Titograd Studio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Podgorica (

 Podgorica is at the
Podgorica is at the
 The Ottoman Empire captured Podgorica in 1474. Podgorica became a kaza of the Sanjak of Scutari (which was historically led by Albanian Pashas). In 1479, The Ottomans built a large fortress in Podgorica, and the existing settlement, with its highly developed merchant connections, became the main Ottoman defensive and attacking bastion in the region. At the beginning of 1474 the Ottoman sultan intended to rebuild Podgorica and Baleč and settle them with 5,000 Muslim families (most of them of Albanian or Slavic origin), in order to stop cooperation between the Principality of Zeta and Albania Veneta.
Podgorica fell again, but this time to the Ottomans in 1484, and the character of the town changed extensively. The Ottomans fortified the city, building towers, gates, and defensive ramparts that give Podgorica the appearance of an Ottoman military city.
Most of today's Montenegro and Podgorica fell under the rule of the Albanian
The Ottoman Empire captured Podgorica in 1474. Podgorica became a kaza of the Sanjak of Scutari (which was historically led by Albanian Pashas). In 1479, The Ottomans built a large fortress in Podgorica, and the existing settlement, with its highly developed merchant connections, became the main Ottoman defensive and attacking bastion in the region. At the beginning of 1474 the Ottoman sultan intended to rebuild Podgorica and Baleč and settle them with 5,000 Muslim families (most of them of Albanian or Slavic origin), in order to stop cooperation between the Principality of Zeta and Albania Veneta.
Podgorica fell again, but this time to the Ottomans in 1484, and the character of the town changed extensively. The Ottomans fortified the city, building towers, gates, and defensive ramparts that give Podgorica the appearance of an Ottoman military city.
Most of today's Montenegro and Podgorica fell under the rule of the Albanian
 After the Berlin Congress in 1878, when Podgorica was annexed to the Principality of Montenegro, marking the end of four centuries of Ottoman rule, and the beginning of a new era for Podgorica and Montenegro. The first forms of capital concentration were seen in 1902 when roads were built to all neighboring towns, and tobacco became Podgorica's first significant commercial product. Then in 1904, a savings bank named Zetska formed the first significant financial institution, and it would soon grow into Podgorička Bank.
World War I marked the end of dynamic development for Podgorica, which by then was the largest city in the newly proclaimed Kingdom of Montenegro. On 10 August 1914, nine military personnel and 13 civilians were killed in Podgorica from an aerial bombardment by Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops. The city was bombed three more times in 1915. Podgorica was occupied, as was the rest of the country, by Austria-Hungary from 1916 to 1918.
After the liberation by the
After the Berlin Congress in 1878, when Podgorica was annexed to the Principality of Montenegro, marking the end of four centuries of Ottoman rule, and the beginning of a new era for Podgorica and Montenegro. The first forms of capital concentration were seen in 1902 when roads were built to all neighboring towns, and tobacco became Podgorica's first significant commercial product. Then in 1904, a savings bank named Zetska formed the first significant financial institution, and it would soon grow into Podgorička Bank.
World War I marked the end of dynamic development for Podgorica, which by then was the largest city in the newly proclaimed Kingdom of Montenegro. On 10 August 1914, nine military personnel and 13 civilians were killed in Podgorica from an aerial bombardment by Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops. The city was bombed three more times in 1915. Podgorica was occupied, as was the rest of the country, by Austria-Hungary from 1916 to 1918.
After the liberation by the
 After the
After the

 The city administration consists of a mayor, city assembly, and a number of secretariats and administrative bodies which together act as a city local government. The city assembly has 61 members, elected directly for four-year terms. The mayor used to be directly elected for a five-year term, but since the new law was introduced in Montenegrin municipalities mayors will be elected by the city assembly and will have to maintain its support during the term. Separate elections are held for the local sub-division of Golubovci since it is part of their administrative autonomy inside Podgorica municipality. Constant questions are raised by various politicians over gaining separate municipality status for Golubovci. In 2018, Tuzi became its own municipality after a vote on the Montenegrin Parliament.
On local elections held on 25 May 2014, the Democratic Party of Socialists won 29 seats in the municipal assembly, one short of 30 needed to form a majority.
The city administration consists of a mayor, city assembly, and a number of secretariats and administrative bodies which together act as a city local government. The city assembly has 61 members, elected directly for four-year terms. The mayor used to be directly elected for a five-year term, but since the new law was introduced in Montenegrin municipalities mayors will be elected by the city assembly and will have to maintain its support during the term. Separate elections are held for the local sub-division of Golubovci since it is part of their administrative autonomy inside Podgorica municipality. Constant questions are raised by various politicians over gaining separate municipality status for Golubovci. In 2018, Tuzi became its own municipality after a vote on the Montenegrin Parliament.
On local elections held on 25 May 2014, the Democratic Party of Socialists won 29 seats in the municipal assembly, one short of 30 needed to form a majority.
Gorica Hill
'' (), city's namesake, which rises above the city centre. The other hills include ''Malo brdo'' ("little hill", ), ''Velje brdo'' ("big hill", )
Ljubović
() and ''Dajbapska gora'' (). Podgorica city proper has an area of , while actual urbanized area is much smaller.
Podgorica,_Montenegro_-_panoramio_(14).jpg, Morača river canyon.
02 - Maja Stosic - Pavlova Strana.jpg, Lake Skadar
Nijagara_-_panoramio.jpg, River Cijevna waterfalls near Podgorica
Zagoric.JPG, Podgorica panoramic view.
 Under the Köppen climate classification, Podgorica is transitional between a
Under the Köppen climate classification, Podgorica is transitional between a

 Podgorica is home to three main religious groups:
Podgorica is home to three main religious groups: 
 The Catholic population mainly consists of the local Albanian minority. The main religious site for the Catholic population located in the Konik neighbourhood is the Church of the Holy Heart of Jesus constructed in 1966, in
The Catholic population mainly consists of the local Albanian minority. The main religious site for the Catholic population located in the Konik neighbourhood is the Church of the Holy Heart of Jesus constructed in 1966, in
 In the early 1990s, the dissolution of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav wars, and the UN-imposed sanctions left Podgorica's industries without traditional markets, suppliers, and available funds. This, combined with typical transition pressures, led to a decline of the industrial base, where many industries collapsed leaving thousands of citizens unemployed. However, some of the industries, including Plantaže, managed to survive the turmoil of the 1990s, and are still major contributors to Montenegrin export and industrial output to this day.
As Montenegro began its push for independence from Serbia in the late 1990s, Podgorica greatly benefited from the increased concentration of government and service sectors. In addition to almost the entire country's government, Podgorica is home to the Montenegro Stock Exchange and other major Montenegrin financial institutions, along with telecommunications carriers, media outlets, Montenegrin flag carrier airline, and other significant institutions and companies.
The large presence of government and service sectors spared the economy of Podgorica from prolonged stagnation in the late 2000s recession, which hit Montenegro hard. Although in mid-2014, some 30% of Montenegro's citizens lived in Podgorica, the municipality accounted for 44% of the country's employed. Out of the entire mass of paid net salaries in Montenegro in that year, some 47% was paid in Podgorica. The average monthly net salary in December 2021 was €537 in Podgorica municipality.
In the early 1990s, the dissolution of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav wars, and the UN-imposed sanctions left Podgorica's industries without traditional markets, suppliers, and available funds. This, combined with typical transition pressures, led to a decline of the industrial base, where many industries collapsed leaving thousands of citizens unemployed. However, some of the industries, including Plantaže, managed to survive the turmoil of the 1990s, and are still major contributors to Montenegrin export and industrial output to this day.
As Montenegro began its push for independence from Serbia in the late 1990s, Podgorica greatly benefited from the increased concentration of government and service sectors. In addition to almost the entire country's government, Podgorica is home to the Montenegro Stock Exchange and other major Montenegrin financial institutions, along with telecommunications carriers, media outlets, Montenegrin flag carrier airline, and other significant institutions and companies.
The large presence of government and service sectors spared the economy of Podgorica from prolonged stagnation in the late 2000s recession, which hit Montenegro hard. Although in mid-2014, some 30% of Montenegro's citizens lived in Podgorica, the municipality accounted for 44% of the country's employed. Out of the entire mass of paid net salaries in Montenegro in that year, some 47% was paid in Podgorica. The average monthly net salary in December 2021 was €537 in Podgorica municipality.


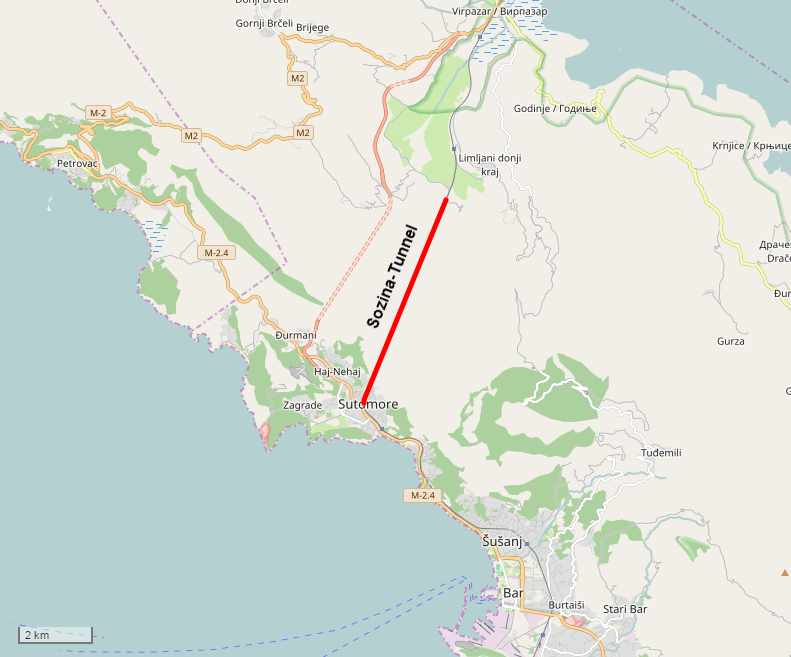 Podgorica's location in central Montenegro makes it a natural hub for rail and road transport. Roads in Montenegro (especially those connecting Podgorica to northern Montenegro and Serbia) are usually inferior to modern European roads. Both major Montenegrin motorway projects,
Podgorica's location in central Montenegro makes it a natural hub for rail and road transport. Roads in Montenegro (especially those connecting Podgorica to northern Montenegro and Serbia) are usually inferior to modern European roads. Both major Montenegrin motorway projects,
 Podgorica is a hub of the X-shaped Montenegrin rail network. The Belgrade–Bar line converges with the line to Nikšić and line to Shkodër at the
Podgorica is a hub of the X-shaped Montenegrin rail network. The Belgrade–Bar line converges with the line to Nikšić and line to Shkodër at the
 Podgorica Airport is located in Zeta Plain, south of Podgorica City centre, and is Montenegro's main international airport. The airport is locally known as Golubovci Airport (Аеродром Голубовци / Aerodrom Golubovci), as it is located within the administrative boundaries of the town of Golubovci. The IATA code of the airport is still TGD because Podgorica was named Titograd, during which time the airport opened. It is the main hub for
Podgorica Airport is located in Zeta Plain, south of Podgorica City centre, and is Montenegro's main international airport. The airport is locally known as Golubovci Airport (Аеродром Голубовци / Aerodrom Golubovci), as it is located within the administrative boundaries of the town of Golubovci. The IATA code of the airport is still TGD because Podgorica was named Titograd, during which time the airport opened. It is the main hub for
File:Novi_Grad,_Podgorica,_Montenegro_-_panoramio_(9).jpg, Cathedral of the Resurrection of Christ interior.
File:Royal Garden in Podgorica.jpg, Former residence of King Nikola I Petrović, today an art gallery.
File: Montenegrin National Theatre.jpg , Montenegrin National Theatre
File:Podgorica, museo nazionale, esterno 01.JPG,
 The most popular sports by far are
The most popular sports by far are
''Stara Varoš'' (''Old town'')
and ''Drač'' is typical of this, with two mosques, a Turkish Clock Tower and narrow, winding streets. When the city was incorporated to Montenegro, the urban core shifted to the other bank of the Ribnica River, where the town developed in a more European style: wider streets with an
file:Independence_Square_PG.jpg, Independence square.
File:Most Milenijum (Millenium Bridge) (9185505567).jpg, Morača river.
File:SaborniHram.JPG, Roman Square and Cathedral of Podgorica.
File:Most Blaža Jovanovića.jpg,
A major advance in Podgorica architecture began in the late 1990s and, since then, the face of the city has changed rapidly. Residential and business construction are proceeding rapidly, incorporating contemporary glass-and-steel architectural trends. In an effort to create a recognizable and modern state capital, city officials are routing significant investments in the city's public spaces. Thus, the city has gained entirely new squares and some monuments. New landmarks include the ''Hristovog Vaskrsenja'' orthodox temple and the Millennium Bridge, the main feature of the Podgorica skyline.
Tourism Organisation of Podgorica
More (mostly modern) buildings of Podgorica
{{Authority control Capitals in Europe Populated places in Podgorica Municipality
Cyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
: Подгорица, ; lit. 'under the hill') is the capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city of Montenegro. The city was formerly known as Titograd (Cyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
: Титоград, ) between 1946 and 1992—in the period that Montenegro formed, as the Socialist Republic of Montenegro in honour of Marshal
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
. The city was largely destroyed during the bombing of Podgorica in World War II and accordingly the city is now dominated by architecture from the following decades of communism. Further but less substantial damage was caused by the 1999 bombing by NATO forces.
The surrounding landscape is predominantly mountainous terrain. The city is just north of the Lake Skadar and close to coastal destinations on the Adriatic Sea. Historically, it was Podgorica's position at the confluence of the Ribnica and Morača rivers and at the meeting-point of the fertile Zeta Plain and Bjelopavlići Valley that encouraged settlement.
Etymology
Podgorica is written inCyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
as Подгорица, ; , ; ''Podgorica'' literally means "area below Gorica". ''Gorica'' ( cyrl, Горица), a diminutive of the word Gora (Cyrillic: Гора) which is another word for Mountain or Hill, means "little/small hill", is the name of one of the cypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word ''cypress'' is derived from Old French ''cipres'', which was imported from Latin ''cypressus'', the ...
