|
SegReg
In statistics and data analysis, the application software SegReg is a free and user-friendly tool for linear segmented regression analysis to determine the breakpoint where the relation between the dependent variable and the independent variable changes abruptly. Features SegReg permits the introduction of one or two independent variables. When two variables are used, it first determines the relation between the dependent variable and the most influential independent variable, where after it finds the relation between the residuals and the second independent variable. Residuals are the deviations of observed values of the dependent variable from the values obtained by segmented regression on the first independent variable. The breakpoint is found numerically by adopting a series tentative breakpoints and performing a linear regression at both sides of them. The tentative breakpoint that provides the largest coefficient of determination (as a parameter for the fit of the regre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmented Regression
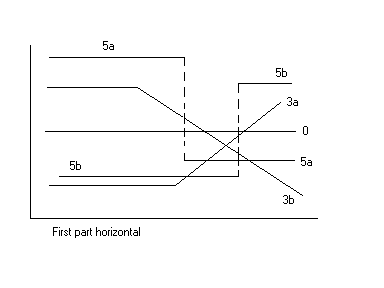
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented regression analysis can also be performed on multivariate data by partitioning the various independent variables. Segmented regression is useful when the independent variables, clustered into different groups, exhibit different relationships between the variables in these regions. The boundaries between the segments are ''breakpoints''. Segmented linear regression is segmented regression whereby the relations in the intervals are obtained by linear regression. Segmented linear regression, two segments Segmented linear regression with two segments separated by a ''breakpoint'' can be useful to quantify an abrupt change of the response function (Yr) of a varying influential factor (x). The breakpoint can be interpreted as a ''critical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watertable Depth
Watertable control is the practice of controlling the height of the water table by drainage. Its main applications are in agricultural land (to improve the crop yield using agricultural drainage systems) and in cities to manage the extensive underground infrastructure that includes the foundations of large buildings, underground transit systems, and extensive utilities (water supply networks, sewerage, storm drains, and underground electrical grids). Description and definitions Subsurface land drainage aims at controlling the water table of the groundwater in originally waterlogged land at a depth acceptable for the purpose for which the land is used. The depth of the water table with drainage is ''greater'' than without. Purpose In agricultural land drainage, the purpose of water table control is to establish a depth of the water table (Figure 1) that does no longer interfere negatively with the necessary farm operations and crop yields (Figure 2, made with the SegReg m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the ''t''-test beyond two means. In other words, the ANOVA is used to test the difference between two or more means. History While the analysis of variance reached fruition in the 20th century, antecedents extend centuries into the past according to Stigler. These include hypothesis testing, the partitioning of sums of squares, experimental techniques and the additive model. Laplace was performing hypothesis testi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression Coefficient
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called ''simple linear regression''; for more than one, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regression focuses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the gradual withdrawal of an ocean. It can also come about through artificial processes such as irrigation and road salt. Natural occurrence Salts are a natural component in soils and water. The ions responsible for salination are: Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Cl−. Over long periods of time, as soil minerals weather and release salts, these salts are flushed or leached out of the soil by drainage water in areas with sufficient precipitation. In addition to mineral weathering, salts are also deposited via dust and precipitation. Salts may accumulate in dry regions, leading to naturally saline soils. This is the case, for example, in large parts of Australia. Human practices can increase the salinity of soils by the addition of salts i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields. Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the creation of better farming tools, new methods of farming and improved crop varieties, have improved yields. The higher the yield and more intensive use of the farmland, the higher the productivity and profitability of a farm; this increases the well-being of farming families. Surplus crops beyond the needs of subsistence agriculture can be sold or bartered. The more grain or fodder a farmer can produce, the more draft animals such as horses and oxen could be supported and harnessed for labour and production of manure. Increased crop yields also means fewer hands are needed on farm, freeing them for industry and commerce. This, in turn, led to the formation and growth of cities, which then translated into an increased demand for foodstuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-test
An ''F''-test is any statistical test in which the test statistic has an ''F''-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most often used when comparing statistical models that have been fitted to a data set, in order to identify the model that best fits the population from which the data were sampled. Exact "''F''-tests" mainly arise when the models have been fitted to the data using least squares. The name was coined by George W. Snedecor, in honour of Ronald Fisher. Fisher initially developed the statistic as the variance ratio in the 1920s. Common examples Common examples of the use of ''F''-tests include the study of the following cases: * The hypothesis that the means of a given set of normally distributed populations, all having the same standard deviation, are equal. This is perhaps the best-known ''F''-test, and plays an important role in the analysis of variance (ANOVA). * The hypothesis that a proposed regression model fits the data well. See Lack-of-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |