terminology of the Low Countries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The
The

/ref> So in this sense ''theodiscus'' referred to the Germanic language spoken in Great Britain, which was later replaced by the name Old English, Englisc. By the late 14th century, ''þēodisc'' had given rise to
 Place names with "low(er)" or ''neder'', ''lage'', ''nieder'', ''nether'', ''nedre'', ''bas'' and ''inferior'' are used everywhere in Europe. They are often used in contrast with an upstream or higher area whose name contains words such as "upper", ''boven'', ''oben'', ''supérieure'' and ''haut''. Both downstream at the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, and low at the plain near the
Place names with "low(er)" or ''neder'', ''lage'', ''nieder'', ''nether'', ''nedre'', ''bas'' and ''inferior'' are used everywhere in Europe. They are often used in contrast with an upstream or higher area whose name contains words such as "upper", ''boven'', ''oben'', ''supérieure'' and ''haut''. Both downstream at the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, and low at the plain near the
 Apart from its topographic usage for the then multi-government area of the Low Countries, the 15th century saw the first attested use of ''Nederlandsch'' as a term for the Dutch language, by extension hinting at a common ethnonym for people living in different fiefdoms. This was used alongside the long-standing ''Duytsch'' (the Early Modern spelling of the earlier ''Dietsc'' or ''Duutsc''). The most common Dutch term for the Dutch language remained ''Nederduytsch'' or ''Nederduitsch'' until it was gradually superseded by ''Nederlandsch'' in the early 1900s, the latter becoming the sole name for the language by 1945. Earlier, from the mid-16th century on, the
Apart from its topographic usage for the then multi-government area of the Low Countries, the 15th century saw the first attested use of ''Nederlandsch'' as a term for the Dutch language, by extension hinting at a common ethnonym for people living in different fiefdoms. This was used alongside the long-standing ''Duytsch'' (the Early Modern spelling of the earlier ''Dietsc'' or ''Duutsc''). The most common Dutch term for the Dutch language remained ''Nederduytsch'' or ''Nederduitsch'' until it was gradually superseded by ''Nederlandsch'' in the early 1900s, the latter becoming the sole name for the language by 1945. Earlier, from the mid-16th century on, the

 From the 17th century onwards, the County of Holland was the most powerful region in the current Netherlands. The counts of Holland were also counts of Hainaut,
From the 17th century onwards, the County of Holland was the most powerful region in the current Netherlands. The counts of Holland were also counts of Hainaut,

 As the Low Country's prime duchy, with the only and oldest scientific centre (the University of Leuven), Brabant has served as a pars pro toto for the whole of the Low Countries, for example in the writings of
As the Low Country's prime duchy, with the only and oldest scientific centre (the University of Leuven), Brabant has served as a pars pro toto for the whole of the Low Countries, for example in the writings of
Origin and History of the term "Dutch"
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Names For The Dutch Language Name of the Dutch language Germanic languages Low Franconian languages Language naming Dutch culture Geography of the Netherlands

 The
The Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
comprise the coastal Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta region in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, whose definition usually includes the modern countries of Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. Both Belgium and the Netherlands derived their names from earlier names for the region, due to ''nether'' meaning "low" and ''Belgica'' being the Latinized name for all the Low Countries, a nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agre ...
that became obsolete after Belgium's secession in 1830.
The Low Countries—and the Netherlands and Belgium—had in their history exceptionally many and widely varying names, resulting in equally varying names in different languages. There is diversity even within languages: the use of one word for the country and another for the adjective form is common. This holds for English, where ''Dutch'' is the adjective form for the country "the Netherlands". Moreover, many languages have the same word for both the country of the Netherlands and the region of the Low Countries, e.g., French (''les Pays-Bas'') and Spanish (''los Países Bajos''). The complicated nomenclature is a source of confusion for outsiders, and is due to the long history of the language, the culture and the frequent change of economic and military power within the Low Countries over the past 2,000 years.
History
The historic Low Countries made up much of Frisia, home to the Frisii, and the Roman provinces ofGallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 5 ...
and Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippine ...
, home to the Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by J ...
and Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
like the Batavi. Throughout the centuries, the names of these ancestors have been in use as a reference to the Low Countries, in an attempt to define a collective identity. But it was in the fourth and fifth centuries that a Frankish confederation of Germanic tribes significantly made a lasting change by entering the Roman provinces and starting to build the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
, of which the Low Countries formed a core part.
By the eighth century, most of the Franks had exchanged their Germanic Franconian languages for the Latin-derived Romances
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
. However, the Franks that stayed in the Low Countries had kept their original language, i.e., Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aro ...
, also known as "Old Low Franconian" among linguists. At the time the language was spoken, it was known as *''þiudisk'', meaning "of the people"—as opposed to the Latin language "of the clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the t ...
"—which is the source of the English word ''Dutch''. Now an international exception, it used to have in the Dutch language itself a cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical e ...
with the same meaning, i.e., ''Diets(c)'' or ''Duuts(c)''.
The designation "low" to refer to the region has also been in use many times. First by the Romans, who called it Germania "Inferior". After the Frankish empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
was divided several times, most of it became the Duchy of Lower Lorraine in the tenth century, where the Low Countries politically have their origin. Lower Lorraine disintegrated into a number of duchies, counties and bishoprics. Some of these became so powerful, that their names were used as a '' pars pro toto'' for the Low Countries, i.e., Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
and to a lesser extent Brabant. Burgundian Burgundian can refer to any of the following:
*Someone or something from Burgundy.
*Burgundians, an East Germanic tribe, who first appear in history in South East Europe. Later Burgundians colonised the area of Gaul that is now known as Burgundy (F ...
, and later Habsburg rulers added one by one the Low Countries' polities in a single territory, and it was at their francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the ...
courts that the term ''les pays de par deçà'' arose, that would develop in ''Les Pays-Bas'' or in English "Low Countries" or "Netherlands".
''Theodiscus'' and derivatives

''Dutch'', ''Diets'' and ''Duyts''
English is the only language to use the adjective ''Dutch'' for the language of the Netherlands and Flanders or something else from the Netherlands. The word is derived fromProto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
. The stem of this word, , meant "people" in Proto-Germanic, and was an adjective-forming suffix, of which is the Modern English form. ' was its Latinised form and used as an adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
referring to the Germanic vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
s of the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
. In this sense, it meant "the language of the common people", that is, the native Germanic language. The term was used as opposed to Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
, the ''non''-native language of writing and the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. It was first recorded in 786, when the Bishop of Ostia
The Roman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of Ostia is an ecclesiastical territory located within the Metropolitan City of Rome in Italy. It is one of the seven suburbicarian dioceses. The incumbent Bishop is cardinal Giovanni Battista Re. Since ...
writes to Pope Adrian I about a synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word mea ...
taking place in Corbridge
Corbridge is a village in Northumberland, England, west of Newcastle and east of Hexham. Villages nearby include Halton, Acomb, Aydon and Sandhoe.
Etymology
Corbridge was known to the Romans as something like ''Corstopitum'' or ''Coriosopit ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, where the decisions are being written down "tam Latine quam theodisce" meaning "in Latin as well as Germanic".M. Philippa e.a. (2003–2009) Etymologisch Woordenboek van het Nederlands iets/ref>Cornelis Dekker: The Origins of Old Germanic Studies in the Low Countrie/ref> So in this sense ''theodiscus'' referred to the Germanic language spoken in Great Britain, which was later replaced by the name Old English, Englisc. By the late 14th century, ''þēodisc'' had given rise to
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
''duche'' and its variants, which were used as a blanket term for all the non-Scandinavian Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
spoken on the European mainland. Historical linguists have noted that the medieval "Duche" itself most likely shows an external Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
influence, in that it shows a voiced alveolar stop rather than the expected voiced dental fricative
The voiced dental fricative is a consonant sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English-speakers as the ''th'' sound in ''father''. Its symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is eth, or and was taken from the Old En ...
. This would be a logical result of the Medieval English wool trade, which brought the English in close linguistic contact with the cloth merchants living in the Dutch-speaking cities of Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Scienc ...
and Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest i ...
, who at the time, referred to their language as ''dietsc''.
Its exact meaning is dependent on context, but tends to be vague regardless. When concerning language, the word ''duche'' could be used as a hypernym for several languages (The North est Contrey which lond spekyn all maner Duche tonge – The North f Europe
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''.
Hi ...
is an area, in which all lands speak all manner of "Dutch" languages) but it could also suggest singular use (In Duche a rudder is a knyght – In "Dutch" a rudder Dutch: ridder">Dutch_language.html" ;"title="f. Dutch language">Dutch: ridderis a knight) in which case linguistic and/or geographic pointers need to be used to determine or approximate what the author would have meant in modern terms, which can be difficult.H. Kurath: Middle English Dictionary, part 14, University of Michigan Press, 1952, 1345. For example, in his poem ''Constantyne'', the English chronicler John Hardyng (1378–1465) specifically mentions the inhabitants of three Dutch-speaking fiefdoms (Flanders, Guelders and Brabant) as travel companions, but also lists the far more general "Dutchemēne" and "Almains", the latter term having an almost equally broad meaning, though being more restricted in its geographical use; usually referring to people and locaties within modern Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, Switzerland and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
:
By early 17th century, general use of the word Dutch had become exceedingly rare in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and it became an exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, o ...
specifically tied to the modern Dutch, i.e. the Dutch-speaking inhabitants of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. Many factors facilitated this, including close geographic proximity, trade and military conflicts, for instance the Anglo-Dutch Wars.M. Philippa e.a. (2003-2009) Etymologisch Woordenboek van het Nederlands uits/ref>L. Weisgerber, Deutsch als Volksname 1953 Due to the latter, "Dutch" also became a pejorative label pinned by English speakers on almost anything they regard as inferior, irregular, or contrary to their own practice. Examples include "Dutch treat" (each person paying for himself), "Dutch courage" (boldness inspired by alcohol), "Dutch wife" (a type of sex doll) and "Double Dutch" (gibberish, nonsense) among others.
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, the word "Dutch" remained somewhat ambiguous until the start of the 19th century. Generally, it referred to the Dutch, their language or the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, but it was also used as an informal monniker (for example in the works of James Fenimore Cooper
James Fenimore Cooper (September 15, 1789 – September 14, 1851) was an American writer of the first half of the 19th century, whose historical romances depicting colonist and Indigenous characters from the 17th to the 19th centuries brought h ...
and Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories " Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Lege ...
) for people who would today be considered Germans or German-speaking, most notably the Pennsylvania Dutch
The Pennsylvania Dutch ( Pennsylvania Dutch: ), also known as Pennsylvania Germans, are a cultural group formed by German immigrants who settled in Pennsylvania during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. They emigrated primarily from German-sp ...
. This lingering ambiguity was most likely caused by close proximity to German-speaking immigrants, who referred to themselves or (in the case of the Pennsylvania Dutch) their language as "Deutsch" or "Deitsch", rather than archaic use of the term "Dutch"
In the Dutch language itself, Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aro ...
