T-72 Operators And Variants on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 – 325 T-72M1/M1M as of 2023.
* – 50 T-72M1 as of 2023.
* – 390 T-72A, T-72B as of 2023.
– 325 T-72M1/M1M as of 2023.
* – 50 T-72M1 as of 2023.
* – 390 T-72A, T-72B as of 2023.  * – 404 T-72A, T-72AV, T-72B, and T-72SIM2 as of 2023.
* – 477 T-72B and 20 T-72B3 mod. 2016 as of 2023. Various T-72 modifications in reserve.
* – 90 T-72M1/M in service as of 2025.IISS 2025
* – 1 operated by the 4 Intelligence Company.
* – 74 M-84A4 Sniper, which is an improved variant of the T-72M, as of 2025 awaiting replacement with the Leopard 2A8 while 30 M-84A4 will be donated to Ukraine.
* – 404 T-72A, T-72AV, T-72B, and T-72SIM2 as of 2023.
* – 477 T-72B and 20 T-72B3 mod. 2016 as of 2023. Various T-72 modifications in reserve.
* – 90 T-72M1/M in service as of 2025.IISS 2025
* – 1 operated by the 4 Intelligence Company.
* – 74 M-84A4 Sniper, which is an improved variant of the T-72M, as of 2025 awaiting replacement with the Leopard 2A8 while 30 M-84A4 will be donated to Ukraine.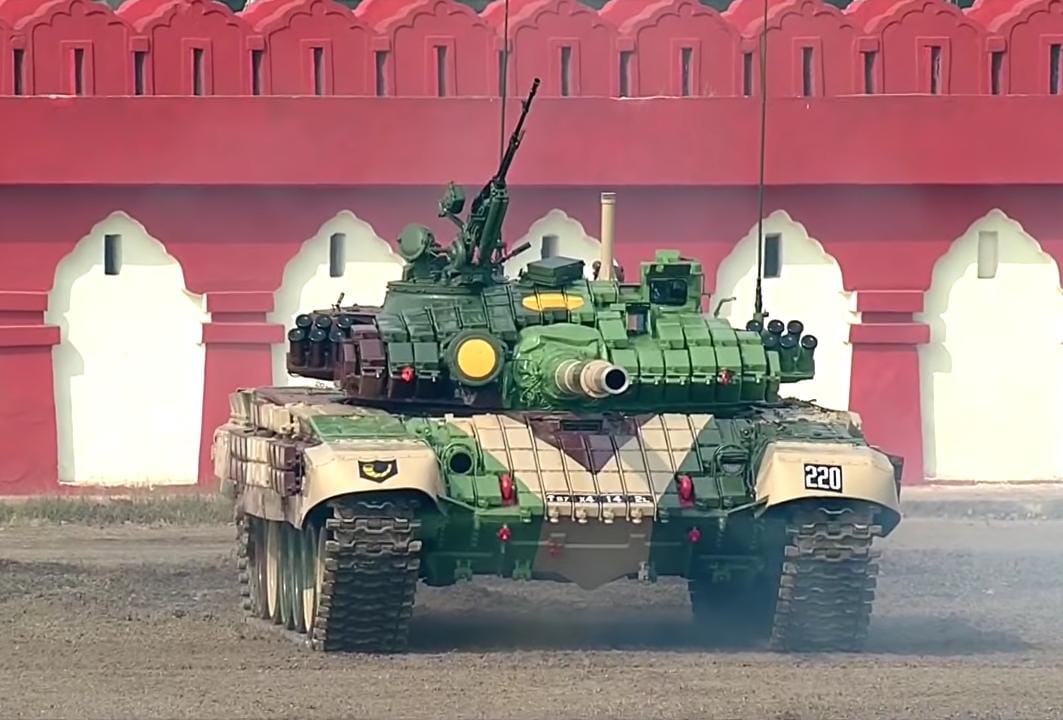 * – 100 T-72AV delivered by Ukraine in 2010.
* – At least 1 captured in Badme War. Current status unknown.
* – 50 bought from Yemen, 171 T-72UA1 vehicles reportedly ordered from Ukraine in 2011.
* –143 T-72B/SIM1 in 2018. Upgraded T-72 SIMs were upgraded in Georgia with assistance of Israel.
* – 44 T-72M1 in service as of 2025. 77 T-72s were donated to the new
* – 100 T-72AV delivered by Ukraine in 2010.
* – At least 1 captured in Badme War. Current status unknown.
* – 50 bought from Yemen, 171 T-72UA1 vehicles reportedly ordered from Ukraine in 2011.
* –143 T-72B/SIM1 in 2018. Upgraded T-72 SIMs were upgraded in Georgia with assistance of Israel.
* – 44 T-72M1 in service as of 2025. 77 T-72s were donated to the new
 * – In 1994 Sierra Leone acquired two T-72s from Poland via Ukraine (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). Another unspecified number of ex-Polish tanks was delivered to Sierra Leone in 1997 also via Ukraine (these vehicles also previously served with Poland).
* – Passed on to successor states:
*
* – In 1994 Sierra Leone acquired two T-72s from Poland via Ukraine (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). Another unspecified number of ex-Polish tanks was delivered to Sierra Leone in 1997 also via Ukraine (these vehicles also previously served with Poland).
* – Passed on to successor states:
*
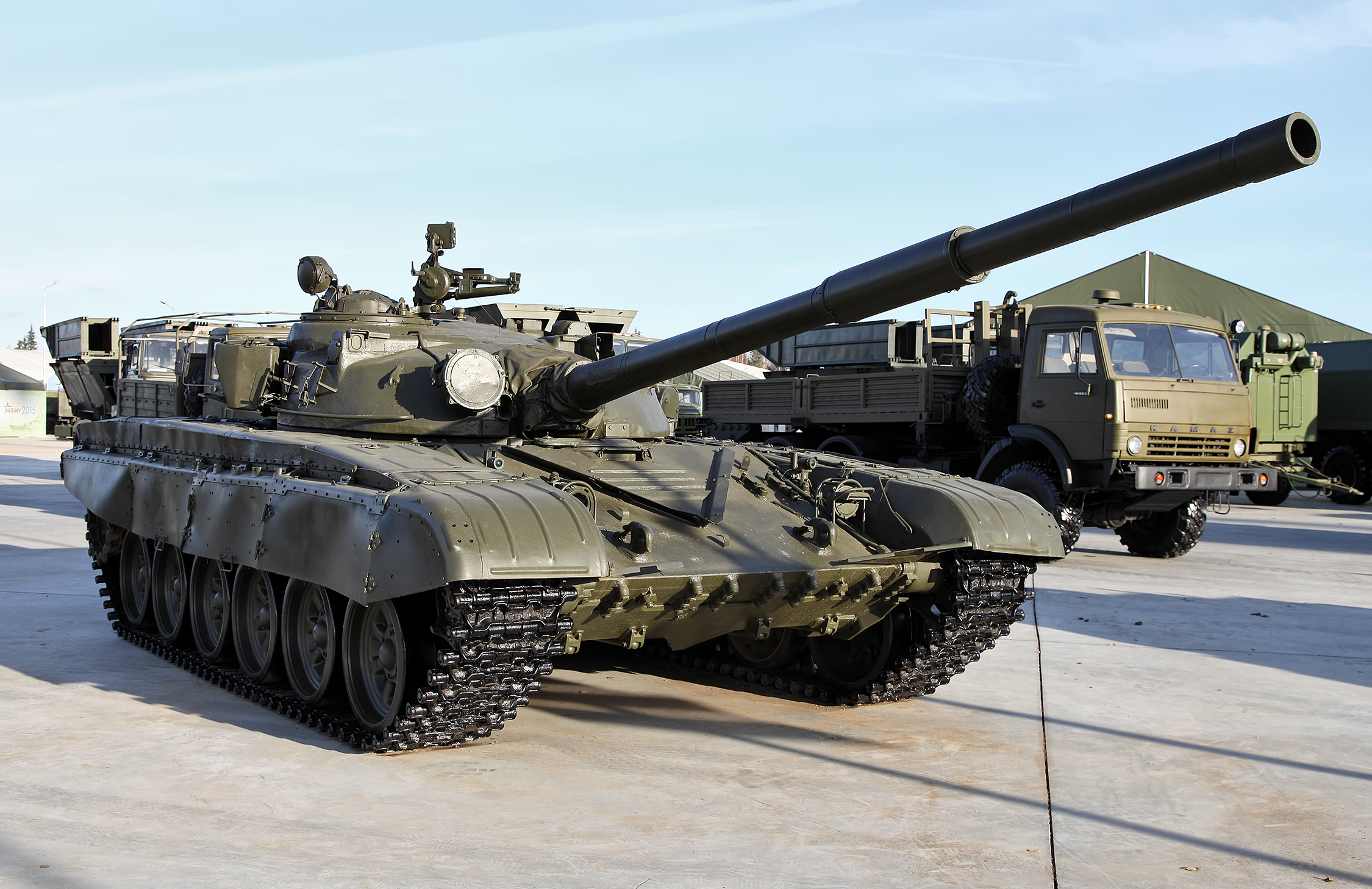
 The T-72 was designed and first built in the Soviet Union.
* T-72 "Ural" (Ob'yekt 172M) (1973): Original version, armed with the 125 mm D-81TM smoothbore tank gun. Unlike the later versions it had the searchlight mounted on left. It also had flipper-type armour panels. It had the TPD-2-49 coincidence
The T-72 was designed and first built in the Soviet Union.
* T-72 "Ural" (Ob'yekt 172M) (1973): Original version, armed with the 125 mm D-81TM smoothbore tank gun. Unlike the later versions it had the searchlight mounted on left. It also had flipper-type armour panels. It had the TPD-2-49 coincidence  :*T-72A obr.1982g: Additional glacis armour with thickness of 16 mm of high resistance steel.
:* T-72A obr.1984g: Late production with new turret, new gunner night sight 1K13-49, new engine. Smoke launchers on the turret side.
:* T-72AK (Ob'yekt 176K): Command version of the T-72A. In NATO code T-72AK was represented by three different designations: T-72AK1, T-72AK2 and T-72AK3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
:*T-72AV: ("V" for ''vzryvnoi'' – explosive) model with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour fitted to hull front and turret.
* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E2, Ob'yekt 172M-E3, Ob'yekt 172M-E4): Soviet export version, similar to the T-72A but with thinner armour and 125 mm D-81T smoothbore tank gun with 44 rounds. It was sold to Iraq and to Syria and was also built in Poland by
:*T-72A obr.1982g: Additional glacis armour with thickness of 16 mm of high resistance steel.
:* T-72A obr.1984g: Late production with new turret, new gunner night sight 1K13-49, new engine. Smoke launchers on the turret side.
:* T-72AK (Ob'yekt 176K): Command version of the T-72A. In NATO code T-72AK was represented by three different designations: T-72AK1, T-72AK2 and T-72AK3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
:*T-72AV: ("V" for ''vzryvnoi'' – explosive) model with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour fitted to hull front and turret.
* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E2, Ob'yekt 172M-E3, Ob'yekt 172M-E4): Soviet export version, similar to the T-72A but with thinner armour and 125 mm D-81T smoothbore tank gun with 44 rounds. It was sold to Iraq and to Syria and was also built in Poland by  :* T-72BA (Ob'yekt 184A/A1): this designation is used to refer to several models of late T-72B, stripped down, refurbished and upgraded with certain core components at
:* T-72BA (Ob'yekt 184A/A1): this designation is used to refer to several models of late T-72B, stripped down, refurbished and upgraded with certain core components at  :* T-72B1 (Ob'yekt 184-1): T-72B without the 9K120 missile system.
::* T-72B1K (Ob'yekt 184K-1): Command version of the T-72B1.
:* T-72B1 (Ob'yekt 184-1): T-72B without the 9K120 missile system.
::* T-72B1K (Ob'yekt 184K-1): Command version of the T-72B1.

 ::* T-72B1MS "White Eagle"(Ob'yekt 184-1MS): T-72B1 modernized by the 61st armour repair factory (today part of the
::* T-72B1MS "White Eagle"(Ob'yekt 184-1MS): T-72B1 modernized by the 61st armour repair factory (today part of the  * (Ob'yekt 184-M3): this upgrade was initiated in 2010 using old stocks of T-72B tanks held in reserve. The purpose was to upgrade old T-72s to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the new T-90A tanks to simplify supply lines. In addition to performing a general overhaul of every vehicle, all tanks were equipped with the more powerful V-92S2 engines and a new steering system in the driver's compartment, and older tracks were replaced with the new universal, twin-pin design. The upgrade program focuses mainly on the implementation of a new fire control system. The tank commander retains an upgraded version of the legacy TKN-3MK sight, which is a passive device with a range of only 600 m at night. The commander also has a separate monitor that displays thermal imagery from the gunner's main sight, and a new turret control panel. The gunner has the new PNM Sosna-U panoramic multi-spectral sensor, which replaced the 1K13 night vision in its mounting; the 1A40-4 FCS with TPD-K1 sight is retained, but as part of the auxiliary sighting system to complement the newer system. The Sosna-U is a multi-channel, panoramic sight stabilized in both vertical and horizontal axes with a built-in laser rangefinder and command guidance module, used with 9M119M missiles. The main advantage of the Sosna-U is the Thales Catherine-FC thermal imager which extends the detection range of a tank-sized target to 10,500 m and the identification range to 3,300 m in both day and night conditions and all weathers. The T-72B3 series vehicles also received the new 2A46M-2 main gun which is reportedly equivalent to the Rheinmetall Rh120 L/44 cannon. The gun-laying and stabilization drives were also replaced by the new 2E42-4 system, and the AZ ammunition auto-loader was modified to accommodate newer generations of 125 mm smoothbore anti-tank ammunition: Vant (depleted uranium) and Mango (tungsten) rounds. There is also a new 9K119 Refleks system, used to launch 9M119 Refleks ATGM through the gun barrel. The B3 upgrade includes a new explosion- and fire-suppression system and an advanced VHF radio system designated R-168-25U-2 AKVEDUK. The variant entered service on 19 October 2012. It was first delivered to the 20th Field Army in summer 2013, and to its Armored Guards Brigade in October 2013. About 2,000 such tanks were in service as of 2020. The cost to upgrade a T-72 to the T-72B3 standard was around 52 million rubles in 2013.
:*T-72B3 obr.2014: a special version of the T-72B3, first seen during the 2014 edition of the Tank Biathlon competition. The most notable upgrades are the stabilized, panoramic, independent PK-PAN commander sight with integrated thermal viewer and a V-92S2 1,000 hp engine.
*T-72B3M obr.2016: a further upgrade of the T-72B3, produced since 2016 by overhauling and upgrading old T-72B tanks from storage. The purpose was to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the T-90 M tank to simplify supply lines. There is a new gun 2A46M-5 with new anti-tank ammunition Svinets-1 (tungsten) and Svinets-2 (depleted uranium). New 2E58 gun stabilizer is responsible for improved aiming time. 9K119M Refleks-M system is used to launch 9M119M Invar (also called Reflex-M) ATGM through gun barrel. New PK-PAN panoramic commander sight with thermal vision only seen on a limited number of vehicles while all the rest are using older TKN-3MK commander`s sight. Retained Sosna-U gunner`s sight and crosswind sensor. New Kalina fire control system, although in simplified form. There is new radio communication equipment as well as GLONASS satellite navigation. Driver is using older TVN-5 periscope with additional display from rear view camera. The automotive performance of the tank was improved with a more powerful V-92S2F engine rated at 1,130 hp (830 kW) coupled to an automatic transmission system and improved drivetrain. Protection is improved by Relikt new generation ERA mounted on sides of both hull and turret, while cage armor was added to the rear.
* (Ob'yekt 184-M3): this upgrade was initiated in 2010 using old stocks of T-72B tanks held in reserve. The purpose was to upgrade old T-72s to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the new T-90A tanks to simplify supply lines. In addition to performing a general overhaul of every vehicle, all tanks were equipped with the more powerful V-92S2 engines and a new steering system in the driver's compartment, and older tracks were replaced with the new universal, twin-pin design. The upgrade program focuses mainly on the implementation of a new fire control system. The tank commander retains an upgraded version of the legacy TKN-3MK sight, which is a passive device with a range of only 600 m at night. The commander also has a separate monitor that displays thermal imagery from the gunner's main sight, and a new turret control panel. The gunner has the new PNM Sosna-U panoramic multi-spectral sensor, which replaced the 1K13 night vision in its mounting; the 1A40-4 FCS with TPD-K1 sight is retained, but as part of the auxiliary sighting system to complement the newer system. The Sosna-U is a multi-channel, panoramic sight stabilized in both vertical and horizontal axes with a built-in laser rangefinder and command guidance module, used with 9M119M missiles. The main advantage of the Sosna-U is the Thales Catherine-FC thermal imager which extends the detection range of a tank-sized target to 10,500 m and the identification range to 3,300 m in both day and night conditions and all weathers. The T-72B3 series vehicles also received the new 2A46M-2 main gun which is reportedly equivalent to the Rheinmetall Rh120 L/44 cannon. The gun-laying and stabilization drives were also replaced by the new 2E42-4 system, and the AZ ammunition auto-loader was modified to accommodate newer generations of 125 mm smoothbore anti-tank ammunition: Vant (depleted uranium) and Mango (tungsten) rounds. There is also a new 9K119 Refleks system, used to launch 9M119 Refleks ATGM through the gun barrel. The B3 upgrade includes a new explosion- and fire-suppression system and an advanced VHF radio system designated R-168-25U-2 AKVEDUK. The variant entered service on 19 October 2012. It was first delivered to the 20th Field Army in summer 2013, and to its Armored Guards Brigade in October 2013. About 2,000 such tanks were in service as of 2020. The cost to upgrade a T-72 to the T-72B3 standard was around 52 million rubles in 2013.
:*T-72B3 obr.2014: a special version of the T-72B3, first seen during the 2014 edition of the Tank Biathlon competition. The most notable upgrades are the stabilized, panoramic, independent PK-PAN commander sight with integrated thermal viewer and a V-92S2 1,000 hp engine.
*T-72B3M obr.2016: a further upgrade of the T-72B3, produced since 2016 by overhauling and upgrading old T-72B tanks from storage. The purpose was to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the T-90 M tank to simplify supply lines. There is a new gun 2A46M-5 with new anti-tank ammunition Svinets-1 (tungsten) and Svinets-2 (depleted uranium). New 2E58 gun stabilizer is responsible for improved aiming time. 9K119M Refleks-M system is used to launch 9M119M Invar (also called Reflex-M) ATGM through gun barrel. New PK-PAN panoramic commander sight with thermal vision only seen on a limited number of vehicles while all the rest are using older TKN-3MK commander`s sight. Retained Sosna-U gunner`s sight and crosswind sensor. New Kalina fire control system, although in simplified form. There is new radio communication equipment as well as GLONASS satellite navigation. Driver is using older TVN-5 periscope with additional display from rear view camera. The automotive performance of the tank was improved with a more powerful V-92S2F engine rated at 1,130 hp (830 kW) coupled to an automatic transmission system and improved drivetrain. Protection is improved by Relikt new generation ERA mounted on sides of both hull and turret, while cage armor was added to the rear.  * (''Boyevaya Mashina Ognemyochikov'') – A transport vehicle for flamethrower-squads armed with RPO launchers. Entered service in 2001.
* BMPT (Ob'yekt 199) – Heavy convoy and close tank support vehicle (''Boyevaya Mashina Podderzhki Tankov''). All new turret armed with 2 × 30 mm 2A42 autocannons (500 rounds), 4 × 9M1201 Ataka-T ATGM and 7.62 mm PKT MG (2,000 rounds). It can be also fitted with 2 × AGS-30 automatic grenade launchers. Features new fire control system with thermal sights and a ballistic computer. Reinforced with 3rd generation "Relikt" ERA on the frontal armor and both sides of hull and turret, slat (cage) armor in the rear. It is equipped with Agat-MR night vision devices, an NBC detection and protection system. There is 902A "Tucha" 81 mm smoke grenade launcher array on each side of the turret and "Shtora-1" active protection system. When the screening system warns the crew of laser tracking, a smoke screen is created by the launch of grenades. The vehicle can be fitted with either the KMT-8 or the EMT mine clearing system. The term BMP-T that is very often found is not correct.
*
* (''Boyevaya Mashina Ognemyochikov'') – A transport vehicle for flamethrower-squads armed with RPO launchers. Entered service in 2001.
* BMPT (Ob'yekt 199) – Heavy convoy and close tank support vehicle (''Boyevaya Mashina Podderzhki Tankov''). All new turret armed with 2 × 30 mm 2A42 autocannons (500 rounds), 4 × 9M1201 Ataka-T ATGM and 7.62 mm PKT MG (2,000 rounds). It can be also fitted with 2 × AGS-30 automatic grenade launchers. Features new fire control system with thermal sights and a ballistic computer. Reinforced with 3rd generation "Relikt" ERA on the frontal armor and both sides of hull and turret, slat (cage) armor in the rear. It is equipped with Agat-MR night vision devices, an NBC detection and protection system. There is 902A "Tucha" 81 mm smoke grenade launcher array on each side of the turret and "Shtora-1" active protection system. When the screening system warns the crew of laser tracking, a smoke screen is created by the launch of grenades. The vehicle can be fitted with either the KMT-8 or the EMT mine clearing system. The term BMP-T that is very often found is not correct.
*
/ref>David Axe
The Russians Have Added Yet Another Layer Of Armor To Their Giant Turtle Tanks
/ref>
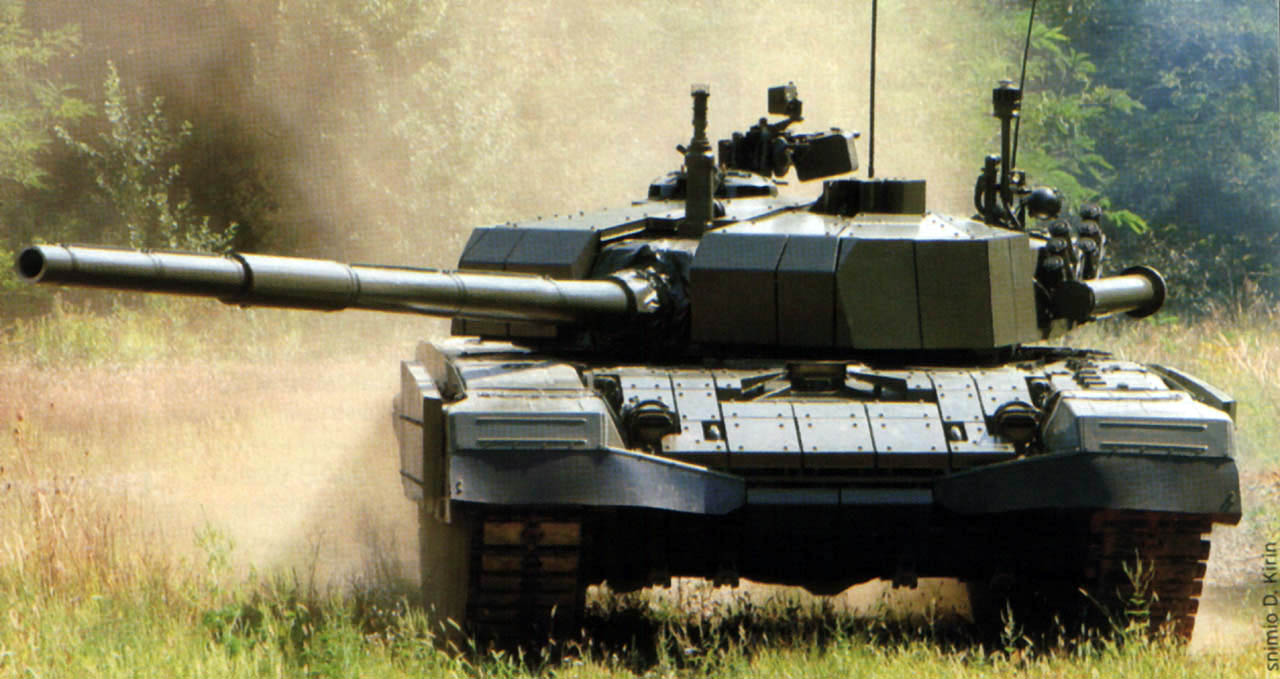 * M-84A – The M-84 is a Yugoslav third generation main battle tank, based on the Soviet T-72, produced in Croatian Đuro Đaković specijalna vozila.
*
* M-84A – The M-84 is a Yugoslav third generation main battle tank, based on the Soviet T-72, produced in Croatian Đuro Đaković specijalna vozila.
*

 These variants are not new builds, but upgrades of a large number of otherwise obsolete T-72 version hulls.
* T-72M4 CZ (2003) – Comprehensive upgrade of every aspect of the T-72M1 resulting in a tank that only superficially resembles the precursor, intended to remedy T-72's failures learned during the
These variants are not new builds, but upgrades of a large number of otherwise obsolete T-72 version hulls.
* T-72M4 CZ (2003) – Comprehensive upgrade of every aspect of the T-72M1 resulting in a tank that only superficially resembles the precursor, intended to remedy T-72's failures learned during the
Optics trade
which significantly improve night vision capabilities and resolution. It uses a laser rangefinder to increase the probability of a first round hit, an improved thermal sight with ballistic computer, an upgraded commander's sight and an upgraded driver's sight. The night vision systems operate fully in passive mode without the use of infrared lights. **Increased ballistic protection with most vulnerable parts covered with reactive armour, significantly increasing the tank's protection against RPGs and HEAT ammunition. The reactive armour added to the tank is the equivalent of 400 millimetres of rolled armour when hit by a warhead. In total, the tank is equipped with 196 boxes of reactive armour. **Significantly improved mobility due to an upgraded power pack with increased engine power to 840 hp and increased acceleration dynamics. **Complete modernization of driver's position with a new digital dashboard. New internal and external communication systems, digital radio enabling encrypted communication. New fire protection system. Periscopic sights with anti-laser protection.
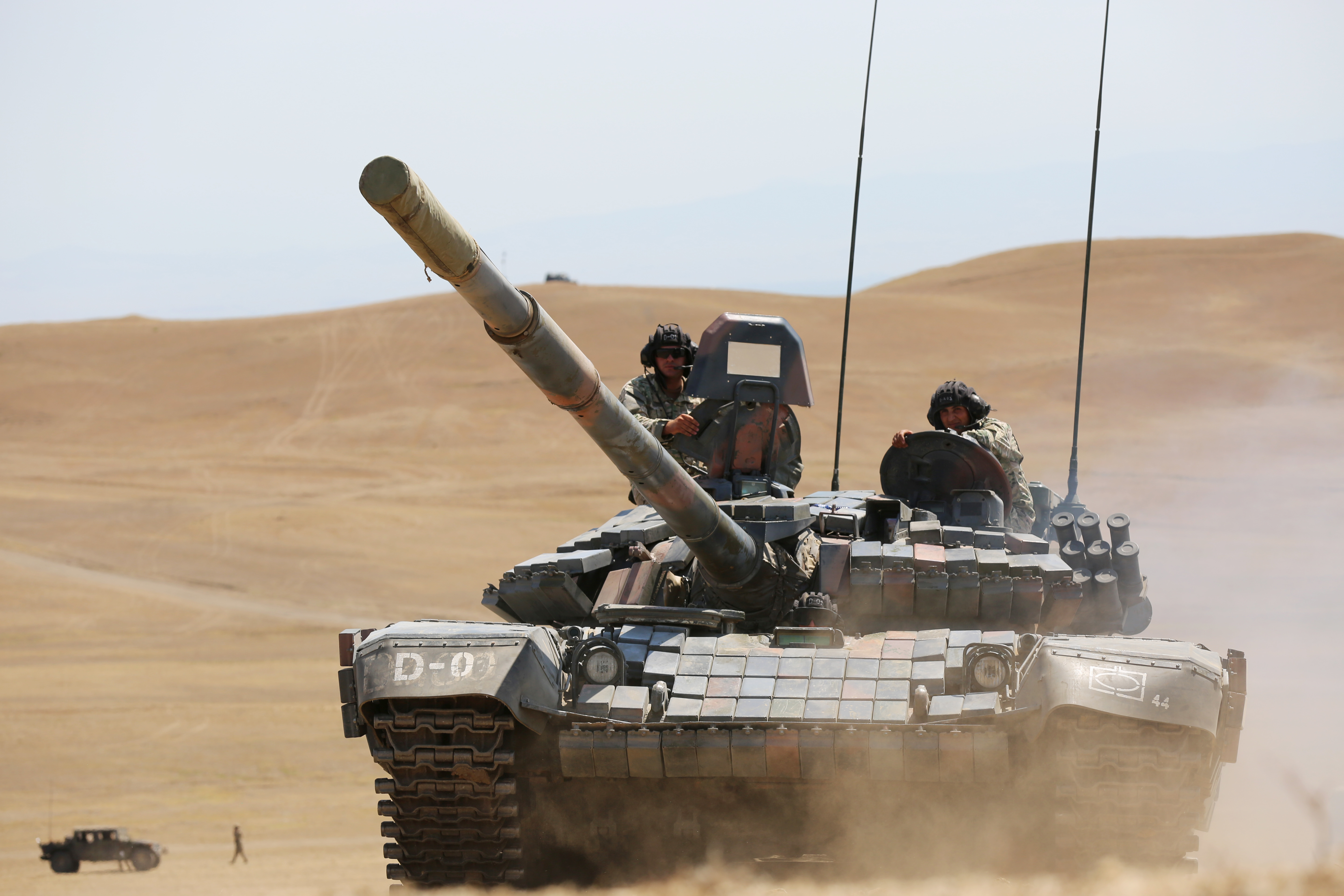 * T-72 SIM-1 – Increased implementation of K-1 reactive and K-5 passive armor. New FALCON command and control system, GPS navigation system and Polish SKO-1T DRAWA-T fire control system with thermal imager and laser rangefinder (from
* T-72 SIM-1 – Increased implementation of K-1 reactive and K-5 passive armor. New FALCON command and control system, GPS navigation system and Polish SKO-1T DRAWA-T fire control system with thermal imager and laser rangefinder (from
 By the late 1970s,
By the late 1970s,
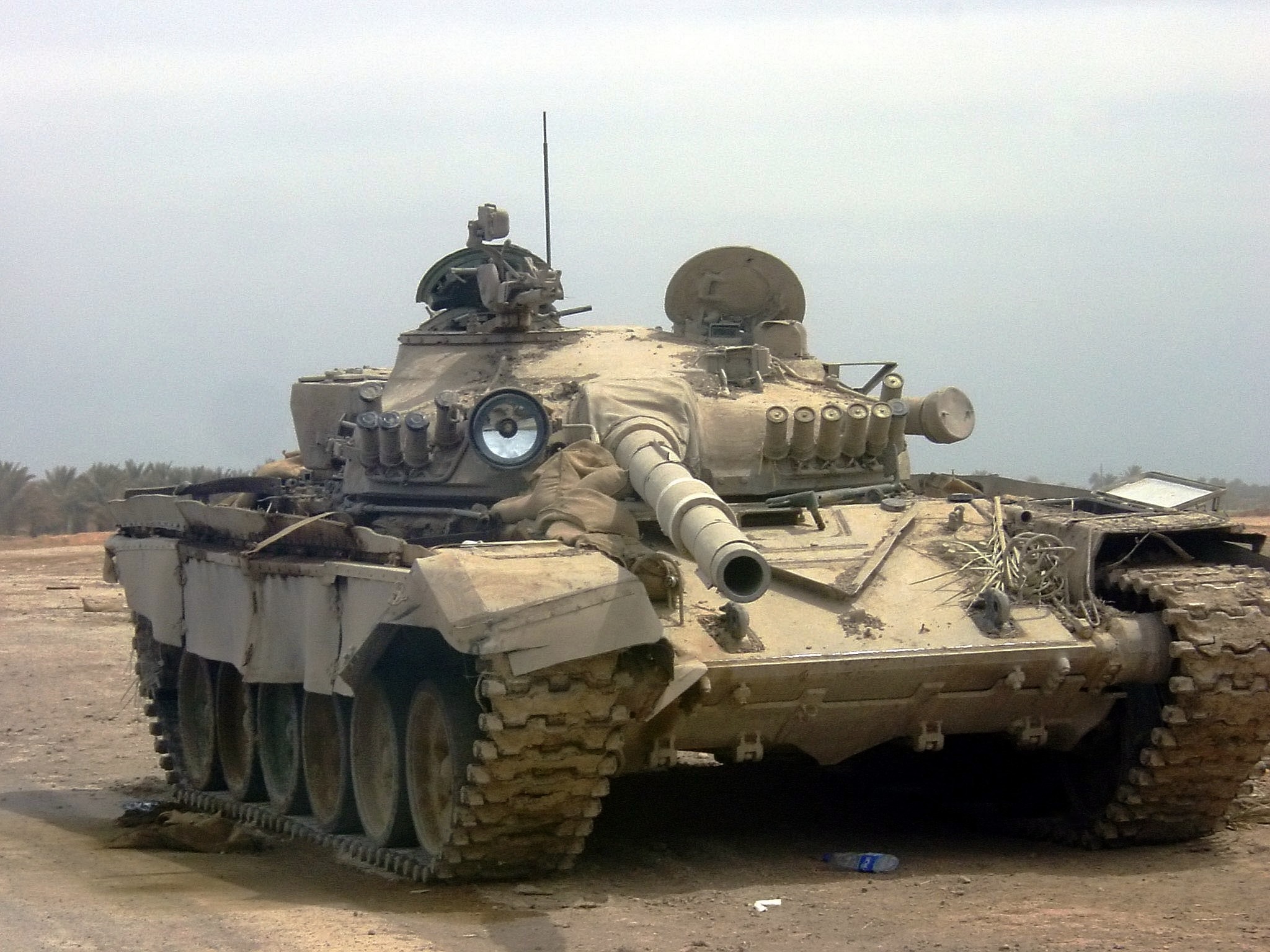 *T-72 Saddam – T-72M modified by Iraq to suit local conditions. Some of the suspension shock absorbers were removed and a searchlight on the right-hand-side of the main armament was added.
*
*T-72 Saddam – T-72M modified by Iraq to suit local conditions. Some of the suspension shock absorbers were removed and a searchlight on the right-hand-side of the main armament was added.
*
:* T-72M1R – Modification of T-72M1. :* ''Jaguar'': When Polish production of the T-72 started in 1982, the Poles considered upgrading them and the first domestic T-72 upgrade program was launched by the Institute of Armament and Equipment of the Polish Army. The project was code-named ''Jaguar'' since that was the designation under which the Soviet Union transferred the technical data package for the T-72. The ''Jaguar'' was never more than a concept. :* ''Wilk'': Beginning in 1986, the Polish T-72 ''Wilk'' project was instituted to allow tank repair plants to upgrade T-72 tanks within their own facilities. In particular, it was proposed that the Soviet-made Volna fire control system be replaced by the Czechoslovak-made Kladivo FCS or by the Polish SKO-1 Mérida, which was originally designed for T-55AM "Merida". Besides the new FCS, the Radomka passive night vision devices were installed in the driver's compartment, as was the Liswarta night sight, Obra laser illumination warning system, Tellur anti-laser smoke grenade launchers, solid or modular metal side skirts and the Polish-developed Erawa-1 or Erawa-2 explosive reactive armour was also fitted. This program was further developed and led to the PT-91. *
*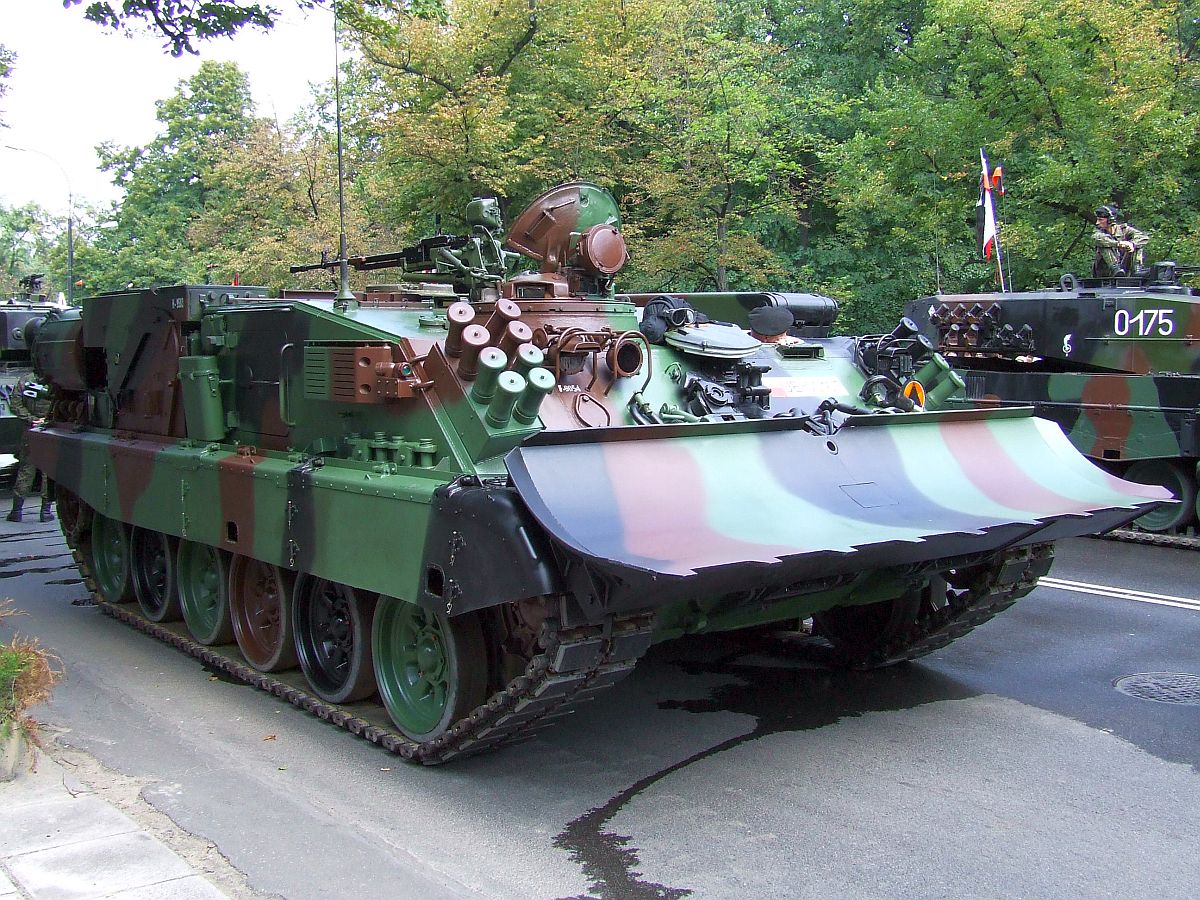  :* WZT-3M – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army
:* M-84AI – A M-84A based variant, made on licence in Yugoslavia – 15 vehicles for Kuwait
:* ARV-3 – A T-72 based variant for Indian Army – 352 vehicles made
* MID Bizon-S – engineering tank based on the PT-91 tank hull
:* MID-M – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army
:* WZT-4 – Armoured recovery vehicle, PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army (technically this vehicle is closely related to MID-M, not the WZT-3)
* SJ-09 – Polish driver training vehicle. The turret has been replaced by a flat-plate cabin with dummy gun barrel. Polish army uses T-72 based vehicles, Malaysian Army has one based on PT-91M.
* PZA Loara – SPAAG prototype based on the T-72 chassis.
:* WZT-3M – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army
:* M-84AI – A M-84A based variant, made on licence in Yugoslavia – 15 vehicles for Kuwait
:* ARV-3 – A T-72 based variant for Indian Army – 352 vehicles made
* MID Bizon-S – engineering tank based on the PT-91 tank hull
:* MID-M – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army
:* WZT-4 – Armoured recovery vehicle, PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army (technically this vehicle is closely related to MID-M, not the WZT-3)
* SJ-09 – Polish driver training vehicle. The turret has been replaced by a flat-plate cabin with dummy gun barrel. Polish army uses T-72 based vehicles, Malaysian Army has one based on PT-91M.
* PZA Loara – SPAAG prototype based on the T-72 chassis.
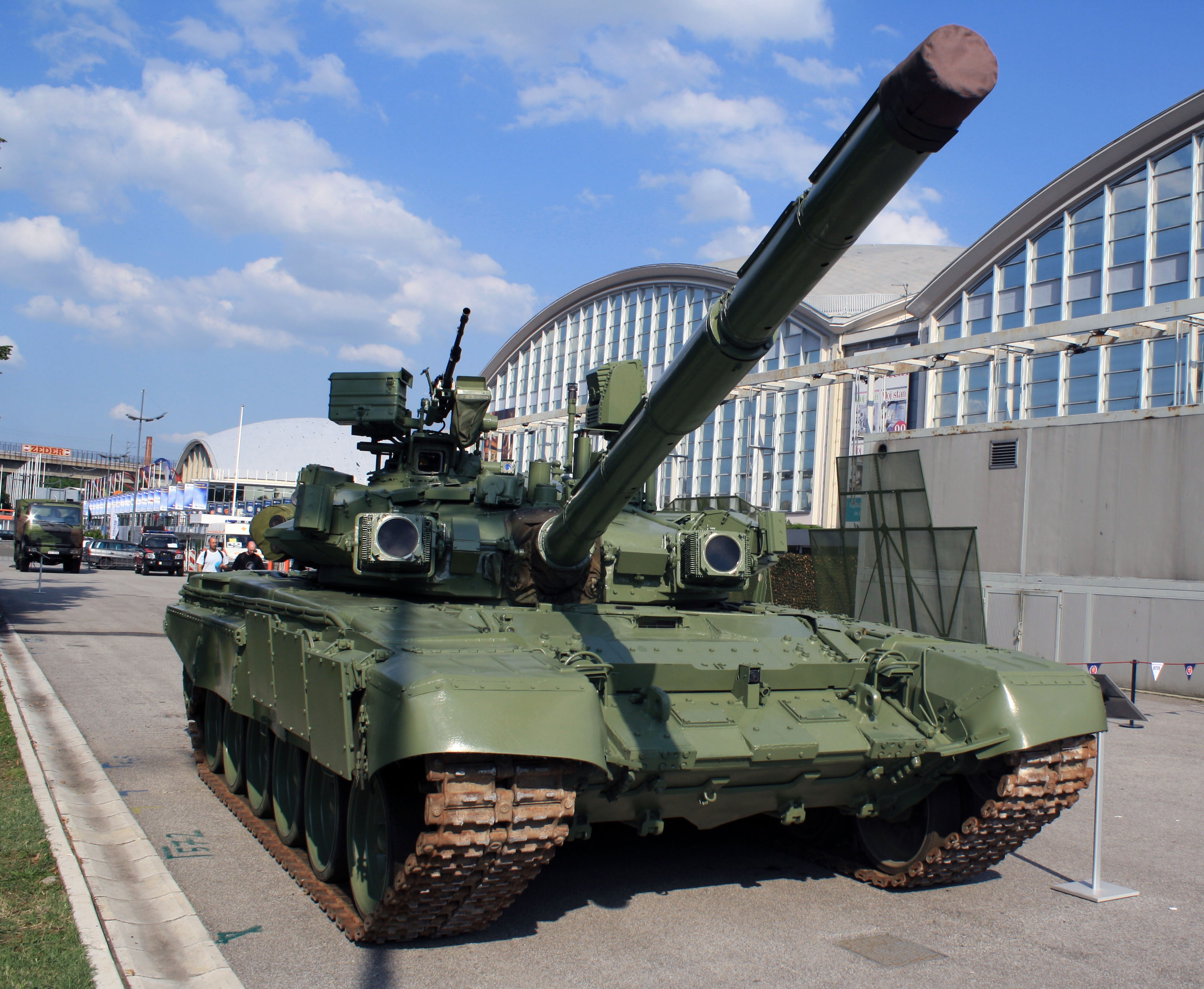

 * Yugoimport T-72 modernization package – Upgraded engine, communication gear and ERA.
*
* Yugoimport T-72 modernization package – Upgraded engine, communication gear and ERA.
*
 * – T-72M1 upgraded with suspension of the driver's seat from hull roof, DSM 16.1 engine monitoring system, ERA armour package around the turret with a flat front section, fire detection and suppression system, improved transmission, improved hull floor protection, laser Detection Warning System, modified electrical harness, PNK-72 driver's night sight, SGS-72A commanders stabilized passive sight, gunner's sight with a large head with two section door, S12U diesel engine, Slovenian EFCS3-72A fire control system and MB smoke grenade dischargers on the each side of the turret. It also has two external sensor rod mounts on turret roof.
* T-72M2 – Slovak modernization. Development was completed but without any order for tank fleet modernization.
* VT-72C – Improved VT-72B produced since 1999 for India. It is fitted with a more powerful Polish S-12U diesel engine and has a modified interior.
* VT-72Ž – Combat engineer tank. Similar to the VT-72B but with a modified telescopic arm with bucket.
* MT-72 – Slovakian scissors-type bridge based on T-72 chassis. When deployed the bridge is 20 m long and will span a gap of 18 m. It is capable of carrying loads of up to 50 tonnes.
* ShKH 2000 "Zuzana" (Zuzanne) – A 155 mm (45 calibers) version (the first prototype of which was completed by ZTS in December 1992) of the Dana 152 mm self-propelled gun-howitzer installed on a modified T-72M1 chassis.
* – T-72M1 upgraded with suspension of the driver's seat from hull roof, DSM 16.1 engine monitoring system, ERA armour package around the turret with a flat front section, fire detection and suppression system, improved transmission, improved hull floor protection, laser Detection Warning System, modified electrical harness, PNK-72 driver's night sight, SGS-72A commanders stabilized passive sight, gunner's sight with a large head with two section door, S12U diesel engine, Slovenian EFCS3-72A fire control system and MB smoke grenade dischargers on the each side of the turret. It also has two external sensor rod mounts on turret roof.
* T-72M2 – Slovak modernization. Development was completed but without any order for tank fleet modernization.
* VT-72C – Improved VT-72B produced since 1999 for India. It is fitted with a more powerful Polish S-12U diesel engine and has a modified interior.
* VT-72Ž – Combat engineer tank. Similar to the VT-72B but with a modified telescopic arm with bucket.
* MT-72 – Slovakian scissors-type bridge based on T-72 chassis. When deployed the bridge is 20 m long and will span a gap of 18 m. It is capable of carrying loads of up to 50 tonnes.
* ShKH 2000 "Zuzana" (Zuzanne) – A 155 mm (45 calibers) version (the first prototype of which was completed by ZTS in December 1992) of the Dana 152 mm self-propelled gun-howitzer installed on a modified T-72M1 chassis.
"Two myths of one battle: Syrian T-72's in 1982 Lebanon war"
in Russian) * Zaloga, Steven J (1993) T-72 Main Battle Tank 1974–93, Osprey Publishing . * Ustyantsev, Sergej Viktorovich; Kolmakov Dmitrij Gennadevich "Boyeviye mashiny Uralvagonzavoda. Tank T-72" * A.V. Karpenko (1996) "Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.)" Nevskij Bastion * * *
Utländska försöksfordon i Sverige , SPHF
{{DEFAULTSORT:T-72 Operators And Variants Main battle tanks of the Cold War Cold War tanks of the Soviet Union Tanks of Finland Czechoslovakia–Soviet Union relations Poland–Soviet Union relations Main battle tanks of Poland Main battle tanks of Slovakia Main battle tanks of Iraq T-72 Vehicle operators by vehicle type
T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet Union, Soviet main battle tanks that entered production in 1973. The T-72 was a development based on the T-64 using thought and design of the previous Object 167M. About 25,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refu ...
is a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
-designed main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
that entered production in 1973. It replaced the T-54/55
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Soviet medium tanks introduced in the years following the Second World War. The first T-54 prototype was completed at Nizhny Tagil by the end of 1945.Steven Zaloga, T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tanks 1944–2 ...
series as the workhorse of Soviet tank forces (while the T-64
The T-64 is a Soviet tank manufactured in Kharkiv, and designed by Alexander Morozov. The tank was introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank divisions, while the T-62 supported i ...
and T-80
The T-80 is a main battle tank (MBT) that was designed and manufactured in the former Soviet Union and manufactured in Russia. The T-80 is based on the T-64, while incorporating features from the later T-72 and changing the engine to a gas turbi ...
served as the Soviet high-technology tanks). In front-line Russian service, T-72s are being upgraded or augmented by the T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard p ...
, itself a modernized version of the T-72B. The T-72 has been exported and produced in many countries.
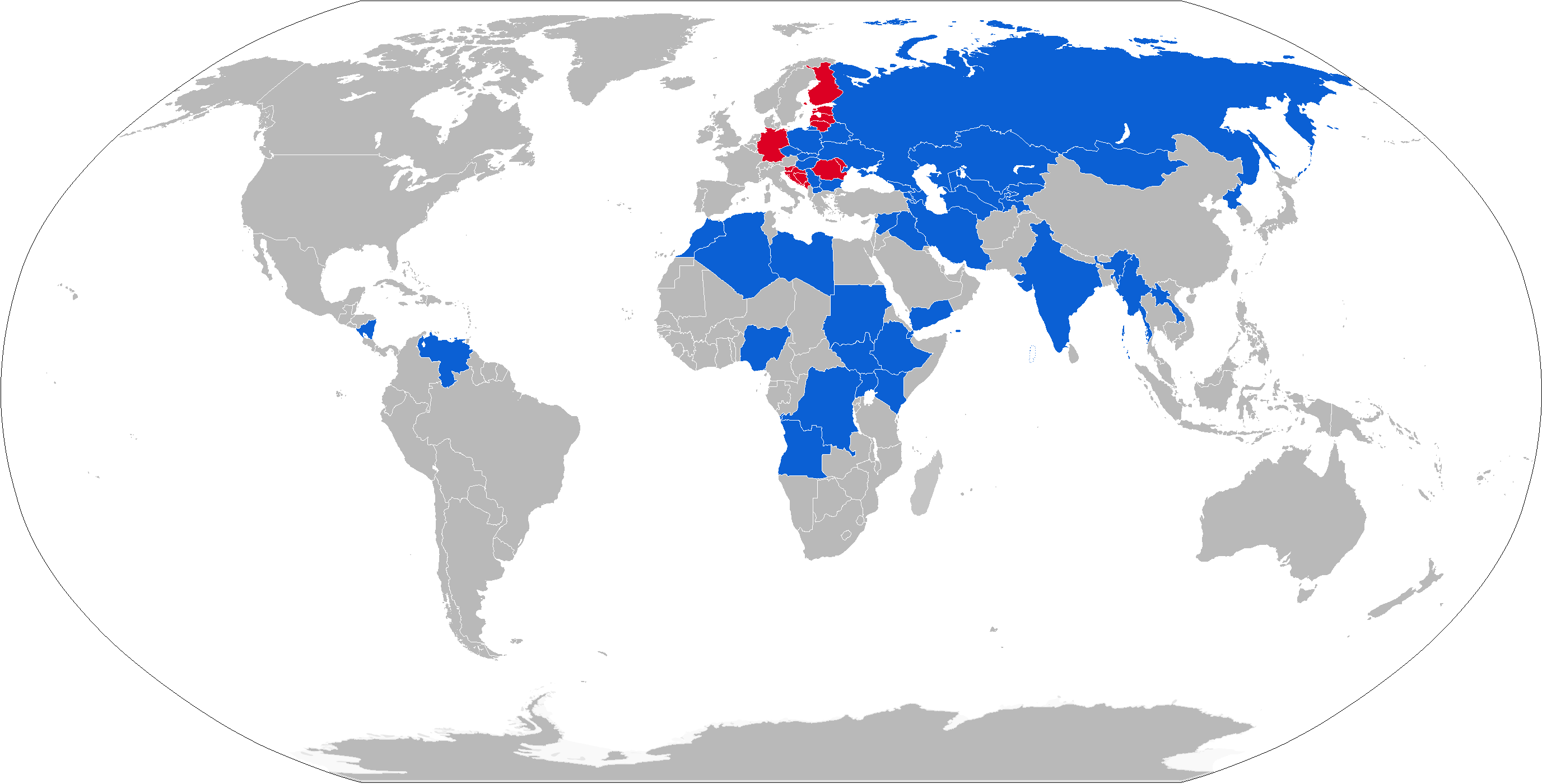
Operators
Current operators
* * – 404 T-72A, T-72AV, T-72B, and T-72SIM2 as of 2023.
* – 477 T-72B and 20 T-72B3 mod. 2016 as of 2023. Various T-72 modifications in reserve.
* – 90 T-72M1/M in service as of 2025.IISS 2025
* – 1 operated by the 4 Intelligence Company.
* – 74 M-84A4 Sniper, which is an improved variant of the T-72M, as of 2025 awaiting replacement with the Leopard 2A8 while 30 M-84A4 will be donated to Ukraine.
* – 404 T-72A, T-72AV, T-72B, and T-72SIM2 as of 2023.
* – 477 T-72B and 20 T-72B3 mod. 2016 as of 2023. Various T-72 modifications in reserve.
* – 90 T-72M1/M in service as of 2025.IISS 2025
* – 1 operated by the 4 Intelligence Company.
* – 74 M-84A4 Sniper, which is an improved variant of the T-72M, as of 2025 awaiting replacement with the Leopard 2A8 while 30 M-84A4 will be donated to Ukraine.International Institute for Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is an international research institute or think tank focusing on defence and security issues. Since 1997, its headquarters have been at Arundel House in London. It has offices on four co ...
: The Military Balance 2025
* – 30 T-72M4CZ
The T-72M4 CZ is an upgraded Czech Republic, Czech version of the Soviet-designed, Czechoslovakia made main battle tank T-72, T-72M. The only user of this tank is the Military of the Czech Republic, Czech Army. Between 2003 and 2006, 30 tanks were ...
in service as of 2025. 50 T-72M1s were donated to Ukraine between 2022 and 2023. Later all usable T-72M1 tanks were donated to Ukraine (last T-72M1s left Czechia in Spring 2025). * – 100 T-72AV delivered by Ukraine in 2010.
* – At least 1 captured in Badme War. Current status unknown.
* – 50 bought from Yemen, 171 T-72UA1 vehicles reportedly ordered from Ukraine in 2011.
* –143 T-72B/SIM1 in 2018. Upgraded T-72 SIMs were upgraded in Georgia with assistance of Israel.
* – 44 T-72M1 in service as of 2025. 77 T-72s were donated to the new
* – 100 T-72AV delivered by Ukraine in 2010.
* – At least 1 captured in Badme War. Current status unknown.
* – 50 bought from Yemen, 171 T-72UA1 vehicles reportedly ordered from Ukraine in 2011.
* –143 T-72B/SIM1 in 2018. Upgraded T-72 SIMs were upgraded in Georgia with assistance of Israel.
* – 44 T-72M1 in service as of 2025. 77 T-72s were donated to the new Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), also referred to as the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraq ...
. Hungary announced it ordered 44 Leopard 2A7+ tanks from Germany, which are to replace the T-72 in the 2020s.
* – 2,418 T-72M1 as of 2025.
* – 480 T-72S as of 2023.
* – 1,000 T-72 Ural (1973), T-72 Ural ''modernization'', T-72M, T-72M1 and Saddam tanks were in service with Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), also referred to as the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraq ...
in 1990. 375 T-72 Ural (1973), T-72 Ural ''modernization'', T-72M, T-72M1, Lion of Babylon and Saddam tanks were in service with Iraqi Regular Army in 2003. Only 125 T-72M1 are in service as of 2009 with the new Iraqi Army. Some T-72S MBTs in service with the PMF. Some T-72s have been upgraded and modernized by Iran with Rakhsh kits.
** − < 63. Entered service for the Peshmerga
The Peshmerga () are the internal security forces of Kurdistan Region. According to the Constitution of Iraq, regional governments are responsible for "the establishment and organization of the internal security forces for the region such as p ...
after 1991.
* – 350 T-72BA as of 2023.
* – 33 T-72M1 possibly ordered by South Sudan from Ukraine, but seized by Kenya after being held ransom en route by Somali pirates in 2008
* – 150 as of 2023
* – T-72B1
* – 150 in 2003.
* – 48 PT-91M delivered by Poland (which is an improved variant of the T-72M1).
* – 40 T-72B, ~60 in storage as of 2023.
* – 100 delivered. 50 T-72A in service as of 2023
* – 300 T-72S. Received from Ukraine between 2000 and 2008
* – 50 T-72B1MS tanks.
* – 10 T-72AV and 31 T-72M1 as of 2023.
* – 78 T-72M1/M1R and 206 PT-91 Twardy
The PT-91 Twardy (, English: Hard) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Deve ...
, which is an improved variant of the T-72M1, as of 2025. 382 T-72 and 232 PT-91 as of 2019. 2008 – 586 T-72M1 and T-72M1D, 135 T-72M1Z (T-72M1 upgraded to PT-91 standard), and 98 PT-91 in service 2006, 2007 – 597, 2005 – 644, 2004 – 649 More than 260 T-72s have been donated to Ukraine in 2022 with more in the next year.
* – 700 T-72A/B/BA and 470 T-72B3 in active service. 909 T-72A and 433 T-72B/BA in store as of 2025.1100 T-72B3, 550 T-72B3M, and more than 1000 T-72B in operation in 2022, 4800 variants of the T-72B in total. As of February 2023, the Russian Army
The Russian Ground Forces (), also known as the Russian Army in English, are the Army, land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Ground Forces are the protection of the state borders, combat on land, ...
operates 400 T-72B/BA, 500 T-72B3, and 250 T-72B3M tanks; the Russian Naval Infantry
The Russian Naval Infantry (), often referred to as Russian Marines in the West, operate as the naval infantry of the Russian Navy. Established in 1705, they are capable of conducting amphibious operations as well as operating as more traditiona ...
operates 170 T-72B/B3/B3Ms; the Russian Airborne Forces
The Russian Airborne Forces () is the airborne separate combat arm of the Russian Armed Forces. It is a rapid response force and strategic reserve that is under the President of Russia, reporting directly to the Chief of the General Staff, and ...
operates 50 T-72B3/B3M; while the 1st Army Corps and 2nd Army Corps operates some T-72A and T-72B tanks. 10,000 T-72 tanks of all variants in different conditions in storage. Many of the T-72 tanks have been left exposed and stored since the early 1990s, and they are likely to be in poor condition.
* – 30 T-72B1MS and 195 M-84
The M-84 is a Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav main battle tank based on the Soviet T-72. It is still in service with Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Serbia, Slovenia and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The ...
, which is an improved variant of the T-72M, as of 2025.
* – 20 T-72M1, still in service at the end of 2018. Another 10 in storage.
* – 96-101 units delivered in two shipments from Ukraine: first, 32 T-72 on the MV ''Faina'' in 2009, and second, 67 T-72 in 20??. 2 T-72 tanks were destroyed during the Heglig Crisis
The Heglig Crisis was a brief war fought between the countries of Sudan and South Sudan in 2012 over oil-rich regions between South Sudan's Unity and Sudan's South Kordofan states. South Sudan invaded and briefly occupied the small border town ...
. 80 T-72AV in service as of 2023
* – 70 T-72AV as of 2023.
* — 10
* – 650 T-72A, T-72AV, T-72AVS, T-72S, T-72M, T-72M1, T-72M1M, T-72M1S, T-72B obr. 1989, T-72B3, T-72 Adra
The T-72 ''Adra'' () or 'Mahmia' is a Syrian tank. It is a domestic upgrade to the T-72M1 that features slat armor, spaced armor, and chains to provide 360 degree protection from RPGs.
Background
In the late ‘70s through the early ‘90s ...
(a domestically improved version of the T-72M1 featuring slat and spaced
''Spaced'' is a British television sitcom created, written by and starring Simon Pegg and Jessica Stevenson, and directed by Edgar Wright, about the comedic, and sometimes surreal and action-packed, misadventures of Daisy Steiner and Tim Bi ...
armor
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
, with later versions also including the "Sarab" active protection system.) and T-72 Shafrah
**Syrian Democratic Forces
The Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) is a Kurds in Syria, Kurdish-led coalition of U.S.-backed Left-wing politics, left-wing ethnic militias and rebel groups, and serves as the official military wing of the Democratic Autonomous Administration ...
− Reported.
* – 28 T-72 Ural/A/AV/B and 3 T-72B1 as of 2023.
* – 650 T-72 and T-72UMG as of 2023.
* – 40 T-72A and 10 T-72B1 as of 2023.
* – 500+ T-72 and PT-91 Twardy as of 2023. In January 2014, Ukraine had 600 T-72 tanks all in storage. They were returned to active service since the War in Donbas
The war in Donbas, or the Donbas war, was a phase of the Russo-Ukrainian War in the eastern Donbas region of Ukraine. The war Timeline of the war in Donbas (2014), began in April 2014, when Russian separatist forces in Ukraine, Russian para ...
, and several were captured and pressed into service during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
, while others were donated by NATO members such as Poland and Czech Republic.
**Russian separatist forces in Donbas
Russian separatist forces in Ukraine, primarily the People's Militias of the Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR), were pro-Russian paramilitaries in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine. They were under the o ...
* – 70 as of 2023.
* – 92 T-72B1, delivered in 2009–2012 from Russia. In June 2012, Russia and Venezuela agreed on deal for 100 more T-72.
* – 39 in 2003.
**
Evaluation / aggressor training
* – 1 donated by Germany to Australian Army for evaluation. * – Former East German tanks received at the end of the Cold War for OPFOR training. Out of service by 2000. * – Used for aggressor training. Its presence was considered classified but released into public after army's invitation events. * – 1 received from Iran in 1980s. * – Acquired 8 former East German T-72s in 1991 primarily to evaluate Soviet armour. One has been preserved, while others are used as targets. * – 90 * – 1 obtained from the exchange of industrial machinery in Romania for scientific research, which is called "Type 64". And as of 2023, a domestically modernized variant equipped with a new turret—reportedly intended for export to third countries—has also been spotted in China.Former operators
* * * − ~20 T-72AV/B and 1 T-72SIM2 as of February 2023, seized by Azerbaijan following the2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh
Between 19 and 20 September 2023, Azerbaijan launched a large-scale military offensive against the political status of Nagorno-Karabakh, self-declared breakaway state of Republic of Artsakh, Artsakh, a move seen as a violation of the 2020 Nago ...
.
* – About 1,700 T-72/T-72M/T-72M1s were produced between 1981 and 1990. The Czechoslovak army had 815 T-72s in 1991. All were passed on to the successor states in 1993:
* – 35 T-72s (from USSR), 219 T-72s (from Poland and Czechoslovakia), 31 T-72Ms (from USSR), 162 T-72Ms (from Poland and Czechoslovakia) and 136 T-72M1s. 135 T-72S were ordered but none delivered before reunification. 75 T-72s were fitted with additional hull armour. Passed on to the unified German state
* – Some 160–170 T-72M1s. About 70 T-72M1s (one armoured brigade) were bought from the Soviet Union and were delivered in 1984, 1985–1988 and 1990. A further 97 T-72M1s (including a small number of command versions T-72M1K and T-72M1K1) were bought from German surplus stocks in 1992–1994. All withdrawn from service in 2006. Scrapped in Jyväskylä
Jyväskylä () is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Central Finland. It is located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Jyväskylä is approximately , while the Jyväskylä sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately ...
or sold as spares to the Czech Republic. At least two Finnish T-72s are still in working order and have been used in showcases.
* – Several were captured from the Syrian army
The Syrian Army is the land force branch of the Syrian Armed Forces. Up until the fall of the Assad regime, the Syrian Arab Army existed as a land force branch of the Syrian Arab Armed Forces, which dominanted the military service of the fo ...
.
* – 30 T-72A and 1 T-72AK delivered from Ukraine in 1999. 8 tanks were donated to Ukraine in June 2022.
* – 31 T-72Ms were bought from the USSR, and received between 1978 and 1979. Withdrawn from service (in long-term storage), 28 tanks are for sale (23 of them need repairs and five are operational). In 2022 it was reported that Romania transferred their fleet of T-72s to Ukraine in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
. * – In 1994 Sierra Leone acquired two T-72s from Poland via Ukraine (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). Another unspecified number of ex-Polish tanks was delivered to Sierra Leone in 1997 also via Ukraine (these vehicles also previously served with Poland).
* – Passed on to successor states:
*
* – In 1994 Sierra Leone acquired two T-72s from Poland via Ukraine (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). Another unspecified number of ex-Polish tanks was delivered to Sierra Leone in 1997 also via Ukraine (these vehicles also previously served with Poland).
* – Passed on to successor states:
* Tigray Defense Forces
The Tigray Defence Forces (TDF; ), colloquially called the ''Tigray Army'' (), is a paramilitary group located in the Tigray region of Ethiopia. It was founded by former generals of the Ethiopian Military in 2020 to combat federal forces enf ...
− Surrendered to the Ethiopian forces in the aftermath of the Tigray War.
* – Bought approximately 18 T-72Ms from the USSR and 72 from Czechoslovakia, later developed the improved M-84
The M-84 is a Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav main battle tank based on the Soviet T-72. It is still in service with Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Serbia, Slovenia and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The ...
.
Variants
Soviet Union and Russia

 The T-72 was designed and first built in the Soviet Union.
* T-72 "Ural" (Ob'yekt 172M) (1973): Original version, armed with the 125 mm D-81TM smoothbore tank gun. Unlike the later versions it had the searchlight mounted on left. It also had flipper-type armour panels. It had the TPD-2-49 coincidence
The T-72 was designed and first built in the Soviet Union.
* T-72 "Ural" (Ob'yekt 172M) (1973): Original version, armed with the 125 mm D-81TM smoothbore tank gun. Unlike the later versions it had the searchlight mounted on left. It also had flipper-type armour panels. It had the TPD-2-49 coincidence rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to Length measurement, measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, suc ...
optical sight
A sight or sighting device is any device used to assist in precise visual alignment (i.e. ''aiming'') of weapons, surveying instruments, aircraft equipment, optical illumination equipment or larger optical instruments with the intended target. ...
protruding from its turret."Czołgi Świata" (World's Tanks or Tanks of the World) magazine issue 20
:*T-72K: Command version of the T-72 "Ural" with an additional R-130M radio. Company command versions were fitted with two additional R-123M/R-173 radios and also carried a 10 m telescopic mast. Battalion and regiment command versions were fitted with two additional R-123M/R-173 radios and the R-130M that used the 10 m mast when it was erected. In NATO code, the T-72K was represented by three different designations: T-72K1, T-72K2 and T-72K3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
:* Robot-2: Remote controlled T-72 "Ural".
:* Ob'yekt 172-2M "Buffalo": Modernization of the T-72 made in the early 1970s. The angle of the front armour slope was changed to 30 degrees. 100% metal side skirts protecting sides of the hull, added armour screens protecting the turret, ammunition storage increased to 45 rounds, modified suspension, added smoke grenade
A smoke grenade is a canister-type grenade used as a signaling device, target or landing zone marking device, or as a screening device for unit movements.
