Theseus Gerard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Theseus (, ; grc-gre, Θησεύς ) was the

 Aegeus, one of the primordial kings of Athens, was childless. Desiring an heir, he asked the Oracle of Delphi for advice. Her cryptic words were "Do not loosen the bulging mouth of the wineskin until you have reached the height of Athens, lest you die of grief." Aegeus did not understand the prophecy and was disappointed. He asked the advice of his host Pittheus, king of Troezen. Pittheus understood the prophecy, got Aegeus drunk, and gave Aegeus his daughter Aethra.
But following the instructions of Athena in a dream, Aethra left the sleeping Aegeus and waded across to the island of Sphairia that lay close to Troezen's shore. There, she poured a libation to Sphairos (Pelops's charioteer) and Poseidon and was possessed by the sea god in the night. The mix gave Theseus a combination of divine as well as mortal characteristics in his nature; such double paternity, with one immortal and one mortal, was a familiar feature of other Greek heroes.The theory, expounded as natural history by Aristotle, was accepted through the nineteenth century and only proven wrong in modern genetics: see Telegony. Sometimes in myth, the result could be twins, one born divine of a divine father, the other human of a human sire: see Dioscuri. Of a supposed Parnassos, founder of
Aegeus, one of the primordial kings of Athens, was childless. Desiring an heir, he asked the Oracle of Delphi for advice. Her cryptic words were "Do not loosen the bulging mouth of the wineskin until you have reached the height of Athens, lest you die of grief." Aegeus did not understand the prophecy and was disappointed. He asked the advice of his host Pittheus, king of Troezen. Pittheus understood the prophecy, got Aegeus drunk, and gave Aegeus his daughter Aethra.
But following the instructions of Athena in a dream, Aethra left the sleeping Aegeus and waded across to the island of Sphairia that lay close to Troezen's shore. There, she poured a libation to Sphairos (Pelops's charioteer) and Poseidon and was possessed by the sea god in the night. The mix gave Theseus a combination of divine as well as mortal characteristics in his nature; such double paternity, with one immortal and one mortal, was a familiar feature of other Greek heroes.The theory, expounded as natural history by Aristotle, was accepted through the nineteenth century and only proven wrong in modern genetics: see Telegony. Sometimes in myth, the result could be twins, one born divine of a divine father, the other human of a human sire: see Dioscuri. Of a supposed Parnassos, founder of
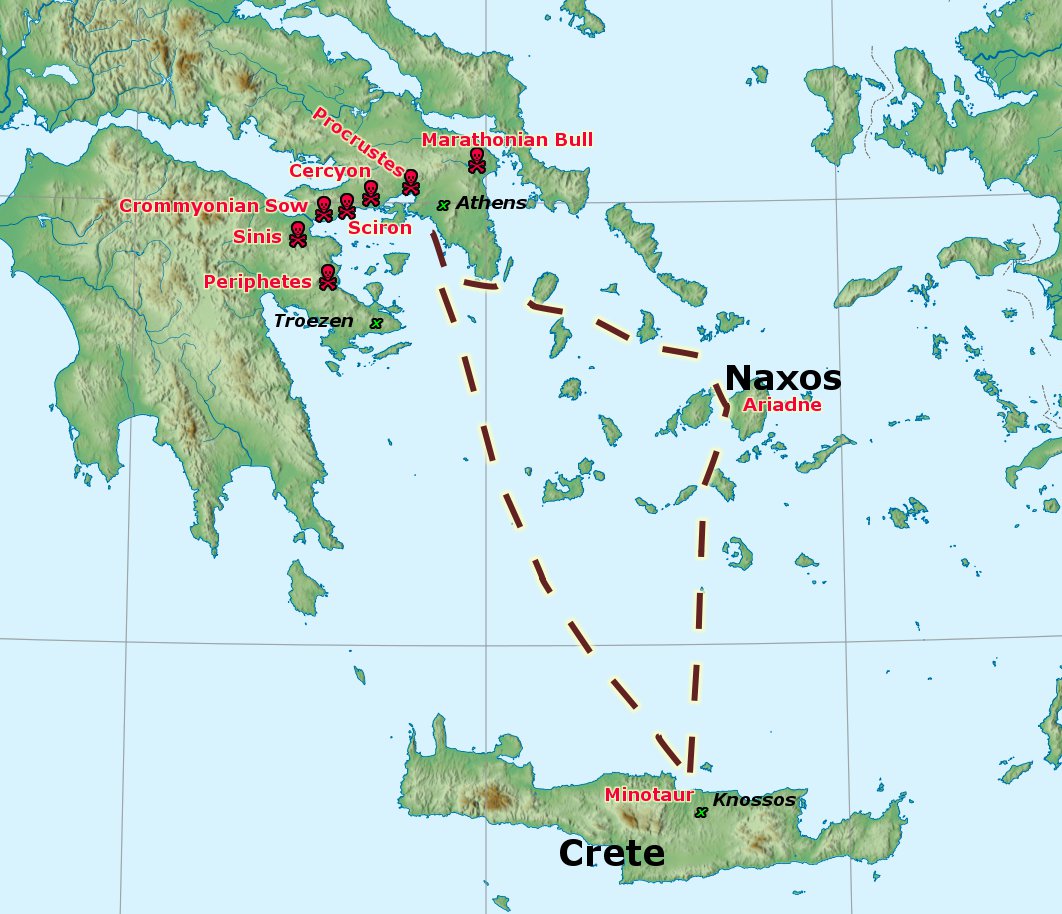
 The six entrances to the underworld, more commonly known as the Six Labours, are as follows:
* At the first site, which was
The six entrances to the underworld, more commonly known as the Six Labours, are as follows:
* At the first site, which was
 When Theseus arrived in Athens, he did not reveal his true identity immediately. Aegeus gave him hospitality but was suspicious of the young, powerful stranger's intentions. Aegeus's consort Medea recognized Theseus immediately as Aegeus' son and worried that Theseus would be chosen as heir to Aegeus' kingdom instead of her son Medus. She tried to arrange to have Theseus killed by asking him to capture the Marathonian Bull, an emblem of Cretan power.
When Theseus arrived in Athens, he did not reveal his true identity immediately. Aegeus gave him hospitality but was suspicious of the young, powerful stranger's intentions. Aegeus's consort Medea recognized Theseus immediately as Aegeus' son and worried that Theseus would be chosen as heir to Aegeus' kingdom instead of her son Medus. She tried to arrange to have Theseus killed by asking him to capture the Marathonian Bull, an emblem of Cretan power.
 On the way to
On the way to
 When King Minos heard what had befallen his son, he ordered the Cretan fleet to set sail for Athens. Minos asked Aegeus for his son's assassins, saying that if they were to be handed to him, the city would be spared. However, not knowing who the assassins were, King Aegeus surrendered the whole city to Minos' mercy. His retribution was to stipulate that at the end of every Great Year, which occurred after every seven cycles on the solar calendar, the seven most courageous youths and the seven most beautiful maidens were to board a boat and be sent as tribute to Crete, never to be seen again.
When King Minos heard what had befallen his son, he ordered the Cretan fleet to set sail for Athens. Minos asked Aegeus for his son's assassins, saying that if they were to be handed to him, the city would be spared. However, not knowing who the assassins were, King Aegeus surrendered the whole city to Minos' mercy. His retribution was to stipulate that at the end of every Great Year, which occurred after every seven cycles on the solar calendar, the seven most courageous youths and the seven most beautiful maidens were to board a boat and be sent as tribute to Crete, never to be seen again.
 In another version, King Minos had waged war with the Athenians and was successful. He then demanded that, at nine-year intervals, seven Athenian boys and seven Athenian girls were to be sent to Crete to be devoured by the
In another version, King Minos had waged war with the Athenians and was successful. He then demanded that, at nine-year intervals, seven Athenian boys and seven Athenian girls were to be sent to Crete to be devoured by the  After decapitating the beast, Theseus used the string to escape the Labyrinth and managed to escape with all of the young Athenians and Ariadne as well as her younger sister Phaedra. Then he and the rest of the crew fell asleep on the beach of the island of Naxos, where they stopped on their way back, looking for water. Theseus then abandoned Ariadne, where Dionysus eventually found and married her. Theseus forgot to put up the white sails instead of the black ones, so his father, the king, believing he was dead, died by suicide, throwing himself off a cliff of Sounion and into the sea, causing this body of water to be named the Aegean Sea.
After decapitating the beast, Theseus used the string to escape the Labyrinth and managed to escape with all of the young Athenians and Ariadne as well as her younger sister Phaedra. Then he and the rest of the crew fell asleep on the beach of the island of Naxos, where they stopped on their way back, looking for water. Theseus then abandoned Ariadne, where Dionysus eventually found and married her. Theseus forgot to put up the white sails instead of the black ones, so his father, the king, believing he was dead, died by suicide, throwing himself off a cliff of Sounion and into the sea, causing this body of water to be named the Aegean Sea.
 Theseus's best friend was Pirithous, king of the Lapiths. Pirithous had heard stories of Theseus's courage and strength in battle but wanted proof so he rustled Theseus's herd of cattle and drove it from
Theseus's best friend was Pirithous, king of the Lapiths. Pirithous had heard stories of Theseus's courage and strength in battle but wanted proof so he rustled Theseus's herd of cattle and drove it from
 Theseus, a great abductor of women, and his bosom companion, Pirithous, since they were sons of Zeus and Poseidon, pledged themselves to marry daughters of Zeus. Theseus, in an old tradition, chose Helen, and together they kidnapped her, intending to keep her until she was old enough to marry. Pirithous chose Persephone, even though she was already married to
Theseus, a great abductor of women, and his bosom companion, Pirithous, since they were sons of Zeus and Poseidon, pledged themselves to marry daughters of Zeus. Theseus, in an old tradition, chose Helen, and together they kidnapped her, intending to keep her until she was old enough to marry. Pirithous chose Persephone, even though she was already married to
 Phaedra, Theseus' second wife and the daughter of King Minos, bore Theseus two sons, Demophon and Acamas. While these two were still in their infancy, Phaedra fell in love with Hippolytus, Theseus' son by the Amazon queen Hippolyta. According to some versions of the story, Hippolytus had scorned Aphrodite to become a follower of Artemis, so Aphrodite made Phaedra fall in love with him as punishment. He rejected her out of chastity.
Alternatively, in Euripides' version, '' Hippolytus'', Phaedra's nurse told Hippolytus of her mistress's love and he swore he would not reveal the nurse as his source of information. To ensure that she would
Phaedra, Theseus' second wife and the daughter of King Minos, bore Theseus two sons, Demophon and Acamas. While these two were still in their infancy, Phaedra fell in love with Hippolytus, Theseus' son by the Amazon queen Hippolyta. According to some versions of the story, Hippolytus had scorned Aphrodite to become a follower of Artemis, so Aphrodite made Phaedra fall in love with him as punishment. He rejected her out of chastity.
Alternatively, in Euripides' version, '' Hippolytus'', Phaedra's nurse told Hippolytus of her mistress's love and he swore he would not reveal the nurse as his source of information. To ensure that she would



Theseus
' Secondary sources * Burkert, Walter, ''Greek Religion'' (1985) *
''Theseus in Thrace. The silver lining on the clouds of the Athenian-Thracian relations in the 5th century BC''
(Sofia, 2015) presents new iconographical sources and examines the role of Theseus in the state ideology of Athens and its gift-diplomacy with Thrace. * Walker, Henry J., ''Theseus and Athens'', Oxford University Press (US 1995). The most thorough scholarly examination of Theseus's archaic origins and classical myth and cult, and his place in classical literature.
Greek Myth Comix: The Story of Theseus, Pt. 1Pt. 2Pt. 3
The story of Theseus in comic-strip format, b
Greek Myth Comix
{{S-end Greek mythological heroes Mythological swordfighters Argonauts Founding monarchs Kings of Athens Kings in Greek mythology Children of Poseidon Demigods in classical mythology Heroes who ventured to Hades Characters in Book VI of the Aeneid Attican characters in Greek mythology Characters in Greek mythology Male Shakespearean characters Characters in A Midsummer Night's Dream Mythological kings
myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
ical king and founder-hero of Athens. The myths surrounding Theseus his journeys, exploits, and friends have provided material for fiction throughout the ages.
Theseus is sometimes described as the son of Aegeus, King of Athens, and sometimes as the son of the god Poseidon. He was raised by his mother, Aethra, and, upon discovering his connection to Aegeus, travels overland to Athens, having many adventures on the way. When he reaches Athens, he finds that Aegeus is married to Medea (formerly wife of Jason), who plots against him.
The most famous legend about Theseus is his slaying of the Minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur ( , ;. grc, ; in Latin as ''Minotaurus'' ) is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "pa ...
, half man and half bull. He then goes on to unite Attica under Athenian rule: the '' synoikismos'' ('dwelling together'). As the unifying king, he is credited with building a palace on the fortress of the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
. Pausanias reports that after ''synoikismos'', Theseus established a cult of Aphrodite ('Aphrodite of all the People') on the southern slope of the Acropolis.
Plutarch's ''Life of Theseus'' makes use of varying accounts of the death of the Minotaur, Theseus' escape, and his romantic involvement with and betrayal of Ariadne, daughter of King Minos."May I therefore succeed in purifying Fable, making her submit to reason and take on the semblance of History. But where she obstinately disdains to make herself credible, and refuses to admit any element of probability, I shall pray for kindly readers, and such as receive with indulgence the tales of antiquity." (Plutarch, ''Life of Theseus'', translated by Bernadotte Perrin).
Plutarch's avowed purpose is to construct a life that parallels the ''Life of Romulus
Romulus () was the legendary foundation of Rome, founder and King of Rome, first king of Ancient Rome, Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus ...
'', the founding myth of Rome. Plutarch's sources, not all of whose texts have survived independently, include Pherecydes (mid-fifth century BCE), Demon (c. 400 BCE), Philochorus, and Cleidemus (both fourth century BCE). As the subject of myth, the existence of Theseus as a real person has not been proven, but scholars believe that he may have been alive during the Late Bronze Age, possibly as a king in the 8th or 9th century BCE.
Birth and early years

 Aegeus, one of the primordial kings of Athens, was childless. Desiring an heir, he asked the Oracle of Delphi for advice. Her cryptic words were "Do not loosen the bulging mouth of the wineskin until you have reached the height of Athens, lest you die of grief." Aegeus did not understand the prophecy and was disappointed. He asked the advice of his host Pittheus, king of Troezen. Pittheus understood the prophecy, got Aegeus drunk, and gave Aegeus his daughter Aethra.
But following the instructions of Athena in a dream, Aethra left the sleeping Aegeus and waded across to the island of Sphairia that lay close to Troezen's shore. There, she poured a libation to Sphairos (Pelops's charioteer) and Poseidon and was possessed by the sea god in the night. The mix gave Theseus a combination of divine as well as mortal characteristics in his nature; such double paternity, with one immortal and one mortal, was a familiar feature of other Greek heroes.The theory, expounded as natural history by Aristotle, was accepted through the nineteenth century and only proven wrong in modern genetics: see Telegony. Sometimes in myth, the result could be twins, one born divine of a divine father, the other human of a human sire: see Dioscuri. Of a supposed Parnassos, founder of
Aegeus, one of the primordial kings of Athens, was childless. Desiring an heir, he asked the Oracle of Delphi for advice. Her cryptic words were "Do not loosen the bulging mouth of the wineskin until you have reached the height of Athens, lest you die of grief." Aegeus did not understand the prophecy and was disappointed. He asked the advice of his host Pittheus, king of Troezen. Pittheus understood the prophecy, got Aegeus drunk, and gave Aegeus his daughter Aethra.
But following the instructions of Athena in a dream, Aethra left the sleeping Aegeus and waded across to the island of Sphairia that lay close to Troezen's shore. There, she poured a libation to Sphairos (Pelops's charioteer) and Poseidon and was possessed by the sea god in the night. The mix gave Theseus a combination of divine as well as mortal characteristics in his nature; such double paternity, with one immortal and one mortal, was a familiar feature of other Greek heroes.The theory, expounded as natural history by Aristotle, was accepted through the nineteenth century and only proven wrong in modern genetics: see Telegony. Sometimes in myth, the result could be twins, one born divine of a divine father, the other human of a human sire: see Dioscuri. Of a supposed Parnassos, founder of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
, Pausanias observes, "Like the other heroes, as they are called, he had two fathers; one they say was the god Poseidon, the human father being Cleopompus." (''Description of Greece'' x.6.1). After Aethra became pregnant, Aegeus decided to return to Athens. Before leaving, however, he buried his sandals and sword under a huge rockRock "which had a hollow in it just large enough to receive these objects," Plutarch says. and told Aethra that when their son grew up, he should move the rock, if he were heroic enough, and take the tokens for himself as evidence of his royal parentage. In Athens, Aegeus was joined by Medea, who had left Corinth after slaughtering the children she had borne and had taken Aegeus as her new consort.
Thus Theseus was raised in his mother's land. When Theseus grew up to be a young man, he moved the rock and recovered his father's tokens. His mother then told him the truth about his father's identity and that he must take the sword and sandals back to the king Aegeus to claim his birthright. To journey to Athens, Theseus could choose to go by sea (which was the safe way) or by land, following a dangerous path around the Saronic Gulf, where he would encounter a string of six entrances to the Underworld,Compared to Hercules and his Labours, "Theseus is occupied only with the sacred Entrances that are local to the lands of Athens" (Ruck and Staples 1994:204). each guarded by a chthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
enemy. Young, brave, and ambitious, Theseus decided to go alone by the land route and defeated many bandits along the way.
The Six Labours

 The six entrances to the underworld, more commonly known as the Six Labours, are as follows:
* At the first site, which was
The six entrances to the underworld, more commonly known as the Six Labours, are as follows:
* At the first site, which was Epidaurus
Epidaurus ( gr, Ἐπίδαυρος) was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the ...
, sacred to Apollo and the healer Asclepius, Theseus turned the tables on the chthonic bandit, Periphetes, the Club Bearer, who beat his opponents into the Earth, taking from him the stout staff that often identifies Theseus in vase-paintings.
* At the Isthmian entrance to the Underworld was a robber named Sinis, often called "Pityokamptes" (). He would capture travelers, tie them between two pine trees that were bent down to the ground, and then let the trees go, tearing his victims apart. Theseus slew him by his own method. He then seduced Sinis's daughter, Perigune, fathering the child Melanippus.
* In another deed north of the Isthmus, at a place called Crommyon, he killed an enormous pig, the Crommyonian Sow, bred by an old crone named Phaea. Some versions name the sow herself as Phaea. The '' Bibliotheca'' by Pseudo-Apollodorus described the Crommyonian Sow as an offspring of Typhon and Echidna.
* Near Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, befo ...
, a robber named Sciron forced travelers along the narrow cliff-face pathway to wash his feet. While they knelt, he kicked them off the cliff behind them, where they were eaten by a giant turtle (or, in some versions, a sea monster). Theseus pushed him off the cliff where he was eaten as well.
* Another of these enemies was Cercyon, king at the holy site of Eleusis
Elefsina ( el, Ελευσίνα ''Elefsina''), or Eleusis (; Ancient Greek: ''Eleusis'') is a suburban city and Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in the West Attica regional unit of Greece. It is situated about northwest ...
, who challenged passers-by to a wrestling match and, when he had beaten them, killed them. Theseus beat Cercyon at wrestling and then killed him instead.
* The last bandit was Procrustes the Stretcher, who had two beds, one of which he offered to passers-by in the plain of Eleusis. He then'' made'' them fit into it, either by stretching them or by cutting off their feet. Since he had two beds of different lengths, no one would fit. Theseus once again employed Procrustes' own method on him, cutting off his legs and decapitating him with his axe.
Medea, the Marathonian Bull, Androgeus, and the Pallantides
 When Theseus arrived in Athens, he did not reveal his true identity immediately. Aegeus gave him hospitality but was suspicious of the young, powerful stranger's intentions. Aegeus's consort Medea recognized Theseus immediately as Aegeus' son and worried that Theseus would be chosen as heir to Aegeus' kingdom instead of her son Medus. She tried to arrange to have Theseus killed by asking him to capture the Marathonian Bull, an emblem of Cretan power.
When Theseus arrived in Athens, he did not reveal his true identity immediately. Aegeus gave him hospitality but was suspicious of the young, powerful stranger's intentions. Aegeus's consort Medea recognized Theseus immediately as Aegeus' son and worried that Theseus would be chosen as heir to Aegeus' kingdom instead of her son Medus. She tried to arrange to have Theseus killed by asking him to capture the Marathonian Bull, an emblem of Cretan power.
 On the way to
On the way to Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
, Theseus took shelter from a storm in the hut of an ancient woman named Hecale
In Greek mythology, Hecale ( grc-gre, Ἑκάλη ''Hekálē'') was an old woman who offered succor to Theseus on his way to capture the Marathonian Bull.
Mythology
On the way to Marathon to capture the Bull, Theseus sought shelter from a st ...
. She swore to make a sacrifice to Zeus if Theseus were successful in capturing the bull. Theseus did capture the bull, but when he returned to Hecale's hut, she was dead. In her honor, Theseus gave her name to one of the demes of Attica, making its inhabitants in a sense her adopted children.
When Theseus returned victorious to Athens, where he sacrificed the Bull, Medea tried to poison him. At the last second, Aegeus recognized the sandals and the sword and knocked the poisoned wine cup from Theseus's hands. Thus father and son were reunited, and Medea fled to Asia.
When Theseus appeared in the town, his reputation had preceded him, as a result of his having traveled along the notorious coastal road from Troezen and slain some of the most feared bandits there. It was not long before the Pallantides' hopes of succeeding the childless Aegeus would be lost if they did not get rid of Theseus (the Pallantides were the sons of Pallas and nephews of King Aegeus, who was then living at the royal court in the sanctuary of Delphic Apollo). So they set a trap for him. One band of them would march on the town from one side while another lay in wait near a place called Gargettus in ambush. The plan was that after Theseus, Aegeus, and the palace guards had been forced out the front, the other half would surprise them from behind. However, Theseus was not fooled. Informed of the plan by a herald named Leos, he crept out of the city at midnight and surprised the Pallantides. "Theseus then fell suddenly upon the party lying in ambush, and slew them all. Thereupon the party with Pallas dispersed," Plutarch reported.
Theseus and the Minotaur
Pasiphaë, wife of KingMinos
In Greek mythology, Minos (; grc-gre, Μίνως, ) was a King of Crete, son of Zeus and Europa. Every nine years, he made King Aegeus pick seven young boys and seven young girls to be sent to Daedalus's creation, the labyrinth, to be eaten ...
of Crete, had several children. The eldest of these, Androgeus
Androgeos or Androgeus (Ancient Greek: Ἀνδρόγεως, la, Androgeum or Androgeōs derived from ''andros'' "of a man" and ''geos'', genitive ''gē'' "earth, land") was the name of two individuals in Classical mythology.
* Androgeus, son of ...
, set sail for Athens to take part in the Panathenaic Games
The Panathenaic Games ( grc, Παναθήναια) were held every four years in Athens in Ancient Greece from 566 BC to the 3rd century AD. These Games incorporated religious festival, ceremony (including prize-giving), athletic competitions, a ...
, which were held there every four years. Being strong and skillful, he did very well, winning some events outright. He soon became a crowd favorite, much to the resentment of the Pallantides, who assassinated him, incurring the wrath of Minos.
 When King Minos heard what had befallen his son, he ordered the Cretan fleet to set sail for Athens. Minos asked Aegeus for his son's assassins, saying that if they were to be handed to him, the city would be spared. However, not knowing who the assassins were, King Aegeus surrendered the whole city to Minos' mercy. His retribution was to stipulate that at the end of every Great Year, which occurred after every seven cycles on the solar calendar, the seven most courageous youths and the seven most beautiful maidens were to board a boat and be sent as tribute to Crete, never to be seen again.
When King Minos heard what had befallen his son, he ordered the Cretan fleet to set sail for Athens. Minos asked Aegeus for his son's assassins, saying that if they were to be handed to him, the city would be spared. However, not knowing who the assassins were, King Aegeus surrendered the whole city to Minos' mercy. His retribution was to stipulate that at the end of every Great Year, which occurred after every seven cycles on the solar calendar, the seven most courageous youths and the seven most beautiful maidens were to board a boat and be sent as tribute to Crete, never to be seen again.
Minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur ( , ;. grc, ; in Latin as ''Minotaurus'' ) is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "pa ...
, a half-man, half-bull monster that lived in the Labyrinth created by Daedalus.
On the third occasion, Theseus volunteered to talk to the monster to stop this horror. He took the place of one of the youths and set off with a black sail, promising to his father, Aegeus, that if successful he would return with a white sail.Plutarch quotes Simonides to the effect that the alternate sail given by Aegeus was not white, but "a scarlet sail dyed with the tender flower of luxuriant holm oak Holm oak may refer to:
* '' Quercus ilex'', tree native to South and Southeast Europe and parts of France
* '' Quercus rotundifolia'', tree native to the Iberian Peninsula and Northwest Africa
* ''Quercus agrifolia
''Quercus agrifolia'', the Cal ...
." (Plutarch, 17.5). Like the others, Theseus was stripped of his weapons when they sailed. On his arrival in Crete, Ariadne, King Minos' daughter, fell in love with Theseus and, on the advice of Daedalus, gave him a ball of thread (a clew), so he could find his way out of the Labyrinth.Ariadne is sometimes represented in vase-paintings with the thread wound on her spindle. That night, Ariadne escorted Theseus to the Labyrinth, and Theseus promised that if he returned from the Labyrinth he would take Ariadne with him. As soon as Theseus entered the Labyrinth, he tied one end of the ball of string to the doorpost and brandished his sword which he had kept hidden from the guards inside his tunic. Theseus followed Daedalus' instructions given to Ariadne: go forwards, always down, and never left or right. Theseus came to the heart of the Labyrinth and upon the sleeping Minotaur. The beast awoke and a tremendous fight occurred. Theseus overpowered the Minotaur with his strength and stabbed the beast in the throat with his sword (according to one '' scholium'' on Pindar's Fifth Nemean Ode, Theseus strangled it).
Ship of Theseus
According to Plutarch's ''Life of Theseus'', the ship Theseus used on his return from Minoan Crete to Athens was kept in the Athenian harbor as a memorial for several centuries."The ship wherein Theseus and the youth of Athens returned had thirty oars, and was preserved by the Athenians down even to the time of Demetrius Phalereus,Demetrius Phalereus was a distinguished orator and statesman, who governed Athens for a decade before being exiled, in 307 BCE. for they took away the old planks as they decayed, putting in new and stronger timber in their place..."The ship had to be maintained in a seaworthy state, for, in return for Theseus's successful mission, the Athenians had pledged to honor Apollo every year henceforth. Thus, the Athenians sent a religious mission to the island of
Delos
The island of Delos (; el, Δήλος ; Attic: , Doric: ), near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island are ...
(one of Apollo's most sacred sanctuaries) on the Athenian state galley—the ship itself—to pay their fealty to the god. To preserve the purity of the occasion, no executions were permitted between the time when the religious ceremony began to when the ship returned from Delos, which took several weeks.
To preserve the ship, any wood that wore out or rotted was replaced; it was thus unclear to philosophers how much of the original ship remained, giving rise to the philosophical question of whether it should be considered "the same" ship or not. Such philosophical questions about the nature of identity are sometimes referred to as the " Ship of Theseus" paradox.
Regardless of these issues, the Athenians preserved the ship. They believed that Theseus had been an actual, historical figure and the ship gave them a tangible connection to their divine provenance.
Theseus and Pirithous
 Theseus's best friend was Pirithous, king of the Lapiths. Pirithous had heard stories of Theseus's courage and strength in battle but wanted proof so he rustled Theseus's herd of cattle and drove it from
Theseus's best friend was Pirithous, king of the Lapiths. Pirithous had heard stories of Theseus's courage and strength in battle but wanted proof so he rustled Theseus's herd of cattle and drove it from Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
and Theseus set out in pursuit. Pirithous took up his arms and the pair met to do battle but were so impressed with each other's gracefulness, beauty and courage they took an oath of friendship and joined the Calydonian boar hunt.
In ''Iliad'' I, Nestor
Nestor may refer to:
* Nestor (mythology), King of Pylos in Greek mythology
Arts and entertainment
* "Nestor" (''Ulysses'' episode) an episode in James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses''
* Nestor Studios, first-ever motion picture studio in Hollywood, L ...
numbers Pirithous and Theseus "of heroic fame" among an earlier generation of heroes of his youth, "the strongest men that Earth has bred, the strongest men against the strongest enemies, a savage mountain-dwelling tribe whom they utterly destroyed." No trace of such an oral tradition, which Homer's listeners would have recognized in Nestor's allusion, survived in the literary epic. Later, Pirithous was preparing to marry Hippodamia
Hippodamia (, ; also Hippodamea and Hippodameia; Ancient Greek: Ἱπποδάμεια "she who masters horses" derived from ''hippos'' "horse" and ''damazein'' "to tame") was a Greek mythological figure. She was the queen of Pisa as the wife ...
. The centaur
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as being ...
s were guests at the wedding feast, but got drunk and tried to abduct the women, including Hippodamia. The Lapiths won the ensuing battle.
In Ovid's '' Metamorphoses'' Theseus fights against and kills Eurytus, the "fiercest of all the fierce centaurs" at the wedding of Pirithous and Hippodamia
Hippodamia (, ; also Hippodamea and Hippodameia; Ancient Greek: Ἱπποδάμεια "she who masters horses" derived from ''hippos'' "horse" and ''damazein'' "to tame") was a Greek mythological figure. She was the queen of Pisa as the wife ...
.
Also according to Ovid, Phaedra, Theseus' wife, felt left out by her husband's love for Pirithous and she used this as an excuse to try to convince her stepson, Hippolytus, to accept being her lover, as Theseus also neglected his son because he preferred to spend long periods with his companion.
Abduction of Persephone and encounter with Hades
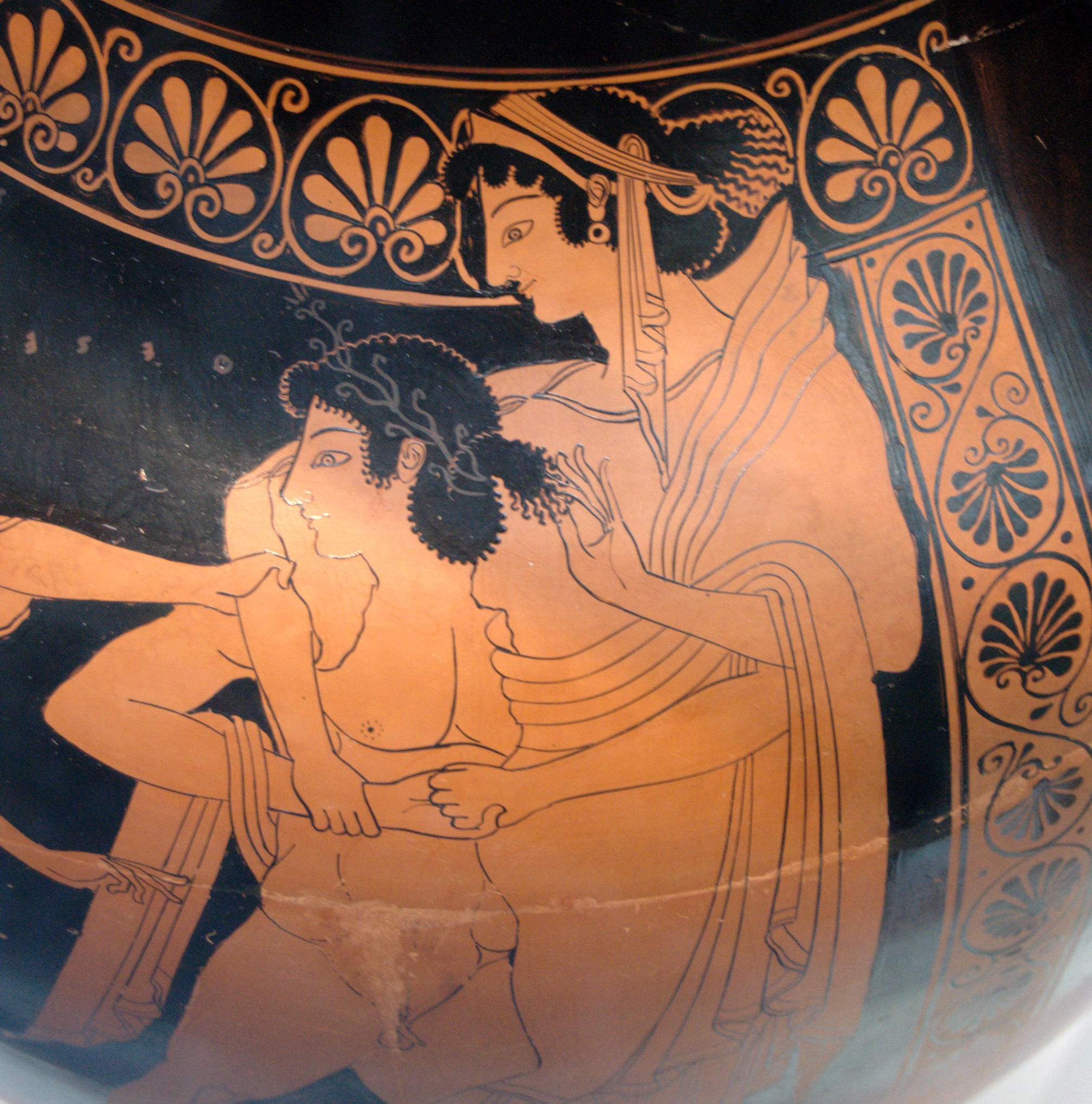
 Theseus, a great abductor of women, and his bosom companion, Pirithous, since they were sons of Zeus and Poseidon, pledged themselves to marry daughters of Zeus. Theseus, in an old tradition, chose Helen, and together they kidnapped her, intending to keep her until she was old enough to marry. Pirithous chose Persephone, even though she was already married to
Theseus, a great abductor of women, and his bosom companion, Pirithous, since they were sons of Zeus and Poseidon, pledged themselves to marry daughters of Zeus. Theseus, in an old tradition, chose Helen, and together they kidnapped her, intending to keep her until she was old enough to marry. Pirithous chose Persephone, even though she was already married to Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
, king of the underworld. They left Helen with Theseus's mother, Aethra at Aphidna, whence she was rescued by the Dioscuri.
On Pirithous's behalf they rather unwisely traveled to the underworld, domain of Persephone and her husband Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
. As they wandered through the outskirts of Tartarus, Theseus sat down to rest on a rock. As he did so he felt his limbs change and grow stiff. He tried to rise but could not. He was fixed to the rock. As he turned to cry out to his friend, he saw that Pirithous too was crying out. Around him gathered the terrible band of Furies with snakes in their hair, torches, and long whips in their hands. Before these monsters, the hero's courage failed and he was led away to eternal punishment.
For many months in half-darkness, Theseus sat immovably fixed to the rock, mourning for both his friend and for himself. In the end, he was rescued by Heracles who had come to the underworld for his 12th task. There he persuaded Persephone to forgive him for the part he had taken in the rash venture of Pirithous. So Theseus was restored to the upper air but Pirithous never left the kingdom of the dead, for when Heracles tried to free Pirithous, the underworld shook. They then decided the task was beyond any hero and left. When Theseus returned to Athens, he found that the Dioscuri had taken Helen and Aethra to Sparta.
Phaedra and Hippolytus
die with dignity
Dignified death, death with dignity, dying with dignity or dignity in dying is an ethical concept that refers to the end-of-life process avoiding suffering and maintaining control and autonomy. In general, it is usually treated as an extension of t ...
, Phaedra wrote to Theseus on a tablet claiming that Hippolytus had raped her before hanging herself. Theseus believed her and used one of the three wishes he had received from Poseidon against his son. The curse caused Hippolytus' horses to be frightened by a sea monster, usually a bull, and drag their rider to his death. Artemis would later tell Theseus the truth, promising to avenge her loyal follower on another follower of Aphrodite.
In a version recounted by the Roman playwright Seneca, entitled '' Phaedra'', after Phaedra told Theseus that Hippolytus had raped her, Theseus called upon Neptune (as he did Poseidon in Euripides' interpretation) to kill his son. Upon hearing the news of Hippolytus' death at the hands of Neptune's sea monster, Phaedra died by suicide out of guilt, for she had not intended for Hippolytus to die.
In yet another version, Phaedra simply told Theseus Hippolytus had raped her and did not kill herself. Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
sent a wild bull that terrified Hippolytus's horses.
A cult grew up around Hippolytus, associated with the cult of Aphrodite. Girls who were about to be married offered locks of their hair to him. The cult believed that Asclepius had resurrected Hippolytus and that he lived in a sacred forest near Aricia in Latium.
Other stories and death of Theseus
According to some sources, Theseus also was one of theArgonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', ...
, although Apollonius of Rhodes states in the '' Argonautica'' that Theseus was still in the underworld at this time. Both statements are inconsistent with Medea being Aegeus' wife by the time Theseus first came to Athens. With Phaedra, Theseus fathered Acamas, who was one of those who hid in the Trojan Horse during the Trojan War. Theseus welcomed the wandering Oedipus
Oedipus (, ; grc-gre, Οἰδίπους "swollen foot") was a mythical Greek king of Thebes. A tragic hero in Greek mythology, Oedipus accidentally fulfilled a prophecy that he would end up killing his father and marrying his mother, thereby ...
and helped Adrastus
In Greek mythology, Adrastus or Adrestus (Ancient Greek: Ἄδραστος or Ἄδρηστος), (perhaps meaning "the inescapable"), was a king of Argos, and leader of the Seven against Thebes. He was the son of the Argive king Talaus, but was ...
to bury the Seven against Thebes.
Lycomedes of the island of Skyros threw Theseus off a cliff after he had lost popularity in Athens. In 475 BCE, in response to an oracle, Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Batt ...
of Athens, having conquered Skyros for the Athenians, identified as the remains of Theseus "a coffin of a great corpse with a bronze spear-head by its side and a sword." (Plutarch, ''Life of Theseus''). The remains found by Cimon were reburied in Athens. The early modern name ''Theseion'' (Temple of Theseus) was mistakenly applied to the Temple of Hephaestus which was thought to be the actual site of the hero's tomb.
Adaptations of the myth


Literature
* Sophocles' tragedy '' Oedipus at Colonus'' features Theseus as a major character. * Euripides' tragedy '' Hippolytus'' and Seneca's '' Phaedra'' revolve around the death of Theseus' son. * InGeoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He wa ...
's epic chivalric romance " The Knight's Tale", one of the '' Canterbury Tales'', Theseus is the duke of Athens, husband of Ypolita, and protector of Emelye, Ypolita's sister, for whom the two knights of Thebes, Arcite and Palamon, do battle.
* Jakob Ayrer wrote the play ''Theseus'' (1618)
* Racine's '' Phèdre'' (1677) features Theseus as well as Hippolytus and the title character Phaedra.
* Theseus is a prominent character as the Duke of Athens in William Shakespeare's plays, ''A Midsummer Night's Dream
''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' is a comedy written by William Shakespeare 1595 or 1596. The play is set in Athens, and consists of several subplots that revolve around the marriage of Theseus and Hippolyta. One subplot involves a conflict amon ...
'' and '' The Two Noble Kinsmen''. Hippolyta also appears in both plays.
* F. L. Lucas
Frank Laurence Lucas (28 December 1894 – 1 June 1967) was an English classical scholar, literary critic, poet, novelist, playwright, political polemicist, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge, and intelligence officer at Bletchley Park during ...
's epic poem ''Ariadne'' (1932) is an epic reworking of the Labyrinth myth: Aegle, one of the sacrificial maidens who accompany Theseus to Crete, is Theseus's sweetheart, the Minotaur is Minos himself in a bull-mask, and Ariadne, learning on Naxos of Theseus's earlier love for Aegle, decides to leave him for the Ideal ionysus
* André Gide's ''Thésée'' (1946) is a fictional autobiography where the mythical hero of Athens, now elderly, narrates his life story from his carefree youth to his killing of the Minotaur.
* Mary Renault's '' The King Must Die'' (1958) is a dramatic retelling of the Theseus legend from his childhood in Troizen until the return from Crete to Athens. While fictional, it is generally faithful to the spirit and flavor of the best-known variations of the original story. The sequel is '' The Bull from the Sea'' (1962), about the hero's later career.
* Evangeline Walton's historical fiction novel '' The Sword is Forged'' (1983) chronicles the story of Theseus and Antiope.
*Fran Ross
Fran Ross (June 25, 1935 – September 17, 1985) was an African-American author best known for her 1974 novel ''Oreo (novel), Oreo''. She briefly wrote comedy for Richard Pryor.
Early childhood
Born on June 25, 1935, in Philadelphia, she was th ...
' 1974 novel ''Oreo'' draws heavily from the Theseus myth.
* Stephen Dobyns
Stephen J. Dobyns (born February 19, 1941) is an American poet and novelist born in Orange, New Jersey.
Life
Dobyns was born on February 19, 1941 in Orange, New Jersey to Lester L., an Episcopal minister, and Barbara Johnston Dobyns. Dobyns was r ...
, wrote the poem ''Theseus within the Labyrinth'' (1986) which provides a retelling of the myth of Ariadne, Theseus and the Minotaur, in particular the feelings of Ariadne.
* In issue No. 12 of the '' Fright Night'' comic series, entitled ''Bull-Whipped'', Theseus and the Minotaur are resurrected by the comic's Aunt Claudia Hinault, who is the reincarnation of Ariadne.
* Kir Bulychov's 1993 book ''An Attempt on Theseus' Life'' () is about a plot to assassinate a man during a virtual reality tour in which he lives through Theseus' life.
* Aleksey Ryabinin
Aleksey Valerievich Ryabinin (russian: link=no, Алексей Валерьевич Рябинин, born April 3, 1970) is a Russian Public Ombudsman for Copyright and Intellectual Property. Russian economist, politician and writer. Member of th ...
's book ''Theseus: The story of ancient gods, goddesses, kings, and warriors'' (2018) provides a retelling of the myths of Theseus, Aegeus, Minotaur, Ariadne, Pirithous and other personages of Greek mythology.
* Troy Denning's 1996 novel ''Pages of Pain'' features an amnesic Theseus fighting to recover his past while interacting with some of the more colorful beings of the Planescape universe.
* Steven Pressfield's novel ''Last of the Amazons
''Last of the Amazons'' is a 2002 novel by Steven Pressfield that recounts the legend of Theseus and the Amazons, set before the threshold of recorded history, a generation before the Trojan War. The novel's theme is the conflict between the nasc ...
'' (2002) attempts to situate Theseus's meeting and subsequent marriage to Antiope, as well as the ensuing war, in a historically plausible setting.
* Jorge Luis Borges presents a variation of the myth in a short story, "The House of Asterion
"The House of Asterion" (original Spanish title: "") is a short story by Argentine writer Jorge Luis Borges. The story was first published in 1947 in the literary magazine ''Los Anales de Buenos Aires'' and republished in Borges's short story c ...
" ().
* British comedian Tony Robinson wrote a version of the Theseus story entitled ''Theseus: Super Hero''.
* In Gene Wolfe's Book of the New Sun, set in a very distant future, the protagonist reads a story which appears to blend the myth of Theseus with the story of Battle of Hampton Roads
The Battle of Hampton Roads, also referred to as the Battle of the ''Monitor'' and ''Virginia'' (rebuilt and renamed from the USS ''Merrimack'') or the Battle of Ironclads, was a naval battle during the American Civil War.
It was fought over t ...
- presumably because of a confusion between the Minotaur and the USS Monitor
USS ''Monitor'' was an ironclad warship built for the Union Navy during the American Civil War and completed in early 1862, the first such ship commissioned by the Navy. ''Monitor'' played a central role in the Battle of Hampton Roads on 9 Mar ...
. (In this version, the Theseus character is now a a student's son.)
Opera, film, television and video game
* '' Thésée'' (1675) is an early French opera byJean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( , , ; born Giovanni Battista Lulli, ; – 22 March 1687) was an Italian-born French composer, guitarist, violinist, and dancer who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he ...
to a libretto
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or Musical theatre, musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the t ...
by Philippe Quinault, based on Ovid.
* '' Teseo'' (1713) is an opera seria
''Opera seria'' (; plural: ''opere serie''; usually called ''dramma per musica'' or ''melodramma serio'') is an Italian musical term which refers to the noble and "serious" style of Italian opera that predominated in Europe from the 1710s to abo ...
by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, ...
to a libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym, based on Quinault.
* The opera '' Hippolyte et Aricie'' (1733) by Jean-Philippe Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; – ) was a French composer and music theory, music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of Fr ...
, based on Racine, features Theseus as a character.
* Fictionalized versions of Theseus and the Minotaur appear in the 1960 Italian sword-and-sandal
Sword-and-sandal, also known as peplum (pepla plural), is a subgenre of largely Italian-made historical, mythological, or Biblical epics mostly set in the Greco-Roman antiquity or the Middle Ages. These films attempted to emulate the big-budget H ...
film '' Teseo contro il Minotauro'' and the 2006 horror film ''Minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur ( , ;. grc, ; in Latin as ''Minotaurus'' ) is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "pa ...
''.
* The video game ''Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
'' has Theseus, along with the Minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur ( , ;. grc, ; in Latin as ''Minotaurus'' ) is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "pa ...
(named Asterius in game) acting as the bosses of Elysium
Elysium (, ), otherwise known as the Elysian Fields ( grc, Ἠλύσιον πεδίον, ''Ēlýsion pedíon'') or Elysian Plains, is a conception of the afterlife that developed over time and was maintained by some Greek religious and philos ...
, the third level of the game.
* The film Immortals (2011), a unique and modernized adaptation of the legend, features Henry Cavill as Theseus in a battle to save humanity from the evil man-King Hyperion, who seeks to release imprisoned Titans to contest the Gods.
References
Notes
Citations
Further reading
Primary sources * Pseudo-Apollodorus, '' Bibliotheca'' * Ovid, Metamorphoses * Plutarch,Theseus
' Secondary sources * Burkert, Walter, ''Greek Religion'' (1985) *
Stephen Dobyns
Stephen J. Dobyns (born February 19, 1941) is an American poet and novelist born in Orange, New Jersey.
Life
Dobyns was born on February 19, 1941 in Orange, New Jersey to Lester L., an Episcopal minister, and Barbara Johnston Dobyns. Dobyns was r ...
, ''Theseus within the Labyrinth'' (1986) https://www.jstor.org/stable/20600617
* Kerényi, Karl, ''The Heroes of the Greeks'' (1959)
* Price, Anne, ''The Quest for Theseus'' (London, 1970) examines the Theseus-Minotaur-Ariadne myth and its historical basis, and later treatments and adaptations of it in Western culture.
* Ruck, Carl A.P. and Danny Staples, ''The World of Classical Myth'': ch. IX "Theseus: making the new Athens" (1994), pp. 203–222.
* Sideris, Athanasios''Theseus in Thrace. The silver lining on the clouds of the Athenian-Thracian relations in the 5th century BC''
(Sofia, 2015) presents new iconographical sources and examines the role of Theseus in the state ideology of Athens and its gift-diplomacy with Thrace. * Walker, Henry J., ''Theseus and Athens'', Oxford University Press (US 1995). The most thorough scholarly examination of Theseus's archaic origins and classical myth and cult, and his place in classical literature.
External links
Greek Myth Comix: The Story of Theseus, Pt. 1
The story of Theseus in comic-strip format, b
Greek Myth Comix
{{S-end Greek mythological heroes Mythological swordfighters Argonauts Founding monarchs Kings of Athens Kings in Greek mythology Children of Poseidon Demigods in classical mythology Heroes who ventured to Hades Characters in Book VI of the Aeneid Attican characters in Greek mythology Characters in Greek mythology Male Shakespearean characters Characters in A Midsummer Night's Dream Mythological kings