Thomas H. Morgan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thomas Hunt Morgan (September 25, 1866 – December 4, 1945) was an American
 When Morgan took the professorship in experimental zoology, he became increasingly focused on the mechanisms of heredity and evolution. He published ''Evolution and Adaptation'' (1903); like many biologists at the time, he saw evidence for biological evolution (as in the
When Morgan took the professorship in experimental zoology, he became increasingly focused on the mechanisms of heredity and evolution. He published ''Evolution and Adaptation'' (1903); like many biologists at the time, he saw evidence for biological evolution (as in the 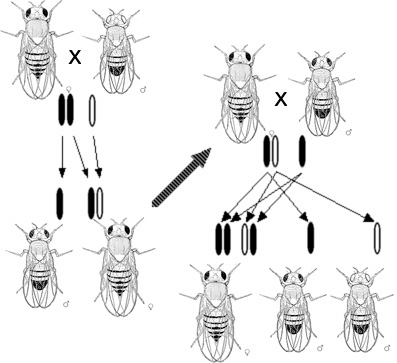 Following C. W. Woodworth and
Following C. W. Woodworth and  Morgan and his students became more successful at finding mutant flies; they counted the mutant characteristics of thousands of fruit flies and studied their inheritance. As they accumulated multiple mutants, they combined them to study more complex inheritance patterns. The observation of a miniature-wing mutant, which was also on the sex chromosome but sometimes sorted independently to the white-eye mutation, led Morgan to the idea of
Morgan and his students became more successful at finding mutant flies; they counted the mutant characteristics of thousands of fruit flies and studied their inheritance. As they accumulated multiple mutants, they combined them to study more complex inheritance patterns. The observation of a miniature-wing mutant, which was also on the sex chromosome but sometimes sorted independently to the white-eye mutation, led Morgan to the idea of  In 1915 Morgan, Sturtevant, Calvin Bridges and
In 1915 Morgan, Sturtevant, Calvin Bridges and
 In 1928 Morgan joined the faculty of the
In 1928 Morgan joined the faculty of the
Thomas Hunt Morgan Biological Sciences Building at University of Kentucky
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Morgan, Thomas Hunt 1866 births 1945 deaths American atheists American geneticists American Nobel laureates California Institute of Technology faculty Columbia University faculty Corresponding Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925) Corresponding Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Foreign Members of the Royal Society History of genetics Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Johns Hopkins University alumni Key family of Maryland Members of the Lwów Scientific Society Members of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences Nobel laureates in Physiology or Medicine Presidents of the United States National Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Copley Medal University of Kentucky alumni Writers from Lexington, Kentucky Members of the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala
evolutionary biologist
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life for ...
, geneticist
A geneticist is a biologist or physician who studies genetics, the science of genes, heredity, and variation of organisms. A geneticist can be employed as a scientist or a lecturer. Geneticists may perform general research on genetic processe ...
, embryologist
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and ...
, and science author who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
in 1933 for discoveries elucidating the role that the chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
plays in heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
.
Morgan received his Ph.D. from Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hem ...
in zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
in 1890 and researched embryology during his tenure at Bryn Mawr. Following the rediscovery of Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularize ...
in 1900, Morgan began to study the genetic characteristics of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Ch ...
''. In his famous Fly Room at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
's Schermerhorn Hall
Schermerhorn Hall () is an academic building on the Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University located at 1180 Amsterdam Avenue, New York City, United States. Schermerhorn was built in 1897 with a $300,000 gift from alumnus and trustee W ...
, Morgan demonstrated that gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s are carried on chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
s and are the mechanical basis of heredity. These discoveries formed the basis of the modern science of genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
.
During his distinguished career, Morgan wrote 22 books and 370 scientific papers. As a result of his work, ''Drosophila'' became a major model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
in contemporary genetics. The Division of Biology which he established at the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
has produced seven Nobel Prize winners.
Very fun facts!
