social statistics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Social statistics is the use of statistical measurement systems to study
 Adolph Quetelet was a proponent of social physics. In his book ''Physique sociale'' he presents distributions of human
Adolph Quetelet was a proponent of social physics. In his book ''Physique sociale'' he presents distributions of human
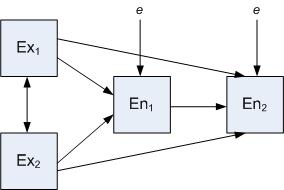

 Methods and concepts used in quantitative social sciences include:
*
Methods and concepts used in quantitative social sciences include:
*
Center for Statistics and Social Sciences, University of WashingtonCenter for the Promotion of Research Involving Innovative Statistical Methodology, New York University, NYCentre for Research Methods, Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Helsinki, FinlandCornell Institute for Social and Economic ResearchHarvard Institute for Quantitative Social ScienceInter-University Consortium for Political and Social ResearchNational Centre for Research Methods, UKSocial Statistics Department, University of ManchesterSocial Statistics Division, School of Social Sciences, University of Southampton, UK
;Statistical databases for social science
Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social ResearchUN Statistics Division- Demographic and Social Statistics
* ttp://www.bls.gov US Bureau of Labor Statisticsbr>International Labour Organisation- LABORSTAUnionstats.com
{{Authority control
human behavior
Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity ( mentally, physically, and socially) of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external stimuli throughout their life. Kagan, Jerome, Marc H. Bornstein, and Richard M. ...
in a social environment. This can be accomplished through polling
Poll, polled, or polling may refer to:
Figurative head counts
* Poll, a formal election
** Election verification exit poll, a survey taken to verify election counts
** Polling, voting to make decisions or determine opinions
** Polling places o ...
a group of people, evaluating a subset of data obtained about a group of people, or by observation and statistical analysis of a set of data that relates to people and their behaviors.
Statistics in the social sciences
History
 Adolph Quetelet was a proponent of social physics. In his book ''Physique sociale'' he presents distributions of human
Adolph Quetelet was a proponent of social physics. In his book ''Physique sociale'' he presents distributions of human height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
s, age of marriage
Marriageable age (or marriage age) is the general age, as a legal age or as the minimum age subject to parental, religious or other forms of social approval, at which a person is legitimately allowed for marriage. Age and other prerequisites to ...
, time of birth and death, time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Ex ...
of human marriages, births and deaths, a survival density for humans and curve describing fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to pr ...
as a function of age. He also developed the Quetelet Index.
Francis Ysidro Edgeworth published "On Methods of Ascertaining Variations in the Rate of Births, Deaths, and Marriages" in 1885 which uses squares of differences for studying fluctuations and George Udny Yule published "On the Correlation of total Pauperism
Pauperism (Lat. ''pauper'', poor) is poverty or generally the state of being poor, or particularly the condition of being a "pauper", i.e. receiving relief administered under the English Poor Laws. From this, pauperism can also be more generally ...
with Proportion of Out-Relief" in 1895.
A numerical calibration
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of kno ...
for the fertility curve was given by Karl Pearson in 1897 in his "The Chances of Death, and Other Studies in Evolution" In this book Pearson also uses standard deviation, correlation and skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined.
For a unimodal ...
for studying humans.
Vilfredo Pareto
Vilfredo Federico Damaso Pareto ( , , , ; born Wilfried Fritz Pareto; 15 July 1848 – 19 August 1923) was an Italians, Italian polymath (civil engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher). He made several important ...
published his analysis of the distribution of income
In economics, income distribution covers how a country's total GDP is distributed amongst its population. Economic theory and economic policy have long seen income and its distribution as a central concern. Unequal distribution of income causes ec ...
in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
in 1897, this is now known as the Pareto principle.
Louis Guttman
Louis (Eliyahu) Guttman (February 10, 1916 – October 25, 1987; he, לואיס (אליהו) גוטמן) was an American sociologist and Professor of Social and Psychological Assessment at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, known primarily for ...
proposed that the values of ordinal variables can be represented by a Guttman scale, which is useful if the number of variables is large and allows the use of techniques such as ordinary least squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the ...
.
Macroeconomic
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
statistical research has provided stylized facts, which include:
* Bowley's law Bowley's law, also known as the law of the constant wage share, is a stylized fact of economics which states that the wage share of a country, i.e., the share of a country's economic output that is given to employees as compensation for their work ...
(1937) regarding the proportion between wages and national output
* The Phillips curve
The Phillips curve is an economic model, named after William Phillips hypothesizing a correlation between reduction in unemployment and increased rates of wage rises within an economy. While Phillips himself did not state a linked relationship ...
(1958) regarding the relation between wages and unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
Statistics and statistical analyses have become a key feature of social science: statistics is employed in economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes ...
, psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between ...
, political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
, sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation an ...
and anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
.
Statistical methods in social sciences
Research design
Research design refers to the overall strategy utilized to carry out research that defines a succinct and logical plan to tackle established research question(s) through the collection, interpretation, analysis, and discussion of data.
