Tonga Major League Seasons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and
 According to
According to
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. As of 2021, according to Johnson's Tribune, Tonga has a population of 104,494, 70% of whom reside on the main island, Tongatapu
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the nation ...
. The country stretches approximately north-south. It is surrounded by Fiji and Wallis and Futuna
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands (; french: Wallis-et-Futuna or ', Fakauvea and Fakafutuna: '), is a French island collectivity in the South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji ...
(France) to the northwest; Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
to the northeast; New Caledonia (France) and Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of no ...
to the west; Niue
Niue (, ; niu, Niuē) is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, northeast of New Zealand. Niue's land area is about and its population, predominantly Polynesian, was about 1,600 in 2016. Niue is located in a triangle between Tong ...
(the nearest foreign territory) to the east; and Kermadec Kermadec or de Kermadec may refer to:
Geography
* Kermadec Islands, a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand
* Kermadec Plate, a long narrow tectonic plate located west of the Kermadec Trench
* Kermadec Trench, ...
(New Zealand) to the southwest. Tonga is about from New Zealand's North Island.
First inhabited roughly 2,500 years ago by the Lapita civilization, Tonga's Polynesian settlers gradually evolved a distinct and strong ethnic identity, language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
, and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
as the Tongan people. They were quick to establish a powerful footing across the South Pacific, and this period of Tongan expansionism and colonization is known as the Tuʻi Tonga Empire
The Tui Tonga Empire, or Tongan Empire, are descriptions sometimes given to Tongan expansionism and projected hegemony in Oceania which began around 950 CE, reaching its peak during the period 1200–1500.
It was centred in Tonga on the island o ...
. From the rule of the first Tongan king, ʻAhoʻeitu
In Tongan mythology, or oral history, Ahoeitu is a son of the god Eitumātupua and a mortal woman, Ilaheva Vaepopua. He became the first king of the Tui Tonga (''Tonga king'') dynasty in the early 10th century, dethroning the previous one with t ...
, Tonga grew into a regional power. It was a thalassocracy
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples ...
that conquered and controlled unprecedented swathes of the Pacific, from parts of the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
and the whole of New Caledonia and Fiji in the west to Samoa and Niue and even as far as parts of modern-day French Polynesia in the east. Tuʻi Tonga became renowned for its economic, ethnic, and cultural influence over the Pacific, which remained strong even after the Samoan revolution of the 13th century and Europeans' discovery of the islands in 1616.see writings of Ata of Kolovai in "O Tama a Aiga" by Morgan Tuimaleali'ifano; writings by Mahina, also coronation edition of Spasifik Magazine, "The Pacific Islands: An Encyclopedia," edited by Lal and Fortune, pp. 133–
From 1900 to 1970, Tonga had British protected-state status. The United Kingdom looked after Tonga's foreign affairs under a Treaty of Friendship, but Tonga never relinquished its sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
to any foreign power. In 2010, Tonga took a decisive step away from its traditional absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism (European history), Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute pow ...
and became a fully-functioning constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
, after legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known ...
reforms paved the way for its first partial representative election
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
s.
Etymology
In manyPolynesian languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austro ...
, including Tongan, the word ''tonga'' (, ; ), comes from ''fakatonga'', which means "southwards", and the archipelago is so named because it is the southernmost group among the island groups of western Polynesia. The word ''tonga'' is cognate to the Hawaiian word "kona", meaning "leeward", which is the origin of the name for the Kona District in Hawai’i.
Tonga became known in the West as the "Friendly Islands" because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the annual ''ʻinasi'' festival, which centres on the donation of the First Fruits
First Fruits is a religious offering of the first agricultural produce of the harvest. In classical Greek, Roman, and Hebrew religions, the first fruits were given to priests as an offering to deity. In Christian faiths, the tithe is similarl ...
to the Tuʻi Tonga
The Tuʻi Tonga is a line of Tongan kings, which originated in the tenth century with the mythical ʻAhoʻeitu, and withdrew from political power in the fifteenth century by yielding to the ''Tuʻi Haʻatakalaua''. The title ended with the death ...
(the islands' monarch), so he received an invitation to the festivities. Ironically, according to the writer William Mariner, the political leaders actually wanted to kill Cook during the gathering, but did not go through with it because they could not agree on a plan of action for accomplishing it.
History
 According to
According to Tongan mythology
Tongan narrative (or Tongan mythology) is a variant of a more general Polynesian narrative in Tonga.
Creation myth
In the beginning there was just the sea and the spirit world, Pulotu, and between them was a rock called Touiao Futuna. On the rock ...
, the demigod Maui drew up a group of islands from the ocean, first appearing Lofanga
Lofanga is an island in Tonga. It is located within the Ha'apai Group in the centre of the country, to northeast of the national capital of Nukualofa. The island had a population of 137 at 2016, and an area of 1.45 km2.Ha'apai Islands and Vava'u, integrating into what became modern-day Tonga.
An Austronesian-speaking group linked to what archaeologists call the  The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616, when the Dutch vessel ''Eendracht'', captained by
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616, when the Dutch vessel ''Eendracht'', captained by
 The prodemocracy movement in Tonga promotes reforms, including better representation in the Parliament for the majority of commoners, and better accountability in matters of state. An overthrow of the monarchy is not part of the movement, and the institution of monarchy continues to hold popular support, even while reforms are advocated. Until recently, the governance issue was generally ignored by the leaders of other countries, but major aid donors and neighbours New Zealand and Australia are now expressing concerns about some Tongan government actions.
Following the precedents of Queen Sālote and the counsel of numerous international advisors, the government of Tonga under King
The prodemocracy movement in Tonga promotes reforms, including better representation in the Parliament for the majority of commoners, and better accountability in matters of state. An overthrow of the monarchy is not part of the movement, and the institution of monarchy continues to hold popular support, even while reforms are advocated. Until recently, the governance issue was generally ignored by the leaders of other countries, but major aid donors and neighbours New Zealand and Australia are now expressing concerns about some Tongan government actions.
Following the precedents of Queen Sālote and the counsel of numerous international advisors, the government of Tonga under King
 King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV and his government made some problematic economic decisions and were accused by democracy activists, including former prime minister ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, of wasting millions of dollars on unwise investments. The problems have mostly been driven by attempts to increase national revenue through a variety of schemes – considering making Tonga a nuclear waste disposal site (an idea floated in the mid 1990s by the current crown prince), and selling Tongan Protected Persons Passports (which eventually forced Tonga to naturalise the purchasers, sparking ethnicity-based concerns within Tonga).
Schemes also included the registering of foreign ships (which proved to be engaged in illegal activities, including shipments for al-Qaeda); claiming geo-orbital satellite slots (the revenue from which seems to belong to the Princess Royal, not the state); holding a long-term charter on an unusable
King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV and his government made some problematic economic decisions and were accused by democracy activists, including former prime minister ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, of wasting millions of dollars on unwise investments. The problems have mostly been driven by attempts to increase national revenue through a variety of schemes – considering making Tonga a nuclear waste disposal site (an idea floated in the mid 1990s by the current crown prince), and selling Tongan Protected Persons Passports (which eventually forced Tonga to naturalise the purchasers, sparking ethnicity-based concerns within Tonga).
Schemes also included the registering of foreign ships (which proved to be engaged in illegal activities, including shipments for al-Qaeda); claiming geo-orbital satellite slots (the revenue from which seems to belong to the Princess Royal, not the state); holding a long-term charter on an unusable  The bill was opposed in the form of a several-thousand-strong protest march in the capital, a call by the Tuʻi Pelehake (a prince, nephew of the king and elected member of parliament) for Australia and other nations to pressure the Tongan government to democratise the electoral system, and a legal writ calling for a judicial investigation of the bill. The latter was supported by some 160 signatures, including seven of the nine elected, "People's Representatives".
The then-Crown Prince Tupoutoʻa and Pilolevu, the Princess Royal, remained generally silent on the issue. In total, the changes threatened to destabilise the polity, fragment support for the status quo, and place further pressure on the monarchy.
In 2005, the government spent several weeks negotiating with striking civil-service workers before reaching a settlement. The civil unrest that ensued was not limited to Tonga; protests outside the King's New Zealand residence made headlines.
Prime Minister Prince ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala) (now King Tupou VI) resigned suddenly on 11 February 2006, and also gave up his other cabinet portfolios. The elected minister of labour, Dr Feleti Sevele, replaced him in the interim.
On 5 July 2006, a driver in
The bill was opposed in the form of a several-thousand-strong protest march in the capital, a call by the Tuʻi Pelehake (a prince, nephew of the king and elected member of parliament) for Australia and other nations to pressure the Tongan government to democratise the electoral system, and a legal writ calling for a judicial investigation of the bill. The latter was supported by some 160 signatures, including seven of the nine elected, "People's Representatives".
The then-Crown Prince Tupoutoʻa and Pilolevu, the Princess Royal, remained generally silent on the issue. In total, the changes threatened to destabilise the polity, fragment support for the status quo, and place further pressure on the monarchy.
In 2005, the government spent several weeks negotiating with striking civil-service workers before reaching a settlement. The civil unrest that ensued was not limited to Tonga; protests outside the King's New Zealand residence made headlines.
Prime Minister Prince ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala) (now King Tupou VI) resigned suddenly on 11 February 2006, and also gave up his other cabinet portfolios. The elected minister of labour, Dr Feleti Sevele, replaced him in the interim.
On 5 July 2006, a driver in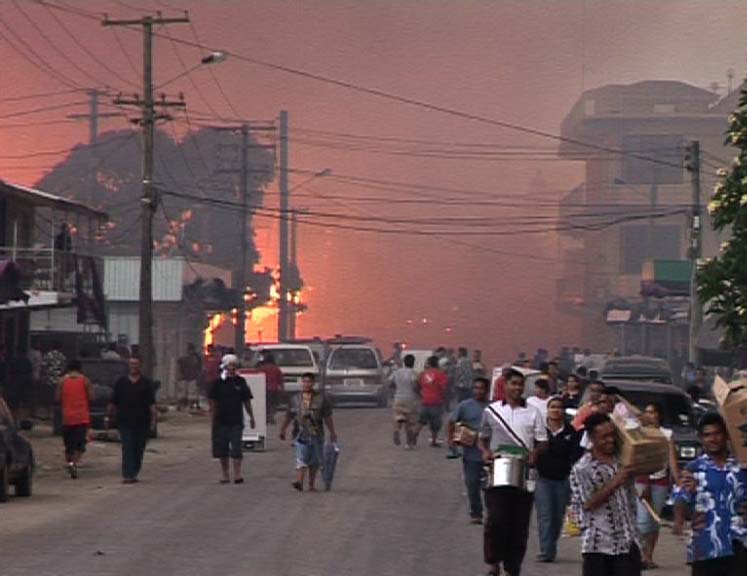  The public expected some changes when George Tupou V succeeded his father in September 2006. On 16 November 2006, rioting broke out in the capital city of
The public expected some changes when George Tupou V succeeded his father in September 2006. On 16 November 2006, rioting broke out in the capital city of
, Matangi Tonga, 12 January 2009. Tonga maintains strong regional ties in the Pacific. It is a full member of the Pacific Islands Forum, the
 Located in
Located in
 The bird life of Tonga includes a total of 73 species, of which two are endemic; the Tongan whistler and the
The bird life of Tonga includes a total of 73 species, of which two are endemic; the Tongan whistler and the


 Tonga's economy is characterised by a large nonmonetary sector and a heavy dependence on remittances from the half of the country's population who live abroad (chiefly in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States). The royal family and the nobles dominate and largely own the monetary sector of the economy – particularly the telecommunications and satellite services. Tonga was named the sixth-most corrupt country in the world by ''Forbes'' magazine in 2008.
Tonga was ranked the 165th-safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 '' Euromoney'' Country Risk rankings.
The manufacturing sector consists of
Tonga's economy is characterised by a large nonmonetary sector and a heavy dependence on remittances from the half of the country's population who live abroad (chiefly in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States). The royal family and the nobles dominate and largely own the monetary sector of the economy – particularly the telecommunications and satellite services. Tonga was named the sixth-most corrupt country in the world by ''Forbes'' magazine in 2008.
Tonga was ranked the 165th-safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 '' Euromoney'' Country Risk rankings.
The manufacturing sector consists of
 Over 70% of the inhabitants live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties remain influential throughout the country. Despite emigration, Tonga grew in population from about 32,000 in the 1930s to more than 90,000 by 1976.
Over 70% of the inhabitants live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties remain influential throughout the country. Despite emigration, Tonga grew in population from about 32,000 in the 1930s to more than 90,000 by 1976.
 Tonga does not have an official state religion. The Constitution of Tonga (Revised 1998) provides for freedom of religion.
In 1928, Queen Salote Tupou III, who was a member of the
Tonga does not have an official state religion. The Constitution of Tonga (Revised 1998) provides for freedom of religion.
In 1928, Queen Salote Tupou III, who was a member of the
 Humans have lived in Tonga for nearly 3,000 years since settlement in late Lapita times. Before the arrival of European explorers in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, Tongans had frequent contacts with their nearest Oceanic neighbours, Fiji and Niue. In the 19th century, with the arrival of Western traders and missionaries, Tongan culture changed, especially in religion. , almost 98% of residents profess Christianity. The people discarded some old beliefs and habits and adopted others.
Humans have lived in Tonga for nearly 3,000 years since settlement in late Lapita times. Before the arrival of European explorers in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, Tongans had frequent contacts with their nearest Oceanic neighbours, Fiji and Niue. In the 19th century, with the arrival of Western traders and missionaries, Tongan culture changed, especially in religion. , almost 98% of residents profess Christianity. The people discarded some old beliefs and habits and adopted others.

 Rugby league has gained some success. Tonga made their first appearance at a Rugby League World Cup in the 1995 Rugby League World Cup, 1995 edition where they went out in the first stage but narrowly lost to New Zealand national rugby league team, New Zealand. They have since appeared in each subsequent Rugby League World Cup tournament. In the 2008 Rugby League World Cup Tonga national rugby league team, Tonga recorded wins against Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland and Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland. Just before the 2017 Rugby League World Cup, 2017 World Cup, various high-profile players, led by Jason Taumalolo and Andrew Fifita, defected from their tier one nations to represent their nation of heritage. This led to them defeating New Zealand in Hamilton at Waikato Stadium on 11 November at that tournament. The national team has since also recorded victories against Great Britain national rugby league team, Great Britain and the world number one Australia national rugby league team, Australia. In addition to the success of the national team, many players of Tongan descent make it big in the Australian National Rugby League competition. These include Jason Taumalolo, Israel Folau, Tyson Frizell, Tevita Pangai Junior, Konrad Hurrell, David Fusitua, Tuimoala Lolohea, Sio Siua Taukeiaho, Jorge Taufua, William Hopoate, Andrew Fifita, Ben Murdoch-Masila, Felise Kaufusi, Willie Mason, Manu Vatuvei, Brent Kite, Fuifui Moimoi, Willie Tonga, Anthony Tupou, Antonio Kaufusi, Michael Jennings (rugby league), Michael Jennings, Tony Williams (rugby league), Tony Williams, Feleti Mateo. Subsequently, some Tongan rugby league players have established successful careers in the Super League such as Antonio Kaufusi.
Rugby league has gained some success. Tonga made their first appearance at a Rugby League World Cup in the 1995 Rugby League World Cup, 1995 edition where they went out in the first stage but narrowly lost to New Zealand national rugby league team, New Zealand. They have since appeared in each subsequent Rugby League World Cup tournament. In the 2008 Rugby League World Cup Tonga national rugby league team, Tonga recorded wins against Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland and Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland. Just before the 2017 Rugby League World Cup, 2017 World Cup, various high-profile players, led by Jason Taumalolo and Andrew Fifita, defected from their tier one nations to represent their nation of heritage. This led to them defeating New Zealand in Hamilton at Waikato Stadium on 11 November at that tournament. The national team has since also recorded victories against Great Britain national rugby league team, Great Britain and the world number one Australia national rugby league team, Australia. In addition to the success of the national team, many players of Tongan descent make it big in the Australian National Rugby League competition. These include Jason Taumalolo, Israel Folau, Tyson Frizell, Tevita Pangai Junior, Konrad Hurrell, David Fusitua, Tuimoala Lolohea, Sio Siua Taukeiaho, Jorge Taufua, William Hopoate, Andrew Fifita, Ben Murdoch-Masila, Felise Kaufusi, Willie Mason, Manu Vatuvei, Brent Kite, Fuifui Moimoi, Willie Tonga, Anthony Tupou, Antonio Kaufusi, Michael Jennings (rugby league), Michael Jennings, Tony Williams (rugby league), Tony Williams, Feleti Mateo. Subsequently, some Tongan rugby league players have established successful careers in the Super League such as Antonio Kaufusi.