''*thiudisk'' evolved into a southern variant ''duutsc'' and a western variant ''dietsc'' in Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
, which were both known as ''duytsch'' in Early Modern Dutch. In the earliest sources, its primary use was to differentiate between Germanic and the Romance dialects, as expressed by the Middle Dutch poet Jan van Boendale, who wrote:J. de Vries (1971), Nederlands Etymologisch Woordenboek
During the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD ...
"Dietsc/Duutsc" was increasingly used as an umbrella term for the specific Germanic dialects spoken in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, its meaning being largely implicitly provided by the regional orientation of medieval Dutch society: apart from the higher echelons of the clergy and nobility, mobility was largely static and hence while "Dutch" could by extension also be used in its earlier sense, referring to what to today would be called Germanic dialects as opposed to Romance dialects, in many cases it was understood or meant to refer to the language now known as Dutch. Apart from the sparsely populated eastern borderlands, there was little to no contact with contemporary speakers of German dialects, let alone a concept of the existence of German as language in its modern sense among the Dutch. Because medieval trade focused on travel by water and with the most heavily populated areas adjacent to Northwestern France, the average 15th century Dutchman stood a far greater chance of hearing French or English than a dialect of the German interior, despite its relative geographical closeness. Medieval Dutch authors had a vague, generalized sense of common linguistic roots between their language and various German dialects, but no concept of speaking the same language existed. Instead they saw their linguistic surroundings mostly in terms of small scale regiolects.L. De Grauwe: Emerging Mother-Tongue Awareness: The special case of Dutch and German in the Middle Ages and the early Modern Period (2002), p. 102.
In the 19th century, the term "Diets" was revived by Dutch linguists and historians as a poetic name for Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
and its literature.
''Nederduits''
In the second half of the 16th century theneologism
A neologism Greek νέο- ''néo''(="new") and λόγος /''lógos'' meaning "speech, utterance"] is a relatively recent or isolated term, word, or phrase that may be in the process of entering common use, but that has not been fully accepted int ...
"Nederduytsch" (literally: Nether-Dutch, Low-Dutch) appeared in print, in a way combining the earlier "Duytsch" and "Nederlandsch" into one compound. The term was preferred by many leading contemporary grammarians such as Balthazar Huydecoper, Arnold Moonen and Jan ten Kate because it provided a continuity with Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
("Duytsch" being the evolution of medieval "Dietsc"), was at the time considered the proper translation of the Roman Province of Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippine ...
(which not only encompassed much of the contemporary Dutch-speaking area / Netherlands, but also added classical prestige to the name) and amplified the dichotomy between Early Modern Dutch and the "Dutch" (German) dialects spoken around the Middle Rhine, Middle and Upper Rhine
The Upper Rhine (german: Oberrhein ; french: Rhin Supérieur) is the section of the Rhine between Basel in Switzerland and Bingen in Germany, surrounded by the Upper Rhine Plain. The river is marked by Rhine-kilometres 170 to 529 (the ...
which had begun to be called ''overlantsch'' of ''hoogdutysch'' (literally: Overlandish, High-"Dutch") by Dutch merchants sailing upriver.G.A.R. de Smet, Die Bezeichnungen der niederländischen Sprache im Laufe ihrer Geschichte; in: Rheinische Vierteljahrsblätter 37 (1973), p. 315-327 Though "Duytsch" forms part of the compound in both Nederduytsch and Hoogduytsch, this should not be taken to imply that the Dutch saw their language as being especially closely related to the German dialects spoken in Southerwestern Germany. On the contrary, the term "Hoogduytsch" specifically came into being as a special category because Dutch travelers visiting these parts found it hard to understand the local vernacular: in a letter dated to 1487 a Flemish merchant from Bruges instructs his agent to conduct trade transactions in Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
in French, rather than the local tongue to avoid any misunderstandings. In 1571 use of "Nederduytsch" greatly increased because the Synod of Emden chose the name "Nederduytsch Hervormde Kerk" as the official designation of the Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church (, abbreviated NHK) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the original denomination of the Dutch Royal Family a ...
. The synods choice of "Nederduytsch" over the more dominant "Nederlandsch", was inspired by the phonological similarities between "neder-" and "nederig" (the latter meaning "humble") and the fact that it did not contain a worldly element ("land"), whereas "Nederlandsch" did.
As the Dutch increasingly referred to their own language as "Nederlandsch" or "Nederduytsch", the term "Duytsch" became more ambiguous. Dutch humanists, started to use "Duytsch" in a sense which would today be called "Germanic", for example in a dialogue recorded in the influential Dutch grammar book "Twe-spraack vande Nederduitsche letterkunst", published in 1584:
Beginning in the second half 16th century, the nomenclature gradually became more fixed, with "Nederlandsch" and "Nederduytsch" becoming the preferred terms for Dutch and with "Hooghduytsch" referring to the language today called German. Initially the word "Duytsch" itself remained vague in exact meaning, but after the 1650s a trend emerges in which "Duytsch" is taken as the shorthand for "Hooghduytsch". This process was probably accelerated by the large number of Germans employed as agricultural day laborers and mercenary soldiers in the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
and the ever increasing popularity of "Nederlandsch" and "Nederduytsch" over "Duytsch", the use of which had already been in decline for over a century, thereby acquiring its current meaning (German) in Dutch.
In the Dutch language itself, ''Diets(c)'' (later ''Duyts'') was used as one of several Exonym and endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, o ...
s. As the Dutch increasingly referred to their own language as "Nederlandsch" or "Nederduytsch", the term "Duytsch" became more ambiguous. Dutch humanists, started to use "Duytsch" in a sense which would today be called "Germanic". Beginning in the second half 16th century, the nomenclature gradually became more fixed, with "Nederlandsch" and "Nederduytsch" becoming the preferred terms for Dutch and with "Hooghduytsch" referring to the language today called German. Initially the word "Duytsch" itself remained vague in exact meaning, but after the 1650s a trend emerges in which "Duytsch" is taken as the shorthand for "Hooghduytsch". This process was probably accelerated by the large number of Germans employed as agricultural day laborers and mercenary soldiers in the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
and the ever increasing popularity of "Nederlandsch" and "Nederduytsch" over "Duytsch", the use of which had already been in decline for over a century, thereby acquiring its current meaning (German) in Dutch.
In the late 19th century "Nederduits" was reintroduced to Dutch through the German language, where prominent linguists, such as the Brothers Grimm
The Brothers Grimm ( or ), Jacob (1785–1863) and Wilhelm (1786–1859), were a brother duo of German academics, philologists, cultural researchers, lexicographers, and authors who together collected and published folklore. They are among th ...
and Georg Wenker, in the nascent field of German and Germanic studies used the term to refer to Germanic dialects which had not taken part in the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probably ...
. Initially this group consisted of Dutch, English, Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
and Frisian, but in modern scholarship only refers to Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
-varieties. Hence in contemporary Dutch, "Nederduits" is used to describe Low German varieties, specifically those spoken in Northern Germany as the varieties spoken in the eastern Netherlands, while related, are referred to as "Nedersaksisch".
Names from low-lying geographical features
 Place names with "low(er)" or ''neder'', ''lage'', ''nieder'', ''nether'', ''nedre'', ''bas'' and ''inferior'' are used everywhere in Europe. They are often used in contrast with an upstream or higher area whose name contains words such as "upper", ''boven'', ''oben'', ''supérieure'' and ''haut''. Both downstream at the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, and low at the plain near the
Place names with "low(er)" or ''neder'', ''lage'', ''nieder'', ''nether'', ''nedre'', ''bas'' and ''inferior'' are used everywhere in Europe. They are often used in contrast with an upstream or higher area whose name contains words such as "upper", ''boven'', ''oben'', ''supérieure'' and ''haut''. Both downstream at the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, and low at the plain near the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
apply to the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. However, the related geographical location of the "upper" ground changed over time tremendously, and rendered over time several names for the area now known as the Low Countries:
*Germania inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippine ...
: Roman province established in AD 89 (parts of Belgium and the Netherlands), downstream from Germania Superior (southern Germany). In the 16th century the term was used again, though without this contrastive counterpart.
* Lower Lorraine: 10th century duchy (covered much of the Low Countries), downstream from Upper Lorraine (northern France)
*Niderlant: Since the 12th century, ''Niderlant'' ("Low land") was mentioned in the Nibelungenlied
The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of German ...
as the region between the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a ...
and the lower Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
. In this context the higher ground began approximately at upstream Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
.
* Les pays de par deçà: used by 15th century Burgundian rulers who resided in the Low Countries, meaning "the lands over here". On the other hand, ''Les pays de par delà'' or "the lands over there" was used for their original homeland Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
(central France).
* Pays d'embas: used by 16th century Habsburg ruler Mary, Queen of Hungary, meaning "land down here", used as opposed to her other possessions on higher grounds in Europe (Austria and Hungary). Possibly developed from "Les pays de par deçà".
Netherlands
 Apart from its topographic usage for the then multi-government area of the Low Countries, the 15th century saw the first attested use of ''Nederlandsch'' as a term for the Dutch language, by extension hinting at a common ethnonym for people living in different fiefdoms. This was used alongside the long-standing ''Duytsch'' (the Early Modern spelling of the earlier ''Dietsc'' or ''Duutsc''). The most common Dutch term for the Dutch language remained ''Nederduytsch'' or ''Nederduitsch'' until it was gradually superseded by ''Nederlandsch'' in the early 1900s, the latter becoming the sole name for the language by 1945. Earlier, from the mid-16th century on, the
Apart from its topographic usage for the then multi-government area of the Low Countries, the 15th century saw the first attested use of ''Nederlandsch'' as a term for the Dutch language, by extension hinting at a common ethnonym for people living in different fiefdoms. This was used alongside the long-standing ''Duytsch'' (the Early Modern spelling of the earlier ''Dietsc'' or ''Duutsc''). The most common Dutch term for the Dutch language remained ''Nederduytsch'' or ''Nederduitsch'' until it was gradually superseded by ''Nederlandsch'' in the early 1900s, the latter becoming the sole name for the language by 1945. Earlier, from the mid-16th century on, the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Re ...
(1568–1648) had divided the Low Countries into the northern Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
(Latin: ''Belgica Foederata'') and the southern Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
(Latin: ''Belgica Regia''), introducing a distinction, i.e. Northern vs. Southern Netherlands; the latter evolved into the present-day Belgium after a brief unification in the early 19th century.
The somewhat dated English adjective "Netherlandish", meaning "from the Low Countries", is derived directly from the Dutch adjective ''Nederlands'' or ''Nederlandsch''. It is typically used in reference to paintings or music produced anywhere in the Low Countries during the 15th and early 16th centuries. There are works of art that are now collectively called "Early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers to the work of artists active in the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands during the 15th- and 16th-century Northern Renaissance period. It flourished especial ...
