Sexually-transmitted Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse,
 * Viral hepatitis ( hepatitis B virus)—saliva, venereal fluids.
* Viral hepatitis ( hepatitis B virus)—saliva, venereal fluids.
(Note: hepatitis A and hepatitis E are transmitted via the fecal-oral route;
 *
*
 Both partners can get tested for STIs before initiating sexual contact, or before resuming contact if a partner engaged in contact with someone else. Many infections are not detectable immediately after exposure, so enough time must be allowed between possible exposures and testing for the tests to be accurate. Certain STIs, particularly certain persistent viruses like HPV, may be impossible to detect.
Some treatment facilities use in-home test kits and have the person return the test for follow-up. Other facilities strongly encourage that those previously infected return to ensure that the infection has been eliminated. Novel strategies to foster re-testing have been the use of text messaging and email as reminders. These types of reminders are now used in addition to phone calls and letters. After obtaining a sexual history, a healthcare provider can encourage risk reduction by providing prevention
Both partners can get tested for STIs before initiating sexual contact, or before resuming contact if a partner engaged in contact with someone else. Many infections are not detectable immediately after exposure, so enough time must be allowed between possible exposures and testing for the tests to be accurate. Certain STIs, particularly certain persistent viruses like HPV, may be impossible to detect.
Some treatment facilities use in-home test kits and have the person return the test for follow-up. Other facilities strongly encourage that those previously infected return to ensure that the infection has been eliminated. Novel strategies to foster re-testing have been the use of text messaging and email as reminders. These types of reminders are now used in addition to phone calls and letters. After obtaining a sexual history, a healthcare provider can encourage risk reduction by providing prevention
STAT!Ref Online Electronic Medical Library
sup> ubscription required/sup> An option for treating partners of patients ( index cases) diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea is
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention

 In 2008, it was estimated that 500 million people were infected with either syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia or trichomoniasis. At least an additional 530 million people have genital herpes and 290 million women have human papillomavirus. STIs other than HIV resulted in 142,000 deaths in 2013. In the United States there were 19 million new cases of sexually transmitted infections in 2010.
In 2010, 19 million new cases of sexually transmitted infections occurred in women in the United States. A 2008
In 2008, it was estimated that 500 million people were infected with either syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia or trichomoniasis. At least an additional 530 million people have genital herpes and 290 million women have human papillomavirus. STIs other than HIV resulted in 142,000 deaths in 2013. In the United States there were 19 million new cases of sexually transmitted infections in 2010.
In 2010, 19 million new cases of sexually transmitted infections occurred in women in the United States. A 2008
 The first well-recorded European outbreak of what is now known as syphilis occurred in 1494 when it broke out among French troops besieging Naples in the Italian War of 1494–98. The disease may have originated from the
The first well-recorded European outbreak of what is now known as syphilis occurred in 1494 when it broke out among French troops besieging Naples in the Italian War of 1494–98. The disease may have originated from the
AIM25
London Lock Hospital records
/ref> Treatment was not always voluntary: in the second half of the 19th century, the Contagious Diseases Acts were used to arrest suspected prostitutes. In 1924, a number of states concluded the Brussels Agreement, whereby states agreed to provide free or low-cost medical treatment at ports for merchant seamen with venereal diseases. A proponent of these approaches was Dr.
 *
*
*
*
CDC Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2010
STD photo library
at
UNFPA: Breaking the Cycle of Sexually Transmitted Infections
at UNFPA
STDs In Color: Sexually Transmitted Disease Facts and Photos
Sexually transmitted diseases in the U.S.
STI Watch: World Health Organization
{{authority control Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Mycoplasma Disease transmission
anal sex
Anal sex or anal intercourse is generally the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure.Sepages 270–271for anal sex information, anpage 118for information about the clitoris. ...
, and oral sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of passing the infection on to others. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge
Penile discharge is fluid that comes from the urethra at the end of the penis that is not urine, precum or semen.
Common causes include infections due to gonorrhea, chlamydia, or trichomoniasis. In gonorrhea the discharge may be white, yellow, ...
, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis.
Common causes in include ...
. Some STIs can cause infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state ...
.
Bacterial STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis
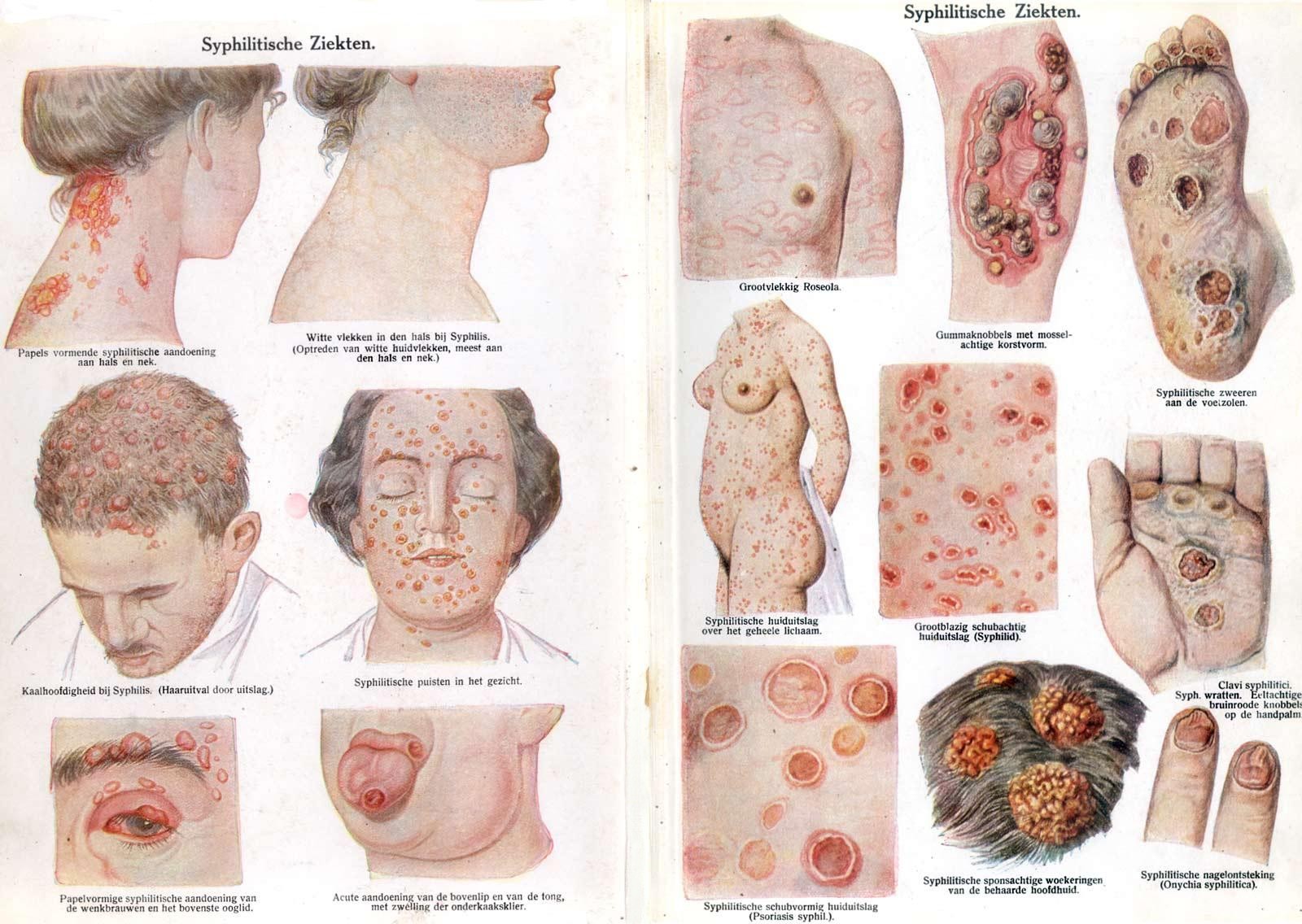
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
. Viral STIs include genital herpes, HIV/AIDS, and genital warts. Parasitic STIs include trichomoniasis. STI diagnostic tests are usually easily available in the developed world, but they are often unavailable in the developing world.
Some vaccinations may also decrease the risk of certain infections including hepatitis B and some types of HPV
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and re ...
. Safe sex
Safe sex is sexual activity using methods or contraceptive devices (such as condoms) to reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially HIV. "Safe sex" is also sometimes referred to as safer se ...
practices, such as use of condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s, having a smaller number of sexual partners, and being in a relationship in which each person only has sex with the other also decreases the risk of STIs. Comprehensive sex education may also be useful. Most STIs are treatable and curable; of the most common infections, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis are curable, while HIV/AIDS and genital herpes are not curable.
In 2015, about 1.1 billion people had STIs other than HIV/AIDS. About 500 million were infected with either syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia or trichomoniasis. At least an additional 530 million people have genital herpes, and 290 million women have human papillomavirus. STIs other than HIV resulted in 108,000 deaths in 2015. In the United States, there were 19 million new cases of STIs in 2010. Historical documentation of STIs in antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
dates back to at least the Ebers Papyrus () and the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
(8th/7th centuries BCE).
There is often shame and stigma associated with STIs. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes those who do not have symptomatic disease.
Signs and symptoms
Not all STIs aresymptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
atic, and symptoms may not appear immediately after infection. In some instances a disease can be carried with no symptoms, which leaves a greater risk of passing the disease on to others. Depending on the disease, some untreated STIs can lead to infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state ...
, chronic pain or death.
The presence of an STI in prepubescent children may indicate sexual abuse.
Cause
Transmission
A sexually transmitted infection present in a pregnant woman may be passed on to the infant before or after birth.Bacterial
*Chancroid
Chancroid ( ) is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidenta ...
('' Haemophilus ducreyi'')
* Chlamydia ('' Chlamydia trachomatis'')
* Gonorrhea (''Neisseria gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular), or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. It causes the sexually transmit ...
'')
* Granuloma inguinale or ('' Klebsiella granulomatis'')
* '' Mycoplasma genitalium''
* '' Mycoplasma hominis''
* Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
('' Treponema pallidum'')
* Ureaplasma infection
''Ureaplasma urealyticum'' is a type of bacteria that can cause infection of the urinary tract and vagina. It can be passed from mother to infant during birth, or be sexually transmitted. ''Ureaplasma urealyticum'' can be found in a majority o ...
Viral
 * Viral hepatitis ( hepatitis B virus)—saliva, venereal fluids.
* Viral hepatitis ( hepatitis B virus)—saliva, venereal fluids.(Note: hepatitis A and hepatitis E are transmitted via the fecal-oral route;
hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
is rarely sexually transmittable, and the route of transmission of hepatitis D (only if infected with B) is uncertain, but may include sexual transmission.)
* Herpes simplex (Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
1, 2) skin and mucosal, transmissible with or without visible blisters
* HIV (''Human Immunodeficiency Virus'')—venereal fluids, semen, breast milk, blood
* HPV
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and re ...
(''Human Papillomavirus'')—skin and mucosal contact. 'High risk' types of HPV cause almost all cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal ...
s, as well as some anal, penile
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do ...
, and vulvar cancer
Vulvar cancer is a cancer of the vulva, the outer portion of the female genitals. It most commonly affects the labia majora. Less often, the labia minora, clitoris, or vaginal glands are affected. Symptoms include a lump, itchiness, changes in t ...
. Some other types of HPV cause genital warts.
* Molluscum contagiosum (molluscum contagiosum virus
''Molluscum contagiosum virus'' (MCV) is a species of DNA virus, DNA poxvirus that causes the human skin infection molluscum contagiosum. Molluscum contagiosum affects about 200,000 people a year, about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. Diagnosi ...
MCV)—close contact
* Zika virus
Parasites
* Crab louse, colloquially known as "crabs" or "pubic lice" (''Pthirus pubis
The crab louse or pubic louse (''Pthirus pubis'') is an insect that is an obligate ectoparasite of humans, feeding exclusively on blood. The crab louse usually is found in the person's pubic hair. Although the louse cannot jump, it can also ...
''). The infestation and accompanying inflammation is Pediculosis pubis
* Scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin ...
('' Sarcoptes scabiei'')
* Trichomoniasis ('' Trichomonas vaginalis''), colloquially known as "trich"
Main types
Sexually transmitted infections include: * Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. In women, symptoms may include abnormal vaginal discharge, burning during urination, and bleeding in between periods, although most women do not experience any symptoms.King, B. (2009). Human Sexuality Today (Sixth ed.). Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc. Symptoms in men include pain when urinating, and abnormal discharge from their penis. If left untreated in both men and women, chlamydia can infect the urinary tract and potentially lead topelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
(PID). PID can cause serious problems during pregnancy and even has the potential to cause infertility. It can cause a woman to have a potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. ...
, in which the egg implants outside of the uterus. However, chlamydia can be cured with antibiotics.
* The two most common forms of herpes are caused by infection with herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
(HSV). HSV-1 is typically acquired orally and causes cold sores, HSV-2 is usually acquired during sexual contact and affects the genitals, however, either strain may affect either site. Some people are asymptomatic or have very mild symptoms. Those that do experience symptoms usually notice them 2 to 20 days after exposure which lasts 2 to 4 weeks. Symptoms can include small fluid-filled blisters, headaches, backaches, itching or tingling sensations in the genital or anal area, pain during urination, flu like symptoms
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, lo ...
, swollen glands, or fever. Herpes is spread through skin contact with a person infected with the virus. The virus affects the areas where it entered the body. This can occur through kissing, vaginal intercourse, oral sex or anal sex. The virus is most infectious during times when there are visible symptoms, however, those who are asymptomatic can still spread the virus through skin contact. The initial infection and symptoms are usually the most severe because the body does not have any antibodies built up. After the primary attack, one might have recurring attacks that are milder or might not even have future attacks. There is no cure for the disease but there are antiviral medications that treat its symptoms and lower the risk of transmission (Valtrex
Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken ...
). Although HSV-1 is typically the "oral" version of the virus, and HSV-2 is typically the "genital" version of the virus, a person with HSV-1 orally CAN transmit that virus to their partner genitally. The virus, either type, will settle into a nerve bundle either at the top of the spine, producing the "oral" outbreak, or a second nerve bundle at the base of the spine, producing the genital outbreak.
* The human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STI in the United States. There are more than 40 different strands of HPV and many do not cause any health problems. In 90% of cases, the body's immune system clears the infection naturally within two years. Some cases may not be cleared and can lead to genital warts (bumps around the genitals that can be small or large, raised or flat, or shaped like cauliflower) or cervical cancer and other HPV related cancers. Symptoms might not show up until advanced stages. It is important for women to get pap smears in order to check for and treat cancers. There are also two vaccines available for women ( Cervarix and Gardasil) that protect against the types of HPV that cause cervical cancer. HPV can be passed through genital-to-genital contact as well as during oral sex. The infected partner might not have any symptoms.
* Gonorrhea is caused by bacterium that lives on moist mucous membranes in the urethra, vagina, rectum, mouth, throat, and eyes. The infection can spread through contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus. Symptoms of gonorrhea usually appear two to five days after contact with an infected partner however, some men might not notice symptoms for up to a month. Symptoms in men include burning and pain while urinating, increased urinary frequency, discharge from the penis (white, green, or yellow in color), red or swollen urethra, swollen or tender testicles, or sore throat. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge, burning or itching while urinating, painful sexual intercourse, severe pain in lower abdomen (if infection spreads to fallopian tubes), or fever (if infection spreads to fallopian tubes); however, many women do not show any symptoms. Antibiotic resistant strains of Gonorrhea are a significant concern, but most cases can be cured with existing antibiotics.
 *
* Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
is an STI caused by a bacterium. Untreated, it can lead to complications and death. Clinical manifestations of syphilis include the ulceration of the uro-genital tract, mouth or rectum; if left untreated the symptoms worsen. In recent years, the prevalence of syphilis has declined in Western Europe, but it has increased in Eastern Europe (former Soviet states). A high incidence of syphilis can be found in places such as Cameroon, Cambodia, Papua New Guinea. Syphilis infections are increasing in the United States.
* Trichomoniasis is a common STI that is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. Trichomoniasis affects both women and men, but symptoms are more common in women. Most patients are treated with an antibiotic called metronidazole, which is very effective.
* HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) damages the body's immune system, which interferes with its ability to fight off disease-causing agents. The virus kills CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
cells, which are white blood cells that help fight off various infections. HIV is carried in body fluids and is spread by sexual activity. It can also be spread by contact with infected blood, breastfeeding, childbirth, and from mother to child during pregnancy. When HIV is at its most advanced stage, an individual is said to have AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
(acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). There are different stages of the progression of and HIV infection. The stages include primary infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, asymptomatic infection, symptomatic infection, and AIDS. In the primary infection stage, an individual will have flu-like symptoms (headache, fatigue, fever, muscle aches) for about two weeks. In the asymptomatic stage, symptoms usually disappear, and the patient can remain asymptomatic for years. When HIV progresses to the symptomatic stage, the immune system is weakened and has a low cell count of CD4+ T cells. When the HIV infection becomes life-threatening, it is called AIDS. People with AIDS fall prey to opportunistic infections and die as a result. When the disease was first discovered in the 1980s, those who had AIDS were not likely to live longer than a few years. There are now antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) available to treat HIV infections. There is no known cure for HIV or AIDS but the drugs help suppress the virus. By suppressing the amount of virus in the body, people can lead longer and healthier lives. Even though their virus levels may be low they can still spread the virus to others.
