Topeka (minor League Baseball) Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
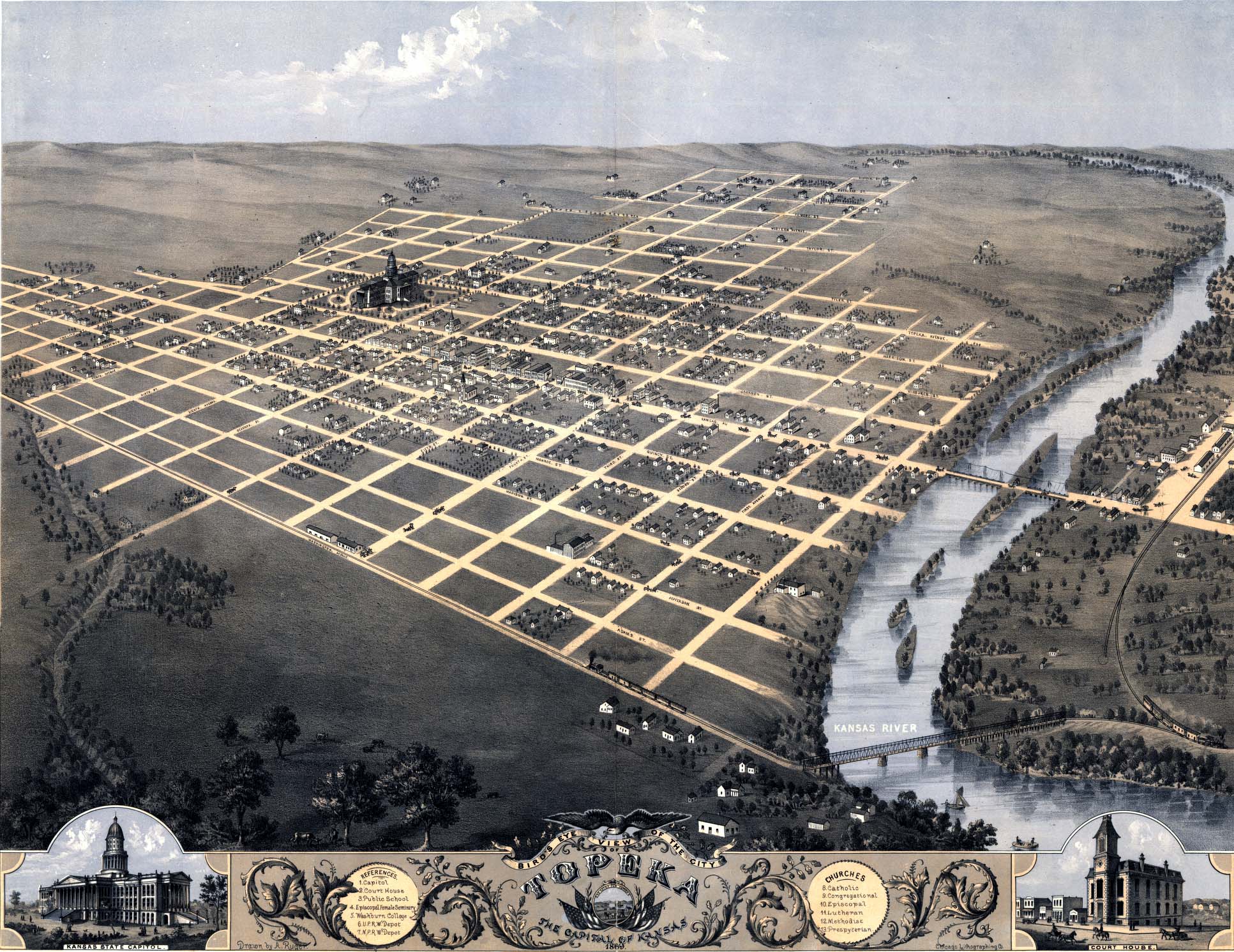 In the early 1850s, traffic along the Oregon Trail was supplemented by trade on a new military road stretching from
In the early 1850s, traffic along the Oregon Trail was supplemented by trade on a new military road stretching from  State officers first used the state capitol in 1869, moving from
State officers first used the state capitol in 1869, moving from
 Home to the first African-American kindergarten west of the Mississippi River, Topeka was the home of Oliver Brown, the named plaintiff in ''
Home to the first African-American kindergarten west of the Mississippi River, Topeka was the home of Oliver Brown, the named plaintiff in '' On June 8, 1966, Topeka was struck by a tornado rated F5 on the
On June 8, 1966, Topeka was struck by a tornado rated F5 on the  Topeka recovered from the 1966 tornado and has sustained steady economic growth. Washburn University, which lost several historic buildings, received financial support from the community and alumni to rebuild many school facilities. Today, university facilities offer more than one million square feet of modern academic and support space.
In 1974,
Topeka recovered from the 1966 tornado and has sustained steady economic growth. Washburn University, which lost several historic buildings, received financial support from the community and alumni to rebuild many school facilities. Today, university facilities offer more than one million square feet of modern academic and support space.
In 1974,  In 1989, Topeka became a motorsports mecca with the opening of
In 1989, Topeka became a motorsports mecca with the opening of
 Topeka is at , in north east Kansas at the intersection of
Topeka is at , in north east Kansas at the intersection of
 Being the state's capital (political), capital city, Topeka's largest employer is the State of Kansas—employing about 8,400 people, or 69% of the city's government workers. Altogether, government workers make up one out of every five employed persons in the city.
The educational, health, and social services industry makes up the largest proportion of the working population (22.4%). The four school districts employ nearly 4,700 people, and
Being the state's capital (political), capital city, Topeka's largest employer is the State of Kansas—employing about 8,400 people, or 69% of the city's government workers. Altogether, government workers make up one out of every five employed persons in the city.
The educational, health, and social services industry makes up the largest proportion of the working population (22.4%). The four school districts employ nearly 4,700 people, and
North Topeka Arts District (NOTO)
as well as th
Topeka Civic Theatre

 * Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site
* Evel Knievel Museum
* Kansas Children's Discovery Center in Gage Park, Topeka, Gage Park
*
* Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site
* Evel Knievel Museum
* Kansas Children's Discovery Center in Gage Park, Topeka, Gage Park
*
Image:StateCapitolAtTopeka1912.png,
Print
Topeka is the home of a daily newspaper, the ''Topeka Capital-Journal''; a bi-weekly newspaper, ''The Topeka Metro News''; and the ''Topeka Metro Voice''. All three newspapers have online versions
The Topeka Metro News - Online Edition
an
CJOnline
.
Topeka - Directory of Public Officials
*
Topeka city map
KDOT {{Authority control Topeka, Kansas, Cities in Kansas Cities in Shawnee County, Kansas County seats in Kansas Populated places established in 1854 Topeka metropolitan area, Kansas 1854 establishments in Kansas Territory Capitals of Kansas
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, Dópikˀe, script=Latn or ) is the
Mixed-blood Kansa">Topeka' rooted in spuds". ''Topeka Capital-Journal'' Mixed-blood Kaw people, Kansa
Native American, Joseph James, called Jojim, is credited with suggesting Topeka's name. The city, laid out in 1854, was one of the Free-State towns founded by Eastern antislavery men immediately after the passage of the Kansas–Nebraska Bill. In 1857, Topeka was chartered as a city. The city is well known for the landmark U.S. Supreme Court case '' Brown_v._Board_of_Education_of_Topeka'',_which_overturned_''Plessy_vs._Ferguson''_and_declared_Racial_segregation_in_the_United_States.html" "title="Plessy_vs._Ferguson.html" ;"title="Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', which overturned ''Plessy vs. Ferguson">Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', which overturned ''Plessy vs. Ferguson'' and declared Racial segregation in the United States">racial segregation Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
in public schools to be unconstitutional.
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
of the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central United States
The Central United States is sometimes conceived as between the Eastern and Western as part of a three-region model, roughly coincident with the U.S. Census' definition of the Midwestern United States plus the western and central portions o ...
. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 126,587. The Topeka metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
, which includes Shawnee, Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Jackson (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name
Places
Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Qu ...
, Jefferson Jefferson may refer to:
Names
* Jefferson (surname)
* Jefferson (given name)
People
* Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), third president of the United States
* Jefferson (footballer, born 1970), full name Jefferson Tomaz de Souza, Brazilian foo ...
, Osage, and Wabaunsee Counties, had a population of 233,870 in the 2010 census.
The name "Topeka" is a Kansa-Osage word that means "place where we dig potatoes", or "a good place to dig potatoes". As a placename, Topeka was first recorded in 1826 as the Kansa name for what is now called the Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
. Topeka's founders chose the name in 1855 because it "was novel, of Indian origin, and euphonious
Phonaesthetics (also spelled phonesthetics in North America) is the study of beauty and pleasantness associated with the sounds of certain words or parts of words. The term was first used in this sense, perhaps by during the mid-20th century and ...
of sound."King, Dick (20 Nov. 2005)Mixed-blood Kansa">Topeka' rooted in spuds". ''Topeka Capital-Journal'' Mixed-blood Kaw people, Kansa
Native American, Joseph James, called Jojim, is credited with suggesting Topeka's name. The city, laid out in 1854, was one of the Free-State towns founded by Eastern antislavery men immediately after the passage of the Kansas–Nebraska Bill. In 1857, Topeka was chartered as a city. The city is well known for the landmark U.S. Supreme Court case '' Brown_v._Board_of_Education_of_Topeka'',_which_overturned_''Plessy_vs._Ferguson''_and_declared_Racial_segregation_in_the_United_States.html" "title="Plessy_vs._Ferguson.html" ;"title="Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', which overturned ''Plessy vs. Ferguson">Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', which overturned ''Plessy vs. Ferguson'' and declared Racial segregation in the United States">racial segregation Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
History
Early history
For many millennia, Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans inhabited the Great Plains of North America. From the 16th to the mid-18th centuries, the Kingdom of France laid claim to large parts of North America. In 1762, late in theFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, France secretly ceded Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
west of the Mississippi River to Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in the Treaty of Fontainebleau. In 1800, Spain returned Louisiana to France. In 1803, the United States purchased the territory, which included most of the land of modern Kansas, from France for $15 million.
19th century
In the 1840s,wagon train
''Wagon Train'' is an American Western series that aired 8 seasons: first on the NBC television network (1957–1962), and then on ABC (1962–1965). ''Wagon Train'' debuted on September 18, 1957, and became number one in the Nielsen ratings ...
s made their way west from Independence, Missouri
Independence is the fifth-largest city in Missouri and the county seat of Jackson County. Independence is a satellite city of Kansas City, Missouri, and is the largest suburb on the Missouri side of the Kansas City metropolitan area. In 2020, ...
, on a journey of , following what came to be known as the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
. About west of Kansas City, Missouri, three half- Kansas Indian sisters married to the French-Canadian Pappan brothers established a ferry service allowing travelers to cross the Kansas River at what is now Topeka. During the 1840s and into the 1850s, travelers could reliably find a way across the river, but little else was in the area.
 In the early 1850s, traffic along the Oregon Trail was supplemented by trade on a new military road stretching from
In the early 1850s, traffic along the Oregon Trail was supplemented by trade on a new military road stretching from Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., and the oldest perma ...
through Topeka to the newly established Fort Riley
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Ge ...
. In 1854, after completion of the first cabin, nine men established the Topeka Town Association. The group included Cyrus K. Holliday, an "idea man", who became mayor of Topeka and founder of the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison and Topeka, Kansas, and ...
. Soon, steamboats were regularly docking at the Topeka landing, depositing meat, lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, and flour and returning eastward with potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es, corn, and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
. By the late 1860s, Topeka had become a commercial hub that offered many Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
comforts.
Topeka was a bastion for the free-state movement during the problems in Kansas Territory between abolitionist and proslavery settlers (the latter of whom controlled the legal government based out of Lecompton
Lecompton (pronounced ) is a city in Douglas County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 588. Lecompton was the ''de jure'' territorial capital of Kansas from 1855 to 1861, and the Douglas County seat f ...
). After southern forces barricaded Topeka in 1856, Topeka's leaders took actions to defend the free-state town from invasion. A militia was organized and stone fortifications were built on Quincy Street. The fortifications seemed to consist of low-lying earthwork levies strengthened by the presence of at least one cannon. The militia manned the fortifications until at least September 1856, when the siege around the town was lifted.
After a decade of abolitionist and proslavery conflict that gave the territory the nickname Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
, Kansas was admitted to the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
in 1861 as the 34th state. Topeka was chosen as the capital, with Dr. Charles Robinson as the first governor. In 1862, Cyrus K. Holliday donated a tract of land to the state for the construction of a state capitol. Construction of the Kansas State Capitol
The Kansas State Capitol, known also as the Kansas Statehouse, is the building housing the executive and legislative branches of government for the U.S. state of Kansas. Located in the city of Topeka, which has served as the capital of Kansas sin ...
began in 1866. About 37 years were needed to build the capitol, first the east wing, and then the west wing, and finally the central building, using Kansas limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
. In fall 1864, a stockade fort, later named Fort Simple Fort Simple was an American fort built in Topeka, Kansas, as a result of Maj. Gen. Sterling Price's Missouri Raid in the late summer and fall of 1864 (see Price's Raid). Topeka had become the permanent capital of the State of Kansas in 1861, but n ...
, was built in the intersection of 6th and Kansas Avenues to protect Topeka, should Confederate forces then in Missouri decide to attack the city. It was abandoned by April 1865 and demolished in April 1867.
 State officers first used the state capitol in 1869, moving from
State officers first used the state capitol in 1869, moving from Constitution Hall
DAR Constitution Hall is a concert hall located at 1776 D Street NW, near the White House in Washington, D.C. It was built in 1929 by the Daughters of the American Revolution to house its annual convention when membership delegations outgrew Me ...
, what is now 427-429 S. Kansas Avenue. Besides being used as the Kansas statehouse from 1863 to 1869, Constitution Hall is the site where antislavery settlers convened in 1855 to write the first of four state constitutions, making it the "Free State Capitol". The National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propert ...
recognizes Constitution Hall in Topeka as headquarters in the operation of the Lane Trail to Freedom on the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
, the chief slave escape passage and free-trade road.
Although the drought of 1860 and the ensuing period of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
slowed the growth of Topeka and the state, Topeka kept pace with the revival and period of growth Kansas enjoyed from the close of the war in 1865 until 1870. In the 1870s, many former slaves, known as Exodusters, settled on the east side of Lincoln Street between Munson and 12th Streets. The area was known as Tennessee Town because so many of them were from the Volunteer State. Dr. Charles Sheldon, pastor of the Central Congregational Church, organized the first African American kindergarten west of the Mississippi in 1893.
Lincoln College, now Washburn University
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
, was established in 1865 in Topeka by a charter issued by the State of Kansas and the General Association of Congregational Ministers and Churches of Kansas. In 1869, the railway started moving westward from Topeka, where general offices and machine shops of the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad system were established in 1878.
During the late 1880s, Topeka passed through a boom period that ended in disaster. Vast speculation on town lots occurred. The 1889 bubble burst, and many investors were ruined. Topeka, however, doubled in population during the period, and was able to weather the depressions of the 1890s.
Early in the 20th century, another kind of boom, this time the automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarde ...
industry, took off, and numerous pioneering companies appeared and disappeared. Topeka was not left out. The Smith Automobile Company
The Smith Automobile Company of Topeka, Kansas was an early United States automobile manufacturing company which produced the Veracity, Smith, and Great Smith lines of automobiles from 1902 to 1911. They were the first automobiles made west of the ...
was founded there in 1902, lasting until 1912.
