Throne In Mata-Utu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a
 In
In
 In the
In the
 In European feudal countries, monarchs often were seated on thrones, based in all likelihood on the Roman magisterial chair. These thrones were originally quite simple, especially when compared to their Asian counterparts. One of the grandest and most important was the Throne of Ivan "the Terrible". Dating from the mid-16th century, it is shaped as a high-backed chair with arm rests, and adorned with ivory and walrus bone plaques intricately carved with mythological, heraldic and life scenes. The plaques carved with scenes from the biblical account of
In European feudal countries, monarchs often were seated on thrones, based in all likelihood on the Roman magisterial chair. These thrones were originally quite simple, especially when compared to their Asian counterparts. One of the grandest and most important was the Throne of Ivan "the Terrible". Dating from the mid-16th century, it is shaped as a high-backed chair with arm rests, and adorned with ivory and walrus bone plaques intricately carved with mythological, heraldic and life scenes. The plaques carved with scenes from the biblical account of
 In the
In the
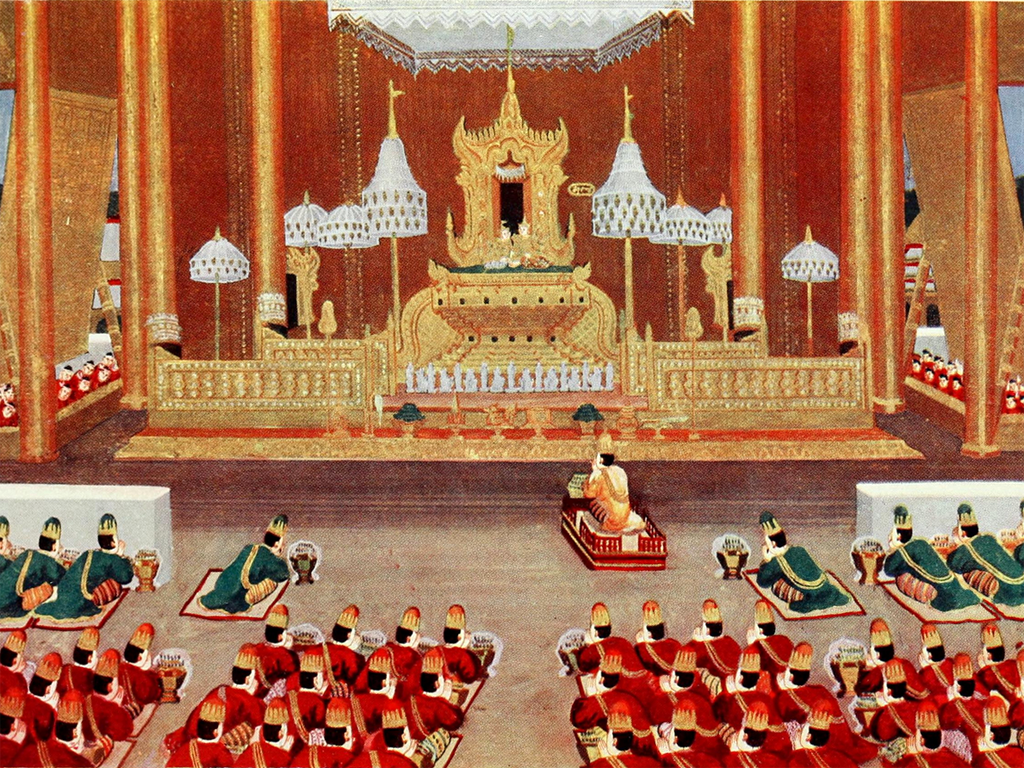 In Burma, the traditional name for a throne is ''
In Burma, the traditional name for a throne is ''
 The Dragon Throne is the term used to identify the throne of the
The Dragon Throne is the term used to identify the throne of the
 During the
During the
By Wilhelm Bendz (1830) * Silver Throne in Stockholm Palace, Sweden, on which Swedish monarchs were crowned * Queen Lovisa Ulrikas throne at Stockholm palace, Sweden
from the 5th century citadel of Sigiri * Stone throne of King Nissankamalla from Sri Lanka]
from the 12th century Polonnaruwa kingdom * Kandian Throne of the Kingdom of Kandy and the Dominion of Ceylon * Peacock Throne of the Mughal Empire, Mughal
File:Golden stool 31 January 1935.jpg, The Assante Golden Stool on its throne, the ''hwedom dwa'' (1935)
File:Musée national d'Ethiopie-Trône de Hailé Sélassié.jpg, Throne of emperor Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia
File:Throne Room - Bardo Palace - Tunis - Tunisia - 1899.jpg, Throne of the bey of Tunis, Bardo Palace
File:Gran Palacio, Bangkok, Tailandia, 2013-08-22, DD 57 (Cropped).jpg, Throne of Thailand in the Grand Palace
File:Royal Throne of Tonga, 1900.jpg, Throne of Tonga
File:Lion throne, Mandalay Palace.jpg, Lion throne, Mandalay Palace
File:Lily Throne, Mandalay Palace.jpg, Lily Throne, Mandalay Palace
File:Saya Chone's "Royal Audience".png, Painting of a royal audience in Burma
File:Singgasana Sultan dan Permaisuri Tidore.jpg, Lion Throne of the Sultan of Tidore
File:Forbiddencitythroneroom01.jpg, Throne of Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing emperors,
File:Celebración de la Pascua Militar 2019 06.jpg, King Felipe VI giving a speech in front of the thrones of the king and queen of Spain, Madrid
File:Prinsjesdag 1979, Juliana en Bernhard in de Ridderzaal, voorlezen troonrede.jpg, Queen Juliana of the Netherlands giving a speech from the throne in the Ridderzaal
File:Serment de Philippe de Belgique.jpg, King Philippe I of Belgium seated on the throne inside the senate during his swearing-in ceremony
File:Coronation Chair Denmark (King).jpg, The Danish throne made out of ivory narwhal tusks
File:San Marino tron kapitanow regentow.jpg, Throne of the Captains-Regent of San Marino, inside the basilica di San Marino
File:Paris Musée Cluny Trône de Dagobert 135.jpg, French Throne of Dagobert, dating to the 7th century
File:SanktEdvardsstol westminster.jpg, King Edward's Chair, Westminster Abbey, England
File:Vojvodski stol.jpg, Duke's Chair of Carantania
File:Throne of Franz Joseph I of Austria 01.jpg, Throne of Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria
File:Thronsaal, Residenz München.jpg, Throne of the Bavarian King, Munich
File:Dublin Castle Throne Room 2018.jpg, Irish Viceregal Throne, Dublin Castle
File:Palácio Nacional da Ajuda, throne room-1.JPG, Thrones of Portugal, Ajuda Palace
File:Zamek Królewski w Warszawie - 05.jpg, Throne of King Stanisław August Poniatowski, Royal Castle, Warsaw
File:Vilnius Valdovu rumai Innen Thron 1.jpg, Throne Room, Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania
File:Vladislav Saal - Thron.jpg, Throne of Bohemia, Prague Castle
File:Kis Tronterem.jpg, Throne Room, Buda Castle
File:Gau Peter the Great (Small Throne) Room 1863.jpg, Imperial throne of Peter I The Great
File:SanGiovanniChiostro2.JPG, Throne of the pope, Basilica di San Giovanni in Laterano, Rome
File:Roma-san giovanni03.jpg, Throne of the pope, Basilica di San Giovanni in Laterano, Rome
File:Honorius3.JPG, Throne of Pope Honorius III
File:Pintoricchio 015.jpg, Throne of Pope Pius II (Enea Silvio Piccolomini)
File:Canterburycathedralthrone.jpg, The Chair of St Augustine in Canterbury Cathedral, England
File:D. Pedro II e o Trono do senado imperial (5317371367).jpg, Throne of the List of monarchs of Brazil, Emperor of Brazil inside the Senate
 A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
or bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy) ...
or the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
itself, an instance of metonymy
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
, and is also used in many expressions such as " the power behind the throne".
Since the early advanced cultures, a throne has been known as a symbol of divine and secular rule and the establishment of a throne as a defining sign of the claim to power and authority. It can be with a high backrest and feature heraldic animals or other decorations as adornment and as a sign of power and strength. A throne can be placed underneath a canopy or baldachin. The throne can stand on steps or a dais
A dais or daïs ( or , American English also but sometimes considered nonstandard)dais
in the Random House Dictionary< ...
and is thus always elevated. The expression "ascend (mount) the throne" takes its meaning from the steps leading up to the dais or platform, on which the throne is placed, being formerly comprised in the word's significance. in the Random House Dictionary< ...
Coats of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its wh ...
or insignia can feature on throne or canopy and represent the dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
. Even in the physical absence of the ruler an empty throne can symbolise the everlasting presence of the monarchical authority.
When used in a political or governmental sense, a throne typically exists in a civilization, nation, tribe, or other politically designated group that is organized or governed under a monarchical system. Throughout much of human history societies have been governed under monarchical systems, in the beginning as autocratic systems and later evolved in most cases as constitutional monarchies
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
within liberal democratic systems, resulting in a wide variety of thrones that have been used by given heads of state. These have ranged from stools in places such as in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to ornate chairs and bench-like designs in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, respectively. Often, but not always, a throne is tied to a philosophical or religious ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
held by the nation or people in question, which serves a dual role in unifying the people under the reigning monarch and connecting the monarch upon the throne to his or her predecessors, who sat upon the throne previously. Accordingly, many thrones are typically held to have been constructed or fabricated out of rare or hard to find materials that may be valuable or important to the land in question. Depending on the size of the throne in question it may be large and ornately designed as an emplaced instrument of a nation's power, or it may be a symbolic chair with little or no precious materials incorporated into the design.
When used in a religious sense, throne can refer to one of two distinct uses. The first use derives from the practice in churches of having a bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
or higher-ranking religious official (archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
, pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
, etc.) sit on a special chair which in church referred to by written sources as a "throne", or “cathedra” (Latin for 'chair') and is intended to allow such high-ranking religious officials a place to sit in their place of worship. The other use for throne refers to a belief among many of the world's monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
and polytheistic religions that the deity or deities that they worship are seated on a throne. Such beliefs go back to ancient times, and can be seen in surviving artwork and texts which discuss the idea of ancient gods (such as the Twelve Olympians
upright=1.8, Fragment of a relief (1st century BC1st century AD) depicting the twelve Olympians carrying their attributes in procession; from left to right: Hestia (scepter), Hermes (winged cap and staff), Aphrodite (veiled), Ares (helmet and s ...
) seated on thrones. In the major Abrahamic religions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, the Throne of God
The Throne of God is the reigning centre of God in the Abrahamic religions: primarily Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The throne is said by various holy books to reside beyond the Seventh Heaven which is called ''Araboth'' ( ''‘ărāḇōṯ' ...
is attested to in religious scriptures and teachings, although the origin, nature, and idea of the Throne of God in these religions differs according to the given religious ideology practiced.
In the west, a throne is most identified as the seat upon which a person holding the title ''King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
'', ''Queen
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother ...
'', ''Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
'', or ''Empress
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
'' sits in a nation using a monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy) ...
political system, although there are a few exceptions, notably with regards to religious officials such as the pope and bishops of various sects of the Christian faith. Changing geo-political tides have resulted in the collapse of several dictatorial and autocratic governments, which in turn have left a number of throne chairs empty. Many of these thrones—such as China's Dragon Throne—survive today as historic examples of nation's previous government.
Antiquity
Thrones were found throughout the canon ofancient furniture
Ancient furniture was made of many different materials, including reeds, wood, stone, metals, straws, and ivory. It could also be decorated in many different ways. Sometimes furniture would be covered with upholstery, upholstery being padding, s ...
. The depiction of monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
s and deities as seated on chairs is a common topos in the iconography of the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
.
The word ''throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monar ...
'' itself is from Greek θρόνος (''thronos''), "seat, chair", in origin a derivation from the PIE
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), swe ...
root ' "to support" (also in ''dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for '' ...
'' "post, sacrificial pole"). Early Greek Διὸς θρόνους (''Dios thronous'') was a term for the "support of the heavens", i.e. the axis mundi
In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles.
In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere.
Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the '' ...
, which term when Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
became an anthropomorphic god was imagined as the "seat of Zeus". In Ancient Greek, a "thronos" was a specific but ordinary type of chair with a footstool
A footstool (foot stool, footrest, foot rest) is a piece of furniture or a support used to elevate the foot. There are two main types of footstool, which can be loosely categorized into those designed for comfort and those designed for functi ...
, a high status object but not necessarily with any connotations of power. The Achaeans (according to Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
) were known to place additional, empty thrones in the royal palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
s and temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
s so that the gods could be seated when they wished to be. The most famous of these thrones was the throne of Apollo in Amyclae
Amyclae or Amyklai ( grc, Ἀμύκλαι) was a city of ancient Laconia, situated on the right or western bank of the Eurotas, 20 stadia south of Sparta, in a district remarkable for the abundance of its trees and its fertility. Amyclae was one o ...
.
The Romans also had two types of thrones—one for the emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
and one for the goddess Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Roma, Queensland, a town
** Roma Airport
** Roma Courthouse
** Electoral district of Roma, defunct
** Town of Roma, defunct town, now part of the Maranoa Regional Council
*Roma Street, Brisbane, a ...
whose statues were seated upon thrones, which became centers of worship.
Persia
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the traditional name of the throne is the ''Takht-e Padeshah''. From the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
era to the last Iranian dynasty Pahlavi
Pahlavi may refer to:
Iranian royalty
*Seven Parthian clans, ruling Parthian families during the Sasanian Empire
*Pahlavi dynasty, the ruling house of Imperial State of Persia/Iran from 1925 until 1979
**Reza Shah, Reza Shah Pahlavi (1878–1944 ...
, the throne was used for sitting shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
s.
Hebrew Bible
The word "throne" inEnglish translations of the Bible
Partial Bible translations into languages of the English people can be traced back to the late 7th century, including translations into Old and Middle English. More than 100 complete translations into English have been written.
In the United S ...
renders Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
'. The pharaoh of the Exodus is described as sitting on a throne (Exodus 11:5, 12:29), but mostly the term refers to the throne of the kingdom of Israel, often called the "throne of David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
" or "throne of Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
". The literal throne of Solomon is described in : "Moreover the king made a great throne of ivory, and overlaid it with the best gold.. The throne had six steps, and the top of the throne was round behind: and there were stays on either side on the place of the seat, and two lions stood beside the stays. And twelve lions stood there on the one side and on the other upon the six steps: there was not the like made in any kingdom." In the Book of Esther
The Book of Esther ( he, מְגִלַּת אֶסְתֵּר, Megillat Esther), also known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as "the Scroll" ("the wikt:מגילה, Megillah"), is a book in the third section (, "Writings") of the Judaism, Jewish ''Tanak ...
(5:3), the same word refers to the throne of the king of Persia.
The God of Israel
God of Israel may refer to:
* God in Judaism, God as understood in Jewish theological discussion
* Yahweh, the national god of the ancient kingdoms of Israel and Judah
* Tetragrammaton, the four Hebrew letters YHWH as the name of God, and various ...
himself is frequently described as sitting on a throne, referred to outside of the Bible as the Throne of God
The Throne of God is the reigning centre of God in the Abrahamic religions: primarily Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The throne is said by various holy books to reside beyond the Seventh Heaven which is called ''Araboth'' ( ''‘ărāḇōṯ' ...
, in the Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
, and in a vision Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
Within the text of the Book of Isaiah, Isaiah himself is referred to as "the ...
(6:1), and notably in Isaiah 66:1, YHWH
The Tetragrammaton (; ), or Tetragram, is the four-letter Hebrew theonym (transliterated as YHWH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four letters, written and read from right to left (in Hebrew), are ''yodh'', '' he'', ''waw'', and '' ...
says of himself "The heaven is my throne, and the earth is my footstool" (this verse is alluded to by Matthew
Matthew may refer to:
* Matthew (given name)
* Matthew (surname)
* ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497
* ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith
* Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Ch ...
5:34-35).
Christian
Biblical
In theNew Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
, the angel Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብር� ...
also refers to this throne in the Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volu ...
(): "He will be great, and will be called the Son of the Highest; and the Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or ar ...
God will give Him the throne of His father David. And He will reign over the house of Jacob forever, and of His kingdom there will be no end."
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
promised his apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
that they would sit upon "twelve thrones", judging the twelve tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( he, שִׁבְטֵי־יִשְׂרָאֵל, translit=Šīḇṭēy Yīsrāʾēl, lit=Tribes of Israel) are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, throu ...
(). John's Revelation states: "And I saw a great white throne, and him that sat on it, from whose face the earth and the heaven fled away" ().
The Apostle Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
speaks of "thrones A throne is a seat of state for a potentate or dignitary.
Throne or Thrones may also mean: People
* Throne (surname)
Arts and entertainment
*The Throne (group), collaboration pseudonym for rappers Jay Z and Kanye West (as on Drake's "Pop Style")
* ...
" in . Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite
Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite (or Dionysius the Pseudo-Areopagite) was a Greek author, Christian theologian and Neoplatonic philosopher of the late 5th to early 6th century, who wrote a set of works known as the ''Corpus Areopagiticum'' or ...
, in his work ''De Coelesti Hierarchia
''De Coelesti Hierarchia'' ( grc-gre, Περὶ τῆς Οὐρανίας Ἱεραρχίας, "On the Celestial Hierarchy") is a Pseudo-Dionysian work on angelology, written in Greek and dated to ca. AD the 5th century; it exerted great influen ...
'' (VI.7), interprets this as referring to one of the ranks of angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles include ...
s (corresponding to the Hebrew ''Arelim'' or '' Ophanim''). This concept was expanded upon by Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
in his '' Summa Theologica'' (I.108), wherein the thrones are concerned with carrying out divine justice.
In Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
times the "Throne of Solomon" was associated with the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother o ...
, who was depicted as the throne upon which Jesus sat. The ivory in the biblical description of the Throne of Solomon was interpreted as representing purity, the gold representing divinity, and the six steps of the throne stood for the six virtues
Virtue ( la, virtus) is moral excellence. A virtue is a trait or quality that is deemed to be morally good and thus is valued as a foundation of principle and good moral being. In other words, it is a behavior that shows high moral standard ...
. was also interpreted as referring to the Virgin Mary, with the entire Psalm describing a royal throne room.
Ecclesiastical
From ancient times,bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
s of the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
, Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
and other churches where episcopal offices exist, have been formally seated on a throne, called a ''cathedra
A ''cathedra'' is the raised throne of a bishop in the early Christian basilica. When used with this meaning, it may also be called the bishop's throne. With time, the related term ''cathedral'' became synonymous with the "seat", or principa ...
'' ( el, κάθεδρα, seat). Traditionally located in the sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a saf ...
, the cathedra symbolizes the bishop's authority to teach the faith (hence the expression " ex cathedra") and to govern his flock.
''Ex cathedra'' refers to the explicative authority, notably the extremely rarely used procedure required for a papal declaration to be 'infallible
Infallibility refers to an inability to be wrong. It can be applied within a specific domain, or it can be used as a more general adjective. The term has significance in both epistemology and theology, and its meaning and significance in both fi ...
' under Roman Catholic canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is th ...
. In several languages the word deriving from ''cathedra'' is commonly used for an academic teaching mandate, the professorial chair.
From the presence of this cathedra (throne), which can be as elaborate and precious as fits a secular prince (even if the prelate is not a prince of the church
The term Prince of the Church is today used nearly exclusively for Catholic cardinals. However, the term is historically more important as a generic term for clergymen whose offices hold the secular rank and privilege of a prince (in the widest s ...
in the secular sense), a bishop's primary church is called a ''cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
''. In the Roman Catholic Church, a basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
—from the Greek ''basilikos'' 'royal'—now refers to the presence there of a papal canopy (''ombrellino
The umbraculum ( it, ombrellone, "big umbrella", in basilicas also conopaeum) is a historic piece of the papal regalia and insignia, once used on a daily basis to provide shade for the pope (Galbreath, 27). Also known as the pavilion, in modern ...
''), part of his regalia, and applies mainly to many cathedrals and Catholic churches of similar importance or splendor. In Roman Antiquity
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
a basilica was secular public hall. Thus, the term basilica may also refer to a church designed after the manner of the ancient Roman basilica. Many of the churches built by the emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
and Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
are of the basilica style.
Some other prelates
A prelate () is a high-ranking member of the Christian clergy who is an ordinary or who ranks in precedence with ordinaries. The word derives from the Latin , the past participle of , which means 'carry before', 'be set above or over' or 'pref ...
besides bishops are permitted the use of thrones, such as abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
s and abbess
An abbess (Latin: ''abbatissa''), also known as a mother superior, is the female superior of a community of Catholic nuns in an abbey.
Description
In the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and Eastern Catholic), Eastern Orthodox, Coptic ...
es. These are often simpler than the thrones used by bishops and there may be restrictions on the style and ornamentation used on them, according to the regulations and traditions of the particular denomination.
As a mark of distinction, Roman Catholic bishops and higher prelates have a right to a canopy above their thrones at certain ecclesiastical functions. It is sometimes granted by special privilege to prelates inferior to bishops, but always with limitations as to the days on which it may be used and the character of its ornamentation. The liturgical color of the canopy should correspond with that of the other vestments. When ruling monarchs attend services, they are also allowed to be seated on a throne that is covered by a canopy, but their seats must be outside the sanctuary.