", although the term it aspires to replace, namely "Flemish primitives", remains in use. In music the Franco-Flemish School
The designation Franco-Flemish School, also called Netherlandish School, Burgundian School, Low Countries School, Flemish School, Dutch School, or Northern School, refers, somewhat imprecisely, to the style of polyphonic vocal music composition ...
is also known as the Netherlandish School. Later art and artists from the southern Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
provinces of the Low Countries are usually called Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium ...
and those from the northern Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
provinces Dutch, but art historians sometimes use "Netherlandish art" for art of the Low Countries
The art of the Low Countries consists of painting, sculpture, architecture, printmaking, pottery and other forms of visual art produced in the Low Countries, and since the 19th century in Belgium in the southern Netherlands and the Netherland ...
produced before 1830, i.e., until the secession of Belgium from the Netherlands to distinguish the period from what came after.
Apart from this largely intellectual use, the term "Netherlandish" as adjective is not commonly used in English, unlike its Dutch equivalent. Many languages, however, do have a cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical e ...
or calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
derived from the Dutch adjective ''Nederlands'':
Toponyms
*Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
: Low Countries provinces held by the House of Valois-Burgundy (1384–1482)
*Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austr ...
: Low Countries provinces held by the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
and later the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
(1482–1581)
*Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
: Dutch Republic (1581–1795)
* Southern Netherlands: comprising present Belgium, Luxembourg and parts of northern France (1579–1794)
*Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
: comprising present Belgium, Luxembourg and parts of northern France (1579–1713)
*Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
: comprising present Belgium, Luxembourg and parts of northern France under Habsburg rule (after 1713)
* Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands: short-lived precursor of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands (1813–1815)
*United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
: unification of the Northern Netherlands and the Southern Netherlands (Belgium and Luxembourg) (1815–1830)
*Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
: kingdom with the Netherlands, Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten as constituent countries
*Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
: European part of the kingdom of the Netherlands
*New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
: Former Dutch colony established in 1625 centred on New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
(the modern New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
)
Low Countries
TheLow Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
( nl, Lage Landen) refers to the historical region ''de Nederlanden'': those principalities located on and near the mostly low-lying land around the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. That region corresponds to all of the Netherlands, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
, forming the Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a Political union, politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in ...
. The name "Benelux" is formed from joining the first two or three letters of each country's name Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg. It was first used to name the customs agreement that initiated the union (signed in 1944) and is now used more generally to refer to the geopolitical and economical grouping of the three countries, while "Low Countries" is used in a more cultural or historical context.
In many languages the nomenclature "Low Countries" can both refer to the cultural and historical region comprising present-day Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, and to "the Netherlands" alone, e.g., ''Les Pays-Bas'' in French, ''Los Países Bajos'' in Spanish and ''i Paesi Bassi'' in Italian. Several other languages have literally translated "Low Countries" into their own language to refer to the Dutch language:
*Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
: ''Nizozemski''
* Czech: ''Nizozemština''
* Irish: ''Ísiltíris''
*Southern Min
Southern Min (), Minnan (Mandarin pronunciation: ) or Banlam (), is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian (especially the Minnan region), most of Taiwan ...
: / (''Kē-tē-gú'')
*Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
: низоземски (''nizozemski'')
* Slovene: ''nizozemščina''
*Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
: ''Iseldireg''
Names from local polities
Flanders (pars pro toto)
Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium ...
( nl, Vlaams) is derived from the name of the County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Y ...
( nl, Graafschap Vlaanderen), in the early Middle Ages the most influential county in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, and the residence of the Burgundian dukes. Due to its cultural importance, "Flemish" became in certain languages a '' pars pro toto'' for the Low Countries and the Dutch language. This was certainly the case in France, since the Flemish are the first Dutch speaking people for them to encounter. In French-Dutch dictionaries of the 16th century, "Dutch" is almost always translated as ''Flameng''.
A calque of ''Vlaams'' as a reference to the language of the Low Countries was also in use in Spain. In the 16th century, when Spain inherited the Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austr ...
, the whole area of the Low Countries was indicated as ''Flandes'', and the inhabitants of ''Flandes'' were called ''Flamencos''. For example, the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Re ...
between the rebellious Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
and the Spanish Empire was called ''Las guerras de Flandes'' and the Spanish army that was based in the Low Countries was named the Army of Flanders ( es, Ejército de Flandes).
The English adjective "Flemish" (first attested as ''flemmysshe'', c. 1325; cf. ''Flæming'', c. 1150), was probably borrowed from Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Frie ...
. The name ''Vlaanderen'' was probably formed from a stem ''flām-'', meaning "flooded area", with a suffix ''-ðr-'' attached. The Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aro ...
form is ''flāmisk'', which becomes ''vlamesc'', ''vlaemsch'' in Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
and ''Vlaams'' in Modern Dutch. Flemish is now exclusively used to describe the majority of Dutch dialects found in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, and as a reference to that region. Calques of ''Vlaams'' in other languages:
Holland (''pars pro toto'')
In many languages including English, (acalque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
of) "Holland" is a common name for the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
as a whole. Even the Dutch use this sometimes, although this may be resented outside the two modern provinces that make up historical Holland. Strictly speaking, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
is only the central-western region of the country comprising two of the twelve provinces. They are North Holland and South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
. However, particularly by outsiders, Holland has long become a '' pars pro toto'' name for the whole nation, similar to the use of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
for the (former) Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, or England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
for the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.
The use is sometimes discouraged. For example, the "Holland" entry in the style guide of ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide ...
'' and ''The Observer
''The Observer'' is a British newspaper Sunday editions, published on Sundays. It is a sister paper to ''The Guardian'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', whose parent company Guardian Media Group, Guardian Media Group Limited acquired it in 1993. ...
'' newspapers states: "Do not use when you mean the Netherlands (of which it is a region), with the exception of the Dutch football team
The Netherlands national football team ( nl, Nederlands voetbalelftal or simply ''Het Nederlands elftal'') has represented the Netherlands in international men's football matches since 1905. The men's national team is controlled by the Royal ...
, which is conventionally known as Holland".
In 2019, the Dutch government announced that it would only communicate and advertise under its real name "the Netherlands" in the future, and stop describing itself as Holland. They stated: “It has been agreed that the Netherlands, the official name of our country, should preferably be used.” From 2019 onwards, the nation’s football team will solely be called the Netherlands in any official setting. Nonetheless, the name "Holland" is still widely used for the Netherlands national football team.Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
and Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
from the 13th to the 15th centuries. Holland remained most powerful during the period of the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, dominating foreign trade, and hence most of the Dutch traders encountered by foreigners were from Holland, which explains why the Netherlands is often called Holland overseas.
After the demise of the Dutch Republic under Napoleon, that country became known as the Kingdom of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( nl, Holland (contemporary), (modern); french: Royaume de Hollande) was created by Napoleon Bonaparte, overthrowing the Batavian Republic in March 1806 in order to better control the Netherlands. Since becoming Empero ...
(1806–1810). This is the only time in history that "Holland" became an official designation of the entire Dutch territory. Around the same time, and the former countship of Holland was dissolved and split up into two provinces, later known as North Holland and South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
, because one Holland province by itself was considered too dominant in area, population and wealth compared to the other provinces. Today the two provinces making up Holland, including the cities of Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
, The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a list of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's ad ...
and Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
, remain politically, economically and demographically dominant – 37% of the Dutch population live there. In most other Dutch provinces, particularly in the south including Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
(Belgium), the word ''Hollander'' is commonly used in either colloquial or pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
sense to refer to the perceived superiority or supposed arrogance of people from the Randstad – the main conurbation of Holland proper and of the Netherlands.
In 2009, members of the First Chamber drew attention to the fact that in Dutch passports, for some EU-languages a translation meaning "Kingdom of Holland" was used, as opposed to "Kingdom of the Netherlands". As replacements for the Estonian ''Hollandi Kuningriik'', Hungarian ''Holland Királyság'', Romanian ''Regatul Olandei'' and Slovak ''Holandské kráľovstvo'', the parliamentarians proposed ''Madalmaade Kuningriik'', ''Németalföldi Királyság'', ''Regatul Țărilor de Jos'' and ''Nizozemské Kráľovstvo'', respectively. Their reasoning was that "if in addition to Holland a recognisable translation of the Netherlands does exist in a foreign language, it should be regarded as the best translation" and that "the Kingdom of the Netherlands has a right to use the translation it thinks best, certainly on official documents". Although the government initially refused to change the text except for the Estonian, recent Dutch passports feature the translation proposed by the First Chamber members. Calques derived from ''Holland'' to refer to the Dutch language in other languages:
} ()
* Bengali: (''olondaj'')
* Bulgarian: холандски (''holandski'')
* Catalan/Valencian: ''holandès''
* Chinese: / (''hélányŭ'')
* Czech: ''holandština''
* Danish: ''hollandsk''
* Estonian: ''hollandi keel''
* Finnish: ''hollanti''
*French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
: ''hollandais''
* Galician: ''holandés''
* Georgian: ჰოლანდიური ''(holandiuri'')
*German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: ''Holländisch''
*Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: Ολλανδικά (''Ollandika'')
* Gujarati: (''Holand'')
*Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
: (''Holandit'')
, valign=top,
*Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of North India, northern, Central India, centr ...
: (''Holand'')
* Hungarian: ''holland''
* Icelandic: ''hollenska''
*Interlingua
Interlingua (; ISO 639 language codes ia, ina) is an international auxiliary language (IAL) developed between 1937 and 1951 by the American International Auxiliary Language Association (IALA). It ranks among the most widely used IALs and is ...
: ''hollandese''
* Irish: ''Ollainnis''
* Italian: ''olandese''
* Japanese: (''Orandago'')
*Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
: ''Hollandica''
* Latvian: ''holandiešu valoda''
*Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
: ''Olandų kalba''
*Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
: холандски (''hólandski'')
* Malay (including Malaysian
Malaysian may refer to:
* Something from or related to Malaysia, a country in Southeast Asia
* Malaysian Malay, a dialect of Malay language spoken mainly in Malaysia
* Malaysian people, people who are identified with the country of Malaysia regar ...
and Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesia ...
): ''Belanda''
*Maltese
Maltese may refer to:
* Someone or something of, from, or related to Malta
* Maltese alphabet
* Maltese cuisine
* Maltese culture
* Maltese language, the Semitic language spoken by Maltese people
* Maltese people, people from Malta or of Malte ...
: ''Olandiż''
* fa, هلندی ()
, valign=top,
* Polish: ''holenderski''
* Portuguese: ''holandês''
* Romanian: ''olandeză''
* Russian: Голландский (''Gollandskij'')
*Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
: холандски (''holandski'')
* Sinhala: ඕලන්දය (''Olandaya'')
* Slovak: ''holandčina''
* Spanish: ''holandés''
*Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
: ''holländska''
*Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
: ''Olandés''
*Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: ''hollandaca''
* Ukrainian: голандська (''holandska'')
* Vietnamese: ''tiếng Hà Lan''
Toponyms:
* County of Holland: former county in the Netherlands, dissolved in the provinces North nd South Holland
*South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
(Zuid-Holland): province in the Netherlands
* North Holland (Noord-Holland): province in the Netherlands
*Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
: region, former county in the Netherlands consisting of the provinces Noord- en Zuid-Holland
*Kingdom of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( nl, Holland (contemporary), (modern); french: Royaume de Hollande) was created by Napoleon Bonaparte, overthrowing the Batavian Republic in March 1806 in order to better control the Netherlands. Since becoming Empero ...
