Sierra Leone,)].
officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
. It is bordered by
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
to the southeast and
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of ,
Sierra Leone has a
tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
, with diverse environments ranging from
savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
to
rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
s. The country has a population of 7,092,113 as of the 2015 census.
The capital and largest city is
Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are subdivided into
16 districts.
Sierra Leone is a
constitutional republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
with a
unicameral parliament
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
and a
directly elected
Direct election is a system of choosing political officeholders in which the voters directly cast ballots for the persons or political party that they desire to see elected. The method by which the winner or winners of a direct election are cho ...
president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
serving a five-year term with a maximum of two terms. The current president is
Julius Maada Bio
Julius Maada Wonie Bio (born 12 May 1964) is a Sierra Leonean politician, and the current president of Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. He is a retired brigadier general in the Sierra Leone Army and was the military head of state of Sierra Leo ...
. Sierra Leone is a
secular nation with
the constitution providing for the separation of state and religion and freedom of conscience (which includes freedom of thoughts and religion).
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
make up about three-quarters of the population, though with an influential
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
minority. Religious tolerance in the West African nation is very high and is generally considered a norm and part of Sierra Leone's cultural identity.
The geographic area has been inhabited for millennia, but Sierra Leone, as the country and its borders are known today, was founded by the
British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
in two phases: first, the coastal Sierra Leone Colony in 1808 (for returning Africans after the
abolition of slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
); second, the inland Protectorate in 1896 (as the Crown needed to establish more dominion inland following the outcome of the
Berlin Conference of 1884-1885). Hence, the country formally became known as the
Sierra Leone Colony and Protectorate
The Colony and Protectorate of Sierra Leone (informally British Sierra Leone) was the British colonial administration in Sierra Leone from 1808 to 1961, part of the British Empire from the abolitionism era until the decolonisation era. The Cr ...
or simply British Sierra Leone.
Sierra Leone gained independence from the United Kingdom on 27 April 1961, and became a
Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
on the same day; the country's name changed to the
Dominion of Sierra Leone.
Sir Milton Margai became Sierra Leone's first
prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
.
[Humphrey J. Fisher (1969), "Elections and Coups in Sierra Leone, 1967". '']The Journal of Modern African Studies
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
'' Vol. 7, No. 4 (December 1969), pp. 611–636 (26 pages).
Published By: Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
Archived
Retrieved October 22, 2021.
During the few decades following independence, Sierra Leone witnessed an increase in political activities, transformations, turmoil, humanitarian and socio-economic crises. The country had its first general elections as an independent nation on 27 May 1961. Margai's
Sierra Leone People's Party
The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since April 4, 2018. The SLPP do ...
(SLPP) won a plurality of parliamentary seats and he was re-elected Prime Minister.
A new constitution was adopted in 1971, paving the way for Sierra Leone becoming a republic, and
Siaka Stevens
Siaka Probyn Stevens (24 August 1905 – 29 May 1988) was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister of Sierra Leone, Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was ofte ...
, leader of the
All People's Congress
The All People's Congress (APC) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, the other being its main political rival the Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP). The APC has been the main opposition party in Sierra Leone since 4 Apr ...
(APC), becoming the first
executive president
An executive president is the head of state who exercises authority over the governance of that state, and can be found in presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary systems.
They contrast with figurehead presidents, common in most parli ...
of the Republic of Sierra Leone. Stevens held on to this position for 14 years (until 1985) under a
one-party system
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system, or single-party system is a type of sovereign state in which only one political party has the right to form the government, usually based on the existing constitution. All other parties ...
of government facilitated by the controversial 1978 Constitution. However, Stevens' hand-picked successor
Joseph Saidu Momoh
Major General Joseph Saidu Momoh, OOR, OBE (January 26, 1937 – August 3, 2003) served as President of Sierra Leone from November 1985 to 29 April 1992.
Early life and education
Joseph Saidu Momoh was born on January 26, 1937, in Binkolo, B ...
promised to return the country to a
multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coal ...
; a new constitution was adopted in 1991 that provided the means for a multi-party democracy.
A brutal civil war broke out the same year, which went on for 11 years with devastating effects on almost everything that defined Sierra Leone as a nation. In just a year after the war broke out (in 1992), President Momoh was ousted in a coup led by Sierra Leone Army captain
Valentine Strasser
Valentine Esegragbo Melvine Strasser (born 26 April 1967) is an ex-military leader who served as Heads of Government of Sierra Leone, head of state of Sierra Leone from 1992 to 1996. Previously a junior military officer he became the world's yo ...
. Strasser was later "ousted" by his army colleague and second-in-command
Julius Maada Bio
Julius Maada Wonie Bio (born 12 May 1964) is a Sierra Leonean politician, and the current president of Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. He is a retired brigadier general in the Sierra Leone Army and was the military head of state of Sierra Leo ...
, for failing to commit to a quick transfer to civilian rule. Bio would then return the country back to a democratic republic in 1996 through a general election.
In early 1996, despite the country going through a brutal civil war, the emergence of the prospect of a transformation back to a multi-party democracy brought fresh hopes and great expectations among a majority of Sierra Leoneans, as the national debate "Peace before Elections vs Elections before Peace" became a hot topic. Eventually, "Elections before Peace" won the debate.
[Kandeh, J. D. (September, 1998)]
"Transition without Rupture: Sierra Leone's Transfer Election of 1996"
''African Studies Review
The ''African Studies Review'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal covering African studies. The journal also publishes book and film reviews. The journal was established in 1958 as the ''African Studies Bulletin'', obtaining its curr ...
''
Flight. 41, No. 2 (September 1998), pp. 91–111. Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
Archived
Retrieved October 25, 2021. Ahmad Tejan Kabbah
Alhaji Ahmad Tejan Kabbah (February 16, 1932 – March 13, 2014) was a Sierra Leonean politician who served twice as the 3rd President of Sierra Leone, from 1996 to 1997 and again from 1998 to 2007. An economist and attorney by profession, Ka ...
won the 1996 presidential election and became the first multi-party democratically elected president of Sierra Leone. Since then, there has been a smooth succession to the presidency all via elections. A brief coup in 1997 led by Sierra Leone Army major
Johnny Paul Koroma
Major Johnny Paul Koroma (born 9 May 1960; declared dead 1 June 2003) was the head of state of Sierra Leone from May 1997 to February 1998.
Youth and education
Koroma was born to Limba people (Sierra Leone), Limba parents in Tombodu, in the ...
ousted Kabbah, who went into exile in
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
. He was reinstated after nine months through military intervention by
ECOMOG
The Economic Community of West African States Monitoring Group (ECOMOG) was a West African multilateral armed force established by the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). ECOMOG was a formal arrangement for separate armies to work ...
. Kabbah's presidency marked the dawn of a new Sierra Leone, which included the end of the civil war in 2002, a focus on fostering national unity and reconciliation, trust in government, peace and stability, the improvement in relations with many countries, and the refounding of the
Sierra Leone Armed Forces
The Republic of Sierra Leone Armed Forces (RSLAF) are the armed forces of Sierra Leone, responsible for the territorial security of Sierra Leone's borders and defending the national interests of Sierra Leone, within the framework of the 1991 S ...
with special assistance and training led by the
Government of the United Kingdom
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal coat of arms of t ...
.
[University of Central Arkansas]
41. Sierra Leone (1961-Present)Archived
Retrieved 22 October 2021.
About 18 ethnic groups inhabit Sierra Leone; the two largest and most influential ones are the
Temne and
Mende peoples. About 2% of the country's population are
Creole people
Creole peoples are ethnic groups formed during the European colonial era, from the mass displacement of peoples brought into sustained contact with others from different linguistic and cultural backgrounds, who converged onto a colonial territo ...
, descendants of freed
African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
and
Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
slaves. English is the official language used in schools and government administration.
Krio is the most widely spoken language across Sierra Leone, spoken by 97% of the country's population. Sierra Leone is rich in natural resources, especially
diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of car ...
,
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
,
bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
and
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
. The country is a member of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
,
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
,
Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS),
Mano River Union
The Mano River Union (MRU) is an international association initially established between Liberia and Sierra Leone by the 3 October 1973 Mano River Declaration. It is named for the Mano River which begins in the Guinea highlands and forms a border ...
,
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
,
IMF,
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
,
WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
,
African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group (AfDB) or (BAD) is a multilateral development finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies i ...
, and
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
. Sierra Leone is home to
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
's first
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
-style university:
Fourah Bay College
Fourah Bay College is a public university in the neighbourhood of Mount Aureol in Freetown, Sierra Leone. Founded on 18 February 1827, it is the first western-style university built in Sub-Saharan Africa and, furthermore, the first university-le ...
(established in 1827).
Etymology
The country takes its name from the
Lion Mountains near Freetown. Originally named (
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
for 'lioness mountains') by Portuguese explorer
Pedro de Sintra
Pedro de Sintra, also known as Pêro de Sintra, Pedro da Cintra or Pedro da Sintra, was a Portuguese explorer. He was among the first Europeans to explore the West African coast. Around 1462 his expedition reached what is now Sierra Leone and named ...
in 1462, the modern name is derived from the
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
spelling, which was introduced by
Venetian explorer
Alvise Cadamosto
Alvise Cadamosto or Alvise da Ca' da Mosto (, also known in Portuguese as ''Luís Cadamosto''; c. 1432 – 18 July 1488) was a Venetian explorer and slave trader, who was hired by the Portuguese prince Henry the Navigator and undertook two known ...
and subsequently copied by other European
mapmakers.
History
Early history



Archaeological finds show that Sierra Leone has been inhabited continuously for at least 2,500 years;
populated successively by societies who migrated from other parts of Africa.
The use of iron was adopted by the ninth century, and by 1000 AD, agriculture was being practised along the coast.
Over time, the climate changed considerably, altering boundaries between different ecological zones, affecting migration and conquest.
Sierra Leone's dense
tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
and swampy environment were considered impenetrable; it was also host to the
tsetse fly
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies), are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glo ...
, which carried a disease fatal to horses and the
zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty ...
cattle used by the
Mande-speaking people. This environment protected its people from conquest by the
Mandinka and other African empires,
[ Fyfe, Christopher]
"Weighing the Probabilities"
Review: ''Landlords and Strangers: Ecology, Society and Trade in Western Africa, 1000–1630'', By George E. Brooks. Boulder: Westview Press, 1994. ().Utting
Utting am Ammersee (until 1953 just Utting) is a municipality in the district of Landsberg in Bavaria in Germany.
History
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world ...
(1931), p. 33. and limited the influence of the
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ...
.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was introduced by
Susu traders, merchants and migrants from the north and east, becoming widely adopted in the 18th century.
Utting
Utting am Ammersee (until 1953 just Utting) is a municipality in the district of Landsberg in Bavaria in Germany.
History
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world ...
(1931), p. 8.
European trading
European contacts within Sierra Leone were among the first in
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
during the 15th century. In 1462,
Portuguese explorer
Portuguese maritime exploration resulted in the numerous territories and maritime routes recorded by the Portuguese as a result of their intensive maritime journeys during the 15th and 16th centuries. Portuguese sailors were at the vanguard of Eu ...
Pedro de Sintra
Pedro de Sintra, also known as Pêro de Sintra, Pedro da Cintra or Pedro da Sintra, was a Portuguese explorer. He was among the first Europeans to explore the West African coast. Around 1462 his expedition reached what is now Sierra Leone and named ...
mapped the hills surrounding what is now Freetown Harbour, naming the shaped formation ''Serra da Leoa'' or "Serra Leoa" (
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
for
Lioness Mountains
The Lion Mountains (also called Lioness Mountains or Peninsula Mountains, originally from pt, Serra Leoa) are a mountain range in Sierra Leone. The range stretches on the Freetown Peninsula by the Atlantic Ocean, southeast of the capital, Free ...
).
[''Kingfisher Geography Encyclopedia''. , p. 180.] The Spanish rendering of this geographic formation is ''Sierra Leona'', which later was adapted, misspelled and became the country's current name. Though according to
Professor
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an Academy, academic rank at university, universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who pr ...
C. Magbaily Fyle, this might have been a misinterpretation from historians. According to Professor Fyle, there has been evidence of travellers calling the region ''Serra Lyoa'' long before 1462 (before the first arrival of Sintra to the region). This would imply that the identity of the person who named Sierra Leone is unknown.
Soon after Sintra's expedition, Portuguese traders started arriving at the harbour. By 1495 they had built a fortified
trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
on the coast.
The
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and
French also started arriving and set up trade near the coast. Different European nations started using Sierra Leone as a trading point for
slave
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
s brought to the coast by African traders from interior areas undergoing wars and conflicts over territory. In 1562, the
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
initiated the
Triangular Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset t ...
when admiral
Sir John Hawkins
Sir John Hawkins (also spelled Hawkyns) (1532 – 12 November 1595) was a pioneering English naval commander, naval administrator and privateer. He pioneered, and was an early promoter of, English involvement in the Atlantic slave trade.
Hawki ...
of the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
transported 300 enslaved Africans – acquired "by the sword and partly by other means" – to the Spanish colony of
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 (Distrito Nacional)
, websi ...
on
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
in the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
area of the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
islands, where he sold them.
Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 ( ...
reached Sierra Leone on 22 July 1580 as the last stop of his voyage along the west coast of Africa.
Bunce Island
Bunce Island (also spelled "Bence," "Bense," or "Bance" at different periods) is an island in the Sierra Leone River. It is situated in Freetown Harbour, the estuary of the Rokel River and Port Loko Creek, about upriver from Sierra Leone's capi ...
, an island on the
Sierra Leone River
The Sierra Leone River is a river estuary on the Atlantic Ocean in Western Sierra Leone. It is formed by the Bankasoka River and Rokel River and is between 4 and 10 miles wide (6–16 km) and 25 miles (40 km) long. It holds the major port ...
, was used as a base for European slavers as a place for
slave ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast ...
s to dock before sailing via the
Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods (first ...
to the Americas. Until the passage of the
Slave Trade Act 1807
The Slave Trade Act 1807, officially An Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not abolish the practice of slavery, it ...
, the island was operated by the London-based firm
Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
*Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
*Grant, Inyo County, C ...
,
Oswald Oswald may refer to:
People
* Oswald (given name), including a list of people with the name
*Oswald (surname), including a list of people with the name
Fictional characters
*Oswald the Reeve, who tells a tale in Geoffrey Chaucer's ''The Canterbu ...
& Company, who occupied it in 1748.
Black Poor of London
In the late 18th century, many African Americans claimed the protection of the
British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
. There were thousands of these
Black Loyalists
Black Loyalists were people of African descent who sided with the Loyalists during the American Revolutionary War. In particular, the term refers to men who escaped enslavement by Patriot masters and served on the Loyalist side because of the Cro ...
, people of African descent who joined the British military forces during the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. Many of these
Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cr ...
had been slaves who had escaped to join the British, lured by promises of freedom (
emancipation
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure economic and social rights, political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranchis ...
). The official documentation known as the ''
Book of Negroes
The ''Book of Negroes'' is a document created by Brigadier General Samuel Birch, under the direction of Sir Guy Carleton, that records names and descriptions of 3,000 Black Loyalists, enslaved Africans who escaped to the British lines during t ...
'' lists thousands of freed slaves whom the British evacuated from the nascent United States and resettled in colonies elsewhere in
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
(north to Canada, or south to the West Indies).
Pro-slavery advocates accused the Black Poor of being responsible for a large proportion of crime in 18th century London. While the broader community included some women, the Black Poor seems to have exclusively consisted of men, some of whom developed relationships with local women and often married them. Slave owner
Edward Long
Edward Long (23 August 1734 – 13 March 1813) was an English-born British colonial administrator, slave owner and historian, and author of a highly controversial work, ''The History of Jamaica'' (1774). He was a polemic defender of slavery.
Li ...
criticized marriage between black men and white women.
However, on the voyage between
Plymouth, England
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth' ...
and Sierra Leone, seventy European girlfriends and wives accompanied the
Black Poor settlers.
Many in London thought that moving them to Sierra Leone would lift them out of poverty. The Sierra Leone Resettlement Scheme was proposed by entomologist
Henry Smeathman
Henry Smeathman (1742–1786) was an English naturalist, best known for his work in entomology and colonial settlement in Sierra Leone.
In 1771 the Quaker physician John Fothergill (physician), John Fothergill, along with two other members of ...
and drew interest from humanitarians like
Granville Sharp
Granville Sharp (10 November 1735 – 6 July 1813) was one of the first British campaigners for the abolition of the slave trade. He also involved himself in trying to correct other social injustices. Sharp formulated the plan to settle black ...
, who saw it as a means of showing the pro-slavery lobby that black people could contribute towards the running of the new colony of Sierra Leone. Government officials soon became involved in the scheme as well, although their interest was spurred by the possibility of resettling a large group of poor citizens elsewhere.
William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
, prime minister and leader of the Tory party, had an active interest in the Scheme because he saw it as a means to repatriate the Black Poor to Africa, since "it was necessary they should be sent somewhere, and be no longer suffered to infest the streets of London".
[
]
Province of Freedom
In January 1787, the ''Atlantic'' and the ''Belisarius'' set sail for Sierra Leone, but bad weather forced them to divert to Plymouth, during which time about 50 passengers died. Another 24 were discharged, and another 23 ran away. Eventually, with some more recruitment, 411 passengers sailed to Sierra Leone in April 1787. On the voyage between Plymouth and Sierra Leone, 96 passengers died.[
In 1787 the British Crown founded a settlement in Sierra Leone in what was called the "]Province of Freedom
Cline Town is an area in Freetown, Sierra Leone. The area is named for Emmanuel Kline, a Hausa Liberated African who bought substantial property in the area. The neighborhood is in the vicinity of Granville Town, a settlement established in 1787 a ...
". About 400 black and 60 white colonists reached Sierra Leone on 15 May 1787. After they established Granville Town, most of the first group of colonists died, owing to disease and warfare with the indigenous African peoples ( Temne), who resisted their encroachment. When the ships left them in September, their numbers had been reduced to "276 persons, namely 212 black men, 30 black women, 5 white men and 29 white women".[
The settlers that remained forcibly captured land from a local African chieftain, but he retaliated, attacking the settlement, which was reduced to a mere 64 settlers comprising 39 black men, 19 black women, and six white women. Black settlers were captured by unscrupulous traders and sold as slaves, and the remaining colonists were forced to arm themselves for their own protection.][ The 64 remaining colonists established a second Granville Town.
]
Nova Scotians
Following the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
, more than 3,000 Black Loyalists had also been settled in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, where they were finally granted land. They founded Birchtown
Birchtown is a community and National Historic Site in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located near Shelburne in the Municipal District of Shelburne County. Founded in 1783, the village was the largest settlement of Black Loyalists and ...
, but faced harsh northern winters and racial discrimination from nearby Shelburne. Thomas Peters pressed British authorities for relief and more aid; together with British abolitionist John Clarkson
John Gibson Clarkson (July 1, 1861 – February 4, 1909) was a Major League Baseball right-handed pitcher. He played from 1882 to 1894. Born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Clarkson played for the Worcester Ruby Legs (1882), Chicago White Stocking ...
, the Sierra Leone Company was established to relocate Black Loyalists who wanted to take their chances in West Africa. In 1792 nearly 1,200 persons from Nova Scotia crossed the Atlantic to build the second (and only permanent) Colony of Sierra Leone and the settlement of Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
on 11 March 1792. In Sierra Leone they were called the Nova Scotian Settlers
The Nova Scotian Settlers, or Sierra Leone Settlers (also known as the Nova Scotians or more commonly as the Settlers) were African-Americans who founded the settlement of Freetown, Sierra Leone and the Colony of Sierra Leone, on March 11, 1792 ...
, the ''Nova Scotians'', or the ''Settlers''. Clarkson initially banned the survivors of Granville Town from joining the new settlement, blaming them for the demise of Granville Town.[ The Settlers built Freetown in the styles they knew from their lives in the ]American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
; they also continued American fashion and American manners. In addition, many continued to practise Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's br ...
in Freetown.
In the 1790s, the Settlers, including adult women, voted for the first time in elections.
Jamaican Maroons and Liberated Africans
The Sierra Leone Company, controlled by London investors, refused to allow the settlers to take freehold
Freehold may refer to:
In real estate
*Freehold (law), the tenure of property in fee simple
*Customary freehold, a form of feudal tenure of land in England
*Parson's freehold, where a Church of England rector or vicar of holds title to benefice p ...
of the land. In 1799 some of the settlers revolted. The Crown subdued the revolt by bringing in forces of more than 500 Jamaican Maroons
Jamaican Maroons descend from Africans who freed themselves from slavery on the Colony of Jamaica and established communities of free black people in the island's mountainous interior, primarily in the eastern parishes. Africans who were ensla ...
, whom they transported from Cudjoe's Town (Trelawny Town)
Cudjoe's Town was located in the mountains in the southern extremities of the parish of St James, close to the border of Westmoreland, Jamaica.
In 1690, a large number of Akan freedom fighters from Sutton's Estate in south-western Jamaica, and th ...
via Nova Scotia in 1800. Led by Colonel Montague James
Montague James (d. c. 1812) was a Maroons, Maroon leader of Cudjoe's Town (Trelawny Town) in the last decade of eighteenth-century Jamaica. It is possible that Maroon colonel Montague James took his name from the white superintendent of Trelawny ...
, the Maroons helped the colonial forces to put down the revolt, and in the process the Jamaican Maroons in Sierra Leone secured the best houses and farms.
On 1 January 1808, Thomas Ludlam (colonial administrator), Thomas Ludlam, the Governor of the Sierra Leone Company and a leading abolitionist, surrendered the company's charter. This ended its 16 years of running the Colony. The British Crown reorganised the Sierra Leone Company as the African Institution; it was directed to improve the local economy. Its members represented both British who hoped to inspire local entrepreneurs and those with interest in the Macauley & Babington Company, which held the (British) monopoly on Sierra Leone trade.
At about the same time (following the Slave Trade Act 1807, abolition of the slave trade in 1807), Royal Navy crews delivered thousands of formerly enslaved Africans to Freetown, after liberating them from illegal slave ships. These recaptives, Liberated Africans or ''recaptives'' were sold for $20 a head as apprentices to the white settlers, Nova Scotian Settlers, and the Jamaican Maroons. Many Liberated Africans were treated poorly and even abused because some of the original settlers considered them their property. Cut off from their various homelands and traditions, the Liberated Africans were forced to assimilate to the Western styles of Settlers and Maroons. For example, some of the Liberated Africans were forced to change their name to a more Western sounding one.[Schwarz, Suzanne (2021]
Reconstructing the Life Histories of Liberated Africans: Sierra Leone in the Early Nineteenth Century
''History in Africa'', Vol. 39 (2012), pp. 175–207 (33). ''Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
''
Archived
Retrieved 27 October 2021. Though some people happily embraced these changes because they considered it as being part of the community, some were not happy with these changes and wanted to keep their own identity. Many Liberated Africans were so unhappy that they risked the possibility of being sold back into slavery by leaving Sierra Leone and going back to their original villages.Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
s, mainly Jamaican Maroons, also immigrated and settled in Freetown. Together these peoples formed the Sierra Leone Creole, Krio ethnicity and an English-based creole languages, English-based creole language, ( Krio), which is the lingua franca and de facto national language used among many of the ethnicities in the country.[ https://www.persee.fr/doc/cea_0008-0055_1991_num_31_121_2116][ Journal of Sierra Leone Studies, Vol. 3; Edition 1, 2014 https://www.academia.edu/40720522/A_Precis_of_Sources_relating_to_genealogical_research_on_the_Sierra_Leone_Krio_people][, originally published by Longman & Dalhousie University Press (1976).]
Colonial era (1800–1961)
 The settlement of Sierra Leone in the 1800s was unique in that the population was composed of displaced Africans who were brought to the colony after the British abolition of the slave trade in 1807. Upon arrival in Sierra Leone, each ''recaptive'' was given a registration number, and information on their physical qualities would be entered into the Register of Liberated Africans. Oftentimes the documentation would be overwhelmingly subjective and would result in inaccurate entries, making them difficult to track. In addition, differences between the Register of Liberated Africans of 1808 and the List of Captured Negroes of 1812 (which emulated the 1808 document) revealed some disparities in the entries of the recaptives, specifically in the names; many recaptives decided to change their given names to more anglicised versions which contributed to the difficulty in tracking them after they arrived in Sierra Leone.
In the early 19th century, Freetown served as the residence of the British colonial governor of the region, who also administered the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast (now Ghana) and the Gambia settlements. Sierra Leone developed as the educational centre of British West Africa. The British established
The settlement of Sierra Leone in the 1800s was unique in that the population was composed of displaced Africans who were brought to the colony after the British abolition of the slave trade in 1807. Upon arrival in Sierra Leone, each ''recaptive'' was given a registration number, and information on their physical qualities would be entered into the Register of Liberated Africans. Oftentimes the documentation would be overwhelmingly subjective and would result in inaccurate entries, making them difficult to track. In addition, differences between the Register of Liberated Africans of 1808 and the List of Captured Negroes of 1812 (which emulated the 1808 document) revealed some disparities in the entries of the recaptives, specifically in the names; many recaptives decided to change their given names to more anglicised versions which contributed to the difficulty in tracking them after they arrived in Sierra Leone.
In the early 19th century, Freetown served as the residence of the British colonial governor of the region, who also administered the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast (now Ghana) and the Gambia settlements. Sierra Leone developed as the educational centre of British West Africa. The British established Fourah Bay College
Fourah Bay College is a public university in the neighbourhood of Mount Aureol in Freetown, Sierra Leone. Founded on 18 February 1827, it is the first western-style university built in Sub-Saharan Africa and, furthermore, the first university-le ...
in 1827, which rapidly became a magnet for English-speaking Africans on the West Coast. For more than a century, it was the only European-style university in western Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
. Samuel Ajayi Crowther was the first student to be enrolled at Fourah Bay.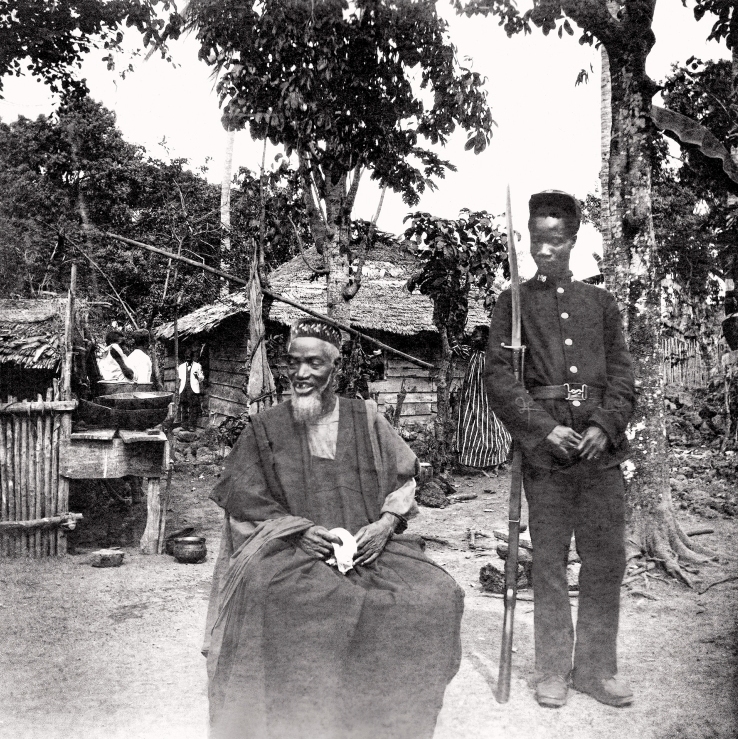 The British interacted mostly with the Krios in Freetown, who did most of the trading with the indigenous peoples of the interior. Educated Krios held numerous positions in the colonial government, giving them status and well-paying positions. Following the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the British decided that they needed to establish more dominion over the inland areas, to satisfy what was described by the European powers as "effective occupation" of territories. In 1896 it annexed these areas, declaring them the Sierra Leone Protectorate.
The British interacted mostly with the Krios in Freetown, who did most of the trading with the indigenous peoples of the interior. Educated Krios held numerous positions in the colonial government, giving them status and well-paying positions. Following the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the British decided that they needed to establish more dominion over the inland areas, to satisfy what was described by the European powers as "effective occupation" of territories. In 1896 it annexed these areas, declaring them the Sierra Leone Protectorate.[Harris, David (2012)]
''Civil War and Democracy in West Africa: Conflict Resolution, Elections and Justice in Sierra Leone and Liberia''
I.B. Tauris, p. 40. With this change, the British began to expand their administration in the region, recruiting British citizens to posts and pushing Krios out of positions in government and even the desirable residential areas in Freetown.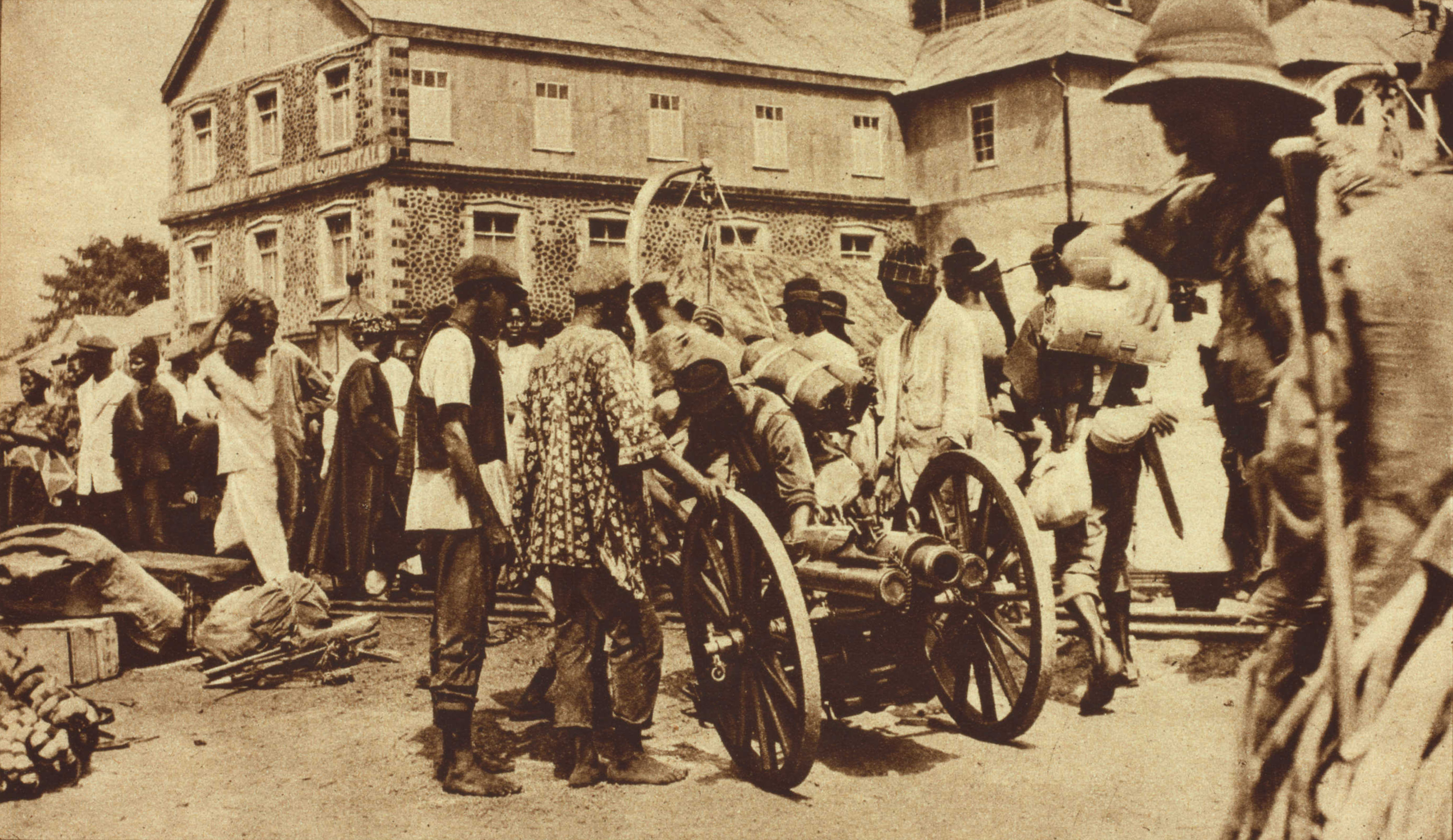 Colonel Frederic Cardew, military governor of the Protectorate, in 1898 established a new tax on dwellings and demanded that the chiefs use their people to maintain roads. The taxes were often higher than the value of the dwellings, and 24 chiefs signed a petition to Cardew, stating how destructive this was; their people could not afford to take time off from their subsistence agriculture. They resisted payment of taxes, tensions over the new colonial requirements and the administration's suspicions towards the chiefs, led to the Hut Tax War of 1898, Hut Tax war of 1898, also called the Temne-Mende War. The British fired first; the northern front of mainly Temne people was led by Bai Bureh. The southern front, consisting mostly of Mende people, entered the conflict somewhat later, for other reasons.
For several months, Bureh's fighters had the advantage over the vastly more powerful British forces but both sides suffered hundreds of fatalities. Bureh surrendered on 11 November 1898 to end the destruction of his people's territory and dwellings. Although the British government recommended leniency, Cardew insisted on sending the chief and two allies into exile in the Gold Coast; his government hanged 96 of the chief's warriors. Bureh was allowed to return in 1905, when he resumed his chieftaincy of Kasseh.
Colonel Frederic Cardew, military governor of the Protectorate, in 1898 established a new tax on dwellings and demanded that the chiefs use their people to maintain roads. The taxes were often higher than the value of the dwellings, and 24 chiefs signed a petition to Cardew, stating how destructive this was; their people could not afford to take time off from their subsistence agriculture. They resisted payment of taxes, tensions over the new colonial requirements and the administration's suspicions towards the chiefs, led to the Hut Tax War of 1898, Hut Tax war of 1898, also called the Temne-Mende War. The British fired first; the northern front of mainly Temne people was led by Bai Bureh. The southern front, consisting mostly of Mende people, entered the conflict somewhat later, for other reasons.
For several months, Bureh's fighters had the advantage over the vastly more powerful British forces but both sides suffered hundreds of fatalities. Bureh surrendered on 11 November 1898 to end the destruction of his people's territory and dwellings. Although the British government recommended leniency, Cardew insisted on sending the chief and two allies into exile in the Gold Coast; his government hanged 96 of the chief's warriors. Bureh was allowed to return in 1905, when he resumed his chieftaincy of Kasseh. Domestic Slavery in Africa, slavery, which continued to be practised by local African elites, was abolished in 1928. A notable event in 1935 was the granting of a monopoly on mineral mining to the Sierra Leone Selection Trust, run by De Beers. The monopoly was scheduled to last 98 years. Mining of diamonds in the east and other minerals expanded, drawing labourers there from other parts of the country.
In 1924, the UK government divided the administration of Sierra Leone into Colony and Protectorate, with different political systems constitutionally defined for each. The Colony was Freetown and its coastal area; the Protectorate was defined as the hinterland areas dominated by local chiefs. Antagonism between the two entities escalated to a heated debate in 1947, when proposals were introduced to provide for a single political system for both the Colony and the Protectorate. Most of the proposals came from leaders of the Protectorate, whose population far outnumbered that in the colony. The Krios, led by I. T. A. Wallace-Johnson, Isaac Wallace-Johnson, opposed the proposals, as they would have resulted in reducing the political power of the Krios in the Colony.
In 1951, Lamina Sankoh (''born'': Etheldred Jones) collaborated with educated protectorate leaders from different groups, including Sir Milton Margai,
Domestic Slavery in Africa, slavery, which continued to be practised by local African elites, was abolished in 1928. A notable event in 1935 was the granting of a monopoly on mineral mining to the Sierra Leone Selection Trust, run by De Beers. The monopoly was scheduled to last 98 years. Mining of diamonds in the east and other minerals expanded, drawing labourers there from other parts of the country.
In 1924, the UK government divided the administration of Sierra Leone into Colony and Protectorate, with different political systems constitutionally defined for each. The Colony was Freetown and its coastal area; the Protectorate was defined as the hinterland areas dominated by local chiefs. Antagonism between the two entities escalated to a heated debate in 1947, when proposals were introduced to provide for a single political system for both the Colony and the Protectorate. Most of the proposals came from leaders of the Protectorate, whose population far outnumbered that in the colony. The Krios, led by I. T. A. Wallace-Johnson, Isaac Wallace-Johnson, opposed the proposals, as they would have resulted in reducing the political power of the Krios in the Colony.
In 1951, Lamina Sankoh (''born'': Etheldred Jones) collaborated with educated protectorate leaders from different groups, including Sir Milton Margai, Siaka Stevens
Siaka Probyn Stevens (24 August 1905 – 29 May 1988) was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister of Sierra Leone, Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was ofte ...
, Mohamed Sanusi Mustapha, John Karefa-Smart, Kande Bureh, Sir Albert Margai, Amadu Wurie and Sir Banja Tejan-Sie joined together with the powerful paramount chiefs in the protectorate to form the Sierra Leone People's Party
The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since April 4, 2018. The SLPP do ...
or SLPP as the party of the Protectorate. The SLPP leadership, led by Sir Milton Margai, negotiated with the British and the educated Krio-dominated colony based in Freetown to achieve independence. Owing to the astute politics of Milton Margai, the educated Protectorate elites were able to join forces with the paramount chiefs in the face of Krio intransigence. Later, Margai used the same skills to win over opposition leaders and moderate Krio elements to achieve independence from the UK.
In November 1951, Margai oversaw the drafting of a new constitution, which united the separate Colonial and Protectorate legislatures and provided a framework for decolonisation.[Advocate Nations of Africa: Sierra Leone](_blank)
In 1953, Sierra Leone was granted local ministerial powers and Margai was elected Chief Minister of Sierra Leone.Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
.
1960 Independence Conference
On 20 April 1960, Milton Margai led a 24-member Sierra Leonean delegation at constitutional conferences that were held with the Government of Queen Elizabeth II and British Colonial Secretary Iain Macleod in negotiations for independence held in London.
Independence (1961) and Margai Administration (1961–1964)
On 27 April 1961, Sir Milton Margai led Sierra Leone to independence from Great Britain and became the country's first Prime Minister. Sierra Leone had its own parliament and its own prime minister, and had the ability to make 100% of its own laws, however, as with countries such as Canada and Australia, Sierra Leone remained a "Dominion" and Queen Elizabeth was Queen of the independent Sierra Leone (1961–1971), Dominion of Sierra Leone. Thousands of Sierra Leoneans took to the streets in celebration. The Dominion of Sierra Leone retained a parliamentary system of government and was a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The leader of the main opposition All People's Congress
The All People's Congress (APC) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, the other being its main political rival the Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP). The APC has been the main opposition party in Sierra Leone since 4 Apr ...
(APC), Siaka Stevens, along with Isaac Wallace-Johnson, another outspoken critic of the SLPP government, were arrested and placed under house arrest in Freetown, along with sixteen others charged with disrupting the independence celebration.
In May 1962, Sierra Leone held its Sierra Leonean general election, 1962, first general election as an independent nation. The Sierra Leone People's Party
The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since April 4, 2018. The SLPP do ...
(SLPP) won a Plurality (voting), plurality of seats in parliament, and Milton Margai was re-elected as prime minister.
Margai was popular among Sierra Leoneans during his time in power, mostly known for his self-effacement. He was neither corrupt nor did he make a lavish display of his power or status. He based the government on the rule of law and the separation of powers, with multiparty political institutions and fairly viable representative structures. Margai used his conservative ideology to lead Sierra Leone without much strife. He appointed government officials to represent various ethnic groups. Margai employed a brokerage style of politics, by sharing political power among political parties and interest groups; especially the involvement of powerful paramount chiefs in the provinces, most of whom were key allies of his government.
After the death of Milton Margai and Albert Margai's tenure (1964–1967)
Upon Milton Margai's unexpected death in 1964, his younger half-brother, Sir Albert Margai, was appointed as Prime Minister by parliament. Sir Albert's leadership was briefly challenged by Foreign Minister John Karefa-Smart, who questioned Sir Albert's succession to the SLPP leadership position. Karefa-Smart led a prominent small minority faction within the SLPP party in opposition of Albert Margai as Prime Minister. However, Karefa-Smart failed to receive broad support within the SLPP in his attempt to oust Albert Margai as both the leader of the SLPP and Prime Minister. The large majority of SLPP members backed Albert Margai over Karefa-Smart. Soon after Albert Margai was sworn in as Prime Minister, he fired several senior government officials who had served in his elder brother Sir Milton's government, viewing them as a threat to his administration, including Karefa-Smart.
Sir Albert resorted to increasingly authoritarian actions in response to protests and enacted several laws against the opposition All People's Congress, whilst attempting to establish a one-party state.
1967 General Election and military coups (1967–1968)
The APC, with its leader Siaka Stevens
Siaka Probyn Stevens (24 August 1905 – 29 May 1988) was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister of Sierra Leone, Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was ofte ...
, narrowly won a small majority of seats in Parliament over the SLPP in a closely contested Sierra Leonean general election, 1967, 1967 general election. Stevens was sworn in as Prime Minister on 21 March 1967.
Within hours after taking office, Stevens was ousted in a bloodless military coup led by Brigadier General David Lansana, the commander of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces
The Republic of Sierra Leone Armed Forces (RSLAF) are the armed forces of Sierra Leone, responsible for the territorial security of Sierra Leone's borders and defending the national interests of Sierra Leone, within the framework of the 1991 S ...
. He was a close ally of Albert Margai, who had appointed him to the position in 1964. Lansana placed Stevens under house arrest in Freetown and insisted that the determination of the Prime Minister should await the election of the tribal representatives to the House. Steven was later freed and fled the country; went into exile in neighbouring Guinea. However, on 23 March 1967, a group of military officers in the Sierra Leone Army led by Brigadier General Andrew Juxon-Smith, staged a counter coup against Commander Lansana. They seized control of the government, arresting Lansana, and suspending the constitution. The group set up the National Reformation Council (NRC), with Andrew Juxon-Smith as its chairman and Head of State of the country.
On 18 April 1968 a group of low ranking soldiers in the Sierra Leone Army who called themselves the Anti-Corruption Revolutionary Movement (ACRM), led by Brigadier General John Amadu Bangura, Sergeants' Coup (Sierra Leone), overthrew the NRC Military junta, junta. The ACRM junta arrested many senior NRC members. They reinstated the constitution and returned power to Stevens, who at last assumed the office of Prime Minister.
Stevens had Bangura arrested in 1970 and charged with conspiracy and treason. He was found guilty and sentenced to death, despite the fact that it was Bangura whose actions led to Stevens return to power.
One-party state and dawn of the 'Republic' (1968–1991)
 Stevens assumed power as Prime Minister again in 1968, following a series of coups, with a great deal of hope and ambition.
Stevens assumed power as Prime Minister again in 1968, following a series of coups, with a great deal of hope and ambition.[Gberie, Lansana (1998). ]
War and state collapse: The case of Sierra Leone
' (M.A. thesis) Wilfrid Laurier University This move led to another major demonstration against the government in many parts of the country, but it was also put down by the army and Stevens' SSD force.
Stevens is generally criticised for dictatorial methods and government corruption, but on a positive note, he kept the country stable and from collapsing into civil war. He created several government institutions that are still in use today. Stevens also reduced ethnic polarisation in government by incorporating members of various ethnic groups into his all-dominant APC government.
Siaka Stevens retired from politics in November 1985 after being in power for eighteen years. The APC named a new presidential candidate to succeed Stevens at party's last delegate conference, held in Freetown in November 1985. The candidate was Major General Joseph Saidu Momoh
Major General Joseph Saidu Momoh, OOR, OBE (January 26, 1937 – August 3, 2003) served as President of Sierra Leone from November 1985 to 29 April 1992.
Early life and education
Joseph Saidu Momoh was born on January 26, 1937, in Binkolo, B ...
, head of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces and Stevens' own choice to succeed him. As head of the armed forces, General Momoh had been loyal to Stevens, who had appointed him to the position. Like Stevens, Momoh was also a member of the minority Limba people (Sierra Leone), Limba ethnic group.
As the sole candidate, Momoh was elected president without opposition and sworn in as Sierra Leone's second president on 28 November 1985 in Freetown. A one-party parliamentary election between APC members was held in May 1986. President Momoh appointed his former military colleague and key ally, Major General Mohamed Tarawalie to succeed him as the head of the Sierra Leone Military. General Tarawalie was also a strong loyalist and key Momoh supporter. President Momoh named James Bambay Kamara as the head of the Sierra Leone Police. Bambay Kamara was also a strong Momoh loyalist and supporter. Momoh broke from former President Siaka Stevens by integrating the powerful SSD into the Sierra Leone Police as a special paramilitary force. Under President Stevens, the SSD had been a powerful personal force used to maintain his hold on power, independent from the Sierra Leone Military and Sierra Leone Police Force. The Sierra Leone Police under Bambay Kamara's leadership was accused of physical violence, arrest and intimidation against critics of President Momoh's government.
President Momoh's strong links with the army and his verbal attacks on corruption earned him much-needed initial support among Sierra Leoneans. With the lack of new faces in the new APC cabinet under president Momoh and the return of many of the old faces from Stevens' government, criticisms soon arose that Momoh was simply perpetuating the rule of Stevens.
The next few years under the Momoh administration were characterised by corruption, which Momoh defused by sacking several senior cabinet ministers. To formalise his war against corruption, President Momoh announced a "Code of Conduct for Political Leaders and Public Servants". After an alleged attempt to overthrow President Momoh in March 1987, more than 60 senior government officials were arrested, including Vice-President Francis Minah, who was removed from office, convicted of plotting the coup, and executed by hanging in 1989, along with five others.
Sierra Leone Civil War (1991–2002) and the NPRC regime (1992–1996)
 In October 1990, owing to mounting pressure from both within and outside the country for political and economic reforms, president Momoh set up a constitutional review commission to assess the 1978 one-party constitution. Based on the commission's recommendations, a constitution re-establishing a multi-party system was approved by the exclusive APC Parliament by a 60% majority vote, becoming effective on 1 October 1991. There was great suspicion that president Momoh was not serious about his promise of political reform, as APC rule continued to be increasingly marked by abuses of power.
The brutal civil war that was going on in neighbouring
In October 1990, owing to mounting pressure from both within and outside the country for political and economic reforms, president Momoh set up a constitutional review commission to assess the 1978 one-party constitution. Based on the commission's recommendations, a constitution re-establishing a multi-party system was approved by the exclusive APC Parliament by a 60% majority vote, becoming effective on 1 October 1991. There was great suspicion that president Momoh was not serious about his promise of political reform, as APC rule continued to be increasingly marked by abuses of power.
The brutal civil war that was going on in neighbouring Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
played a significant role in the outbreak of fighting in Sierra Leone. Charles Taylor (Liberia), Charles Taylor – then leader of the National Patriotic Front of Liberia – reportedly helped form the Revolutionary United Front, Revolutionary United Front (RUF) under the command of former Sierra Leonean army corporal Foday Sankoh, Foday Saybana Sankoh, an ethnic Temne from Tonkolili District in Northern Sierra Leone. Sankoh was a British trained former army corporal who had also undergone guerrilla training in Libya. Taylor's aim was for the RUF to attack the bases of Nigerian dominated peacekeeping troops in Sierra Leone who were opposed to his rebel movement in Liberia.
On 29 April 1992, a group of young soldiers in the Sierra Leone Army, led by seven army officers—Lieutenant Sahr Sandy, Captain Valentine Strasser, Solomon Musa, Lieutenant Solomon "SAJ" Musa, Captain Komba Mondeh, Lieutenant Tom Nyuma, Captain Julius Maada Bio and Captain Komba Kambo—staged a military coup that sent president Momoh into exile in Guinea, and the young soldiers established the National Provisional Ruling Council (NPRC), with 25-year-old Captain Valentine Strasser as its chairman and Head of State of the country.Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
. In his first public broadcast to the nation following the 1996 coup, Brigadier Bio stated that his support for returning Sierra Leone to a democratically elected civilian government and his commitment to ending the civil war were his motivations for the coup.
Kabbah's tenure: government, "dawn of a new republic", the AFRC and end of the Civil War (1996–2007)
Promises of a return to civilian rule were fulfilled by Bio. Prior to conducting the election, Sierra Leoneans and international stakeholders were involved in a major debate on whether the nation should focus on trying to end the long running civil war, or to conduct elections and hence returning governance back to a civilian-led administration with a multi-party system of parliament that would provide the foundation for long-lasting peace and national prosperity. Following the 1995 National Consultative Conference at the Bintumani Hotel in Freetown, dubbed "Bintumani I", which was a Strasser-led initiative, another National Consultative Conference at the same Bintumani Hotel in Freetown, dubbed "Bintumani II", was initiated by the Bio administration that involved both national and international stakeholders, in an effort to find a viable solution to the issues plaguing the country.Johnny Paul Koroma
Major Johnny Paul Koroma (born 9 May 1960; declared dead 1 June 2003) was the head of state of Sierra Leone from May 1997 to February 1998.
Youth and education
Koroma was born to Limba people (Sierra Leone), Limba parents in Tombodu, in the ...
, launched a military coup which sent President Kabbah into exile in Guinea and they established the Armed Forces Revolutionary Council (AFRC). Corporal Gborie quickly went to the Sierra Leone Broadcasting Services headquarters in New England, Freetown to announce the coup to a shocked nation and to alert all soldiers across the country to report for guard duty. The soldiers immediately released Koroma from prison and installed him as their chairman and Head of State.
Koroma suspended the constitution, banned demonstrations, shut down all private radio stations in the country and invited the RUF to join the new junta government, with its leader Foday Sankoh as the Vice-Chairman of the new AFRC-RUF coalition junta government. Within days, Freetown was overwhelmed by the presence of the RUF combatants who came to the city in thousands. The Kamajors, a group of traditional fighters mostly from the Mende ethnic group under the command of deputy Defence Minister Samuel Hinga Norman, remained loyal to President Kabbah and defended the Southern part of Sierra Leone from the soldiers.
After nine months in office, the junta was overthrown by the Nigerian-led ECOMOG forces, and the democratically elected government of president Kabbah was reinstated in February 1998. On 19 October 1998, 24 soldiers in the Sierra Leone army—including Gborie, Brigadier Hassan Karim Conteh, Colonel Samuel Francis Koroma, Major Kula Samba and Colonel Abdul Karim Sesay—were executed by firing squad after they were convicted in a court martial in Freetown, some for orchestrating the 1997 coup that overthrew President Kabbah and others for failure to reverse the mutiny.
In October 1999, the United Nations agreed to send peacekeeping, peacekeepers to help restore order and disarm the rebels. The first of the 6,000-member force began arriving in December, and the UN Security Council voted in February 2000 to increase the force to 11,000, and later to 13,000. But in May, when nearly all Nigerian forces had left and UN forces were trying to disarm the RUF in eastern Sierra Leone, Foday Sankoh, Sankoh's forces clashed with the UN troops, and some 500 peacekeepers were taken hostage as the peace accord effectively collapsed. The hostage crisis resulted in more fighting between the RUF and the government as UN troops launched Operation Khukri to end the siege. The Operation was successful with Indian and British Special Forces being the main contingents.
The situation in the country deteriorated to such an extent that British troops were deployed in Operation Palliser, originally simply to evacuate foreign nationals. However, the British exceeded their original mandate and took full military action to finally defeat the rebels and restore order. The British were the catalyst for the ceasefire that ended the civil war. Elements of the British Army, together with administrators and politicians, remained after withdrawal to help train the armed forces, improve the infrastructure of the country and administer financial and material aid. Tony Blair, the Prime Minister of Britain at the time of the British intervention, is regarded as a hero by the people of Sierra Leone, many of whom are keen for more British involvement.
Between 1991 and 2001, about List of wars by death toll, 50,000 people were killed in Sierra Leone's civil war. Hundreds of thousands of people were forced from their homes and many became refugees in Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
and Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
. In 2001, UN forces moved into rebel-held areas and began to disarm rebel soldiers. By January 2002, the war was declared over. In May 2002, Ahmad Tejan Kabbah, Kabbah was re-elected president by a landslide. By 2004, the disarmament process was complete. Also in 2004, a UN-backed war crimes court began holding trials of senior leaders from both sides of the war. In December 2005, UN peacekeeping forces pulled out of Sierra Leone.
2007 General Election and the re-emergence of APC
In August 2007, Sierra Leone held presidential and parliamentary elections. However, no presidential candidate won the 50% plus one vote majority stipulated in the constitution on the first round of voting. A runoff election was held in September 2007, and Ernest Bai Koroma, the candidate of the main opposition APC, was elected president. Koroma was re-elected president for a second (and final) term in November 2012.
Struggle with the Ebola epidemic (2014–2016)
In 2014, an Ebola virus epidemic in Sierra Leone began that widely affected the country,[Sierra Leone](_blank)
Internationalsos.com. Retrieved 24 February 2017. including forcing Sierra Leone to declare a state of emergency. By the end of 2014 there were nearly 3000 deaths and about 10,000 cases of the disease in Sierra Leone.
14 August 2017 mudslides
Several mudslides occurred in the early hours of 14 August 2017 in and near the country's capital Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
.
2018 General election
In 2018, Sierra Leone held a general election. The presidential election, in which neither candidate reached the required threshold of 55%, went to a second round of voting, in which Julius Maada Bio
Julius Maada Wonie Bio (born 12 May 1964) is a Sierra Leonean politician, and the current president of Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. He is a retired brigadier general in the Sierra Leone Army and was the military head of state of Sierra Leo ...
was elected with 51% of the vote.
Geography

 Sierra Leone is located on the southwest coast of
Sierra Leone is located on the southwest coast of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
, lying mostly between latitudes 7th parallel north, 7° and 10th parallel north, 10°N (a small area is south of 7°), and longitudes 10th meridian west, 10° and 14th meridian west, 14°W. The country is bordered by Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
to the north and east, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west and southwest.Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
sits on a coastal peninsula, situated next to the Sierra Leone Harbour.
The climate is tropical, with two seasons determining the agricultural cycle: the rainy season from May to November, and a dry season from December to May, which includes harmattan, when cool, dry winds blow in off the Sahara Desert and the night-time temperature can be as low as . The average temperature is and varies from around during the year.
Biodiversity
Sierra Leone is home to four terrestrial ecoregions: Guinean montane forests, Western Guinean lowland forests, Guinean forest-savanna mosaic, and Guinean mangroves.[Butler, Rhett (2005)]
''Sierra Leone: Environmental Profile''
mongabay.com On paper, 55 protected areas covered 4.5% of Sierra Leone as of 2003. The country has 2,090 known species of higher plants, 147 mammals, 626 birds, 67 reptiles, 35 amphibians, and 99 fish species.rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
in Sierra Leone.
Government and politics
Sierra Leone is a constitutional republic with a Direct democracy, directly elected president and a unicameral legislature. The current system of the Government of Sierra Leone is based on the 1991 Constitution of Sierra Leone, Sierra Leone Constitution. Sierra Leone has a dominant unitary state, unitary central government and a weak local government. The executive branch of the Government of Sierra Leone, headed by the president of Sierra Leone has extensive powers and influences. The president is the most powerful government official in Sierra Leone.[Hanatu Kabbah (November 2006)]
Sierra Leone Legal System and Legal Research
nyulawglobal.org
Within the confines of the 1991 Constitution, supreme legislative powers are vested in Parliament of Sierra Leone, Parliament, which is the law-making body of the nation. Supreme executive authority rests in the president and members of his cabinet and judicial power with the judiciary of which the Chief Justice of Sierra Leone is the head.
The president is the head of state, the head of government and the commander-in-chief of the Military of Sierra Leone, Sierra Leone Armed Forces. The president appoints and heads a cabinet of ministers, which must be approved by the Parliament. The president is elected by Direct election, popular vote to a maximum of two five-year terms. The president is the highest and most influential position within the government of Sierra Leone.
To be elected president of Sierra Leone, a candidate must gain at least 55% of the vote. If no candidate gets 55%, there is a two-round system, second-round runoff between the top two candidates.
The current president of Sierra Leone is former military junta leader Julius Maada Bio
Julius Maada Wonie Bio (born 12 May 1964) is a Sierra Leonean politician, and the current president of Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. He is a retired brigadier general in the Sierra Leone Army and was the military head of state of Sierra Leo ...
.Sierra Leone People's Party
The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since April 4, 2018. The SLPP do ...
, the current ruling party in Sierra Leone.
Next to the president is the Vice President of Sierra Leone, vice-president, who is the second highest-ranking government official in the executive branch of the Sierra Leone Government. As designated by the Sierra Leone Constitution, the vice-president is to become the new president of Sierra Leone upon the death, resignation, or removal of the President.
Parliament
The Parliament of Sierra Leone is unicameral, with 146 seats. Each of the country's 14 districts is represented in parliament. 132 members are elected concurrently with the presidential elections; the other 16 seats are filled by paramount chiefs from the country's 16 Administrative division, administrative districts. The Sierra Leone parliament is led by the Speaker of Parliament, who is the overall leader of Parliament and is directly elected by sitting members of parliament. The current speaker of the Sierra Leone parliament is Abass Bundu, who was elected by members of parliament on 21 January 2014.
The current members of the Parliament of Sierra Leone were elected in the 2012 Sierra Leone parliamentary election. The APC currently has 68 of the 132 elected parliamentary seats and the Sierra Leone People's Party
The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since April 4, 2018. The SLPP do ...
(SLPP) has 49 of the elected 132 parliamentary seats. Sierra Leone's two most dominant political party, parties, the APC and the SLPP, collectively won every elected seat in Parliament in the 2012 Sierra Leone parliamentary election. To be qualified as a Member of Parliament, the person must be a citizen of Sierra Leone, must be at least 21 years old, must be able to speak, read and write the English language with a degree of proficiency to enable him to actively take part in proceedings in Parliament; and must not have any criminal conviction.
Judiciary
 The judicial power of Sierra Leone is vested in the judiciary, headed by the Chief Justice of Sierra Leone and comprising the Supreme Court of Sierra Leone, which is the highest court in the country, meaning that its rulings, therefore, cannot be appealed against. Other courts include the High Court of Justice, the Court of Appeal, the magistrate courts, and traditional courts in rural villages. The president appoints and parliament approves Justices for the three courts. The Judiciary have jurisdiction in all civil and criminal matters throughout the country. The current acting chief justice of Sierra Leone is Desmond Babatunde Edwards.
The judicial power of Sierra Leone is vested in the judiciary, headed by the Chief Justice of Sierra Leone and comprising the Supreme Court of Sierra Leone, which is the highest court in the country, meaning that its rulings, therefore, cannot be appealed against. Other courts include the High Court of Justice, the Court of Appeal, the magistrate courts, and traditional courts in rural villages. The president appoints and parliament approves Justices for the three courts. The Judiciary have jurisdiction in all civil and criminal matters throughout the country. The current acting chief justice of Sierra Leone is Desmond Babatunde Edwards.
Foreign relations
The Sierra Leonean Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation is responsible for foreign policy of Sierra Leone. Sierra Leone has diplomatic relations that include China, Russia, Libya, Iran, and Cuba.
Sierra Leone has good relations with the West, including the United States, and has maintained historical ties with the United Kingdom and other former British Empire, British colonies through its membership of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
. The United Kingdom has played a major role in providing aid to the former colony, together with administrative help and military training since intervening to end the Civil War in 2000.
Former President Siaka Stevens
Siaka Probyn Stevens (24 August 1905 – 29 May 1988) was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister of Sierra Leone, Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was ofte ...
' government had sought closer relations with other West African countries under the Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS) a policy continued by the current government. Sierra Leone, along with Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, form the Mano River Union
The Mano River Union (MRU) is an international association initially established between Liberia and Sierra Leone by the 3 October 1973 Mano River Declaration. It is named for the Mano River which begins in the Guinea highlands and forms a border ...
(MRU). It is primarily designed to implement development projects and promote regional economic integration between the three countries.
Sierra Leone is also a member of the United Nations and its specialised agencies, the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
, the African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group (AfDB) or (BAD) is a multilateral development finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies i ...
(AFDB), the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
(OIC), and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
Military
The Military of Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone Armed Forces (RSLAF), are the unified armed forces of Sierra Leone responsible for the territorial security of Sierra Leone's border and defending the national interests of Sierra Leone within the framework of its international obligations. The armed forces were formed after independence in 1961, based on elements of the former British Royal West African Frontier Force present in the country. The Sierra Leone Armed Forces consist of around 15,500 personnel, comprising the largest Sierra Leone Army, the Sierra Leone Navy and the Sierra Leone Air Wing.
The president of Sierra Leone is the Commander in Chief of the military, with the Minister of Defence responsible for defence policy and the formulation of the armed forces. The current Sierra Leonean Defence Minister is retired Major Alfred Paolo Conteh. The Military of Sierra Leone also has a Chief of the Defence Staff (Sierra Leone), Chief of the Defence Staff who is a uniformed military official responsible for the administration and the operational control of the Sierra Leone military. Brigadier General Alfred Nelson-Williams who was appointed by president Koroma succeeded the retired Major General Edward Sam M'boma on 12 September 2008 as the Chief of Defence Staff of the Military.
When Sierra Leone gained independence in 1961, the Royal Sierra Leone Military Force was created from the Sierra Leone Battalion of the West African Frontier Force.[''Area Handbook for Sierra Leone''](_blank)
Irving Kaplan, U.S. Government Printing Office, 1976, page 337 The military seized control in 1968, bringing the National Reformation Council into power. On 19 April 1971, when Sierra Leone became a republic, the Royal Sierra Leone Military Forces were renamed the Republic of Sierra Leone Military Force (RSLMF).
Law enforcement
Law enforcement in Sierra Leone is primarily the responsibility of the Sierra Leone Police (SLP), which is accountable to the Minister of Internal Affairs (appointed by the president). Sierra Leone Police was established by the British colony in 1894; it is one of the oldest police forces in West Africa. It works to prevent crime, protect life and property, detect and prosecute offenders, maintain public order, ensure safety and security, and enhance access to justice. The Sierra Leone Police is headed by the Inspector General of Police, the professional head of the Sierra Leone Police force, who is appointed by the president of Sierra Leone.
Each one of Districts of Sierra Leone, Sierra Leone's 14 districts is headed by a district police commissioner who is the professional head of their respective district. These Police Commissioners report directly to the Inspector General of Police at the Sierra Leone Police headquarters in Freetown. The current Inspector General of Police is Brima Acha Kamara, who was appointed to the position by former president Ahmad Tejan Kabbah
Alhaji Ahmad Tejan Kabbah (February 16, 1932 – March 13, 2014) was a Sierra Leonean politician who served twice as the 3rd President of Sierra Leone, from 1996 to 1997 and again from 1998 to 2007. An economist and attorney by profession, Ka ...
.
Human rights
Male LGBT rights in Sierra Leone, same-sex sexual activity is illegal under Section 61 of the Offences against the Person Act 1861, and imprisonment for life is possible.
Excessive police brutality is also a frequent problem. Protesters have been killed by security forces, as have prison rioters (in one incident at Freetown Central Prison, Pademba Road Prison, 30 inmates and one correction officer were killed). Multiple allegations were made during the COVID-19 lockdown period of police attacking people trying to obtain basic necessities.
Administrative divisions
 The Republic of Sierra Leone is composed of five regions: the Northern Province, Sierra Leone, Northern Province, North West Province, Sierra Leone, North West Province, Southern Province, Sierra Leone, Southern Province, the Eastern Province, Sierra Leone, Eastern Province, and the Western Area. Four provinces are further divided into 14 districts; the Western Area is divided into two districts.
The provincial districts are divided into 186 chiefdoms, which have traditionally been led by paramount chiefs, recognised by the British administration in 1896 at the time of organising the Protectorate of Sierra Leone. The Paramount Chiefs are influential, particularly in villages and small rural towns.
The Republic of Sierra Leone is composed of five regions: the Northern Province, Sierra Leone, Northern Province, North West Province, Sierra Leone, North West Province, Southern Province, Sierra Leone, Southern Province, the Eastern Province, Sierra Leone, Eastern Province, and the Western Area. Four provinces are further divided into 14 districts; the Western Area is divided into two districts.
The provincial districts are divided into 186 chiefdoms, which have traditionally been led by paramount chiefs, recognised by the British administration in 1896 at the time of organising the Protectorate of Sierra Leone. The Paramount Chiefs are influential, particularly in villages and small rural towns.[Tristan Reed and James A. Robinson, ''The Chiefdoms of Sierra Leone''](_blank)
''Scholar'', Harvard University, 15 July 2013, accessed 30 April 2014 Each chiefdom has ruling families that were recognised at that time; the Tribal Authority, made up of local notables, elects the paramount chief from the ruling families.[Daron Acemoglu, Tristan Reed. and James A. Robinson]
"Chiefs: Economic Development and Elite Control of Civil Society in Sierra Leone"
, Stanford University, 29 August 2013, accessed 30 April 2014
Within the context of local governance, the districts are governed as ''localities''. Each has a directly elected local district council to exercise authority and carry out functions at a local level.
Economy

 By the 1990s, economic activity was declining and economic infrastructure had become seriously degraded. Over the next decade, much of the formal economy was destroyed in the country's civil war. Since the end of hostilities in January 2002, massive infusions of outside assistance have helped Sierra Leone begin to recover.
Much of the recovery will depend on the success of the government's efforts to limit corruption by officials, which many feel was the chief cause of the civil war. A key indicator of success will be the effectiveness of government management of its diamond sector.
There is high unemployment, particularly among the youth and ex-combatants. Authorities have been slow to implement reforms in the civil service, and the pace of the privatisation programme is also slackening and donors have urged its advancement.
The currency is the Sierra Leonean leone, leone. The central bank is the Bank of Sierra Leone. Sierra Leone operates a floating exchange rate system, and foreign currencies can be exchanged at any of the commercial banks, recognised foreign exchange Service bureau, bureaux and most hotels. Credit card use is limited in Sierra Leone, though they may be used at some hotels and restaurants. There are a few internationally linked automated teller machines that accept Visa cards in Freetown operated by ProCredit Bank.
By the 1990s, economic activity was declining and economic infrastructure had become seriously degraded. Over the next decade, much of the formal economy was destroyed in the country's civil war. Since the end of hostilities in January 2002, massive infusions of outside assistance have helped Sierra Leone begin to recover.
Much of the recovery will depend on the success of the government's efforts to limit corruption by officials, which many feel was the chief cause of the civil war. A key indicator of success will be the effectiveness of government management of its diamond sector.
There is high unemployment, particularly among the youth and ex-combatants. Authorities have been slow to implement reforms in the civil service, and the pace of the privatisation programme is also slackening and donors have urged its advancement.
The currency is the Sierra Leonean leone, leone. The central bank is the Bank of Sierra Leone. Sierra Leone operates a floating exchange rate system, and foreign currencies can be exchanged at any of the commercial banks, recognised foreign exchange Service bureau, bureaux and most hotels. Credit card use is limited in Sierra Leone, though they may be used at some hotels and restaurants. There are a few internationally linked automated teller machines that accept Visa cards in Freetown operated by ProCredit Bank.
Agriculture
 Two-thirds of the population of Sierra Leone are directly involved in subsistence agriculture.
Two-thirds of the population of Sierra Leone are directly involved in subsistence agriculture.
Mining
Rich in minerals, Sierra Leone has relied on mining, especially diamonds, for its economic base. The country is among the top ten diamond producing nations. Mineral exports remain the main currency earner. Sierra Leone is a major producer of gem-quality diamonds. Though rich in diamonds, it has historically struggled to manage their exploitation and export.
Sierra Leone is known for its blood diamonds that were mined and sold to diamond conglomerates during the Sierra Leone Civil War, civil war, to buy the weapons that fuelled its atrocities. In the 1970s and early 1980s, economic growth rate slowed because of a decline in the mining sector and increasing corruption among government officials.
Annual production of Sierra Leone's diamond estimates range between US$250 million–$300 million. Some of that is Smuggling, smuggled, where it is possibly used for money laundering or financing illicit activities. Formal exports have dramatically improved since the civil war, with efforts to improve the management of them having some success. In October 2000, a UN-approved certification system for exporting diamonds from the country was put in place and led to a dramatic increase in legal exports. In 2001, the government created a mining community development fund (Ministry of Mineral Resources (Sierra Leone), DACDF), which returns a portion of diamond export taxes to diamond mining communities. The fund was created to raise local communities' stake in the legal diamond trade.
Sierra Leone has one of the world's largest deposits of rutile, a titanium ore used as paint pigment and welding rod coatings.
Transport infrastructure
 There are several systems of transport in Sierra Leone, which has a road, air and water infrastructure, including a network of highways and several airports. There are of highways in Sierra Leone, of which
There are several systems of transport in Sierra Leone, which has a road, air and water infrastructure, including a network of highways and several airports. There are of highways in Sierra Leone, of which Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
, Sherbro Island and Pepel.
There are ten regional airports in Sierra Leone, and one international airport. The Lungi International Airport located in the coastal town of Lungi, Sierra Leone, Lungi in Northern Sierra Leone is the primary airport for domestic and international travel to or from Sierra Leone. Passengers cross the river to Aberdeen Heliports in Freetown by hovercraft, ferry or a helicopter. Helicopters are also available from the airport to other major cities in the country. The airport has Pavement (material), paved runways longer than . The other airports have unpaved runways, and seven have runways from long; the remaining two have shorter runways.
Sierra Leone appears on the EU list of prohibited countries with regard to the certification of airlines. This means that no airline registered in Sierra Leone may operate services of any kind within the European Union. This is due to substandard safety standards.
As of May 2014, the country's only Lungi International Airport, international airport had regularly scheduled direct flights to London, Paris, Brussels and most major cities in West Africa.
In September 2014 there were many Districts with travel restrictions including Kailahun, Kenema, Bombali, Tonkolili, and Port Loko because of Ebola virus epidemic in Sierra Leone, Ebola.
Energy in Sierra Leone

Overview
As of 2016, about 12% of the population of Sierra Leone had access to electricity. Of that 12%, 10% was in the capital Freetown, and the remaining 90% of the country used 2% of the nation's electricity.
Solar energy
In conjunction with the UK's Department for International Development (DFID), Sierra Leone has set the goal to provide solar power to all of its citizens by 2025.
Hydroelectric power
As of 2012, Sierra Leone has 3 main hydroelectric plants. The first is the Guma plant which was decommissioned in 1982, the second is the Dodo Plant which is located in the Eastern Province, and finally the Bumbuna Dam, Bumbuna plant.World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, the African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group (AfDB) or (BAD) is a multilateral development finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies i ...
, and the Italian company Salini Impregilo.
Demographics
 In 2019 Sierra Leone had a population of 7,813,215
In 2019 Sierra Leone had a population of 7,813,215Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
over the course of 2007. Of the refugees remaining in Sierra Leone, nearly all were Liberian.
Religion
 Sierra Leone is officially a secular state.
Sierra Leone is officially a secular state. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and Christianity are the two main religions in the country. The constitution of Sierra Leone provides for freedom of religion and the Sierra Leone Government generally protects it. The Sierra Leonean Government is constitutionally forbidden from establishing a state religion, though Muslim and Christian prayers are usually held in the country at the beginning of major political occasions, including presidential inaugurations and the official opening of the new session of Parliament.
Surveys of the religious make up of Sierra Leone vary widely, though Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
make up the majority of the population. Based on 2015 estimates of the population of Sierra Leone, 77% of the population are Muslims, 22% are Christians, and 1% practise African traditional religion.
According to a 2020 estimates by the Pew Research Center 78.5% of Sierra Leone's population are Muslims (mostly Sunni Islam, Sunni), 20.4% are Christians (mostly Protestantism, Protestants) and 1.1% belong to a traditional African religion or other beliefs. The Inter-Religious Council of Sierra Leone estimated that 77% of Sierra Leone's population are Muslims, 21% are Christians, and 2% are followers of traditional African religion. Most of Sierra Leone's ethnic groups are Muslim majority, including the country's two largest ethnic groups: the Mende and Temne.
Sierra Leone is regarded as one of the most religiously tolerant countries in the world. Most the major Muslim and Christian holidays are officially Public holiday, national holidays in the country, and religious conflict is rare.
The country is home to the Sierra Leone Inter-Religious Council, which is made up of both Christian and Muslim religious leaders to promote peace and tolerance throughout the country. The Islamic holidays of Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha and Mawlid, Maulid-un-Nabi (Birthday of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad) are observed as Public holidays in Sierra Leone, national holidays in Sierra Leone. The Christian holidays of Christmas, Boxing Day, Good Friday and Easter are also national holidays in Sierra Leone. In politics the overwhelming majority of Sierra Leoneans vote for a candidate without regard of the candidate being a Muslim or a Christian. All of Sierra Leone's Heads of State have been Christians except Ahmad Tejan Kabbah, who was a Muslim.
The overwhelming majority of Sierra Leonean Muslims, are adherent to the Sunni tradition of Islam in practice. Most of the Mosques and Islamic schools across Sierra Leone are based in Sunni Islam. Ahmadiyya Muslims make up about 10% of the country's Muslim population. Sierra Leone has a vibrant Ahmaddiya Muslim population, especially in the southern city of Bo, Sierra Leone, Bo, which is home to a large Ahmadiyya Muslim population. There are five hundred Ahmadiyya Mosque across Sierra Leone. Shia Islam does not have a strong presence in Sierra Leone, and there are virtually no Shia Muslims in the country. Most Sierra Leonean Muslims of the Sunni and Ahmadiyya sect generally pray together in the same mosque. The vast majority of Sierra Leonean Muslims are adherent to the Maliki school of Sunni Islam. The Maliki school is by far the largest and most dominant Islamic school of jurisprudence across Sierra Leone. Many Ahmadiyya Muslims in Sierra Leone also follow the Maliki Jurisprudence.
The Sierra Leone Islamic Supreme Council is the highest Islamic religious organisation in Sierra Leone and is made up of the country's Imams, Islamic scholars, and other Islamic clerics across the country. Sheikh Muhammad Taha Jalloh is the president of the Sierra Leone Supreme Islamic Council. The United Council of Imams, is an influential Islamic religious body in Sierra Leone, that is made up of all imams of mosques throughout Sierra Leone. The president of the United Council of Imam is Sheikh Alhaji Muhammad Habib Sheriff. The two largest mosques in Sierra Leone are the Freetown Central Mosque and the Ghadafi Central Mosque (built by former Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi), both located in the capital Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
.
The large majority of Sierra Leonean Christians are Protestant, of which the largest groups are the Wesleyan – Methodists.
Ethnic groups
 Sierra Leone is home to about sixteen ethnic groups, each with its own language. The largest and most influential are the Temne at about 35.5% and the Mende at about 33.2%. The Temne predominate in the Northern Province, Sierra Leone, Northern Sierra Leone and Western Area, Sierra Leone, some areas around the capital of Sierra Leone. The Mende predominate in Southern Province, Sierra Leone, South-Eastern Sierra Leone (with the exception of Kono District).
The vast majority of Temne are Muslims at over 85%; with a significant Christian minority at about 10%. The Mende are also Muslim majority at about 70%, though with a large Christian minority at about 30%. Sierra Leone's national politics centres on the competition between the north-west, dominated by the Temne, and the south-east dominated by the Mende. The vast majority of the Mende support the Sierra Leone People's Party; while the majority of the Temne support the All People's Congress.
The Mende, who are believed to be descendants of the Mane people, Mane, originally occupied the Liberian hinterland. They began moving into Sierra Leone slowly and peacefully in the eighteenth century. The Temne are said to have migrated from Futa Jallon, which is in present-day
Sierra Leone is home to about sixteen ethnic groups, each with its own language. The largest and most influential are the Temne at about 35.5% and the Mende at about 33.2%. The Temne predominate in the Northern Province, Sierra Leone, Northern Sierra Leone and Western Area, Sierra Leone, some areas around the capital of Sierra Leone. The Mende predominate in Southern Province, Sierra Leone, South-Eastern Sierra Leone (with the exception of Kono District).
The vast majority of Temne are Muslims at over 85%; with a significant Christian minority at about 10%. The Mende are also Muslim majority at about 70%, though with a large Christian minority at about 30%. Sierra Leone's national politics centres on the competition between the north-west, dominated by the Temne, and the south-east dominated by the Mende. The vast majority of the Mende support the Sierra Leone People's Party; while the majority of the Temne support the All People's Congress.
The Mende, who are believed to be descendants of the Mane people, Mane, originally occupied the Liberian hinterland. They began moving into Sierra Leone slowly and peacefully in the eighteenth century. The Temne are said to have migrated from Futa Jallon, which is in present-day Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
.
The third-largest ethnic group are the Limba people (Sierra Leone), Limba at about 8.4% of the population. The Limba are indigenous peoples, native people of Sierra Leone. They have no tradition of origin, and it is believed that they have lived in Sierra Leone since before the European encounter. The Limba are primarily found in Northern Sierra Leone, particularly in Bombali District, Bombali, Kambia District, Kambia and Koinadugu District. The Limba are about 60% Christian and 40% Muslims. The Limba are close political allies of the neighbouring Temne.
Since independence, the Limba have traditionally been influential in Sierra Leone's politics, along with the Mende. The vast majority of Limba support the All People's Congress (APC) political party. Sierra Leone's first and second presidents, Siaka Stevens
Siaka Probyn Stevens (24 August 1905 – 29 May 1988) was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister of Sierra Leone, Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was ofte ...
and Joseph Saidu Momoh
Major General Joseph Saidu Momoh, OOR, OBE (January 26, 1937 – August 3, 2003) served as President of Sierra Leone from November 1985 to 29 April 1992.
Early life and education
Joseph Saidu Momoh was born on January 26, 1937, in Binkolo, B ...
, respectively, were both ethnic Limba. Sierra Leone's former defense minister Paolo Conteh, Alfred Paolo Conteh is an ethnic Limba.
One of the biggest minority ethnic groups are the Fula people, Fula at around 3.8% of the population. Descendants of seventeenth- and eighteenth-century Fula migrant settlers from the Fouta Djalon region of Guinea, they live primarily in the northeast and the western area of Sierra Leone. The Fula are virtually all Muslims at over 99%. The Fula are primarily merchant, traders, and many live in middle-class homes. Because of their trading, the Fulas are found in nearly all parts of the country.
The other ethnic groups are the Mandingo people of Sierra Leone, Mandingo (also known as Mandinka people, Mandinka). They are descendants of traders from Guinea who migrated to Sierra Leone during the late nineteenth to mid-twentieth centuries. The Mandinka are predominantly found in the east and the northern part of the country. They predominate in the large towns, most notably Karina, Sierra Leone, Karina, in Bombali District in the north; Kabala, Sierra Leone, Kabala and Falaba in Koinadugu District in the north; and Yengema, Kono District in the east of the country. Like the Fula, the Mandinka are virtually all Muslims at over 99℅. Sierra Leone's third president, Ahmad Tejan Kabbah, and Sierra Leone's first Vice-President, Sorie Ibrahim Koroma, were both ethnic Mandingo.
Next in proportion are the Kono people, Kono, who live primarily in Kono District in Eastern Sierra Leone. The Kono are descendants of migrants from Guinea; today their workers are known primarily as diamond miners. The majority of the Kono ethnic group are Christians, though with an influential Muslim minority. Sierra Leone's former Vice-President Samuel Sam-Sumana, Alhaji Samuel Sam-Sumana is an ethnic Kono.
The small but significant Krio people (descendants of freed African American, West Indian and Liberated African slaves who settled in Freetown between 1787 and about 1885) make up about 3% of the population. They primarily occupy the capital city of Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
and its surrounding Western Area. Krio culture reflects the Western culture and ideals within which many of their ancestors originated – they also had close ties with British officials and colonial administration during years of development.
The Krio have traditionally dominated Sierra Leone's judiciary and Freetown's elected city council. One of the first ethnic groups to become educated according to Western traditions, they have traditionally been appointed to positions in the civil service, beginning during the colonial years. They continue to be influential in the civil service. The Krios are virtually all Christians at about 99%.
The Oku people are the descendants of liberated muslim Yoruba people, Yorubas from Southwest Nigeria, who were released from slave ships and resettled in Sierra Leone as Liberated Africans in Sierra Leone, Liberated Africans or came as settlers in the mid-19th century. The Oku people are related to the Krio and primarily reside in the communities of Fourah Bay, Fula Town, and Aberdeen in Freetown. The Oku are virtually all Muslims at about 99%.
Other minority ethnic groups are the Kuranko people, Kuranko, who are related to the Mandingo and are largely Muslims. The Kuranko are believed to have begun arriving in Sierra Leone from Guinea in about 1600 and settled in the north, particularly in Koinadugu District. The Kuranko are primarily farmers; leaders among them have traditionally held several senior positions in the Military. The current Governor of the Bank of Sierra Leone Kaifala Marah is an ethnic Kuranko. The Kuranko are largely Muslim majority.
The Loko people, Loko in the north are native people of Sierra Leone, believed to have lived in Sierra Leone since the time of European encounter. Like the neighbouring Temne, the Loko are Muslim majority. The Susu people, Susu and their related Yalunka people, Yalunka are traders; both groups are primarily found in the far north in Kambia and Koinadugu District close to the border with Guinea. The Susu and Yalunka kingdom was established in the early fifth seventh century before the Mali empire, which was extended from Mali, Senegal, Guinea Bissau, Guinea Conakry to the northern part of Sierra Leone. They are the original owners of the Futa Djallon region covered by a vars land area both the Susu and Yalunka people are descendants of the Mande people. They are virtually all Muslims. The Yalunka also spelled Jallonke, Yalonga, Djallonké, Djallonka or Dialonké, are Mande people who have lived in the Djallon, a mountainous region in Sierra Leone, Mali, Senegal, Guinea Bissau and Guinea Conakry West Africa over 520 years ago. The name Yalunka literally means "inhabitants of the Jallon (mountains)". Manga Sewa was born in Falaba, Solima chiefdom, in the Northern Province of British Sierra Leone to Yalunka parents. His father was a Yalunka paramount chief of Solima, a prosperous chieftaincy. Its capital, Falaba, was on the rich trading routes leading to the coast. Manga Sewa's father had several wives and dozens of children. are traders; both groups are primarily found in the far north in Kambia District, Kambia and Koinadugu District close to the border with Guinea. The Susu and Yalunka are both descendants of migrants from Guinea; they both are virtually all Muslims at over 99%.
The Kissi people, Kissi live further inland in South-Eastern Sierra Leone. They predominate in the large town of Koindu and its surrounding areas in Kailahun District. The vast majority of Kissi are Christians. The much smaller Vai people, Vai and Kru people, Kru peoples are primarily found in Kailahun District, Kailahun and Pujehun Districts near the border with Liberia. The Kru predominate in the Kroubay neighbourhood in the capital of Freetown. The Vai are largely Muslim majority at about 90%, while the Kru are virtually all Christians at over 99%.
On the coast in Bonthe District in the south are the Sherbro people, Sherbro. Native to Sierra Leone, they have occupied Sherbro Island since it was founded. The Sherbro are primarily fisherman and farmers, and they are predominantly found in Bonthe District. The Sherbro are virtually all Christians, and their paramount chiefs had a history of intermarriage with British colonists and traders.
A small number of Sierra Leoneans are of partial or full Lebanese people, Lebanese ancestry, descendants of traders who first came to the nation in the 19th century. They are locally known as Sierra Leonean-Lebanese. The Sierra Leonean-Lebanese community are primarily traders and they mostly live in middle-class households in the urban areas, primarily in Freetown, Bo, Sierra Leone, Bo, Kenema, Koidu, Koidu Town and Makeni.
Gender equality
Household
Although women account for about 50 per cent of the population in Sierra Leone, only 28 per cent are household heads.
War
Children who have been forced to be part of a war have experienced severe mental and emotional damage in Sierra Leone. However, the damage and way to deal with the effects of war depends on the gender of the kids. Both genders experienced and were involved in high levels of violence. Females, experiencing higher levels of rapes, presented greater signs of depression and anxiety.
Female economy
Women face discrimination when it comes to obtaining financial, social, and cultural help to start a business.
Education
 Education in Sierra Leone is legally required for all children for six years at primary education, primary level (Class P1-P6) and three years in junior secondary education, but a shortage of schools and teachers has made implementation impossible.
Education in Sierra Leone is legally required for all children for six years at primary education, primary level (Class P1-P6) and three years in junior secondary education, but a shortage of schools and teachers has made implementation impossible.[ ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.''] Two thirds of the adult population of the country are illiterate.
The Sierra Leone Civil War resulted in the destruction of 1,270 primary schools, and in 2001, 67% of all school-age children were out of school.Fourah Bay College
Fourah Bay College is a public university in the neighbourhood of Mount Aureol in Freetown, Sierra Leone. Founded on 18 February 1827, it is the first western-style university built in Sub-Saharan Africa and, furthermore, the first university-le ...
, founded in 1827 (the oldest university in West Africa), University of Makeni (established initially in September 2005 as The Fatima Institute, the college was granted university status in August 2009, and assumed the name University of Makeni, or UNIMAK), and Njala University, primarily located in Bo District. Njala University was established as the Njala Agricultural Experimental Station in 1910 and became a university in 2005. Teacher training colleges and religious seminaries are found in many parts of the country.
Health
The Central Intelligence Agency, CIA estimated that the average life expectancy in Sierra Leone was 57.39 years.Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
.
Medical care is not readily accessible, with doctors and hospitals out of reach for many villagers. While free health care may be provided in some villages, the medical staff is poorly paid and sometimes charge for their services, taking advantage of the fact that the villagers are not aware of their right to free medical care.
A dialysis machine, the first of its kind in the country, was donated by Israel.
Emergency medical response
Having had no formal emergency medical services previously, the First Responder Coalition of Sierra Leone (FRCSL) was formed in June 2019 in Makeni to facilitate the development of Emergency medical responder, emergency first responder programs nationwide.
Endemic and infectious diseases
Sierra Leone suffers from epidemic outbreaks of diseases, including yellow fever, cholera, Ebola, lassa fever and meningitis.[
]
Maternal and child health
According to 2017 estimates, Sierra Leone has the third highest maternal mortality rate in the world.[ Country Comparison: Maternal Mortality Rate](_blank)
. ''The World Factbook'' Central Intelligence Agency. For every 100 liveborn children, one mother dies due to complications of giving birth.Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
, the second busiest hospital in Sierra Leone, delivering up to 3000 babies each year. The centre provides free surgery for women suffering from this condition.
The centre provides a variety of maternal and child health services and is supported by not for profit organisations such as Freedom from Fistula, The Aminata Maternal Foundation, and UNFPA.
Mental health
Mental healthcare in Sierra Leone is almost non-existent. Many sufferers try to cure themselves with the help of traditional healers. During the Sierra Leone Civil War, Civil War (1991–2002), many soldiers took part in atrocities and many children were forced to fight. This left them traumatised, with an estimated 400,000 people (by 2009) being mentally ill. Thousands of former child soldiers have fallen into substance abuse as they try to blunt their memories.
Potable water supply
The water supply in Sierra Leone is characterised by limited access to safe drinking water. Despite efforts by the government and numerous non-governmental organisations, access has not much improved since the end of the Sierra Leone Civil War in 2002, stagnating at about 50% and even declining in rural areas.[WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme for Water Supply and Sanitation (updated March 2010) ] It is hoped that a new dam in Orugu, for which China committed financing in 2009, will alleviate water scarcity.
2014 Ebola outbreak
Ebola is prevalent in Africa where social and economic inequalities are common. The central African countries are the most prevalent of EVD; like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Sudan, Uganda, and Gabon
In 2014 there was an outbreak of the Ebola virus in West Africa. As of 19 October 2014, there had been 3,706 cases of Ebola in Sierra Leone, and 1,259 deaths, including that of the leading physician trying to control the outbreak, Sheik Umar Khan. In early August 2014 Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
closed its borders to Sierra Leone to help contain the spreading of the virus, which originated in Guinea, as more new cases of the disease were being reported in Sierra Leone than in Guinea. Aside from the human cost, the outbreak was severely eroding the economy. By September 2014, with the closure of borders, the cancellation of airline flights, the evacuation of foreign workers and a collapse of cross-border trade, the national deficit of Sierra Leone and other affected countries was widening to the point where the IMF was considering expanding its financial support.[.]
Culture
Polygamy
37 per cent of married women in Sierra Leone were in polygamous marriages in 2008.
Food and customs
 Rice is the staple food of Sierra Leone and is consumed at virtually every meal daily. The rice is prepared in numerous ways, and topped with a variety of sauces made from some of Sierra Leone's favourite toppings, including potato leaves, cassava leaves, Corchorus, crain crain, okra soup, fried fish and peanut, groundnut stew.
Along the streets of towns and cities across Sierra Leone, one can find foods consisting of fruit, vegetables and snacks such as fresh mangoes, oranges, pineapple, fried Plantain (cooking), plantains, ginger beer, fried potato, fried cassava with pepper sauce; small bags of popcorn or peanuts, bread, roasted corn, or skewers of grilled meat or shrimp.
Poyo is a popular Sierra Leonean drink. It is a sweet, lightly fermented palm wine, and is found in bars in towns and villages across the country. Poyo bars are areas of lively informal debate about politics, Association football, football, basketball, entertainment and other issues.
Rice is the staple food of Sierra Leone and is consumed at virtually every meal daily. The rice is prepared in numerous ways, and topped with a variety of sauces made from some of Sierra Leone's favourite toppings, including potato leaves, cassava leaves, Corchorus, crain crain, okra soup, fried fish and peanut, groundnut stew.
Along the streets of towns and cities across Sierra Leone, one can find foods consisting of fruit, vegetables and snacks such as fresh mangoes, oranges, pineapple, fried Plantain (cooking), plantains, ginger beer, fried potato, fried cassava with pepper sauce; small bags of popcorn or peanuts, bread, roasted corn, or skewers of grilled meat or shrimp.
Poyo is a popular Sierra Leonean drink. It is a sweet, lightly fermented palm wine, and is found in bars in towns and villages across the country. Poyo bars are areas of lively informal debate about politics, Association football, football, basketball, entertainment and other issues.
Media
 Media in Sierra Leone began with the introduction of the first printing press in Africa at the start of the 19th century. A strong free journalistic tradition developed with the creation of several newspapers. In the 1860s, the country became a journalist hub for Africa, with professionals travelling to the country from across the continent. At the end of the 19th century, the industry went into decline, and when radio was introduced in the 1930s, it became the primary communication media in the country.
The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Service (SLBS) was created by the colonial government in 1934 making it the earliest English language radio broadcaster service in West Africa. The service began broadcasting television in 1963, with coverage extended to all the districts in the country in 1978. In April 2010, the SLBS merged with the
Media in Sierra Leone began with the introduction of the first printing press in Africa at the start of the 19th century. A strong free journalistic tradition developed with the creation of several newspapers. In the 1860s, the country became a journalist hub for Africa, with professionals travelling to the country from across the continent. At the end of the 19th century, the industry went into decline, and when radio was introduced in the 1930s, it became the primary communication media in the country.
The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Service (SLBS) was created by the colonial government in 1934 making it the earliest English language radio broadcaster service in West Africa. The service began broadcasting television in 1963, with coverage extended to all the districts in the country in 1978. In April 2010, the SLBS merged with the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
peacekeeping radio station in Sierra Leone to form the Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation, the government-owned current national broadcaster in Sierra Leone.
The Sierra Leone constitution guarantees freedom of speech, and freedom of the press; however, the government maintains strong control of media, and at times restricts these rights in practice. Some subjects are seen as taboo by society and members of the political elite; imprisonment and violence have been used by the political establishment against journalists. Radio is the most popular and most-trusted media in Sierra Leone, with 85% of people having access to a radio and 72% of people in the country listening to the radio daily.
Radio is the most popular and most-trusted media in Sierra Leone, with 85% of people having access to a radio and 72% of people in the country listening to the radio daily.
Arts
The arts in Sierra Leone are a mixture of tradition and hybrid African and western styles.
File: Temne. Ode-Lay Mask Brooklyn Museum.jpg, Odelay mask by Temne people. Brooklyn Museum.
File: Sierra Leone Koindu dance.jpg, The Koindu dance
Sports
 Association football is by far the most popular sport in Sierra Leone. Children, youth and adult are frequently seen playing street football across Sierra Leone. There are organised youth and adult football tournaments across the country, and there are various primary and secondary schools with football teams across Sierra Leone.
The Sierra Leone national football team, popularly known as the Leone Stars, represents the country in international competitions. It has never qualified for the FIFA World Cup but participated in the 1994 African Cup of Nations, 1994 and 1996 African Cup of Nations. When the national football team, the Leone Stars, have a match, Sierra Leoneans across the country come together united in support of the national team and people rush to their local radio and television stations to follow the live match. The country's national television network, The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC) broadcasts the national football team live match, along with many local radio stations across the country.
When the Leone Stars win an important match, many youth across the county rush to the street to celebrate. Many of the Sierra Leone national team footballers play for teams based in Europe although virtually all of them started professional football in the Sierra Leone National Premier League. Many of the national team footballers are celebrities across Sierra Leone and they are often well known by the general population. Some of Sierra Leonean international footballers include Mohamed Kallon, Mohamed Bangura (footballer), Mohamed Bangura, Rodney Strasser, Kei Kamara, Ibrahim Teteh Bangura, Mustapha Dumbuya, Christian Caulker, Al Bangura, Alhassan Bangura, Sheriff Suma, Osman Kakay, Mohamed Kamara, Umaru Bangura and Julius Wobay, Julius Gibrilla Woobay.
The Sierra Leone National Premier League is the top professional football league in Sierra Leone and is controlled by the Sierra Leone Football Association. Fourteen clubs from across the country compete in the Sierra Leone Premier League. The two biggest and most successful football clubs are East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool. East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool have an intense rivalry and when they play each other the national stadium in Freetown is often sold out and supporters of both clubs often clash with each other before and after the game. There is a huge police presence inside and outside the national stadium during a match between the two great rivals to prevent a clash. Many Sierra Leonean youth follow the local football league.
Many Sierra Leonean youth, children and adults follow the major football leagues in Europe, particularly the English Premier League, Italian Serie A, Spanish La Liga, German Bundesliga and French Ligue 1.
The Sierra Leone cricket team represents Sierra Leone in international cricket competitions and is among the best in West Africa. It became an affiliate member of the International Cricket Council in 2002. It made its international debut at the 2004 African Affiliates Championship, where it finished last of eight teams. But at the equivalent tournament in 2006, Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League, it finished as runner-up to Mozambique, and just missed promotion to Division Two.
In 2009, the Sierra Leone Under-19 team finished second in the African Under-19 Championship in Zambia, thus qualifying for the Under-19 World Cup qualifying tournament with nine other teams. However, the team was unable to obtain Canadian visas to play in the tournament, which was held in Toronto.
Sierra Leone is the first African country to join the International Floorball Federation.
Association football is by far the most popular sport in Sierra Leone. Children, youth and adult are frequently seen playing street football across Sierra Leone. There are organised youth and adult football tournaments across the country, and there are various primary and secondary schools with football teams across Sierra Leone.
The Sierra Leone national football team, popularly known as the Leone Stars, represents the country in international competitions. It has never qualified for the FIFA World Cup but participated in the 1994 African Cup of Nations, 1994 and 1996 African Cup of Nations. When the national football team, the Leone Stars, have a match, Sierra Leoneans across the country come together united in support of the national team and people rush to their local radio and television stations to follow the live match. The country's national television network, The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC) broadcasts the national football team live match, along with many local radio stations across the country.
When the Leone Stars win an important match, many youth across the county rush to the street to celebrate. Many of the Sierra Leone national team footballers play for teams based in Europe although virtually all of them started professional football in the Sierra Leone National Premier League. Many of the national team footballers are celebrities across Sierra Leone and they are often well known by the general population. Some of Sierra Leonean international footballers include Mohamed Kallon, Mohamed Bangura (footballer), Mohamed Bangura, Rodney Strasser, Kei Kamara, Ibrahim Teteh Bangura, Mustapha Dumbuya, Christian Caulker, Al Bangura, Alhassan Bangura, Sheriff Suma, Osman Kakay, Mohamed Kamara, Umaru Bangura and Julius Wobay, Julius Gibrilla Woobay.
The Sierra Leone National Premier League is the top professional football league in Sierra Leone and is controlled by the Sierra Leone Football Association. Fourteen clubs from across the country compete in the Sierra Leone Premier League. The two biggest and most successful football clubs are East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool. East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool have an intense rivalry and when they play each other the national stadium in Freetown is often sold out and supporters of both clubs often clash with each other before and after the game. There is a huge police presence inside and outside the national stadium during a match between the two great rivals to prevent a clash. Many Sierra Leonean youth follow the local football league.
Many Sierra Leonean youth, children and adults follow the major football leagues in Europe, particularly the English Premier League, Italian Serie A, Spanish La Liga, German Bundesliga and French Ligue 1.
The Sierra Leone cricket team represents Sierra Leone in international cricket competitions and is among the best in West Africa. It became an affiliate member of the International Cricket Council in 2002. It made its international debut at the 2004 African Affiliates Championship, where it finished last of eight teams. But at the equivalent tournament in 2006, Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League, it finished as runner-up to Mozambique, and just missed promotion to Division Two.
In 2009, the Sierra Leone Under-19 team finished second in the African Under-19 Championship in Zambia, thus qualifying for the Under-19 World Cup qualifying tournament with nine other teams. However, the team was unable to obtain Canadian visas to play in the tournament, which was held in Toronto.
Sierra Leone is the first African country to join the International Floorball Federation.
Tourism
Sierra Leone's Freetown is a favourite destination for tourists. Although the sector was seriously affected during the Civil War, there has been a steady improvement in recent years.[Sylvester Gasopan Goba (August 2014]
Sierra Leone Tourism: sector overview
International Growth Centre
Archived
Retrieved 18 November 2021. The city has a lot to offer to tourists. There is a vast expanse of beaches stretching along the Freetown Peninsula. The Lumley-Aberdeen beach stretches all the way from Cape Sierra Leone down to Lumley. There are also other popular beaches like the world renowned River Number 2 Beach, Laka Beach, Tokeh Beach, Bureh Beach, and Mama Beach. The Tacugama Chimpanzee Sanctuary, which is located within the peninsula's vast rainforest reserve, just a few kilometres from the centre of Freetown, has a collection of rare and endangered chimpanzees. Other popular destinations for tourists include the Freetown Cotton Tree, located in Central Freetown, a significant national monument and integral to the founding of the city; Bunce Island, which is a boat ride from the city, is home to the ruins of the slave fortress that was being used during the Transatlantic slave trade; the Sierra Leone Museum, which has a collection of both precolonial as well as colonial artifacts and other items of historical significance; the National Railway Museum; or take a journey around the city's coastline with the popular Sea Coach Express. The Aberdenn-Lumley area is a favourite destination for those venturing into the city's nightlife.
See also
* Outline of Sierra Leone
Notes
References
Further reading
*
* Harris, David (2012)
''Civil War and Democracy in West Africa: Conflict Resolution, Elections and Justice in Sierra Leone and Liberia''
I.B. Tauris.
* Imodale Caulker-Burnett
''The Caulkers of Sierra Leone: The Story of a Ruling Family and Their Times''
(Xlibris, 2010)
*
*
*
*
*
Fiction and memoir
* Massucco W
''Life does not lose its value/La Vita non perde valore''
documentary, Bluindaco Productions, 2012. La vita non perde valore, Link: ''La vita non perde valore''.
* Bonnet, Laurent
''Salone, a novel en Terre Krio''
Vents d'Ailleurs, 2012
* Ishmael Beah, Beah, Ishmael. ''A Long Way Gone: Memoirs of a Boy Soldier'' (2007). Sarah Crichton Books: New York. A Long Way Gone, Link: ''A Long Way Gone''.
* Delia Jarrett-Macauley, Jarrett-Macauley, Delia, ''Moses, Citizen & Me'' – novel, Granta Books (2005), . Winner of the Orwell Prize 2006.
''The Peace Corps, Sierra Leone, and Me''
Secondary sources
*
External links
; Government
The Republic of Sierra Leone
official government site
Ministry of Mineral Resources
official government minerals site
thepatrioticvanguard.com ''The Patriotic Vanguard''
– official government newspaper
;General information
Country Profile
BBC News
Sierra Leone
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Sierra Leone
''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
*
*
*
Key Development Forecasts for Sierra Leone
International Futures
;News media
''Awareness Times''
Newspaper
''The New People''
Newspaper
News headline links
AllAfrica.com
Sierra Leone News & Blog
, Current Sierra Leone News & Blog
;Trade
Sierra Leone 2002 Summary Trade Statistics
; Tourism
Sierra Leone National Tourist Board
Official Government site
; Telecommunication
Sierra Leone
telecom
; Other
Friends of Sierra Leone
Schools for Salone
non-profit dedicated to rebuilding schools
ENCISS
civil society and governance
The Auradicals Club
Student Club in Fourah Bay College
Sierra Leone Web
''Sweet Salone''
2008 film on new music in Sierra Leone
War Crimes Trials in Sierra Leone
Hurrarc – Human Rights Respect Awareness Raising Campaigners
Sierra Leone NGO
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20140629064622/http://www.storiesfromlakkabeach.com/ ''Stories from Lakka Beach''], 2011 documentary about life in a post-conflict beach town
{{Authority control
Sierra Leone,
1961 establishments in Sierra Leone
Countries in Africa
Economic Community of West African States
English-speaking countries and territories
Least developed countries
Member states of the African Union
Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Member states of the United Nations
Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations
States and territories established in 1961
West African countries


 Archaeological finds show that Sierra Leone has been inhabited continuously for at least 2,500 years; populated successively by societies who migrated from other parts of Africa. The use of iron was adopted by the ninth century, and by 1000 AD, agriculture was being practised along the coast. Over time, the climate changed considerably, altering boundaries between different ecological zones, affecting migration and conquest.
Sierra Leone's dense
Archaeological finds show that Sierra Leone has been inhabited continuously for at least 2,500 years; populated successively by societies who migrated from other parts of Africa. The use of iron was adopted by the ninth century, and by 1000 AD, agriculture was being practised along the coast. Over time, the climate changed considerably, altering boundaries between different ecological zones, affecting migration and conquest.
Sierra Leone's dense  The settlement of Sierra Leone in the 1800s was unique in that the population was composed of displaced Africans who were brought to the colony after the British abolition of the slave trade in 1807. Upon arrival in Sierra Leone, each ''recaptive'' was given a registration number, and information on their physical qualities would be entered into the Register of Liberated Africans. Oftentimes the documentation would be overwhelmingly subjective and would result in inaccurate entries, making them difficult to track. In addition, differences between the Register of Liberated Africans of 1808 and the List of Captured Negroes of 1812 (which emulated the 1808 document) revealed some disparities in the entries of the recaptives, specifically in the names; many recaptives decided to change their given names to more anglicised versions which contributed to the difficulty in tracking them after they arrived in Sierra Leone.
In the early 19th century, Freetown served as the residence of the British colonial governor of the region, who also administered the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast (now Ghana) and the Gambia settlements. Sierra Leone developed as the educational centre of British West Africa. The British established
The settlement of Sierra Leone in the 1800s was unique in that the population was composed of displaced Africans who were brought to the colony after the British abolition of the slave trade in 1807. Upon arrival in Sierra Leone, each ''recaptive'' was given a registration number, and information on their physical qualities would be entered into the Register of Liberated Africans. Oftentimes the documentation would be overwhelmingly subjective and would result in inaccurate entries, making them difficult to track. In addition, differences between the Register of Liberated Africans of 1808 and the List of Captured Negroes of 1812 (which emulated the 1808 document) revealed some disparities in the entries of the recaptives, specifically in the names; many recaptives decided to change their given names to more anglicised versions which contributed to the difficulty in tracking them after they arrived in Sierra Leone.