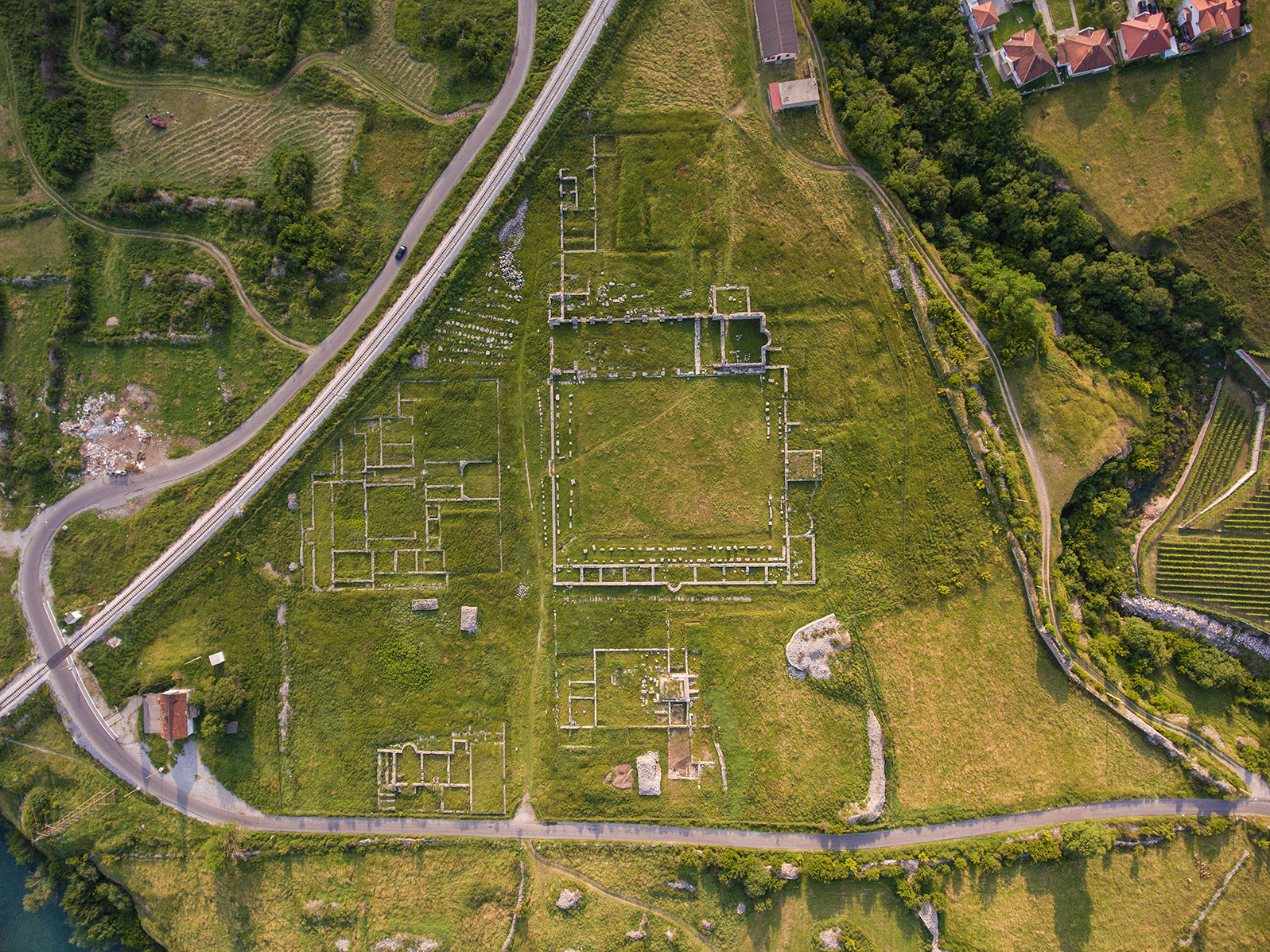
-covered hillocks that overlooks the city center. Some three kilometres () north-west of Podgorica lie the ruins of the Roman-era town of Doclea, from which the Roman Emperor Diocletian's mother hailed. In later centuries, Romans "corrected" the name to , guessing wrongly that an ''i'' had been lost in vulgar speech. is the later South Slavic version of same word. At its foundation (some time before the 11th century), the town was called (In Illyrian or nowadays Albanian language means Black Hole). In the Middle Ages, it was known as Ribnica ( cyrl, Рибница, ). The name Podgorica was used from 1326. From 1946 to 1992, the city was named Titograd ( cyrl, Титоград) in honour of Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
, the President of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1953 to 1980. In 1992 the city changed its name to "Podgorica", which it remains today.
History
Early history

 Podgorica is at the
Podgorica is at the crossroads
Crossroads, crossroad, cross road or similar may refer to:
* Crossroads (junction), where four roads meet
Film and television Films
* ''Crossroads'' (1928 film), a 1928 Japanese film by Teinosuke Kinugasa
* ''Cross Roads'' (film), a 1930 Brit ...
of several historically important routes, near the rivers Zeta, Morača, Cijevna, Ribnica, Sitnica and Mareza in the valley of Lake Skadar and near the Adriatic Sea, in fertile lowlands with favourable climate. The earliest human settlements were in prehistory: the oldest physical remains are from the late Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
.
In the Iron Age, the area between the Zeta and Bjelopavlići valleys was occupied by two Illyrian tribes, the Labeates and the Docleatae
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greek ...
. The population of the town of Doclea was 8,000–10,000, in which all core urban issues were resolved. The high population density (in an area of about radius) was made possible by the geographical position, favorable climate, and economic conditions and by the defensive positions that were of great importance at that time.
Middle Ages
From the fifth century AD, with the arrival of the first Slavic and Avar tribes and the beginning of the break-up of the Roman Empire, the area bore witness to many noteworthy events. With time, the fortifications ceased their function, and new towns were built; a new settlement probably named after the Ribnica river, on whose banks it was built, Ribnica, was established. It was first mentioned during the reign of the Nemanjić dynasty, as part of the Serbian kingdom. The importance of Ribnica was its position as crossroads in communications with the west. The name Podgorica was first mentioned in 1326 in a court document of the Kotor archives. The city was economically strong: trade routes between the Republic of Ragusa and Serbia, well developed at that time, were maintained via the road that led to Podgorica through Trebinje and Nikšić. As a busy crossroads, Podgorica was a vibrant regional center of trade and communication. This boosted its development, economic power, military strength, and strategic importance.Ottoman Empire
 The Ottoman Empire captured Podgorica in 1474. Podgorica became a kaza of the Sanjak of Scutari (which was historically led by Albanian Pashas). In 1479, The Ottomans built a large fortress in Podgorica, and the existing settlement, with its highly developed merchant connections, became the main Ottoman defensive and attacking bastion in the region. At the beginning of 1474 the Ottoman sultan intended to rebuild Podgorica and Baleč and settle them with 5,000 Muslim families (most of them of Albanian or Slavic origin), in order to stop cooperation between the Principality of Zeta and Albania Veneta.
Podgorica fell again, but this time to the Ottomans in 1484, and the character of the town changed extensively. The Ottomans fortified the city, building towers, gates, and defensive ramparts that give Podgorica the appearance of an Ottoman military city.
Most of today's Montenegro and Podgorica fell under the rule of the Albanian
The Ottoman Empire captured Podgorica in 1474. Podgorica became a kaza of the Sanjak of Scutari (which was historically led by Albanian Pashas). In 1479, The Ottomans built a large fortress in Podgorica, and the existing settlement, with its highly developed merchant connections, became the main Ottoman defensive and attacking bastion in the region. At the beginning of 1474 the Ottoman sultan intended to rebuild Podgorica and Baleč and settle them with 5,000 Muslim families (most of them of Albanian or Slavic origin), in order to stop cooperation between the Principality of Zeta and Albania Veneta.
Podgorica fell again, but this time to the Ottomans in 1484, and the character of the town changed extensively. The Ottomans fortified the city, building towers, gates, and defensive ramparts that give Podgorica the appearance of an Ottoman military city.
Most of today's Montenegro and Podgorica fell under the rule of the Albanian Bushati
The Bushati family ( sq, Bushatllinjtë) was a prominent Ottoman Albanian family that ruled the Pashalik of Scutari from 1757 to 1831.
Origins
They are descendants of the medieval Bushati tribe, a pastoralist tribe (''fis'') in northern Albani ...
Family of Shkodra between 1760 and 1831, which ruled independently from the Imperial authority of the Ottoman Sultan.
In 1864, Podgorica became a ''kaze'' of the Scutari Vilayet called Böğürtlen ("blackberry", also known as Burguriçe).
On 7 October 1874, in a violent reaction over the murder of a local named Juso Mučin Krnić, Ottoman forces killed at least 15 people in Podgorica. The massacre was widely reported outside of Montenegro and ultimately contributed to the buildup to the Montenegrin-Ottoman War.
The end of the Montenegrin-Ottoman War in 1878 resulted in the Congress of Berlin recognizing vast territories, including that of Podgorica, as part of the newly recognized Kingdom of Montenegro. At that time there were about 1,500 houses in Podgorica, with more than 8,000 people living there – of Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and Muslim faiths flourishing together.