: puppet state set up by Napoleon who took the name of the leading province for the whole country (1806–1810)
* New Holland (''Nova Hollandia''):'' historical name for mainland Australia (1644–1824)
* New Holland: Dutch colony in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
(1630–1654)
*Holland, Michigan
Holland is a city in the western region of the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated near the eastern shore of Lake Michigan on Lake Macatawa, which is fed by the Macatawa River (formerly known locally as the Black R ...
* Hollandia (city)
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso ...
: between 1910 and 1949 the capital of a district of the same name in West New Guinea, now Jayapura
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sud ...
Brabant (pars pro toto)
Desiderius Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' w ...
in the early 16th century.
Perhaps of influence for this pars pro toto usage is the Brabantian holding of the ducal title of Lower Lorraine. In 1190, after the death of Godfrey III, Henry I became Duke of Lower Lorraine, where the Low Countries have their political origin. However, by that time the title had lost most of its territorial authority. According to protocol, all his successors were thereafter called Dukes of Brabant and Lower Lorraine (often called Duke of Lothier).
Brabant symbolism served again a role as national symbols during the formation of Belgium. The national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europe ...
of Belgium is called the Brabançonne (English: "the Brabantian"), and the Belgium flag has taken its colors from the Brabant coat of arms: black, yellow and red. This was influenced by the Brabant Revolution (french: Révolution brabançonne, nl, Brabantse Omwenteling), sometimes referred to as the "Belgian Revolution of 1789–90" in older writing, that was an armed insurrection that occurred in the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
(modern-day Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
) between October 1789 and December 1790. The revolution led to the brief overthrow of Habsburg rule
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
and the proclamation of a short-lived polity, the United Belgian States. Some historians have seen it as a key moment in the formation of a Belgian nation-state, and an influence on the Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
...
of 1830.
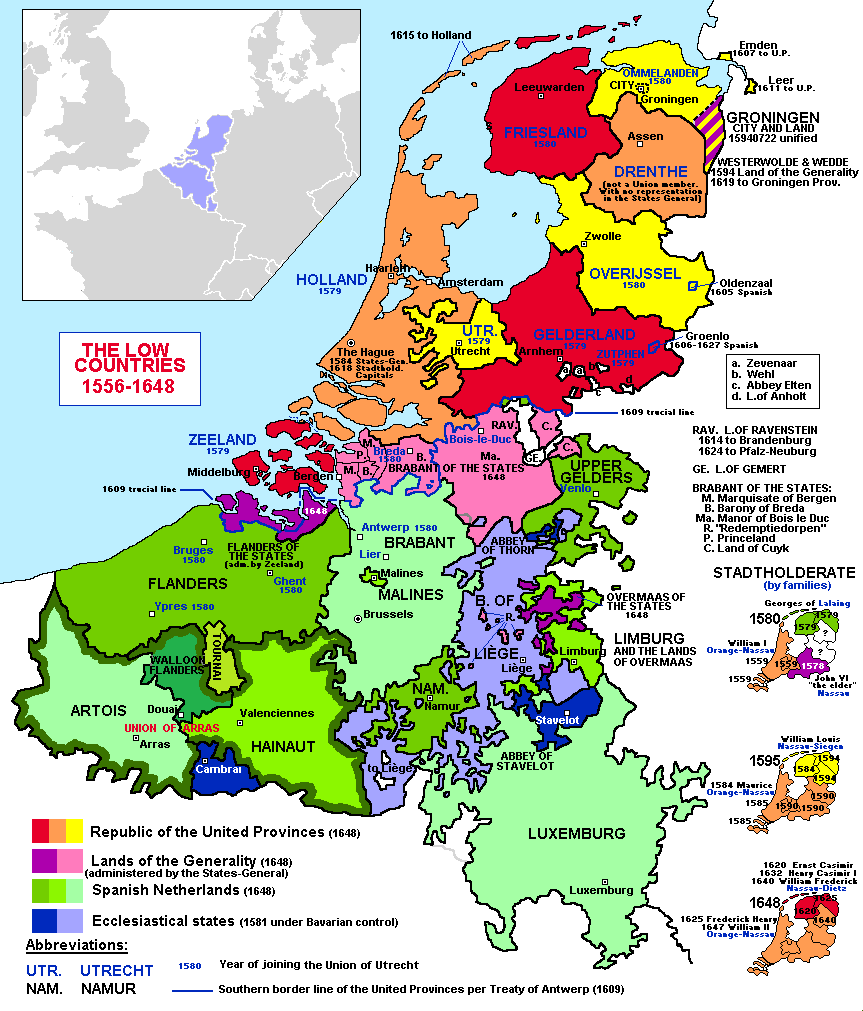
Seventeen and Seven Provinces
Holland, Flanders and 15 other counties, duchies and bishoprics in the Low Countries were united as theSeventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more State (polity), states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some e ...
during the 16th century, covered by the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 was an edict, promulgated by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, reorganising the Seventeen Provinces of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg into one indivisible territory, while retaining existing cus ...
of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infant ...
, which freed the provinces from their archaic feudal obligations.
In 1566, Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal fro ...
, heir of Charles V, sent an army of Spanish mercenaries to suppress political upheavals to the Seventeen Provinces. A number of southern provinces ( Hainaut, Artois, Walloon Flanders, Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Na ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
and Limburg) united in the Union of Arras
The Union of Arras ( Dutch: ''Unie van Atrecht'', French: ''Union d'Arras'', Spanish: ''Unión de Arrás'') was an alliance between the County of Artois, the County of Hainaut and the city of Douai in the Habsburg Netherlands in early 1579 dur ...