In the Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
, the bishop's throne will often combine features of the monastic choir stall (''kathisma
A kathisma (Greek: κάθισμα; Slavonic: каѳисма, ''kai-isma''), literally, "seat", is a division of the Psalter, used in the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Rite Catholic churches. The word may also describe a hymn sung at Matins, a sea ...
'') with appurtenances inherited from the Byzantine court, such as a pair of lions seated at the foot of the throne.
The term "throne" is often used in reference to patriarchs to designate their ecclesiastical authority; for instance, "the Ecumenical Throne" refers to the authority of the ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of th ...
.
Western bishops may also use a faldstool to fulfill the liturgical purpose of the cathedra when not in their own cathedral.
Papal
 In the
In the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, the pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
is an elected monarch
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected monarch, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, and the ...
, both under canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is th ...
as supreme head of the church, and under international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
as the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
—styled "sovereign pontiff"—of the Vatican City State
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
(the sovereign state within the city of Rome established by the 1929 Lateran Treaty
The Lateran Treaty ( it, Patti Lateranensi; la, Pacta Lateranensia) was one component of the Lateran Pacts of 1929, agreements between the Kingdom of Italy under King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy and the Holy See under Pope Pius XI to settle ...
). Until 1870, the pope was the elected monarch of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
, which for centuries constituted one of the largest political powers on the divided Italian peninsula. To this day, the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome ...
maintains officially recognised diplomatic status, and papal nuncio
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international or ...
s and legates
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer ...
are deputed on diplomatic mission
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
s throughout the world.
The pope's throne (''Cathedra Romana'') is located in the apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In ...
of the Archbasilica of St. John Lateran, his cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
as Bishop of Rome
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
.
In the apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In ...
of Saint Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican ( it, Basilica Papale di San Pietro in Vaticano), or simply Saint Peter's Basilica ( la, Basilica Sancti Petri), is a church built in the Renaissance style located in Vatican City, the papal e ...
, above the "Altar of the Chair" lies the ''Cathedra Petri'', a throne believed to have been used by St Peter himself and other earlier popes; this relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
is enclosed in a gilt bronze casting and forms part of a huge monument designed by Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
.
Unlike at his cathedral (Archbasilica of St. John Lateran), there is no permanent ''cathedra
A ''cathedra'' is the raised throne of a bishop in the early Christian basilica. When used with this meaning, it may also be called the bishop's throne. With time, the related term ''cathedral'' became synonymous with the "seat", or principa ...
'' for the pope in St Peter's Basilica, so a removable throne is placed in the basilica for the pope's use whenever he presides over a liturgical ceremony. Prior to the liturgical reforms that occurred in the wake of the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st Catholic ecumenical councils, ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions) ...
, a huge removable canopied throne was placed above an equally removable dais in the choir side of the "Altar of the Confession" (the high altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganis ...
above the tomb of St Peter and beneath the monumental bronze baldachin); this throne stood between the apse and the Altar of the Confession.
This practice has fallen out of use with the 1960s and 1970s reform of Papal liturgy and, whenever the pope celebrates Mass in St. Peter's Basilica, a simpler portable throne is now placed on platform in front of the Altar of the Confession. Whenever Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereign ...
celebrated the Liturgy of the Hours
The Liturgy of the Hours (Latin: ''Liturgia Horarum'') or Divine Office (Latin: ''Officium Divinum'') or ''Opus Dei'' ("Work of God") are a set of Catholic prayers comprising the canonical hours, often also referred to as the breviary, of the ...
at St Peter's, a more elaborate removable throne was placed on a dais to the side of the Altar of the Chair. When the pope celebrates Mass on the basilica steps facing St. Peter's Square, portable thrones are also used.
In the past, the pope was also carried on occasions in a portable throne, called the '' sedia gestatoria''. Originally, the ''sedia'' was used as part of the elaborate procession surrounding papal ceremonies that was believed to be the most direct heir of pharaonic
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ann ...
splendor, and included a pair of flabella
A flabellum (plural flabella), in Christian liturgical use, is a fan made of metal, leather, silk, parchment or feathers, intended to keep away insects from the consecrated Body and Blood of Christ and from the priest, as well as to show hon ...
(fans made from ostrich feathers) to either side. Pope John Paul I at first abandoned the use of these implements, but later in his brief reign began to use the ''sedia'' so that he could be seen more easily by the crowds. The use of the ''sedia'' was abandoned by Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
in favor of the so-called " popemobile" when outside. Near the end of his pontificate, Pope John Paul II had a specially constructed throne on wheels that could be used inside.
Prior to 1978, at the papal conclave
A papal conclave is a gathering of the College of Cardinals convened to elect a Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop of Rome, also known as the pope. Catholics consider the pope to be the Apostolic succession, apostolic successor of Saint ...
, each cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
was seated on a throne in the Sistine Chapel during the balloting. Each throne had a canopy over it. After a successful election, once the new pope accepted election and decided by what name he would be known, the cardinals would all lower their canopies, leaving only the canopy over the newly elected pope. This was the new pope's first throne. This tradition was dramatically portrayed in the 1968 film ''The Shoes of the Fisherman The Shoes of the Fisherman may refer to:
* ''The Shoes of the Fisherman'' (novel), a 1963 novel by the writer Morris West
* ''The Shoes of the Fisherman'' (film), a 1968 film based on the novel
{{disambiguation ...
''.