Matangi Tonga
' – online newspaper * ''Times of Tonga, Taimi o Tonga'' (''Times of Tonga'') – controversial newspaper * ''Keleʻa'' – newspaper * ''Talaki'' – newspaper * ''Tonga Chronicle, Kalonikali'' – newspaper * ''Tauʻataina'' – newspaper * ''Kakalu'' – newspaper * Tonga Broadcasting Commission (Television Tonga, Television Tonga 2, Radio Tonga 1, Radio Tonga 2 – Kool 90FM, Radio Tonga, 103FM)
Tonga
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Tonga
from UCB Libraries GovPubs * * {{Authority control Tonga, 1970 establishments in Oceania Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean British Western Pacific Territories Christian states Commonwealth monarchies Countries in Oceania Countries in Polynesia English-speaking countries and territories Former British protectorates Island countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the United Nations Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1970
Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
covered from Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
to Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
, and then on to inhabit Tonga sometime between 1500 and 1000 BC. Scholars still debate exactly when Tonga was first settled, but thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
dating confirms that settlers had arrived in the earliest known inhabited town, Nukuleka, by 888 BC, ± 8 years. Tonga's precontact history was shared via oral history, which was passed down from generation to generation.
By the 12th century, Tongans and the Tongan monarch, the Tuʻi Tonga
The Tuʻi Tonga is a line of Tongan kings, which originated in the tenth century with the mythical ʻAhoʻeitu, and withdrew from political power in the fifteenth century by yielding to the ''Tuʻi Haʻatakalaua''. The title ended with the death ...
, had acquired a reputation across the central Pacificfrom Niue, Samoa, Rotuma
Rotuma is a Fijian dependency, consisting of Rotuma Island and nearby islets. The island group is home to a large and unique Polynesian indigenous ethnic group which constitutes a recognisable minority within the population of Fiji, known as " ...
, Wallis & Futuna, New Caledonia to Tikopia
Tikopia is a high island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It forms a part of the Melanesian nation state of Solomon Islands but is culturally Polynesian. The first Europeans arrived on 22 April 1606 as part of the Spanish expedition of Pedro F ...
, leading some historians to speak of a Tuʻi Tonga Empire having existed during that period. Civil wars are known to have occurred in Tonga in the 15th and 17th centuries.
 The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616, when the Dutch vessel ''Eendracht'', captained by
The Tongan people first encountered Europeans in 1616, when the Dutch vessel ''Eendracht'', captained by Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten ( – 1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean.
Biography
Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born in c. 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, Seve ...
, made a short visit to the islands for the purpose of engaging in trade. Later, other Dutch explorers arrived, including Jacob Le Maire
Jacob Le Maire (c. 1585 – 22 December 1616) was a Dutch mariner who circumnavigated the earth in 1615 and 1616. The strait between Tierra del Fuego and Isla de los Estados was named the Le Maire Strait in his honour, though not without controver ...
(who visited the northern island of Niuatoputapu
Niuatoputapu is a high island in the island nation of Tonga, Pacific Ocean. Its highest point is , and its area is . Its name means ''sacred island''. Older European names for the island are Traitors Island or Keppel Island.
Niuatoputapu is ...
); and Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch seafarer, explorer, and merchant, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first known European explorer to reach New ...
(who visited Tongatapu and Haʻapai) in 1643. Later noteworthy European visitors included James Cook, of the British Royal Navy, in 1773, 1774, and 1777; Spanish Navy explorers Francisco Mourelle de la Rúa in 1781; Alessandro Malaspina
Alejandro Malaspina (November 5, 1754 – April 9, 1810) was a Tuscan explorer who spent most of his life as a Spanish naval officer. Under a Spanish royal commission, he undertook a voyage around the world from 1786 to 1788, then, from 1789 t ...
in 1793; the first London missionaries in 1797; and a Wesleyan Methodist minister, Reverend Walter Lawry, in 1822.
Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
vessels were among the earliest regular Western visitors. The first of these on record is the ''Ann and Hope'', which was reported to have been seen among the islands of Tonga in June 1799. The last known whaling visitor was the ''Albatross'' in 1899. That ship arrived in Tonga seeking a resupply of water, food, and wood. The islands most regularly visited by Westerners were Ata, 'Eua, Ha'apai, Tongatapu and Vava'u. Sometimes, Tongan men were recruited to serve as crewmen on these vessels.
The United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
visited Tonga in 1840.
In 1845, an ambitious young Tongan warrior, strategist, and orator named Tāufaʻāhau united Tonga into a kingdom. He held the chiefly title of Tuʻi Kanokupolu, but had been baptised by Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
missionaries with the name ''Siaosi'' ("George") in 1831. In 1875, with the help of missionary Shirley Waldemar Baker
Shirley Waldemar Baker (1836 – 16 November 1903) was a Methodist missionary in Tonga. He was the founder of the Free Church of Tonga and enjoyed significant influence during the reign of George Tupou I, who made him prime minister.
Early life ...
, he declared Tonga a constitutional monarchy; formally adopted the Western royal style; emancipated the "serfs"; enshrined a code of law, land tenure, and freedom of the press; and limited the power of the chiefs.
Tonga became a protected state under a Treaty of Friendship with Britain on 18 May 1900, when European settlers and rival Tongan chiefs unsuccessfully tried to oust the man who had succeeded Tāufaʻāhau as king. The treaty posted no higher permanent representative on Tonga than a British consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
(1901–1970). Under the protection of Britain, Tonga maintained its sovereignty, and remained the only Pacific nation to retain its monarchical government. The Tongan monarchy follows an uninterrupted succession of hereditary rulers from one family.
The 1918 flu pandemic
The 1918–1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the misnomer Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case was ...
, brought to Tonga by a ship from New Zealand, killed 1,800 Tongans, a mortality rate of about 8%.
The Treaty of Friendship and Tonga's protection status ended in 1970 under arrangements that had been established by Tonga's Queen Salote Tupou III before her death in 1965. Owing to its British ties, Tonga joined the Commonwealth in 1970 (atypically as a country that had its own monarch, rather than having the United Kingdom's monarch, along with Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Lesotho, and Eswatini). Tonga became a member of the United Nations in September 1999. While exposed to colonial pressures, Tonga has always governed itself, which makes it unique in the Pacific.
In January 2022, the Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha'apai volcano, north of the main island of Tongatapu, erupted, causing a tsunami which inundated parts of the archipelago, including the capital Nukualofa. The eruption affected the kingdom heavily, cutting off most communications and killing four people in Tonga, including a British national who ran an animal shelter and died trying to save her dogs. In Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, two women drowned due to abnormal tsunami waves. It took around five weeks to repair a submarine fiber optic cable used in the Tonga Cable System
Tonga Cable System is a submarine fiber-optic cable system connecting Tonga with Fiji, where it connects to other international networks. It is long and was activated in 2013. It has cable landing points at Sopu, a suburb of Nukuʻalofa in Tong ...
for internet and telephone connectivity. Business magnate Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The ...
directed his company SpaceX to provide emergency internet services to households remaining under blackout via a Starlink
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX, providing satellite Internet access coverage to 45 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone service after 2023. SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As ...
satellite infrastructure network based in neighbouring Fiji.
Politics
Tonga is aconstitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
. It is the only remaining indigenous monarchy in the Pacific islands (see also Hawaiʻi
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
). Reverence for the monarch replaces that held in earlier centuries for the sacred paramount chief, the Tuʻi Tonga. Criticism of the monarch is held to be contrary to Tongan culture and etiquette. Tonga provides for its citizens a free and mandatory education for all, secondary education with only nominal fees, and foreign-funded scholarships for postsecondary education.
 The prodemocracy movement in Tonga promotes reforms, including better representation in the Parliament for the majority of commoners, and better accountability in matters of state. An overthrow of the monarchy is not part of the movement, and the institution of monarchy continues to hold popular support, even while reforms are advocated. Until recently, the governance issue was generally ignored by the leaders of other countries, but major aid donors and neighbours New Zealand and Australia are now expressing concerns about some Tongan government actions.