20th century
 Home to the first African-American kindergarten west of the Mississippi River, Topeka was the home of Oliver Brown, the named plaintiff in ''
Home to the first African-American kindergarten west of the Mississippi River, Topeka was the home of Oliver Brown, the named plaintiff in ''Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision by the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segrega ...
'', which was the case responsible for eliminating the standard of "separate but equal", and requiring racial integration in American public schools. In 1960, the Census Bureau reported Topeka's population as 91.8% White and 7.7% Black.
At the time the suit was filed, only the elementary schools were segregated in Topeka, and Topeka High School
Topeka High School (THS) is a public secondary school in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It serves students in grades 9 to 12, and is one of five high schools operated by the Topeka USD 501 school district. In the 2010–2011 school year, there ...
had been fully integrated since its inception in 1871. Furthermore, Topeka High School was the only public high school in the city of Topeka. Other rural high schools existed, such as Washburn Rural High School—created in 1918—and Seaman High School—created in 1920. Highland Park High School became part of the Topeka school system in 1959 along with the opening of Topeka West High School in 1961. A Catholic high school —Assumption High School, later renamed Capitol Catholic High School, then in 1939 again renamed, to Hayden High School after its founder, Father Francis Hayden — also served the city beginning in 1911.
Monroe Elementary, a segregated school that figured in the historic ''Brown v. Board of Education'' decision, through the efforts of the Brown Foundation working with the Kansas Congressional delegation place in the early 1990s, is now Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site. The Brown Foundation is largely responsible for the content of the interpretive exhibits at the historic site. The National Historic Site was opened by President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
on May 17, 2004.
Topeka has struggled with the burden of racial discrimination even after ''Brown''. New lawsuits attempted unsuccessfully to force suburban school districts that ring the city to participate in racial integration with the inner-city district. In the late 1980s, a group of citizens calling themselves the Task Force to Overcome Racism in Topeka formed to address the problem in a more organized way.
 On June 8, 1966, Topeka was struck by a tornado rated F5 on the
On June 8, 1966, Topeka was struck by a tornado rated F5 on the Fujita scale
The Fujita scale (F-Scale; ), or Fujita–Pearson scale (FPP scale), is a scale for rating tornado intensity, based primarily on the damage tornadoes inflict on human-built structures and vegetation. The official Fujita scale category is deter ...
. It started on the southwest side of town, moving northeast, passing over a local landmark named Burnett's Mound. According to a local Indian legend, this mound was thought to protect the city from tornadoes if left undisturbed. A few years prior to the tornado strike, development began near the mound, including a water tank constructed near the top of the mound against the warnings of local Native Americans. The tornado went on to rip through the city, hitting the downtown area and Washburn University. Total repair cost was put at $100 million, making it, at the time, one of the most costly tornadoes in American history. Even to this day, with inflation factored in, the Topeka tornado stands as one of the most costly on record. It also helped bring to prominence future CBS and A&E broadcaster Bill Kurtis
Bill Kurtis (born William Horton Kuretich; September 21, 1940), is an American television journalist, television producer, narrator, and news anchor.
Kurtis was studying to become a lawyer in the 1960s, when he was asked to fill in on a tempora ...
, who became well known for his televised admonition to "...take cover, for God's sake, take cover!" on WIBW-TV
WIBW-TV (channel 13) is a television station in Topeka, Kansas, United States, affiliated with CBS and owned by Gray Television. The station's studios are located on Commerce Place (next to the interchange of I-70, I-470, US 40, US 75 and K-4) ...
during the tornado. (The city is home of a National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
Forecast Office that serves 23 counties in north-central, northeast, and east-central Kansas).
 Topeka recovered from the 1966 tornado and has sustained steady economic growth. Washburn University, which lost several historic buildings, received financial support from the community and alumni to rebuild many school facilities. Today, university facilities offer more than one million square feet of modern academic and support space.
In 1974,
Topeka recovered from the 1966 tornado and has sustained steady economic growth. Washburn University, which lost several historic buildings, received financial support from the community and alumni to rebuild many school facilities. Today, university facilities offer more than one million square feet of modern academic and support space.
In 1974, Forbes Air Force Base
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also rep ...
closed and more than 10,000 people left Topeka, influencing the city's growth patterns for years to come. During the 1980s, Topeka citizens voted to build a new airport and convention center and to change the form of city government. West Ridge Mall
West Ridge Mall is an enclosed shopping mall in Topeka, Kansas. The mall has three open anchor stores: Dillard's, Furniture Mall of Kansas, and JCPenney. There are two vacant anchors that were formerly Sears and Burlington. It is the third largest ...
opened in 1988, replacing the White Lakes Mall
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, which opened in 1964.
 In 1989, Topeka became a motorsports mecca with the opening of
In 1989, Topeka became a motorsports mecca with the opening of Heartland Park Topeka
Heartland Motorsports Park, formerly known as Heartland Park Topeka, is a multi-purpose motorsports facility south of downtown Topeka, Kansas near the Topeka Regional Airport.
When it opened in 1989, Heartland Motorsports Park was the first new ...
. The Topeka Performing Arts Center opened in 1991. In the early 1990s, the city experienced business growth with Reser's Fine Foods locating in Topeka and expansions for Santa Fe and Hill's Pet Nutrition.
During the 1990s, voters approved bond issues for public school improvements, including magnet schools, technology, air conditioning, classrooms, and a sports complex. Voters also approved a quarter-cent sales tax for a new law-enforcement center, and in 1996, approved an extension of the sales tax for the East Topeka Interchange connecting the Oakland Expressway, K-4, I-70, and the Kansas Turnpike. During the 1990s, Shawnee County voters approved tax measures to expand the Topeka and Shawnee County Public Library. The Kansas Legislature and governor also approved legislation to replace the majority of the property tax supporting Washburn University with a countywide sales tax.
21st century
In 2000, the citizens again voted to extend the quarter-cent sales tax, this time for the economic development of Topeka and Shawnee County. In August, 2004, Shawnee County citizens voted to repeal the 2000 quarter-cent sales tax and replace it with a 12-year, half-cent sales tax designated for economic development, roads, and bridges. Each year, the sales tax provides $5 million designated for business development and job creation incentives, and $9 million for roads and bridges. Planning is under way to continue to redevelop areas along the Kansas River, which runs west to east through Topeka. In the Kansas River Corridor through the center of town, downtown Topeka has experienced apartment and condominium loft development, and façade and streetscape improvements.Google, Kansas
On March 1, 2010, Topeka MayorBill Bunten
William Wallace Bunten (April 5, 1930 – February 29, 2020) was an American politician from Kansas. He served as mayor of Topeka, Kansas, having been elected to a four-year term in 2005 and re-elected in 2009. Before being elected mayor, he serv ...
issued a proclamation calling for Topeka to be known for the month of March as "Google, Kansas, the capital city of fiber optics." The name change came from Ryan Gigous, who wanted to "re-brand" the city with a simple gesture. This was to help "support continuing efforts to bring Google's fiber experiment" to Topeka, though it was not a legal name change. Lawyers advised the city council and mayor against an official name change. Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
jokingly announced it would change its name to Topeka to "honor that moving gesture" on April 1, 2010 (April Fools' Day
April Fools' Day or All Fools' Day is an annual custom on 1 April consisting of practical jokes and hoaxes. Jokesters often expose their actions by shouting "April Fools!" at the recipient. Mass media can be involved in these pranks, which may ...
) and changed its home page to say Topeka. In its official blog, Google announced this change thus affected all of its services as well as its culture, e.g. "Googlers" to "Topekans", "Project Virgle" to "Project Vireka", and proper usage of "Topeka" as an adjective and not a verb, to avoid the trademark becoming genericized
A generic trademark, also known as a genericized trademark or proprietary eponym, is a trademark or brand name that, because of its popularity or significance, has become the generic term for, or synonymous with, a general class of products or ...
.
Geography
 Topeka is at , in north east Kansas at the intersection of
Topeka is at , in north east Kansas at the intersection of I-70
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of I-695 in Baltimore, Maryland, and is the fifth-longest Interstate in the c ...
and U.S. Highway 75
U.S. Route 75 is a major north–south U.S. Highway that extends in the central United States. The highway's northern terminus is in Noyes, Minnesota, at the Canadian border, where it once continued as Manitoba Highway 75 on the other sid ...
. It is the origin of I-335 which is a portion of the Kansas Turnpike
The Kansas Turnpike is a , freeway-standard toll road that lies entirely within the US state of Kansas. It runs in a general southwest–northeast direction from the Oklahoma border to Kansas City. It passes through several major Kansas cities, ...
running from Topeka to Emporia, Kansas. Topeka is also on U.S. Highway 24 (about east of Manhattan, Kansas
Manhattan is a city and county seat of Riley County, Kansas, United States, although the city extends into Pottawatomie County. It is located in northeastern Kansas at the junction of the Kansas River and Big Blue River. As of the 2020 c ...
) and U.S. Highway 40 (about west of Lawrence, Kansas). US 40 is coincident with I-70 west from Topeka. According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
, the city has a total area of , of which are covered by water.
Climate
In 2007, ''Forbes'' named Topeka as one of the leading U.S. cities in terms of having the greatest variations in temperature, precipitation, and wind. Topeka has ahumid continental
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfa''), with hot, somewhat humid summers and cool to cold, fairly dry winters, and is in USDA plant hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most wide ...
6a. Over the course of a year, the monthly daily average temperature ranges from in January to in July. The maximum temperature reaches an average of 41.5 afternoons per year and reaches an average of 3.5 afternoons per year. The minimum temperature falls below an average of four mornings per year, and 21 afternoons per year stay below freezing. The average window for freezing temperatures is October 15 through April 17.
The area receives nearly of precipitation during a typical year, with the largest share being received in May and June—the April through June period averages 33 days of measurable precipitation. Generally, the spring and summer have the most rainfall, with autumn and winter being fairly dry. During a typical year, the total amount of precipitation may vary from . Much of the rainfall is delivered by thunderstorms. These can be severe, producing frequent lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an avera ...
, large hail, and sometimes tornadoes. An average of 100 days of measurable precipitation occur per year. Winter snowfall is light, as is the case in most of the state, as a result of the dry, sunny weather patterns that dominate Kansas winters, which do not allow for sufficient moisture for significant snowfall. Winter snowfall averages . Measurable (≥) snowfall occurs an average of 12.9 days per year, with at least of snow being received on five of those days. Snow depth of at least an inch occurs an average of 20 days per year.
Demographics
2010 census
As of thecensus
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
of 2010, the city had 127,473 people, 53,943 households, and 30,707 families. The population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
was . The 59,582 housing units averaged . The city's racial makeup
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
was 76.2% White, 11.3% African American, 1.4% Native American, 1.3% Asian, 4.8% from other races, and 4.9% from two or more races. Hispanics or Latinos of any race were 13.4% of the population. Non-Hispanic Whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Ame ...
were 69.7% of the population in 2010, down from 86.3% in 1970.
Of the 53,943 households, 29.5% had children under 18 living with them, 37.9% were married couples living together, 14.2% had a female householder with no husband present, 4.8% had a male householder with no wife present, and 43.1% were not families. About 35.9% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12% had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 2.29, and the average family size was 2.99.
The city's age distribution was 24.4% under age 18, 9.8% from 18 to 24; 26.1% from 25 to 44, 25.4% from 45 to 64, and 14.3% were 65 or older. The median age in the city was 36 years. The city's gender makeup was 47.8% male and 52.2% female.
2000 census
As of the 2000 census, 122,377 people, 52,190 households, and 30,687 families were residing in the city. The population density was 2,185.0 people per square mile (843.6/km). There were 56,435 housing units at an average density of 1,007.6 per square mile (389.0/km). The city'sracial makeup
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
was 78.5% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
, 11.7% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 1.31% Native American, 1.09% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 4.10% from other races, and 3.26% from two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
. Hispanics or Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
s of any race were 8.9% of the population.
Of the 52,190 household
A household consists of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is i ...
s, 28.0% had children under 18 living with them, 41.8% were married couples living together, 13.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 41.2% were not families. About 35.0% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.7% had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 2.27, and the average family size was 2.94.
About 24.3% of the city's population was under age 18, 9.9% was from age 18 to 24, 28.9% was from age 25 to 44, 21.9% was from age 45 to 64, and 15.1% was age 65 or older. The median age was 36 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.4 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 88.4 males.
As of 2000, the city's median household income was $35,928, and the median family income was $45,803. Males had a median income of $32,373 versus $25,633 for females. The city's per capita income was $19,555. About 8.5% of families and 12.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 16.7% of those under age 18 and 8.2% of those age 65 or over.
Crime
Although Topeka experienced problems with crime in the 1990s, the city's crime rates have improved since. Overall, crime in Topeka was down nearly 18% in the first half of 2008, compared with the same period of 2007. Topeka police reported a 6.4% drop in crime from 2007 to 2008, including significant reductions in business robberies and aggravated assaults and batteries, as well as thefts. On October 11, 2011, the Topeka city council agreed to repeal the ordinance banning domestic violence in an effort to force the Shawnee County District Attorney to prosecute the cases. Shawnee County District Attorney Chad Taylor (Kansas), Chad Taylor said the DA "would no longer prosecute misdemeanors committed in Topeka, including domestic battery, because his office could no longer do so after county commissioners cut his budget by 10%." The next day, Taylor said his office would "commence the review and filing of misdemeanors decriminalized by the City of Topeka." The same day, 17% of the employees in the district attorney's office were announced to be laid off.Religion
Topeka is sometimes cited as the home of Pentecostalism, as it was the site of Charles Fox Parham's Bethel Bible College, where glossolalia was first claimed as the evidence of a spiritual experience referred to as the baptism of the Holy Spirit in 1901. It is also the home of Reverend Charles Sheldon, author of ''In His Steps'', and was the site where the famous question "What would Jesus do?" originated in a sermon of Sheldon's at Central Congregational Church. The First Presbyterian Church in Topeka is one of the few churches in the U.S. to have its sanctuary completely decorated with Louis Comfort Tiffany, Tiffany stained glass (another is St. Luke's United Methodist in Dubuque, Iowa; another is the Emmanuel Episcopal Church in Cumberland, Maryland). The Roman Catholic population is large, and the city is home to nine Roman Catholic parishes, five of which feature elementary schools. Grace Episcopal Cathedral (Topeka, Kansas), Grace Cathedral of the Episcopal Diocese of Kansas is a large Gothic Revival structure in the city. Topeka also has a claim in the history of the Baháʼí Faith in Kansas. Not only does the city have the oldest continuous Baháʼí community in Kansas (beginning in 1906), but the community also has roots to the first Baháʼí community in Kansas, in Enterprise, in 1897. This was the second Baháʼí community in the Western Hemisphere. Topeka is home of the Westboro Baptist Church, a hate group according to the Southern Poverty Law Center. The church has garnered worldwide media attention for picketing the funerals of U.S. servicemen and women for what church members claim as "necessary to combat the fight for equality for gays and lesbians." They have sometimes successfully raised lawsuits against the city of Topeka. Across the street from them is the Equality House, a pro-LGBT home where volunteers of Planting Peace can stay. It is painted in rainbow colors and serves as a home for social workers caring for the LGBT+ community, directly opposite the property of the Homophobia, homophobic Westboro Baptist Church.Economy
 Being the state's capital (political), capital city, Topeka's largest employer is the State of Kansas—employing about 8,400 people, or 69% of the city's government workers. Altogether, government workers make up one out of every five employed persons in the city.
The educational, health, and social services industry makes up the largest proportion of the working population (22.4%). The four school districts employ nearly 4,700 people, and
Being the state's capital (political), capital city, Topeka's largest employer is the State of Kansas—employing about 8,400 people, or 69% of the city's government workers. Altogether, government workers make up one out of every five employed persons in the city.
The educational, health, and social services industry makes up the largest proportion of the working population (22.4%). The four school districts employ nearly 4,700 people, and Washburn University
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
employs about 1,650. Three of the largest employers are Stormont-Vail HealthCare (with about 3,100 employees), St. Francis Health Center (1,800), and Colmery-O'Neil Veterans Administration Hospital (900).
The retail trade employs more than a tenth of the working population (11.5%) with Wal-Mart and Dillons having the greater share. Nearly another tenth is employed in manufacturing (9.0%). Top manufacturers include Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company, Hill's Pet Nutrition, Frito-Lay, and Jostens Printing and Publishing. Jostens announced plans in May 2012 to move production from its Topeka facility to Clarksville, Tennessee, affecting about 372 employee positions. Southwest Publishing & Mailing Corporation, a smaller employer, has its headquarters in Topeka.
Other industries are finance, insurance, real estate, and rental and leasing (7.8%); professional, scientific, management, administrative, and waste management services (7.6%); arts, entertainment, recreation, accommodation and food services (7.2%); construction (6.0%); transportation and warehousing, and utilities (5.8%); and wholesale trade (3.2%). Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas is the largest insurance employer, with about 1,800 employees. BNSF Railway is the largest transportation employer, with about 1,100. Evergy employs nearly 800. About a tenth of the working population is employed in public administration (9.9%).
Major employers in Topeka include:
* BNSF Railroad
* Capitol Federal Savings Bank
* CoreFirst Bank & Trust
* Evergy, Evergy, Inc.
* Frito-Lay
* Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company
* Hill's Pet Nutrition
* Sports Car Club of America
* Topeka Public Schools USD 501
* University of Kansas Health System
* Washburn University
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
Arts and culture
Arts
The Topeka Symphony Orchestra was founded in 1957. Topeka is home to broad areas of fine art, specifically in thNorth Topeka Arts District (NOTO)
as well as th
Topeka Civic Theatre
Points of interest

 * Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site
* Evel Knievel Museum
* Kansas Children's Discovery Center in Gage Park, Topeka, Gage Park
*
* Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site
* Evel Knievel Museum
* Kansas Children's Discovery Center in Gage Park, Topeka, Gage Park
* Kansas State Capitol
The Kansas State Capitol, known also as the Kansas Statehouse, is the building housing the executive and legislative branches of government for the U.S. state of Kansas. Located in the city of Topeka, which has served as the capital of Kansas sin ...
, with murals by John Steuart Curry, including the portrait of John Brown towering over "Bleeding Kansas" and the Kansas prairie, and topped with the sculpture of a native warrior named Ad Astra (from the state motto Ad Astra per Aspera, meaning "To the Stars Through Difficulty".)
* Kansas Expocentre and Landon Arena
* Combat Air Museum at Forbes Field (Kansas), Forbes Field
* Heartland Park Topeka
Heartland Motorsports Park, formerly known as Heartland Park Topeka, is a multi-purpose motorsports facility south of downtown Topeka, Kansas near the Topeka Regional Airport.
When it opened in 1989, Heartland Motorsports Park was the first new ...
, a major drag racing and road racing course just south of the city.
* Kansas Museum of History
* Reinisch Rose Garden and Doran Rock Garden, both parts of Gage Park.
* Topeka High School
Topeka High School (THS) is a public secondary school in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It serves students in grades 9 to 12, and is one of five high schools operated by the Topeka USD 501 school district. In the 2010–2011 school year, there ...
* Topeka & Shawnee County Public Library
* Topeka Zoo, famous as the birthplace of the first golden eagle chick hatched in captivity and as the first zoo in the nation to have an indoor rain forest.
* Old Prairie Town at Ward-Meade Historic Site
* Washburn University
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
, the last city-chartered university in the United States.
* Westboro (Topeka), Westboro Neighborhood
* Potwin Neighborhood, originally its own town, Potwin has now been surrounded by the City of Topeka, though it maintains its own mayor and traditions, including the Easter brunch and Fourth of July Parade.
* Kansas Judicial Center, where both the Kansas Supreme Court, Supreme Court and Court of Appeals for the state sit.
* Cedar Crest (mansion), Cedar Crest, the Kansas Governor's Mansion on a hilltop overlooking the massive MacLennan Park.
* Great Overland Station, home of the Kansas Hall of Fame.
* The Upstage Gallery
Sports
Government
City
The current mayor of Topeka is Mike Padilla. The city manager is Bill Cochran. The city manager is responsible to the Topeka's City Council, which consists of the mayor and nine members elected from separate districts within the city. The city council members select the deputy mayor, Spencer Duncan, from among themselves. The deputy mayor chairs the Committee of the Whole and represents the City of Topeka at official functions whenever the mayor is unavailable. The city manager also guides the council through the meetings but cannot vote.State
Kansas State Capitol
The Kansas State Capitol, known also as the Kansas Statehouse, is the building housing the executive and legislative branches of government for the U.S. state of Kansas. Located in the city of Topeka, which has served as the capital of Kansas sin ...
in 1912
Image:Old Governor's Mansion, Topeka, KS.jpg, Old Governor's Mansion (1887), replaced by Cedar Crest (mansion), ''Cedar Crest'' in 1963 and demolished the following year
Image:Curtis Building in Topeka.jpg, The Charles Curtis State Office Building (2001), facing the capitol
Education
Elementary and secondary education
Topeka is served by four public school (government funded), public school districts, including: * Seaman USD 345 (serving North Topeka) * Auburn–Washburn USD 437 (serving west and southwest Topeka) * Shawnee Heights USD 450 (serving extreme east and southeast Topeka) * Topeka USD 501 (serving inner-city Topeka) Topeka is also home to several private and parochial schools such as Topeka Collegiate and Cair Paravel-Latin School. There are also elementary and junior high schools supported by other Christian denominations. Hayden High School, a Catholic high school is also in Topeka, as well as Cornerstone Family Schools, a non-denominational Christianity, Christian organization that offers junior and senior high school athletics to home-school families in the northeast Kansas area. Cornerstone's mascot is "the Saints".Post-secondary education
Topeka has several colleges, universities, technical schools and branch campuses of other universities around the state. These include the following: *Washburn University
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
* Friends University (Topeka Campus)
* Washburn Institute of Technology
* Baker University School of Nursing (Topeka Campus)
* University of Kansas Health Center (St. Francis Campus)
*Rasmussen College (Topeka Campus)
Media
The Topeka Metro News - Online Edition
an
CJOnline
.
Radio
The following radio stations are city of license, licensed to Topeka: AM FM Additionally, most of the Kansas City stations provide at least grade B coverage of Topeka. KANU-FM in Lawrence (in the Kansas City market) serves as Topeka's NPR member station.Television
The following television stations are city of license, licensed to Topeka:Infrastructure
Transportation
I-70
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of I-695 in Baltimore, Maryland, and is the fifth-longest Interstate in the c ...
, Interstate 470 (Kansas), I-470, and I-335 all go through the City of Topeka. I-335 is part of the Kansas Turnpike
The Kansas Turnpike is a , freeway-standard toll road that lies entirely within the US state of Kansas. It runs in a general southwest–northeast direction from the Oklahoma border to Kansas City. It passes through several major Kansas cities, ...
where it passes through Topeka. Other major highways include: U.S. Route 24 (Kansas), US-24, U.S. Route 40 (Kansas), US-40, U.S. Route 75 (Kansas), US-75, and K-4 (Kansas highway), K-4. Major roads within the city include NW/SW Topeka Blvd. SW Wanamaker Road. N/S Kansas Ave. SW/SE 29th St. SE/SW 21st St. SE California Ave. SW Gage Blvd. and SW Fairlawn Rd.
Topeka Regional Airport (FOE) formerly known as Forbes Field is in south Topeka in Pauline, Kansas. Forbes Field also serves as an Air National Guard base, home of the highly decorated 190th Air Refueling Wing. Manhattan Regional Airport (MHK) in Manhattan, Kansas
Manhattan is a city and county seat of Riley County, Kansas, United States, although the city extends into Pottawatomie County. It is located in northeastern Kansas at the junction of the Kansas River and Big Blue River. As of the 2020 c ...
is the next closest commercial airport; Kansas City International Airport (MCI) in Kansas City is the closest major airport. Philip Billard Municipal Airport (TOP) is located in Topeka's Oakland area.
Passenger rail service provided by Amtrak stops at the Topeka (Amtrak station), Topeka Station. Service is via the Chicago-to-Los Angeles Southwest Chief during the early morning hours and makes intermediate stops at Lawrence (Amtrak station), Lawrence and Union Station (Kansas City, Missouri), Kansas City. The Kansas Department of Transportation has asked Amtrak to study additional service, including daytime service to Oklahoma City. The Burlington Northern Santa Fe railroad and Union Pacific Railroad provide freight service as well as several short line railroads throughout the state.
Greyhound Lines provides bus service westward towards Denver, Colorado, eastward to Kansas City, Missouri, southwest to Wichita, Kansas.
The Topeka Metropolitan Transit Authority provides local transit service. The agency offers bus service from 6 am to 6:30 pm Monday through Friday, and 7 am to 5 pm on Saturday. It also provides demand response general public taxi service which operates evenings from 8 pm until 11:30 pm and on Sundays.
Utilities
* Electricity: Evergy * Home telephone: AT&T Inc., AT&T and Cox Communications, Cox * Cable: Cox Communications and AT&T * Satellite TV: Dish and DirecTV * Gas: Kansas Gas Service * Water and sewer: City of Topeka * Sanitation: Shawnee County Waste Management * Internet: Cox Communications, Cox (cable), AT&T Inc., AT&T (fiber, DSL, and fixed wireless), and other providers.Health care
Topeka has two major hospitals, Stormont-Vail and The University of Kansas Hospital - St. Francis Campus. Both are in central Topeka. Topeka is also home to the Colmery-O'Neil United States Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Medical Clinic and Topeka ER & Hospital.Notable people
See also
* Great Flood of 1951 * Tornado outbreak sequence of June 1966, 1966 F5 tornadoNotes
References
Further reading
External links
*Topeka - Directory of Public Officials
*
Topeka city map
KDOT {{Authority control Topeka, Kansas, Cities in Kansas Cities in Shawnee County, Kansas County seats in Kansas Populated places established in 1854 Topeka metropolitan area, Kansas 1854 establishments in Kansas Territory Capitals of Kansas