Medieval and early modern periods
 In European feudal countries, monarchs often were seated on thrones, based in all likelihood on the Roman magisterial chair. These thrones were originally quite simple, especially when compared to their Asian counterparts. One of the grandest and most important was the Throne of Ivan "the Terrible". Dating from the mid-16th century, it is shaped as a high-backed chair with arm rests, and adorned with ivory and walrus bone plaques intricately carved with mythological, heraldic and life scenes. The plaques carved with scenes from the biblical account of
In European feudal countries, monarchs often were seated on thrones, based in all likelihood on the Roman magisterial chair. These thrones were originally quite simple, especially when compared to their Asian counterparts. One of the grandest and most important was the Throne of Ivan "the Terrible". Dating from the mid-16th century, it is shaped as a high-backed chair with arm rests, and adorned with ivory and walrus bone plaques intricately carved with mythological, heraldic and life scenes. The plaques carved with scenes from the biblical account of King David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
’s life are of particular relevance, as David was seen as the ideal for Christian monarchs. In practice, any chair the monarch occupied in a formal setting served as a "throne", though there were often special chairs used only for this kept in places the monarch often went to. Thrones began to be made in pairs, for the king and queen, which remained common in later periods. Sometimes they are identical, or the queen's throne may be slightly less grand.
The throne of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
( Magnaura) included elaborate automaton
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton – Definition and More ...
s of singing birds. In the ' regency' (nominally an Ottoman province, de facto an independent realm) of the bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
of Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, the throne was called ''kursi''.
Although medieval examples tended to be retained in the early modern period, having acquired the aura of tradition, when new thrones were made they either continued medieval styles or were just very grand and elaborate versions of contemporary chairs or armchairs.
South Asia
 In the
In the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, the traditional Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
name for the throne was ''siṃhāsana'' (lit., seat of a lion). In the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
times the throne was called ''Shāhī takht'' (). The term ''gadi'' or ''gaddi'' (, also called ''rājgaddī'') referred to a seat with a cushion used as a throne by Indian princes. That term was usually used for the throne of a Hindu princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
's ruler, while among Muslim princes or Nawabs, save exceptions such as the Travancore State
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
royal family, the term ''musnad'' (), also spelt as ''musnud'', was more common, even though both seats were similar.
The Throne of Jahangir was built by Mughal emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
in 1602 and is located at the ''Diwan-i-Khas
Diwan or Divan is a term of Persian origin referring to various types of reception halls. The term occurs in various examples of Islamic architecture, where it can also refer to a government council chamber (related to the ''divan''), as well as in ...
'' (hall of private audience) at the Agra Fort.
The Peacock Throne was the seat of the Mughal emperors
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
of India. It was commissioned in the early 17th century by Emperor Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
and was located in the Red Fort
The Red Fort or Lal Qila () is a historic fort in Old Delhi, Delhi in India that served as the main residence of the Mughal Emperors. Emperor Shah Jahan commissioned construction of the Red Fort on 12 May 1638, when he decided to shift hi ...
of Delhi. The original throne was subsequently captured and taken as a war trophy in 1739 by the Persian king Nadir Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian h ...
and has been lost ever since. A replacement throne based on the original was commissioned afterwards and existed until the Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the fo ...
.
Maharaja Ranjit Singh's throne
Maharaja Ranjit Singh's throne was made by the goldsmith Hafez Muhammad Multani about 1820 to 1830, for the eponymous ruler of the Sikh empire. It is made of a wood and resin core, covered with sheets of repoussé, chased and engraved gold.
was made by the goldsmith Hafez Muhammad Multani about 1820 to 1830. Made of wood and resin core, covered with sheets of repoussé, chased and engraved gold.
The Golden Throne or Chinnada Simhasana or Ratna Simahasana in Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
is the royal seat of the rulers of the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
. The Golden Throne is kept at Mysore Palace.
Southeast Asia
 In Burma, the traditional name for a throne is ''
In Burma, the traditional name for a throne is ''palin
The surname Palin is a name of British origin, either English or Welsh. Possible derivations include an anglicization of the Welsh patronymic ''ap Heilyn'' ("son of Heilyn") or a reference to the English placenames Poling, West Sussex or Sea Pallin ...
,'' from the Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or ''Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravāda'' Buddhism ...
term ''pallaṅka'', which means "couch" or "sofa." The Burmese ''palin'' in pre-colonial times was used to seat the sovereign and his main consort, and is today used to seat religious leaders such as sayadaw
A sayadaw ( my, ဆရာတော်, ; , and alternatively spelled ''hsayadaw'', ''sayado'', ''sayāḍo'' or ''sayāḍaw'') is a Burmese Buddhist title used to reference the senior monk or abbot of a monastery. Some distinguished sayadaws wo ...
s, and images of the Buddha. Royal thrones are called ''yazapalin'' (ရာဇပလ္လင်), while thrones seating images or statues of the Buddha are called ''gaw pallin'' (ဂေါ့ပလ္လင်) or ''samakhan'' (စမ္မခဏ်), from the Pali term ''sammakhaṇḍa''.
East Asia
 The Dragon Throne is the term used to identify the throne of the
The Dragon Throne is the term used to identify the throne of the emperor of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heave ...
. As the dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
was the emblem of divine imperial power, the throne of the emperor, who was considered a living god, was known as the Dragon Throne. The term can refer to very specific seating, as in the special seating in various structures in the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a Chinese palace, palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples includ ...
of Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
or in the palaces of the Old Summer Palace
The Old Summer Palace, also known as Yuanmingyuan () or Yuanmingyuan Park, originally called the Imperial Gardens (), and sometimes called the Winter Palace, was a complex of palaces and gardens in present-day Haidian District, Beijing, China. I ...
. In an abstract sense, the "Dragon Throne" also refers rhetorically
Rhetoric () is the Art (skill), art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the Trivium, three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuad ...
to the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and to the monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy) ...
itself. The Daoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor (; 16 September 1782 – 26 February 1850), also known by his temple name Emperor Xuanxong of Qing, born Mianning, was the seventh Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning ...
is said to have referred to his throne as "the divine utensil."
The throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monar ...
of the emperors
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
are often referred to as ''ngai vàng'' ("golden throne") or ''ngôi báu'' (大寳/寶座) literally "great precious" (seat/position). The throne is always adorned with the pattern and motif of the Vietnamese dragon, which is the exclusive and privileged symbol of the Vietnamese emperors. The last existing imperial throne in Vietnam is the throne of the Nguyễn emperors placed in the Hall of Supreme Harmony at the Imperial City of Huế
The Imperial City ( vi, Hoàng thành; Chữ Hán: 皇城) is a walled enclosure within the citadel (''Kinh thành''; Chữ Hán: 京城) of the city of Huế, the former imperial capital of Vietnam during the Nguyễn dynasty. It contains the pa ...
. It is designated as a national treasure of Vietnam. In Vietnamese folk religion, the gods, deities and ancestral spirits are believed to seat figuratively on thrones at places of worship. Therefore, on Vietnamese altars, there are various types of liturgical "throne" often decorated with red paint and golden gilding.
The Phoenix Throne
The Phoenix Throne (''eojwa'') is the term used to identify the throne of the hereditary monarchs of Korea. In an abstract sense, the Phoenix Throne also refers rhetorically to the head of state of the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897) and the Empir ...
(御座/어좌 ''eojwa'') is the term used to identify the throne of the king of Korea
This is a list of monarchs of Korea, arranged by dynasty. Names are romanized according to the South Korean Revised Romanization of Korean. McCune–Reischauer romanizations may be found at the articles about the individual monarchs.
Gojoseon
G ...
. In an abstract sense, the Phoenix Throne also refers rhetorically
Rhetoric () is the Art (skill), art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the Trivium, three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuad ...
to the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
of the Joseon dynasty
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and re ...
(1392–1897) and the Empire of Korea (1897–1910). The throne is located at Gyeongbok Palace in Seoul.
The is the term used to identify the throne of the emperor of Japan
The Emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his positio ...
. The term also can refer to very specific seating, such as the ''takamikura'' (高御座) throne in the Shishin-den at Kyoto Imperial Palace.
The throne of the Ryukyu Kingdom is located in Shuri Castle, Naha.
Modern period
 During the
During the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the throne in St. George's Hall (the "Greater Throne Room") in the Winter Palace
The Winter Palace ( rus, Зимний дворец, Zimnij dvorets, p=ˈzʲimnʲɪj dvɐˈrʲɛts) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the Emperor of all the Russias, Russian Emperor from 1732 to 1917. The p ...
was regarded as ''the'' throne of Russia. It sits atop a seven-stepped dais
A dais or daïs ( or , American English also but sometimes considered nonstandard)dais
in the Random House Dictionary< ...
with a in the Random House Dictionary< ...
proscenium arch
A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor ...
above and the symbol of the imperial family behind (the two-headed eagle
In heraldry and vexillology, the double-headed eagle (or double-eagle) is a charge associated with the concept of Empire. Most modern uses of the symbol are directly or indirectly associated with its use by the late Byzantine Empire, original ...
). Peter I's Room (the "Smaller Throne Room") is modest in comparison to the former. The throne was made for Empress
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Anna Ivanovna in London. There is also a throne in the Grand Throne Room of the Peterhof Palace.
In some countries with a monarchy, thrones are still used and have important symbolic and ceremonial meaning. Among the most famous thrones still in usage are St Edward's Chair
The Coronation Chair, known historically as St Edward's Chair or King Edward's Chair, is an ancient wooden chair on which British monarchs sit when they are invested with regalia and crowned at their coronations. It was commissioned in 1296 by ...
, on which the British monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiwi ...
is crowned, and the thrones used by monarchs during the state opening of parliaments in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Canada, Australia, and Japan (see above) among others.
Some republics use distinctive throne-like chairs in some state ceremonial. The president of Ireland sits on a former Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, viceregal throne during his or her inauguration ceremony, while Lord mayor, lords mayor and Lord provost, lords provost of many United Kingdom, British and Ireland, Irish cities often preside over local councils from throne-like chairs.
Owing to its symbolic nature, a toilet is often jokingly referred to as "a throne".
List
* The Throne of SolomonEurope
* Throne of Apollo inAmyclae
Amyclae or Amyklai ( grc, Ἀμύκλαι) was a city of ancient Laconia, situated on the right or western bank of the Eurotas, 20 stadia south of Sparta, in a district remarkable for the abundance of its trees and its fertility. Amyclae was one o ...
* St. Edward's Chair in Westminster Abbey, London, where British monarchs are crowned. It at one time contained the Stone of Scone (also called the Stone of Destiny) upon which the Kings of Scotland were crowned
* Chairing of the Bard in Wales is an ancient ceremonial procedure which dates back to at least 1176, in which the winning poet is chaired Prifardd, Y Prifardd (The Chief Bard) at the Eisteddfod, National Eisteddfod
* Chair of St Augustine in Canterbury Cathedral, where Archbishop of Canterbury, Archbishops of Canterbury are inaugurated
* Aachen Throne, Throne of Charlemagne in the Aachen Cathedral, cathedral at Aachen, Germany
* Imperial Throne of Goslar, Imperial Throne of the medieval German kings and emperors in Goslar, Germany.
* Throne of the King of Aragon, Valencia, Majorca, Sardinia, Corsica and Sicilia and Count of Barcelona Martin of Aragon, Martin I the Elder
* Ivory Throne of Ivan the Terrible
* papal Chair of Saint Peter and '' sedia gestatoria''
* Throne Chair of Denmark, made of narwhal tusks.By Wilhelm Bendz (1830) * Silver Throne in Stockholm Palace, Sweden, on which Swedish monarchs were crowned * Queen Lovisa Ulrikas throne at Stockholm palace, Sweden
Africa
* Golden Throne of pharaoh Tutankhamun * Golden Stool of the Ashanti Empire * Throne of David of theEmperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
s of Ethiopia
* Nigerian chieftaincy, Chieftaincy Stools of List of Nigerian traditional states, Nigeria
Asia
* Dragon Throne of the Table of Chinese monarchs, Emperors of China * Imperial Throne of Vietnam, Golden Throne of the List of monarchs of Vietnam, Emperors ofVietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
* Chrysanthemum Throne of the List of Emperors of Japan, Emperors of Japan (:ja:高御座)
* Phoenix Throne
The Phoenix Throne (''eojwa'') is the term used to identify the throne of the hereditary monarchs of Korea. In an abstract sense, the Phoenix Throne also refers rhetorically to the head of state of the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897) and the Empir ...
of the List of monarchs of Korea, Kings of Korea
* Lion Throne of the Dalai Lama of Tibet
* Lion Throne of Sikkim
* The Lion Throne of Myanmar, Lion Throne of konbaung of Burma,(Myanmar)
* Lotus Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Bumblebee Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Hamsa (bird), Hamsa Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Deer Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Elephant Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Conch Throne of Konbaung of Burma
* Stone throne of King Kasyapa from Sri Lanka]from the 5th century citadel of Sigiri * Stone throne of King Nissankamalla from Sri Lanka]
from the 12th century Polonnaruwa kingdom * Kandian Throne of the Kingdom of Kandy and the Dominion of Ceylon * Peacock Throne of the Mughal Empire, Mughal
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
s of India
* Sun Throne of Persia/Iran
* Marble Throne and Sun Throne of the Persian Empire, Persian Shahs
* Peacock Throne of Korea
* Peacock Throne at Montchobo, then at Inwa, Ava, ancient capitals of Burma
* Saridhaleys "ivory throne" and the sighsana "lion throne" of the Maldives sultanate
* Sandalwood throne at Bikaner Fort
* Maharaja Ranjit Singh's throne
Maharaja Ranjit Singh's throne was made by the goldsmith Hafez Muhammad Multani about 1820 to 1830, for the eponymous ruler of the Sikh empire. It is made of a wood and resin core, covered with sheets of repoussé, chased and engraved gold.
* Tupou Throne of the Kingdom of Tonga (Polynesian island country)
* Golden Throne (Mysore), Golden Throne in Mysore India
In popular culture
A Song of Ice and Fire / Game of Thrones
* Iron Throne (A Song of Ice and Fire), The Iron Throne * The Salt ThroneFantasy
* Ember Throne of Vulcanius * Wave Throne of Great Waterton * Airean Throne of Skyreland Warhammer 40,000 *Warhammer 40,000#The Imperium of Man, The Golden Throne *Skull Throne of Khorne (shared with Warhammer Fantasy (setting), Warhammer Fantasy and Warhammer Age of Sigmar)Gallery
Africa
Asia-Pacific
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a Chinese palace, palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples includ ...
of China
File:The Throne of Kandyan Kings.jpg, Throne of Kandyan Sinhalese people, Sinhalese Monarchs.
File:Chowmahalla Palace (22737529483).jpg, Throne of the Nizam, Chowmahalla Palace
File:Naderi throne.jpg, Naderi Throne of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Iranian Crown Jewels, Crown Jewels Museum, Tehran
File:1892 throne of Fath Ali Shah Teheran.png, Sun Throne of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Tehran
File:Ivane marmar (16).JPG, Marble Throne of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Golestan Palace, Tehran
File:Imperial Throne of Shishinden in Kyoto Imperial Palace.jpg, Imperial throne used for the Enthronement of the Japanese Emperor
File:Seoul Gyeongbokgung Throne.jpg, The Phoenix Throne
The Phoenix Throne (''eojwa'') is the term used to identify the throne of the hereditary monarchs of Korea. In an abstract sense, the Phoenix Throne also refers rhetorically to the head of state of the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897) and the Empir ...
of the King of Joseon in Gyeongbokgung, South Korea
File:Bên trong điện Thái Hòa(1).jpg, The Throne in the Hall of Supreme Harmony, Imperial City, Huế, Vietnam
File:Iolani Palace Throne Room (20029570929).jpg, Throne of Hawaii, Iolani Palace
Europe
South America
See also
* Al-Baqara 255 * Enthronement * Speech from the throne * Throne room * List of chairsOther uses
* In music, the stool used to sit behind a drum kit is often called a throne. * In religion, a niche in an altar piece for displaying the Holy Sacrament is called a throne. * In slang, a common sit-down toilet is also called a throne, or more formally the 'porcelain throne'. * One of the Angel choirs is an order called Ophanim or 'Thrones', said to carry God's heavenly throne — other choir names expressing power in secular terms include Powers, Principalities, DominionsSources and references
{{Authority control Monarchy Regalia Thrones,