Following the precedents of Queen Sālote and the counsel of numerous international advisors, the government of Tonga under King
The prodemocracy movement in Tonga promotes reforms, including better representation in the Parliament for the majority of commoners, and better accountability in matters of state. An overthrow of the monarchy is not part of the movement, and the institution of monarchy continues to hold popular support, even while reforms are advocated. Until recently, the governance issue was generally ignored by the leaders of other countries, but major aid donors and neighbours New Zealand and Australia are now expressing concerns about some Tongan government actions.
Following the precedents of Queen Sālote and the counsel of numerous international advisors, the government of Tonga under King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV
Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV (born Siaosi Tāufaʻāhau Tupoulahi; 4 July 1918 – 10 September 2006) was the King of Tonga, from the death of his mother, Queen Sālote Tupou III, in 1965 until his own death in 2006.
Immediately prior to his death, ...
(reigned 1965–2006) monetised the economy, internationalised the medical and education systems, and enabled access by commoners to increasing forms of material wealth (houses, cars, and other commodities), education, and overseas travel.
Male homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to pe ...
is illegal in Tonga, with a maximum penalty of 10 years' imprisonment. Tongans have universal access to a national health care system. The Constitution of Tonga
The Constitution of Tonga is supreme law under which the Government of Tonga operates. It was enacted by King George Tupou I on 4 November 1875. It stipulates the makeup of the Tongan Government and the balance between its executive, legislatur ...
protects land ownership; land cannot be sold to foreigners (although it may be leased).
Political culture
 King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV and his government made some problematic economic decisions and were accused by democracy activists, including former prime minister ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, of wasting millions of dollars on unwise investments. The problems have mostly been driven by attempts to increase national revenue through a variety of schemes – considering making Tonga a nuclear waste disposal site (an idea floated in the mid 1990s by the current crown prince), and selling Tongan Protected Persons Passports (which eventually forced Tonga to naturalise the purchasers, sparking ethnicity-based concerns within Tonga).
Schemes also included the registering of foreign ships (which proved to be engaged in illegal activities, including shipments for al-Qaeda); claiming geo-orbital satellite slots (the revenue from which seems to belong to the Princess Royal, not the state); holding a long-term charter on an unusable
King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV and his government made some problematic economic decisions and were accused by democracy activists, including former prime minister ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, of wasting millions of dollars on unwise investments. The problems have mostly been driven by attempts to increase national revenue through a variety of schemes – considering making Tonga a nuclear waste disposal site (an idea floated in the mid 1990s by the current crown prince), and selling Tongan Protected Persons Passports (which eventually forced Tonga to naturalise the purchasers, sparking ethnicity-based concerns within Tonga).
Schemes also included the registering of foreign ships (which proved to be engaged in illegal activities, including shipments for al-Qaeda); claiming geo-orbital satellite slots (the revenue from which seems to belong to the Princess Royal, not the state); holding a long-term charter on an unusable Boeing 757
The Boeing 757 is an American narrow-body airliner designed and built by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
The then-named 7N7, a twinjet successor for the 727 (a trijet), received its first orders in August 1978.
The prototype completed its mai ...
that was sidelined in Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about ...
Airport, leading to the collapse of Royal Tongan Airlines; and approving a factory for exporting cigarettes to China (against the advice of Tongan medical officials and decades of health-promotion messaging).
The king proved vulnerable to speculators with big promises and lost reportedly US$26 million to Jesse Bogdonoff, a financial adviser who called himself the king's court jester
A jester, court jester, fool or joker was a member of the household of a nobleman or a monarch employed to entertain guests during the medieval and Renaissance eras. Jesters were also itinerant performers who entertained common folk at fairs and ...
. The police imprisoned prodemocracy leaders, and the government repeatedly confiscated the newspaper ''The Tongan Times'' (printed in New Zealand and sold in Tonga) because the editor had been vocally critical of the king's mistakes. Notably, the ''Keleʻa'', produced specifically to critique the government and printed in Tonga by prodemocracy leader ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, was not banned during that time. Pōhiva, however, had been subjected to harassment in the form of barratry (frequent lawsuits).
In mid-2003, the government passed a radical constitutional amendment to "Tonganize" the press, by licensing and limiting freedom of the press, so as to protect the image of the monarchy. The amendment was defended by the government and by royalists on the basis of traditional cultural values. Licensure criteria include 80% ownership by Tongans living in the country. , those papers denied licenses under the new act included the ''Taimi ʻo Tonga'' (''Tongan Times''), the ''Keleʻa,'' and the ''Matangi Tonga''while those permitted licenses were uniformly church-based or progovernment.
 The bill was opposed in the form of a several-thousand-strong protest march in the capital, a call by the Tuʻi Pelehake (a prince, nephew of the king and elected member of parliament) for Australia and other nations to pressure the Tongan government to democratise the electoral system, and a legal writ calling for a judicial investigation of the bill. The latter was supported by some 160 signatures, including seven of the nine elected, "People's Representatives".
The then-Crown Prince Tupoutoʻa and Pilolevu, the Princess Royal, remained generally silent on the issue. In total, the changes threatened to destabilise the polity, fragment support for the status quo, and place further pressure on the monarchy.
In 2005, the government spent several weeks negotiating with striking civil-service workers before reaching a settlement. The civil unrest that ensued was not limited to Tonga; protests outside the King's New Zealand residence made headlines.
Prime Minister Prince ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala) (now King Tupou VI) resigned suddenly on 11 February 2006, and also gave up his other cabinet portfolios. The elected minister of labour, Dr Feleti Sevele, replaced him in the interim.
On 5 July 2006, a driver in
The bill was opposed in the form of a several-thousand-strong protest march in the capital, a call by the Tuʻi Pelehake (a prince, nephew of the king and elected member of parliament) for Australia and other nations to pressure the Tongan government to democratise the electoral system, and a legal writ calling for a judicial investigation of the bill. The latter was supported by some 160 signatures, including seven of the nine elected, "People's Representatives".
The then-Crown Prince Tupoutoʻa and Pilolevu, the Princess Royal, remained generally silent on the issue. In total, the changes threatened to destabilise the polity, fragment support for the status quo, and place further pressure on the monarchy.
In 2005, the government spent several weeks negotiating with striking civil-service workers before reaching a settlement. The civil unrest that ensued was not limited to Tonga; protests outside the King's New Zealand residence made headlines.
Prime Minister Prince ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala) (now King Tupou VI) resigned suddenly on 11 February 2006, and also gave up his other cabinet portfolios. The elected minister of labour, Dr Feleti Sevele, replaced him in the interim.
On 5 July 2006, a driver in Menlo Park, California
Menlo Park is a city at the eastern edge of San Mateo County within the San Francisco Bay Area of California in the United States. It is bordered by San Francisco Bay on the north and east; East Palo Alto, Palo Alto, and Stanford to the south ...
, caused the deaths of Prince Tuʻipelehake ʻUluvalu, his wife, and their driver. Tuʻipelehake, 55, was the cochairman of the constitutional reform commission, and a nephew of the king.
 The public expected some changes when George Tupou V succeeded his father in September 2006. On 16 November 2006, rioting broke out in the capital city of
The public expected some changes when George Tupou V succeeded his father in September 2006. On 16 November 2006, rioting broke out in the capital city of Nukuʻalofa
Nukualofa (; ) is the capital and largest city of Tonga. It is located on the north coast of the island of Tongatapu, in the country's southernmost island group.
History
First western records of Nukualofa
On 10 June 1777, British captain Jam ...
when it seemed that the parliament would adjourn for the year without having made any advances in increasing democracy in government. Pro-democracy activists burned and looted shops, offices, and government buildings. As a result, more than 60% of the downtown area was destroyed and as many as six people died. The disturbances were ended by action from Tongan Security Forces and troops from New Zealand-led Joint Task Force.
On 29 July 2008, the Palace announced that King George Tupou V would relinquish much of his power and would surrender his role in day-to-day governmental affairs to the Prime Minister. The royal chamberlain said that this was being done to prepare the monarchy for 2010, when most of the first parliament would be elected, and added: "The Sovereign of the only Polynesian kingdom ... is voluntarily surrendering his powers to meet the democratic aspirations of many of his people." The previous week, the government said the king had sold state assets that had contributed to much of the royal family's wealth.
On 15 March 2012, King George Tupou V contracted pneumonia and was brought to Queen Mary Hospital in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
. He was later diagnosed with leukaemia. His health deteriorated significantly shortly thereafter, and he died at 3:15 pm on 18 March 2012. He was succeeded by his brother Tupou VI
Tupou VI (; born 12 July 1959) is the King of Tonga. He is the younger brother and successor of the late King George Tupou V. He was officially confirmed by his brother on 27 September 2006 as the heir presumptive to the Throne of Tonga, as his ...
, who was crowned on 4 July 2015.
Foreign relations
Tonga's foreign policy was described byMatangi Tonga
''Matangi Tonga'' is an online newspaper providing Tongan news in both English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', ...
as "Look East"specifically, as establishing closer diplomatic and economic relations with Asia (which actually lies to the north-west of the Pacific kingdom). As of 2021, China has attained great influence in Tonga, financing infrastructure projects including a new royal palace, and holding two thirds of the country's foreign debt.
Tonga retains cordial relations with the United States. Although it remains on good terms with the United Kingdom, the two countries do not maintain particularly close relations, and the United Kingdom closed its High Commission in Tonga in 2006, although the UK High Commission was re-established in January 2020 after a 14-year absence. Tonga's relations with Oceania's regional powers, Australia and New Zealand, are good."Tonga's diplomatic community grows", Matangi Tonga, 12 January 2009. Tonga maintains strong regional ties in the Pacific. It is a full member of the Pacific Islands Forum, the
South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission
The Pacific Islands Applied Geoscience Commission (SOPAC) was an inter-governmental regional organisation dedicated to providing services to promote sustainable development in the countries it serves. In 2010, its functions had been transferred to ...
, the South Pacific Tourism Organisation
The Pacific Tourism Organisation (SPTO) formerly known as the South Pacific Tourism Organisation is an intergovernmental organisation for the tourism sector in the South Pacific. The SPTO markets, promotes, and develops tourism in the Pacific in o ...
, the Pacific Regional Environment Programme
The Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP) is an intergovernmental organisation based in Apia, Samoa with more than 90 staff members. The organisation is held accountable by the governments and administrations of the Pa ...
, and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community
The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa, ...
.
Military
The Tongan government supported the American "coalition of the willing
The term ''coalition of the willing'' refers to an international alliance focused on achieving a particular objective, usually of military or political nature.
Usage
*One early use was by President Bill Clinton in June 1994 in relation to possib ...
" action in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
and deployed 40+ soldiers (as part of an American force) in late 2004. The contingent returned home on 17 December 2004. In 2007 a second contingent went to Iraq, and two more were sent during 2008 as part of continued support for the coalition. Tongan involvement concluded at the end of 2008 with no reported loss of life.
In 2010, Brigadier General Tauʻaika ʻUtaʻatu, commander of the Tonga Defence Services
His Majesty's Armed Forces (HMAF) is the military of Tonga. It is composed of three operational components and two support elements (logistics and training groups).
The mission of HMAF is to: "Defend the sovereignty of the Kingdom of Tonga".
Th ...
, signed an agreement in London committing a minimum of 200 troops to co-operate with Britain's International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. The task completed in April 2014 and the UK presented Operational Service Medals to each of the soldiers involved during a parade held in Tonga.
Tonga has contributed troops and police to the Bougainville conflict in Papua-New Guinea and to the Australian-led RAMSI
The Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI), also known as Operation Helpem Fren, Operation Anode and Operation Rata (by New Zealand), was created in 2003 in response to a request for international aid by the Governor-General of ...
force in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
.
Administrative divisions
Tonga is subdivided into five administrative divisions: ʻEua, Haʻapai,Niuas
Niua is a division of the Kingdom of Tonga, namely the northernmost group of islands. It consists of three islands (Niuafoʻou, Niuatoputapu and Tafahi) which together have an area of 71.69 km2 and a population of 1,150. The largest village is ...
, Tongatapu
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the nation ...
, and Vavaʻu
Vavau is an island group, consisting of one large island ( ʻUtu Vavaʻu) and 40 smaller ones, in Tonga. It is part of Vavaʻu District, which includes several other individual islands. According to tradition, the Maui god created both Tongata ...
.
Geography
 Located in
Located in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, Tonga is an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
, directly south of Samoa and about two-thirds of the way from Hawai'i to New Zealand. Its 171 islands, 45 of them inhabited, are divided into three main groups – Vava'u, Ha'apai, and Tongatapu – and cover an -long north–south line.
The largest island, Tongatapu
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the nation ...
, on which the capital city of Nukuʻalofa
Nukualofa (; ) is the capital and largest city of Tonga. It is located on the north coast of the island of Tongatapu, in the country's southernmost island group.
History
First western records of Nukualofa
On 10 June 1777, British captain Jam ...
is located, covers . Geologically the Tongan islands are of two types: most have a limestone base formed from uplifted coral formations; others consist of limestone overlaying a volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
base.
Climate
Tonga has atropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southea ...
( ''Af'') with a distinct warm period (December–April), during which the temperatures rise above , and a cooler period (May–November), with temperatures rarely rising above . The temperature and rainfall range from and on Tongatapu in the south to and on the more northerly islands closer to the Equator.
The average wettest period is around March with on average . The average daily humidity is 80%. The highest temperature recorded in Tonga was on 11 February 1979 in Vava'u. The coldest temperature recorded in Tonga was on 8 September 1994 in Fua'amotu. Temperatures of or lower are usually measured in the dry season and are more frequent in southern Tonga than in the northern islands. The tropical cyclone season currently runs from 1 November to 30 April, though tropical cyclones can form and affect Tonga outside of the season. According to the WorldRiskReport 2021, Tonga ranks third among the countries with the highest disaster risk worldwide – mainly due to the country's exposure to multiple natural hazards.
Ecology
Tonga contains the Tongan tropical moist forests terrestrial ecoregion. In Tonga, dating back to Tongan legend, flying bats are considered sacred and are the property of the monarchy. Thus, they are protected and cannot be harmed or hunted. As a result, flying fox bats have thrived in many of the islands of Tonga. The bird life of Tonga includes a total of 73 species, of which two are endemic; the Tongan whistler and the
The bird life of Tonga includes a total of 73 species, of which two are endemic; the Tongan whistler and the Tongan megapode
The Tongan megapode (''Megapodius pritchardii'') is a species of bird in the megapode family, Megapodiidae, currently endemic to Tonga. The species is also known as the Polynesian megapode, and as the Niuafo'ou megapode after the island of Niua ...
. Five species have been introduced by humans, and eight are rare or accidental. Seven species are globally threatened.
Economy


 Tonga's economy is characterised by a large nonmonetary sector and a heavy dependence on remittances from the half of the country's population who live abroad (chiefly in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States). The royal family and the nobles dominate and largely own the monetary sector of the economy – particularly the telecommunications and satellite services. Tonga was named the sixth-most corrupt country in the world by ''Forbes'' magazine in 2008.
Tonga was ranked the 165th-safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 '' Euromoney'' Country Risk rankings.
The manufacturing sector consists of
Tonga's economy is characterised by a large nonmonetary sector and a heavy dependence on remittances from the half of the country's population who live abroad (chiefly in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States). The royal family and the nobles dominate and largely own the monetary sector of the economy – particularly the telecommunications and satellite services. Tonga was named the sixth-most corrupt country in the world by ''Forbes'' magazine in 2008.
Tonga was ranked the 165th-safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 '' Euromoney'' Country Risk rankings.
The manufacturing sector consists of handicrafts
A handicraft, sometimes more precisely expressed as artisanal handicraft or handmade, is any of a wide variety of types of work where useful and decorative objects are made completely by one’s hand or by using only simple, non-automated re ...
and a few other very small-scale industries, which contribute only about 3% of GDP. Commercial business activities also are inconspicuous, and to a large extent, are dominated by the same large trading companies found throughout the South Pacific. In September 1974, the country's first commercial trading bank, the Bank of Tonga, opened.
Tonga's development plans emphasise a growing private sector, upgrading agricultural productivity, revitalising the squash and vanilla-bean industries, developing tourism, and improving communications and transport. Substantial progress has been made, but much work remains to be done. A small, growing construction sector is developing in response to the inflow of aid money and remittances from Tongans abroad. In recognition of such a crucial contribution, the government has created a new department in the Prime Minister's Office with the purpose of catering for the needs of Tongans living abroad. In 2007, the Tongan Parliament amended citizenship laws to allow Tongans to hold dual citizenship.
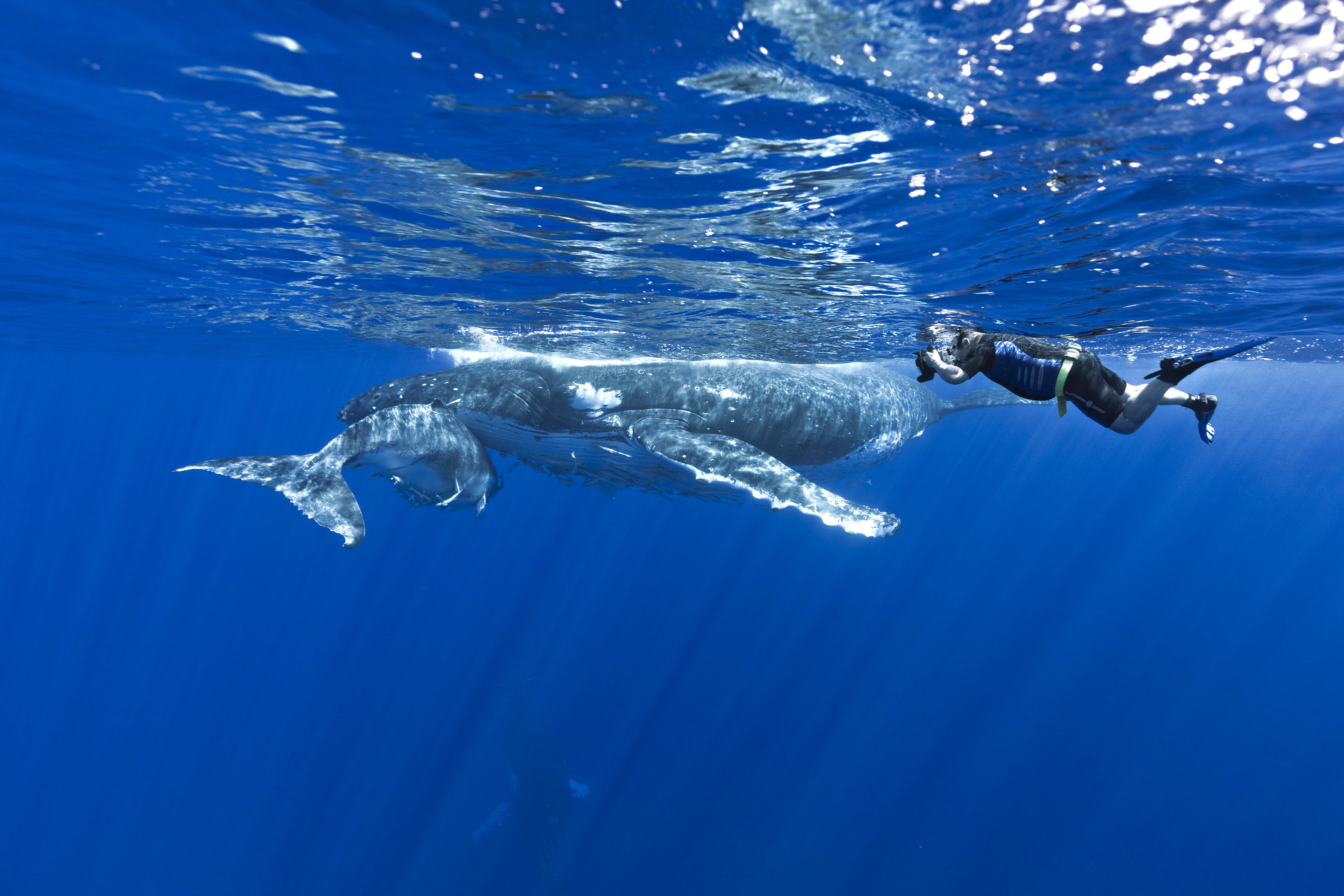
The tourist industry is relatively undeveloped. The government recognises that tourism can play a major role in economic development, and efforts are being made to increase this source of revenue. Cruise ships often stop in Vavaʻu, with a reputation for its whale watching
Whale watching is the practice of observing whales and dolphins (cetaceans) in their natural habitat. Whale watching is mostly a recreational activity (cf. birdwatching), but it can also serve scientific and/or educational purposes.Hoyt, E. 2 ...
, game fishing, surfing, beaches, and is increasingly becoming a major player in the South Pacific tourism market.
Tonga's postage stamps, featuring colourful and often unusual designs (including heart-shaped and banana-shaped stamps), are popular with philatelists
Philately (; ) is the study of postage stamps and postal history. It also refers to the collection and appreciation of stamps and other philatelic products. Philately involves more than just stamp collecting or the study of postage; it is possi ...
.
In 2005, the country became eligible to become a member of the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
. After an initial voluntary delay, Tonga became a full member of the WTO on 27 July 2007.
The Tonga Chamber of Commerce and Industry, incorporated in 1996, endeavours to represent the interests of its members, private sector businesses, and to promote economic growth in the Kingdom.
Tonga is home to some 106,000 people. More than double that number live overseas, mainly in the US, New Zealand, and Australia. Remittances from the overseas population have been declining since the onset of the 2008 global economic crisis. The tourism industry is improving, but remains modest at under 90,000 tourists per year.
Agriculture
In Tonga, agriculture and forestry (together with fisheries) provide the majority of employment, foreign exchange earnings, and food. Rural Tongans rely on bothplantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
and subsistence agriculture. Plants grown for both market cash crops and home use include bananas, coconuts, coffee bean
A coffee bean is a seed of the '' Coffea'' plant and the source for coffee. It is the pip inside the red or purple fruit often referred to as a coffee cherry. Just like ordinary cherries, the coffee fruit is also a so-called stone fruit. Even th ...
s, vanilla bean
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla ('' V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from which ...
s, and root crops
Root vegetables are underground plant parts eaten by humans as food. Although botany distinguishes true roots (such as taproots and tuberous roots) from non-roots (such as bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and tubers, although some contain both hypocotyl ...
such as cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, sweet potato, and taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
. , two-thirds of agricultural land was in root crops.
The processing of coconuts into copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from co ...
and desiccated (dried) coconut was once the only significant industry, and only commercial export. Deteriorating prices on the world market and lack of replanting brought this once vibrant industry, as in most island nations of the South Pacific, to a complete standstill.
Swine and poultry are the major types of livestock. Horses are kept for draft purposes, primarily by farmers working their'' ʻapi ʻuta'' (a plot of bushland). More cattle are being raised, and beef imports are declining.
The traditional feudal land ownership system meant that farmers had no incentive to invest in planting long-term tree crops on land they did not own. In the late 20th century, kava and vanilla from larger plantations became the main agricultural exports, together with squash. The export of squash to Japan, beginning in 1987, once brought relief to Tonga's struggling economy, but local farmers became increasingly wary of the Japanese market due to price fluctuations, and the huge financial risks involved.
Energy
Energy in Tonga mostly comes from imported diesel. Energy consumption in Tonga is projected to reach around 66 gigawatt hours by 2020. The country aimed to reach 50% of renewable energy by 2020. In 2019, Tonga announced the construction of a 6-megawatt solar farm on Tongatapu. The plant will be the second-largest solar plant in the Pacific upon completion. In view of the decreasing reliability offossil-fuel electricity
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels may ...
generation, its increasing costs, and negative environmental side effects, renewable energy solutions have attracted the government's attention. Together with IRENA, Tonga has planned a renewable energy based strategy to power the main and outer islands. The strategy focuses on solar home systems that turn individual households into small power plants. It calls for the involvement of local operators, finance institutions, and technicians to provide sustainable business models and strategies to ensure the effective operation, management, and maintenance once the systems are installed.
The Pacific Centre for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency was established in Tonga in 2016 to advise the private sector on related policy matters, provide capacity development and promote business investment. The centre facilitates a financial mechanism offering competitive grants for start-ups to spur the adoption of renewable energy by the business sector. The centre is part of the Global Network of Regional Sustainable Energy Centres and SIDS DOCK framework designed to attract international investment in the renewable energy sector.
With the assistance of IRENA, Tonga has developed the 2010–2020 Tonga Energy Road Map, which aims for a 50% reduction of diesel importation. This was to be accomplished through a range of appropriate renewable technologies, including wind and solar, as well as innovative efficiencies. As of 2018, Tonga was generating 10% of its electricity from renewable sources.
Demographics
 Over 70% of the inhabitants live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties remain influential throughout the country. Despite emigration, Tonga grew in population from about 32,000 in the 1930s to more than 90,000 by 1976.
Over 70% of the inhabitants live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties remain influential throughout the country. Despite emigration, Tonga grew in population from about 32,000 in the 1930s to more than 90,000 by 1976.
Ethnic groups
According to the government portal, Tongans, Polynesian by ethnicity with a mixture ofMelanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n, represent more than 98% of the inhabitants. About 1.5% are mixed Tongans and the rest are European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
(the majority are British), mixed European, and other Pacific Islanders
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oce ...
. In 2001, about 3,000 to 4,000 Chinese lived there, comprising 3 to 4% of the total Tongan population. The 2006 Nukuʻalofa riots mainly targeted Chinese-owned businesses, leading to the emigration of several hundred Chinese so that only about 300 remain.
Languages
Tongan is the official language, along with English. APolynesian language
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austro ...
, it is closely related to Wallisian (Uvean), Niuean, and Hawai'ian.
Religion
 Tonga does not have an official state religion. The Constitution of Tonga (Revised 1998) provides for freedom of religion.
In 1928, Queen Salote Tupou III, who was a member of the
Tonga does not have an official state religion. The Constitution of Tonga (Revised 1998) provides for freedom of religion.
In 1928, Queen Salote Tupou III, who was a member of the Free Wesleyan Church of Tonga
The Free Wesleyan Church of Tonga (FWCT; Tongan: ''Siasi Uēsiliana Tau‘atāina ‘o Tonga'') is a Methodist denomination in Tonga. It is the largest Christian denomination in the nation and is often mistaken to be its state church. It has it ...
, established the Free Wesleyan Church as the state religion of Tonga. The chief pastor of the Free Wesleyan Church serves as the representative of the people of Tonga and of the church at the coronation of a king or queen of Tonga, where he anoints and crowns the monarch. In opposition to the establishment of the Free Wesleyan Church as a state religion, the Church of Tonga separated from the Free Wesleyan Church in 1928.
Islam in Tonga is a small minority religion in the country. Muslims in Tonga belong to Sunni denomination. Al-Khadeejah Mosque is a prominent mosque in Tonga.
Everyday life is heavily influenced by Polynesian traditions and by the Christian faith; for example, all commerce and entertainment activities cease on Sunday, from the beginning of the day at midnight, to the end of the day at midnight. The constitution declares the Sabbath sacred forever. The official figures from the latest government census show that 90% of the population are affiliated with a Christian church or sect, with the four major church affiliations in the kingdom:
* Free Wesleyan Church of Tonga
The Free Wesleyan Church of Tonga (FWCT; Tongan: ''Siasi Uēsiliana Tau‘atāina ‘o Tonga'') is a Methodist denomination in Tonga. It is the largest Christian denomination in the nation and is often mistaken to be its state church. It has it ...
(36,592 or 36%)
* The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
(18,554 or 18%)
* Roman Catholicism in Tonga, Roman Catholics (15,441 or 15%)
* Free Church of Tonga (11,863 or 12%)
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints sent missionaries in 1891 to visit King Siaosi (George) Tupo, where they obtained permission to preach.
Health
By some published surveys, Tonga has one of the highest obesity rates in the world. World Health Organization data published in 2014 indicate that Tonga stands fourth overall in terms of List of countries by Body Mass Index (BMI), countries listed by mean body mass index data. In 2011, 90% of the adult population were considered overweight using NIH interpretation of body mass index (BMI) data, with more than 60% of those obesity, obese. 70% of Tongan females aged 15–85 are obese. Tonga and Nauru have the world's highest overweight and obese populations. In late October 2021, Tonga reported its first case of COVID-19 based on a New Zealand air passenger's positive test.Education
Primary education between ages 6 and 14 is compulsory and free in state schools. Mission schools provide about 8% of the primary and 90% of the secondary level of education. State schools make up for the rest. Higher education includes teacher training, nursing, and medical training, a small private university, a woman's business college, and a number of private agricultural schools. Most levels of higher education are pursued overseas. Tongans enjoy a relatively high level of education, with a 98.9% literacy rate, and higher education up to and including medical and graduate degrees (pursued mostly overseas). They hold the body of academic knowledge created by their scholars in high esteem and the Kukū Kaunaka Collection, which comprises every doctoral and master's dissertation written by any Tongan in any country is archived by Seu'ula Johansson-Fua at the Institute for Education in Tonga.Emigration
Contemporary Tongans often have strong ties to overseas lands. Many Tongans have emigrated to Tongan Australians, Australia, Tongan New Zealanders, New Zealand, or the Tongan Americans, United States to seek employment and a higher standard of living. In 2018, 82,389 Tongans lived in New Zealand. The United States is the preferred destination for many Tongan emigrants, and as of 2000, 36,840 Tongans were living in the US. More than 8,000 Tongans live in Australia. The Tongan diaspora retains close ties to relatives at home, and a significant portion of Tonga's income derives from remittances to family members (often aged) who prefer to remain in Tonga.Culture
 Humans have lived in Tonga for nearly 3,000 years since settlement in late Lapita times. Before the arrival of European explorers in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, Tongans had frequent contacts with their nearest Oceanic neighbours, Fiji and Niue. In the 19th century, with the arrival of Western traders and missionaries, Tongan culture changed, especially in religion. , almost 98% of residents profess Christianity. The people discarded some old beliefs and habits and adopted others.
Humans have lived in Tonga for nearly 3,000 years since settlement in late Lapita times. Before the arrival of European explorers in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, Tongans had frequent contacts with their nearest Oceanic neighbours, Fiji and Niue. In the 19th century, with the arrival of Western traders and missionaries, Tongan culture changed, especially in religion. , almost 98% of residents profess Christianity. The people discarded some old beliefs and habits and adopted others.