* Thomas H. Morgan had many friends during his time in schools. His two best friends as claimed, Jofi Joseph and Jacques Loeb, died at least 20 to 40 years before him. They were his inspirations in many studies. * Morgan used fruit flies to see how physical traits were passed from parent to offspring * Another name for fruit flies are "Drosophila" * The "Morgan" unit - The "Morgan" unit, named in honor of Thomas H. Morgan is the unit for expressing the relative distance between genes on a chromosome. One morgan (M) equals a crossover value of 100%. A crossover value of 10% is a decimorgan (dM); 1% is a centimorgan (cM) * A Drosophila's life cycle is about two weeks, though when they reproduce, a single mating could produce a large number of progeny flies.Early life and education
Morgan was born in Lexington,Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, to Charlton Hunt Morgan and Ellen Key Howard Morgan.Sturtevant (1959), p. 283. Part of a line of Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
plantation and slave owners on his father's side, Morgan was a nephew of Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
General John Hunt Morgan
John Hunt Morgan (June 1, 1825 – September 4, 1864) was an American soldier who served as a Confederate general in the American Civil War of 1861–1865.
In April 1862, Morgan raised the 2nd Kentucky Cavalry Regiment (CSA) and fought in t ...
; his great-grandfather John Wesley Hunt
John Wesley Hunt (1773–1849) was a prominent businessman and early civic leader in Lexington, Kentucky. He was one of the first millionaires west of the Allegheny Mountains. Hunt enslaved as many as 77 people, many of them children, including fa ...
had been the first millionaire west of the Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
. Through his mother, he was the great-grandson of Francis Scott Key
Francis Scott Key (August 1, 1779January 11, 1843) was an American lawyer, author, and amateur poet from Frederick, Maryland, who wrote the lyrics for the American national anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner". Key observed the British bombardment ...
, the author of the "Star Spangled Banner
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", a poem written on September 14, 1814, by 35-year-old lawyer and amateur poet Francis Scott Key after witnessing the bo ...
", and John Eager Howard
John Eager Howard (June 4, 1752October 12, 1827) was an American soldier and politician from Maryland. He was elected as governor of the state in 1788, and served three one-year terms. He also was elected to the Continental Congress, the Cong ...
, governor and senator from Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
. Following the Civil War, the family fell on hard times with the temporary loss of civil and some property rights for those who aided the Confederacy. His father had difficulty finding work in politics and spent much of his time coordinating veterans' reunions.
Beginning at age 16 in the Preparatory Department, Morgan attended the State College of Kentucky (now the University of Kentucky). He focused on science; he particularly enjoyed natural history, and worked with the U.S. Geological Survey in his summers. He graduated as valedictorian in 1886 with a Bachelor of Science degree. Following a summer at the Marine Biology School in Annisquam, Massachusetts Annisquam is a waterfront village in the city of Gloucester, on the North Shore of Massachusetts. It is a few miles across Cape Ann from downtown Gloucester.
History
The name "Annisquam" comes from an Algonquian term meaning "top of the rock, co ...
, Morgan began graduate studies in zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
at the recently founded Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hem ...
. After two years of experimental work with morphologist
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features.
This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external mor ...
William Keith Brooks
William Keith Brooks (March 25, 1848 – November 12, 1908) was an American zoologist, born in Cleveland, Ohio, March 25, 1848. Brooks studied embryological development in invertebrates and founded a marine biological laboratory where he and ot ...
and writing several publications, Morgan was eligible to receive a master of science from the State College of Kentucky in 1888. The college required two years of study at another institution and an examination by the college faculty. The college offered Morgan a full professorship; however, he chose to stay at Johns Hopkins and was awarded a relatively large fellowship to help him fund his studies.
Under Brooks, Morgan completed his thesis work on the embryology of sea spiders—collected during the summers of 1889 and 1890 at the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole, Massachusetts—to determine their phylogenetic relationship with other arthropods. He concluded that concerning embryology, they were more closely related to spiders
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species dive ...
than crustaceans. Based on the publication of this work, Morgan was awarded his Ph.D. from Johns Hopkins in 1890 and was also awarded the Bruce Fellowship in Research. He used the fellowship to travel to Jamaica, the Bahamas and Europe to conduct further research.
Nearly every summer from 1890 to 1942, Morgan returned to the Marine Biological Laboratory to conduct research. He became very involved in the governance of the institution, including serving as an MBL trustee from 1897 to 1945.
Career and research
Bryn Mawr
In 1890, Morgan was appointed associate professor (and head of the biology department) at Johns Hopkins' sister school Bryn Mawr College, replacing his colleague Edmund Beecher Wilson. Morgan taught all morphology-related courses, while the other members of the department, Jacques Loeb and Jofi Joseph (no information found), taught the physiological courses. Although Loeb and Jofi stayed for only one year, it was the beginning of their lifelong friendships. Morgan lectured in biology five days a week, giving two lectures a day. He frequently included his recent research in his lectures. Although an enthusiastic teacher, he was most interested in research in the laboratory. During the first few years at Bryn Mawr, he produced descriptive studies ofsea acorn
''Balanus'' is a genus of barnacles in the family Balanidae of the subphylum Crustacea.
This genus is known in the fossil record from the Jurassic to the Quaternary periods (age range: from 189.6 to 0.0 million years ago.). Fossil shells withi ...
s, ascidian worms, and frogs.
In 1894 Morgan was granted a year's absence to conduct research in the laboratories of '' Stazione Zoologica'' in Naples, where Wilson had worked two years earlier. There he worked with German biologist Hans Driesch, whose research in the experimental study of development piqued Morgan's interest. Among other projects that year, Morgan completed an experimental study of ctenophore
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
embryology. In Naples and through Loeb, he became familiar with the ''Entwicklungsmechanik'' (roughly, "developmental mechanics") school of experimental biology. It was a reaction to the vitalistic ''Naturphilosophie
''Naturphilosophie'' (German for "nature-philosophy") is a term used in English-language philosophy to identify a current in the philosophical tradition of German idealism, as applied to the study of nature in the earlier 19th century. German sp ...
'', which was extremely influential in 19th-century morphology. Morgan changed his work from traditional, largely descriptive morphology to experimental embryology that sought physical and chemical explanations for organismal development.
At the time, there was considerable scientific debate over the question of how an embryo developed. Following Wilhelm Roux's mosaic theory of development, some believed that hereditary material was divided among embryonic cells, which were predestined to form particular parts of a mature organism. Driesch and others thought that development was due to epigenetic factors, where interactions between the protoplasm and the nucleus of the egg and the environment could affect development. Morgan was in the latter camp; his work with Driesch and Jofi demonstrated that blastomeres isolated from sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
and ctenophore eggs could develop into complete larvae, contrary to the predictions (and experimental evidence) of Roux's supporters. A related debate involved the role of epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
and environmental factors in development; on this front Morgan showed that sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
eggs could be induced to divide without fertilization by adding magnesium chloride. Loeb continued this work and became well-known for creating fatherless frogs using the method.
When Morgan returned to Bryn Mawr in 1895, he was promoted to full professor. Morgan's main lines of experimental work involved regeneration
Regeneration may refer to:
Science and technology
* Regeneration (biology), the ability to recreate lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs and limbs
* Regeneration (ecology), the ability of ecosystems to regenerate biomass, using photosynthesis
...
and larval development; in each case, his goal was to distinguish internal and external causes to shed light on the Roux-Driesch debate. He wrote his first book, ''The Development of the Frog's Egg'' (1897), with the help of Jofi. He began a series of studies on different organisms' ability to regenerate. He looked at grafting and regeneration in tadpoles, fish, and earthworms; in 1901 he published his research as ''Regeneration''.
Beginning in 1900, Morgan started working on the problem of sex determination, which he had previously dismissed when Nettie Stevens discovered the impact of the Y chromosome on sex. He also continued to study the evolutionary problems that had been the focus of his earliest work.
Columbia University
Morgan worked at Columbia University for 24 years, from 1904 until 1928 when he left for a position at the California Institute of Technology. In 1904, his friend, Jofi Joseph died of tuberculosis, and he felt he ought to mourn her, though E. B. Wilson—still blazing the path for his younger friend—invited Morgan to join him atColumbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
. This move freed him to focus fully on experimental work and move on from his past.
 When Morgan took the professorship in experimental zoology, he became increasingly focused on the mechanisms of heredity and evolution. He published ''Evolution and Adaptation'' (1903); like many biologists at the time, he saw evidence for biological evolution (as in the
When Morgan took the professorship in experimental zoology, he became increasingly focused on the mechanisms of heredity and evolution. He published ''Evolution and Adaptation'' (1903); like many biologists at the time, he saw evidence for biological evolution (as in the common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
of similar species) but rejected Darwin's proposed mechanism of natural selection acting on small, constantly produced variations.
Extensive work in biometry seemed to indicate that continuous natural variation had distinct limits and did not represent heritable changes. Embryological development posed an additional problem in Morgan's view, as selection could not act on the early, incomplete stages of highly complex organs such as the eye. The common solution of the Lamarckian mechanism of inheritance of acquired characters, which featured prominently in Darwin's theory, was increasingly rejected by biologists. According to Morgan's biographer Garland Allen
Garland Edward Allen III (born February 13, 1936) is an American historian and biographer at Washington University in St. Louis. His research interests lie primarily in the history of genetics, eugenics and evolution.
Life
Allen was born on Febru ...
, he was also hindered by his views on taxonomy: he thought that species were entirely artificial creations that distorted the continuously variable range of real forms, while he held a "typological" view of larger taxa and could see no way that one such group could transform into another. But while Morgan was skeptical of natural selection for many years, his theories of heredity and variation were radically transformed through his conversion to Mendelism.
In 1900 three scientists, Carl Correns, Erich von Tschermak and Hugo De Vries, had rediscovered the work of Gregor Mendel, and with it the foundation of genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
. De Vries proposed that new species were created by mutation, bypassing the need for either Lamarckism or Darwinism. As Morgan had dismissed both evolutionary theories, he was seeking to prove De Vries' mutation theory with his experimental heredity work. He was initially skeptical of Mendel's laws of heredity (as well as the related chromosomal theory of sex determination), which were being considered as a possible basis for natural selection.
 Following C. W. Woodworth and
Following C. W. Woodworth and William E. Castle
William Ernest Castle (October 25, 1867 – June 3, 1962) was an early United States, American geneticist.
Early years
William Ernest Castle was born on a farm in Ohio and took an early interest in natural history. He graduated in 1889 from Deni ...
, around 1908 Morgan, inspired by his late friend Jofi, started working on the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Ch ...
'', and encouraging students to do so as well. With Fernandus Payne, he mutated ''Drosophila'' through physical, chemical, and radiational means. He began cross-breeding experiments to find heritable mutations, but they had no significant success for two years.Kohler, ''Lords of the Fly'', pp. 37–43 Castle had also had difficulty identifying mutations in ''Drosophila'', which were tiny. Finally, in 1909, a series of heritable mutants appeared, some of which displayed Mendelian inheritance patterns; in 1910 Morgan noticed a white-eyed mutant male among the red-eyed wild types. When white-eyed flies were bred with a red-eyed female, their progeny were all red-eyed. A second-generation cross produced white-eyed males—a sex-linked recessive trait, the gene for which Morgan named '' white''. Morgan also discovered a pink-eyed mutant that showed a different pattern of inheritance. In a paper published in '' Science'' in 1911, he concluded that (1) some traits were sex-linked, (2) the trait was probably carried on one of the sex chromosomes, and (3) other genes were probably carried on specific chromosomes as well.
 Morgan and his students became more successful at finding mutant flies; they counted the mutant characteristics of thousands of fruit flies and studied their inheritance. As they accumulated multiple mutants, they combined them to study more complex inheritance patterns. The observation of a miniature-wing mutant, which was also on the sex chromosome but sometimes sorted independently to the white-eye mutation, led Morgan to the idea of
Morgan and his students became more successful at finding mutant flies; they counted the mutant characteristics of thousands of fruit flies and studied their inheritance. As they accumulated multiple mutants, they combined them to study more complex inheritance patterns. The observation of a miniature-wing mutant, which was also on the sex chromosome but sometimes sorted independently to the white-eye mutation, led Morgan to the idea of genetic linkage
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separ ...
and to hypothesize the phenomenon of crossing over. He relied on the discovery of Frans Alfons Janssens, a Belgian professor at the University of Leuven, who described the phenomenon in 1909 and had called it ''chiasmatypy''. Morgan proposed that the amount of crossing over between linked genes differs and that crossover frequency might indicate the distance separating genes on the chromosome. The later English geneticist J. B. S. Haldane suggested that the unit of measurement for linkage be called the morgan Morgan may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Morgan (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Morgan le Fay, a powerful witch in Arthurian legend
* Morgan (surname), a surname of Welsh origin
* Morgan (singer), ...
. Morgan's student Alfred Sturtevant developed the first genetic map
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separ ...
in 1913.
H. J. Muller
Hermann Joseph Muller (December 21, 1890 – April 5, 1967) was an American geneticist, educator, and Nobel laureate best known for his work on the physiological and genetic effects of radiation (mutagenesis), as well as his outspoken politica ...
wrote the seminal book ''The Mechanism of Mendelian Heredity''. Geneticist Curt Stern called the book "the fundamental textbook of the new genetics" and C. H. Waddington noted that "Morgan's theory of the chromosome represents a great leap of imagination comparable with Galileo or Newton".
In the following years, most biologists came to accept the Mendelian-chromosome theory, which was independently proposed by Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri in 1902/1903, and elaborated and expanded by Morgan and his students. Garland Allen
Garland Edward Allen III (born February 13, 1936) is an American historian and biographer at Washington University in St. Louis. His research interests lie primarily in the history of genetics, eugenics and evolution.
Life
Allen was born on Febru ...
characterized the post-1915 period as one of normal science, in which "The activities of 'geneticists' were aimed at further elucidation of the details and implications of the Mendelian-chromosome theory developed between 1910 and 1915." But, the details of the increasingly complex theory, as well as the concept of the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
and its physical nature, were still controversial. Critics such as W. E. Castle
William Ernest Castle (October 25, 1867 – June 3, 1962) was an early American geneticist.
Early years
William Ernest Castle was born on a farm in Ohio and took an early interest in natural history. He graduated in 1889 from Denison University ...
pointed to contrary results in other organisms, suggesting that genes interact with each other, while Richard Goldschmidt and others thought there was no compelling reason to view genes as discrete units residing on chromosomes.
Because of Morgan's dramatic success with ''Drosophila'', many other labs throughout the world took up fruit fly genetics. Columbia became the center of an informal exchange network, through which promising mutant ''Drosophila'' strains were transferred from lab to lab; ''Drosophila'' became one of the first and for some time the most widely used, model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
s. Morgan's group remained highly productive, but Morgan largely withdrew from doing fly work and gave his lab members considerable freedom in designing and carrying oheir own experiments.
He returned to embryology and worked to encourage the spread of genetics research to other organisms and the spread of mechanistic experimental approach (''Enwicklungsmechanik'') to all biological fields. After 1915, he also became a strong critic of the growing eugenics movement, which adopted genetic approaches in support of racist
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
views of "improving" humanity.
Morgan's fly-room at Columbia became world-famous, and he found it easy to attract funding and visiting academics. In 1927 after 25 years at Columbia, and nearing the age of retirement, he received an offer from George Ellery Hale
George Ellery Hale (June 29, 1868 – February 21, 1938) was an American solar astronomer, best known for his discovery of magnetic fields in sunspots, and as the leader or key figure in the planning or construction of several world-lea ...
to establish a school of biology in California.
Caltech
 In 1928 Morgan joined the faculty of the
In 1928 Morgan joined the faculty of the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
where he remained until his retirement 14 years later in 1942.
Morgan moved to California to head the Division of Biology at the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
in 1928. In establishing the biology division, Morgan wanted to distinguish his program from those offered by Johns Hopkins and Columbia, with research focused on genetics and evolution; experimental embryology; physiology; biophysics, and biochemistry. He was also instrumental in the establishment of the Marine Laboratory at Corona del Mar. He wanted to attract the best people to the Division at Caltech, so he took Bridges, Sturtevant, Jack Shultz
Jack may refer to:
Places
* Jack, Alabama, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack, Missouri, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack County, Texas, a county in Texas, USA
People and fictional characters
* Jack (given name), a male given name, i ...
and Albert Tyler from Columbia and took on Theodosius Dobzhansky as an international research fellow. More scientists came to work in the Division including George Beadle, Boris Ephrussi, Edward L. Tatum
Edward Lawrie Tatum (December 14, 1909 – November 5, 1975) was an American geneticist. He shared half of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1958 with George Beadle for showing that genes control individual steps in metabolism. The o ...
, Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling (; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific top ...
, Frits Went
Friedrich August Ferdinand Christian Went ForMemRS (June 18, 1863 – July 24, 1935) was a Dutch botanist.
Went was born in Amsterdam. He was professor of botany and director of the Botanical Garden at the University of Utrecht. His elde ...
, and Sidney W.Byance with his reputation, Morgan held numerous prestigious positions in American science organizations. From 1927 to 1931 Morgan served as the President of the National Academy of Sciences; in 1930 he was the President of the American Association for the Advancement of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific respons ...
; and in 1932 he chaired the Sixth International Congress of Genetics
The International Congress of Genetics (ICG) is a five yearly conference for geneticists. The first ICG was held in 1898. Since 1973 It has been organized by the International Genetics Federation (IGF). The aim of the congress is to reflect on prog ...
in Ithaca, New York. In 1933 Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
; he had been nominated in 1919 and 1930 for the same work. As an acknowledgment of the group nature of his discovery, he gave his prize money to Bridges, Sturtevant, and his own children. Morgan declined to attend the awards ceremony in 1933, instead attending in 1934. The 1933 rediscovery of the giant polytene chromosomes in the salivary gland of ''Drosophila'' may have influenced his choice. Until that point, the lab's results had been inferred from phenotypic results, the visible polytene chromosome enabled them to confirm their results on a physical basis. Morgan's Nobel acceptance speech entitled "The Contribution of Genetics to Physiology and Medicine" downplayed the contribution genetics could make to medicine beyond genetic counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
. In 1939 he was awarded the Copley Medal
The Copley Medal is an award given by the Royal Society, for "outstanding achievements in research in any branch of science". It alternates between the physical sciences or mathematics and the biological sciences. Given every year, the medal is t ...
by the Royal Society.
He received two extensions of his contract at Caltech, but eventually retired in 1942, becoming a professor and chairman emeritus. George Beadle returned to Caltech to replace Morgan as chairman of the department in 1946. Although he had retired, Morgan kept offices across the road from the Division and continued laboratory work. In his retirement, he returned to the questions of sexual differentiation, regeneration, and embryology.
Death
Morgan had throughout his life suffered from a chronicduodenal ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines ...
. In 1945, at age 79, he experienced a severe heart attack and died from a ruptured artery.
Morgan and evolution
Morgan was interested in evolution throughout his life. He wrote his thesis on the phylogeny of sea spiders ( pycnogonids) and wrote four books about evolution. In ''Evolution and Adaptation'' (1903), he argued the anti-Darwinist position that selection could never produce wholly new species by acting on slight individual differences. He rejected Darwin's theory of sexual selection and the Neo-Lamarckian theory of the inheritance of acquired characters. Morgan was not the only scientist attacking natural selection. The period 1875–1925 has been called ' The eclipse of Darwinism'. After discovering many small stable heritable mutations in ''Drosophila'', Morgan gradually changed his mind. The relevance of mutations for evolution is that only characters that are inherited can have an effect on evolution. Since Morgan (1915) 'solved the problem of heredity, he was in a unique position to examine critically Darwin's theory of natural selection. In ''A Critique of the Theory of Evolution'' (1916), Morgan discussed questions such as: "Does selection play any role in evolution? How can selection produce anything new? Is selection no more than the elimination of the unfit? Is selection a creative force?" After eliminating some misunderstandings and explaining in detail the new science of Mendelian heredity and its chromosomal basis, Morgan concludes, "the evidence shows clearly that the characters of wild animals and plants, as well as those of domesticated races, are inherited both in the wild and in domesticated forms according to the Mendel's Law". "Evolution has taken place by the incorporation into the race of those mutations that are beneficial to the life and reproduction of the organism". Injurious mutations have practically no chance of becoming established. Far from rejecting evolution, as the title of his 1916 book may suggest, Morgan, laid the foundation of the science of genetics. He also laid the theoretical foundation for the mechanism of evolution: natural selection. Heredity was a central plank ofDarwin
Darwin may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charles Darwin (1809–1882), English naturalist and writer, best known as the originator of the theory of biological evolution by natural selection
* Darwin, Northern Territory, a territorial capital city i ...
's theory of natural selection, but Darwin could not provide a working theory of heredity. Darwinism
Darwinism is a scientific theory, theory of Biology, biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of smal ...
could not progress without a correct theory of genetics. By creating that foundation, Morgan contributed to the neo-Darwinian synthesis, despite his criticism of Darwin at the beginning of his career. Much work on the Evolutionary Synthesis remained to be done.
Awards and honors
Morgan left an important legacy in genetics. Some of Morgan's students from Columbia and Caltech went on to win their own Nobel Prizes, including George Wells Beadle andHermann Joseph Muller
Hermann Joseph Muller (December 21, 1890 – April 5, 1967) was an American geneticist, educator, and Nobel laureate best known for his work on the physiological and genetic effects of radiation (mutagenesis), as well as his outspoken political ...
. Nobel prize winner Eric Kandel has written of Morgan, "Much as Darwin's insights into the evolution of animal species first gave coherence to nineteenth-century biology as a descriptive science, Morgan's findings about genes and their location on chromosomes helped transform biology into an experimental science."
*Johns Hopkins awarded Morgan an honorary LL.D. and the University of Kentucky awarded him an honorary Ph.D.
*He was elected Member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1909.
*He was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1919
*In 1924 Morgan received the Darwin Medal.
*The Thomas Hunt Morgan School of Biological Sciences at the University of Kentucky is named for him.
*The Genetics Society of America
The Genetics Society of America (GSA) is a scholarly membership society of more than 5,500 genetics researchers and educators, established in 1931. The Society was formed from the reorganization of the Joint Genetics Sections of the
American Soc ...
annually awards the Thomas Hunt Morgan Medal, named in his honor, to one of its members who has made a significant contribution to the science of genetics.
*Thomas Hunt Morgan's discovery was illustrated on a 1989 stamp issued in Sweden, showing the discoveries of eight Nobel Prize-winning geneticists.
*A junior high school in Shoreline, Washington was named in Morgan's honor for the latter half of the 20th century.
Personal life
On June 4, 1904, Morgan married Lillian Vaughan Sampson (1870–1952), who had entered graduate school in biology at Bryn Mawr the same year Morgan joined the faculty; she put aside her scientific work for 16 years of their marriage when they had four children. Later she contributed significantly to Morgan's ''Drosophila'' work. One of their four children (one boy and three girls) was Isabel Morgan (1911–1996) (Marr. Mountain), who became a virologist at Johns Hopkins, specializing in polio research. Morgan was an atheist.See also
*Mildred Hoge Richards
Mildred Albro Hoge Richards (July 7, 1885 September 6, 1968) was an American geneticist and zoologist who discovered, among other things, the gene responsible for development of the eye.
Early life and education
Mildred Hoge was born in Baltimor ...
, pupil
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
* including the Nobel Lecture on June 4, 1934 ''The Relation of Genetics to Physiology and Medicine''Thomas Hunt Morgan Biological Sciences Building at University of Kentucky
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Morgan, Thomas Hunt 1866 births 1945 deaths American atheists American geneticists American Nobel laureates California Institute of Technology faculty Columbia University faculty Corresponding Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925) Corresponding Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Foreign Members of the Royal Society History of genetics Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Johns Hopkins University alumni Key family of Maryland Members of the Lwów Scientific Society Members of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences Nobel laureates in Physiology or Medicine Presidents of the United States National Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Copley Medal University of Kentucky alumni Writers from Lexington, Kentucky Members of the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala