testosterone patch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 Testosterone was marketed as a
Testosterone was marketed as a
 Testosterone can be administered by
Testosterone can be administered by
pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
, an androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This inc ...
and anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids, also known more properly as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS), are steroidal androgens that include natural androgens like testosterone (medication), testosterone as well as synthetic androgens that are structurally related ...
(AAS) medication and naturally occurring
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synt ...
steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wi ...
, concerns its pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (fo ...
, pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
, and various routes of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
.
Testosterone is a naturally occurring
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synt ...
and bioidentical
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), also known as bioidentical hormone therapy (BHT) or natural hormone therapy, is the use of hormones that are identical on a molecular level with endogenous hormones in hormone replacement therapy. ...
AAS, or an agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ...
of the androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in th ...
, the biological target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
of androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This inc ...
s like endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, es ...
testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
and dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
(DHT).
Testosterone is used by both men and women and can be taken by a variety of different routes of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
.
Routes of administration
Testosterone can be taken by a variety of differentroutes of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
. These include oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or oral ...
, buccal, sublingual
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their prima ...
, intranasal
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs thus locally delivered ...
, transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
(gel
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still di ...
s, cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
s, patch
Patch or Patches may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Patch Johnson, a fictional character from ''Days of Our Lives''
* Patch (''My Little Pony''), a toy
* "Patches" (Dickey Lee song), 1962
* "Patches" (Chairmen of the Board song) ...
es, solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Soluti ...
s), vaginal
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hyme ...
(creams, gels, suppositories
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver medications by insertion into a body orifice where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, each to insert into a different sections: rectal su ...
), rectal
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the le ...
(suppositories), by intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have l ...
or subcutaneous injection
Injection or injected may refer to:
Science and technology
* Injective function, a mathematical function mapping distinct arguments to distinct values
* Injection (medicine), insertion of liquid into the body with a syringe
* Injection, in broadca ...
(in oil solution
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
s or aqueous suspension
In chemistry, a suspension is a Mixture#Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixture of a fluid that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be macroscopic, visible to the naked eye, usual ...
s), and as a subcutaneous implant
In medicine, a subcutaneous implant, or subcutaneous pellet, is an implant that is delivered under the skin into the subcutaneous tissue by surgery or injection and is used to deliver a drug for a long period of time. Examples of drugs that can ...
. The pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
of testosterone, including its bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, biological half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the bl ...
, and other parameters, differ by route of administration. Likewise, the potency
Potency may refer to:
* Potency (pharmacology), a measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system
* Virility
* Cell potency, a measure of the differentiation potential of stem cells
* In homeopathic dilutions, potency is a measure of how ...
of testosterone, and its local effects in certain tissues, for instance the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
, differ by route of administration as well. In particular, the oral route is subject to a high first-pass effect, which results in high levels of testosterone in the liver and consequent hepatic androgenic effects, as well as low potency due to first-pass metabolism in the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
s and liver into metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s like dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
and androgen conjugates. Conversely, this is not the case for non-oral routes, which bypass the first pass.
Different testosterone routes and dosages can achieve widely varying circulating testosterone levels. For purposes of comparison with normal physiological circumstances, circulating levels of total testosterone in men range from about 250 to 1,100 ng/dL (mean 630 ng/dL) and in women range from about 2 to 50 ng/dL (mean 32 ng/dL). Testosterone levels decline with age in men. In women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
(PCOS), a condition of androgen excess
Hyperandrogenism is a medical condition characterized by high levels of androgens. It is more common in women than men. Symptoms of hyperandrogenism may include acne, seborrhea (inflamed skin), pattern hair loss, hair loss on the scalp, hirsuti ...
, testosterone levels are typically around 50 to 80 ng/dL, with a range of about 30 to 140 ng/dL. Total testosterone levels are about 20-fold and free testosterone levels about 40-fold higher in men than in women on average. Similarly, testosterone production is approximately 30 times higher in men than in women.
Oral administration
Oral testosterone
Testosterone is well-absorbed but extensivelymetabolized
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
with oral administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are in ...
due to the first pass through the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
s and liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
. It is rapidly and completely inactivated in men at doses of less than 200 mg. In large doses, such as 200 mg however, significant increases in circulating testosterone levels become apparent. In addition, while a 60 mg dose has no effect on testosterone levels in men, this dose does measurably increase testosterone levels in prepubertal boys and women. The oral bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
of testosterone in young women after a single 25 mg dose was found to be 3.6 ± 2.5%. High levels of testosterone are also achieved with a 60 mg dose of oral testosterone in men with liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
. These findings are attributed to induction of liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s by testosterone and consequent activation of its own metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
. Substitution dosages of oral testosterone in men are in the range of 400 to 800 mg/day. Such doses exceed the amount of testosterone produced by the body, which is approximately 7 mg/day, by approximately 100-fold. The elimination half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the bl ...
of oral testosterone is rapid at about 5 to 7 hours. As a result, it requires administration several times per day in divided doses. Due to its limitations, such as the high doses required and necessity of multiple daily doses, oral testosterone is not used clinically in its unmodified form.
Oral testosterone has been studied in combination with a 5α-reductase inhibitor
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes of ...
to reduce its first-pass metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemi ...
and improve its bioavailability.
Oral testosterone undecanoate
Instead of in its free unesterified form, testosterone is used by oral administration in the form oftestosterone undecanoate
Testosterone undecanoate, sold under the brand names Andriol and Aveed among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication that is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, including hormone therapy for tran ...
. Due to the unique chemical properties afforded by its long fatty acid ester chain, this testosterone ester
This is a list of androgen esters, including esters (as well as ethers) of natural androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS) like nandrolone (19-nortestosterone).
Esters of na ...
is partially absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
into the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
, thereby bypassing a portion of first-pass metabolism in the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
and producing measurable increases in testosterone levels at much lower doses than free testosterone. Of oral testosterone undecanoate that reaches circulation, 90 to 100% is transported lymphatically. However, its duration
Duration may refer to:
* The amount of time elapsed between two events
* Duration (music) – an amount of time or a particular time interval, often cited as one of the fundamental aspects of music
* Duration (philosophy) – a theory of time and ...
remains short, with an elimination half-life of 1.6 hours and a mean residence time
The residence time of a fluid parcel is the total time that the parcel has spent inside a control volume (e.g.: a chemical reactor, a Lake retention time, lake, a human body). The residence time of a Set (mathematics), set of parcels is quantified ...
of 3.7 hours. Oral testosterone undecanoate is provided as 40 mg oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
-filled capsules and requires administration 2 to 4 times per day (i.e., 80 to 160 mg/day) for substitution in men. It must be taken with food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
containing at least a moderate or "normal" amount of fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
in order to achieve adequate absorption. In addition, there is very high interindividual variability
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, ...
in levels of testosterone with oral testosterone undecanoate. The bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
of oral testosterone undecanoate taken with food is 3 to 7%. Inappropriately high levels of testosterone have been observed with 10 to 40 mg/day oral testosterone undecanoate in women. The oral bioavailability of testosterone undecanoate in young women after a single 40 mg dose was found to be 6.8 ± 3.3%.
A novel self-emulsifying formulation of oral testosterone undecanoate in 300-mg capsules for use once per day is under development.
First-pass effect and differences
Oral testosterone and oral testosterone undecanoate are nothepatotoxic
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn fro ...
, unlike orally administered 17α-alkylated anabolic steroids such as methyltestosterone
Methyltestosterone, sold under the brand names Android, Metandren, and Testred among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, at low ...
and fluoxymesterone
Fluoxymesterone, sold under the brand names Halotestin and Ultandren among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, breast cancer in w ...
but similarly to parenteral
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
routes and forms of bioidentical
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), also known as bioidentical hormone therapy (BHT) or natural hormone therapy, is the use of hormones that are identical on a molecular level with endogenous hormones in hormone replacement therapy. ...
testosterone like injections.
Buccal administration
Testosterone can be used bybuccal administration
Buccal administration is a topical route of administration by which drugs held or applied in the buccal () area (in the cheek) diffuse through the oral mucosa ( tissues which line the mouth) and enter directly into the bloodstream. Buccal admini ...
(e.g., brand name Striant).
Sublingual administration
Testosterone can be used bysublingual administration
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their primar ...
. A 10 mg sublingual tablet
Tablet may refer to:
Medicine
* Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill"
Computing
* Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the s ...
with the brand name Testoral was previously marketed for use one to four times per day in men.
Inhalational administration
Testosterone has been studied byinhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
.
Intranasal administration
Testosterone can be used byintranasal administration
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs thus locally delivere ...
(e.g., brand name Natesto).
Transdermal administration
Testosterone is available fortransdermal administration
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
in the form of gel
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still di ...
s, cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
s, scrotal
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum co ...
and non-scrotal patch
Patch or Patches may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Patch Johnson, a fictional character from ''Days of Our Lives''
* Patch (''My Little Pony''), a toy
* "Patches" (Dickey Lee song), 1962
* "Patches" (Chairmen of the Board song) ...
es, and axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
ry solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Soluti ...
s.
Transdermal testosterone gel has a bioavailability of about 8 to 14% when administered to recommended skin sites including the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
, arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the ...
s, shoulders
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder mak ...
, and thigh
In human anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone ...
s. Scrotal
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum co ...
skin is the thinnest skin of the body and has enhanced absorption characteristics relative to other skin areas. Application of testosterone gels and creams to the scrotum has been studied and achieves much higher levels of testosterone than conventional skin sites. Scrotal application of testosterone requires approximately 5-fold lower doses relative to non-scrotal application.
The development of transdermal preparations of testosterone (and of progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the m ...
) has been more difficult than the case of estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development of f ...
. This is because testosterone levels in men are about 100 to 1,000 times higher than estradiol levels in women (300 to 1,000 ng/dL vs. 50 to 150 pg/mL, respectively). Non-scrotal testosterone patches were assessed and were found to be ineffective in raising testosterone levels in men. As a result, scrotal testosterone patches were initially marketed. Subsequently, however, non-scrotal testosterone patches with special permeation enhancers that could successfully increase testosterone levels were developed and marketed. However, non-scrotal testosterone patches nonetheless require a large skin area for application (up to 60 cm2) and must be replaced daily.
Supraphysiological levels of dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
(DHT) occur with scrotal application of testosterone, whereas this does not occur with non-scrotal transdermal application. This is due to the high expression
Expression may refer to:
Linguistics
* Expression (linguistics), a word, phrase, or sentence
* Fixed expression, a form of words with a specific meaning
* Idiom, a type of fixed expression
* Metaphorical expression, a particular word, phrase, o ...
of 5α-reductase
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes of ...
in scrotal skin. Estradiol levels are similar with scrotal versus non-scrotal application of transdermal testosterone.
Low-dose transdermal testosterone patches in women have been found to result in testosterone levels of 64 ng/dL with 150 μg/day and 102 ng/dL with 300 μg/day. When testosterone is used transdermally in women or transmen, hair growth at the application sites can happen.
Vaginal administration
In those who are biologically female, testosterone can be used byvaginal administration
Intravaginal administration is a route of administration where the substance is applied inside the vagina. Pharmacologically, it has the potential advantage to result in effects primarily in the vagina or nearby structures (such as the vaginal po ...
of cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
s, suppositories
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver medications by insertion into a body orifice where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, each to insert into a different sections: rectal su ...
, and vaginal ring
Vaginal rings (also known as intravaginal rings, or V-Rings) are polymeric drug delivery devices designed to provide controlled release of drugs for intravaginal administration over extended periods of time. The ring is inserted into the vagina a ...
s available from compounding pharmacies
In the field of pharmacy, compounding (performed in compounding pharmacies) is preparation of a custom formulation of a medication to fit a unique need of a patient that cannot be met with commercially available products. This may be done for me ...
.
Rectal administration
 Testosterone was marketed as a
Testosterone was marketed as a suppository
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver medications by insertion into a body orifice where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, each to insert into a different sections: rectal su ...
for rectal administration
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum's blood vessels,The rectum has numerous blood vessels available to absorb drugs. and flow into the body's ci ...
by Ferring Pharmaceuticals
Ferring Pharmaceuticals is a Swiss multinational biopharmaceutical company specialising in areas such as reproductive health, maternal health, gastroenterology and urology. Ferring has been developing treatments for mothers and babies for over 50 ...
from the early 1960s under brand names such as Rektandron and Testosteron. Rectal administration of testosterone avoids the first-pass effect with oral administration similarly to other non-oral routes. A single 40 mg dose of rectal testosterone has been found to result in maximal testosterone levels of almost 1,200 ng/dL within 30 minutes. Subsequently, testosterone levels steadily decline, reaching levels of about 700 ng/dL after 4 hours and levels of about 400 ng/dL after 8 hours. Other studies have also assessed the use of rectal testosterone, with similar findings. Rectal use of testosterone requires administration two or three times per day to maintain adequate testosterone levels. The route is poorly accepted, owing to its inconvenience. Rectal testosterone has been used in transmasculine hormone therapy
Masculinizing hormone therapy, also known as transmasculine hormone therapy, or female-to-male (or FTM) hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy and gender affirming therapy which is used to change the secondary sexual characteristics of tr ...
.
Intramuscular injection
 Testosterone can be administered by
Testosterone can be administered by intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have ...
either as an aqueous suspension
In chemistry, a suspension is a Mixture#Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixture of a fluid that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be macroscopic, visible to the naked eye, usual ...
of testosterone or as an oil solution
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
or aqueous suspension of testosterone ester
This is a list of androgen esters, including esters (as well as ethers) of natural androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS) like nandrolone (19-nortestosterone).
Esters of na ...
s such as testosterone propionate
Testosterone propionate, sold under the brand name Testoviron among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It has also been used to treat breast cance ...
, testosterone enanthate
Testosterone enanthate, sold under the brand names Delatestryl and Xyosted among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone th ...
, testosterone cypionate
Testosterone cypionate, sold under the brand name Depo-Testosterone among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone therapy fo ...
, testosterone undecanoate
Testosterone undecanoate, sold under the brand names Andriol and Aveed among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication that is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, including hormone therapy for tran ...
, and testosterone isobutyrate
Testosterone isobutyrate, sold under the brand names Agovirin-Depot and Perandren M among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid medication and a testosterone ester which is used for indications such as low testosterone levels in men and de ...
. An even longer-acting testosterone ester that was developed but ultimately never marketed is testosterone buciclate
Testosterone buciclate (developmental code names 20 Aet-1, CDB-1781) is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed. It was developed in collaboration by the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the N ...
. These preparations are prodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug ...
s of progesterone that have a long-lasting depot effect
A depot injection is a term for an injection formulation of a medication which releases slowly over time to permit less frequent administration of a medication. They are designed to increase medication adherence and consistency, especially in pa ...
when injected into muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
or fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
, ranging from days to months in duration
Duration may refer to:
* The amount of time elapsed between two events
* Duration (music) – an amount of time or a particular time interval, often cited as one of the fundamental aspects of music
* Duration (philosophy) – a theory of time and ...
.
The bioavailability of drugs that are administered intramuscularly is generally almost 95%.
As oil solutions by intramuscular injection, the elimination half-lives of testosterone esters are 0.8 days for testosterone propionate, 4.5 days for testosterone enanthate, 20.9 days (in tea seed oil
Tea seed oil (also known as ''camellia oil'', ''camellia seed oil'', ''teanut oil'') is an edible plant oil. It is obtained from the seeds of ''Camellia oleifera''.
''Camellia sasanqua'' is also given as a source of 'tea seed oil.
Description
Th ...
) and 33.9 days (in caster oil) for testosterone undecanoate, and 29.5 days for testosterone buciclate. The pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
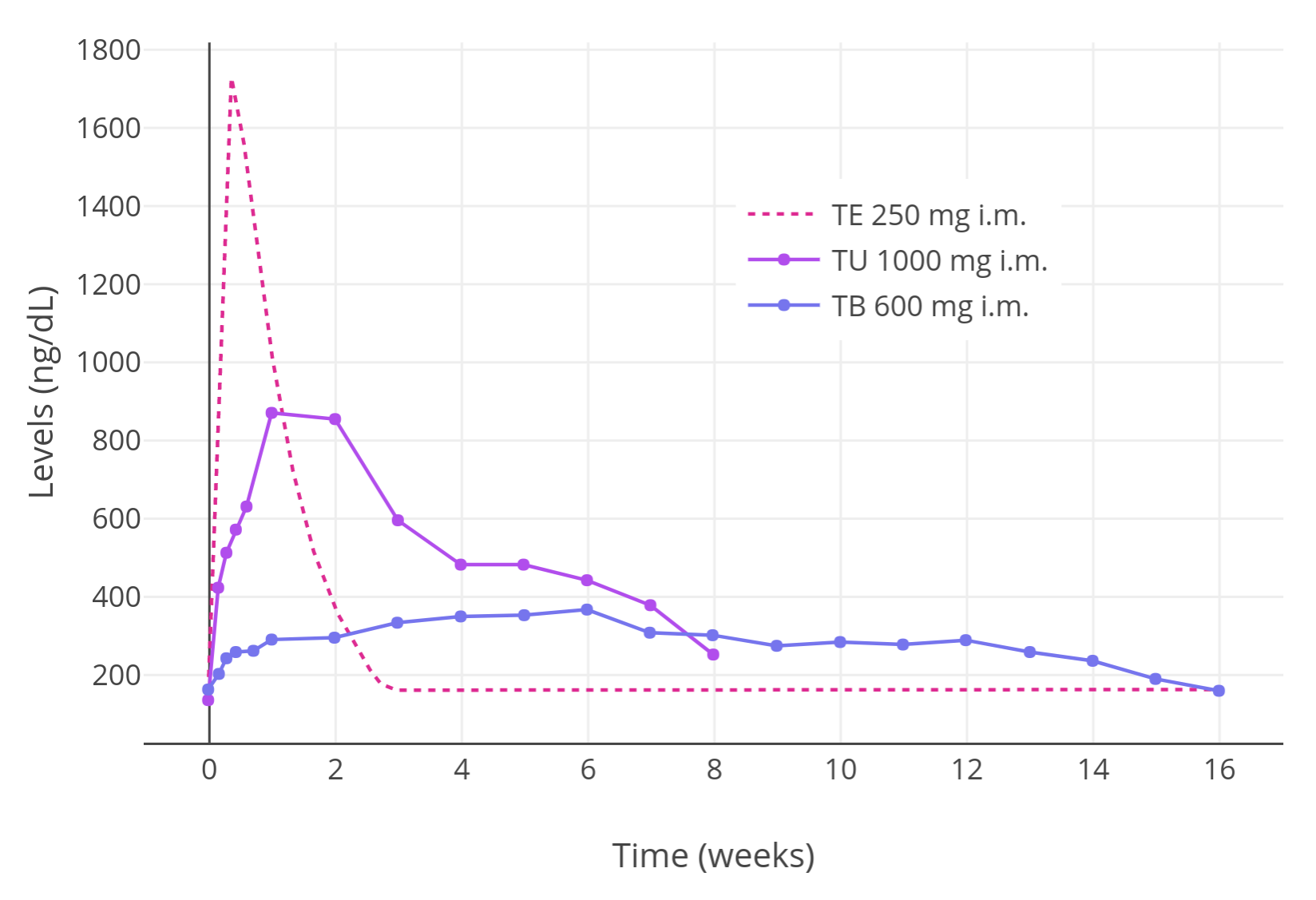
of testosterone cypionate are said to be the same as those of testosterone enanthate, with "extremely comparable" patterns of testosterone release. Due to their varying and different elimination half-lives, the different intramuscular testosterone esters are administered with differing frequencies. Testosterone propionate is injected two to three times per week, testosterone enanthate and testosterone cypionate are injected once every two to four weeks, and testosterone undecanoate and testosterone buciclate are injected once every 10 to 14 weeks. Due to its relatively short duration, testosterone propionate is now relatively little used and testosterone undecanoate is the preferred testosterone ester for intramuscular use. Testosterone undecanoate and testosterone buciclate can be injected intramuscularly as infrequently as four times per year.
High doses of testosterone esters by intramuscular injection have been studied in healthy young men. Levels of testosterone with intramuscular injections of testosterone cypionate were about 700 ng/dL for 100 mg/week, 1100 ng/dL for 250 mg/week, and 2000 ng/dL for 500 mg/week. In another study, testosterone levels with 600 mg/week testosterone enanthate by intramuscular injection were 2,800–3,200 ng/dL.
Intramuscular injection of testosterone propionate as an oil solution, aqueous suspension, and emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Althoug ...
has been compared.
Intramuscular injection of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
-containing biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
microsphere
Microparticles are particles between 0.1 and 100 μm in size. Commercially available microparticles are available in a wide variety of materials, including ceramics, glass, polymers, and metals. Microparticles encountered in daily life includ ...
s has been studied.
Subcutaneous injection
Testosterone esters liketestosterone enanthate
Testosterone enanthate, sold under the brand names Delatestryl and Xyosted among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone th ...
and testosterone cypionate
Testosterone cypionate, sold under the brand name Depo-Testosterone among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone therapy fo ...
can be given by subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, ...
instead of intramuscular injection. Studies have shown that subcutaneous injection of testosterone and closely related esters in oil like testosterone cypionate
Testosterone cypionate, sold under the brand name Depo-Testosterone among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone therapy fo ...
, testosterone enantate, and nandrolone decanoate
Nandrolone decanoate, sold under the brand name Deca-Durabolin among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used primarily in the treatment of anemias and wasting syndromes, as well as osteoporosis in menopausal wo ...
is effective and has similar pharmacokinetics to intramuscular injection.
Subcutaneous implant
Testosterone can be administered in the form of a subcutaneous pellet implant. The bioavailability of testosterone when administered as a subcutaneous pellet implant is virtually 100%. Levels of testosterone vary considerably between individuals, but are fairly constant within individuals. The absorption half-life of subdermal testosterone implants is 2.5 months. The replacement interval is once every four to six months. A single 50 mg testosterone pellet implanted every 4 to 6 months has been found to result in testosterone levels of 70 to 90 ng/dL in women.Intravenous injection
Testosterone esters like testosterone enanthate arehydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
into testosterone so rapidly in the blood that testosterone and testosterone enanthate have nearly identical pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
when administered via intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
.
General
Absorption
The oralbioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
of testosterone is very low. The bioavailability of oral testosterone undecanoate is 3 to 7%. Topical testosterone gels have a bioavailability of about 8 to 14% when administered to recommended skin sites including the abdomen, arms, shoulders, and thighs. The bioavailability of testosterone by subcutaneous implant is virtually 100%. The bioavailability of drugs that are administered intramuscularly is generally almost 95%.
Distribution
In the circulation, 97.0 to 99.5% of testosterone is bound to plasma proteins, with 0.5 to 3.0% unbound. It is tightly bound to SHBG and weakly toalbumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins ...
. Of circulating testosterone, 30 to 44% is bound to SHBG while 54 to 68% is bound to albumin. Testosterone that is unbound is referred to as ''free testosterone'' and testosterone that is bound to albumin is referred to as ''bioavailable testosterone''. Unlike testosterone that is bound to SHBG, bioavailable testosterone is bound to plasma proteins weakly enough such that, similarly to free testosterone, it may be biologically active, at least to a certain extent. When referenced collectively (i.e., free, bioavailable, and SHBG-bound), circulating testosterone is referred to as ''total testosterone''.
Metabolism
Testosterone ismetabolized
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
primarily in the liver mainly (90%) by reduction via 5α- and 5β-reductase and conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
* Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
* Complex conjugation, the chang ...
via glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve glycosid ...
and sulfation
Sulfation is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected less directly. Regardless of the mechanism, the ...
. The major urinary
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, con ...
metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s of testosterone are androsterone glucuronide
Androsterone glucuronide (ADT-G) is a major circulating and urinary metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It accounts for 93% of total androgen glucuronides in women. ADT-G is formed from androsterone by UDP-glucuronosyltransf ...
and etiocholanolone glucuronide.
The elimination half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the bl ...
of testosterone varies depending on the route of administration and formulation and on whether or not it is esterified. The elimination half-life of testosterone in the blood or by intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
is only about 10 minutes. Conversely, testosterone and testosterone ester
This is a list of androgen esters, including esters (as well as ethers) of natural androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS) like nandrolone (19-nortestosterone).
Esters of na ...
s in oil solution
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
or crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
aqueous suspension
In chemistry, a suspension is a Mixture#Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixture of a fluid that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be macroscopic, visible to the naked eye, usual ...
administered by intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have l ...
or subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, ...
have much longer half-lives, in the range of days to months, due to slow release from the injection site.
Elimination
Testosterone and its metabolites are eliminated inurine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excretion, excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cel ...
. It is excreted
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after lea ...
mainly as androsterone glucuronide
Androsterone glucuronide (ADT-G) is a major circulating and urinary metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It accounts for 93% of total androgen glucuronides in women. ADT-G is formed from androsterone by UDP-glucuronosyltransf ...
and etiocholanolone glucuronide. It is also excreted to a small extent as other conjugates such as testosterone glucuronide (1%), testosterone sulfate (0.03%), and androstanediol glucuronide
3α-Androstanediol glucuronide (3α-ADG) is a metabolite formed from human androgens; compounds involved in the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics. It is formed by the glucuronidation of both dihydrotestosterone and testosterone ...
s. Only a very small amount of testosterone (less than 0.01%) is found unchanged in the urine.
See also
* Pharmacodynamics of estradiol *Pharmacokinetics of estradiol
The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.
Estradiol is a naturally occurring and bioidentical estrogen, ...
* Pharmacodynamics of progesterone
* Pharmacokinetics of progesterone
The pharmacokinetics of progesterone, concerns the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration of progesterone.
Progesterone is a naturally occurring and bioidentical progestogen, or an agonist of the progesterone rec ...
*
References
Further reading
* * {{Portal bar, Medicine Testosterone Medication pharmacology