SegReg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

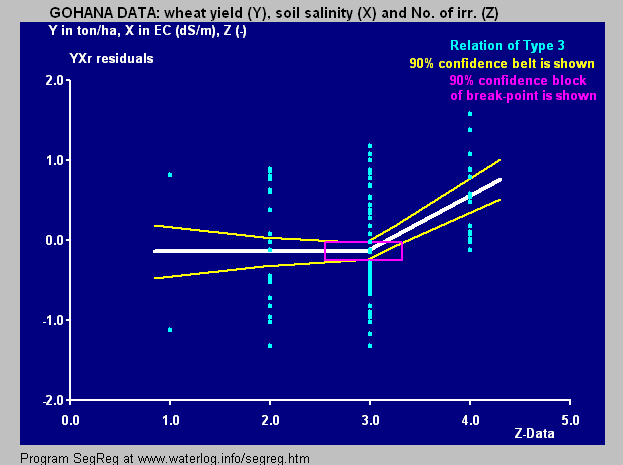
 SegReg permits the introduction of one or two independent variables. When two variables are used, it first determines the relation between the dependent variable and the most influential independent variable, where after it finds the relation between the residuals and the second independent variable. Residuals are the deviations of observed values of the dependent variable from the values obtained by segmented regression on the first independent variable.
The breakpoint is found numerically by adopting a series tentative breakpoints and performing a linear regression at both sides of them. The tentative breakpoint that provides the largest
SegReg permits the introduction of one or two independent variables. When two variables are used, it first determines the relation between the dependent variable and the most influential independent variable, where after it finds the relation between the residuals and the second independent variable. Residuals are the deviations of observed values of the dependent variable from the values obtained by segmented regression on the first independent variable.
The breakpoint is found numerically by adopting a series tentative breakpoints and performing a linear regression at both sides of them. The tentative breakpoint that provides the largest
 As an alternative to regressions at both sides of the breakpoint (threshold), the method of partial regression can be used to find the longest possible horizontal stretch with insignificant regression coefficient, outside of which there is a definite slope with a significant regression coefficient. The alternative method can be used for segmented regressions of Type 3 and Type 4 when it is the intention to detect a tolerance level of the dependent variable for varying quantities of the independent, explanatory, variable (also called predictor).Free software fo
As an alternative to regressions at both sides of the breakpoint (threshold), the method of partial regression can be used to find the longest possible horizontal stretch with insignificant regression coefficient, outside of which there is a definite slope with a significant regression coefficient. The alternative method can be used for segmented regressions of Type 3 and Type 4 when it is the intention to detect a tolerance level of the dependent variable for varying quantities of the independent, explanatory, variable (also called predictor).Free software fo
partial regression
/ref> The attached figure concerns the same data as shown in the blue graph in the infobox at the top of this page. Here, the wheat crop has a tolerance for soil salinity up to the level of EC=7.1 dS/m instead of 4.6 in the blue figure. However, the fit of the data beyond the threshold is not as well as in the blue figure that has been made using the principle of minimization of the sum of squares of deviations of the observed values from the regression lines over the whole domain of explanatory variable X (i.e. maximization of the coefficient of determination), while the partial regression is designed only to find the point where the horizontal trend changes into a sloping trend.
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
and data analysis
Data analysis is a process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, enco ...
, the application software
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a c ...
SegReg is a free and user-friendly tool for linear segmented regression
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented r ...
analysis to determine the breakpoint where the relation between the dependent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand ...
and the independent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand ...
changes abruptly.
Features


 SegReg permits the introduction of one or two independent variables. When two variables are used, it first determines the relation between the dependent variable and the most influential independent variable, where after it finds the relation between the residuals and the second independent variable. Residuals are the deviations of observed values of the dependent variable from the values obtained by segmented regression on the first independent variable.
The breakpoint is found numerically by adopting a series tentative breakpoints and performing a linear regression at both sides of them. The tentative breakpoint that provides the largest
SegReg permits the introduction of one or two independent variables. When two variables are used, it first determines the relation between the dependent variable and the most influential independent variable, where after it finds the relation between the residuals and the second independent variable. Residuals are the deviations of observed values of the dependent variable from the values obtained by segmented regression on the first independent variable.
The breakpoint is found numerically by adopting a series tentative breakpoints and performing a linear regression at both sides of them. The tentative breakpoint that provides the largest coefficient of determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s).
It is a statistic used i ...
(as a parameter for the fit of the regression lines to the observed data values) is selected as the true breakpoint. To assure that the lines at both sides of the breakpoint intersect each other exactly at the breakpoint, SegReg employs two methods and selects the method giving the best fit.
SegReg recognizes many types of relations and selects the ultimate type on the basis of statistical criteria like the significance of the regression coefficients. The SegReg output provides statistical confidence belt
In frequentist statistics, a confidence interval (CI) is a range of estimates for an unknown parameter. A confidence interval is computed at a designated ''confidence level''; the 95% confidence level is most common, but other levels, such as 9 ...
s of the regression lines and a confidence block for the breakpoint. The confidence level can be selected as 90%, 95% and 98% of certainty.
To complete the confidence statements, SegReg provides an analysis of variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statisticia ...
and an Anova
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician ...
table.
During the input phase, the user can indicate a preference for or an exclusion of a certain type. The preference for a certain type is only accepted when it is statistically significant, even when the significance of another type is higher.
ILRI provides examples of application to magnitudes like crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the c ...
, watertable depth Watertable control is the practice of controlling the height of the water table by drainage. Its main applications are in agricultural land (to improve the crop yield using agricultural drainage systems) and in cities to manage the extensive under ...
, and soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
.
A list of publications in which SegReg is used can be consulted.
Equations
When only one independent variable is present, the results may look like: * X < BP > Y = A1.X + B1 + RY * X > BP > Y = A2.X + B2 + RY where BP is the breakpoint, Y is the dependent variable, X the independent variable, A theregression coefficient
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is cal ...
, B the regression constant, and RY the residual of Y.
When two independent variables are present, the results may look like:
* X < BPX > Y = A1.X + B1 + RY
* X > BPX > Y = A2.X + B2 + RY
* Z < BPZ > RY = C1.Z + D1
* Z > BPZ > RY = C2.Z + D2
where, additionally, BPX is BP of X, BPZ is BP of Z, Z is the second independent variable, C is the regression coefficient
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is cal ...
, and D the regression constant for the regression of RY on Z.
Substituting the expressions of RY in the second set of equations into the first set yields:
* X < BPX and Z < BPZ > Y = A1.X + C1.Z + E1
* X < BPX and Z > BPZ > Y = A1.X + C2.Z + E2
* X > BPX and Z < BPZ > Y = A2.X + C1.Z + E3
* X > BPX and Z > BPZ > Y = A2.X + C2.Z + E4
where E1 = B1+D1, E2 = B1+D2, E3 = B2+D1, and E4 = B2+D2 .
Alternative
 As an alternative to regressions at both sides of the breakpoint (threshold), the method of partial regression can be used to find the longest possible horizontal stretch with insignificant regression coefficient, outside of which there is a definite slope with a significant regression coefficient. The alternative method can be used for segmented regressions of Type 3 and Type 4 when it is the intention to detect a tolerance level of the dependent variable for varying quantities of the independent, explanatory, variable (also called predictor).Free software fo
As an alternative to regressions at both sides of the breakpoint (threshold), the method of partial regression can be used to find the longest possible horizontal stretch with insignificant regression coefficient, outside of which there is a definite slope with a significant regression coefficient. The alternative method can be used for segmented regressions of Type 3 and Type 4 when it is the intention to detect a tolerance level of the dependent variable for varying quantities of the independent, explanatory, variable (also called predictor).Free software fopartial regression
/ref> The attached figure concerns the same data as shown in the blue graph in the infobox at the top of this page. Here, the wheat crop has a tolerance for soil salinity up to the level of EC=7.1 dS/m instead of 4.6 in the blue figure. However, the fit of the data beyond the threshold is not as well as in the blue figure that has been made using the principle of minimization of the sum of squares of deviations of the observed values from the regression lines over the whole domain of explanatory variable X (i.e. maximization of the coefficient of determination), while the partial regression is designed only to find the point where the horizontal trend changes into a sloping trend.
See also
*Segmented regression
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented r ...
References
{{reflist Statistical software Pascal (programming language) software