Sport
Rugby union
Rugby union is the national sport, and the Tonga national rugby union team, national team (ʻIkale Tahi, or Sea Eagles) has performed quite well on the international stage. Tonga has competed in six Rugby World Cups since 1987 Rugby World Cup, 1987. The 2007 Rugby World Cup, 2007 and 2011 Rugby World Cups were Tonga's most successful to date, both winning two out of four matches and in a running chance for the quarterfinals. In the 2007 Rugby World Cup, Tonga won its first two matches, against the United States national rugby union team, USA 25–15, and Samoa national rugby union team, Samoa 19–15. They came very close to upsetting the eventual winners of the 2007 tournament, the South African Springboks, losing 30–25. A defeat by England National Rugby Union Team, England, 36–20 in their last pool game ended their hopes of making the knockout stages. Nevertheless, by picking up third place in their pool games behind South Africa and England, Tonga earned automatic qualification for the 2011 Rugby World Cup in New Zealand. In 2011 Rugby World Cup Pool A, Pool A of the 2011 Rugby World Cup, Tonga beat both Japan national rugby union team, Japan 31–18 and 5th ranked eventual finalist France national rugby union team, France 19–14 in the latter pool stages. However, a previous heavy defeat by the All Blacks at the tournament's opener (41–10) and a subsequent tight defeat by Canada national rugby union team, Canada (25–20) meant that Tonga lost out to France (who also lost to All Blacks, NZ) for the quarter finals due to 2 bonus points and a points difference of 46. Tonga's best result before 2007 came in 1995 Rugby World Cup, 1995, when they beat Ivory Coast national rugby union team, Côte d'Ivoire 29–11, and 1999 Rugby World Cup, 1999 when they beat Italy 28–25 (although with only 14 men they lost heavily to England, 101–10). Tonga perform the Kailao, Ikale Tahi war dance or Sipi Tau (a form of Kailao) before all their matches. Tonga used to compete in the Pacific Tri-Nations against Samoa and Fiji, which has now been replaced by the World Rugby Pacific Nations Cup, which now involves Japan national rugby union team, Japan, Canada national rugby union team, Canada, and the United States national rugby union team, United States. At club level, there are the Datec Cup Provincial Championship and the Pacific Rugby Cup. Rugby union is governed by the Tonga Rugby Football Union, which was a member of the Pacific Islands Rugby Alliance and contributed to the Pacific Islanders rugby union team, before they were disbanded in 2009. Many players of Tongan descent – e.g., Jonah Lomu, Israel Folau, Viliami Ofahengaue, Viliami "William" ʻOfahengaue, Malakai Fekitoa, Ben Afeaki, Charles Piutau, Frank Halai, Sekope Kepu, George Smith (rugby union), George Smith, Cliff Palu, Wycliff Palu, Sitaleki Timani, Salesi Ma'afu, Anthony Faingaa, Anthony and Saia Faingaa, Mark Gerrard, Cooper Vuna, Doug Howlett, Toutai Kefu and Tatafu Polota-Nau – have played for either the All Blacks or the Wallabies. British and Irish Lions, British and Irish Lion and Welsh international player Taulupe Faletau, Taulupe "Toby" Faletau is Tongan born and the son of Tongan international Kuli Faletau. Taulupe's cousins and England international players Billy Vunipola, Billy and Mako Vunipola (who is also a British and Irish Lion), are sons of former Tonga rugby captain Fe'ao Vunipola. Rugby is popular among the nation's schools, and students from schools such as Tonga College and Tupou College are regularly offered scholarships in New Zealand, Australia and Japan.Rugby league
 Rugby league has gained some success. Tonga made their first appearance at a Rugby League World Cup in the 1995 Rugby League World Cup, 1995 edition where they went out in the first stage but narrowly lost to New Zealand national rugby league team, New Zealand. They have since appeared in each subsequent Rugby League World Cup tournament. In the 2008 Rugby League World Cup Tonga national rugby league team, Tonga recorded wins against Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland and Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland. Just before the 2017 Rugby League World Cup, 2017 World Cup, various high-profile players, led by Jason Taumalolo and Andrew Fifita, defected from their tier one nations to represent their nation of heritage. This led to them defeating New Zealand in Hamilton at Waikato Stadium on 11 November at that tournament. The national team has since also recorded victories against Great Britain national rugby league team, Great Britain and the world number one Australia national rugby league team, Australia. In addition to the success of the national team, many players of Tongan descent make it big in the Australian National Rugby League competition. These include Jason Taumalolo, Israel Folau, Tyson Frizell, Tevita Pangai Junior, Konrad Hurrell, David Fusitua, Tuimoala Lolohea, Sio Siua Taukeiaho, Jorge Taufua, William Hopoate, Andrew Fifita, Ben Murdoch-Masila, Felise Kaufusi, Willie Mason, Manu Vatuvei, Brent Kite, Fuifui Moimoi, Willie Tonga, Anthony Tupou, Antonio Kaufusi, Michael Jennings (rugby league), Michael Jennings, Tony Williams (rugby league), Tony Williams, Feleti Mateo. Subsequently, some Tongan rugby league players have established successful careers in the Super League such as Antonio Kaufusi.
Rugby league has gained some success. Tonga made their first appearance at a Rugby League World Cup in the 1995 Rugby League World Cup, 1995 edition where they went out in the first stage but narrowly lost to New Zealand national rugby league team, New Zealand. They have since appeared in each subsequent Rugby League World Cup tournament. In the 2008 Rugby League World Cup Tonga national rugby league team, Tonga recorded wins against Ireland national rugby league team, Ireland and Scotland national rugby league team, Scotland. Just before the 2017 Rugby League World Cup, 2017 World Cup, various high-profile players, led by Jason Taumalolo and Andrew Fifita, defected from their tier one nations to represent their nation of heritage. This led to them defeating New Zealand in Hamilton at Waikato Stadium on 11 November at that tournament. The national team has since also recorded victories against Great Britain national rugby league team, Great Britain and the world number one Australia national rugby league team, Australia. In addition to the success of the national team, many players of Tongan descent make it big in the Australian National Rugby League competition. These include Jason Taumalolo, Israel Folau, Tyson Frizell, Tevita Pangai Junior, Konrad Hurrell, David Fusitua, Tuimoala Lolohea, Sio Siua Taukeiaho, Jorge Taufua, William Hopoate, Andrew Fifita, Ben Murdoch-Masila, Felise Kaufusi, Willie Mason, Manu Vatuvei, Brent Kite, Fuifui Moimoi, Willie Tonga, Anthony Tupou, Antonio Kaufusi, Michael Jennings (rugby league), Michael Jennings, Tony Williams (rugby league), Tony Williams, Feleti Mateo. Subsequently, some Tongan rugby league players have established successful careers in the Super League such as Antonio Kaufusi.
Olympics
Aside from rugby, Tonga has also produced athletes who have competed at both the Summer and Winter Olympics. Tonga's only Olympic medal came from the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, where Paea Wolfgramm won silver in Boxing at the 1996 Summer Olympics – Super heavyweight, super heavyweight boxing. One athlete attended the 2018 Winter Olympics in Pyeongchang, South Korea.American football
Several Tongans have been football players in the National Football League, including Tuineau Alipate, Spencer Folau, Lakei Heimuli, Steve Kaufusi, Ma'ake Kemoeatu, Deuce Lutui, Siupeli Malamala, Tim Manoa, Stan Mataele, Vili Maumau, Alfred Pupunu, Vai Sikahema, Star Lotulelei, Vita Vea, and Peter Tuipulotu.Grasso, John (2013). ''Historical Dictionary of Football''. Scarecrow Press. Page 492. .Media
*Matangi Tonga
' – online newspaper * ''Times of Tonga, Taimi o Tonga'' (''Times of Tonga'') – controversial newspaper * ''Keleʻa'' – newspaper * ''Talaki'' – newspaper * ''Tonga Chronicle, Kalonikali'' – newspaper * ''Tauʻataina'' – newspaper * ''Kakalu'' – newspaper * Tonga Broadcasting Commission (Television Tonga, Television Tonga 2, Radio Tonga 1, Radio Tonga 2 – Kool 90FM, Radio Tonga, 103FM)
See also
* Outline of Tonga * List of islands and towns in TongaNotes
References
Further reading
Ethnography, culture, and history
* ''On the Edge of the Global: Modern Anxieties in a Pacific Island Nation'' (2011) by Niko Besnier. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, * ''Islanders of the South: Production, Kinship and Ideology in the Polynesian Kingdom of Tonga'' (1993) by Paul van der Grijp. Leiden: KITLV Press. * ''Identity and Development: Tongan Culture, Agriculture, and the Perenniality of the Gift'' (2004) by Paul van der Grijp. Leiden: KITLV Press. * ''Manifestations of Mana: Political Power and Divine Inspiration in Polynesia'' (2014) by Paul van der Grijp. Vienna and Berlin: LIT Verlag. * ''Becoming Tongan: An Ethnography of Childhood'' by Helen Morton * ''Queen Salote of Tonga: The Story of an Era, 1900–65'' by Elizabeth Wood-Ellem * ''Tradition Versus Democracy in the South Pacific: Fiji, Tonga and Western Samoa'' by Stephanie Lawson * ''Voyages: From Tongan Villages to American Suburbs'' Cathy A. Small * ''Friendly Islands: A History of Tonga'' (1977). Noel Rutherford. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. * ''Tonga and the Tongans: Heritage and Identity'' (2007) Elizabeth Wood-Ellem. Alphington, Vic.: Tonga Research Association, * ''Early Tonga: As the Explorers Saw it 1616–1810''. (1987). Edwin N Ferdon. Tucson: University of Arizona Press; * ''The Art of Tonga'' (Ko e ngaahi'aati'o Tonga) by Keith St Cartmail. (1997) Honolulu : University of Hawai`i Press. * ''The Tonga Book'' by Paul. W. Dale * ''Tonga'' by James SiersWildlife and environment
* ''Birds of Fiji, Tonga and Samoa'' by Dick Watling * ''A Guide to the Birds of Fiji and Western Polynesia: Including American Samoa, Niue, Samoa, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu and Wallis and Futuna'' by Dick Watling * ''Guide to the Birds of the Kingdom of Tonga'' by Dick WatlingTravel guides
* ''Lonely Planet Guide: Samoan Islands and Tonga'' by Susannah Farfor and Paul Smitz * ''Moon Travel Guide: Samoa-Tonga'' by David StanleyBibliography
*Fiction
*External links
Tonga
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Tonga
from UCB Libraries GovPubs * * {{Authority control Tonga, 1970 establishments in Oceania Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean British Western Pacific Territories Christian states Commonwealth monarchies Countries in Oceania Countries in Polynesia English-speaking countries and territories Former British protectorates Island countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the United Nations Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1970