Viruses in semen
Twenty-seven different viruses have been identified in semen. Information on whether or not transmission occurs or whether the viruses cause disease is uncertain. Some of these microbes are known to be sexually transmitted.Pathophysiology
Many STIs are (more easily) transmitted through the mucous membranes of the penis, vulva,rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the s ...
, urinary tract and (less often—depending on type of infection) the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
, throat, respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
and eyes. The visible membrane covering the head of the penis is a mucous membrane, though it produces no mucus (similar to the lips of the mouth). Mucous membranes differ from skin in that they allow certain pathogens into the body. The amount of contact with infective sources which causes infection varies with each pathogen but in all cases, a disease may result from even light contact from fluid carriers like venereal fluids onto a mucous membrane.
Some STIs such as HIV can be transmitted from mother to child either during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Healthcare professionals suggest safer sex, such as the use of condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s, as a reliable way of decreasing the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases during sexual activity, but safer sex cannot be considered to provide complete protection from an STI. The transfer of and exposure to bodily fluids, such as blood transfusions and other blood products, sharing injection needles, needle-stick injuries (when medical staff are inadvertently jabbed or pricked with needles during medical procedures), sharing tattoo needles, and childbirth are other avenues of transmission. These different means put certain groups, such as medical workers, and haemophiliacs and drug users, particularly at risk.
It is possible to be an asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
carrier of sexually transmitted diseases. In particular, sexually transmitted diseases in women often cause the serious condition of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Diagnosis
Testing
An examination (exam or evaluation) or test is an educational assessment intended to measure a test-taker's knowledge, skill, aptitude, physical fitness, or classification in many other topics (e.g., beliefs). A test may be administered verba ...
may be for a single infection, or consist of a number of tests for a range of STIs, including tests for syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
, trichomonas
''Trichomonas'' is a genus of anaerobic excavate parasites of vertebrates. It was first discovered by Alfred François Donné in 1836 when he found these parasites in the pus of a patient suffering from vaginitis, an inflammation of the vagina. ...
, gonorrhea, chlamydia, herpes, hepatitis, and HIV. No procedure tests for all infectious agents.
STI tests may be used for a number of reasons:
* as a diagnostic test to determine the cause of symptoms or illness
* as a screening test to detect asymptomatic or presymptomatic infections
* as a check that prospective sexual partners are free of disease before they engage in sex without safer sex precautions (for example, when starting a long term mutually monogamous sexual relationship, in fluid bonding, or for procreation).
* as a check prior to or during pregnancy, to prevent harm to the baby
* as a check after birth, to check that the baby has not caught an STI from the mother
* to prevent the use of infected donated blood or organs
* as part of the process of contact tracing from a known infected individual
* as part of mass epidemiological surveillance
Early identification and treatment results in less chance to spread disease, and for some conditions may improve the outcomes of treatment. There is often a window period
In medicine, the window period for a test designed to detect a specific disease (particularly infectious disease) is the time between first infection and when the test can reliably detect that infection. In antibody-based testing, the window period ...
after initial infection during which an STI test will be negative. During this period, the infection may be transmissible. The duration of this period varies depending on the infection and the test. Diagnosis may also be delayed by reluctance of the infected person to seek a medical professional. One report indicated that people turn to the Internet rather than to a medical professional for information on STIs to a higher degree than for other sexual problems.
Classification
Until the 1990s, STIs were commonly known as ''venereal diseases'', an antiquatedeuphemism
A euphemism () is an innocuous word or expression used in place of one that is deemed offensive or suggests something unpleasant. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes ...
derived from the Latin , being the adjectival form of Venus, the Roman goddess
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, ''Roman mythology'' may also refer to the modern study of these representat ...
of love. However, in the post-classical education era the euphemistic effect was entirely lost, and the common abbreviation "VD" held only negative connotations. Other former euphemisms for STIs include "blood diseases" and "social diseases". The present euphemism is in the use of the initials "STI" rather than in the words they represent. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the more inclusive term ''sexually transmitted infection'' since 1999. Public health officials originally introduced the term ''sexually transmitted infection'', which clinicians are increasingly using alongside the term ''sexually transmitted disease'' in order to distinguish it from the former.
Prevention
Strategies for reducing STI risk include: vaccination,mutual monogamy
Mutual monogamy is a form of monogamy that exists when two partners agree to be sexually active with only one another. Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship reduces the risk of acquiring a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It i ...
, reducing the number of sexual partners, and abstinence. Behavioral counseling for all sexually active adolescents and for adults who are at increased risk. Such interactive counseling, which can be resource-intensive, is directed at a person's risk, the situations in which risk occurs, and the use of personalized goal-setting strategies.
The most effective way to prevent sexual transmission of STIs is to avoid contact of body parts or fluids which can lead to transfer with an infected partner. Not all sexual activities involve contact: cybersex, phone sex
Phone sex is a conversation between two or more people by means of the telephone which is sexually explicit and is intended to provoke sexual arousal in one or more participants. All parties participate voluntarily; it is typically accompanied ...
or masturbation
Masturbation is the sexual stimulation of one's own genitals for sexual arousal or other sexual pleasure, usually to the point of orgasm. The stimulation may involve hands, fingers, everyday objects, sex toys such as vibrators, or combinatio ...
from a distance are methods of avoiding contact. Proper use of condoms reduces contact and risk. Although a condom is effective in limiting exposure, some disease transmission may occur even with a condom. Both partners can get tested for STIs before initiating sexual contact, or before resuming contact if a partner engaged in contact with someone else. Many infections are not detectable immediately after exposure, so enough time must be allowed between possible exposures and testing for the tests to be accurate. Certain STIs, particularly certain persistent viruses like HPV, may be impossible to detect.
Some treatment facilities use in-home test kits and have the person return the test for follow-up. Other facilities strongly encourage that those previously infected return to ensure that the infection has been eliminated. Novel strategies to foster re-testing have been the use of text messaging and email as reminders. These types of reminders are now used in addition to phone calls and letters. After obtaining a sexual history, a healthcare provider can encourage risk reduction by providing prevention
Both partners can get tested for STIs before initiating sexual contact, or before resuming contact if a partner engaged in contact with someone else. Many infections are not detectable immediately after exposure, so enough time must be allowed between possible exposures and testing for the tests to be accurate. Certain STIs, particularly certain persistent viruses like HPV, may be impossible to detect.
Some treatment facilities use in-home test kits and have the person return the test for follow-up. Other facilities strongly encourage that those previously infected return to ensure that the infection has been eliminated. Novel strategies to foster re-testing have been the use of text messaging and email as reminders. These types of reminders are now used in addition to phone calls and letters. After obtaining a sexual history, a healthcare provider can encourage risk reduction by providing prevention counseling
Counseling is the professional guidance of the individual by utilizing psychological methods especially in collecting case history data, using various techniques of the personal interview, and testing interests and aptitudes.
This is a list of co ...
. Prevention counseling is most effective if provided in a nonjudgmental and empathetic manner appropriate to the person's culture, language, gender, sexual orientation, age, and developmental level. Prevention counseling for STIs is usually offered to all sexually active adolescents and to all adults who have received a diagnosis, have had an STI in the past year, or have multiple sex partners.
Vaccines
Vaccines are available that protect against some viral STIs, such as hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and some types ofHPV
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and re ...
. Vaccination before initiation of sexual contact is advised to assure maximal protection. The development of vaccines to protect against gonorrhea is ongoing.
Condoms
Condoms andfemale condom
An internal condom (also known as a femidom or female condom) is a barrier device that is used during sexual intercourse as a barrier contraceptive to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Meant as an al ...
s only provide protection when used properly as a barrier, and only to and from the area that they cover. Uncovered areas are still susceptible to many STIs.
In the case of HIV, sexual transmission routes almost always involve the penis, as HIV cannot spread through unbroken skin; therefore, properly shielding the penis with a properly worn condom from the vagina or anus effectively stops HIV transmission. An infected fluid to broken skin borne direct transmission of HIV would not be considered "sexually transmitted", but can still theoretically occur during sexual contact. This can be avoided simply by not engaging in sexual contact when presenting open, bleeding wounds.
Other STIs, even viral infections, can be prevented with the use of latex, polyurethane or polyisoprene condoms as a barrier. Some microorganisms and viruses are small enough to pass through the pores in natural skin condoms but are still too large to pass through latex or synthetic condoms.
Proper male condom usage entails:
* Not putting the condom on too tight at the tip by leaving room for ejaculation. Putting the condom on too tightly can and often does lead to failure.
* Wearing a condom too loose can defeat the barrier
* Avoiding inverting or spilling a condom once worn, whether it has ejaculate in it or not
* If a user attempts to unroll the condom, but realizes they have it on the wrong side, then this condom may not be effective
* Being careful with the condom if handling it with long nails
* Avoiding the use of oil-based lubricants (or anything with oil in it) with latex condoms, as oil can eat holes into them
* Using flavored condoms for oral sex only, as the sugar in the flavoring can lead to yeast infections if used to penetrate
In order to best protect oneself and the partner from STIs, the old condom and its contents are to be treated as infectious and properly disposed of. A new condom is used for each act of intercourse, as multiple usages increase the chance of breakage, defeating the effectiveness as a barrier.
In the case of female condoms, the device consists of two rings, one in each terminal portion. The larger ring should fit snugly over the cervix and the smaller ring remains outside the vagina, covering the vulva. This system provides some protection of the external genitalia.
Other
The cap was developed after the cervicaldiaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
. Both cover the cervix and the main difference between the diaphragm and the cap is that the latter must be used only once, using a new one in each sexual act. The diaphragm, however, can be used more than once. These two devices partially protect against STIs (they do not protect against HIV).
Researchers had hoped that nonoxynol-9, a vaginal microbicide would help decrease STI risk. Trials, however, have found it ineffective and it may put women at a higher risk of HIV infection. There is evidence that vaginal dapivirine
Dapivirine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor developed at Janssen Therapeutics (formerly Tibotec Therapeutics). The International Partnership for Microbicides has held exclusive worldwide rights to dapivirine since 2014, buildin ...
probably reduces HIV in women who have sex with men, other types of vaginal microbicides have not demonstrated effectiveness for HIV or STI's.
There is little evidence that school-based interventions such as sexual and reproductive health education programmes on contraceptive choices and condoms are effective on improving the sexual and reproductive health of adolescents. Incentive-based programmes may reduce adolescent pregnancy but more data is needed to confirm this.
Screening
Specific age groups, persons who participate in risky sexual behavior, or those have certain health conditions may require screening. The CDC recommends that sexually active women under the age of 25 and those over 25 at risk should be screened for chlamydia and gonorrhea yearly. Appropriate times for screening are during regular pelvic examinations and preconception evaluations.Nucleic acid amplification tests
A nucleic acid test (NAT) is a technique used to detect a particular nucleic acid sequence and thus usually to detect and identify a particular species or subspecies of organism, often a virus or bacterium that acts as a pathogen in blood, tiss ...
are the recommended method of diagnosis for gonorrhea and chlamydia. This can be done on either urine in both men and women, vaginal or cervical swabs in women, or urethral swabs in men. Screening can be performed:
* to assess the presence of infection and prevent tubal infertility in women
* during the initial evaluation before infertility treatment
* to identify HIV infection
* for men who have sex with men
* for those who may have been exposed to hepatitis C
* for HCV
Management
In the case of rape, the person can be treated prophylacticly with antibiotics. &nbsSTAT!Ref Online Electronic Medical Library
sup> ubscription required/sup> An option for treating partners of patients ( index cases) diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea is
patient-delivered partner therapy
Patient-delivered (partner) therapy (PDT or PDPT), is the practice of treating the sex partners of people diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by providing prescriptions or medications to the person to take to their partner without the health car ...
, which is the clinical practice of treating the sex partners of index cases by providing prescriptions or medications to the patient to take to his/her partner without the health care provider first examining the partner.Expedited Partner Therapy in the Management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (2 February 2006)U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention
Epidemiology
CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency, under the United S ...
study found that 25–40% of U.S. teenage girls has a sexually transmitted disease. Out of a population of almost 295,270,000 people there were 110 million new and existing cases of eight sexually transmitted infections.
Over 400,000 sexually transmitted infections were reported in England in 2017, about the same as in 2016, but there were more than 20% increases in confirmed cases of gonorrhoea and syphilis. Since 2008 syphilis cases have risen by 148%, from 2,874 to 7,137, mostly among men who have sex with men. The number of first cases of genital warts in 2017 among girls aged 15–17 years was just 441, 90% less than in 2009 – attributed to the national human papilloma virus immunisation programme.
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
is among the leading causes of death in present-day Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
. HIV/AIDS is transmitted primarily via unprotected sexual intercourse. More than 1.1 million persons are living with HIV/AIDS in the United States
The AIDS epidemic, caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), found its way to the United States between the 1970s and 1980s, but was first noticed after doctors discovered clusters of Kaposi's sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia in homosexua ...
, and it disproportionately impacts African Americans. Hepatitis B is also considered a sexually transmitted disease because it can be spread through sexual contact. The highest rates are found in Asia and Africa and lower rates are in the Americas and Europe. Approximately two billion people worldwide have been infected with the hepatitis B virus.
History
 The first well-recorded European outbreak of what is now known as syphilis occurred in 1494 when it broke out among French troops besieging Naples in the Italian War of 1494–98. The disease may have originated from the
The first well-recorded European outbreak of what is now known as syphilis occurred in 1494 when it broke out among French troops besieging Naples in the Italian War of 1494–98. The disease may have originated from the Columbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
. From Naples, the disease swept across Europe, killing more than five million people. As Jared Diamond describes it, " en syphilis was first definitely recorded in Europe in 1495, its pustules often covered the body from the head to the knees, caused flesh to fall from people's faces, and led to death within a few months," rendering it far more fatal than it is today. Diamond concludes," 1546, the disease had evolved into the disease with the symptoms so well known to us today." Gonorrhea is recorded at least up to 700 years ago and associated with a district in Paris formerly known as "Le Clapiers". This is where the prostitutes were to be found at that time.
Prior to the invention of modern medicines, sexually transmitted diseases were generally incurable, and treatment was limited to treating the symptoms of the disease. The first voluntary hospital for venereal diseases was founded in 1746 at London Lock Hospital.Archives in London and the M25 areaAIM25
London Lock Hospital records
/ref> Treatment was not always voluntary: in the second half of the 19th century, the Contagious Diseases Acts were used to arrest suspected prostitutes. In 1924, a number of states concluded the Brussels Agreement, whereby states agreed to provide free or low-cost medical treatment at ports for merchant seamen with venereal diseases. A proponent of these approaches was Dr.
Nora Wattie
Nora Wattie (1900–1994) MBChB (Aberdeen), DPH (Cambridge) was a pioneer of social medicine, setting up Glasgow’s internationally renowned ante-natal care service (both before and after the creation of the National Health Service).
Throughou ...
, OBE, Venereal Diseases Officer in Glasgow from 1929, encouraged contact tracing and volunteering for treatment, rather than the prevailing more judgemental view and published her own research on improving sex education and maternity care.
The first effective treatment for a sexually transmitted disease was salvarsan, a treatment for syphilis. With the discovery of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s, a large number of sexually transmitted diseases became easily curable, and this, combined with effective public health campaigns against STIs, led to a public perception during the 1960s and 1970s that they have ceased to be a serious medical threat.
During this period, the importance of contact tracing in treating STIs was recognized. By tracing the sexual partners of infected individuals, testing them for infection, treating the infected and tracing their contacts, in turn, STI clinics could effectively suppress infections in the general population.
In the 1980s, first genital herpes and then AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
emerged into the public consciousness as sexually transmitted diseases that could not be cured by modern medicine. AIDS, in particular, has a long asymptomatic period—during which time HIV (the human immunodeficiency virus, which causes AIDS) can replicate and the disease can be transmitted to others—followed by a symptomatic period, which leads rapidly to death unless treated. HIV/AIDS entered the United States from Haiti in about 1969. Recognition that AIDS threatened a global pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
led to public information campaigns and the development of treatments that allow AIDS to be managed by suppressing the replication of HIV for as long as possible. Contact tracing continues to be an important measure, even when diseases are incurable, as it helps to contain infection.
See also
*List of sexually transmitted infections by prevalence
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), are infections that are commonly spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex and oral sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * This provides an overview of pre-modern medicine's approach to the diseases.External links
CDC Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2010
STD photo library
at
Dermnet
DermNet is a worldwide clinical resource website about dermatology and skin conditions. Its co-founder and former editor-in-chief is dermatologist and Adjunct Associate Professor Amanda Oakley. The website was launched in 1996 under the umbrella ...
UNFPA: Breaking the Cycle of Sexually Transmitted Infections
at UNFPA
STDs In Color: Sexually Transmitted Disease Facts and Photos
Sexually transmitted diseases in the U.S.
STI Watch: World Health Organization
{{authority control Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Mycoplasma Disease transmission