In the early 19th century, Freetown served as the residence of the British colonial governor of the region, who also administered the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast (now Ghana) and the Gambia settlements. Sierra Leone developed as the educational centre of British West Africa. The British established  The British interacted mostly with the Krios in Freetown, who did most of the trading with the indigenous peoples of the interior. Educated Krios held numerous positions in the colonial government, giving them status and well-paying positions. Following the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the British decided that they needed to establish more dominion over the inland areas, to satisfy what was described by the European powers as "effective occupation" of territories. In 1896 it annexed these areas, declaring them the Sierra Leone Protectorate.Harris, David (2012)
The British interacted mostly with the Krios in Freetown, who did most of the trading with the indigenous peoples of the interior. Educated Krios held numerous positions in the colonial government, giving them status and well-paying positions. Following the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the British decided that they needed to establish more dominion over the inland areas, to satisfy what was described by the European powers as "effective occupation" of territories. In 1896 it annexed these areas, declaring them the Sierra Leone Protectorate.Harris, David (2012) Colonel Frederic Cardew, military governor of the Protectorate, in 1898 established a new tax on dwellings and demanded that the chiefs use their people to maintain roads. The taxes were often higher than the value of the dwellings, and 24 chiefs signed a petition to Cardew, stating how destructive this was; their people could not afford to take time off from their subsistence agriculture. They resisted payment of taxes, tensions over the new colonial requirements and the administration's suspicions towards the chiefs, led to the Hut Tax War of 1898, Hut Tax war of 1898, also called the Temne-Mende War. The British fired first; the northern front of mainly Temne people was led by Bai Bureh. The southern front, consisting mostly of Mende people, entered the conflict somewhat later, for other reasons.
For several months, Bureh's fighters had the advantage over the vastly more powerful British forces but both sides suffered hundreds of fatalities. Bureh surrendered on 11 November 1898 to end the destruction of his people's territory and dwellings. Although the British government recommended leniency, Cardew insisted on sending the chief and two allies into exile in the Gold Coast; his government hanged 96 of the chief's warriors. Bureh was allowed to return in 1905, when he resumed his chieftaincy of Kasseh. The defeat of the Temne and Mende in the Hut Tax war ended mass resistance to the Protectorate and colonial government, but intermittent rioting and labour unrest continued throughout the colonial period. Riots in 1955 and 1956 involved "tens of thousands" of Sierra Leoneans in the Protectorate.
Colonel Frederic Cardew, military governor of the Protectorate, in 1898 established a new tax on dwellings and demanded that the chiefs use their people to maintain roads. The taxes were often higher than the value of the dwellings, and 24 chiefs signed a petition to Cardew, stating how destructive this was; their people could not afford to take time off from their subsistence agriculture. They resisted payment of taxes, tensions over the new colonial requirements and the administration's suspicions towards the chiefs, led to the Hut Tax War of 1898, Hut Tax war of 1898, also called the Temne-Mende War. The British fired first; the northern front of mainly Temne people was led by Bai Bureh. The southern front, consisting mostly of Mende people, entered the conflict somewhat later, for other reasons.
For several months, Bureh's fighters had the advantage over the vastly more powerful British forces but both sides suffered hundreds of fatalities. Bureh surrendered on 11 November 1898 to end the destruction of his people's territory and dwellings. Although the British government recommended leniency, Cardew insisted on sending the chief and two allies into exile in the Gold Coast; his government hanged 96 of the chief's warriors. Bureh was allowed to return in 1905, when he resumed his chieftaincy of Kasseh. The defeat of the Temne and Mende in the Hut Tax war ended mass resistance to the Protectorate and colonial government, but intermittent rioting and labour unrest continued throughout the colonial period. Riots in 1955 and 1956 involved "tens of thousands" of Sierra Leoneans in the Protectorate.
 Domestic Slavery in Africa, slavery, which continued to be practised by local African elites, was abolished in 1928. A notable event in 1935 was the granting of a monopoly on mineral mining to the Sierra Leone Selection Trust, run by De Beers. The monopoly was scheduled to last 98 years. Mining of diamonds in the east and other minerals expanded, drawing labourers there from other parts of the country.
In 1924, the UK government divided the administration of Sierra Leone into Colony and Protectorate, with different political systems constitutionally defined for each. The Colony was Freetown and its coastal area; the Protectorate was defined as the hinterland areas dominated by local chiefs. Antagonism between the two entities escalated to a heated debate in 1947, when proposals were introduced to provide for a single political system for both the Colony and the Protectorate. Most of the proposals came from leaders of the Protectorate, whose population far outnumbered that in the colony. The Krios, led by I. T. A. Wallace-Johnson, Isaac Wallace-Johnson, opposed the proposals, as they would have resulted in reducing the political power of the Krios in the Colony.
In 1951, Lamina Sankoh (''born'': Etheldred Jones) collaborated with educated protectorate leaders from different groups, including Sir Milton Margai,
Domestic Slavery in Africa, slavery, which continued to be practised by local African elites, was abolished in 1928. A notable event in 1935 was the granting of a monopoly on mineral mining to the Sierra Leone Selection Trust, run by De Beers. The monopoly was scheduled to last 98 years. Mining of diamonds in the east and other minerals expanded, drawing labourers there from other parts of the country.
In 1924, the UK government divided the administration of Sierra Leone into Colony and Protectorate, with different political systems constitutionally defined for each. The Colony was Freetown and its coastal area; the Protectorate was defined as the hinterland areas dominated by local chiefs. Antagonism between the two entities escalated to a heated debate in 1947, when proposals were introduced to provide for a single political system for both the Colony and the Protectorate. Most of the proposals came from leaders of the Protectorate, whose population far outnumbered that in the colony. The Krios, led by I. T. A. Wallace-Johnson, Isaac Wallace-Johnson, opposed the proposals, as they would have resulted in reducing the political power of the Krios in the Colony.
In 1951, Lamina Sankoh (''born'': Etheldred Jones) collaborated with educated protectorate leaders from different groups, including Sir Milton Margai,  Stevens assumed power as Prime Minister again in 1968, following a series of coups, with a great deal of hope and ambition. Much trust was placed upon him as he championed multi-party politics. Stevens had campaigned on a platform of bringing the tribes together under socialist principles. During his first decade or so in power, Stevens renegotiated some of what he called "useless prefinanced schemes" contracted by his predecessors, both Albert Margai of the SLPP and Juxon-Smith of the NRC. Some of these policies by the SLPP and the NRC were said to have left the country in an economically deprived state.
Stevens reorganised the country's oil refinery, the government-owned Cape Sierra Hotel, and a cement factory. He cancelled Juxon-Smith's construction of a church and mosque on the grounds of Victoria Park (now known as ''Freetown Amusement Park'' – since 2017). Stevens began efforts that would later improve transportation and movements between the provinces and the city of Freetown. Roads and hospitals were constructed in the provinces, and Paramount Chiefs and provincial peoples became a prominent force in Freetown.
Under the pressure of several coup attempts, real or perceived, Stevens' rule grew more and more authoritarian, and his relationship with some of his ardent supporters deteriorated. He removed the SLPP party from competitive politics in general elections, some believed, through the use of violence and intimidation. To maintain the support of the military, Stevens retained the popular John Amadu Bangura as head of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces.
After the return to civilian rule, by-elections were held (beginning in autumn 1968) and an all-APC cabinet was appointed. Calm was not completely restored. In November 1968, unrest in the provinces led Stevens to declare a state of emergency across the country. Many senior officers in the Sierra Leone Army were greatly disappointed with Stevens' policies and his handling of the Sierra Leone Military, but none could confront Stevens. Brigadier General Bangura, who had reinstated Stevens as Prime Minister, was widely considered the only person who could control Stevens. The army was devoted to Bangura, and this made him potentially dangerous to Stevens. In January 1970, Bangura was arrested and charged with Conspiracy (crime), conspiracy and plotting to commit a coup against the Stevens government. After a trial that lasted a few months, Bangura was convicted and Capital punishment, sentenced to death. On 29 March 1970, Brigadier Bangura was executed by hanging in Freetown.
After the execution of Bangura, a group of soldiers loyal to the executed general held a mutiny in Freetown and other parts of the country in opposition to Stevens' government. Dozens of soldiers were arrested and convicted by a court martial in Freetown for their participation in the mutiny against the president. Among the soldiers arrested was a little-known army corporal, Foday Sankoh, a strong Bangura supporter, who would later form the Revolutionary United Front, Revolutionary United Front (RUF). Corporal Sankoh was convicted and jailed for seven years at the Pademba Road Prison in Freetown.
In April 1971, a new republican constitution was adopted under which Stevens became president. In the 1972 by-elections, the opposition SLPP complained of intimidation and procedural obstruction by the APC and militia. These problems became so severe that the SLPP boycotted the Sierra Leonean general election, 1973, 1973 general election; as a result the APC won 84 of the 85 elected seats.
An alleged plot to overthrow president Stevens failed in 1974 and its leaders were executed. In mid-1974, Guinean soldiers, as requested by Stevens, were stationed in the country to help maintain his hold on power, as Stevens was a close ally of then-Guinean president Ahmed Sékou Touré. In March 1976, Stevens was elected without opposition for a second five-year term as president. On 19 July 1975, 14 senior army and government officials, including David Lansana, former cabinet minister Mohamed Sorie Forna (father of writer Aminatta Forna), Brigadier General Ibrahim Bash Taqi and Lieutenant Habib Lansana Kamara were executed after being convicted of attempting a coup to topple president Stevens' government.
In 1977, a nationwide student demonstration against the government disrupted Sierra Leone politics. The demonstration was quickly put down by the army and Stevens' own personal Special Security Division (SSD), a heavily armed paramilitary force he had created to protect him and maintain his hold on power. SSD officers were loyal to Stevens and were deployed across the country to clamp down on any rebellion or protest against Stevens' government. Sierra Leonean parliamentary election, 1977, A general election was called later that year in which corruption was again endemic; the APC won 74 seats and the SLPP 15. In 1978, the APC-dominant parliament approved a new constitution making the country a one-party state. The 1978 constitution made the APC the only legal political party in Sierra Leone.Gberie, Lansana (1998).
Stevens assumed power as Prime Minister again in 1968, following a series of coups, with a great deal of hope and ambition. Much trust was placed upon him as he championed multi-party politics. Stevens had campaigned on a platform of bringing the tribes together under socialist principles. During his first decade or so in power, Stevens renegotiated some of what he called "useless prefinanced schemes" contracted by his predecessors, both Albert Margai of the SLPP and Juxon-Smith of the NRC. Some of these policies by the SLPP and the NRC were said to have left the country in an economically deprived state.
Stevens reorganised the country's oil refinery, the government-owned Cape Sierra Hotel, and a cement factory. He cancelled Juxon-Smith's construction of a church and mosque on the grounds of Victoria Park (now known as ''Freetown Amusement Park'' – since 2017). Stevens began efforts that would later improve transportation and movements between the provinces and the city of Freetown. Roads and hospitals were constructed in the provinces, and Paramount Chiefs and provincial peoples became a prominent force in Freetown.
Under the pressure of several coup attempts, real or perceived, Stevens' rule grew more and more authoritarian, and his relationship with some of his ardent supporters deteriorated. He removed the SLPP party from competitive politics in general elections, some believed, through the use of violence and intimidation. To maintain the support of the military, Stevens retained the popular John Amadu Bangura as head of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces.
After the return to civilian rule, by-elections were held (beginning in autumn 1968) and an all-APC cabinet was appointed. Calm was not completely restored. In November 1968, unrest in the provinces led Stevens to declare a state of emergency across the country. Many senior officers in the Sierra Leone Army were greatly disappointed with Stevens' policies and his handling of the Sierra Leone Military, but none could confront Stevens. Brigadier General Bangura, who had reinstated Stevens as Prime Minister, was widely considered the only person who could control Stevens. The army was devoted to Bangura, and this made him potentially dangerous to Stevens. In January 1970, Bangura was arrested and charged with Conspiracy (crime), conspiracy and plotting to commit a coup against the Stevens government. After a trial that lasted a few months, Bangura was convicted and Capital punishment, sentenced to death. On 29 March 1970, Brigadier Bangura was executed by hanging in Freetown.
After the execution of Bangura, a group of soldiers loyal to the executed general held a mutiny in Freetown and other parts of the country in opposition to Stevens' government. Dozens of soldiers were arrested and convicted by a court martial in Freetown for their participation in the mutiny against the president. Among the soldiers arrested was a little-known army corporal, Foday Sankoh, a strong Bangura supporter, who would later form the Revolutionary United Front, Revolutionary United Front (RUF). Corporal Sankoh was convicted and jailed for seven years at the Pademba Road Prison in Freetown.
In April 1971, a new republican constitution was adopted under which Stevens became president. In the 1972 by-elections, the opposition SLPP complained of intimidation and procedural obstruction by the APC and militia. These problems became so severe that the SLPP boycotted the Sierra Leonean general election, 1973, 1973 general election; as a result the APC won 84 of the 85 elected seats.
An alleged plot to overthrow president Stevens failed in 1974 and its leaders were executed. In mid-1974, Guinean soldiers, as requested by Stevens, were stationed in the country to help maintain his hold on power, as Stevens was a close ally of then-Guinean president Ahmed Sékou Touré. In March 1976, Stevens was elected without opposition for a second five-year term as president. On 19 July 1975, 14 senior army and government officials, including David Lansana, former cabinet minister Mohamed Sorie Forna (father of writer Aminatta Forna), Brigadier General Ibrahim Bash Taqi and Lieutenant Habib Lansana Kamara were executed after being convicted of attempting a coup to topple president Stevens' government.
In 1977, a nationwide student demonstration against the government disrupted Sierra Leone politics. The demonstration was quickly put down by the army and Stevens' own personal Special Security Division (SSD), a heavily armed paramilitary force he had created to protect him and maintain his hold on power. SSD officers were loyal to Stevens and were deployed across the country to clamp down on any rebellion or protest against Stevens' government. Sierra Leonean parliamentary election, 1977, A general election was called later that year in which corruption was again endemic; the APC won 74 seats and the SLPP 15. In 1978, the APC-dominant parliament approved a new constitution making the country a one-party state. The 1978 constitution made the APC the only legal political party in Sierra Leone.Gberie, Lansana (1998).  In October 1990, owing to mounting pressure from both within and outside the country for political and economic reforms, president Momoh set up a constitutional review commission to assess the 1978 one-party constitution. Based on the commission's recommendations, a constitution re-establishing a multi-party system was approved by the exclusive APC Parliament by a 60% majority vote, becoming effective on 1 October 1991. There was great suspicion that president Momoh was not serious about his promise of political reform, as APC rule continued to be increasingly marked by abuses of power.
The brutal civil war that was going on in neighbouring
In October 1990, owing to mounting pressure from both within and outside the country for political and economic reforms, president Momoh set up a constitutional review commission to assess the 1978 one-party constitution. Based on the commission's recommendations, a constitution re-establishing a multi-party system was approved by the exclusive APC Parliament by a 60% majority vote, becoming effective on 1 October 1991. There was great suspicion that president Momoh was not serious about his promise of political reform, as APC rule continued to be increasingly marked by abuses of power.
The brutal civil war that was going on in neighbouring  The judicial power of Sierra Leone is vested in the judiciary, headed by the Chief Justice of Sierra Leone and comprising the Supreme Court of Sierra Leone, which is the highest court in the country, meaning that its rulings, therefore, cannot be appealed against. Other courts include the High Court of Justice, the Court of Appeal, the magistrate courts, and traditional courts in rural villages. The president appoints and parliament approves Justices for the three courts. The Judiciary have jurisdiction in all civil and criminal matters throughout the country. The current acting chief justice of Sierra Leone is Desmond Babatunde Edwards.
The judicial power of Sierra Leone is vested in the judiciary, headed by the Chief Justice of Sierra Leone and comprising the Supreme Court of Sierra Leone, which is the highest court in the country, meaning that its rulings, therefore, cannot be appealed against. Other courts include the High Court of Justice, the Court of Appeal, the magistrate courts, and traditional courts in rural villages. The president appoints and parliament approves Justices for the three courts. The Judiciary have jurisdiction in all civil and criminal matters throughout the country. The current acting chief justice of Sierra Leone is Desmond Babatunde Edwards.
 Two-thirds of the population of Sierra Leone are directly involved in subsistence agriculture. Agriculture accounted for 58 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2007.
Agriculture is the largest employer with 80 per cent of the population working in the sector. Rice is the most important staple crop in Sierra Leone with 85 per cent of farmers cultivating rice during the rainy season and an annual consumption of 76 kg per person.
Two-thirds of the population of Sierra Leone are directly involved in subsistence agriculture. Agriculture accounted for 58 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2007.
Agriculture is the largest employer with 80 per cent of the population working in the sector. Rice is the most important staple crop in Sierra Leone with 85 per cent of farmers cultivating rice during the rainy season and an annual consumption of 76 kg per person.
 There are several systems of transport in Sierra Leone, which has a road, air and water infrastructure, including a network of highways and several airports. There are of highways in Sierra Leone, of which are paved (about 8% of the roads). Sierra Leone's highways are linked to Conakry, Guinea, and Monrovia, Liberia.
Sierra Leone has the largest natural harbour on the African continent, allowing international shipping through the Queen Elizabeth II Quay in the Cline Town, Sierra Leone, Cline Town area of eastern Freetown or through Government Wharf in central Freetown. There are of waterways in Sierra Leone, of which are navigable year-round. Major port cities are Bonthe,
There are several systems of transport in Sierra Leone, which has a road, air and water infrastructure, including a network of highways and several airports. There are of highways in Sierra Leone, of which are paved (about 8% of the roads). Sierra Leone's highways are linked to Conakry, Guinea, and Monrovia, Liberia.
Sierra Leone has the largest natural harbour on the African continent, allowing international shipping through the Queen Elizabeth II Quay in the Cline Town, Sierra Leone, Cline Town area of eastern Freetown or through Government Wharf in central Freetown. There are of waterways in Sierra Leone, of which are navigable year-round. Major port cities are Bonthe,  In 2019 Sierra Leone had a population of 7,813,215 and a growth rate of 2.216% a year. The country's population is mostly young, with an estimated 41.7% under 15, and rural, with an estimated 62% of people living outside the cities. As a result of migration to cities, the population is becoming more urban with an estimated rate of urbanisation growth of 2.9% a year.
Population density varies greatly within Sierra Leone. The Western Area Urban District, including Freetown, the capital and largest city, has a population density of 1,224 persons per square km. The largest district geographically, Koinadugu District, Koinadugu, has a much lower density of 21.4 persons per square km.
English is the official language, spoken at schools, government administration and in the media. Krio (derived from English and several indigenous African languages, and the language of the Sierra Leone Krio people) is the most widely spoken language in virtually all parts of Sierra Leone. As the Krio language is spoken by 90% of the country's population, it unites all the different ethnic groups, especially in their trade and interaction with each other.
After the contribution made by the Bangladesh UN Peacekeeping Force in the Sierra Leone Civil War under the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone, the government of Ahmad Tejan Kabbah declared Bengali language, Bengali an honorary official language in December 2002.
According to the ''World Refugee Survey 2008'', published by the US Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, Sierra Leone had a population of 8,700 refugees and asylum seekers at the end of 2007. Nearly 20,000 Liberian refugees voluntarily returned to
In 2019 Sierra Leone had a population of 7,813,215 and a growth rate of 2.216% a year. The country's population is mostly young, with an estimated 41.7% under 15, and rural, with an estimated 62% of people living outside the cities. As a result of migration to cities, the population is becoming more urban with an estimated rate of urbanisation growth of 2.9% a year.
Population density varies greatly within Sierra Leone. The Western Area Urban District, including Freetown, the capital and largest city, has a population density of 1,224 persons per square km. The largest district geographically, Koinadugu District, Koinadugu, has a much lower density of 21.4 persons per square km.
English is the official language, spoken at schools, government administration and in the media. Krio (derived from English and several indigenous African languages, and the language of the Sierra Leone Krio people) is the most widely spoken language in virtually all parts of Sierra Leone. As the Krio language is spoken by 90% of the country's population, it unites all the different ethnic groups, especially in their trade and interaction with each other.
After the contribution made by the Bangladesh UN Peacekeeping Force in the Sierra Leone Civil War under the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone, the government of Ahmad Tejan Kabbah declared Bengali language, Bengali an honorary official language in December 2002.
According to the ''World Refugee Survey 2008'', published by the US Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, Sierra Leone had a population of 8,700 refugees and asylum seekers at the end of 2007. Nearly 20,000 Liberian refugees voluntarily returned to  Education in Sierra Leone is legally required for all children for six years at primary education, primary level (Class P1-P6) and three years in junior secondary education, but a shortage of schools and teachers has made implementation impossible. ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.'' Two thirds of the adult population of the country are illiterate.
The Sierra Leone Civil War resulted in the destruction of 1,270 primary schools, and in 2001, 67% of all school-age children were out of school. The situation has improved considerably since then with primary school enrolment doubling between 2001 and 2005 and the reconstruction of many schools since the end of the war. Students at primary schools are usually 6 to 12 years old, and in secondary schools 13 to 18. Primary education is free and Compulsory education, compulsory in government-sponsored Public school (government funded), public schools.
The country has three universities:
Education in Sierra Leone is legally required for all children for six years at primary education, primary level (Class P1-P6) and three years in junior secondary education, but a shortage of schools and teachers has made implementation impossible. ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.'' Two thirds of the adult population of the country are illiterate.
The Sierra Leone Civil War resulted in the destruction of 1,270 primary schools, and in 2001, 67% of all school-age children were out of school. The situation has improved considerably since then with primary school enrolment doubling between 2001 and 2005 and the reconstruction of many schools since the end of the war. Students at primary schools are usually 6 to 12 years old, and in secondary schools 13 to 18. Primary education is free and Compulsory education, compulsory in government-sponsored Public school (government funded), public schools.
The country has three universities: 
 Rice is the staple food of Sierra Leone and is consumed at virtually every meal daily. The rice is prepared in numerous ways, and topped with a variety of sauces made from some of Sierra Leone's favourite toppings, including potato leaves, cassava leaves, Corchorus, crain crain, okra soup, fried fish and peanut, groundnut stew.
Along the streets of towns and cities across Sierra Leone, one can find foods consisting of fruit, vegetables and snacks such as fresh mangoes, oranges, pineapple, fried Plantain (cooking), plantains, ginger beer, fried potato, fried cassava with pepper sauce; small bags of popcorn or peanuts, bread, roasted corn, or skewers of grilled meat or shrimp.
Poyo is a popular Sierra Leonean drink. It is a sweet, lightly fermented palm wine, and is found in bars in towns and villages across the country. Poyo bars are areas of lively informal debate about politics, Association football, football, basketball, entertainment and other issues.
Rice is the staple food of Sierra Leone and is consumed at virtually every meal daily. The rice is prepared in numerous ways, and topped with a variety of sauces made from some of Sierra Leone's favourite toppings, including potato leaves, cassava leaves, Corchorus, crain crain, okra soup, fried fish and peanut, groundnut stew.
Along the streets of towns and cities across Sierra Leone, one can find foods consisting of fruit, vegetables and snacks such as fresh mangoes, oranges, pineapple, fried Plantain (cooking), plantains, ginger beer, fried potato, fried cassava with pepper sauce; small bags of popcorn or peanuts, bread, roasted corn, or skewers of grilled meat or shrimp.
Poyo is a popular Sierra Leonean drink. It is a sweet, lightly fermented palm wine, and is found in bars in towns and villages across the country. Poyo bars are areas of lively informal debate about politics, Association football, football, basketball, entertainment and other issues.
 Media in Sierra Leone began with the introduction of the first printing press in Africa at the start of the 19th century. A strong free journalistic tradition developed with the creation of several newspapers. In the 1860s, the country became a journalist hub for Africa, with professionals travelling to the country from across the continent. At the end of the 19th century, the industry went into decline, and when radio was introduced in the 1930s, it became the primary communication media in the country.
The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Service (SLBS) was created by the colonial government in 1934 making it the earliest English language radio broadcaster service in West Africa. The service began broadcasting television in 1963, with coverage extended to all the districts in the country in 1978. In April 2010, the SLBS merged with the
Media in Sierra Leone began with the introduction of the first printing press in Africa at the start of the 19th century. A strong free journalistic tradition developed with the creation of several newspapers. In the 1860s, the country became a journalist hub for Africa, with professionals travelling to the country from across the continent. At the end of the 19th century, the industry went into decline, and when radio was introduced in the 1930s, it became the primary communication media in the country.
The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Service (SLBS) was created by the colonial government in 1934 making it the earliest English language radio broadcaster service in West Africa. The service began broadcasting television in 1963, with coverage extended to all the districts in the country in 1978. In April 2010, the SLBS merged with the  Radio is the most popular and most-trusted media in Sierra Leone, with 85% of people having access to a radio and 72% of people in the country listening to the radio daily. These levels do vary between areas of the country, with the Western Area having the highest levels and Kailahun the lowest. Stations mainly consist of local commercial stations with a limited broadcast range, combined with a few stations with national coverage – Capital Radio Sierra Leone being the largest of the commercial stations.
The United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNIOSIL) ran one of the most popular stations in the country, broadcasting programs in a range of languages. The UN mission was restructured in 2008 and it was decided that the United Nations Radio, UN Radio would be merged with SLBS to form the new Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC). This merger eventually happened in 2011 after the necessary legislation was enacted. SLBC transmits radio on FM broadcasting, FM and has two television services, one of which is uplinked by satellite for international consumption. FM relays of the BBC World Service (in Freetown, Bo, Kenema and Makeni), Radio France Internationale (Freetown only) and Voice of America (Freetown only) are also broadcast.
Outside the capital Freetown and other major cities, television is not watched by a great many people, although Bo, Kenema and Makeni are served by their own relays of the main SLBC service. There are three free terrestrial television stations in Sierra Leone, one run by the government SLBC and the other two are private stations in Freetown, Star TV which is run by the owner of the ''Standard-Times'' newspaper and AYV – Africa Young Voices. Several religious funded TV stations operate intermittently. Two other commercial TV operators (ABC and AIT) closed after they were not profitable. In 2007, a pay-per-view service was also introduced by GTV as part of a pan-African television service in addition to the nine-year-old sub-Saharan Digital satellite television service (DStv) originating from Multichoice Africa in South Africa. GTV subsequently went out of business, leaving DStv as the only provider of subscription satellite television in the country. Several organisations planned to operate digital terrestrial subscription TV services, with Multichoice's Go TV having built infrastructure ahead of getting a licence and ultimately failing to get a licence. ITV and SATCON are currently operational.
Internet access in Sierra Leone has been sparse but is on the increase, especially since the introduction of 3G/4G cellular phone services across the country. There are several main internet service providers (ISPs) operating in the country. Freetown has internet cafés and other businesses offering internet access. Problems experienced with access to the Internet include an intermittent electricity supply and a slow connection speed in the country outside Freetown.
Radio is the most popular and most-trusted media in Sierra Leone, with 85% of people having access to a radio and 72% of people in the country listening to the radio daily. These levels do vary between areas of the country, with the Western Area having the highest levels and Kailahun the lowest. Stations mainly consist of local commercial stations with a limited broadcast range, combined with a few stations with national coverage – Capital Radio Sierra Leone being the largest of the commercial stations.
The United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNIOSIL) ran one of the most popular stations in the country, broadcasting programs in a range of languages. The UN mission was restructured in 2008 and it was decided that the United Nations Radio, UN Radio would be merged with SLBS to form the new Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC). This merger eventually happened in 2011 after the necessary legislation was enacted. SLBC transmits radio on FM broadcasting, FM and has two television services, one of which is uplinked by satellite for international consumption. FM relays of the BBC World Service (in Freetown, Bo, Kenema and Makeni), Radio France Internationale (Freetown only) and Voice of America (Freetown only) are also broadcast.
Outside the capital Freetown and other major cities, television is not watched by a great many people, although Bo, Kenema and Makeni are served by their own relays of the main SLBC service. There are three free terrestrial television stations in Sierra Leone, one run by the government SLBC and the other two are private stations in Freetown, Star TV which is run by the owner of the ''Standard-Times'' newspaper and AYV – Africa Young Voices. Several religious funded TV stations operate intermittently. Two other commercial TV operators (ABC and AIT) closed after they were not profitable. In 2007, a pay-per-view service was also introduced by GTV as part of a pan-African television service in addition to the nine-year-old sub-Saharan Digital satellite television service (DStv) originating from Multichoice Africa in South Africa. GTV subsequently went out of business, leaving DStv as the only provider of subscription satellite television in the country. Several organisations planned to operate digital terrestrial subscription TV services, with Multichoice's Go TV having built infrastructure ahead of getting a licence and ultimately failing to get a licence. ITV and SATCON are currently operational.
Internet access in Sierra Leone has been sparse but is on the increase, especially since the introduction of 3G/4G cellular phone services across the country. There are several main internet service providers (ISPs) operating in the country. Freetown has internet cafés and other businesses offering internet access. Problems experienced with access to the Internet include an intermittent electricity supply and a slow connection speed in the country outside Freetown.
 Association football is by far the most popular sport in Sierra Leone. Children, youth and adult are frequently seen playing street football across Sierra Leone. There are organised youth and adult football tournaments across the country, and there are various primary and secondary schools with football teams across Sierra Leone.
The Sierra Leone national football team, popularly known as the Leone Stars, represents the country in international competitions. It has never qualified for the FIFA World Cup but participated in the 1994 African Cup of Nations, 1994 and 1996 African Cup of Nations. When the national football team, the Leone Stars, have a match, Sierra Leoneans across the country come together united in support of the national team and people rush to their local radio and television stations to follow the live match. The country's national television network, The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC) broadcasts the national football team live match, along with many local radio stations across the country.
When the Leone Stars win an important match, many youth across the county rush to the street to celebrate. Many of the Sierra Leone national team footballers play for teams based in Europe although virtually all of them started professional football in the Sierra Leone National Premier League. Many of the national team footballers are celebrities across Sierra Leone and they are often well known by the general population. Some of Sierra Leonean international footballers include Mohamed Kallon, Mohamed Bangura (footballer), Mohamed Bangura, Rodney Strasser, Kei Kamara, Ibrahim Teteh Bangura, Mustapha Dumbuya, Christian Caulker, Al Bangura, Alhassan Bangura, Sheriff Suma, Osman Kakay, Mohamed Kamara, Umaru Bangura and Julius Wobay, Julius Gibrilla Woobay.
The Sierra Leone National Premier League is the top professional football league in Sierra Leone and is controlled by the Sierra Leone Football Association. Fourteen clubs from across the country compete in the Sierra Leone Premier League. The two biggest and most successful football clubs are East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool. East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool have an intense rivalry and when they play each other the national stadium in Freetown is often sold out and supporters of both clubs often clash with each other before and after the game. There is a huge police presence inside and outside the national stadium during a match between the two great rivals to prevent a clash. Many Sierra Leonean youth follow the local football league.
Many Sierra Leonean youth, children and adults follow the major football leagues in Europe, particularly the English Premier League, Italian Serie A, Spanish La Liga, German Bundesliga and French Ligue 1.
The Sierra Leone cricket team represents Sierra Leone in international cricket competitions and is among the best in West Africa. It became an affiliate member of the International Cricket Council in 2002. It made its international debut at the 2004 African Affiliates Championship, where it finished last of eight teams. But at the equivalent tournament in 2006, Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League, it finished as runner-up to Mozambique, and just missed promotion to Division Two.
In 2009, the Sierra Leone Under-19 team finished second in the African Under-19 Championship in Zambia, thus qualifying for the Under-19 World Cup qualifying tournament with nine other teams. However, the team was unable to obtain Canadian visas to play in the tournament, which was held in Toronto.
Sierra Leone is the first African country to join the International Floorball Federation.
Association football is by far the most popular sport in Sierra Leone. Children, youth and adult are frequently seen playing street football across Sierra Leone. There are organised youth and adult football tournaments across the country, and there are various primary and secondary schools with football teams across Sierra Leone.
The Sierra Leone national football team, popularly known as the Leone Stars, represents the country in international competitions. It has never qualified for the FIFA World Cup but participated in the 1994 African Cup of Nations, 1994 and 1996 African Cup of Nations. When the national football team, the Leone Stars, have a match, Sierra Leoneans across the country come together united in support of the national team and people rush to their local radio and television stations to follow the live match. The country's national television network, The Sierra Leone Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC) broadcasts the national football team live match, along with many local radio stations across the country.
When the Leone Stars win an important match, many youth across the county rush to the street to celebrate. Many of the Sierra Leone national team footballers play for teams based in Europe although virtually all of them started professional football in the Sierra Leone National Premier League. Many of the national team footballers are celebrities across Sierra Leone and they are often well known by the general population. Some of Sierra Leonean international footballers include Mohamed Kallon, Mohamed Bangura (footballer), Mohamed Bangura, Rodney Strasser, Kei Kamara, Ibrahim Teteh Bangura, Mustapha Dumbuya, Christian Caulker, Al Bangura, Alhassan Bangura, Sheriff Suma, Osman Kakay, Mohamed Kamara, Umaru Bangura and Julius Wobay, Julius Gibrilla Woobay.
The Sierra Leone National Premier League is the top professional football league in Sierra Leone and is controlled by the Sierra Leone Football Association. Fourteen clubs from across the country compete in the Sierra Leone Premier League. The two biggest and most successful football clubs are East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool. East End Lions and Mighty Blackpool have an intense rivalry and when they play each other the national stadium in Freetown is often sold out and supporters of both clubs often clash with each other before and after the game. There is a huge police presence inside and outside the national stadium during a match between the two great rivals to prevent a clash. Many Sierra Leonean youth follow the local football league.
Many Sierra Leonean youth, children and adults follow the major football leagues in Europe, particularly the English Premier League, Italian Serie A, Spanish La Liga, German Bundesliga and French Ligue 1.
The Sierra Leone cricket team represents Sierra Leone in international cricket competitions and is among the best in West Africa. It became an affiliate member of the International Cricket Council in 2002. It made its international debut at the 2004 African Affiliates Championship, where it finished last of eight teams. But at the equivalent tournament in 2006, Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League, it finished as runner-up to Mozambique, and just missed promotion to Division Two.
In 2009, the Sierra Leone Under-19 team finished second in the African Under-19 Championship in Zambia, thus qualifying for the Under-19 World Cup qualifying tournament with nine other teams. However, the team was unable to obtain Canadian visas to play in the tournament, which was held in Toronto.
Sierra Leone is the first African country to join the International Floorball Federation.