(1579), and begun negotiations for a peace treaty with Spain. In response, nine northern provinces united in the Union of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht ( nl, Unie van Utrecht) was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.
History
The Union of Utrecht is ...
(1579) against Spain. After the Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
and the Brabant where reconquered by Spain, the remaining seven provinces ( Frisia, Gelre
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
, Overijssel, Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the fourth-largest city and a municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Nethe ...
and Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
) signed 2 years later the declaration of independence of the Seven United Provinces. Since then, several ships of the Royal Netherlands Navy have bared that name.
Names from tribes of the pre-Migration Period
Belgae
The nomenclature ''Belgica'' is harking back to the ancient local tribe of theBelgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by J ...
and the Roman province named after that tribe Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 5 ...
. Although a derivation of that name is now reserved for the Kingdom of Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, from the 15th to the 17th century the name was the usual Latin translation to refer to the entire Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, which was on maps sometimes heroically visualised as the Leo Belgicus.
Other use:
*Lingua Belgica: Latinized name for the Dutch language in 16th century dictionaries, popular under the influence of Humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
*Belgica Foederata
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
: literally "United Belgium", Latinized name for the Dutch Republic (also known as United Netherlands, Northern Netherlands or United Provinces), after the northern part of the Low Countries declared its independence from the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
*Belgica Regia
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the Au ...
: literally "King's Belgium", Latinized name for the Southern Netherlands, remained faithful to the Spanish king
* Nova Belgica: Latined name for the former colony New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
* Fort Belgica: fort built by the Dutch in the Indonesian Banda Islands
The Banda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Banda) are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java, and constitute an administrative district (''kecamatan'') within the Centr ...
in the 17th century.
* United Belgian States: also known as "United Netherlandish States" ( nl, Verenigde Nederlandse Staten) or "United States of Belgium", short-lived Belgian precursor state established after the Brabant Revolution against the Habsburg (1790)
*Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
: state in Europe
Batavi
Throughout the centuries the Dutch attempted to define their collective identity by looking at their ancestors, the Batavi. As claimed by the Roman historianTacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
, the Batavi where a brave Germanic tribe living in the Netherlands, probably in the Betuwe region. In Dutch, the adjective ''Bataafs'' ("Batavian") was used from the 15th to the 18th century, meaning "of, or relating to the Netherlands" (but not the southern Netherlands).
Other use:
* Lingua Batava or Batavicus: in use as Latin names for the Dutch language
* Batavisme: in French an expression copied from the Dutch language
* Batave: in French a person from the Netherlands
* Batavian Legion {{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
The Batavian Legion (''légion batave'' or ''légion franche étrangère batave'') was a unit of Dutch volunteers under French command, created and dissolved in 1793.
History
The project to re ...
: a unit of Dutch volunteers under French command, created and dissolved in 1793
* Batavian Revolution
The Batavian Revolution ( nl, De Bataafse Revolutie) was a time of political, social and cultural turmoil at the end of the 18th century that marked the end of the Dutch Republic and saw the proclamation of the Batavian Republic. The period of ...
: political, social and cultural turmoil in the Netherlands (end 18th century)
* Batavian Republic ( nl, Bataafse Republiek; french: République Batave), Dutch client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
of France (1795–1806)
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residency ...
: capital city of the Dutch East Indies, corresponds to the present-day city of Jakarta
Frisii
Names from confederations of Germanic tribes
Franconian
Frankish was the West Germanic language spoken by theFranks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
between the 4th and 8th century. Between the fifth and ninth centuries, the languages spoken by the Salian Franks in Belgium and the Netherlands evolved into Old Low Franconian ( nl, Oudnederfrankisch), which formed the beginning of a separate Dutch language and is synonymous with Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aro ...
. Compare the synonymous usage, in a linguistic context, of Old English versus Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
.
Frisian
Frisii were an ancient tribe who lived in the coastal area of the Netherlands in Roman times. After theMigration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
, coming from the east, settled the region. Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
in the south, who were familiar with Roman texts, called the coastal region Frisia, and hence its inhabitants Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany ...
, even though not all of the inhabitants had Frisian ancestry. After a Frisian Kingdom emerged in the mid-7th century in the Netherlands, with its center of power the city of Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the fourth-largest city and a municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Nethe ...
, the Franks conquered the Frisians and converted them to Christianity. From that time on a colony of Frisians was living in Rome and thus the old name for the people from the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
who came to Rome has remained in use in the national church of the Netherlands in Rome, which is called the Frisian church
The Church of Saints Michael and Magnus ( it, Santi Michele e Magno, fy, Friezetsjerke, nl, Friezenkerk) is a Roman Catholic church in Rome, Italy, dedicated to Saint Michael the Archangel and the Bishop Saint Magnus of Anagni. It lies on the n ...
( nl, Friezenkerk; it, chiesa nazionale dei Frisoni). In 1989, this church was granted to the Dutch community in Rome.
See also
*Name of the Franks
The name of the Franks (Latin ''Franci''), alongside the derived names of '' Francia'' and '' Franconia'' (and the adjectives ''Frankish'' and ''Franconian''), are derived from the name given to a Germanic tribal confederation which emerged in t ...
* Netherlands (disambiguation)
* List of place names of Dutch origin
References
External links
Origin and History of the term "Dutch"
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Names For The Dutch Language Name of the Dutch language Germanic languages Low Franconian languages Language naming Dutch culture Geography of the Netherlands
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
Netherlandic studies