Signals Intelligence Service Cryptographers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech,
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech,
 Two main types of signals encountered in practice are ''
Two main types of signals encountered in practice are ''
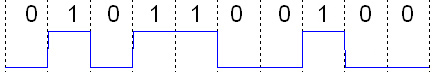 A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or
A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or
 Signals can be classified as continuous or
Signals can be classified as continuous or
 Signal processing is the manipulation of signals. A common example is signal transmission between different locations. The embodiment of a signal in electrical form is made by a transducer that converts the signal from its original form to a waveform expressed as a current or a voltage, or electromagnetic radiation, for example, an optical signal or radio transmission. Once expressed as an electronic signal, the signal is available for further processing by electrical devices such as electronic amplifiers and filters, and can be transmitted to a remote location by a transmitter and received using radio receivers.
Signal processing is the manipulation of signals. A common example is signal transmission between different locations. The embodiment of a signal in electrical form is made by a transducer that converts the signal from its original form to a waveform expressed as a current or a voltage, or electromagnetic radiation, for example, an optical signal or radio transmission. Once expressed as an electronic signal, the signal is available for further processing by electrical devices such as electronic amplifiers and filters, and can be transmitted to a remote location by a transmitter and received using radio receivers.
 In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech,
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information.
In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typically provided by a sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
, and often the original form of a signal is converted to another form of energy using a transducer. For example, a microphone converts an acoustic signal to a voltage waveform, and a speaker does the reverse.
Another important property of a signal is its entropy or information content. Information theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification (science), quantification, computer data storage, storage, and telecommunication, communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist a ...
serves as the formal study of signals and their content. The information of a signal is often accompanied by noise, which primarily refers to unwanted modifications of signals, but is often extended to include unwanted signals conflicting with desired signals (crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk is any phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, induc ...
). The reduction of noise is covered in part under the heading of signal integrity
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal. In digital electronics, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog in nature, ...
. The separation of desired signals from background noise is the field of signal recovery, one branch of which is estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their valu ...
, a probabilistic approach to suppressing random disturbances.
Engineering disciplines such as electrical engineering have advanced the design, study, and implementation of systems involving transmission
Transmission may refer to:
Medicine, science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual transmission
*** ...
, storage
Storage may refer to:
Goods Containers
* Dry cask storage, for storing high-level radioactive waste
* Food storage
* Intermodal container, cargo shipping
* Storage tank
Facilities
* Garage (residential), a storage space normally used to store car ...
, and manipulation of information. In the latter half of the 20th century, electrical engineering itself separated into several disciplines: electronic engineering and computer engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineers ...
developed to specialize in the design and analysis of systems that manipulate physical signals, while design engineering
A design engineer is an engineer focused on the engineering design process in any of the various engineering disciplines (including civil, mechanical, electrical, chemical, textiles, aerospace, nuclear, manufacturing, systems, and structural /buil ...
developed to address the functional design of signals in user–machine interfaces.
Definitions
Definitions specific to sub-fields are common: * In electronics and telecommunications, ''signal'' refers to any time-varying voltage, current, or electromagnetic wave that carries information. * In signal processing, signals are analog and digital representations of analog physical quantities. * Ininformation theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification (science), quantification, computer data storage, storage, and telecommunication, communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist a ...
, a signal is a codified message, that is, the sequence of states in a communication channel that encodes a message.
* In a communication system, a ''transmitter'' encodes a ''message'' to create a signal, which is carried to a ''receiver'' by the communication channel. For example, the words " Mary had a little lamb" might be the message spoken into a telephone. The telephone transmitter converts the sounds into an electrical signal. The signal is transmitted to the receiving telephone by wires; at the receiver it is reconverted into sounds.
* In telephone networks, signaling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, for example common-channel signaling, refers to phone number and other digital control information rather than the actual voice signal.
Classification
Signals can be categorized in various ways. The most common distinction is between discrete and continuous spaces that the functions are defined over, for example, discrete and continuous-time domains.Discrete-time signal
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "po ...
s are often referred to as '' time series'' in other fields. Continuous-time signal
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "po ...
s are often referred to as ''continuous signals''.
A second important distinction is between discrete-valued and continuous-valued. Particularly in digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are ...
, a digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at ...
may be defined as a sequence of discrete values, typically associated with an underlying continuous-valued physical process. In digital electronics, digital signals are the continuous-time waveform signals in a digital system, representing a bit-stream.
Signals may also be categorized by their spatial distributions as either point source signals (PSSs) or distributed source signals (DSSs).
In Signals and Systems, signals can be classified according to many criteria, mainly: according to the different feature of values, classified into analog signal
An analog signal or analogue signal (see spelling differences) is any continuous signal representing some other quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies c ...
s and digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at ...
s; according to the determinacy of signals, classified into deterministic signals and random signals; according to the strength of signals, classified into energy signals and power signals.
Analog and digital signals
analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
'' and ''digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
''. The figure shows a digital signal that results from approximating an analog signal by its values at particular time instants. Digital signals are '' quantized'', while analog signals are continuous.
Analog signal
An analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another time varying signal. For example, in an analogaudio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals, or a series of binary numbers for digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies in the audio frequency range of r ...
, the instantaneous voltage of the signal varies continuously with the sound pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone ...
. It differs from a digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at ...
, in which the continuous quantity is a representation of a sequence of discrete values which can only take on one of a finite number of values.
The term ''analog signal'' usually refers to electrical signals; however, analog signals may use other mediums such as mechanical, pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
or hydraulic. An analog signal uses some property of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses rotary position as the signal to convey pressure information. In an electrical signal, the voltage, current, or frequency of the signal may be varied to represent the information.
Any information may be conveyed by an analog signal; often such a signal is a measured response to changes in physical phenomena, such as sound, light, temperature, position, or pressure. The physical variable is converted to an analog signal by a transducer. For example, in sound recording, fluctuations in air pressure (that is to say, sound) strike the diaphragm of a microphone which induces corresponding electrical fluctuations. The voltage or the current is said to be an ''analog'' of the sound.
Digital signal
 A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or
A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
of an optical or other electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical c ...
, acoustic pressure, the magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material. Movement within this field is described by direction and is either Axial or Di ...
of a magnetic storage media, etc. Digital signals are present in all digital electronics, notably computing equipment and data transmission.
With digital signals, system noise, provided it is not too great, will not affect system operation whereas noise always degrades the operation of analog signals to some degree.
Digital signals often arise via sampling of analog signals, for example, a continually fluctuating voltage on a line that can be digitized by an analog-to-digital converter circuit, wherein the circuit will read the voltage level on the line, say, every 50 microseconds and represent each reading with a fixed number of bits. The resulting stream of numbers is stored as digital data on a discrete-time and quantized-amplitude signal. Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s and other digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
devices are restricted to discrete time.
Energy and power
According to the strengths of signals, practical signals can be classified into two categories: energy signals and power signals. Energy signals: Those signals' energy are equal to a finite positive value, but their average powers are 0; Power signals: Those signals' average power are equal to a finite positive value, but their energy are infinite.Deterministic and random
Deterministic signals are those whose values at any time are predictable and can be calculated by a mathematical equation. Random signals are signals that take on random values at any given time instant and must be modeledstochastic
Stochastic (, ) refers to the property of being well described by a random probability distribution. Although stochasticity and randomness are distinct in that the former refers to a modeling approach and the latter refers to phenomena themselv ...
ally.
Even and odd
An even signal satisfies the condition or equivalently if the following equation holds for all and in the domain of : : An odd signal satisfies the condition or equivalently if the following equation holds for all and in the domain of : :Periodic
A signal is said to be periodic if it satisfies the condition: or Where: = fundamental time period, = fundamental frequency. A periodic signal will repeat for every period.Time discretization
discrete time
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "po ...
. In the mathematical abstraction, the domain of a continuous-time signal is the set of real numbers (or some interval thereof), whereas the domain of a discrete-time (DT) signal is the set of integers (or other subsets of real numbers). What these integers represent depends on the nature of the signal; most often it is time.
A continuous-time signal is any function which is defined at every time ''t'' in an interval, most commonly an infinite interval. A simple source for a discrete-time signal is the sampling of a continuous signal, approximating the signal by a sequence of its values at particular time instants.
Amplitude quantization
If a signal is to be represented as a sequence of digital data, it is impossible to maintain exact precision - each number in the sequence must have a finite number of digits. As a result, the values of such a signal must be quantized into a finite set for practical representation. Quantization is the process of converting a continuous analog audio signal to a digital signal with discrete numerical values of integers.Examples of signals
Naturally occurring signals can be converted to electronic signals by varioussensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s. Examples include:
* '' Motion''. The motion of an object can be considered to be a signal and can be monitored by various sensors to provide electrical signals. For example, radar can provide an electromagnetic signal for following aircraft motion. A motion signal is one-dimensional (time), and the range is generally three-dimensional. Position is thus a 3-vector signal; position and orientation of a rigid body is a 6-vector signal. Orientation signals can be generated using a gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rota ...
.
* '' Sound''. Since a sound is a vibration of a medium (such as air), a sound signal associates a pressure value to every value of time and possibly three space coordinates indicating the direction of travel. A sound signal is converted to an electrical signal by a microphone, generating a voltage signal as an analog of the sound signal. Sound signals can be sampled at a discrete set of time points; for example, compact discs (CDs) contain discrete signals representing sound, recorded at 44,100 Hz
In digital audio, 44,100 Hz (alternately represented as 44.1 kHz) is a common sampling frequency. Analog audio is often recorded by sampling it 44,100 times per second, and then these samples are used to reconstruct the audio signal w ...
; since CDs are recorded in stereo
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
, each sample contains data for a left and right channel, which may be considered to be a 2-vector signal. The CD encoding is converted to an electrical signal by reading the information with a laser, converting the sound signal to an optical signal.
* ''Image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
s''. A picture or image consists of a brightness or color signal, a function of a two-dimensional location. The object's appearance is presented as emitted or reflected light, an electromagnetic signal. It can be converted to voltage or current waveforms using devices such as the charge-coupled device. A 2D image can have a continuous spatial domain, as in a traditional photograph or painting; or the image can be discretized in space, as in a digital image
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as ''pixels'', each with ''finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions ...
. Color images are typically represented as a combination of monochrome images in three primary colors.
* '' Videos''. A video signal is a sequence of images. A point in a video is identified by its two-dimensional position in the image and by the time at which it occurs, so a video signal has a three-dimensional domain. Analog video has one continuous domain dimension (across a scan line) and two discrete dimensions (frame and line).
* Biological ''membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges ...
s''. The value of the signal is an electric potential (voltage). The domain is more difficult to establish. Some cells or organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s have the same membrane potential throughout; neurons generally have different potentials at different points. These signals have very low energies, but are enough to make nervous systems work; they can be measured in aggregate by the techniques of electrophysiology.
*The output of a thermocouple, which conveys temperature information.
*The output of a pH meter which conveys acidity information.
Signal processing
 Signal processing is the manipulation of signals. A common example is signal transmission between different locations. The embodiment of a signal in electrical form is made by a transducer that converts the signal from its original form to a waveform expressed as a current or a voltage, or electromagnetic radiation, for example, an optical signal or radio transmission. Once expressed as an electronic signal, the signal is available for further processing by electrical devices such as electronic amplifiers and filters, and can be transmitted to a remote location by a transmitter and received using radio receivers.
Signal processing is the manipulation of signals. A common example is signal transmission between different locations. The embodiment of a signal in electrical form is made by a transducer that converts the signal from its original form to a waveform expressed as a current or a voltage, or electromagnetic radiation, for example, an optical signal or radio transmission. Once expressed as an electronic signal, the signal is available for further processing by electrical devices such as electronic amplifiers and filters, and can be transmitted to a remote location by a transmitter and received using radio receivers.
Signals and systems
InElectrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
programs, signals are covered in a class and field of study known as ''signals and systems''. Depending on the school, undergraduate EE students generally take the class as juniors or seniors, normally depending on the number and level of previous linear algebra and differential equation classes they have taken.
The field studies input and output signals, and the mathematical representations between them known as systems, in four domains: Time, Frequency, ''s'' and ''z''. Since signals and systems are both studied in these four domains, there are 8 major divisions of study. As an example, when working with continuous-time signals (''t''), one might transform from the time domain to a frequency or ''s'' domain; or from discrete time (''n'') to frequency or ''z'' domains. Systems also can be transformed between these domains like signals, with continuous to ''s'' and discrete to ''z''.
Signals and systems is a subset of the field of Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, ...
ing. It involves circuit analysis and design via mathematical modeling and some numerical methods, and was updated several decades ago with Dynamical systems tools including differential equations, and recently, Lagrangians. Students are expected to understand the modeling tools as well as the mathematics, physics, circuit analysis, and transformations between the 8 domains.
Because mechanical engineering topics like friction, dampening etc. have very close analogies in signal science (inductance, resistance, voltage, etc.), many of the tools originally used in ME transformations (Laplace and Fourier transforms, Lagrangians, sampling theory, probability, difference equations, etc.) have now been applied to signals, circuits, systems and their components, analysis and design in EE. Dynamical systems that involve noise, filtering and other random or chaotic attractors and repellers have now placed stochastic sciences and statistics between the more deterministic discrete and continuous functions in the field. (Deterministic as used here means signals that are completely determined as functions of time).
EE taxonomists are still not decided where signals and systems falls within the whole field of signal processing vs. circuit analysis and mathematical modeling, but the common link of the topics that are covered in the course of study has brightened boundaries with dozens of books, journals, etc. called Signals and Systems, and used as text and test prep for the EE, as well as, recently, computer engineering exams.
See also
* * Current loop – a signaling system in widespread use for process control *Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in deci ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * {{Authority control Engineering concepts Digital signal processing Signal processing Telecommunication theory