The Petrović and Karađorđević monarchies
 After the Berlin Congress in 1878, when Podgorica was annexed to the Principality of Montenegro, marking the end of four centuries of Ottoman rule, and the beginning of a new era for Podgorica and Montenegro. The first forms of capital concentration were seen in 1902 when roads were built to all neighboring towns, and tobacco became Podgorica's first significant commercial product. Then in 1904, a savings bank named Zetska formed the first significant financial institution, and it would soon grow into Podgorička Bank.
World War I marked the end of dynamic development for Podgorica, which by then was the largest city in the newly proclaimed Kingdom of Montenegro. On 10 August 1914, nine military personnel and 13 civilians were killed in Podgorica from an aerial bombardment by Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops. The city was bombed three more times in 1915. Podgorica was occupied, as was the rest of the country, by Austria-Hungary from 1916 to 1918.
After the liberation by the
After the Berlin Congress in 1878, when Podgorica was annexed to the Principality of Montenegro, marking the end of four centuries of Ottoman rule, and the beginning of a new era for Podgorica and Montenegro. The first forms of capital concentration were seen in 1902 when roads were built to all neighboring towns, and tobacco became Podgorica's first significant commercial product. Then in 1904, a savings bank named Zetska formed the first significant financial institution, and it would soon grow into Podgorička Bank.
World War I marked the end of dynamic development for Podgorica, which by then was the largest city in the newly proclaimed Kingdom of Montenegro. On 10 August 1914, nine military personnel and 13 civilians were killed in Podgorica from an aerial bombardment by Austro-Hungarian Aviation Troops. The city was bombed three more times in 1915. Podgorica was occupied, as was the rest of the country, by Austria-Hungary from 1916 to 1918.
After the liberation by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in 1918, the controversial Podgorica Assembly marked the end of Montenegrin statehood, as Montenegro was merged with the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
and incorporated into the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. The population of urban Podgorica during this interwar period was approximately 14,000.
During the interwar period (1918–1941), Podgorica had public bathrooms as most residents did not have their own. However, the ''Imperial'' hotel built in 1925 had two bathrooms, which was unprecedented at the time. It was one of at least six hotels built in the city during the interwar period.
World War II
Yugoslav coup d'état
The Yugoslav coup d'état took place on 27 March 1941 in Belgrade, Kingdom of Yugoslavia, when the regency led by Prince Paul of Yugoslavia was overthrown and King Peter II fully assumed monarchical powers. The coup was planned and conducted ...
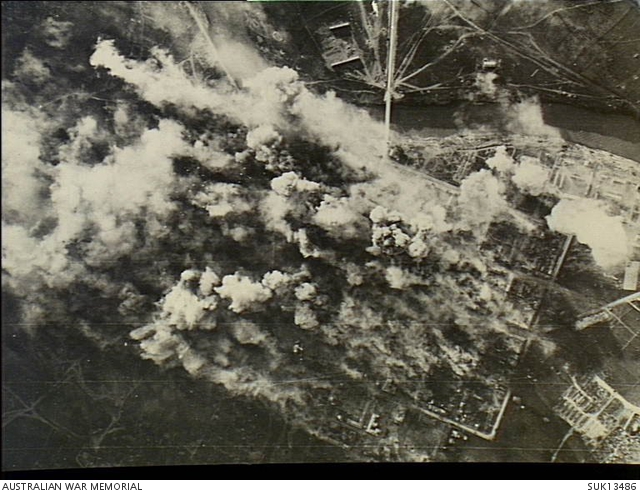
on 27 March 1941, demonstrations supporting the coup took place in Podgorica. As a result of the coup, Yugoslavia turned against its previous alliance with the Axis powers and was subsequently invaded. Podgorica was bombed over 80 times throughout the course of the war. The city was first bombed by the Luftwaffe on 6 April 1941. On 5 May 1944, Podgorica was bombed by the USAAF in an attack against Axis forces, although the bombardment that day killed approximately 400 civilians.Kovačević, Branislav. ''Savezničko bombardovanje Crne Gore 1943. – 1944. godine''. Svjedočanstvo. Podgorica, 2003. (pg. 57) The city was liberated on 19 December 1944. According to the Belgrade Museum of Genocide Victims, a total of 1,691 people were killed in Podgorica over the course of the war.
Socialist Yugoslavia
On 12 July 1946,Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
made one of his early visits to Podgorica from the ''Radovče'' hotel, where he spoke to a crowd. It was the first of fifteen total visits made by Tito to the city after World War II.
On 25 July 1948, the vice president of the People's Parliament of Montenegro, Andrija Mugoša, along with secretary Gavron Cemović, signed a law changing the name of Podgorica into "Titovgrad". The law was "retroactively" activated such that the name change applied to any records starting from 13 July 1946, when it became the capital of Montenegro within the newly formed Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. However, in a glaring contradiction, the "Službeni list" or legal code of Yugoslavia recorded the name "Titograd" without the letter "v". Ultimately, "Titograd" was used over "Titovgrad".
In addition to the new name, Titograd saw the establishment of new factories. The Radoje Dakić factory, built-in 1946 for the production of heavy machinery, became one of the largest employers in Titograd. In 1964, Radoje Dakić guaranteed hired workers an apartment in the city. In the late 1960s, the cities of Titograd, Zadar, and Mostar competed to be selected as the location of Yugoslavia's expanding aluminum industry. In a highly politicized selection process, Titograd was ultimately chosen and the Kombinat was constructed in 1969. In 1974, the public Veljko Vlahović University
The University of Montenegro ( cnr, Универзитет Црнe Горe / Univerzitet Crne Gore) is a national public university of Montenegro.
Its central administration and majority of constitutive Faculty (division), faculties are located i ...
was founded in Titograd. On 15 April 1979, the city suffered damage by a 6.9 magnitude earthquake.
Titograd was the site of massive protests during Yugoslavia's anti-bureaucratic revolution. On 10 January 1989, over 10,000 people protested in the city. By the turn of the decade, Titograd was recognized as the city with the most greenery in Yugoslavia, along with Banja Luka.
Contemporary history
As Yugoslavia began to break up, Titograd was renamed to Podgorica after a referendum on 2 April 1992. On 25 May 1992, Podgorica was the site of a Serbian Radical Party rally of approximately 10,000 supporters, during which a Montenegrin Bosniak man named Adem Šabotić attempted to assassinate Vojislav Šešelj via hand bomb after his supporters chanted references to killing Muslims. Šešelj, his bodyguards, and a few bystanders were injured after the bomb detonated but no one was killed. Otherwise, the Yugoslav wars largely bypassed Podgorica, but the entire country was greatly affected with severe economic stagnation and hyperinflation lasting throughout the 1990s due to international sanctions. In 1999, Podgorica was subject to airstrikes during the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia. On 13 July 2005, the newly constructed Millennium Bridge opened for traffic. Following the results of the independence referendum in May 2006, Podgorica saw significant development as the capital of an independent state, including the reconstruction and renaming of the former Ivan Milutinović Square to Independence Square. On 13 October 2008, at least 10,000 people protestedKosovo's declaration of independence
The 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, which proclaimed the Republic of Kosovo to be a state independent from Serbia, was adopted at a meeting held on 17 February 2008 by 109 out of the 120 members of the Assembly of Kosovo, including the P ...
. On 19 December 2008, the Moscow Bridge opened for pedestrians.
On 7 August 2013, the 60-year old Hotel ''Crna Gora'' was demolished to make way for the new Hilton
Hilton or Hylton may refer to:
Companies
* Hilton Worldwide Holdings, Inc., a global hospitality company based in the United States that owns several hotel chains and subsidiary companies containing the Hilton name
** Hilton Hotels & Resorts, fla ...
in its place, which opened in 2016. Construction of the Cathedral of Christ's Resurrection finished after 20 years on 7 October 2013.
In October 2015, protests took place in Podgorica ahead of Montenegro's accession into NATO. After a demonstration of at least 5,000 to 8,000 people, the police used tear gas to disperse demonstrators from the parliament. Protests in the city continued through the 2016 Montenegrin parliamentary election
Parliamentary elections were held in Montenegro on 16 October 2016. The ruling Democratic Party of Socialists (DPS) remained the largest party, winning 36 of the 81 seats, and subsequently formed a coalition government with the new Social Democra ...
. On 22 February 2018, a Yugoslav Army veteran killed himself at the US embassy in Podgorica.
Administration

 The city administration consists of a mayor, city assembly, and a number of secretariats and administrative bodies which together act as a city local government. The city assembly has 61 members, elected directly for four-year terms. The mayor used to be directly elected for a five-year term, but since the new law was introduced in Montenegrin municipalities mayors will be elected by the city assembly and will have to maintain its support during the term. Separate elections are held for the local sub-division of Golubovci since it is part of their administrative autonomy inside Podgorica municipality. Constant questions are raised by various politicians over gaining separate municipality status for Golubovci. In 2018, Tuzi became its own municipality after a vote on the Montenegrin Parliament.
On local elections held on 25 May 2014, the Democratic Party of Socialists won 29 seats in the municipal assembly, one short of 30 needed to form a majority.
The city administration consists of a mayor, city assembly, and a number of secretariats and administrative bodies which together act as a city local government. The city assembly has 61 members, elected directly for four-year terms. The mayor used to be directly elected for a five-year term, but since the new law was introduced in Montenegrin municipalities mayors will be elected by the city assembly and will have to maintain its support during the term. Separate elections are held for the local sub-division of Golubovci since it is part of their administrative autonomy inside Podgorica municipality. Constant questions are raised by various politicians over gaining separate municipality status for Golubovci. In 2018, Tuzi became its own municipality after a vote on the Montenegrin Parliament.
On local elections held on 25 May 2014, the Democratic Party of Socialists won 29 seats in the municipal assembly, one short of 30 needed to form a majority. Democratic Front Democratic Front is a name used by political parties and alliances in several countries, such as:
*Democratic Front (Albania)
*Democratic Front for the Liberation of Angola
*Democratic Front (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
*Democratic Front (Cyprus)
* Demo ...
won 17 seats, SNP won 8 seats, while coalition made of Positive Montenegro
Positive Montenegro ( cnr, italic=no, Pozitivna Crna Gora; Позитивна Црна Гора) was a centrist, social-liberal political party in Montenegro. The party was founded in May 2012 by former environmental activist Darko Pajović.
His ...
and SDP won 5 seats. After lengthy negotiations, SDP dissolved coalition with Pozitivna and made an arrangement on forming a majority with DPS, similar to one they have in national government. While SDP is a longtime partner of DPS at the national level, it has been in opposition to Podgorica municipal assembly in 2010–2014 period.
Since October 2014, the position of the mayor is held by DPS
DPS may refer to:
Schools United States
* Dalton Public Schools, the public school district in Dalton, Georgia
* Dearborn Public Schools, the public school district in Dearborn, Michigan
* Decatur Public Schools District 61, the public school sys ...
official, Slavoljub Stijepović, replacing Podgorica mayor od 14 years, Miomir Mugoša. Since October 2018, the position of the Mayor is held by DPS
DPS may refer to:
Schools United States
* Dalton Public Schools, the public school district in Dalton, Georgia
* Dearborn Public Schools, the public school district in Dearborn, Michigan
* Decatur Public Schools District 61, the public school sys ...
Vicepredsident dr Ivan Vuković, replacing Slavoljub Stijepović.
City Assembly
Local subdivisions
The municipality of Podgorica consists of ''Podgorica City Proper'' and one subdivision (called ''city municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
,'' градске општине, ''gradske opštine''), which is Golubovci.
The entire municipality of Podgorica is further divided into 57 ''local communities
A local community has been defined as a group of interacting people living in a common location. The word is often used to refer to a group that is organized around common values and is attributed with social cohesion within a shared geographical l ...
'' (мјесне заједнице, ''mjesne zajednice''), bodies in which the citizens participate in decisions on matters of relevance to the local community.
Geography
Podgorica is located in central Montenegro. The area is crossed with rivers and the city itself is only north of Lake Skadar. The Morača and Ribnica rivers flow through the city, while the Zeta, Cijevna, Sitnica and Mareza flow nearby. ''Morača'' is the largest river in the city, being wide near downtown, and having carved a deep canyon for the length of its course through the city. Except for the Morača and Zeta, other rivers have an appearance of small creeks. The richness in bodies of water is a major feature of the city. In contrast to most of Montenegro, Podgorica lies in a mainly flat area at the northern end of the Zeta plain, at an elevation of . The only exceptions are hills which overlook the city. The most significant is high 'Gorica Hill
'' (), city's namesake, which rises above the city centre. The other hills include ''Malo brdo'' ("little hill", ), ''Velje brdo'' ("big hill", )
Ljubović
() and ''Dajbapska gora'' (). Podgorica city proper has an area of , while actual urbanized area is much smaller.
Climate
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa'') and a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csa''), since the driest summer month gets slightly less than of precipitation, with summer highs around and winter highs around . Although the city is only some north of the Adriatic Sea, an arm of the Mediterranean, Mount Rumija acts as a natural barrier, separating Skadar Lake basin and Podgorica area from the sea, thus limiting temperate maritime influence on the local climate.
The mean annual rainfall is , making Podgorica by far the wettest capital in Europe, Ljubljana being second with . The temperature exceeds on about 135 days each year and the median daily temperature is . The number of rainy days is about 120, and those with a strong wind around 60. An occasional strong northerly wind influences the climate in the winter, with a wind chill
Wind chill or windchill (popularly wind chill factor) is the lowering of body temperature due to the passing-flow of lower-temperature air.
Wind chill numbers are always lower than the air temperature for values where the formula is valid. When ...
effect lowering the perceived temperature by a few degrees.
The all-time maximum snowfall record was beaten on 11 February 2012, when of snowfall were measured. Before that, the biggest snowfall in Podgorica was in 1954, when of snowfall was recorded. Maximum temperature was recorded on 24 August 2007, at , while all time minimum was , on 4 February 1956.
Demography
In the Ottoman defter of 1485, 40 households were listed. In 1614, there was over 900 households. Although medium-sized by European standards, Podgorica is by far the largest city in Montenegro: almost a quarter of Montenegrin citizens live there. According to the 2011 census, there are 185,937 people in Podgorica Capital City, which is analogous to the metropolitan area, and includes the small towns of Tuzi and Golubovci, while 150,977 people live within the city proper. Out of the total population of Podgorica 48.73% are male and 51.27% are female. The average age of the population is 35.7.Religion
 Podgorica is home to three main religious groups:
Podgorica is home to three main religious groups: Orthodox Christians
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churc ...
, Sunni Muslims
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
and Catholic Christians
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
The Orthodox Christian population mostly originates from the local Montenegrin and Serb population, which accepted Orthodox Christianity in Middle Ages after a major split during The Great Schism. They represent the major religious group. There are various Eastern Orthodox churches in the city including St. George Church which originates from the 13th century, and the Cathedral of the Resurrection of Christ which is the largest church in the city to have been recently erected.
The Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
population mostly originates from local Bosniaks
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry ...
, as well as Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
. There are several mosques in Podgorica.

 The Catholic population mainly consists of the local Albanian minority. The main religious site for the Catholic population located in the Konik neighbourhood is the Church of the Holy Heart of Jesus constructed in 1966, in
The Catholic population mainly consists of the local Albanian minority. The main religious site for the Catholic population located in the Konik neighbourhood is the Church of the Holy Heart of Jesus constructed in 1966, in Brutalist
Brutalist architecture is an architectural style that emerged during the 1950s in the United Kingdom, among the reconstruction projects of the post-war era. Brutalist buildings are characterised by Minimalism (art), minimalist constructions th ...
style which makes this object unique. Other Catholic churches are located in eastern suburb Tuzi.
Economy
Podgorica is not only the administrative center of Montenegro but also its main economic engine. Most of Montenegro's industrial, financial, and commercial base is in Podgorica. Before World War I, most of Podgorica's economy was in trade and small-scale manufacturing, which was an economic model established during the long rule of the Ottoman Empire. After World War II, Podgorica became Montenegro's capital and a focus of the rapid urbanization and industrialization of the SFRY era. Industries such as aluminium and tobacco processing,textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, engineering, vehicle production, and wine production were established in and around the city. In 1981, Podgorica's GDP per capita was 87% of the Yugoslav average.
 In the early 1990s, the dissolution of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav wars, and the UN-imposed sanctions left Podgorica's industries without traditional markets, suppliers, and available funds. This, combined with typical transition pressures, led to a decline of the industrial base, where many industries collapsed leaving thousands of citizens unemployed. However, some of the industries, including Plantaže, managed to survive the turmoil of the 1990s, and are still major contributors to Montenegrin export and industrial output to this day.
As Montenegro began its push for independence from Serbia in the late 1990s, Podgorica greatly benefited from the increased concentration of government and service sectors. In addition to almost the entire country's government, Podgorica is home to the Montenegro Stock Exchange and other major Montenegrin financial institutions, along with telecommunications carriers, media outlets, Montenegrin flag carrier airline, and other significant institutions and companies.
The large presence of government and service sectors spared the economy of Podgorica from prolonged stagnation in the late 2000s recession, which hit Montenegro hard. Although in mid-2014, some 30% of Montenegro's citizens lived in Podgorica, the municipality accounted for 44% of the country's employed. Out of the entire mass of paid net salaries in Montenegro in that year, some 47% was paid in Podgorica. The average monthly net salary in December 2021 was €537 in Podgorica municipality.
In the early 1990s, the dissolution of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav wars, and the UN-imposed sanctions left Podgorica's industries without traditional markets, suppliers, and available funds. This, combined with typical transition pressures, led to a decline of the industrial base, where many industries collapsed leaving thousands of citizens unemployed. However, some of the industries, including Plantaže, managed to survive the turmoil of the 1990s, and are still major contributors to Montenegrin export and industrial output to this day.
As Montenegro began its push for independence from Serbia in the late 1990s, Podgorica greatly benefited from the increased concentration of government and service sectors. In addition to almost the entire country's government, Podgorica is home to the Montenegro Stock Exchange and other major Montenegrin financial institutions, along with telecommunications carriers, media outlets, Montenegrin flag carrier airline, and other significant institutions and companies.
The large presence of government and service sectors spared the economy of Podgorica from prolonged stagnation in the late 2000s recession, which hit Montenegro hard. Although in mid-2014, some 30% of Montenegro's citizens lived in Podgorica, the municipality accounted for 44% of the country's employed. Out of the entire mass of paid net salaries in Montenegro in that year, some 47% was paid in Podgorica. The average monthly net salary in December 2021 was €537 in Podgorica municipality.
Tourism
Further cultural and historic monuments in and around Podgorica are Sahat-kula Adzi-pasa Osmanagica, the ruins of the Ribnica fortress, remnants of the city of Doclea, Stara Varoš, and Vezirov. Podgorica has excellent transit connections with other centres. At nine kilometres from the city is the International Airport, with railway and bus stations close to one another.
Media
Podgorica is the media hub of Montenegro. It is home to the headquarters of the state-owned public television broadcaster RTCG. Commercial broadcasters in Podgorica include RTV A1, TV Vijesti, Nova M, Gradska TV andPrva TV
Prva (; sr-Cyrl, Прва) or Prva Srpska Televizija ( sr-Cyrl, Прва српска телевизија, lit=First Serbian Television), is a Serbian commercial television network with national coverage.
Launched on 31 December 2006 at 7&nbs ...
. It was announced that the city's local television will be launched soon. Their programmes can be received in much of Montenegro.
All Montenegro's daily newspapers (oldest Montenegrin daily newspaper '' Pobjeda'', '' Vijesti'', '' Dnevne Novine'' and '' Dan'') are published in Podgorica.
Transport
Public transport
Public transport in Podgorica consists of 11 urban and 16 suburban bus lines. The city-owned ''AD Gradski saobraćaj'' public transport company used to be the sole bus operator until the 1990s, when private carriers were introduced. The company went bankrupt in 2001, and buses were since operated solely by private carriers. Public transport faces competition from very popular dispatched taxi services. De-regulation and stiff competition have made taxi services very affordable. Over 20 taxi companies are operating in Podgorica with close to 800 vehicles in service. Usually, taxi companies provide a high level of service, with relatively new and uniform car fleets andGPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
-tracked vehicles.

Roads
 Podgorica's location in central Montenegro makes it a natural hub for rail and road transport. Roads in Montenegro (especially those connecting Podgorica to northern Montenegro and Serbia) are usually inferior to modern European roads. Both major Montenegrin motorway projects,
Podgorica's location in central Montenegro makes it a natural hub for rail and road transport. Roads in Montenegro (especially those connecting Podgorica to northern Montenegro and Serbia) are usually inferior to modern European roads. Both major Montenegrin motorway projects, Bar-Boljare motorway
The A-1 motorway, otherwise known as the Bar-Boljare motorway ( Montenegrin: Auto-put Bar — Boljare), is a motorway in Montenegro.
It is part of the larger international project between Montenegro and Serbia that connects to the Belgrade� ...
and Nudo–Božaj motorway, will pass near Podgorica. The first phase of newly constructed motorway A-1 (Bar-Boljari) will be open on July 13. 2022. The newly built Sozina tunnel (4.2 km) shortened the journey from Podgorica to Bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
(Montenegro's main seaport) to under 30 minutes. Also, a new road bypass has been constructed in 2011, to remove transport routes from north to south of the country, out of the city center. A south-western bypass has also been planned , with the same goal of moving heavy transport out of the city core. Podgorica is also characteristic of its extensive network of multi-lane boulevards which make inner-city transport quick and effective. Traffic over the Morača River also goes fluently since river banks are very well connected with 6 vehicular and 3 pedestrian bridges.
The main transit connections of Podgorica are:
* north ( E65, E80), towards Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
and on to Central Europe
* west ( E762), towards Nikšić, Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
and on to Western Europe
* south ( E65, E80) towards the Adriatic coast
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the ...
* east ( E762), towards Albania
Rail
 Podgorica is a hub of the X-shaped Montenegrin rail network. The Belgrade–Bar line converges with the line to Nikšić and line to Shkodër at the
Podgorica is a hub of the X-shaped Montenegrin rail network. The Belgrade–Bar line converges with the line to Nikšić and line to Shkodër at the Podgorica Rail Station
The Podgorica Railway Station ( cnr, Жељезничка станица Подгорица, Željeznička stanica Podgorica) is a railway station located in Podgorica, Montenegro.
The first railway station in Podgorica was built in 1927 near the ...
. The station itself is located to the southeast of the main city square. Podgorica's main railway link (for both passenger and freight traffic) is Belgrade–Bar. The link to Nikšić was recently under reconstruction ( electrification); afterwards, passenger service started in October 2012. The rail link to Shkodër
Shkodër ( , ; sq-definite, Shkodra) is the fifth-most-populous city of the Republic of Albania and the seat of Shkodër County and Shkodër Municipality. The city sprawls across the Plain of Mbishkodra between the southern part of Lake Shkod ...
is used as freight-only.
Air
 Podgorica Airport is located in Zeta Plain, south of Podgorica City centre, and is Montenegro's main international airport. The airport is locally known as Golubovci Airport (Аеродром Голубовци / Aerodrom Golubovci), as it is located within the administrative boundaries of the town of Golubovci. The IATA code of the airport is still TGD because Podgorica was named Titograd, during which time the airport opened. It is the main hub for
Podgorica Airport is located in Zeta Plain, south of Podgorica City centre, and is Montenegro's main international airport. The airport is locally known as Golubovci Airport (Аеродром Голубовци / Aerodrom Golubovci), as it is located within the administrative boundaries of the town of Golubovci. The IATA code of the airport is still TGD because Podgorica was named Titograd, during which time the airport opened. It is the main hub for Air Montenegro
To Montenegro a.d (stylised as ''ToMontenegro'' and ''2Montenegro''), is the flag carrier of Montenegro, which is branded and operates under the name Air Montenegro (Montenegrin Cyrillic: Ер Монтенегро), a new company opened in ear ...
and Di Air
Adriatic Airways is an airline based in Podgorica, Montenegro. It operates international charter flights from Podgorica and Tivat to neighbouring countries. Its main base is Podgorica Airport, with a hub at Tivat Airport.
