase in army sizes necessary to attack these forts. "Wars became a series of protracted sieges," Parker suggests, and open-pitch battles became "irrelevant" in regions where the ''trace Italienne'' existed. Ultimately, Parker argues, "military geography", in other words, the existence or absence of the ''trace Italienne'' in a given area, shaped military strategy in the early modern period. This is a profound alteration of the Military Revolution thesis originally proposed by Michael Roberts in 1955.
Parker's emphasis on the fortification as the key element has attracted substantial criticism from some academics, such as John A. Lynn and M. S. Kingra, particularly with respect to the claimed causal link between the new fortress design and increases in army sizes during this period.Kingra, Mahinder S. 'The Trace Italienne and the Military Revolution During the Eighty Years' War, 1567–1648.' The Journal of Military History 57, No. 3 (July, 1993): 431–446
 In the nineteenth century, with the development of more powerful
In the nineteenth century, with the development of more powerful
Cataneo, Hieronymus, ''De arte bellica, sive, De designandis ac construendis arcibus & propugnaculis, necnon & de ijs oppugnandis, expugnandis, ac propugnandis: de itinere exercitus, ac castrametatione: quando expediat manus cum hoste conserere, ac tandem, quid imperatori sit in procinctu cauendum vel eligendum'', (1600)
at World Atlas
{{DEFAULTSORT:Star Fort Warfare of the Early Modern period Italian inventions


 A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder duri ...
came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.
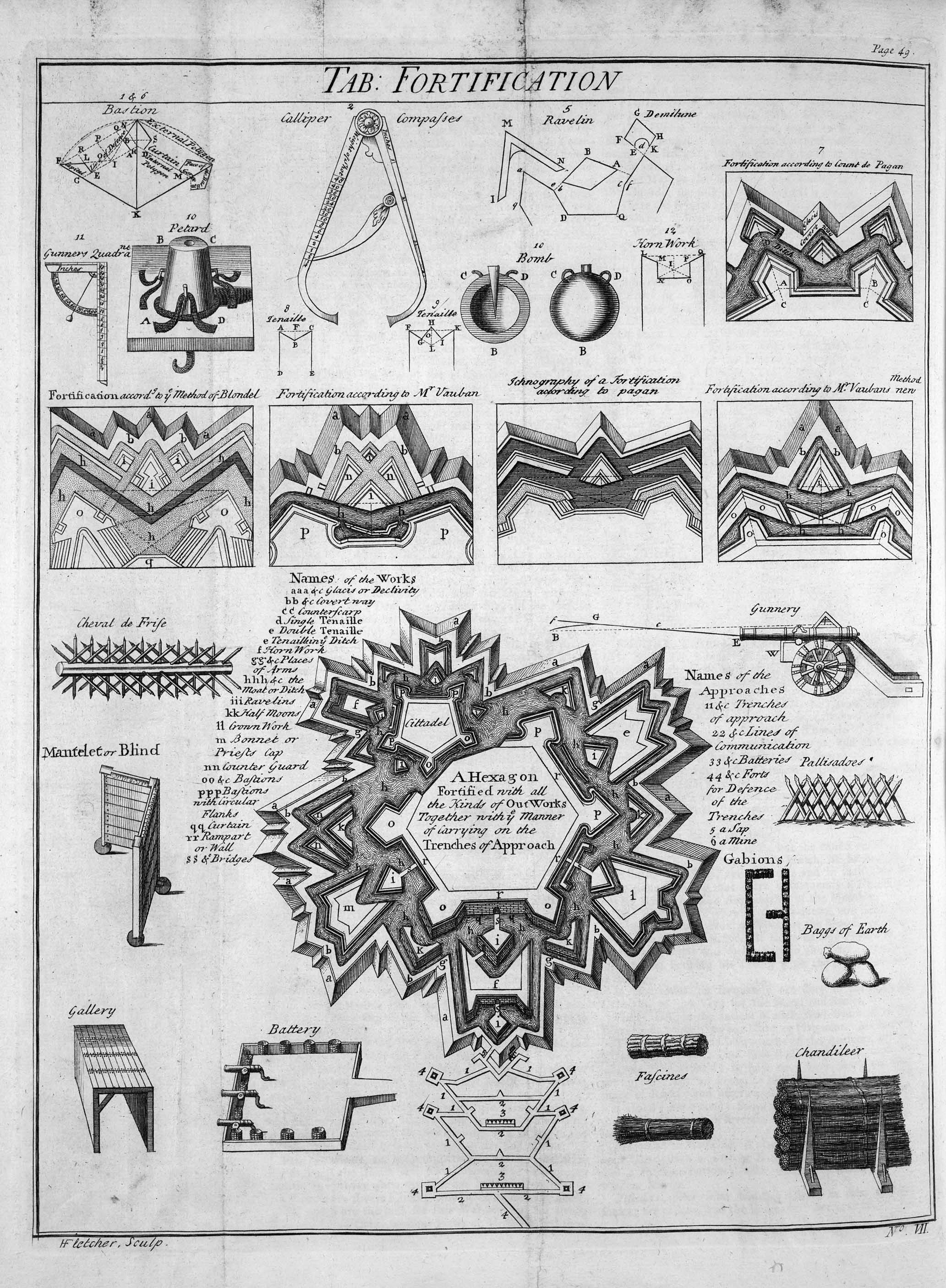
The design of the fort is normally a polygon with bastions at the corners of the walls. These outcroppings eliminated protected blind spots, called "dead zones", and allowed fire along the curtain from positions protected from direct fire. Many bastion forts also feature cavaliers, which are raised secondary structures based entirely inside the primary structure.
Origins
 Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high
Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as ...
s. From there, arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers ...
s were shot at the enemies. The enemies' hope was to either ram the gate or climb over the wall with ladders and overcome the defenders. For the invading force, these fortifications proved quite difficult to overcome, and accordingly, fortresses occupied a key position in warfare.
Passive ring-shaped ('' Enceinte'') fortifications of the Medieval era proved vulnerable to damage or destruction when attackers directed cannon fire on to perpendicular masonry wall. In addition, attackers that could get close to the wall were able to conduct undermining operations in relative safety, as the defenders could not shoot at them from nearby walls, until the development of Machicolation
A machicolation (french: mâchicoulis) is a floor opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement, through which stones or other material, such as boiling water, hot sand, quicklime or boiling cooking oil, could be dropped on attackers at ...
. In contrast, the bastion fortress was a very flat structure composed of many triangular bastions, specifically designed to cover each other, and a ditch. To counteract the cannonballs, defensive walls were made lower and thicker. To counteract the fact that lower walls were easier to climb, the ditch was widened so that attacking infantry were still exposed to fire from a higher elevation, including enfilading fire from the bastions.
The outer side of the ditch was usually provided with a glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glaci ...
to deflect cannonballs aimed at the lower part of the main wall. Further structures, such as ravelins, tenailles, hornworks or crownworks, and even detached forts could be added to create complex outer works to further protect the main wall from artillery, and sometimes provide additional defensive positions. They were built of many materials, usually earth and brick, as brick does not shatter on impact from a cannonball as stone does.
Bastion fortifications were further developed in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries, primarily in response to the French invasion of the Italian peninsula. The French army was equipped with new cannon and bombards that were easily able to destroy traditional fortifications built in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. Star forts were employed by Michelangelo in the defensive earthworks of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
, and refined in the sixteenth century by Baldassare Peruzzi and Vincenzo Scamozzi. The design spread out of Italy in the 1530s and 1540s.
It was employed heavily throughout Europe for the following three centuries. Italian engineers were heavily in demand throughout Europe to help build the new fortifications. The late-seventeenth-century architects Menno van Coehoorn and especially Vauban, Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ve ...
's military engineer, are considered to have taken the form to its logical extreme. "Fortresses... acquired ravelins
A ravelin is a triangular fortification or detached outwork, located in front of the innerworks of a fortress (the curtain walls and bastions). Originally called a ''demi-lune'', after the ''lunette'', the ravelin is placed outside a castle ...
and redoubts, bonnettes and lunettes, tenailles and tenaillons, counterguards and crownworks and hornworks
A hornwork is an element of the Italian bastion system of fortification. Its face is flanked with a pair of demi-bastions.
It is distinguished from a crownwork, because crownworks contain full bastions at their centers. They are both outwork
...
and curvettes and fausse brayes and scarps and cordons and banquettes and counterscarps..."
The star-shaped fortification had a formative influence on the patterning of the Renaissance ideal city: "The Renaissance was hypnotized by one city type which for a century and a half—from Filarete to Scamozzi—was impressed upon all utopian schemes: this is the star-shaped city." In the 19th century, the development of the explosive shell changed the nature of defensive fortifications. Elvas
Elvas () is a Portuguese municipality, former episcopal city and frontier fortress of easternmost central Portugal, located in the district of Portalegre in Alentejo. It is situated about east of Lisbon, and about west of the Spanish fortress ...
, in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
is considered by some to be the best surviving example of the Dutch school of fortifications.
Slopes
When the newly-effective manoeuvrable siege cannon came into military strategy in the fifteenth century, the response frommilitary engineers
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics be ...
was to arrange for the walls to be embedded into ditches fronted by earthen slopes (glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glaci ...
) so that they could not be attacked by destructive direct fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, ...
and to have the walls topped by earthen banks that absorbed and largely dissipated the energy of plunging fire. Where conditions allowed, as in Fort Manoel in Malta, the ditches were cut into the native rock, and the wall at the inside of the ditch was simply unquarried native rock. As the walls became lower, they also became more vulnerable to assault.
Dead zone
The rounded shape that had previously been dominant for the design of turrets created "dead space", or "dead zones", which were relatively sheltered from defending fire, because direct fire from other parts of the defences could not be directed around curved walls. To prevent this, what had previously been round or square turrets were extended into diamond-shaped points to eliminate potential cover for attacking troops. The ditches and walls channelled the attackers into carefully constructed zwinger, bailey, or similar " kill zone" areas where the attackers had no place to shelter from the fire of the defenders.Enfilade
A further and more subtle change was to move from a passive model of defence to an active one. The lower walls were more vulnerable to being stormed, and the protection that the earthen banking provided against direct fire failed if the attackers could occupy the slope on the outside of the ditch and mount an attacking cannon there. Therefore, the shape was designed to make maximum use of ''enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
'' (or flanking) fire against any attackers who should reach the base of any of the walls. The indentations in the base of each point on the star sheltered cannons. Those cannons would have a clear line of fire directly down the edge of the neighbouring points, while their point of the star was protected by fire from the base of those points. The evolution of these ideas can be seen in transitional fortifications such as Sarzana in northwest Italy.
Other changes
 Thus forts evolved complex shapes that allowed defensive batteries of cannon to command interlocking
Thus forts evolved complex shapes that allowed defensive batteries of cannon to command interlocking fields of fire
The field of fire of a weapon (or group of weapons) is the area around it that can easily and effectively be reached by gunfire. The term 'field of fire' is mostly used in reference to machine guns. Their fields of fire incorporate the beaten zon ...
. Forward batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
commanded the slopes which defended walls deeper in the complex from direct fire. The defending cannon were not simply intended to deal with attempts to storm the walls, but to actively challenge attacking cannon and deny them approach close enough to the fort to engage in direct fire against the vulnerable walls.
The key to the fort's defence moved to the outer edge of the ditch surrounding the fort, known as the covered way, or covert way. Defenders could move relatively safely in the cover of the ditch and could engage in active countermeasures to keep control of the glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glaci ...
, the open slope that lay outside the ditch, by creating defensive earthworks to deny the enemy access to the glacis and thus to firing points that could bear directly onto the walls and by digging counter mines to intercept and disrupt attempts to mine the fort walls.
Compared to medieval fortifications, forts became both lower and larger in area, providing defence in depth, with tiers of defences that an attacker needed to overcome in order to bring cannon to bear on the inner layers of defences.
Firing emplacements for defending cannon were heavily defended from bombardment by external fire, but open towards the inside of the fort, not only to diminish their usefulness to the attacker should they be overcome, but also to allow the large volumes of smoke that the defending cannon would generate to dissipate.
 Fortifications of this type continued to be effective while the attackers were armed only with cannon, where the majority of the damage inflicted was caused by momentum from the impact of solid shot. Because only low explosives such as black powder were available, explosive shells were largely ineffective against such fortifications. The development of mortars, high explosives, and the consequent large increase in the destructive power of explosive shells and thus plunging fire rendered the intricate geometry of such fortifications irrelevant. Warfare was to become more mobile. It took, however, many years to abandon the old fortress thinking.
Fortifications of this type continued to be effective while the attackers were armed only with cannon, where the majority of the damage inflicted was caused by momentum from the impact of solid shot. Because only low explosives such as black powder were available, explosive shells were largely ineffective against such fortifications. The development of mortars, high explosives, and the consequent large increase in the destructive power of explosive shells and thus plunging fire rendered the intricate geometry of such fortifications irrelevant. Warfare was to become more mobile. It took, however, many years to abandon the old fortress thinking.

Construction
Bastion forts were very expensive.Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
's 22 bastions cost 11 million florins, and Siena in 1544 bankrupted itself to pay for its defences. For this reason, bastion forts were often improvised from earlier defences. Medieval curtain walls were torn down, and a ditch was dug in front of them. The earth used from the excavation was piled behind the walls to create a solid structure. While purpose-built fortifications would often have a brick fascia because of the material's ability to absorb the shock of artillery fire, many improvised defences cut costs by leaving this stage out and instead opting for more earth. Improvisation could also consist of lowering medieval round towers and infilling them with earth to strengthen the structures.
It was also often necessary to widen and deepen the ditch outside the walls to create a more effective barrier to frontal assault and mining. Engineers from the 1520s were also building massive, gently sloping banks of earth called glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glaci ...
in front of ditches so that the walls were almost totally hidden from horizontal artillery fire. The main benefit of the glaces was to deny enemy artillery the ability to fire point-blank. The lower the angle of elevation, the higher the stopping power.

 The first key instance of a ''trace Italianate'' was at the Papal port of Civitavecchia, where the original walls were lowered and thickened because the stone tended to shatter under bombardment.
The first key instance of a ''trace Italianate'' was at the Papal port of Civitavecchia, where the original walls were lowered and thickened because the stone tended to shatter under bombardment.
Effectiveness
The first major battle which truly showed the effectiveness of ''trace Italienne'' was the defence ofPisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the ...
in 1500 against a combined Florentine and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
army. With the original medieval fortifications beginning to crumble to French cannon fire, the Pisans constructed an earthen rampart behind the threatened sector. It was discovered that the sloping earthen rampart could be defended against escalade
{{Unreferenced, date=May 2007
Escalade is the act of scaling defensive walls or ramparts with the aid of ladders. Escalade was a prominent feature of sieges in ancient and medieval warfare, and though it is no longer common in modern war ...
and was also much more resistant to cannon fire than the curtain wall it had replaced.
The second siege was that of Padua in 1509. A monk engineer named Fra Giocondo, trusted with the defence of the Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
city, cut down the city's medieval wall and surrounded the city with a broad ditch that could be swept by flanking fire from gun ports set low in projections extending into the ditch. Finding that their cannon fire made little impression on these low ramparts, the French and allied besiegers made several bloody and fruitless assaults and then withdrew.
The new type of fortification also played a role in the numerous Mediterranean wars, slowing down the Ottoman expansion. Although Rhodes had been partially upgraded to the new type of fortifications after the 1480 siege, it was still conquered in 1522; nevertheless it was a long and bloody siege, and the besieged had no hope of outside relief because the island was close to the Ottoman power base and far from any allies. On the other hand, the Ottomans failed to take Corfu in 1537 in no small part because of the new fortifications, and several attempts spanning almost two centuries (another major one was in 1716) also failed.
 Two star forts were built by the Order of Saint John on the island of Malta in 1552, Fort Saint Elmo and Fort Saint Michael. Fort Saint Elmo played a critical role in the Ottoman siege of 1565 when it managed to hold out heavy bombardment for over a month. Eventually it fell, but the Ottoman casualties were very high, and it bought time for the relief force which arrived from
Two star forts were built by the Order of Saint John on the island of Malta in 1552, Fort Saint Elmo and Fort Saint Michael. Fort Saint Elmo played a critical role in the Ottoman siege of 1565 when it managed to hold out heavy bombardment for over a month. Eventually it fell, but the Ottoman casualties were very high, and it bought time for the relief force which arrived from Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
to relieve the rest of the besieged island. The star fort therefore played a crucial and decisive role in the siege.
After the fall of Venice to Napoleon, Corfu was occupied in 1797 by the French republican armies. The now ancient fortifications were still of some value at this point. A Russian–Ottoman–English alliance led at sea by Admiral Ushakov
Fyodor Fyodorovich Ushakov ( rus, Фёдор Фёдорович Ушако́в, p=ʊʂɐˈkof; – ) was an 18th century Russian naval commander and admiral. He is notable for winning every engagement he participated in as the Admiral of ...
and with troops sent by Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
retook Corfu in 1799 after a four-month siege, when the garrison led by general Louis François Jean Chabot
Louis François Jean Chabot (27 April 1757 in Niort – 11 March 1837 in Sansais) was a French general. He was in charge of the French forces at the Siege of Corfu (1798–99) when a combined Russian and Ottoman force captured the island ...