Incorporat ...
, survey methodology
Survey methodology is "the study of survey methods".
As a field of applied statistics concentrating on human-research surveys, survey methodology studies the sampling of individual units from a population and associated techniques of survey da ...
and survey sampling In statistics, survey sampling describes the process of selecting a sample of elements from a target population to conduct a survey.
The term " survey" may refer to many different types or techniques of observation. In survey sampling it most ofte ...
* Delphi method }
The Delphi method or Delphi technique ( ; also known as Estimate-Talk-Estimate or ETE) is a structured communication technique or method, originally developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method which relies on a panel of experts. The ...
Statistical techniques include:
Covariance based methods
*Regression analysis
In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable (often called the 'outcome' or 'response' variable, or a 'label' in machine learning parlance) and one ...
* Canonical correlation
* Causal analysis
* Multilevel models
* Factor analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed ...
* Linear discriminant analysis
* Path analysis
* Structural Equation Modeling
Probability based methods
*Probit
In probability theory and statistics, the probit function is the quantile function associated with the standard normal distribution. It has applications in data analysis and machine learning, in particular exploratory statistical graphics and s ...
and logit
In statistics, the logit ( ) function is the quantile function associated with the standard logistic distribution. It has many uses in data analysis and machine learning, especially in data transformations.
Mathematically, the logit is the ...
* Item response theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) (also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring ...
* Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics is a theory in the field of statistics based on the Bayesian interpretation of probability where probability expresses a ''degree of belief'' in an event. The degree of belief may be based on prior knowledge about the event, ...
* Stochastic process
* Latent class model In statistics, a latent class model (LCM) relates a set of observed (usually discrete) multivariate variables to a set of latent variables. It is a type of latent variable model. It is called a latent class model because the latent variable is dis ...
Distance based methods
* Cluster analysis *Multidimensional scaling
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) is a means of visualizing the level of similarity of individual cases of a dataset. MDS is used to translate "information about the pairwise 'distances' among a set of n objects or individuals" into a configurati ...
Methods for categorical data
* Classification analysis * Cohort analysisUsage and applications
Social scientists use social statistics for many purposes, including: * theevaluation
Evaluation is a
systematic determination and assessment of a subject's merit, worth and significance, using criteria governed by a set of standards. It can assist an organization, program, design, project or any other intervention or initiative to ...
of the quality of services available to a group or organization,
* analyzing behaviors of groups of people in their environment and special situations,
* determining the wants of people through statistical sampling
* evaluation of wage expenditures and savings
* preventing industrial diseases
* prevention of industrial accidents
* labour dispute
A labor dispute is a disagreement between an employer and employees regarding the terms of employment. This could include disputes regarding conditions of employment, fringe benefits, hours of work, tenure, and wages to be negotiated during co ...
s, such as supporting the Anthracite Coal Strike Commission of 1902-1903
* supporting governments in times of peace and war
Reliability
The use of statistics has become so widespread in the social sciences that many universities such as Harvard, have developed institutes focusing on "quantitative social science." Harvard's Institute for Quantitative Social Science focuses mainly on fields likepolitical science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
that incorporate the advanced causal statistical models that Bayesian method
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and e ...
s provide. However, some experts in causality feel that these claims of causal statistics are overstated.J. Pearl, Bayesianism and causality, or, why I am only a half-bayesian http://ftp.cs.ucla.edu/pub/stat_ser/r284-reprint.pdf There is a debate regarding the uses and value of statistical methods in social science, especially in political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
, with some statisticians questioning practices such as data dredging that can lead to unreliable policy conclusions of political partisans who overestimate the interpretive power that non-robust statistical methods such as simple and multiple linear regression allow. Indeed, an important axiom that social scientists cite, but often forget, is that " correlation does not imply causation." For example, it appears widely accepted that the lower numbers of women in decision making positions in politics, business and science is good evidence of gender discrimination
Sexism is prejudice or discrimination based on one's sex or gender. Sexism can affect anyone, but it primarily affects women and girls.There is a clear and broad consensus among academic scholars in multiple fields that sexism refers primaril ...
. But where men suffer adverse statistical indicators such as greater imprisonment rates or a higher suicide rate, that is not usually accepted as evidence of gender bias
Sexism is prejudice or discrimination based on one's sex or gender. Sexism can affect anyone, but it primarily affects women and girls.There is a clear and broad consensus among academic scholars in multiple fields that sexism refers primari ...
acting against them.
Further reading
* * * *Irvine, John, Miles, Ian, Evans, Jeff, (editors), "Demystifying Social Statistics ", London : Pluto Press, 1979. * *References
External links
* ;Social science statistics centersCenter for Statistics and Social Sciences, University of Washington
;Statistical databases for social science
Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research
* ttp://www.bls.gov US Bureau of Labor Statisticsbr>International Labour Organisation- LABORSTA
{{Authority control