Stanisław August Poniatowski on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, was

 Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski was born on 17 January 1732 in
Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski was born on 17 January 1732 in
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
and Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties that managed to stay in power—House ...
from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
.
Born into wealthy Polish aristocracy, Poniatowski arrived as a diplomat at the Russian imperial court in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in 1755 at the age of 22 and became intimately involved with the future empress Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
. With her connivance, he was elected Elected may refer to:
* "Elected" (song), by Alice Cooper, 1973
* ''Elected'' (EP), by Ayreon, 2008
*The Elected, an American indie rock band
See also
*Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population ...
King of Poland by the Polish Diet in September 1764 following the death of Augustus III
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
. Contrary to expectations, Poniatowski attempted to reform and strengthen the large but ailing Commonwealth. His efforts were met with external opposition from neighbouring Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
, Russia and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, all committed to keeping the Commonwealth weak. From within he was opposed by conservative interests, which saw the reforms as a threat to their traditional liberties and privileges granted centuries earlier.
The defining crisis of his early reign was the War of the Bar Confederation (1768–1772) that led to the First Partition of Poland (1772). The later part of his reign saw reforms wrought by the Diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
(1788–1792) and the Constitution of 3 May 1791
The Constitution of 3 May 1791,; lt, Gegužės trečiosios konstitucija titled the Governance Act, was a constitution adopted by the Great Sejm ("Four-Year Sejm", meeting in 1788–1792) for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a dual mo ...
. These reforms were overthrown by the 1792 Targowica Confederation
The Targowica Confederation ( pl, konfederacja targowicka, , lt, Targovicos konfederacija) was a confederation established by Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Petersburg, with the backing of the Russian Empress Cather ...
and by the Polish–Russian War of 1792
The Polish–Russian War of 1792 (also, War of the Second Partition, and in Polish sources, War in Defence of the Constitution ) was fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on one side, and the Targowica Confederation (conservat ...
, leading directly to the Second Partition of Poland
The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of three partitions (or partial annexations) that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian W ...
(1793), the Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Pr ...
(1794) and the final and Third Partition of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polis ...
(1795), marking the end of the Commonwealth. Stripped of all meaningful power, Poniatowski abdicated in November 1795 and spent the last years of his life as a captive in Saint Petersburg's Marble Palace
Marble Palace (Мраморный дворец) is one of the first Neoclassical palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is situated between the Field of Mars and Palace Quay, slightly to the east from New Michael Palace.
Design and pre-1917 o ...
.
A controversial figure in Poland's history, he is criticized primarily for his failure to resolutely stand against and prevent the partitions
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
, which led to the destruction of the Polish state. On the other hand, he is remembered as a great patron of the arts and sciences who laid the foundation for the Commission of National Education
The Commission of National Education ( pl, Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, KEN; lt, Edukacinė komisija) was the central educational authority in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, created by the Sejm and King Stanisław II August on October 1 ...
, the first institution of its kind in the world, and sponsored many architectural landmarks.
Youth

 Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski was born on 17 January 1732 in
Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski was born on 17 January 1732 in Wołczyn
Wołczyn (german: Konstadt) is a town in Kluczbork County, Opole Voivodeship, southern Poland, with 5,907 inhabitants . According to 2011 data, it covers , and is the seat of Gmina Wołczyn. It is located within the historic region of Lower Siles ...
(then in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and now Voŭčyn, Belarus). He was one of eight surviving children, and the fourth son, of Princess Konstancja Czartoryska and of Count Stanisław Poniatowski, Ciołek coat of arms, Castellan
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant o ...
of Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
, who started as a Lithuanian domestic servant
A domestic worker or domestic servant is a person who works within the scope of a residence. The term "domestic service" applies to the equivalent occupational category. In traditional English contexts, such a person was said to be "in service ...
. His older brothers were Kazimierz Poniatowski
Prince Kazimierz Poniatowski (15 September 1721 – 13 April 1800) was a Polish Szlachcic, ''podkomorzy wielki koronny'' (1742–1773), Lieutenant general of the Royal Polish forces, ''generał wojsk koronnych''. Knight of the Order of the ...
(1721–1800), a Podkomorzy at Court, Franciszek Poniatowski (1723–1749), Canon of Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral ( pl, Katedra Wawelska), formally titled the Royal Archcathedral Basilica of Saints Stanislaus and Wenceslaus, is a Roman Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it is part of the ...
who suffered from Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
and Aleksander Poniatowski (1725–1744), an officer killed in the Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's W ...
. His younger brothers were, Andrzej Poniatowski
Prince Andrzej Poniatowski (16 July 1734/5 – Vienna, 3/5 March 1773) was a Polish nobleman ( Szlachcic), General and Field Marshal.
Andrzej was a son of Count Stanisław Poniatowski, Castellan of Kraków, and Princess Konstancja Czartoryska, ...
(1734–1773), an Austrian Feldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; en, general field marshal, field marshal general, or field marshal; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several L ...
, Michał Jerzy Poniatowski
Prince Michał Jerzy Poniatowski (12 October 1736 – 12 August 1794) was a Polish nobleman.
Abbot of Tyniec and Czerwińsk (''opat tyniecki i czerwinski''), Bishop of Płock and Coadjutor Bishop of Kraków (''koadiutor krakowski'') from 17 ...
(1736–94) who became Primate of Poland
This is a list of archbishops of the Archdiocese of Gniezno, who are simultaneously primates of Poland since 1418.Ludwika Zamoyska (1728–1804) and Izabella Branicka (1730–1808). Among his nephews was Prince
 The following year Poniatowski was apprenticed to the office of
The following year Poniatowski was apprenticed to the office of  In Saint Petersburg, Williams introduced Poniatowski to the 26-year-old Catherine Alexeievna, the future empress Catherine the Great. The two became lovers. Whatever his feelings for Catherine, it is likely Poniatowski also saw an opportunity to use the relationship for his own benefit, using her influence to bolster his career.
Poniatowski had to leave St. Petersburg in July 1756 due to court intrigue. Through the combined influence of Catherine, of Russian empress
In Saint Petersburg, Williams introduced Poniatowski to the 26-year-old Catherine Alexeievna, the future empress Catherine the Great. The two became lovers. Whatever his feelings for Catherine, it is likely Poniatowski also saw an opportunity to use the relationship for his own benefit, using her influence to bolster his career.
Poniatowski had to leave St. Petersburg in July 1756 due to court intrigue. Through the combined influence of Catherine, of Russian empress

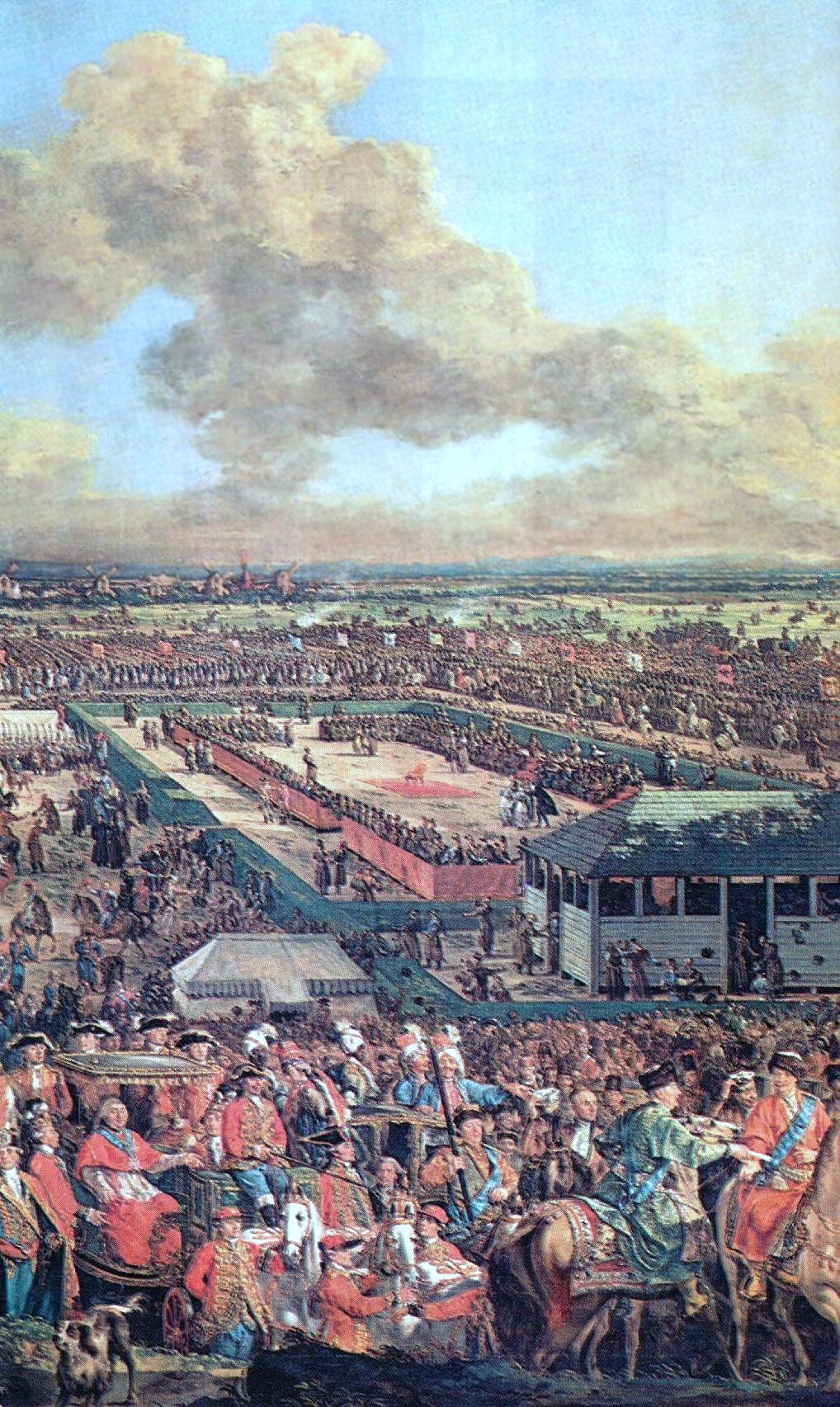 Upon the death of Poland's King
Upon the death of Poland's King  "Stanisław August", as he now styled himself combining the names of his two immediate royal predecessors, began his rule with only mixed support within the nation. It was mainly the small nobility who favoured his election. In his first years on the throne he attempted to introduce a number of reforms. He founded the Knights School, and began to form a diplomatic service, with semi-permanent diplomatic representatives throughout Europe, Russia and the
"Stanisław August", as he now styled himself combining the names of his two immediate royal predecessors, began his rule with only mixed support within the nation. It was mainly the small nobility who favoured his election. In his first years on the throne he attempted to introduce a number of reforms. He founded the Knights School, and began to form a diplomatic service, with semi-permanent diplomatic representatives throughout Europe, Russia and the
 Although Poniatowski protested against the First Partition of the Commonwealth (1772), he was powerless to do anything about it. He considered
Although Poniatowski protested against the First Partition of the Commonwealth (1772), he was powerless to do anything about it. He considered
 Reforms became possible again in the late 1780s. In the context of the wars being waged against the Ottoman Empire by both the
Reforms became possible again in the late 1780s. In the context of the wars being waged against the Ottoman Empire by both the
 Shortly thereafter, conservative Polish nobility formed the Confederation of Targowica, Targowica Confederation to overthrow the Constitution, which they saw as a threat to the traditional freedoms and privileges they enjoyed. The confederates aligned themselves with Russia's Catherine the Great, and the Russian army entered Poland, marking the start of the
Shortly thereafter, conservative Polish nobility formed the Confederation of Targowica, Targowica Confederation to overthrow the Constitution, which they saw as a threat to the traditional freedoms and privileges they enjoyed. The confederates aligned themselves with Russia's Catherine the Great, and the Russian army entered Poland, marking the start of the
 Poniatowski's plans had been ruined by the
Poniatowski's plans had been ruined by the  Poniatowski died of a stroke on 12 February 1798. Paul I sponsored a royal state funeral, and on 3 March he was buried at the Catholic Church of St. Catherine (Saint Petersburg), Catholic Church of St. Catherine in St. Petersburg. In 1938, when the Soviet Union planned to demolish the Church, his remains were transferred to the Second Polish Republic and interred in a church at Vowchyn, Wołczyn, his birthplace. This was done in secret and caused controversy in Poland when the matter became known. In 1990, due to the poor state of the Wołczyn church (then in the Byelorussian SSR), his body was once more exhumed and was brought to Poland, to St. John's Cathedral, Warsaw, St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw, where on 3 May 1791 he had celebrated the adoption of the Constitution that he had coauthored. A third funeral ceremony was held on 14 February 1995.
Poniatowski died of a stroke on 12 February 1798. Paul I sponsored a royal state funeral, and on 3 March he was buried at the Catholic Church of St. Catherine (Saint Petersburg), Catholic Church of St. Catherine in St. Petersburg. In 1938, when the Soviet Union planned to demolish the Church, his remains were transferred to the Second Polish Republic and interred in a church at Vowchyn, Wołczyn, his birthplace. This was done in secret and caused controversy in Poland when the matter became known. In 1990, due to the poor state of the Wołczyn church (then in the Byelorussian SSR), his body was once more exhumed and was brought to Poland, to St. John's Cathedral, Warsaw, St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw, where on 3 May 1791 he had celebrated the adoption of the Constitution that he had coauthored. A third funeral ceremony was held on 14 February 1995.
 Stanisław August Poniatowski has been called the Polish Enlightenment's most important patron of the arts. His cultural projects were attuned to his socio-political aims of overthrowing the myth of the Golden Freedoms and the traditional ideology of Sarmatism. His weekly "Thursday Dinners" were considered the most scintillating social functions in the Polish capital.
He founded National Theatre, Warsaw, Warsaw's National Theatre, Poland's first public theatre, and sponsored an associated Ballet schoolsballet school. He remodeled Ujazdów Castle, Ujazdów Palace and the Royal Castle, Warsaw, Royal Castle in Warsaw, and erected the elegant Łazienki Palace, Łazienki (Royal Baths) Palace in Warsaw's Lazienki, Park, Łazienki, Park. He involved himself deeply in the detail of his architectural projects, and his eclectic style has been dubbed the "Stanisław August style" by Polish art historian Władysław Tatarkiewicz. His chief architects included Domenico Merlini and Johann Christian Kammsetzer, Jan Kammsetzer.
He was also patron to numerous painters. They included Poles such as his protégée, Anna Rajecka and Franciszek Smuglewicz, Jan Bogumił Plersch, son of Jan Jerzy Plersch, Józef Wall, and Zygmunt Vogel, as well as foreign painters including, Marcello Bacciarelli, Bernardo Bellotto, Jean Pillement, Ludwik Marteau, and Per Krafft the Elder. His retinue of sculptors, headed by André-Jean Lebrun, included Giacomo Monaldi, Franz Pinck, and Tommaso Righi. Jan Filip Holzhaeusser was his court engraver and the designer of many commemorative medals. According to a 1795 inventory, Stanisław August's art collection, spread among numerous buildings, contained 2,889 pieces, including works by Rembrandt, Rubens, and van Dyck. His plan to create a large gallery of paintings in Warsaw was disrupted by the Partitions of Poland, dismemberment of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Most of the paintings that he had ordered for it can now be seen in London's Dulwich Picture Gallery. Poniatowski also planned to found an Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw, Academy of Fine Arts, but this finally came about only after his abdication and departure from Warsaw.
Poniatowski accomplished much in the realm of education and literature. He established the School of Chivalry, also called the "Cadet Corps", which functioned from 1765 to 1794 and whose alumni included Tadeusz Kościuszko. He supported the creation of the
Stanisław August Poniatowski has been called the Polish Enlightenment's most important patron of the arts. His cultural projects were attuned to his socio-political aims of overthrowing the myth of the Golden Freedoms and the traditional ideology of Sarmatism. His weekly "Thursday Dinners" were considered the most scintillating social functions in the Polish capital.
He founded National Theatre, Warsaw, Warsaw's National Theatre, Poland's first public theatre, and sponsored an associated Ballet schoolsballet school. He remodeled Ujazdów Castle, Ujazdów Palace and the Royal Castle, Warsaw, Royal Castle in Warsaw, and erected the elegant Łazienki Palace, Łazienki (Royal Baths) Palace in Warsaw's Lazienki, Park, Łazienki, Park. He involved himself deeply in the detail of his architectural projects, and his eclectic style has been dubbed the "Stanisław August style" by Polish art historian Władysław Tatarkiewicz. His chief architects included Domenico Merlini and Johann Christian Kammsetzer, Jan Kammsetzer.
He was also patron to numerous painters. They included Poles such as his protégée, Anna Rajecka and Franciszek Smuglewicz, Jan Bogumił Plersch, son of Jan Jerzy Plersch, Józef Wall, and Zygmunt Vogel, as well as foreign painters including, Marcello Bacciarelli, Bernardo Bellotto, Jean Pillement, Ludwik Marteau, and Per Krafft the Elder. His retinue of sculptors, headed by André-Jean Lebrun, included Giacomo Monaldi, Franz Pinck, and Tommaso Righi. Jan Filip Holzhaeusser was his court engraver and the designer of many commemorative medals. According to a 1795 inventory, Stanisław August's art collection, spread among numerous buildings, contained 2,889 pieces, including works by Rembrandt, Rubens, and van Dyck. His plan to create a large gallery of paintings in Warsaw was disrupted by the Partitions of Poland, dismemberment of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Most of the paintings that he had ordered for it can now be seen in London's Dulwich Picture Gallery. Poniatowski also planned to found an Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw, Academy of Fine Arts, but this finally came about only after his abdication and departure from Warsaw.
Poniatowski accomplished much in the realm of education and literature. He established the School of Chivalry, also called the "Cadet Corps", which functioned from 1765 to 1794 and whose alumni included Tadeusz Kościuszko. He supported the creation of the  He supported the development of the sciences, particularly cartography; he hired a personal cartographer, Karol de Perthees, even before he was elected king. A plan he initiated to map the entire territory of the Commonwealth, however, was never finished. At the Royal Castle in Warsaw, he organized an astronomical observatory and supported astronomers Jan Śniadecki and Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt. He also sponsored historical studies, including the collection, cataloging and copying of historical manuscripts. He encouraged publications of biographies of famous Polish historical figures, and sponsored paintings and sculptures of them.
For his contributions to the arts and sciences, Poniatowski was awarded in 1766 a royal Fellow of the Royal Society, Fellowship of the Royal Society, where he became the first royal Fellow outside British royalty. In 1778 he was awarded fellowship of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and in 1791 of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy of Sciences.
He also supported the development of industry and manufacturing, areas in which the Commonwealth lagged behind most of Western Europe. Among the endeavours in which he invested were the manufacture of cannons and firearms and the mining industry.
Poniatowski himself left several literary works: his memoirs, some political brochures and recorded speeches from the Sejm. He was considered a great orator and a skilled conversationalist.
He supported the development of the sciences, particularly cartography; he hired a personal cartographer, Karol de Perthees, even before he was elected king. A plan he initiated to map the entire territory of the Commonwealth, however, was never finished. At the Royal Castle in Warsaw, he organized an astronomical observatory and supported astronomers Jan Śniadecki and Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt. He also sponsored historical studies, including the collection, cataloging and copying of historical manuscripts. He encouraged publications of biographies of famous Polish historical figures, and sponsored paintings and sculptures of them.
For his contributions to the arts and sciences, Poniatowski was awarded in 1766 a royal Fellow of the Royal Society, Fellowship of the Royal Society, where he became the first royal Fellow outside British royalty. In 1778 he was awarded fellowship of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and in 1791 of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy of Sciences.
He also supported the development of industry and manufacturing, areas in which the Commonwealth lagged behind most of Western Europe. Among the endeavours in which he invested were the manufacture of cannons and firearms and the mining industry.
Poniatowski himself left several literary works: his memoirs, some political brochures and recorded speeches from the Sejm. He was considered a great orator and a skilled conversationalist.
 King Stanisław Augustus remains a controversial figure. In Polish historiography and in popular works, he has been criticized or marginalized by authors such as, Szymon Askenazy, Joachim Lelewel, Jerzy Łojek whom Andrzej Zahorski describes as Poniatowski's most vocal critic among modern historians, Tadeusz Korzon, Karol Zyszewski and Krystyna Zienkowska; whereas more neutral or positive views have been expressed by Paweł Jasienica, Walerian Kalinka, Władysław Konopczyński, Stanisław Mackiewicz, Emanuel Rostworowski and Stanisław Wasylewski.
King Stanisław Augustus remains a controversial figure. In Polish historiography and in popular works, he has been criticized or marginalized by authors such as, Szymon Askenazy, Joachim Lelewel, Jerzy Łojek whom Andrzej Zahorski describes as Poniatowski's most vocal critic among modern historians, Tadeusz Korzon, Karol Zyszewski and Krystyna Zienkowska; whereas more neutral or positive views have been expressed by Paweł Jasienica, Walerian Kalinka, Władysław Konopczyński, Stanisław Mackiewicz, Emanuel Rostworowski and Stanisław Wasylewski.
 When elected to the throne, he was seen by many as simply an "instrument for displacing the somnolent Saxons from the throne of Poland", yet as the British historian, Norman Davies notes, "''he turned out to be an ardent patriot, and a convinced reformer.''" Still, according to many, his reforms did not go far enough, leading to accusations that he was being overly cautious, even indecisive, a fault to which he himself admitted. His decision to rely on Russia has been often criticized. Poniatowski saw Russia as a "lesser evil" – willing to support the notional "independence" of a weak Poland within the Russian sphere of influence. However, in the event Russia imposed the Partitions of Poland rather than choose to support internal reform. He was accused by others of weakness and subservience, even of treason, especially in the years following the Second Partition of Poland, Second Partition. During the
When elected to the throne, he was seen by many as simply an "instrument for displacing the somnolent Saxons from the throne of Poland", yet as the British historian, Norman Davies notes, "''he turned out to be an ardent patriot, and a convinced reformer.''" Still, according to many, his reforms did not go far enough, leading to accusations that he was being overly cautious, even indecisive, a fault to which he himself admitted. His decision to rely on Russia has been often criticized. Poniatowski saw Russia as a "lesser evil" – willing to support the notional "independence" of a weak Poland within the Russian sphere of influence. However, in the event Russia imposed the Partitions of Poland rather than choose to support internal reform. He was accused by others of weakness and subservience, even of treason, especially in the years following the Second Partition of Poland, Second Partition. During the
 Poniatowski has been the subject of numerous biographies and many works of art. Voltaire, who saw Poniatowski as a model reformist, based his character, King Teucer in the play ''Les Lois de Minos'' (1772) on Poniatowski. At least 58 contemporary poems were dedicated to him or praised him. Since then, he has been a major character in many works of Józef Ignacy Kraszewski, in the ''Rok 1794'' trilogy by Władysław Stanisław Reymont, in the novels of Tadeusz Łopalewski, and in the dramas of Ignacy Grabowski, Tadeusz Miciński, Roman Brandstaetter and Bogdan Śmigielski. He is discussed in Luise Mühlbach's novel ''Joseph II and His Court'', and appears in Jane Porter's 1803 novel, ''Thaddeus of Warsaw''.
On screen he has been played by Wieńczysław Gliński in the 1976 ''3 Maja'' directed by Grzegorz Królikiewicz. He appears in Catherine the Great (TV series), a Russian TV series.
Poniatowski is depicted in numerous portraits, medals and coins. He is prominent in Jan Matejko's work, especially in the 1891 painting, ''Constitution of May 3, 1791 (painting), Constitution of 3 May 1791'' and in another large canvas, ''Rejtan (painting), Rejtan'', and in his series of portraits of Polish monarchs. A bust of Poniatowski was unveiled in Łazienki Palace in 1992. A number of cities in Poland have streets named after him, including
Poniatowski has been the subject of numerous biographies and many works of art. Voltaire, who saw Poniatowski as a model reformist, based his character, King Teucer in the play ''Les Lois de Minos'' (1772) on Poniatowski. At least 58 contemporary poems were dedicated to him or praised him. Since then, he has been a major character in many works of Józef Ignacy Kraszewski, in the ''Rok 1794'' trilogy by Władysław Stanisław Reymont, in the novels of Tadeusz Łopalewski, and in the dramas of Ignacy Grabowski, Tadeusz Miciński, Roman Brandstaetter and Bogdan Śmigielski. He is discussed in Luise Mühlbach's novel ''Joseph II and His Court'', and appears in Jane Porter's 1803 novel, ''Thaddeus of Warsaw''.
On screen he has been played by Wieńczysław Gliński in the 1976 ''3 Maja'' directed by Grzegorz Królikiewicz. He appears in Catherine the Great (TV series), a Russian TV series.
Poniatowski is depicted in numerous portraits, medals and coins. He is prominent in Jan Matejko's work, especially in the 1891 painting, ''Constitution of May 3, 1791 (painting), Constitution of 3 May 1791'' and in another large canvas, ''Rejtan (painting), Rejtan'', and in his series of portraits of Polish monarchs. A bust of Poniatowski was unveiled in Łazienki Palace in 1992. A number of cities in Poland have streets named after him, including
 A few historians believe that he later contracted a secret marriage with Elżbieta Szydłowska. However, according to Wirydianna Fiszerowa, a contemporary who knew them both, this rumour only spread after the death of Poniatowski, was generally disbelieved, and moreover, was circulated by Elżbieta herself, so the marriage is considered by most to be unlikely.
He had several notable lovers, including Elżbieta Branicka, who acted as his political adviser and financier, and had children with two of them. With Magdalena Agnieszka Sapieżyna (1739–1780), he became the father of Konstancja Żwanowa (1768–1810) and Michał Cichocki (1770–1828). With Elżbieta Szydłowska (1748–1810), he became the father of Stanisław Konopnicy-Grabowski (1780–1845), Michał Grabowski (1773–1812), Kazimierz Grabowski (1770-?), Konstancja Grabowska and Izabela Grabowska (1776–1858).
A few historians believe that he later contracted a secret marriage with Elżbieta Szydłowska. However, according to Wirydianna Fiszerowa, a contemporary who knew them both, this rumour only spread after the death of Poniatowski, was generally disbelieved, and moreover, was circulated by Elżbieta herself, so the marriage is considered by most to be unlikely.
He had several notable lovers, including Elżbieta Branicka, who acted as his political adviser and financier, and had children with two of them. With Magdalena Agnieszka Sapieżyna (1739–1780), he became the father of Konstancja Żwanowa (1768–1810) and Michał Cichocki (1770–1828). With Elżbieta Szydłowska (1748–1810), he became the father of Stanisław Konopnicy-Grabowski (1780–1845), Michał Grabowski (1773–1812), Kazimierz Grabowski (1770-?), Konstancja Grabowska and Izabela Grabowska (1776–1858).
p. 9
/ref> * : Order of Saint Andrew (1764)''Kawalerowie i statuty Orderu Orła Białego 1705–2008''. Zamek Królewski w Warszawie: 2008, p. 186.
website
on descendants of
''Stanisław August w Petersburgu'' (Stanisław August in Saint Petersburg), "Życie Literackie", No. 43, 1987, p. 1, 6.
(Official page of the Royal Łazienki Museum in Warsaw)
Poniatowski, in: The Historical Geography of the Ciołek clan AD 950–1950
Poniatowski's memoirs
Works by Stanisław August Poniatowski
in digital library Polona {{DEFAULTSORT:Poniatowski, Stanislaw August 1732 births 1798 deaths People from Kamenets District People from Brest Litovsk Voivodeship Poniatowski family, Stanislaw August Poniatowski Czartoryski family, Stanislaw Poniatowski 18th-century Polish nobility Polish Roman Catholics Polish people of Scottish descent Grand Dukes of Lithuania, Stanislas II Members of the Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Diplomats of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 18th-century diplomats 18th-century Polish monarchs German diplomats Fellows of the Royal Society Monarchs who abdicated, Stanislas II 18th-century philanthropists Polish philanthropists Lovers of Catherine the Great Military personnel of the Russian Empire Military personnel of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Polish writers in French Polish educational theorists Enlightenment philosophers Polish political writers 18th-century Polish–Lithuanian landowners People from the Russian Empire of Polish descent Polish male writers Museum founders Polish art collectors Polish memoirists Bibliophiles Polish book and manuscript collectors People of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 Targowica confederates Kościuszko insurgents Polish prisoners and detainees Prisoners and detainees of Russia Polish exiles Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Honorary members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Virtuti Militari Burials at St. John's Archcathedral, Warsaw Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland) Royal reburials Polish Enlightenment
Józef Poniatowski
Prince Józef Antoni Poniatowski (; 7 May 1763 – 19 October 1813) was a Polish general, minister of war and army chief, who became a Marshal of the French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars.
A nephew of king Stanislaus Augustus of Poland (), ...
(1763–1813), son of Andrzej. He was a great-grandson of poet and courtier Jan Andrzej Morsztyn
Jan Andrzej Morsztyn (1621–93) was a Polish poet, member of the landed nobility, and official in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He was '' starosta'' of Zawichost, Tymbark and Kowal. He was also pantler of Sandomierz (1647–58), Royal S ...
and through his great-grandmother, Catherine Gordon, lady-in-waiting
A lady-in-waiting or court lady is a female personal assistant at a court, attending on a royal woman or a high-ranking noblewoman. Historically, in Europe, a lady-in-waiting was often a noblewoman but of lower rank than the woman to whom sh ...
to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga
Marie Louise Gonzaga ( pl, Ludwika Maria; 18 August 1611 – 10 May 1667) was Queen of Poland and Grand Duchess of Lithuania by marriage to two kings of Poland and grand dukes of Lithuania, brothers Władysław IV and John II Casimir. Together ...
, he was related to the House of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fi ...
and thereby connected to the leading families of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. The Poniatowski family
The House of Poniatowski (plural: ''Poniatowscy'') is a prominent Polish family that was part of the nobility of Poland. A member of this family, Stanisław Poniatowski, was elected as King of Poland and reigned from 1764 until his abdicatio ...
had achieved high status among the Polish nobility ( szlachta) of the time.
He spent the first few years of his childhood in Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
. He was temporarily kidnapped as a toddler, on the orders of Józef Potocki
Józef Potocki (; 1673–1751) was a Polish nobleman ( szlachcic), magnate, Great Hetman of the Crown.
Józef was considered as the richest magnate in Poland at that time. He was Voivode of Kijów Voivodship (Kyiv, also Kiev) from 1702 to 1744, ...
, Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
of Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, as a reprisal for his father's support for King Augustus III
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
and held for some months in Kamieniec-Podolski. He was returned to his parents in Gdańsk. Later he moved with his family to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
. He was initially educated by his mother, then by private tutors, including Russian ambassador Herman Karl von Keyserling
Count Hermann Karl von Keyserling (1697–1764) was a Russian diplomat from the Keyserlingk family of Baltic German nobility based in the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia.
Life
In 1733, the nobility of Courland sent Keyserling to Saint Peter ...
. He had few friends in his teenage years and instead developed a fondness for books which continued throughout his life. He went on his first foreign trip in 1748, with elements of the Imperial Russian army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
as it advanced into the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
to aid Maria Theresia
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
's troops during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's W ...
which ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)
The 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, sometimes called the Treaty of Aachen, ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
The two main antagonists in the war, B ...
. This enabled Poniatowski both to visit the city, also known as Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
, and to venture into the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. On his return journey he stopped in Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
.
Political career
 The following year Poniatowski was apprenticed to the office of
The following year Poniatowski was apprenticed to the office of Michał Fryderyk Czartoryski
Prince Michał Fryderyk Czartoryski (1696–1775) was a Polish nobleman, the Duke of Klewań and , magnate, and Knight of the Order of the White Eagle (from 1726). He headed Poland's Czartoryski " Familia".
He served as Steward of Lithuania fr ...
, the then Deputy Chancellor of Lithuania
Chancellor of Poland ( pl, Kanclerz - , from la, cancellarius) was one of the highest officials in the historic Poland. This office functioned from the early Polish kingdom of the 12th century until the end of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwea ...
. In 1750, he travelled to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
where he met a British diplomat, Charles Hanbury Williams
Sir Charles Hanbury Williams, KB (8 December 1708 – 2 November 1759) was a Welsh diplomat, writer and satirist. He was a Member of Parliament from 1734 until his death.
Early life
Hanbury was the son of a Welsh ironmaster and Member of Parl ...
, who became his mentor and friend. In 1751, Poniatowski was elected to the Treasury Tribunal in Radom
Radom is a city in east-central Poland, located approximately south of the capital, Warsaw. It is situated on the Mleczna River in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), having previously been the seat of a separate Radom Voivodeship (1975–1 ...
, where he served as a commissioner. He spent most of January 1752 at the Austrian court in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. Later that year, after serving at the Radom Tribunal and meeting King Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
, he was elected deputy of the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
(Polish parliament). While there his father secured for him the title of Starosta of Przemyśl. In March 1753, he travelled to Hungary and Vienna, where he again met with Williams. He returned to the Netherlands, where he met many key members of that country's political and economic sphere. By late August he had arrived in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, where he moved among the elites. In February 1754, he travelled on to Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, where he spent some months. There, he was befriended by Charles Yorke
Charles Yorke PC (30 December 172220 January 1770) was briefly Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain. His father was also Lord Chancellor, and he began his career as a Member of Parliament. He served successively as Solicitor-General and Att ...
, the future Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. He returned to the Commonwealth later that year, however he eschewed the Sejm, as his parents wanted to keep him out of the political furore surrounding the Ostrogski family
The House of Ostrogski ( pl, Ostrogscy, lt, Ostrogiškiai, ua, Острозькі - ''Ostroz'ki'') was one of the more prominent families in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The f ...
's land inheritance (see: fee tail
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust established by deed or settlement which restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents the property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise alien ...
– ''Ordynacja Ostrogska''). The following year he received the title of ''Stolnik
Pantler (, , russian: сто́льник, ) was a court office in Lithuania, Poland, and Russia, responsible for serving the royal table, then an honorary court title and a district office.
Stolnik in Crown of Poland
In the Crown of Poland und ...
'' of Lithuania.
Poniatowski owed his rise and influence to his family connections with the powerful Czartoryski family
The House of Czartoryski (feminine form: Czartoryska, plural: Czartoryscy; lt, Čartoriskiai) is a Polish princely family of Lithuanian- Ruthenian origin, also known as the Familia. The family, which derived their kin from the Gediminids dynas ...
and their political faction, known as the '' Familia'', with whom he had grown close. It was the ''Familia'' who sent him in 1755 to Saint Petersburg in the service of Williams, who had been nominated British ambassador to Russia.
 In Saint Petersburg, Williams introduced Poniatowski to the 26-year-old Catherine Alexeievna, the future empress Catherine the Great. The two became lovers. Whatever his feelings for Catherine, it is likely Poniatowski also saw an opportunity to use the relationship for his own benefit, using her influence to bolster his career.
Poniatowski had to leave St. Petersburg in July 1756 due to court intrigue. Through the combined influence of Catherine, of Russian empress
In Saint Petersburg, Williams introduced Poniatowski to the 26-year-old Catherine Alexeievna, the future empress Catherine the Great. The two became lovers. Whatever his feelings for Catherine, it is likely Poniatowski also saw an opportunity to use the relationship for his own benefit, using her influence to bolster his career.
Poniatowski had to leave St. Petersburg in July 1756 due to court intrigue. Through the combined influence of Catherine, of Russian empress Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
and of chancellor Bestuzhev-Ryumin, Poniatowski was able to rejoin the Russian court now as ambassador of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
the following January. Still in St Petersburg, he appears to have been a source of intrigue between various European governments, some supporting his appointment, others demanding his withdrawal. He eventually left the Russian capital on 14 August 1758.
Poniatowski attended the Sejms of 1758, 1760 and 1762. He continued his involvement with the ''Familia'', and supported a pro-Russian and anti-Prussian stance in Polish politics. His father died in 1762, leaving him a modest inheritance. In 1762, when Catherine ascended the Russian throne, she sent him several letters professing her support for his own ascension to the Polish throne, but asking him to stay away from St. Petersburg. Nevertheless, Poniatowski hoped that Catherine would consider his offer of marriage, an idea seen as plausible by some international observers. He participated in the failed plot by the ''Familia'' to stage a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
against King Augustus III
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was List of Polish monarchs, King of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as List of rulers of Saxony, El ...
. In August 1763, however, Catherine advised him and the ''Familia'' that she would not support a coup as long as King Augustus was alive.
Kingship
Years of hope
 Upon the death of Poland's King
Upon the death of Poland's King Augustus III
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
in October 1763, lobbying began for the election of the new king. Catherine threw her support behind Poniatowski. The Russians spent about 2.5m rubles in aid of his election. Poniatowski's supporters and opponents engaged in some military posturing and even minor clashes. In the end, the Russian army was deployed only a few kilometres from the election sejm
Royal elections in Poland (Polish language, Polish: ''wolna elekcja'', lit. ''free election'') were the elections of individual King, kings, rather than dynasties, to the Polish throne. Based on traditions dating to the very beginning of the Polis ...
, which met at Wola
Wola (, ) is a district in western Warsaw, Poland, formerly the village of Wielka Wola, incorporated into Warsaw in 1916. An industrial area with traditions reaching back to the early 19th century, it underwent a transformation into an office (co ...
near Warsaw. In the event, there were no other serious contenders, and during the convocation sejm on 7 September 1764, 32-year-old Poniatowski was elected king, with 5,584 votes. He swore the pacta conventa
''Pacta conventa'' (Latin for "articles of agreement") was a contractual agreement, from 1573 to 1764 entered into between the "Polish nation" (i.e., the szlachta (nobility) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and a newly elected king upon ...
on 13 November, and a formal coronation took place in Warsaw on 25 November. The new king's "uncles" in the ''Familia'' would have preferred another nephew on the throne, Prince Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski
Prince Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski (1 December 1734 – 19 March 1823) was an influential Polish aristocrat, writer, literary and theater critic, linguist, traveller and statesman. He was a great patron of arts and a candidate for the Polish crow ...
, characterized by one of his contemporaries as "''débauché, si non dévoyé''" (French: "debauched if not depraved"), but Czartoryski had declined to seek office.
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. On 7 May 1765, Poniatowski established the Order of the Knights of Saint Stanislaus, in honour of Saint Stanislaus of Krakow, Bishop and Martyr, Poland's and his own patron saint, as the country's second order of chivalry
An order of chivalry, order of knighthood, chivalric order, or equestrian order is an order (distinction), order of knights, typically founded during or inspired by the original Catholic Military order (religious society), military orders of the ...
, to reward Poles and others for noteworthy service to the King. Together with the ''Familia'' he tried to reform the ineffective system of government, by reducing the powers of the hetmans
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military co ...
(Commonwealth's top military commanders) and treasurers, moving them to commissions elected by the Sejm and accountable to the King. In his memoirs, Poniatowski called this period the "years of hope." The ''Familia'', which was interested in strengthening its own power base, was dissatisfied with his conciliatory attitude as he reached out to many former opponents of their policies. This uneasy alliance between Poniatowski and the ''Familia'' continued for most of the first decade of his rule. One of the points of contention between Poniatowski and the ''Familia'' concerned the rights of religious minorities in Poland. Whereas Poniatowski reluctantly supported a policy of religious tolerance
Religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, mistaken, or harmful". ...
, the ''Familia'' was opposed to it. The growing rift between Poniatowski and the ''Familia'' was exploited by the Russians, who used the issue as a pretext to intervene in the Commonwealth's internal politics and to destabilize the country. Catherine had no wish to see Poniatowski's reform succeed. She had supported his ascent to the throne to ensure the Commonwealth remained a virtual puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its o ...
under Russian control, so his attempts to reform the Commonwealth's ailing government structures were a threat to the ''status quo''.
The Bar Confederation and First Partition of Poland
Matters came to a head in 1766. During the Sejm in October of that year, Poniatowski attempted to push through a radical reform, restricting the disastrous '' liberum veto'' provision. He was opposed by conservatives such as Michał Wielhorski, who were supported by the Prussian and Russian ambassadors and who threatened war if the reform was passed. The dissidents, supported by the Russians, formed theRadom Confederation Radom Confederation ( pl, Konfederacja radomska, lt, Radomo konfederacija) was a konfederacja of nobility (''szlachta'') in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth formed in Radom on 23 June 1767 to prevent reforms and defend the '' Golden Liberties' ...
. Abandoned by the ''Familia'', Poniatowski's reforms failed to pass at the Repnin Sejm
The Repnin Sejm ( pl, Sejm Repninowski) was a Sejm (session of the parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1767 and 1768 in Warsaw. This session followed the Sejms of 1764 to 1766, where the newly elected King ...
, named after Russian ambassador Nicholas Repnin
Prince Nikolai Vasilyevich Repnin (russian: Никола́й Васи́льевич Репни́н; – ) was an Imperial Russian statesman and general from the Repnin princely family who played a key role in the dissolution of the Polish–Lit ...
, who promised to guarantee with all the might of the Russian Empire the Golden Liberties
Golden Liberty ( la, Aurea Libertas; pl, Złota Wolność, lt, Auksinė laisvė), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( pl, Rzeczpospolita Szlachecka or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a po ...
of the Polish nobility, enshrined in the Cardinal Laws The Cardinal Laws ( pl, Prawa kardynalne) were a quasi-constitution enacted in Warsaw, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, by the Repnin Sejm of 1767–68. Enshrining most of the conservative laws responsible for the inefficient functioning of the Co ...
.
Although it had abandoned the cause of Poniatowski's reforms, the ''Familia'' did not receive the support it expected from the Russians who continued to press for the conservatives' rights. Meanwhile, other factions now rallied under the banner of the Bar Confederation, aimed against the conservatives, Poniatowski and the Russians. After an unsuccessful attempt to raise allies in Western Europe, France, Britain and Austria, Poniatowski and the ''Familia'' had no choice but to rely more heavily on the Russian Empire, which treated Poland as a protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
. In the War of the Bar Confederation (1768–1772), Poniatowski supported the Russian army's repression of the Bar Confederation. In 1770, the Council of the Bar Confederation proclaimed him dethroned. The following year, he was kidnapped by Bar Confederates and was briefly held prisoner outside of Warsaw, but he managed to escape. In view of the continuing weakness of the Polish-Lithuanian state, Austria, Russia, and Prussia collaborated to threaten military intervention in exchange for substantial territorial concessions from the Commonwealth – a decision they made without consulting Poniatowski or any other Polish parties.
 Although Poniatowski protested against the First Partition of the Commonwealth (1772), he was powerless to do anything about it. He considered
Although Poniatowski protested against the First Partition of the Commonwealth (1772), he was powerless to do anything about it. He considered abdication
Abdication is the act of formally relinquishing monarchical authority. Abdications have played various roles in the succession procedures of monarchies. While some cultures have viewed abdication as an extreme abandonment of duty, in other societ ...
, but decided against it.
During the Partition Sejm
The Partition Sejm ( pl, Sejm Rozbiorowy) was a Sejm lasting from 1773 to 1775 in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, convened by its three neighbours (the Russian Empire, Prussia and Austria) in order to legalize their First Partition of Pol ...
of 1773–1775, in which Russia was represented by ambassador Otto von Stackelberg, with no allied assistance forthcoming from abroad and with the armies of the partitioning powers occupying Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
to compel the Sejm by force of arms, no alternative was available save submission to their will. Eventually Poniatowski and the Sejm acceded to the "partition treaty". At the same time, several other reforms were passed. The Cardinal Laws The Cardinal Laws ( pl, Prawa kardynalne) were a quasi-constitution enacted in Warsaw, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, by the Repnin Sejm of 1767–68. Enshrining most of the conservative laws responsible for the inefficient functioning of the Co ...
were confirmed and guaranteed by the partitioning powers. Royal prerogative was restricted, so that the King lost the power to confer titular roles, and military promotions, to appoint ministers and senators. Starostwo territories, and Crown lands would be awarded by auction. The Sejm also created two notable institutions: the Permanent Council
The Permanent Council () was the highest administrative authority in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth between 1775 and 1789 and the first modern executive government in Europe. As is still typically the case in contemporary parliamentary pol ...
, a government body in continuous operation, and the Commission of National Education
The Commission of National Education ( pl, Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, KEN; lt, Edukacinė komisija) was the central educational authority in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, created by the Sejm and King Stanisław II August on October 1 ...
. The partitioning powers intended the council to be easier to control than the unruly Sejms, and indeed it remained under the influence of the Russian Empire. Nevertheless, it was a significant improvement on the earlier Commonwealth governance. The new legislation was guaranteed by the Russian Empire, giving it licence to interfere in Commonwealth politics when legislation it favoured was threatened.
The aftermath of the Partition Sejm
The Partition Sejm ( pl, Sejm Rozbiorowy) was a Sejm lasting from 1773 to 1775 in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, convened by its three neighbours (the Russian Empire, Prussia and Austria) in order to legalize their First Partition of Pol ...
saw the rise of a conservative faction opposed to the Permanent Council, seeing it as a threat to their Golden Freedoms. This faction was supported by the Czartoryski family, but not by Poniatowski, who proved to be quite adept at making the Council follow his wishes. This marked the formation of new anti-royal and pro-royal factions in Polish politics. The royal faction was made up primarily of people indebted to the King, who planned to build their careers on service to him. Few were privy to his plans for reforms, which were kept hidden from the conservative opposition and Russia. Poniatowski scored a political victory during the Sejm of 1776, which further strengthened the council. Chancellor Andrzej Zamoyski
Count Andrzej Hieronim Franciszek Zamoyski (12 February 1716 – 10 February 1792) was a Polish noble ( szlachcic). Knight of the Order of the White Eagle, awarded on 3 August 1758 in Warsaw.
He was the 10th Ordynat of the ''Zamość Ordy ...
was tasked with the codification of the Polish law, a project that became known as the Zamoyski Code
Zamoyski Code ( pl, Kodeks Zamoyskiego, links=no or ''Zbiór praw sądowych na mocy konstytucji roku 1776 przez J.W. Andrzeja Zamoyskiego ekskanclerza koronnego ułożony...'' These sentiments were used by two foreign powers, which did not want to ...
. Russia supported some, but not all, of the 1776 reforms, and to prevent Poniatowski from growing too powerful, it supported the opposition during the Sejm of 1778. This marked the end of Poniatowski's reforms, as he found himself without sufficient support to carry them through.
The Great Sejm and the Constitution of 3 May 1791
In the 1780s, Catherine appeared to favour Poniatowski marginally over the opposition, but she did not support any of his plans for significant reform. Despite repeated attempts, Poniatowski failed to confederate the sejms, which would have made them immune to the ''liberum veto''. Thus, although he had a majority in the Sejms, Poniatowski was unable to pass even the smallest reform. TheZamoyski Code
Zamoyski Code ( pl, Kodeks Zamoyskiego, links=no or ''Zbiór praw sądowych na mocy konstytucji roku 1776 przez J.W. Andrzeja Zamoyskiego ekskanclerza koronnego ułożony...'' These sentiments were used by two foreign powers, which did not want to ...
was rejected by the Sejm of 1780, and opposition attacks on the King dominated the Sejms of 1782 and 1786.
 Reforms became possible again in the late 1780s. In the context of the wars being waged against the Ottoman Empire by both the
Reforms became possible again in the late 1780s. In the context of the wars being waged against the Ottoman Empire by both the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, Poniatowski tried to draw Poland into the Austro-Russian alliance
Austro-Russian Alliance refers to the treaty signed by the Austrian Empire and the Russian Empire in May–June 1781. Russia was previously allied with Prussia ( Russo-Prussian Alliance). However, with time, Russia's attention was increasingly dra ...
, seeing a war with the Ottomans as an opportunity to strengthen the Commonwealth. Catherine gave permission for the next Sejm to be called, as she considered some form of limited military alliance with Poland against the Ottomans might be useful.
The Polish-Russian alliance was not implemented, as in the end the only acceptable compromise proved unattractive to both sides. However, in the ensuing Four-Year Sejm of 1788–92 (known as the Great Sejm
The Great Sejm, also known as the Four-Year Sejm ( Polish: ''Sejm Wielki'' or ''Sejm Czteroletni''; Lithuanian: ''Didysis seimas'' or ''Ketverių metų seimas'') was a Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was held in War ...
), Poniatowski threw his lot in with the reformers associated with the Patriotic Party
, colorcode = #E4433E
, leader1_title = Leaders
, leader1_name = Ignacy Potocki Adam Kazimierz CzartoryskiStanisław Małachowski
, foundation =
, dissolution =
, headquarters = Kraków
, ideology = Pro-Reform Constituti ...
of Stanisław Małachowski, Ignacy Potocki
Count Roman Ignacy Potocki, generally known as Ignacy Potocki (; 1750–1809), was a Polish nobleman, member of the influential magnate Potocki family, owner of Klementowice and Olesin (near Kurów), a politician, writer, and office holder. H ...
and Hugo Kołłątaj
Hugo Stumberg Kołłątaj, also spelled ''Kołłątay'' (pronounced , 1 April 1750 – 28 February 1812), was a prominent Polish constitutional reformer and educationalist, and one of the most prominent figures of the Polish Enlightenment. He s ...
, and co-authored the Constitution of 3 May 1791
The Constitution of 3 May 1791,; lt, Gegužės trečiosios konstitucija titled the Governance Act, was a constitution adopted by the Great Sejm ("Four-Year Sejm", meeting in 1788–1792) for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a dual mo ...
. The Constitution introduced sweeping reforms. According to Jacek Jędruch
Jacek Jędruch (Warsaw, Poland, 1927 – Athens, Greece, 1995) was a Polish-American nuclear engineer and historian of Polish representative government.
Life
During World War II, Jędruch participated in the Polish Resistance movement. Aft ...
, the Constitution, despite its liberal provisions, "fell somewhere below the French, above the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
, and left the General State Laws for the Prussian States
The General State Laws for the Prussian States (german: Allgemeines Landrecht für die Preußischen Staaten, ALR) were an important code of Prussia, promulgated in 1792 and codified by Carl Gottlieb Svarez and Ernst Ferdinand Klein, under the ...
(in German: ''Allgemeines Landrecht für die Preußischen Staaten'') far behind", but was "no match for the American Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
".
George Sanford notes that the Constitution gave Poland "a constitutional monarchy close to the British model of the time." According to a contemporary account, Poniatowski himself described it, as "founded principally on those of England and the United States of America, but avoiding the faults and errors of both, and adapted as much as possible to the local and particular circumstances of the country." The Constitution of 3 May remained to the end a work in progress. A new civil
Civil may refer to:
*Civic virtue, or civility
*Civil action, or lawsuit
* Civil affairs
*Civil and political rights
*Civil disobedience
*Civil engineering
*Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism
*Civilian, someone not a membe ...
and criminal code (provisionally called the "Stanisław Augustus Code") was among the proposals. Poniatowski also planned a reform to improve the situation of Polish Jews.
In foreign policy, spurned by Russia, Poland turned to another potential ally, the Triple Alliance (1788), Triple Alliance, represented on the Polish diplomatic scene primarily by the Kingdom of Prussia, which led to the formation of the ultimately futile Polish–Prussian alliance. The pro-Prussian shift was not supported by Poniatowski, who nevertheless acceded to the decision of the majority of Sejm deputies. The passing of the Constitution of 3 May, although officially applauded by Frederick William II of Prussia, who sent a congratulatory note to Warsaw, caused further worry in Prussia. The contacts of Polish reformers with the revolutionary National Assembly (French Revolution), French National Assembly were seen by Poland's neighbours as evidence of a conspiracy and a threat to their absolute monarchies. Prussian statesman Ewald von Hertzberg expressed the fears of European conservatives: "The Poles have given the ''coup de grâce'' to the Prussian monarchy by voting in a constitution", elaborating that a strong Commonwealth would likely demand the return of the lands Prussia acquired in the First Partition; a similar sentiment was later expressed by Prussian Foreign Minister, Count Friedrich Wilhelm von der Schulenburg (surname), Schulenburg-Kehnert. Russia's wars with the Ottomans and Gustav III's Russian War, Sweden having ended, Catherine was furious over the adoption of the Constitution, which threatened Russian influence in Poland. One of Russia's chief foreign policy authors, Alexander Bezborodko, upon learning of the Constitution, commented that "the worst possible news have arrived from Warsaw: the Polish king has become almost sovereign."
War in Defence of the Constitution and fall of the Commonwealth
 Shortly thereafter, conservative Polish nobility formed the Confederation of Targowica, Targowica Confederation to overthrow the Constitution, which they saw as a threat to the traditional freedoms and privileges they enjoyed. The confederates aligned themselves with Russia's Catherine the Great, and the Russian army entered Poland, marking the start of the
Shortly thereafter, conservative Polish nobility formed the Confederation of Targowica, Targowica Confederation to overthrow the Constitution, which they saw as a threat to the traditional freedoms and privileges they enjoyed. The confederates aligned themselves with Russia's Catherine the Great, and the Russian army entered Poland, marking the start of the Polish–Russian War of 1792
The Polish–Russian War of 1792 (also, War of the Second Partition, and in Polish sources, War in Defence of the Constitution ) was fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on one side, and the Targowica Confederation (conservat ...
, also known as the War in Defence of the Constitution. The Sejm voted to increase the Polish Army to 100,000 men, but due to insufficient time and funds this number was never achieved. Poniatowski and the reformers could field only a 37,000-man army, many of them untested recruits. This army, under the command of the King's nephew Józef Poniatowski
Prince Józef Antoni Poniatowski (; 7 May 1763 – 19 October 1813) was a Polish general, minister of war and army chief, who became a Marshal of the French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars.
A nephew of king Stanislaus Augustus of Poland (), ...
and Tadeusz Kościuszko, managed to defeat the Russians or fight them to a draw on several occasions. Following the victorious Battle of Zieleńce, in which Polish forces were commanded by his nephew, the King founded a new order, the Order of Virtuti Militari, to reward Poles for exceptional military leadership and courage in combat.
Despite Polish requests, Prussia refused to honour its alliance obligations. In the end, the numerical superiority of the Russians was too great, and defeat looked inevitable. Poniatowski's attempts at negotiations with Russia proved futile. In July 1792, when Warsaw was threatened with siege by the Russians, the king came to believe that surrender was the only alternative to total defeat. Having received assurances from Russian ambassador Yakov Bulgakov that no territorial changes would occur, a cabinet of ministers called the Guard of Laws (or Guardians of Law, pl, Straż Praw) voted eight to four in favor of surrender. On 24 July 1792, Poniatowski joined the Targowica Confederation. The Polish Army disintegrated. Many reform leaders, believing their cause lost, went into self-exile, although they hoped that Poniatowski would be able to negotiate an acceptable compromise with the Russians, as he had done in the past. Poniatowski had not saved the Commonwealth, however. He and the reformers had lost much of their influence, both within the country and with Catherine. Neither were the Targowica Confederates victorious. To their surprise, there ensued the Partitions of Poland#Second Partition, Second Partition of Poland. With the new deputies bribed or intimidated by the Russian troops, the Grodno Sejm took place. On 23 November 1793, it annulled all acts of the Great Sejm, including the Constitution. Faced with his powerlessness, Poniatowski once again considered abdication; in the meantime he tried to salvage whatever reforms he could.
Final years
 Poniatowski's plans had been ruined by the
Poniatowski's plans had been ruined by the Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Pr ...
. The King had not encouraged it, but once it began he supported it, seeing no other honourable option. Its defeat marked the end of the Commonwealth. Poniatowski tried to govern the country in the brief period after the fall of the Uprising, but on 2 December 1794, Catherine demanded he leave Warsaw, a request to which he acceded on 7 January 1795, leaving the capital under Russian military escort and settling briefly in Grodno. On 24 October 1795, the Act of the final, Third Partition of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polis ...
was signed. One month and one day later, on 25 November, Poniatowski signed his abdication.
Reportedly, his sister, Ludwika Maria Zamoyska and her daughter also his favourite niece, Urszula Zamoyska, who had been threatened with confiscation of their property, had contributed to persuading him to sign the abdication: they feared that his refusal would lead to a Russian confiscation of their properties and their ruin.
Catherine died on 17 November 1796, succeeded by her son, Paul I of Russia. On 15 February 1797, Poniatowski left for Saint Petersburg. He had hoped to be allowed to travel abroad, but was unable to secure permission to do so. A virtual prisoner in St. Petersburg's Marble Palace
Marble Palace (Мраморный дворец) is one of the first Neoclassical palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is situated between the Field of Mars and Palace Quay, slightly to the east from New Michael Palace.