, being short of provisions and having lost the key island of Vido at the entrance of the port, surrendered and was allowed passage back to France.
Role in the military revolution
 According to Geoffrey Parker in his article, ''The Military Revolution 1560–1660: A Myth?'', the appearance of the ''trace Italienne'' in early modern Europe, and the difficulty of taking such fortifications, resulted in a profound change in military strategy, most importantly, Parker argued, an increase in army sizes necessary to attack these forts. "Wars became a series of protracted sieges," Parker suggests, and open-pitch battles became "irrelevant" in regions where the ''trace Italienne'' existed. Ultimately, Parker argues, "military geography", in other words, the existence or absence of the ''trace Italienne'' in a given area, shaped military strategy in the early modern period. This is a profound alteration of the Military Revolution thesis originally proposed by Michael Roberts in 1955.
Parker's emphasis on the fortification as the key element has attracted substantial criticism from some academics, such as John A. Lynn and M. S. Kingra, particularly with respect to the claimed causal link between the new fortress design and increases in army sizes during this period.Kingra, Mahinder S. 'The Trace Italienne and the Military Revolution During the Eighty Years' War, 1567–1648.' The Journal of Military History 57, No. 3 (July, 1993): 431–446
According to Geoffrey Parker in his article, ''The Military Revolution 1560–1660: A Myth?'', the appearance of the ''trace Italienne'' in early modern Europe, and the difficulty of taking such fortifications, resulted in a profound change in military strategy, most importantly, Parker argued, an increase in army sizes necessary to attack these forts. "Wars became a series of protracted sieges," Parker suggests, and open-pitch battles became "irrelevant" in regions where the ''trace Italienne'' existed. Ultimately, Parker argues, "military geography", in other words, the existence or absence of the ''trace Italienne'' in a given area, shaped military strategy in the early modern period. This is a profound alteration of the Military Revolution thesis originally proposed by Michael Roberts in 1955.
Parker's emphasis on the fortification as the key element has attracted substantial criticism from some academics, such as John A. Lynn and M. S. Kingra, particularly with respect to the claimed causal link between the new fortress design and increases in army sizes during this period.Kingra, Mahinder S. 'The Trace Italienne and the Military Revolution During the Eighty Years' War, 1567–1648.' The Journal of Military History 57, No. 3 (July, 1993): 431–446
Obsolescence
 In the nineteenth century, with the development of more powerful
In the nineteenth century, with the development of more powerful artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieg ...
and explosive shells, star forts were replaced by simpler but more robust polygonal fort
A polygonal fort is a type of fortification originating in France in the late 18th century and fully developed in Germany in the first half of the 19th century. Unlike earlier forts, polygonal forts had no bastions, which had proved to be vulnerab ...
s. In the twentieth century, with the development of tanks and aerial warfare during and after the First World War, fixed fortifications became and have remained less important than in previous centuries.
Star forts reappeared during the early 21st century French intervention in Mali where they were built by the 17th Parachute Engineer Regiment
The 17th Parachute Engineer Regiment (french: 17e Régiment de Génie Parachutiste, List of French paratrooper units, 17e RGP) is heir to the traditions of the 17th Colonial Engineer Regiment (french: :fr:17e régiment colonial du génie, 17e Ré ...
.
See also
* Venetian Works of Defence - AUNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
comprising six of the most outstanding examples of early bastion fort design.
* Suomenlinna - A later example of the bastion fort and a World Heritage Site, built in 1758.
* Crenellation
* List of established military terms
* List of star forts
* Mathematics and architecture
* Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban
* Menno van Coehoorn
* Erik Dahlberg
Notes
References
* af Hällström, Olof (2004) ''Sveaborg – The island fortress off Helsinki'', * Duffy, C. (1975) ''Fire & Stone, The Science of Fortress Warfare 1660–1860'',External links
Cataneo, Hieronymus, ''De arte bellica, sive, De designandis ac construendis arcibus & propugnaculis, necnon & de ijs oppugnandis, expugnandis, ac propugnandis: de itinere exercitus, ac castrametatione: quando expediat manus cum hoste conserere, ac tandem, quid imperatori sit in procinctu cauendum vel eligendum'', (1600)
at World Atlas
{{DEFAULTSORT:Star Fort Warfare of the Early Modern period Italian inventions