Smoke grenades are generally more complex and emit a far larger amount of smoke than sm ...
dischargers (SGDs), engine power boosted to .
:* T-72 "Ural-1" (Ob'yekt 172M1) (1976): new 2A46 main gun, new armour on the turret.
* T-72A (Ob'yekt 172M-1) (1979): An improved version of the basic T-72 "Ural". Large numbers of early-production T-72 "Ural" models were modernized in the 1980s. Searchlight has been placed on the right-hand side of turret, blanking off the TPD-2-49 coincidence optical rangefinder and replaced by the TPD-K1 laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter or laser distance meter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by ...
, added plastic armour track skirts covering the upper part of the suspension with separate panels protecting the sides of the fuel and stowage panniers instead of the flipper-type armor panels used on the T-72 "Ural", the turret front and top being heavily reinforced with composite armour better known by its US codename – "Dolly Parton", an electronic fire control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a Director (military), director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs th ...
, MB smoke grenade launchers, flipper armour mount on front mudguards, internal changes, and a slight weight increase.
 :*T-72A obr.1982g: Additional glacis armour with thickness of 16 mm of high resistance steel.
:* T-72A obr.1984g: Late production with new turret, new gunner night sight 1K13-49, new engine. Smoke launchers on the turret side.
:* T-72AK (Ob'yekt 176K): Command version of the T-72A. In NATO code T-72AK was represented by three different designations: T-72AK1, T-72AK2 and T-72AK3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
:*T-72AV: ("V" for ''vzryvnoi'' – explosive) model with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour fitted to hull front and turret.
* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E2, Ob'yekt 172M-E3, Ob'yekt 172M-E4): Soviet export version, similar to the T-72A but with thinner armour and 125 mm D-81T smoothbore tank gun with 44 rounds. It was sold to Iraq and to Syria and was also built in Poland by
:*T-72A obr.1982g: Additional glacis armour with thickness of 16 mm of high resistance steel.
:* T-72A obr.1984g: Late production with new turret, new gunner night sight 1K13-49, new engine. Smoke launchers on the turret side.
:* T-72AK (Ob'yekt 176K): Command version of the T-72A. In NATO code T-72AK was represented by three different designations: T-72AK1, T-72AK2 and T-72AK3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
:*T-72AV: ("V" for ''vzryvnoi'' – explosive) model with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour fitted to hull front and turret.
* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E2, Ob'yekt 172M-E3, Ob'yekt 172M-E4): Soviet export version, similar to the T-72A but with thinner armour and 125 mm D-81T smoothbore tank gun with 44 rounds. It was sold to Iraq and to Syria and was also built in Poland by Bumar-Łabędy
Bumar-Łabędy is a Polish manufacturer of military vehicles and Heavy equipment, construction equipment, based in Gliwice, Upper Silesia. It is a division of the Polish Armaments Group. History
Zakłady Mechaniczne "BUMAR-ŁABĘDY" S.A. based in ...
. and Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
.
:* T-72MK (T-72M(K)): Export version of T-72AK. It is a command vehicle for battalion commanders and has additional radio equipment including the R-130M radio, AB-1-P/30-M1-U generator and a TNA-3 navigation system. The main external difference is a 10 m telescopic antenna stowed under the rear of the stowage box during travel. An additional antenna base for this telescopic antenna is mounted on the left side of the turret. Because of the additional equipment the number of rounds for the 125 mm tank gun had to be lowered from 44 to 38. In NATO code the T-72MK was represented by three different designations: T-72MK1, T-72MK2 and T-72MK3 which represented the company command version, battalion command version and regiment command version.
* T-72M-E (Ob'yekt 172M-E): Soviet export version armed with the 125 mm D-81T smoothbore tank gun with 44 rounds.
::* T-72M fitted with a French 155 mm F1 turret for trials in India.
::* T-72M fitted with a British 155 mm Vickers T6 turret for trials in India.
* T-72M1 (Ob'yekt 172M-E5, Ob'yekt 172M-E6): Soviet export version, with thicker armour and similar to T-72A obr.1979g. It also is fitted with 7+5 smoke grenade dischargers on turret front. It was also built in Poland and ex-Czechoslovakia.
:* : Commander's variant with additional radios.
:* : T-72M1 with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour ("V" for ''vzryvnoi'' – explosive).
:* T-72S "Shilden" (T-72M1M1, Ob'yekt 172M-E8): Export version of the T-72B with only 155 ERA bricks, simplified NBC system, no anti-radiation lining etc.
* (Ob'yekt 184) (NATO code: SMT M1988): (1985) (SMT – Soviet Medium Tank) Equipped with a new 2A46M main gun with a new 2E42-2 stabilisation system. Much improved version of 1A40-1 fire control system, 1K13-49 gunner's sight which allows the use of 9M119 Svir
The 9K120 ''Svir'', 9K119 ''Refleks'', 9K119M ''Refleks-M'' (NATO reporting name AT-11 ''Sniper'') are laser beam riding, guided anti-tank missile systems developed in the Soviet Union. Both are designed to be fired from smoothbore 125 mm tan ...
gun-launched anti-tank guided missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulde ...
. Thicker armour, 20 mm of appliqué armour on the front of the hull , front and top of the turret were heavily reinforced with composite armour better known by its US codename "Super Dolly Parton". New V-84-1 engine with 840 hp (626 kW). On early models the smoke dischargers were mounted on the turret front (as on the T-72A), later they were grouped on the left side of the turret to prepare for the installation of ERA bricks.
:* T-72BK (Ob'yekt 184K): Command version of the T-72B, recognisable by having multiple radio antennas and a radio mast stowage under rear turret bin.
 :* T-72BA (Ob'yekt 184A/A1): this designation is used to refer to several models of late T-72B, stripped down, refurbished and upgraded with certain core components at
:* T-72BA (Ob'yekt 184A/A1): this designation is used to refer to several models of late T-72B, stripped down, refurbished and upgraded with certain core components at Uralvagonzavod
UralVagonZavod () is a Russian machine-building company located in Nizhny Tagil, Russia.
It is one of the largest scientific and industrial complexes in Russia and the largest main battle tank manufacturer in the world. Etymology
The name ''У� ...
between 1998 and 2005. There are several features common to all upgraded T-72BA models; front of the turret and front of the hull reinforced with Kontakt-5
Kontakt-5 is a type of second-generation explosive reactive armour (ERA) originating in the Soviet Union. Due to the shortcomings of Kontakt-1, NII Stali developed a new type of reactive armor, Kontakt-5, so that it also affects the penetration c ...
ERA, the frontal floor plate reinforced against mines, the driver's seat is now suspended from the ceiling instead of being fixed to the floor and the driver's station has a new steering system as well as a new TVN-5 night sight. These tanks are equipped with the V-84MS engine using an upgraded exhaust system and newly developed twin-pin tracks (used on the T-90A). The upgrade also included the integration of a DWE-BS wind sensor whose mast is located on the rear, left part of turret and which feeds information into the 1A40 fire control system automatically. Tanks upgraded after the year 2000 received an improved 1A40-01M fire control system which makes use of a TBV digital ballistic computer. The tanks can also fire the 9M119M Refleks laser-guided anti-tank missile through the use of a 1K13-49 sight. The most recent T-72BA tanks made in 2005 feature the latest iteration of the 1A40 FCS, designated 1A40-M2. While the upgraded tanks retained the original 2A46M main gun, more importantly, they received a much improved 2E42-4 stabilization system which significantly improved accuracy – especially during firing on the move. Approximately 750 tanks were upgraded to the T-72BA standard.
 :* T-72B1 (Ob'yekt 184-1): T-72B without the 9K120 missile system.
::* T-72B1K (Ob'yekt 184K-1): Command version of the T-72B1.
:* T-72B1 (Ob'yekt 184-1): T-72B without the 9K120 missile system.
::* T-72B1K (Ob'yekt 184K-1): Command version of the T-72B1.

 ::* T-72B1MS "White Eagle"(Ob'yekt 184-1MS): T-72B1 modernized by the 61st armour repair factory (today part of the
::* T-72B1MS "White Eagle"(Ob'yekt 184-1MS): T-72B1 modernized by the 61st armour repair factory (today part of the Uralvagonzavod
UralVagonZavod () is a Russian machine-building company located in Nizhny Tagil, Russia.
It is one of the largest scientific and industrial complexes in Russia and the largest main battle tank manufacturer in the world. Etymology
The name ''У� ...
group), first unveiled at the Engineering Technologies 2012 forum, painted all white, hence the unofficial nickname "White Eagle". The protection of the tank is unchanged, with the Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour used in protecting vehicles, especially modern tanks, against shaped charges and hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is ''explosive reactive armour'' (ERA), but variants include ...
being retained, and the cannon is unchanged. A modernised V-84MS engine is installed, but its power output is the same as the older one. An auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115&n ...
is added. The electronics are heavily upgraded, including a rear camera for the driver, a GPS/GLONASS navigation system, a "Falcon's Eye" third generation panoramic thermal sight
A thermographic weapon sight, thermal imagery scope or thermal weapon sight is a sighting device combining a compact thermographic camera and an aiming reticle. They can be mounted on a variety of small arms as well as some heavier weapons.
As w ...
for the commander, a Sosna-U thermal gunner sight, an automatic target-tracking system, a chassis management system, a meteorological mast, and the capability to use 9M119 Svir/Refleks barrel-launched ATGMs. Lastly, a Kord remotely controlled AA machine gun is added. These improvements increase the weight from 44.1 to 47.3 tonnes. Currently (2019) in service with Laos, Nicaragua and Serbia
:* T-72B obr.1989g: T-72B equipped with advanced Kontakt-5
Kontakt-5 is a type of second-generation explosive reactive armour (ERA) originating in the Soviet Union. Due to the shortcomings of Kontakt-1, NII Stali developed a new type of reactive armor, Kontakt-5, so that it also affects the penetration c ...
explosive reactive armour, composite armour in sides of turret as well. Often called T-72BM or T-72B(M) but this is not correct. NATO code: SMT M1990.
:* T-72B obr.1990g: Additionally fitted with new FCS, crosswind
A crosswind is any wind that has a perpendicular component to the line or direction of travel. This affects the aerodynamics of many forms of transport. Moving non- parallel to the wind direction creates a crosswind component on the object and t ...
sensor and sometimes V-92S2 engine.
::* T-72B obr.1990g with an improved commander's cupola with a larger sight.
:* T-72B2 ''Rogatka'' obr.2006g (Ob'yekt 184M) (also referred to as T-72BM in documents): T-72B upgrade proposal code-named ''Rogatka''. First shown at the 2006 Russian Arms Expo, it was equipped with a new fire-control system including a Sosna-U thermal sight, and a new 125 mm 2A46M-5 main gun. The autoloader was replaced with the model found on the T-90A, and allowed for the use of longer, more modern ammunition. A new V-92S2 1,000 hp diesel engine was added. The new ''Relikt'' third-generation ERA replaced the Kontakt-5 ERA on the front of the tank, while slat armour
Slat armor (or slat armour in British English), also known as bar armor, cage armor, and standoff armor, is a type of vehicle armor designed to protect against high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) attacks, as used by anti-tank guided missiles (ATG ...
was added on the flanks. TShU-1-11 laser warning receiver
A laser warning receiver is a warning system used as a passive military defence. It detects, analyzes, and locates directions of laser emissionsPDF version4.53 MB) from laser guidance systems and laser rangefinders. Then it alerts the crew and can ...
s were placed on the turret front. The prototype was shown equipped with the Nakidka camouflage kit. The price of this modernisation was deemed too high, and it was not serially produced. However, some of its features were used in the T-72B3
The T-72 is a Soviet-designed main battle tank that entered production in 1973. It replaced the T-54/55 series as the workhorse of Soviet tank forces (while the T-64 and T-80 served as the Soviet high-technology tanks). In front-line Russian serv ...
modernisation package.
* T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard p ...
(Ob'yekt 188) – A further development of the T-72, incorporating many features of the heavier, more complex T-80. It was first called upgraded T-72B(Усовершенствованный танк Т-72Б)
 * (Ob'yekt 184-M3): this upgrade was initiated in 2010 using old stocks of T-72B tanks held in reserve. The purpose was to upgrade old T-72s to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the new T-90A tanks to simplify supply lines. In addition to performing a general overhaul of every vehicle, all tanks were equipped with the more powerful V-92S2 engines and a new steering system in the driver's compartment, and older tracks were replaced with the new universal, twin-pin design. The upgrade program focuses mainly on the implementation of a new fire control system. The tank commander retains an upgraded version of the legacy TKN-3MK sight, which is a passive device with a range of only 600 m at night. The commander also has a separate monitor that displays thermal imagery from the gunner's main sight, and a new turret control panel. The gunner has the new PNM Sosna-U panoramic multi-spectral sensor, which replaced the 1K13 night vision in its mounting; the 1A40-4 FCS with TPD-K1 sight is retained, but as part of the auxiliary sighting system to complement the newer system. The Sosna-U is a multi-channel, panoramic sight stabilized in both vertical and horizontal axes with a built-in laser rangefinder and command guidance module, used with 9M119M missiles. The main advantage of the Sosna-U is the Thales Catherine-FC thermal imager which extends the detection range of a tank-sized target to 10,500 m and the identification range to 3,300 m in both day and night conditions and all weathers. The T-72B3 series vehicles also received the new 2A46M-2 main gun which is reportedly equivalent to the Rheinmetall Rh120 L/44 cannon. The gun-laying and stabilization drives were also replaced by the new 2E42-4 system, and the AZ ammunition auto-loader was modified to accommodate newer generations of 125 mm smoothbore anti-tank ammunition: Vant (depleted uranium) and Mango (tungsten) rounds. There is also a new 9K119 Refleks system, used to launch 9M119 Refleks ATGM through the gun barrel. The B3 upgrade includes a new explosion- and fire-suppression system and an advanced VHF radio system designated R-168-25U-2 AKVEDUK. The variant entered service on 19 October 2012. It was first delivered to the 20th Field Army in summer 2013, and to its Armored Guards Brigade in October 2013. About 2,000 such tanks were in service as of 2020. The cost to upgrade a T-72 to the T-72B3 standard was around 52 million rubles in 2013.
:*T-72B3 obr.2014: a special version of the T-72B3, first seen during the 2014 edition of the Tank Biathlon competition. The most notable upgrades are the stabilized, panoramic, independent PK-PAN commander sight with integrated thermal viewer and a V-92S2 1,000 hp engine.
*T-72B3M obr.2016: a further upgrade of the T-72B3, produced since 2016 by overhauling and upgrading old T-72B tanks from storage. The purpose was to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the T-90 M tank to simplify supply lines. There is a new gun 2A46M-5 with new anti-tank ammunition Svinets-1 (tungsten) and Svinets-2 (depleted uranium). New 2E58 gun stabilizer is responsible for improved aiming time. 9K119M Refleks-M system is used to launch 9M119M Invar (also called Reflex-M) ATGM through gun barrel. New PK-PAN panoramic commander sight with thermal vision only seen on a limited number of vehicles while all the rest are using older TKN-3MK commander`s sight. Retained Sosna-U gunner`s sight and crosswind sensor. New Kalina fire control system, although in simplified form. There is new radio communication equipment as well as GLONASS satellite navigation. Driver is using older TVN-5 periscope with additional display from rear view camera. The automotive performance of the tank was improved with a more powerful V-92S2F engine rated at 1,130 hp (830 kW) coupled to an automatic transmission system and improved drivetrain. Protection is improved by Relikt new generation ERA mounted on sides of both hull and turret, while cage armor was added to the rear.
* (Ob'yekt 184-M3): this upgrade was initiated in 2010 using old stocks of T-72B tanks held in reserve. The purpose was to upgrade old T-72s to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the new T-90A tanks to simplify supply lines. In addition to performing a general overhaul of every vehicle, all tanks were equipped with the more powerful V-92S2 engines and a new steering system in the driver's compartment, and older tracks were replaced with the new universal, twin-pin design. The upgrade program focuses mainly on the implementation of a new fire control system. The tank commander retains an upgraded version of the legacy TKN-3MK sight, which is a passive device with a range of only 600 m at night. The commander also has a separate monitor that displays thermal imagery from the gunner's main sight, and a new turret control panel. The gunner has the new PNM Sosna-U panoramic multi-spectral sensor, which replaced the 1K13 night vision in its mounting; the 1A40-4 FCS with TPD-K1 sight is retained, but as part of the auxiliary sighting system to complement the newer system. The Sosna-U is a multi-channel, panoramic sight stabilized in both vertical and horizontal axes with a built-in laser rangefinder and command guidance module, used with 9M119M missiles. The main advantage of the Sosna-U is the Thales Catherine-FC thermal imager which extends the detection range of a tank-sized target to 10,500 m and the identification range to 3,300 m in both day and night conditions and all weathers. The T-72B3 series vehicles also received the new 2A46M-2 main gun which is reportedly equivalent to the Rheinmetall Rh120 L/44 cannon. The gun-laying and stabilization drives were also replaced by the new 2E42-4 system, and the AZ ammunition auto-loader was modified to accommodate newer generations of 125 mm smoothbore anti-tank ammunition: Vant (depleted uranium) and Mango (tungsten) rounds. There is also a new 9K119 Refleks system, used to launch 9M119 Refleks ATGM through the gun barrel. The B3 upgrade includes a new explosion- and fire-suppression system and an advanced VHF radio system designated R-168-25U-2 AKVEDUK. The variant entered service on 19 October 2012. It was first delivered to the 20th Field Army in summer 2013, and to its Armored Guards Brigade in October 2013. About 2,000 such tanks were in service as of 2020. The cost to upgrade a T-72 to the T-72B3 standard was around 52 million rubles in 2013.
:*T-72B3 obr.2014: a special version of the T-72B3, first seen during the 2014 edition of the Tank Biathlon competition. The most notable upgrades are the stabilized, panoramic, independent PK-PAN commander sight with integrated thermal viewer and a V-92S2 1,000 hp engine.
*T-72B3M obr.2016: a further upgrade of the T-72B3, produced since 2016 by overhauling and upgrading old T-72B tanks from storage. The purpose was to use the same gun, ammunition, ATGM, ERA etc. as the T-90 M tank to simplify supply lines. There is a new gun 2A46M-5 with new anti-tank ammunition Svinets-1 (tungsten) and Svinets-2 (depleted uranium). New 2E58 gun stabilizer is responsible for improved aiming time. 9K119M Refleks-M system is used to launch 9M119M Invar (also called Reflex-M) ATGM through gun barrel. New PK-PAN panoramic commander sight with thermal vision only seen on a limited number of vehicles while all the rest are using older TKN-3MK commander`s sight. Retained Sosna-U gunner`s sight and crosswind sensor. New Kalina fire control system, although in simplified form. There is new radio communication equipment as well as GLONASS satellite navigation. Driver is using older TVN-5 periscope with additional display from rear view camera. The automotive performance of the tank was improved with a more powerful V-92S2F engine rated at 1,130 hp (830 kW) coupled to an automatic transmission system and improved drivetrain. Protection is improved by Relikt new generation ERA mounted on sides of both hull and turret, while cage armor was added to the rear. Kontakt-5
Kontakt-5 is a type of second-generation explosive reactive armour (ERA) originating in the Soviet Union. Due to the shortcomings of Kontakt-1, NII Stali developed a new type of reactive armor, Kontakt-5, so that it also affects the penetration c ...
ERA is retained over the frontal arc and turret top. There is also increased protection against AT land mines. The Russian Defense Ministry ordered several hundred T-72B3M tanks, and received the first twenty in early 2017. The cost to upgrade a T-72 to the T-72B3 obr.2016 standard was around 78.9 million rubles in 2016.
::*Unmanned version of T-72B3M is (as of December 2018) under development.
:*T-72B3M obr.2022: It is the most recent upgrade of the T-72B3, based on combat experience gained during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
. New TKN-3TP commander`s sight with thermal vision (range 3000 m) is installed. New TVK-2 driver's dual channel sight (night vision 250 m). The tank is fitted with the same armament as the previous obr. 2016 model, however its protection has been enhanced. Previously, the back of the turret was without any additional protection and now there are metal boxes with Relikt explosive reactive armour
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour used in protecting vehicles, especially modern tanks, against shaped charges and hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is ''explosive reactive armour'' (ERA), but variants include ...
(ERA). Lower parts of the turret are covered by a metal net designed to improve protection against rocket-propelled grenade
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG), also known colloquially as a rocket launcher, is a Shoulder-fired missile, shoulder-fired anti-tank weapon that launches rockets equipped with a Shaped charge, shaped-charge explosive warhead. Most RPGs can ...
s, similar to that of the T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard p ...
M. Additional Kontakt-5 blocks installed right and left of the gun mantlet as well as on the turret top. The void in ERA coverage caused by the smoke grenade dischargers on the turret is now protected by Kontakt-1 ERA. Lower frontal hull plate is now covered with Kontakt-1 ERA. Relikt ERA plates are covering entire length of the chassis, fender/idler area and also attached to cage armor over engine compartment. Mechanism to open the armored protection panel for the Sosna-U sighting system is added, replacing the previous configuration which used bolts that had to be unscrewed manually before combat.
:*T-72B3A (2024): Basically, this is previously described model T-72B3M obr. 2022 with fully functional active protection system (APS) Sovershenstvo-A and experimental electronic warfare station Volnorez for disrupting /jamming enemy drones.
*T-72B Obr. 2023: mobilization model, produced by overhauling and upgrading existing 30+ years old T-72B and T-72BA tanks during regular maintenance in armor repair plants. The purpose was to unify different models in order to simplify supply lines. There is brand new dual channel TKN-3TP commander`s sight with thermal vision range 3000 m. New 1PN96MT-02 gunner`s sight (thermal vision range 3500 m, laser rangefinder, ballistic computer) coupled with the old TPD-K1 sight (day channel, ATGM guidance, laser rangefinder 4000 m). Combination of Kontakt-5, 4S24 and Relikt ERA all-around vehicle copied from T-72B3M obr.2022. Anti-RPG net below the turret. These vehicles were made without crosswind sensor and Sosna-U sight because of increased production during the war. Everything else was upgraded to the level of basic T-72B3 (main gun 2A46M-2, gun stabilizer 2E42-4, fire control system 1A40-4, driver's sight TVN-5, steering system, twin-pin tracks, 1000 hp engine, frontal floor plate reinforced against mines, driver seat suspended from the ceiling).
 * (''Boyevaya Mashina Ognemyochikov'') – A transport vehicle for flamethrower-squads armed with RPO launchers. Entered service in 2001.
* BMPT (Ob'yekt 199) – Heavy convoy and close tank support vehicle (''Boyevaya Mashina Podderzhki Tankov''). All new turret armed with 2 × 30 mm 2A42 autocannons (500 rounds), 4 × 9M1201 Ataka-T ATGM and 7.62 mm PKT MG (2,000 rounds). It can be also fitted with 2 × AGS-30 automatic grenade launchers. Features new fire control system with thermal sights and a ballistic computer. Reinforced with 3rd generation "Relikt" ERA on the frontal armor and both sides of hull and turret, slat (cage) armor in the rear. It is equipped with Agat-MR night vision devices, an NBC detection and protection system. There is 902A "Tucha" 81 mm smoke grenade launcher array on each side of the turret and "Shtora-1" active protection system. When the screening system warns the crew of laser tracking, a smoke screen is created by the launch of grenades. The vehicle can be fitted with either the KMT-8 or the EMT mine clearing system. The term BMP-T that is very often found is not correct.
*
* (''Boyevaya Mashina Ognemyochikov'') – A transport vehicle for flamethrower-squads armed with RPO launchers. Entered service in 2001.
* BMPT (Ob'yekt 199) – Heavy convoy and close tank support vehicle (''Boyevaya Mashina Podderzhki Tankov''). All new turret armed with 2 × 30 mm 2A42 autocannons (500 rounds), 4 × 9M1201 Ataka-T ATGM and 7.62 mm PKT MG (2,000 rounds). It can be also fitted with 2 × AGS-30 automatic grenade launchers. Features new fire control system with thermal sights and a ballistic computer. Reinforced with 3rd generation "Relikt" ERA on the frontal armor and both sides of hull and turret, slat (cage) armor in the rear. It is equipped with Agat-MR night vision devices, an NBC detection and protection system. There is 902A "Tucha" 81 mm smoke grenade launcher array on each side of the turret and "Shtora-1" active protection system. When the screening system warns the crew of laser tracking, a smoke screen is created by the launch of grenades. The vehicle can be fitted with either the KMT-8 or the EMT mine clearing system. The term BMP-T that is very often found is not correct.
* TOS-1
TOS-1 Buratino (, Heavy Flamethrower System) is a Soviet 220 mm 30-barrel (original system, Object 634 or TOS-1M) or 24-barrel (Object 634B or TOS-1A Solntsepyok) multiple rocket launcher capable of using thermobaric warheads, mounted on a ...
– Large box-type multi-barrel rocket launcher with 30 tubes that replaces turret.
* TZM-T – Reloading vehicle for the TOS-1 mobile multi-barrel rocket launcher.
* (''Bronirovannaya Remonto-Evakuatsionna Mashina'') – Armoured recovery vehicle with a hydraulic crane with capacity of 12 tonnes mounted at the front of the hull on the left side. It also has a main winch with capacity of 25 tons which can be increased to 100 tonnes, auxiliary winch, hydraulically operated dozer/stabilizing blade at the front of the hull, towing equipment and a complete range of tools and recovery equipment.
* IMR-2
The IMR-2 is a Soviet Union, Soviet and Russian tracked military engineering vehicle built on T-72 main battle tank chassis. IMR stands for ''Inzhenernaya Mashina Razgrazhdeniya'' (), meaning "Clearing Engineering Vehicle".
Development of the IMR ...
(''Inzhenernaya Mashina Razgrashdeniya'') – Combat engineering vehicle
A military engineering vehicle is a vehicle built for construction work or for the transportation of combat engineering, combat engineers on the battlefield. These vehicles may be modified civilian equipment (such as the Armored bulldozer, armo ...
(CEV). It has a telescoping crane arm which can lift between 5 and 11 metric tons and utilizes a pincers for uprooting trees. Pivoted at the front of the vehicle is a dozer blade that can be used in a V-configuration or as a straight dozer blade. When not required it is raised clear of the ground. On the vehicle's rear, a mine-clearing system is mounted.
:* IMR-2M1 – Simplified model without the mine-clearing system. Entered service in 1987.
:* IMR-2M2 – Improved version that is better suited for operations in dangerous situations, for example in contaminated areas. It entered service in 1990 and has a modified crane arm with bucket instead off the pincers.
:* IMR-2MA – Latest version with bigger operator's cabin armed with a 12.7 mm machine gun NSV.
::* Klin-1 – Remote controlled IMR-2.
* MTU-72 (Ob'yekt 632) (''Tankovyj Mostoukladchik'') – bridge layer based on T-72 chassis. The overall layout and operating method of the system are similar to those of the MTU-20 and MTU bridgelayers. The bridge, when laid, has an overall length of 20 meters. The bridge has a maximum capacity of 50,000 kg, is 3.3 meters wide, and can span a gap of 18 m. By itself, the bridge weighs 6400 kg. The time required to lay the bridge is 3 minutes, and 8 minutes for retrieval.
* BMR-3 (''Bronirovannaja Mashina Razminirovanija'') – Mine clearing vehicle.
* RKhM-7 "Berloga-1" (''Razvedivatel'naya Khimicheskaya Mashina'') – NBC reconnaissance vehicle without turret and with fixed superstructure.
*Tsar Mangal
The Tsar Mangal (, Tsar Mangal, lit: King's Grill) or Turtle Tank refers to Armored Fighting Vehicles that were fabricated from T-62, T-72 and T-80 tanks used by Russian Forces, and modified with extensive improvised steel roof and siding, as w ...
( Turtle Tank), a makeshift armored vehicle with improvised armor and anti-drone protection, equipped with demining rollers. The first specimen was based on T-72.Появились кадры изнутри танка "Царь-мангал" ВС РФ с защитой от дронов и мин/ref>David Axe
The Russians Have Added Yet Another Layer Of Armor To Their Giant Turtle Tanks
/ref>
Azerbaijan
* T-72A Aslan - Modernizated option of the T-72 by Azerbaijani Ministry of Defence Industry developed by the Israeli companyElbit Systems
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an Israel-based international military technology company and defense contractor. Founded in 1966 by Elron, Elbit Systems is the primary provider of the Israeli military's land-based equipment and unmanned aerial v ...
. The tank is equipped with a computerized control system, a GPS-based navigation system, a “friend or foe” determination system, thermal imagers for the commander and gunner, and a mounted remote sensing system.
Belarus
* T-72BM2 - Modernization of the T-72B.Bulgaria
* T-72M2 – New night vision and thermal devices, anti-radiation cladding, rubber side skirts, C4I and IR suppression coating. * T-72M1 Mod. 2022 – T-72M1 modernised with Elbit's Thermal Imaging Fire Control System, giving the gunner 3rd generation+ thermal imaging capabilities along with a new laser range finder capable of lasing up to 9 km away. The system also includes abattlefield management system
A battlefield management system (BMS) is a system meant to integrate information acquisition and processing to enhance command and control of a military unit through multiple other C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligenc ...
, four laser warning receives, a new fire control system with a metrological sensor, new thermal sleeve for the 2A46 125 mm gun
The 2A46 (also called D-81TM) is a 125 mm/L48 smoothbore cannon of Soviet origin used in several main battle tanks. It was designed by OKB-9 (Artillery Plant No. 9) in Yekaterinburg.
Description
It was developed by the Spetstekhnika Design ...
, and thermal night time cameras for the driver. The T-72M1 Mod. 2022 is also one of the few T-72s to receive an auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115&n ...
(APU) that allows the tank to have a "silent watch" capability, allowing it to operate all its system with the engine turned off to save fuel and reduce the tank's thermal emissions and acoustic signature. The tank was modernised locally at "Terem - Khan Krum" EOOD in Targovishte.
Croatia
 * M-84A – The M-84 is a Yugoslav third generation main battle tank, based on the Soviet T-72, produced in Croatian Đuro Đaković specijalna vozila.
*
* M-84A – The M-84 is a Yugoslav third generation main battle tank, based on the Soviet T-72, produced in Croatian Đuro Đaković specijalna vozila.
* M-84D
The Croatian M-84D, also known as the M-84A5 (D), is a proposed upgrade variant of existing M-84 tanks, originally developed in SFRY, Yugoslavia, with improvements to engine, armor, armament and electronics.
Description
The M-84D is equipped wi ...
– Proposed upgrade of the M-84A4 with technology developed for M-95 Degman prototype.
* M-95 Degman – 3rd generation prototype tank based on the Yugoslav M-91 Vihor prototype.
Czechoslovakia
* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E3) (1985) – This model was built under licence by ZŤS Martin (nowadays Slovakia). In Western sources it is often referred to as T-72G which might be the designator for the version exported to the Middle East. In the late 1980s the tanks produced for the Czechoslovak army and for export as well were fitted with some improvements from the Soviet T-72A programme, including rubber side skirts (instead of "gill armour") and 902B "Tucha" smoke grenade launchers. * T-72M1 (Ob'yekt 172M-E5) (1986) – This export version of the T-72A was also built by ZŤS. An external difference with the Soviet original is the reduced number of KMT mounts on the lower glacis plate. * () (''vyprošťovací tank'') – Czechoslovakarmoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle (ARV) is typically a powerful tank or armoured personnel carrier (APC) chassis modified for use during combat for military vehicle recovery (towing) or repair of battle-damaged, stuck, and/or inoperable armoured f ...
(ARV) based on T-72 chassis.
:* () – Czechoslovak ARV based on BREM-1 with dozer blade with prominent rams mounted on the front of the vehicle, hydraulic crane on the right side of vehicle and a large built-up superstructure at the front of the hull with a large tackle block in front of it.
Czech Republic
 These variants are not new builds, but upgrades of a large number of otherwise obsolete T-72 version hulls.
* T-72M4 CZ (2003) – Comprehensive upgrade of every aspect of the T-72M1 resulting in a tank that only superficially resembles the precursor, intended to remedy T-72's failures learned during the
These variants are not new builds, but upgrades of a large number of otherwise obsolete T-72 version hulls.
* T-72M4 CZ (2003) – Comprehensive upgrade of every aspect of the T-72M1 resulting in a tank that only superficially resembles the precursor, intended to remedy T-72's failures learned during the Gulf War
, combatant2 =
, commander1 =
, commander2 =
, strength1 = Over 950,000 soldiers3,113 tanks1,800 aircraft2,200 artillery systems
, page = https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GAOREPORTS-PEMD-96- ...
. The automotive performance was enhanced with a Perkins
Perkins is a surname derived from the Anglo-Saxon corruption of the kin of Pierre (from Pierre kin to Pierrekin to Perkins), introduced into England by the Norman Conquest. It is found throughout mid- and southern England.
Another derivation com ...
CV12-1000 1,000 hp (740 kW) water-cooled diesel engine coupled to a Nimda XTG-411-6 automatic transmission. All drive train work was done by the Israeli firm Nimda and involved minor modifications of the tank's hull and the driver's compartment. The upgrade added new Czech-manufactured Dyna-72 ERA for protection against HEAT and kinetic rounds impacting the frontal aspects of the turret and hull, and against top-attack ATGMs and sub-munitions with ERA tiles covering the turret roof. Survivability is enhanced with the Polish-made Obra laser warning system integrated with a series of DGO-1 smoke grenade dischargers on each side of turret, a Deugra fire suppression system, REDA NBC suite and electromagnetic mine plow. The most important improvement in firepower comes from the use of the Galileo Avionica TURMS-T computerized FCS (similar to that used on the C1 Ariete) which enables a "hunter-killer" mode of operation; the commander has a panoramic day/night sight with built-in laser rangefinder and Attila thermal camera and can engage targets independently, while the gunner has his own primary sight with thermal channel. The FCS has sensors that correct for thermal distortion of the barrel, the temperature of the ammunition propellant, meteorological conditions, totaling 22 sensor clusters installed at several points on the turret. A new 125/EPpSV-97 APFSDS round was developed for use with the new tank which can defeat 540 mm of RHA at 2,000 m. The Czech tanks were also equipped with a rear-view camera, a new intercom, navigational system, the DITA 72/97B auto-diagnostic system and improvements to the suspension due to the increase in the weight of the T-72M4 CZ by 4 tonnes. Curiously, the obsolete 2A46 main gun was retained as was the original 2E28M stabilization system, which was modestly upgraded with new hydraulic drives and gyroscopic sensors, resulting in only marginal improvements in first-hit probability despite the sophisticated and expensive TURMS-T FCS. The published probability of hitting a stationary target on the move is said to be between 65 and 75% with the first fired round. In comparison, the Leopard 2A4 from the mid-1980s can achieve a first round hit probability on the move of 75-85% at 2,000 m and as high as 90% with a skilled crew. The original tender called for an order of 350 tanks, which was downgraded to 140 in the face of dwindling defense budgets and finally amounted to a commitment for only 35 tanks to be upgraded to the T-72M4 CZ standard. One of the reasons for this drastic reduction was due to the escalating unit cost of the upgrade — from an initial estimate of 3.7M—and closing on a final cost of US$5.2M per tank.
:* – Modernized VT-72 (BREM-72) ARV with T-72M4CZ upgrades including the power pack and communications upgrades.
* , also known as (2017) – modernization of the T-72M1 by Czech company Excalibur Army, introduced in 2019. This version offers several modernization packages depending on buyer's preferences. These include increased armour protection, better power pack, better protection against WMDs, modern optical and targeting systems, remote control of the external 12.7 mm machine gun, new fire-control system, modern communications system, new fire protection system and more.
* , also known as (2022) – modernization of the T-72 (various versions) to 3rd-generation standard by which includes:
**New opto-electronic devices and an upgraded night vision block for all three crew members from companOptics trade
which significantly improve night vision capabilities and resolution. It uses a laser rangefinder to increase the probability of a first round hit, an improved thermal sight with ballistic computer, an upgraded commander's sight and an upgraded driver's sight. The night vision systems operate fully in passive mode without the use of infrared lights. **Increased ballistic protection with most vulnerable parts covered with reactive armour, significantly increasing the tank's protection against RPGs and HEAT ammunition. The reactive armour added to the tank is the equivalent of 400 millimetres of rolled armour when hit by a warhead. In total, the tank is equipped with 196 boxes of reactive armour. **Significantly improved mobility due to an upgraded power pack with increased engine power to 840 hp and increased acceleration dynamics. **Complete modernization of driver's position with a new digital dashboard. New internal and external communication systems, digital radio enabling encrypted communication. New fire protection system. Periscopic sights with anti-laser protection.
East Germany
* T-72M – This designator was not only used for the standard T-72M, but also for 75 basic T-72s that were upgraded by RWN in 1986. These tanks (''Kampfpanzer'') were fitted with rubber side skirts, smoke grenade launchers "Tucha" and the additional 16 mm steel plate on the upper glacis plate.Deutsche Militärfahrzeuge, page 559 * T-72M "Übergangsversion" – East German army designator for 23 late-production T-72Ms from Poland, fitted with the additional hull armour. Delivered in 1986. * T-72(K) and T-72(K1) – East German army designators for command tanks (''Führungspanzer''). * T-72TK – East German designation for VT-72B (BRAM-72B). The vehicle was planned to enter service with NVA in 1990, but only one was actually handed over to IB-9 (''Instandsetzungsbatallion 9'') at Drögeheide (Torgelow). Two others were still in Grossenhain (Central tank workshop near Dresden) on 3 October 1990. At this place the tanks got fitted with relevant NVA kit and the cranes were tested/certified. * BLP 72 (''Brückenlegepanzer'') – The East-German army had plans to develop a new bridgelayer tank that should have been ready for series production from 1987 but after several difficulties the project was canceled. * FAB 172M or FAP 172U (''Fahrausbildungspanzer'') – Driver training vehicle. Three vehicles were made by using the chassis of the cancelled BLP 72 project.Georgia
 * T-72 SIM-1 – Increased implementation of K-1 reactive and K-5 passive armor. New FALCON command and control system, GPS navigation system and Polish SKO-1T DRAWA-T fire control system with thermal imager and laser rangefinder (from
* T-72 SIM-1 – Increased implementation of K-1 reactive and K-5 passive armor. New FALCON command and control system, GPS navigation system and Polish SKO-1T DRAWA-T fire control system with thermal imager and laser rangefinder (from PT-91 Twardy
The PT-91 Twardy (, English: Hard) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Deve ...
). It has also a friend-or-foe recognition system.
India
 By the late 1970s,
By the late 1970s, Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
HQ had decided to acquire new-generation replacements for its UK-origin fleet of Centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC ...
and Vijayanta
The ''Vijayanta'' () was a main battle tank built in India based on a licensed design of the Vickers Mk.1. The Vijayanta was the first indigenous tank of the Indian Army.
The prototype was completed in 1963 and the tank entered service on Decem ...
MBTs (based on the Vickers MBT
The Vickers MBT is a series of main battle tanks (MBTs) developed as a private venture by British company Vickers-Armstrongs for export. The design makes use of proven components, such as the L7 gun of the Centurion tank, Centurion, the Leyland ...
), and consequently, paper evaluations concerning the firepower and mobility characteristics of the two principal contenders being offered for full in-country production— French-origin AMX-40 and the British-origin Chieftain 800 — were conducted by the Indian Army. By early 1980, the Army chose the 43-tonne AMX-40 MBT, which was still in its design-stage. It was to be powered by a 1,100 hp Poyaud V12X 12-cylinder diesel engine coupled with a LSG-3000 automatic power shift transmission built by RENK
The Renk Group AG is a German global manufacturer of transmissions, engines, hybrid drive systems, vehicle suspension systems, plain bearings, couplings, and testing systems. The company builds special gearboxes for tanks, frigates, icebreakers, ...
Aktiengesellschaft of Germany offering a power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement ...
of 25.6 hp/tonne, and armed with a 120 mm smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars. Some examples of smoothbore weapons are muskets, blunderbusses, and flintlock pistols. ...
cannon. However, AMX-40 had only marginal protection by the standards of 1980's. After the General elections in 1980, Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and stateswoman who served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India from 1966 to 1977 and again from 1980 un ...
requested additional evaluation, including MBTs from the USSR, following which the Soviet Union's Ministry of Foreign Economic Relations (which after 1991 morphed into Oboronexport, then Rosoboronservice and ultimately Rosoboronexport
JSC Rosoboronexport (ROE; , ''Rosoboroneksport'') is the sole state intermediary agency for Russia's exports/imports of defense-related and dual use products, technologies and services. The Rosoboronexport Federal State Unitary Enterprise (FSU ...
State Corp) made a formal offer to India's Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
(MoD) for supplying the 37-tonne T-72M Ob'yekt 172M-E4 MBT off-the-shelf, and according an approval for licensed-production of the 41.5-tonne T-72M-1982 Ob'yekt 172M-E6 to the MoD-owned Heavy Vehicles Factory
Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF) is an armoured vehicle and battle tank manufacturing factory located at Avadi in Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is managed by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVANI) of the Ministry of Defence, Gover ...
(HVF) in Avadi
Avadi () is a city Located within the Chennai metropolitan area, Its the headquarters of Avadi Police, Avadi City Police, Avadi City Municipal Corporation, Avadi City Corporation and Avadi taluk, Avadi Taluk located within the Thiruvallur dist ...
. By early 1981, two T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet Union, Soviet main battle tanks that entered production in 1973. The T-72 was a development based on the T-64 using thought and design of the previous Object 167M. About 25,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refu ...
Ms—powered by a 780 hp diesel engine, armed with 125 mm 2A46M smoothbore gun and offering a power-to-weight ratio of 20 hp/tonne, were subjected to an exhaustive series of in-country firepower and mobility trials by the Army. After review of trial results, T-72M and T-72-1982 (powered by a Model V-84MS four-stroke 12-cylinder multi-fuel engine developing 840 hp and offering a power-to-weight ratio of 18.8 hp/tone) were selected as Army's future MBTs. Throughout the 1980s, India continued to induct T-72 tanks followed by a licensed production line in Heavy Vehicles Factory
Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF) is an armoured vehicle and battle tank manufacturing factory located at Avadi in Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is managed by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVANI) of the Ministry of Defence, Gover ...
(HVF) in Avadi
Avadi () is a city Located within the Chennai metropolitan area, Its the headquarters of Avadi Police, Avadi City Police, Avadi City Municipal Corporation, Avadi City Corporation and Avadi taluk, Avadi Taluk located within the Thiruvallur dist ...
, India since 1984.
Request for information
A request for information (RFI) is a common business process whose purpose is to collect written information about the capabilities of various suppliers. Normally it follows a format that can be used for comparative purposes.
An RFI is primarily ...
was issued in November 2023 to upgrade around 1,000 tanks with new engines, fire control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a Director (military), director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs th ...
& other modern systems at (US$270 million). A contract was signed with Rosoboronexport
JSC Rosoboronexport (ROE; , ''Rosoboroneksport'') is the sole state intermediary agency for Russia's exports/imports of defense-related and dual use products, technologies and services. The Rosoboronexport Federal State Unitary Enterprise (FSU ...
to procure 1,000 bhp engines in March 2025 at a cost of $248 million. A total of 1,000 engines are to be procured under the contract of which 200 engines to be directly imported, 800 to be assembled by Heavy Vehicles Factory
Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF) is an armoured vehicle and battle tank manufacturing factory located at Avadi in Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is managed by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVANI) of the Ministry of Defence, Gover ...
from completely knocked down and semi knocked down kits. Procurement under 'Buy & Make' category.
The Indian Army has operated and tested several variants of the T-72, including:
* Ajeya MK1 () – Indian version of the T-72M1. In parallel with buying various T-72M off-the-shelf from the Soviet Union, India also launched its domestic production at Heavy Vehicles Factory
Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF) is an armoured vehicle and battle tank manufacturing factory located at Avadi in Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is managed by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVANI) of the Ministry of Defence, Gover ...
.
* Ajeya MK2 – Indian version of the T-72M1 with ERA and banks of 6 smoke grenade-launchers on each side.
* Combat Improved Ajeya (Not to be confused with Ajeya MK2) - For a rather long time the Indian Army did not intend to modernize its T-72 tanks since it was relying on their own tank project, the Arjun. However, the Arjun program had been undergoing difficulties. As a result, they adopted the Operation Rhino plan aimed at re-equipping 1,500 T-72M1 tanks. The upgrade program provides for installation of a Polish SKO-1T DRAWA-T fire control system/thermal imager supplied by the Polish PCO/Cenzin (from PT-91 Twardy
The PT-91 Twardy (, English: Hard) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Deve ...
), DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is an agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in the Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, charged with the military's research and development, headqu ...
explosive reactive armour
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour used in protecting vehicles, especially modern tanks, against shaped charges and hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is ''explosive reactive armour'' (ERA), but variants include ...
, a navigation system from Israel's Tamam, German Litef or South African RDI, a locally developed laser illumination warning system, new radios manufactured by Tadiran or GES Marconi and an improved NBC protection system will be fitted. The tank is planned to be powered by a S-1000 engine made by the Polish firm PZL-Wola (also from PT-91 Twardy
The PT-91 Twardy (, English: Hard) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Deve ...
). It is also upgraded with new fire detection and suppression systems and laser warning systems on either side of the turret. Indian sources often say that 1,800–2,000 T-72M1 tanks will be upgraded top to bottom while the rest will undergo only partial improvement.
* Tank EX – Indian integration of the Arjun turret onto the T-72 hull, Prototype only. Did not enter production as it was rejected by the Indian Army.
Iran
*Raad-2
Raad-2 (Persian:رعد-۲ 'Thunder-2') is an Iranian self-propelled howitzer.
Development
In early September 1997, it was reported that Iran had successfully tested a locally built rapid fire mobile field gun known as ''Raad''-2 (Thunder-2).
It ...
- Iranian 155 mm self-propelled howitzer
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled mo ...
based on the T-72 hull.
*T-72M Rakhsh - Iranian T-72M upgrade, equipped with a variant of Kontakt-5
Kontakt-5 is a type of second-generation explosive reactive armour (ERA) originating in the Soviet Union. Due to the shortcomings of Kontakt-1, NII Stali developed a new type of reactive armor, Kontakt-5, so that it also affects the penetration c ...
ERA among many upgrades.
Iraq
Lion of Babylon
The Lion of Babylon is an ancient Babylonian symbol.Benjamin Sass, Joachim Marzahn. Aramaic and figural stamp impressions on bricks of the sixth century B.C. from Babylon. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, 2010. Pp. 181-182.
History
Antiquity
The ...
(Asad Babil) – Iraqi-assembled version of the T-72M1.
Poland
* T-72M/T-72M1 –Licensed, standard T-72 models produced in Poland :* T-72M (Ob'yekt 172M-E3) – This export version of the T-72 was built under licence by Bumar-Łabędy inGliwice
Gliwice (; , ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder River, Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the regional capital ...
starting in 1982. Like Soviet tanks, the Polish T-72M was initially fitted with "gill" armour; later the tanks were upgraded with rubber side skirts and 902W ''Tucha'' smoke grenade launchers. Late production models have an additional 16 mm steel plate welded on the upper glacis plate, like in the T-72M1.
:* T-72M1 (Ob'yekt 172M-E5) – This export version of the T-72A was also built under licence in Poland since 1983. The most obvious external difference relative to Soviet analogs is the reduced number of KMT mounting points on the lower hull glacis plate. It is the first version to feature ceramic sand bars "kwartz" rods in the turret cavity and High Hardness Steel appliqué armor on upper glacis.
:* T-72M1D – Polish designation for T-72M1K."War Technology":* T-72M1R – Modification of T-72M1. :* ''Jaguar'': When Polish production of the T-72 started in 1982, the Poles considered upgrading them and the first domestic T-72 upgrade program was launched by the Institute of Armament and Equipment of the Polish Army. The project was code-named ''Jaguar'' since that was the designation under which the Soviet Union transferred the technical data package for the T-72. The ''Jaguar'' was never more than a concept. :* ''Wilk'': Beginning in 1986, the Polish T-72 ''Wilk'' project was instituted to allow tank repair plants to upgrade T-72 tanks within their own facilities. In particular, it was proposed that the Soviet-made Volna fire control system be replaced by the Czechoslovak-made Kladivo FCS or by the Polish SKO-1 Mérida, which was originally designed for T-55AM "Merida". Besides the new FCS, the Radomka passive night vision devices were installed in the driver's compartment, as was the Liswarta night sight, Obra laser illumination warning system, Tellur anti-laser smoke grenade launchers, solid or modular metal side skirts and the Polish-developed Erawa-1 or Erawa-2 explosive reactive armour was also fitted. This program was further developed and led to the PT-91.
 *
* PT-91 Twardy
The PT-91 Twardy (, English: Hard) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Deve ...
– A Polish main battle tank based on T-72M1 developed sometime between the late 1980s and early 1990s and involving use of a new digital fire-control system, newly developed ERA and an uprated powerplant. This formed the basis for a whole line of derivative vehicles. PT-91 was a result of previous T-72 upgrade programs.
** PT-91M Pendekar – Production export variant for Malaysia with Sagem Savan-15 fire control system, a new 1,000 hp powerpack with Renk automatic transmission bringing its top speed to 70 km/h. Its main gun have been changed to a ZTS 2A46MS 125 mm gun, a 7.62 mm FN MAG coaxial machine gun and a 12.7 mm FN Browning M2 HB AA machine gun. This variant is also equipped with Sagem panoramic sight, a Sagem laser gyro inertial navigation system, turret stabilisation system, Obra-3 laser-warning system, integrated with 81 mm smoke grenade launchers, CBRN warning and protection system, Thales communication systems. ERAWA 2 Explosive Reactive Armour, and German-made tank tracks (Diehl Defence). Two prototypes made (renamed PT-91E and PT-91Ex), 48 serial PT-91M Pendekar vehicles produced 2007–2009.
* WZT-3 WZT (''Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego'' – armoured recovery vehicle) was a Polish post-World War II armoured recovery vehicle series. It consists of five versions.
The first two, WZT-1 and WZT-2 were built on T-55, T-55/T-55A hull, the WZT-3 was ...
– ARV
ARV may refer to:
* Antiviral drug, Antiretroviral drug, any drug used to treat retroviral infections, primarily in the management of HIV/AIDS
* arv, ISO 639-3 language code for the Arbore language, an East Cushitic language
* Average rectified v ...
based on the T-72M. It is armed with a 12.7 mm (1⁄2 in) machine-gun fitted to the commander's hatch. Standard equipment includes: crane with telescopic jib that can lift a maximum load of fifteen tonnes, front-mounted stabilizing dozer blade, main and secondary winches.
 :* WZT-3M – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army
:* M-84AI – A M-84A based variant, made on licence in Yugoslavia – 15 vehicles for Kuwait
:* ARV-3 – A T-72 based variant for Indian Army – 352 vehicles made
* MID Bizon-S – engineering tank based on the PT-91 tank hull
:* MID-M – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army
:* WZT-4 – Armoured recovery vehicle, PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army (technically this vehicle is closely related to MID-M, not the WZT-3)
* SJ-09 – Polish driver training vehicle. The turret has been replaced by a flat-plate cabin with dummy gun barrel. Polish army uses T-72 based vehicles, Malaysian Army has one based on PT-91M.
* PZA Loara – SPAAG prototype based on the T-72 chassis.
:* WZT-3M – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army
:* M-84AI – A M-84A based variant, made on licence in Yugoslavia – 15 vehicles for Kuwait
:* ARV-3 – A T-72 based variant for Indian Army – 352 vehicles made
* MID Bizon-S – engineering tank based on the PT-91 tank hull
:* MID-M – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army
:* WZT-4 – Armoured recovery vehicle, PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army (technically this vehicle is closely related to MID-M, not the WZT-3)
* SJ-09 – Polish driver training vehicle. The turret has been replaced by a flat-plate cabin with dummy gun barrel. Polish army uses T-72 based vehicles, Malaysian Army has one based on PT-91M.
* PZA Loara – SPAAG prototype based on the T-72 chassis.
Romania
*TR-125
The TR-125 () prototype main battle tank is a redesigned T-72 made in Romania with Romanian components only. Number 125 in the designation stands for the 125 mm A555 smoothbore tank gun. It is now designated P-125 (P stands for Prototype).
...
– Romanian prototype tank based on T-72 with extra armour, new FCS, new gun, modified suspension and more powerful diesel engine. A reverse engineered vehicle, it was larger in dimensions than the T-72. Its name stands for ''Tanc Românesc 125'' ("Romanian Tank 125"), with "125" indicating the gun caliber of 125 mm.
Serbia

 * Yugoimport T-72 modernization package – Upgraded engine, communication gear and ERA.
*
* Yugoimport T-72 modernization package – Upgraded engine, communication gear and ERA.
* M-84AS The M-84AS prototype main battle tank is a modernized version of the M-84 produced by Yugoimport SDPR in Serbia. M-84AS is sometimes referred to as ''M-84AB1'' and ''M-2001'' and is based mostly on imported components.
Design
The modernization giv ...
– Is a prototype tank using an M-84A tank modernized to T-90 level by Yugoimport SDPR.
* M-84AS1 – Is a substantially modernized version of the M-84
The M-84 is a Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav main battle tank based on the Soviet T-72. It is still in service with Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Serbia, Slovenia and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The ...
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank or simply tank,Ogorkiewicz 2018 p222 is a tank that fills the role of armour-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more po ...
* M-84AI – Armoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle (ARV) is typically a powerful tank or armoured personnel carrier (APC) chassis modified for use during combat for military vehicle recovery (towing) or repair of battle-damaged, stuck, and/or inoperable armoured f ...
created from the chassis of a M-84A. Completed with the help of Polish experts, resulting in a vehicle similar to the WZT-3 WZT (''Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego'' – armoured recovery vehicle) was a Polish post-World War II armoured recovery vehicle series. It consists of five versions.
The first two, WZT-1 and WZT-2 were built on T-55, T-55/T-55A hull, the WZT-3 was ...
. Standard equipment includes: A TD-50 crane, front-mounted stabilizing dozer blade, main and secondary winches.
Slovakia
 * – T-72M1 upgraded with suspension of the driver's seat from hull roof, DSM 16.1 engine monitoring system, ERA armour package around the turret with a flat front section, fire detection and suppression system, improved transmission, improved hull floor protection, laser Detection Warning System, modified electrical harness, PNK-72 driver's night sight, SGS-72A commanders stabilized passive sight, gunner's sight with a large head with two section door, S12U diesel engine, Slovenian EFCS3-72A fire control system and MB smoke grenade dischargers on the each side of the turret. It also has two external sensor rod mounts on turret roof.
* T-72M2 – Slovak modernization. Development was completed but without any order for tank fleet modernization.
* VT-72C – Improved VT-72B produced since 1999 for India. It is fitted with a more powerful Polish S-12U diesel engine and has a modified interior.
* VT-72Ž – Combat engineer tank. Similar to the VT-72B but with a modified telescopic arm with bucket.
* MT-72 – Slovakian scissors-type bridge based on T-72 chassis. When deployed the bridge is 20 m long and will span a gap of 18 m. It is capable of carrying loads of up to 50 tonnes.
* ShKH 2000 "Zuzana" (Zuzanne) – A 155 mm (45 calibers) version (the first prototype of which was completed by ZTS in December 1992) of the Dana 152 mm self-propelled gun-howitzer installed on a modified T-72M1 chassis.
* – T-72M1 upgraded with suspension of the driver's seat from hull roof, DSM 16.1 engine monitoring system, ERA armour package around the turret with a flat front section, fire detection and suppression system, improved transmission, improved hull floor protection, laser Detection Warning System, modified electrical harness, PNK-72 driver's night sight, SGS-72A commanders stabilized passive sight, gunner's sight with a large head with two section door, S12U diesel engine, Slovenian EFCS3-72A fire control system and MB smoke grenade dischargers on the each side of the turret. It also has two external sensor rod mounts on turret roof.
* T-72M2 – Slovak modernization. Development was completed but without any order for tank fleet modernization.
* VT-72C – Improved VT-72B produced since 1999 for India. It is fitted with a more powerful Polish S-12U diesel engine and has a modified interior.
* VT-72Ž – Combat engineer tank. Similar to the VT-72B but with a modified telescopic arm with bucket.
* MT-72 – Slovakian scissors-type bridge based on T-72 chassis. When deployed the bridge is 20 m long and will span a gap of 18 m. It is capable of carrying loads of up to 50 tonnes.
* ShKH 2000 "Zuzana" (Zuzanne) – A 155 mm (45 calibers) version (the first prototype of which was completed by ZTS in December 1992) of the Dana 152 mm self-propelled gun-howitzer installed on a modified T-72M1 chassis.
South Africa
* T-72 "Tiger" – The modernization package from Lyttelton Engineering Works included two large sights installed on the front of the turret. South Africa also offered a self-propelled artillery conversion for existing T-72s, rearming the chassis with a turret adopted from theG6 howitzer
The G6, sometimes denoted as the G6 ''Rhino'', is a South African self-propelled howitzer. It was developed as a turreted, self-propelled variant of the G5 howitzer series, mating the gun to a six-wheeled mine-protected armoured chassis. Des ...
.''Jane's Armour and Artillery, 2005–2006'', : p. 101.
Syria
* T-72A/M1 - Syrian unmarked modernization. Instead of the TPN-3-49, the T-72 tanks are equipped with thermal imaging sights designated as "Viper-72", locally produced. The maximum range of the sight is up to 4 kilometers. The sight is made of foreign components since 2018. *T-72 Adra
The T-72 ''Adra'' () or 'Mahmia' is a Syrian tank. It is a domestic upgrade to the T-72M1 that features slat armor, spaced armor, and chains to provide 360 degree protection from RPGs.
Background
In the late ‘70s through the early ‘90s ...
– Syrian upgrade featuring slat and spaced armour as extra protection against HEAT.
* T-72 Shafrah – Syrian upgrade featuring brackets placed on the tank’s turret, which have a number of angled plates welded onto them. Some tanks have sideskirts (most appear to at least have sideskirt mounts consisting of two metal beams above road-wheels), which follow a similar pattern, but the welded plates are not angled. Armor plates are made of RHA (1.5 mm – 2 mm).
* T-72M1S – Syrian-Italian upgrade with the addition of the Galileo Avionica TURMS-T computerised FCS, including infrared cameras, improved gun stabilisation, stabilised sights for the gunner and the commander, and capability to launch 9M119 Refleks ATGMs. 124 T-72M1s and T-72AVs were upgraded to this standard between 2015 and 2018Very few of the upgraded T-72AVs retained their explosive reactive armour after being upgraded.
* Golan-1000 – A rocket system which carries three massive 500 mm rounds, each packed with 500 kg of high-explosive fragmentation ammunition. Built on a T-72 tank chassis, the rocket system has been in use with the Syrian Army since May 2018.
Ukraine
During theRusso-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
's invasion by Russia phase from 2022 onward Ukrainian forces have used captured Russian tanks, including T-72s.
* T-72AM "Banan"– unveiled in 1992, the first Ukrainian T-72A upgrade covered extensively with early-generation Kontakt-1 ERA tiles (V-shaped array around the sides of the turret and an array on side skirts). It is powered by the 6TD-1 or 6TD-2 diesel engine (1,250 hp) from the T-84 and features additional smoke grenade launchers.
* – Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau
Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau (), often simply called Morozov Design Bureau or abbreviated KMDB, is a state-owned Ukrainian company in Kharkiv which designs armoured vehicles, including the T-80UD and T-84 main battle tanks, a ...
(KMDB) modernization package aimed at improving the automotive and firepower capabilities of the tank with components mostly derived from the T-80UD program, including an improved 6TD-1 engine rated at 1,000 hp or 1,200 hp (881 kW) 6TD-2, new drivetrain components from the T-80UD, an improved engine cooling system, turbocharger and air filter. These upgrades improve upon the T-72B tank's mobility and bring the upgraded vehicle up to par with the T-80UD. Further improvements were made to the fire-control system, which is now an adaptation of the 1A45 ''Irtysh'' system, with 1G46 day sight, TKN-4S, TPN-4 or TPN-4 Buran-Catherine night sights (the latter equipped with thermal viewer) which also enables the use of 9M119M Invar laser-guided missiles launched from the main gun. The tank turret was covered in Kontakt-5 ERA tiles and the main gun was upgraded to the newer 2A46M1 variant, and coupled with a significantly more precise 2E42M main gun stabilization system. However, with most of the tank's components reliant upon the T-80UD, this variant has not had any export success.
* – This modernization package was unveiled in 1997 by KMDB and includes an improved 6TD-1 engine, Kontakt-5 or Nizh ERA, a modern fire suppression system and an advanced Sagem
SAGEM (, translated as "Company of General Applications of Electricity and Mechanics") was a French company involved in defense electronics, consumer electronics, and communication systems.
Founded in 1924, SAGEM initially specialised in mechani ...
SAVAN 15MP fire-control system with the multi-channel thermal SAVAN 15MP (gunner) and panoramic SFIM VS580 (commander) sights. But the capabilities of the FCS were not fully utilized since the tank retained the obsolete 2E42-2 stabilization system and 2A46M main gun. The upgrade is offered jointly with Sagem of France, and PSP Bohemia of the Czech Republic.
* – KMDB main armament package first offered in 1999 with the T-72AG and T-72MP upgrades, which includes an auto-loaded KBM-2 120 mm main gun, developed with the French-based GIAT Industries
KNDS France (formerly known as Nexter, GIAT Industries or ''Groupement des Industries de l'Armée de Terre'', Army Industries Group) is a French government-owned weapons manufacturer, based in Versailles. The company was wholly government-owned ...
and capable of firing NATO-standard ammunition or ATGM
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder ...
s. This upgrade includes a new 2E42-M stabilizer and a new auto-loader system housed in the redesigned turret bustle and similar to that used in the Leclerc main battle tank with a capacity of 20 single fixed rounds and further 20 stored in the hull in place of the legacy AZ auto-loading mechanism. The high costs involved with such an extensive modification have thus far driven away potential buyers.
* – A relatively simple upgrade developed for smaller defense budgets of the nations of the developing world, but one that has seen commercial success. The original V-46 engine was replaced with a newer 5TDFMA two-stroke diesel making 1,050 hp (775 kW) and fitted with an enhanced cooling system for use in tropical environments, which allows the tank to be operated for extended periods at temperatures exceeding 55 °C. The tank was also equipped with an EA-10-2 APU with an output of 10 kW, allowing the vehicle's systems to be fully powered when stationary without running the main engine, thus drastically reducing fuel consumption. An air conditioner remains optional. Protection is enhanced with the use of Nizh ERA tiles on the turret while retaining the Kontakt-1 tiles on the hull (however Nizh tiles are compatible with Kontakt-1 mounting points and can be retrofitted). The main gun, stabilizer and FCS remain unchanged compared to the T-72B. Ethiopia purchased the T-72UA1 with 72 tanks delivered in 2011 and 99 in 2012. The Ukrainian army
The Ukrainian Ground Forces (SVZSU, ), also referred to as the Ukrainian army, is a land force, and one of the eight Military branch, branches of the Armed Forces of Ukraine. It was formed from Ukrainian units of the Soviet Army after Declaratio ...
became a customer in 2014 in response to an immediate need following the eruption of the War in Donbass
The war in Donbas, or the Donbas war, was a phase of the Russo-Ukrainian War in the eastern Donbas region of Ukraine. The war began in April 2014, when Russian paramilitaries seized several towns. Ukraine's military launched an operation ...
. It is believed that less than 30 vehicles were ordered.
* – Upgraded version of the T-72B ("E" stands for "Export") showed at IDEX 2011 and developed together with the T-64E. The hull front and sides are protected by Kontakt-1 ERA tiles, while the turret front, sides (sides' frontal part) and top are homogeneously protected by Nizh armor. The engine is upgraded, it is a 5TDFMA-1 multi-fuel diesel engine, developing 1050 hp. The tank features also air conditioning, day-and-night sighting system with integrated laser rangefinder and ATGM capability. The weight is 42.7 t, giving the tank a power/weight ratio of 24,6 hp/t.
* – Ukrainian T-72 upgrade. The unique compact design of the Ukrainian-developed BMT-72 power pack, based on that of the T-84, made it possible not only to considerably increase the power capabilities of the vehicle, but also to introduce into the vehicle design a troop compartment. The troop compartment is located between the fighting compartment and the power pack compartment. In the troop compartment roof there is a set of three hatches in slightly raised portion of the hull roof behind turret that allow the troops to get in or dismount the vehicle. There are also steps on the end of each catwalk at rear of vehicle. The main visual difference between BMT-72 and T-72 is a seventh pair of roadwheels.
:* T-72AMT Obr.2022 Mobilization Model with new TPN1-49-23UM night sight and no "Luna" infrared searchlight. Standard T-72 open-type machine gun mount installation and standard T-72 tracks with a sequential hinges system.
* BTS-5B – Ukrainian version of the BREM-1.
Yugoslavia
*M-84
The M-84 is a Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav main battle tank based on the Soviet T-72. It is still in service with Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Serbia, Slovenia and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The ...
– Indigenous main battle tank based on the T-72M but with several upgrades.
* M-84A – Improved version based on the T-72M1, with new SUV-M-84 computerized fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hum ...
, including the DNNS-2 gunner's day/night sight, with independent stabilization in two planes and integral Laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter or laser distance meter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by ...
. Other upgrades include a stronger 1,000 hp engine.
:* M-84AK – Command version of M-84A fitted with land navigation equipment.
* M-84AB – Export version of M-84A. About 150 were exported to Kuwait.
:* M-84ABK – Command version of M-84AB fitted with land navigation equipment.
:* M-84ABN – Navigation version of M-84AB fitted with extensive communication equipments, land navigation equipment, and a generator for the command role.
Notes
References
* Sewell, Stephen 'Cookie' (1998). in ''Armor'' vol. 108, no. 4, p. 21. Fort Knox, KY: US Army Armor Center. ISSN 0004-2420. (PDF format) * Christopher. F. Foss, Jane's Armour and Artillery 2005–2006. . * Leizin, Uri (2004"Two myths of one battle: Syrian T-72's in 1982 Lebanon war"
in Russian) * Zaloga, Steven J (1993) T-72 Main Battle Tank 1974–93, Osprey Publishing . * Ustyantsev, Sergej Viktorovich; Kolmakov Dmitrij Gennadevich "Boyeviye mashiny Uralvagonzavoda. Tank T-72" * A.V. Karpenko (1996) "Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.)" Nevskij Bastion * * *
Utländska försöksfordon i Sverige , SPHF
{{DEFAULTSORT:T-72 Operators And Variants Main battle tanks of the Cold War Cold War tanks of the Soviet Union Tanks of Finland Czechoslovakia–Soviet Union relations Poland–Soviet Union relations Main battle tanks of Poland Main battle tanks of Slovakia Main battle tanks of Iraq T-72 Vehicle operators by vehicle type