Stefan Uroš V on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saint Stefan Uroš V ( sr-cyrl, Свети Стефан Урош V, ; 13362/4 December 1371), known in historiography and folk tradition as Uroš the Weak ( sr-cyr, Урош Нејаки, Uroš Nejaki), was the second Emperor (
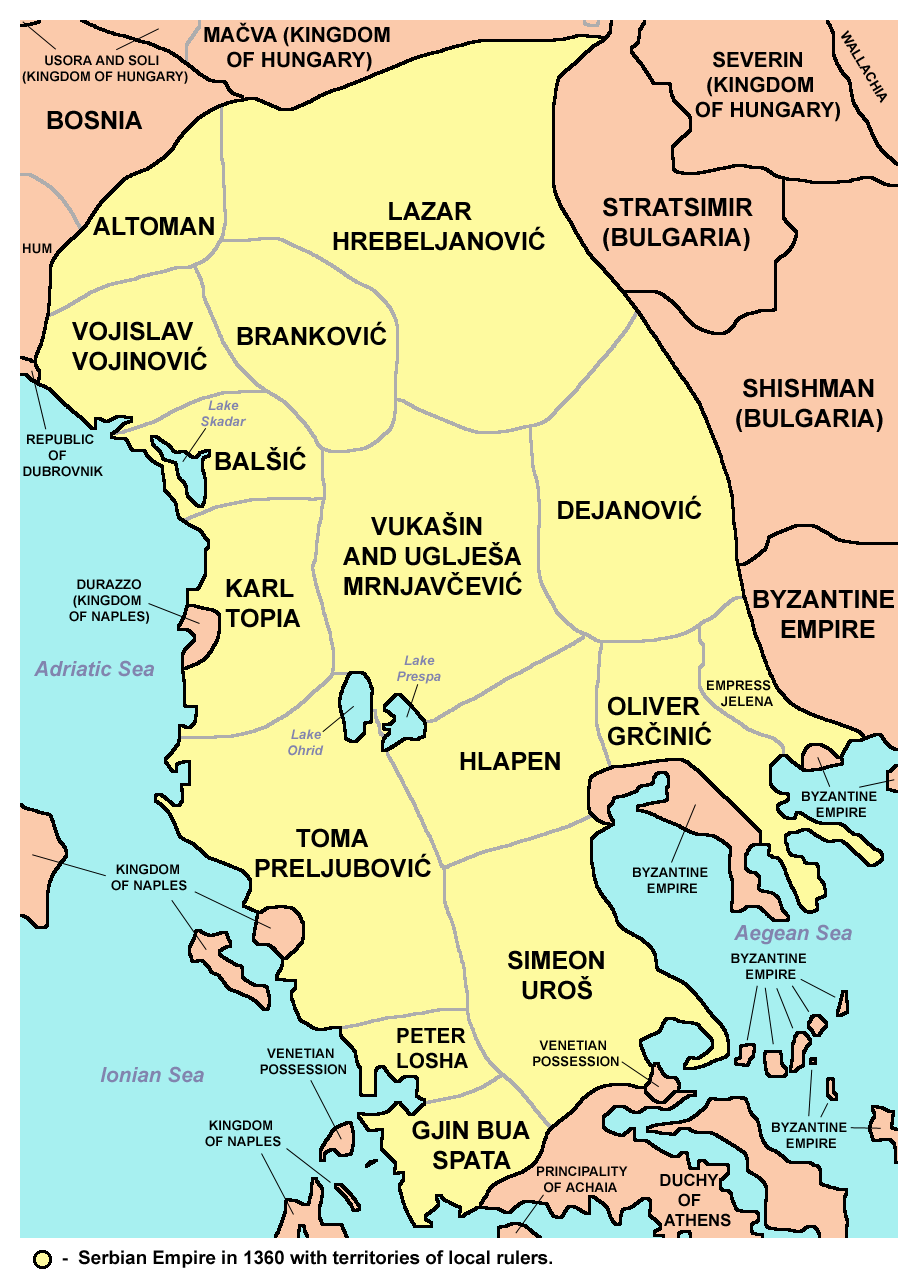 Stefan Uroš V died childless in December 1371, after much of the
Stefan Uroš V died childless in December 1371, after much of the
 Today, Stefan Uroš V is viewed mostly in contrast to his able and strong-willed father, as a lacking and indecisive ruler, unable to keep the Serbian nobility under his control, whose weak and unassertive personality greatly contributed to the fall of the Empire and the eventual destruction of the Serbian state by the Ottomans. In Serbian folklore and epic poems he is often described as a just, well-intentioned ruler of pleasant appearance but weak character. While this view is popular among historians as well, some argue that he was not especially incompetent in his role as Emperor of Serbia, and that the decline of the empire was much less spectacular and started much later into his rule than popular opinion suggests. For a long time, it was considered a historical fact that he was murdered by his co-ruler, Vukašin Mrnjavčević, but eventually Vukašin was proven to have died before the Emperor.
In 1825
Today, Stefan Uroš V is viewed mostly in contrast to his able and strong-willed father, as a lacking and indecisive ruler, unable to keep the Serbian nobility under his control, whose weak and unassertive personality greatly contributed to the fall of the Empire and the eventual destruction of the Serbian state by the Ottomans. In Serbian folklore and epic poems he is often described as a just, well-intentioned ruler of pleasant appearance but weak character. While this view is popular among historians as well, some argue that he was not especially incompetent in his role as Emperor of Serbia, and that the decline of the empire was much less spectacular and started much later into his rule than popular opinion suggests. For a long time, it was considered a historical fact that he was murdered by his co-ruler, Vukašin Mrnjavčević, but eventually Vukašin was proven to have died before the Emperor.
In 1825
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
) of the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
(1355–1371), and before that he was Serbian King and co-ruler (since 1346) with his father, Emperor Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gr ...
.
Early life
Stefan Uroš V was the only son of Stefan Uroš IV Dušan byHelena of Bulgaria
Helena of Bulgaria, Empress of Serbia ( bg, Елена, sr, Јелена; c. 1315–1374) was a Bulgarian princess, and the Queen and Empress consort of Serbia by marriage to Serbian King and later Emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55). She w ...
, the sister of Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria
Ivan Alexander ( bg, Иван Александър, transliterated ''Ivan Aleksandǎr'', ; original spelling: ІѠАНЪ АЛЄѮАНдРЪ), also sometimes Anglicized as John Alexander, ruled as Emperor (''Tsar'') of Bulgaria from 1331 to 1371, ...
. He had been crowned as king (second highest title) in the capacity of heir and co-ruler after Dušan was crowned emperor in 1346. Although by the time of his succession as sole ruler and emperor in 1355 Stefan Uroš V was no longer a minor, he remained heavily dependent on his mother and various members of the court.
Reign
left, 200px, Depiction in the Serbian_Orthodox_Monastery_of_Visoki_Dečani,_Serbia.html" ;"title="Visoki_Dečani.html" ;"title="Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani">Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani, Serbia">Visoki_Dečani.html" ;"title="Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani">Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani, Serbia The account of the contemporary John VI Kantakouzenos describes a descent of the Serbian Empire into disintegration soon after death of Uroš' father and his accession. However, Kantakouzenos mainly focused on the Greek lands rather than the Serbian core lands. Further the general disorder long with the powerlessness of the center represents the situation that arose much later in Uroš's reign. According to Mihaljčić, during the initial years of his rule the threats to the territorial integrity of Uroš's empire in the south came mainly from external attacks. The death of Uroš's father was quickly followed by the death ofPreljub
Preljub ( sr-Cyrl, Прељуб; c. 1312–1356) was a Serbian magnate who served Emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55) as '' vojvoda'' (general). He participated in the southern conquests and held Thessaly with the rank of ''caesar'' (''kesar'') i ...
, who governed Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
. In the spring of 1356, Nikephoros Orsini landed a force on the coast of Thessaly and quickly overran it. He then followed up this success by driving despot Simeon Uroš
Simeon Uroš ( sr-cyr, Симеон Урош, gr, Συμεών Ούρεσης; 1326–1370), nicknamed Siniša (Синиша), was a self-proclaimed Emperor of Serbs and Greeks, from 1356 to 1370. He was son of Serbian King Stephen Uroš III a ...
from Aetolia
Aetolia ( el, Αἰτωλία, Aἰtōlía) is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional units of Greece, regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania.
Geography
The Achelous ...
and Acarnania
Acarnania ( el, Ἀκαρνανία) is a region of west-central Greece that lies along the Ionian Sea, west of Aetolia, with the Achelous River for a boundary, and north of the gulf of Calydon, which is the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth. Today i ...
. Simeon was paternal uncle and the closest male relative of young Emperor Uroš. Retreating to Epirus and western Macedonia, he seized Kostur and proclaimed himself Tsar in hope of becoming co-ruler, or even replacing young Uroš on the Serbian throne. His claim was not widely welcomed, and the support he gained was limited to the some southern regions. The Sabor (state council) held in Skoplje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; r ...
did not accept Simeon's claims and following the endorsement of the magnates, Uroš became more energetic in his political activities, publishing a number of charters. In 1358, Simeon attacked the Skadar region, trying to capture the old Serbia region of Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; grc, ζῆτα, el, ζήτα, label= Demotic Greek, classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived f ...
, but was defeated. Defeated in the north, Simeon again turned to south, retaking Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich ...
and Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
in 1359, where he continued to rule with the title "emperor of Serbs and Greeks".
There is one account, early in his reign, that is in contrast to his general record of incompetence. In 1356, Matthew Kantakouzenos, a pretender to the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
throne, gathered an army of 5,000 Turks and marched on Serres
Sérres ( el, Σέρρες ) is a city in Macedonia, Greece, capital of the Serres regional unit and second largest city in the region of Central Macedonia, after Thessaloniki.
Serres is one of the administrative and economic centers of Northe ...
, the Serbian-held capital of Jovan Uglješa Jovan may refer to:
*Jovan (given name), a list of people with this given name
*Jovan, Mawal, a village on the western coastal region of Maharashtra, India
*Jōvan Musk, a cologne
*Deli Jovan, a mountain in eastern Serbia
*Róbert Jován (born 1967 ...
. Uroš V, whose mother ruled from Serres, decided to raise an army to defend his mother. In 1357, when Matthew and his Turks attacked, the Serbian army under Vojihna
Vojihna or Vojin of Drama ( sr-cyr, Војихна ; ca 1298–1360), was a Serbian nobleman that rose through the ranks and became one of the most acclaimed military commanders (''voivode'') and dukes of Stephen Uroš IV Dušan of Serbia during ...
of Drama (a major player in that region) came to aid. The Turks were defeated. Matthew Kantakouzenos was captured and held hostage until his ransom was paid by the Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
John V Palaiologos
John V Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Ἰωάννης Παλαιολόγος, ''Iōánnēs Palaiológos''; 18 June 1332 – 16 February 1391) was Byzantine emperor from 1341 to 1391, with interruptions.
Biography
John V was the son of E ...
.
In following years, the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
gradually fragmented into a conglomeration of principalities, some of which did not even nominally acknowledge Uroš's rule. His position was not helped by his mother Helena, who started to rule autonomously from Serres in alliance with Jovan Uglješa Jovan may refer to:
*Jovan (given name), a list of people with this given name
*Jovan, Mawal, a village on the western coastal region of Maharashtra, India
*Jōvan Musk, a cologne
*Deli Jovan, a mountain in eastern Serbia
*Róbert Jován (born 1967 ...
. A similarly autonomous posture was assumed by the Dejanović family, the Balšić family, Nikola Altomanović
Nikola Altomanović ( sr-Cyrl, Никола Алтомановић; died after 1395) was a 14th-century Serbian župan of the House of Vojinović. He ruled the areas from Rudnik, over Polimlje, Podrinje, east Herzegovina with Trebinje, reaching ...
. By 1365, the most powerful Serbian nobleman became Uglješa's brother Vukašin Mrnjavčević
Vukašin (Cyrillic script: Вукашин) is an old Slavic name of Serbian origin. It is composed from two words: Vuk (wolf) and sin (son), so it means sin vuka (son of wolf). In some places in Croatia and Bosnia it can be found as a surname.
...
who became co-ruler with Emperor Uroš and was granted the title of Serbian King. By 1369, as Uroš was childless, Vukašin designated his eldest son Prince Marko
Marko Mrnjavčević ( sr-cyr, Марко Мрњавчевић, ; – 17 May 1395) was the ''de jure'' Serbian king from 1371 to 1395, while he was the ''de facto'' ruler of territory in western Macedonia centered on the town of Prilep. He ...
as heir to the throne, with the title of "young king".
 Stefan Uroš V died childless in December 1371, after much of the
Stefan Uroš V died childless in December 1371, after much of the Serbian nobility Serbian nobility ( sr, српска властела / srpska vlastela, српско властелинство / srpsko vlastelinstvo or српско племство / srpsko plemstvo) refers to the historical privileged order or class (aristocrac ...
had been destroyed by the Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
in the Battle of Maritsa earlier that year. The exact cause of his death at a relatively young age remains unknown. Vukašin's son Prince Marko
Marko Mrnjavčević ( sr-cyr, Марко Мрњавчевић, ; – 17 May 1395) was the ''de jure'' Serbian king from 1371 to 1395, while he was the ''de facto'' ruler of territory in western Macedonia centered on the town of Prilep. He ...
inherited his father's royal title, but real power in northern Serbia was held by Lazar Hrebeljanović
Lazar Hrebeljanović ( sr-cyr, Лазар Хребељановић; ca. 1329 – 15 June 1389) was a medieval Serbian ruler who created the largest and most powerful state on the territory of the disintegrated Serbian Empire. Lazar's state, ...
. The latter did not assume the imperial or royal titles (associated with the Nemanjić dynasty
The House of Nemanjić ( sr-Cyrl, Немањић, Немањићи; Nemanjić, Nemanjići, ) was the most prominent dynasty of Serbia in the Middle Ages. This princely, royal, and later imperial house produced twelve Serbian monarchs, who rul ...
), and in 1377 accepted King Tvrtko I of Bosnia
Stephen Tvrtko I ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Stjepan/Stefan Tvrtko, Стјепан/Стефан Твртко; 1338 – 10 March 1391) was the first king of Bosnia. A member of the House of Kotromanić, he succeeded his uncle Stephen II ...
(a maternal grandson of Stefan Dragutin
Stefan Dragutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Драгутин, hu, Dragutin István; 1244 – 12 March 1316) was King of Serbia from 1276 to 1282. From 1282, he ruled a separate kingdom which included northern Serbia, and (from 1284) the neig ...
) as titular king of Serbia. Serbia proper became a vassal of the Ottomans in 1390, but remained effectively ruled by the Lazarević
Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Лазаревић) is a South Slavic surname derived from a masculine given name '' Lazar''. It may refer to:
*Branko Lazarević (born 1984), Serbian football player
* Dejan Lazarević (footballer) (born 1990), Slovenian pr ...
family and then by their Branković successors until the fall of Smederevo
Smederevo ( sr-Cyrl, Смедерево, ) is a city and the administrative center of the Podunavlje District in eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube, about downstream of the Serbian capital, Belgrade.
According to ...
in 1459.
Following the great conquests of his father, Uroš became a victim of new nobles in a Serbia enriched by recent war and pillaging. The maintaining of order and state instruments was impossible because of weak or nonexistent infrastructure between the old and new territories. The exceptional modesty and tolerance of this ruler was the main reason he was called "the weak", and also the reason he was canonized 211 years after his death.
Stefan Uroš V was canonized by the Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches.
The majori ...
. His body is kept in the Jazak monastery on Fruška Gora
Fruška gora ( sr-Cyrl, Фрушка гора; hu, Tarcal-hegység) is a mountain in Syrmia, administratively part of Serbia with a part of its western side extending into eastern Croatia. The area under Serbian administration forms the countr ...
mountain.
Legacy
 Today, Stefan Uroš V is viewed mostly in contrast to his able and strong-willed father, as a lacking and indecisive ruler, unable to keep the Serbian nobility under his control, whose weak and unassertive personality greatly contributed to the fall of the Empire and the eventual destruction of the Serbian state by the Ottomans. In Serbian folklore and epic poems he is often described as a just, well-intentioned ruler of pleasant appearance but weak character. While this view is popular among historians as well, some argue that he was not especially incompetent in his role as Emperor of Serbia, and that the decline of the empire was much less spectacular and started much later into his rule than popular opinion suggests. For a long time, it was considered a historical fact that he was murdered by his co-ruler, Vukašin Mrnjavčević, but eventually Vukašin was proven to have died before the Emperor.
In 1825
Today, Stefan Uroš V is viewed mostly in contrast to his able and strong-willed father, as a lacking and indecisive ruler, unable to keep the Serbian nobility under his control, whose weak and unassertive personality greatly contributed to the fall of the Empire and the eventual destruction of the Serbian state by the Ottomans. In Serbian folklore and epic poems he is often described as a just, well-intentioned ruler of pleasant appearance but weak character. While this view is popular among historians as well, some argue that he was not especially incompetent in his role as Emperor of Serbia, and that the decline of the empire was much less spectacular and started much later into his rule than popular opinion suggests. For a long time, it was considered a historical fact that he was murdered by his co-ruler, Vukašin Mrnjavčević, but eventually Vukašin was proven to have died before the Emperor.
In 1825 Stefan Stefanović
Stefan Stefanović ( sr-cyr, Стефан Стефановић; 1807–1828) was a Serbian writer and playwright who is best remembered for the popular play about Stefan Uroš V of Serbia.
Biography
Stefan Stefanović, who lived and worked in ...
, a Serbian writer living in the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
wrote a tragic play called ''The Death of Uroš V'', which drew inspiration from both facts and folk tradition about Uroš, including the aforementioned belief that he was killed by King Vukašin.
See also
*List of Serbian monarchs
This is an archontological list of Serbian monarchs, containing monarchs of the medieval principalities, to heads of state of modern Serbia.
The Serbian monarchy dates back to the Early Middle Ages. The Serbian royal titles used include Kny ...
* Serbian nobility conflict (1369)
The Serbian nobility conflict in 1369 was a conflict between two powerful sides of the Serbian nobility, one supporting magnate Nikola Altomanović, and one supporting the Mrnjavčević family in Macedonia and Greece. In 1369, a battle was fought ...
* History of Serbia
The history of Serbia covers the historical development of Serbia and of its predecessor states, from the Early Stone Age to the present state, as well as that of the Serbian people and of the areas they ruled historically. Serbian habitation ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *''Translated with small changes from small encyclopedia " Sveznanje" published by "Narodno delo",Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, in 1937 which is today in public domain.''
, -
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stefan Uros 05 of Serbia
14th-century Serbian emperors
14th-century Serbian monarchs
Eastern Orthodox monarchs
Nemanjić dynasty
1336 births
1371 deaths
Burials at Serbian Orthodox monasteries and churches
Serbian people of Bulgarian descent
Eastern Orthodox royal saints
Serbian saints of the Eastern Orthodox Church
Royal reburials
Sons of emperors