Design and pre-1917 o ...
, he subsisted on a pension granted to him by Catherine. Despite financial troubles, he still supported some of his former allies, and continued to try to represent the Polish cause at the Russian court. He also worked on his memoirs.
Legacy
Patron of culture
 Stanisław August Poniatowski has been called the Polish Enlightenment's most important patron of the arts. His cultural projects were attuned to his socio-political aims of overthrowing the myth of the Golden Freedoms and the traditional ideology of Sarmatism. His weekly "Thursday Dinners" were considered the most scintillating social functions in the Polish capital.
He founded National Theatre, Warsaw, Warsaw's National Theatre, Poland's first public theatre, and sponsored an associated Ballet schoolsballet school. He remodeled Ujazdów Castle, Ujazdów Palace and the Royal Castle, Warsaw, Royal Castle in Warsaw, and erected the elegant Łazienki Palace, Łazienki (Royal Baths) Palace in Warsaw's Lazienki, Park, Łazienki, Park. He involved himself deeply in the detail of his architectural projects, and his eclectic style has been dubbed the "Stanisław August style" by Polish art historian Władysław Tatarkiewicz. His chief architects included Domenico Merlini and Johann Christian Kammsetzer, Jan Kammsetzer.
He was also patron to numerous painters. They included Poles such as his protégée, Anna Rajecka and Franciszek Smuglewicz, Jan Bogumił Plersch, son of Jan Jerzy Plersch, Józef Wall, and Zygmunt Vogel, as well as foreign painters including, Marcello Bacciarelli, Bernardo Bellotto, Jean Pillement, Ludwik Marteau, and Per Krafft the Elder. His retinue of sculptors, headed by André-Jean Lebrun, included Giacomo Monaldi, Franz Pinck, and Tommaso Righi. Jan Filip Holzhaeusser was his court engraver and the designer of many commemorative medals. According to a 1795 inventory, Stanisław August's art collection, spread among numerous buildings, contained 2,889 pieces, including works by Rembrandt, Rubens, and van Dyck. His plan to create a large gallery of paintings in Warsaw was disrupted by the Partitions of Poland, dismemberment of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Most of the paintings that he had ordered for it can now be seen in London's Dulwich Picture Gallery. Poniatowski also planned to found an Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw, Academy of Fine Arts, but this finally came about only after his abdication and departure from Warsaw.
Poniatowski accomplished much in the realm of education and literature. He established the School of Chivalry, also called the "Cadet Corps", which functioned from 1765 to 1794 and whose alumni included Tadeusz Kościuszko. He supported the creation of the
Stanisław August Poniatowski has been called the Polish Enlightenment's most important patron of the arts. His cultural projects were attuned to his socio-political aims of overthrowing the myth of the Golden Freedoms and the traditional ideology of Sarmatism. His weekly "Thursday Dinners" were considered the most scintillating social functions in the Polish capital.
He founded National Theatre, Warsaw, Warsaw's National Theatre, Poland's first public theatre, and sponsored an associated Ballet schoolsballet school. He remodeled Ujazdów Castle, Ujazdów Palace and the Royal Castle, Warsaw, Royal Castle in Warsaw, and erected the elegant Łazienki Palace, Łazienki (Royal Baths) Palace in Warsaw's Lazienki, Park, Łazienki, Park. He involved himself deeply in the detail of his architectural projects, and his eclectic style has been dubbed the "Stanisław August style" by Polish art historian Władysław Tatarkiewicz. His chief architects included Domenico Merlini and Johann Christian Kammsetzer, Jan Kammsetzer.
He was also patron to numerous painters. They included Poles such as his protégée, Anna Rajecka and Franciszek Smuglewicz, Jan Bogumił Plersch, son of Jan Jerzy Plersch, Józef Wall, and Zygmunt Vogel, as well as foreign painters including, Marcello Bacciarelli, Bernardo Bellotto, Jean Pillement, Ludwik Marteau, and Per Krafft the Elder. His retinue of sculptors, headed by André-Jean Lebrun, included Giacomo Monaldi, Franz Pinck, and Tommaso Righi. Jan Filip Holzhaeusser was his court engraver and the designer of many commemorative medals. According to a 1795 inventory, Stanisław August's art collection, spread among numerous buildings, contained 2,889 pieces, including works by Rembrandt, Rubens, and van Dyck. His plan to create a large gallery of paintings in Warsaw was disrupted by the Partitions of Poland, dismemberment of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Most of the paintings that he had ordered for it can now be seen in London's Dulwich Picture Gallery. Poniatowski also planned to found an Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw, Academy of Fine Arts, but this finally came about only after his abdication and departure from Warsaw.
Poniatowski accomplished much in the realm of education and literature. He established the School of Chivalry, also called the "Cadet Corps", which functioned from 1765 to 1794 and whose alumni included Tadeusz Kościuszko. He supported the creation of the Commission of National Education
The Commission of National Education ( pl, Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, KEN; lt, Edukacinė komisija) was the central educational authority in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, created by the Sejm and King Stanisław II August on October 1 ...
, considered to be the world's first Ministry of Education. In 1765 he helped found the ''Monitor (Polish newspaper), Monitor'', one of the first Polish newspapers and the leading periodical of the Polish Enlightenment. He sponsored many articles that appeared in the ''Monitor''. Writers and poets who received his patronage included, Stanisław Trembecki, Franciszek Salezy Jezierski, Franciszek Bohomolec and Franciszek Zabłocki. He also supported publishers including, Piotr Świtkowski, and library owners such as Józef Lex.
 He supported the development of the sciences, particularly cartography; he hired a personal cartographer, Karol de Perthees, even before he was elected king. A plan he initiated to map the entire territory of the Commonwealth, however, was never finished. At the Royal Castle in Warsaw, he organized an astronomical observatory and supported astronomers Jan Śniadecki and Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt. He also sponsored historical studies, including the collection, cataloging and copying of historical manuscripts. He encouraged publications of biographies of famous Polish historical figures, and sponsored paintings and sculptures of them.
For his contributions to the arts and sciences, Poniatowski was awarded in 1766 a royal Fellow of the Royal Society, Fellowship of the Royal Society, where he became the first royal Fellow outside British royalty. In 1778 he was awarded fellowship of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and in 1791 of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy of Sciences.
He also supported the development of industry and manufacturing, areas in which the Commonwealth lagged behind most of Western Europe. Among the endeavours in which he invested were the manufacture of cannons and firearms and the mining industry.
Poniatowski himself left several literary works: his memoirs, some political brochures and recorded speeches from the Sejm. He was considered a great orator and a skilled conversationalist.
He supported the development of the sciences, particularly cartography; he hired a personal cartographer, Karol de Perthees, even before he was elected king. A plan he initiated to map the entire territory of the Commonwealth, however, was never finished. At the Royal Castle in Warsaw, he organized an astronomical observatory and supported astronomers Jan Śniadecki and Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt. He also sponsored historical studies, including the collection, cataloging and copying of historical manuscripts. He encouraged publications of biographies of famous Polish historical figures, and sponsored paintings and sculptures of them.
For his contributions to the arts and sciences, Poniatowski was awarded in 1766 a royal Fellow of the Royal Society, Fellowship of the Royal Society, where he became the first royal Fellow outside British royalty. In 1778 he was awarded fellowship of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and in 1791 of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy of Sciences.
He also supported the development of industry and manufacturing, areas in which the Commonwealth lagged behind most of Western Europe. Among the endeavours in which he invested were the manufacture of cannons and firearms and the mining industry.
Poniatowski himself left several literary works: his memoirs, some political brochures and recorded speeches from the Sejm. He was considered a great orator and a skilled conversationalist.
Conflicting assessments
 King Stanisław Augustus remains a controversial figure. In Polish historiography and in popular works, he has been criticized or marginalized by authors such as, Szymon Askenazy, Joachim Lelewel, Jerzy Łojek whom Andrzej Zahorski describes as Poniatowski's most vocal critic among modern historians, Tadeusz Korzon, Karol Zyszewski and Krystyna Zienkowska; whereas more neutral or positive views have been expressed by Paweł Jasienica, Walerian Kalinka, Władysław Konopczyński, Stanisław Mackiewicz, Emanuel Rostworowski and Stanisław Wasylewski.
King Stanisław Augustus remains a controversial figure. In Polish historiography and in popular works, he has been criticized or marginalized by authors such as, Szymon Askenazy, Joachim Lelewel, Jerzy Łojek whom Andrzej Zahorski describes as Poniatowski's most vocal critic among modern historians, Tadeusz Korzon, Karol Zyszewski and Krystyna Zienkowska; whereas more neutral or positive views have been expressed by Paweł Jasienica, Walerian Kalinka, Władysław Konopczyński, Stanisław Mackiewicz, Emanuel Rostworowski and Stanisław Wasylewski.
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Pr ...
, there were rumours that Polish Jacobins had been planning a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
and Poniatowski's assassination. Another line of criticism alleged poor financial management on his part. Poniatowski actually had little personal wealth. Most of his income came from Crown Estates and monopolies. His lavish patronage of the arts and sciences was a major drain on the royal treasury. He also supported numerous public initiatives, and attempted to use the royal treasury to cover the state's expenses when tax revenues were insufficient. The Sejm promised several times to compensate his treasury to little practical effect. Nonetheless contemporary critics frequently accused him of being a spendthrift.
Andrzej Zahorski dedicated a book to a discussion of Poniatowski, ''The Dispute over Stanisław August'' (''Spór o Stanisława Augusta'', Warsaw, 1988). He notes that the discourse concerning Poniatowski is significantly coloured by the fact that he was the last King of Poland – the King who failed to save the country. This failure, and his prominent position, rendered him a convenient scapegoat for many. Zahorski argues that Poniatowski made the error of joining the Targowica Confederation. Although he wanted to preserve the integrity of the Polish state, it was far too late for that – he succeeded instead in cementing the damage to his own reputation for succeeding centuries.
Remembrance
 Poniatowski has been the subject of numerous biographies and many works of art. Voltaire, who saw Poniatowski as a model reformist, based his character, King Teucer in the play ''Les Lois de Minos'' (1772) on Poniatowski. At least 58 contemporary poems were dedicated to him or praised him. Since then, he has been a major character in many works of Józef Ignacy Kraszewski, in the ''Rok 1794'' trilogy by Władysław Stanisław Reymont, in the novels of Tadeusz Łopalewski, and in the dramas of Ignacy Grabowski, Tadeusz Miciński, Roman Brandstaetter and Bogdan Śmigielski. He is discussed in Luise Mühlbach's novel ''Joseph II and His Court'', and appears in Jane Porter's 1803 novel, ''Thaddeus of Warsaw''.
On screen he has been played by Wieńczysław Gliński in the 1976 ''3 Maja'' directed by Grzegorz Królikiewicz. He appears in Catherine the Great (TV series), a Russian TV series.
Poniatowski is depicted in numerous portraits, medals and coins. He is prominent in Jan Matejko's work, especially in the 1891 painting, ''Constitution of May 3, 1791 (painting), Constitution of 3 May 1791'' and in another large canvas, ''Rejtan (painting), Rejtan'', and in his series of portraits of Polish monarchs. A bust of Poniatowski was unveiled in Łazienki Palace in 1992. A number of cities in Poland have streets named after him, including
Poniatowski has been the subject of numerous biographies and many works of art. Voltaire, who saw Poniatowski as a model reformist, based his character, King Teucer in the play ''Les Lois de Minos'' (1772) on Poniatowski. At least 58 contemporary poems were dedicated to him or praised him. Since then, he has been a major character in many works of Józef Ignacy Kraszewski, in the ''Rok 1794'' trilogy by Władysław Stanisław Reymont, in the novels of Tadeusz Łopalewski, and in the dramas of Ignacy Grabowski, Tadeusz Miciński, Roman Brandstaetter and Bogdan Śmigielski. He is discussed in Luise Mühlbach's novel ''Joseph II and His Court'', and appears in Jane Porter's 1803 novel, ''Thaddeus of Warsaw''.
On screen he has been played by Wieńczysław Gliński in the 1976 ''3 Maja'' directed by Grzegorz Królikiewicz. He appears in Catherine the Great (TV series), a Russian TV series.
Poniatowski is depicted in numerous portraits, medals and coins. He is prominent in Jan Matejko's work, especially in the 1891 painting, ''Constitution of May 3, 1791 (painting), Constitution of 3 May 1791'' and in another large canvas, ''Rejtan (painting), Rejtan'', and in his series of portraits of Polish monarchs. A bust of Poniatowski was unveiled in Łazienki Palace in 1992. A number of cities in Poland have streets named after him, including Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
.
Family
Poniatowski never married. In his youth, he had loved his cousin Elżbieta Czartoryska (1736–1816), Elżbieta Czartoryska, but her father August Aleksander Czartoryski disapproved because he did not think him influential or rich enough. When this was no longer an issue, she was already married. His ''pacta conventa
''Pacta conventa'' (Latin for "articles of agreement") was a contractual agreement, from 1573 to 1764 entered into between the "Polish nation" (i.e., the szlachta (nobility) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and a newly elected king upon ...
'' specified that he should marry a Polish noblewoman, although he himself always hoped to marry into some royal family.
Upon his accession to the throne, he had hopes of marrying Catherine II, writing to her on 2 November 1763 in a moment of doubt, "If I desired the throne, it was because I saw you on it." When she made it clear through his envoy Rzewuski that she would not marry him, there were hopes of an Austrian archduchess, Archduchess Maria Elisabeth of Austria (1743–1808). A marriage to Princess Sophia Albertina of Sweden was suggested despite the religious differences, but this match was opposed by his sisters, Ludwika Maria Poniatowska and Izabella Poniatowska, and nothing came of it. The ceremonial role of queen and hostess of his court was played by his favourite niece, Urszula Zamoyska.
 A few historians believe that he later contracted a secret marriage with Elżbieta Szydłowska. However, according to Wirydianna Fiszerowa, a contemporary who knew them both, this rumour only spread after the death of Poniatowski, was generally disbelieved, and moreover, was circulated by Elżbieta herself, so the marriage is considered by most to be unlikely.
He had several notable lovers, including Elżbieta Branicka, who acted as his political adviser and financier, and had children with two of them. With Magdalena Agnieszka Sapieżyna (1739–1780), he became the father of Konstancja Żwanowa (1768–1810) and Michał Cichocki (1770–1828). With Elżbieta Szydłowska (1748–1810), he became the father of Stanisław Konopnicy-Grabowski (1780–1845), Michał Grabowski (1773–1812), Kazimierz Grabowski (1770-?), Konstancja Grabowska and Izabela Grabowska (1776–1858).
A few historians believe that he later contracted a secret marriage with Elżbieta Szydłowska. However, according to Wirydianna Fiszerowa, a contemporary who knew them both, this rumour only spread after the death of Poniatowski, was generally disbelieved, and moreover, was circulated by Elżbieta herself, so the marriage is considered by most to be unlikely.
He had several notable lovers, including Elżbieta Branicka, who acted as his political adviser and financier, and had children with two of them. With Magdalena Agnieszka Sapieżyna (1739–1780), he became the father of Konstancja Żwanowa (1768–1810) and Michał Cichocki (1770–1828). With Elżbieta Szydłowska (1748–1810), he became the father of Stanisław Konopnicy-Grabowski (1780–1845), Michał Grabowski (1773–1812), Kazimierz Grabowski (1770-?), Konstancja Grabowska and Izabela Grabowska (1776–1858).
Issue
Titles, honours and arms
The English translation of the Polish text of the 1791 Constitution gives his title as ''Stanisław August, by the grace of God and the will of the people, King of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland, Grand Duke of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania and Duke of Ruthenia, Royal Prussia, Prussia, Duchy of Masovia, Masovia, Duchy of Samogitia, Samogitia,Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, Volhynia, Podolia, Podlasie, Duchy of Livonia, Livonia, Smolensk, Severia and Chernihiv.''
National
* : Order of the White Eagle (Poland), Order of the White Eagle (1756) * : Order of Saint Stanislaus (1765) * : Order of Virtuti Militari (1792)Foreign
* Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia: Order of the Black Eagle (5 April 1764)''Liste der Ritter des Königlich Preußischen Hohen Ordens vom Schwarzen Adler'' (1851), "Von Seiner Majestät dem Könige Friedrich II. ernannte Ritterp. 9
/ref> * : Order of Saint Andrew (1764)''Kawalerowie i statuty Orderu Orła Białego 1705–2008''. Zamek Królewski w Warszawie: 2008, p. 186.
See also
* History of Poland (1569–1795) * Poles in the United Kingdom * Warsaw Society of Friends of LearningNotes
a Sources vary as to whether Konstancja Grabowska and Kazimierz Grabowski were Poniatowski's children. They are listed as such by several sources, including Jerzy Michalski's article on Stanisław August Poniatowski in the Polish Biographical Dictionary. However, Marek Jerzy Minakowski'website
on descendants of
Great Sejm
The Great Sejm, also known as the Four-Year Sejm ( Polish: ''Sejm Wielki'' or ''Sejm Czteroletni''; Lithuanian: ''Didysis seimas'' or ''Ketverių metų seimas'') was a Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was held in War ...
participants lists neither Kazimierz Grabowski nor Konstancja Grabowska as Poniatowski's children; and for Elżbieta Szydłowska, it lists only Kazimierz Grabowski as Jan Jerzy Grabowski's child.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * *Bibliography
* Marek Żukow-Karczewski''Stanisław August w Petersburgu'' (Stanisław August in Saint Petersburg), "Życie Literackie", No. 43, 1987, p. 1, 6.
External links
*(Official page of the Royal Łazienki Museum in Warsaw)
Poniatowski, in: The Historical Geography of the Ciołek clan AD 950–1950
Poniatowski's memoirs
Works by Stanisław August Poniatowski
in digital library Polona {{DEFAULTSORT:Poniatowski, Stanislaw August 1732 births 1798 deaths People from Kamenets District People from Brest Litovsk Voivodeship Poniatowski family, Stanislaw August Poniatowski Czartoryski family, Stanislaw Poniatowski 18th-century Polish nobility Polish Roman Catholics Polish people of Scottish descent Grand Dukes of Lithuania, Stanislas II Members of the Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Diplomats of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 18th-century diplomats 18th-century Polish monarchs German diplomats Fellows of the Royal Society Monarchs who abdicated, Stanislas II 18th-century philanthropists Polish philanthropists Lovers of Catherine the Great Military personnel of the Russian Empire Military personnel of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Polish writers in French Polish educational theorists Enlightenment philosophers Polish political writers 18th-century Polish–Lithuanian landowners People from the Russian Empire of Polish descent Polish male writers Museum founders Polish art collectors Polish memoirists Bibliophiles Polish book and manuscript collectors People of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 Targowica confederates Kościuszko insurgents Polish prisoners and detainees Prisoners and detainees of Russia Polish exiles Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Honorary members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Virtuti Militari Burials at St. John's Archcathedral, Warsaw Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland) Royal reburials Polish Enlightenment