History
The airline was ...
.
Education
Most of Montenegro's higher education establishments are in Podgorica including the University of Montenegro, the country's most significant university. The university has the following faculties: *Faculty of Political Sciences
A faculty is a division within a university or college comprising one subject area or a group of related subject areas, possibly also delimited by level (e.g. undergraduate). In American usage such divisions are generally referred to as colleges ...
* Faculty of Law
A faculty is a division within a university or college comprising one subject area or a group of related subject areas, possibly also delimited by level (e.g. undergraduate). In American usage such divisions are generally referred to as colleges ...
* Faculty of Economics
* Faculty of Electrical Engineering
* Faculty of Metallurgy and Technology
* Faculty for Information Technology
* Faculty of Civil Engineering
* Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
* Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
* Faculty of Medicine
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
* Faculty of Pharmacy
* Faculty of Architecture
This is a list of architecture schools at colleges and universities around the world.
An architecture school (also known as a school of architecture or college of architecture), is an institution specializing in architectural education.
Africa
...
* Faculty of Biotechnology
The university's scientific research institutes are also in the Podgorica: Institute of Foreign Languages, Institute of Biotechnology and the Institute of History
The Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts (CANU) is in Podgorica, as well as the parallel scholars' academy DANU.
There are a number of private institutions for higher education including the Mediterranean University which was founded in 2006 as the first private university in Montenegro and the University of Donja Gorica. The municipality of Podgorica has 34 elementary schools and 10 secondary schools, including one gymnasium. The first secondary school established in Podgorica is Gymnasium "Slobodan Škerović"
The Gymnasium "Slobodan Škerović" ( Montenegrin : Gimnazija "Slobodan Škerović" ''Гимназија "Слободан Шкеровић"''), also known as the Podgorica Gymnasium ( Montenegrin: Podgorička gimnazija ''Подгоричка ги ...
which first opened in 1907. The rebuilt economic high school offers new features and higher quality education. The "Radosav Ljumović National Library" is considered the most comprehensive in Montenegro.
Culture
Podgorica is home to many Montenegrin cultural institutions and events. It hosts the Montenegrin National Theatre and a number of museums and galleries. The Montenegrin National Theatre is the most significant theatre not only in Podgorica but in all of Montenegro. Podgorica is also host to the City Theatre (''Gradsko pozorište''), which includes the Children's Theatre and the Puppet Theatre. Although not as rich in museums and galleries as the historic royal capitalCetinje
Cetinje (, ) is a town in Montenegro. It is the former royal capital (''prijestonica'' / приjестоница) of Montenegro and is the location of several national institutions, including the official residence of the president of Montenegro ...
, there are several noteworthy museums:
* The Podgorica City Museum (''Muzej grada Podgorice'') preserves Podgorica's rich heritage. Founded in 1950, it has four categories: archaeological, ethnographic, historical, and cultural-historical. It houses artifacts that date back to the Roman and Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
n eras.
* The Archaeological Research Centre (''Centar za arheološka istraživanja'') was founded in 1961. Its mission is to gather, classify, restore and display archaeological sites.
* The Marko Miljanov Museum (''Muzej Marka Miljanova'') in Medun shows life in 19th century Montenegro.
* The Natural History Museum (''Prirodnjački muzej'') displays specimens of Montenegrin flora and fauna. This museum has no exhibition space of its own, despite many proposals and initiatives to build one.
There is a notable art gallery in the ''Dvorak'' ''Petrovića'' ( Petrović Castle) complex in Podgorica's largest public park. King Nicholas's castle, ''Perjanički Dom'' (House of the Honour Guard), castle chapel and surrounding buildings were converted to an art gallery in 1984. Since 1995, it has been part of the Modern Arts Centre (''Centar savremenih umjetnosti'') and houses approximately 1,500 works of art. The historic Cinema of Culture (''Kino Kultura''), which was founded in 1949, was closed in November 2008 due to continuous financial losses it generated. It was the only cinema in the city for 6 decades. The building of the former cinema will be converted to host the Podgorica City Theatre. Shortly after its closure, a Ster-Kinekor (later acquired by Cineplexx) 6-screen multiplex cinema opened at BIG Podgorica shopping mall.
A significant cultural institution of over fifty years' standing is the Budo Tomović Cultural-Informational Centre (''KIC Budo Tomović''). It is a public institution that organizes various artistic events, including Podgorica Cultural Summer (''Podgoričko Kulturno Ljeto''), FIAT – International Alternative Theatre Festival (''Festival Internacionalnog Alternativnog Teatra''), DEUS – December Arts Scene (''Decembarska Umjetnička Scena'').
Sport
 The most popular sports by far are
The most popular sports by far are football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
and basketball. Basketball became especially popular with the success in the late 20th and early 21st centuries of KK Budućnost, both in Regional and European competitions.
Football in Podgorica has a long tradition associated with Budućnost. World-famous players Predrag Mijatović and Dejan Savićević were born in Podgorica and made their debut in that team. The club FK Zeta from the Podgorica suburb of Golubovci has also reached the former first league of Serbia and Montenegro. These clubs, along with Sutjeska from Nikšić, usually compete with each other for leading position in the First League of Montenegro
The First League of Montenegro ( Montenegrin: ''Prva crnogorska fudbalska liga'' — ''Prva CFL'' — ''1. CFL''; ) is the top football league in Montenegro. Founded in 2006, competition is headed by the Football Association of Montenegro. 10 te ...
.
Other clubs from Podgorica and its surroundings play in the Montenegrin First League e.g. OFK Titograd & Kom. One of the most popular clubs from the suburbs is FK Ribnica from Konik, FK Zabjelo from Zabjelo and FK Podgorica
Fudbalski klub Podgorica, formerly known as OFK Mladost 1970, is a football club from the southwestern part of Podgorica, Montenegro. It was founded in 1970, the club was reactivated during 2014. In the summer 2019, the club was renamed to FK Po ...
from ''Donja Gorica''.
The volleyball team OK Budućnost and the women's handball team ŽRK Budućnost T-Mobile have had significant success in European competition. Budućnost Podgorica Budućnost means "the future" in many Slavic languages, and it may also refer to:
*SD Budućnost Podgorica, a sports society from Podgorica, Montenegro
** KK Budućnost Podgorica, a professional basketball club
FK Budućnost may refer to:
* FK Bud ...
is the most important sports club in Podgorica. Its name means ''Future''.
Chess is another popular sport and some famous global chess players, like Slavko Dedić
Slavko Dedić is a Montenegrin chess player. He participated in dozens international tournaments, including the European Championship 2009. Dedić is a member of Chess club "Šahmatik" from Budva. In 2014, Slavko Dedić became a national chess ...
, are born in Podgorica.
Sporting events like the annual Podgorica Marathon, Coinis no limits Triathlon, and the ''Morača River'' jumps attract international competitors.
Podgorica was the host of 2009 FINA Men's Water Polo World League
The 2009 FINA Men's Water Polo World League was the eighth edition of the annual event, organised by the world's governing body in aquatics, the FINA. After a preliminary round organized by continent, the Super Final was held in Podgorica, Monten ...
.
Venues
Podgorica has a number of sporting venues; some are under reconstruction and expansion. The main ones are: * Podgorica City Stadium. It has a capacity of 11,264 and it is the home ofFK Budućnost Podgorica
Fudbalski Klub Budućnost Podgorica (Cyrillic: Будућност Подгорица, , lit. "Future") is a Montenegrin football club from Podgorica, Montenegro. It is competing in the Montenegrin First League. Its colours are blue and white.
...
and the Montenegro national football team. It is the only venue in Montenegro that complies with FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' ( French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
standards for international football matches.
*Morača Sports Center
Morača Sports Centre ( Montenegrin: ''Sportski centar Morača'', Спортски центар Морача) is a multi-sports venue that is located in Podgorica, Montenegro.
The venue is located in the new part of Podgorica, on the right bank of ...
, a multi-functional indoor sports facility. It has a capacity of 6 000 seats. It hosted one group of EuroBasket 2005, while other games were played in Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, Vršac, and Novi Sad.
*Bemax Arena, newly opened, basketball indoor and outdoor sports facility. It has a capacity of 2.400 seats.
Almost every football club in Podgorica has its own stadium, although these are often only fields with small stands or no stands at all.
Other notable venues are the Stadion malih sportova under Gorica hill and the sport shooting range under Ljubović hill. There are many other sports facilities around the city, most notably indoor soccer
Indoor soccer or arena soccer (known internationally as indoor football, fast football, or showball) is five-a-side version of minifootball, derived from association football and adapted to be played in walled hardcourt indoor arena. Indoor socc ...
fields.
Cityscape
Podgorica's mixture of architectural styles reflects the turbulent history of the city and country: as one régime replaced another, the corresponding style was introduced. As part of the Ottoman Empire until 1878, Podgorica has some examples of Ottoman architecture. The oldest parts of the city''Stara Varoš'' (''Old town'')
and ''Drač'' is typical of this, with two mosques, a Turkish Clock Tower and narrow, winding streets. When the city was incorporated to Montenegro, the urban core shifted to the other bank of the Ribnica River, where the town developed in a more European style: wider streets with an
orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''.
By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in ...
layout. This part of the city is today traditionally regarded as the city center and is called ''Nova Varoš'' (''New town'').
During World War II, Podgorica was almost razed to the ground, being bombed over 80 times. After liberation, rebuilding began as in other cities of the communist-ruled SFRY. Mass residential blocks were erected, with basic design typical of Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
countries. All that part of the city on the right bank of the Morača River was built this way.
The main contemporary traffic arteries were laid out during this period, which extended the orthogonal street layout of the city center, to the south and west. Residential and infrastructural developments in the SFRY era have mostly shaped the layout of today's Podgorica and accommodated the unprecedented population growth that followed World War II.
Blažo Jovanović Bridge
Blažo Jovanović bridge ( cnr, Мост Блажа Јовановића, Most Blaža Jovanovića) is a bridge across the Morača river in Podgorica, Montenegro. The bridge is located near the confluence of the Ribnica and Morača rivers and is p ...
over the Morača.
File:Podgorica EKIP and Prva TV IMG 1286 82 Bulevar Džordža Vašingtona.JPG, Office building at George Washington Street
File:Blok 5 i 6.jpg, Highrise housing in Podgorica.
File:Delta City - panoramio.jpg, alt=Delta Shopping Mall., BIG Podgorica
File:Bulevar Svetog Petra Cetinjskog, 2019.jpg, St Peter of Cetinje Boulevard
File:AerodromPodgorica.jpg, Podgorica Airport
File:Morača Sports Center.jpg, Morača Sports Center
Morača Sports Centre ( Montenegrin: ''Sportski centar Morača'', Спортски центар Морача) is a multi-sports venue that is located in Podgorica, Montenegro.
The venue is located in the new part of Podgorica, on the right bank of ...
Notable people
Below are some of the most notable people who were either born or spent most of their lives in Podgorica: *Božidar Vuković
Božidar Vuković ( sr-Cyrl, Божидар Вуковић, it, Dionisio della Vecchia, lat, Dionisius a Vetula; c. 1460 — c. 1539) was one of the first printers and editors of Serbian books in Montenegro. He founded the famous Vuković print ...
, one of the first South Slavic printers
*Blažo Jovanović
Blažo Jovanović (Serbo-Croatian Cyrillic; Блажо Јовановић; ; 28 March 1907 – 4 February 1976) was a Montenegrin politician and revolutionary army commander in the Yugoslav Partisans. He served as the first President of the People ...
, communist politician
* Dejan Savićević, football player
* Predrag Mijatović, football player
*Stevan Jovetić
Stevan Jovetić ( cnr, Стеван Јоветић, ; born 2 November 1989) is a Montenegrin footballer who plays as a striker for Bundesliga club Hertha BSC and captains the Montenegro national team.
Jovetić's primary position is a second s ...
, football player
* Milos Raonic, Canadian tennis player
* Duško Vujošević, Montenegrin basketball coach
* Marko Miljanov, general, clan chief and writer
*Vojo Stanić
Vojo Stanić ( Montenegrin: Vojo Stanić/Војо Станић, born 3 February 1924) is a Montenegrin painter and sculptor.
Biography
Vojo Stanić was born in Podgorica, and grew up in Nikšić. He completed ''Academy of Sculpture'' in Belg ...
, sculptor and painter
* Risto Stijović, sculptor and painter
* Borislav Pekić, novelist
* Anđela Bulatović, handball player
*Zoran Filipović
Zoran Filipović ( sr-Cyrl, Зоран Филиповић, ; born 6 February 1953) is a Montenegrin former football coach and player, best known for his playing stints with Red Star Belgrade and S.L. Benfica.
Club career
Filipović, born 6 Febr ...
football player and coach
* Duško Radinović, football player
* Simon Vukčević, football player
*Refik Šabanadžović
Refik Šabanadžović (born 2 August 1965) is a Bosnian former professional footballer who played as a midfielder and defender.
Born in Montenegro, at the time part of SFR Yugoslavia, Šabanadžović played internationally for Yugoslavia and u ...
football player
*Dejan Zlatičanin
Dejan Zlatičanin (born 23 April 1984) is a Montenegrin professional boxer. He is the first Montenegrin to win a boxing world title, having held the WBC lightweight title from 2016 to 2017.
Professional career
Zlatičanin made his professional ...
, boxer
* Dejan Radonjić, basketball player and coach
* Nikola Bulatović, basketball player
*Ljiljana Mugoša
Ljiljana Vučević, née Mugoša (born April 10, 1962 in Podgorica, Montenegro), is a former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav Team handball, handball player who competed in the 1984 Summer Olympics and in the 1988 Summer Ol ...
, handball player
*Svetlana Mugoša-Antić
Svetlana Antić, née Mugoša (born November 13, 1964 in Podgorica, Montenegro), is a former Yugoslav handball player who competed in the 1984 Summer Olympics and in the 1988 Summer Olympics.
In 1984, she was a member of the Yugoslav hand ...
, handball player
*Nikola Mirotić
Nikola Mirotić ( sr-cyrl, Никола Миротић; born 11 February 1991) is a Montenegrin-Spanish professional basketball player for FC Barcelona of the Liga ACB and the EuroLeague. The power forward is a four-time All-EuroLeague Team memb ...
, Spanish basketball player
*Ivan Strugar
Ivan Strugar (born December 18, 1974) is a Montenegrin kickboxer. He is a winner of numerous trophies and accolades both in amateur and professional competition, and is one of the most popular sportsmen in Montenegro. He currently fights in W ...
, kick-boxer
* Jovanka Radičević, handball player
* Slavko Kalezić, singer and actor
* Nenad Knežević "Knez", pop singer
* Sergej Ćetković, pop singer
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Podgorica istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Ankara, Turkey
* Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy a ...
, Italy
* Naousa, Greece
* Skopje, North Macedonia
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Partner cities
* Yerevan, ArmeniaSee also
*Outline of Montenegro
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Montenegro:
Montenegro – sovereign country located on the Balkan Peninsula in Southern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south and borders Croatia ...
* Podgorica Capital City
Notes
* * *References
External links
* * *Tourism Organisation of Podgorica
More (mostly modern) buildings of Podgorica
{{Authority control Capitals in Europe Populated places in Podgorica Municipality