Samoa Constitution Order, 1920 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a
A Footnote to History: Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa
'' at Gutenberg. Even as they descended into ever greater interclan warfare, what most alarmed Stevenson was the Samoans' economic innocence. In 1894, just months before his death, he addressed the island chiefs:
 The Germans, in particular, began to show great commercial interest in the Samoan Islands, especially on the island of Upolu, where German firms monopolised
The Germans, in particular, began to show great commercial interest in the Samoan Islands, especially on the island of Upolu, where German firms monopolised 
 American and British warships shelled Apia on 15 March 1899, including the USS ''Philadelphia''. Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States quickly resolved to end the hostilities and divided the island chain at the Tripartite Convention of 1899, signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574
The eastern island-group became a territory of the United States (the Tutuila Islands in 1900 and officially Manu'a in 1904) and was known as American Samoa. The western islands, by far the greater landmass, became German Samoa. The United Kingdom had vacated all claims in Samoa and in return received (1) termination of German rights in Tonga, (2) all of the Solomon Islands south of Bougainville, and (3) territorial alignments in West Africa.
American and British warships shelled Apia on 15 March 1899, including the USS ''Philadelphia''. Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States quickly resolved to end the hostilities and divided the island chain at the Tripartite Convention of 1899, signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574
The eastern island-group became a territory of the United States (the Tutuila Islands in 1900 and officially Manu'a in 1904) and was known as American Samoa. The western islands, by far the greater landmass, became German Samoa. The United Kingdom had vacated all claims in Samoa and in return received (1) termination of German rights in Tonga, (2) all of the Solomon Islands south of Bougainville, and (3) territorial alignments in West Africa.
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima
Apolima is the smallest of the four inhabited islands of Samoa. It lies in the Apolima Strait, between the country's two largest islands: Upolu to the east, and Savai'i to the west.
The island has one village settlement, Apolima Tai, with a po ...
); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands
The Aleipata Islands are a group of four uninhabited islands off the eastern end of Upolu Island, Samoa. The islands are eroded volcanic tuff rings, and consist of a small northern pair on Upolu's barrier reef, and a larger southern pair outside ...
( Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu
Fanuatapu, an uninhabited island, is a volcanic tuff ring off the eastern tip of Upolu Island, Samoa. It is the smallest and easternmost of the four Aleipata Islands, with an area of 15 hectares. It has an automated lighthouse.
See also
* Samo ...
and Namua
Namu'a is a small, uninhabited island off the east coast of Upolu island in Samoa. It is one of four small islands in the Aleipata Islands grouping.
The island is a 10-minute boat ride from Upolu Island, and has beach fale accommodation for vis ...
). Samoa is located west of American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
, northeast of Tonga (closest foreign country), northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga.
T ...
. The Lapita
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language
Samoan ( or ; ) is a Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alon ...
and Samoan cultural identity.
Samoa is a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation In mathematics, a unitary representation of a grou ...
parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
with 11 administrative divisions
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
. It is a sovereign state and a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. Western Samoa was admitted to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
on 15 December 1976. Because of the Samoans' seafaring skills, pre-20th-century European explorers referred to the entire island group (which includes American Samoa) as the "Navigator Islands". The country was a colony of the German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
from 1899 to 1915, then came under a joint British and New Zealand colonial administration until 1 January 1962, when it became independent.
History
Early history
Samoa was discovered and settled by theLapita people
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
(Austronesian people who spoke Oceanic languages), who travelled from Island Melanesia. The earliest human remains found in Samoa are dated to between roughly 2,900 and 3,500 years ago. The remains were discovered at a Lapita site at Mulifanua
Mulifanua is a village on the north-western tip of the island of Upolu, in Samoa. In the modern era, it is the capital of Aiga-i-le-Tai district. Mulifanua wharf is the main ferry terminal for inter-island vehicle and passenger travel across th ...
, and the scientists' findings were published in 1974. The Samoans' origins have been studied in modern times through scientific research on Polynesian genetics, linguistics and anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavi ...
. Although this research is ongoing, a number of theories have been proposed. One theory is that the original Samoans were Austronesians
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
who arrived during a final period of eastward expansion of the Lapita peoples out of Southeast Asia and Melanesia between 2,500 and 1,500 BCE.
Intimate sociocultural and genetic ties were maintained between Samoa, Fiji, and Tonga, and the archaeological record supports oral tradition and native genealogies that indicate interisland voyaging and intermarriage between precolonial Samoans, Fijians, and Tongans. Notable figures in Samoan history included the Tui Manu'a
The title Tui Manuʻa was the title of the ruler or paramount chief of the Manuʻa Islands in present-day American Samoa.
The Tuʻi Manuʻa Confederacy, or Samoan Empire, are descriptions sometimes given to Samoan expansionism and projecte ...
line, Queen Salamasina Queen Salamasina (floruit in the 1500s) was a powerful and high-ranking woman in Samoan social history. She held the four papā (district) titles which gave her the paramount status of Tafa‘ifā ('one supported by four') on the western islands of ...
, King Fonoti and the four ''tama-a-aiga'': Malietoa
Mālietoa ( ''Mālietoa'') is a state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa. It is the titular head of one of the two great royal families of Samoa: Sā Malietoa. Literally translated as "great warrior", the title's orig ...
, Tupua Tamasese
Tupua (known as Tupua Tamasese) is a state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa, known as the Tama-a-Aiga or 'Sons of the Great Families'). It is the titular head of one of Samoa's two great royal families - Sā Tupua, the ...
, Mata'afa, and Tuimalealiifano. Nafanua
Nafanua was a historical ''ali'i'' (chief/queen) and ''toa'' (warrior) of Samoa from the Sā Tonumaipe'ā clan, who took four ''pāpā'' (district) titles, the leading ali'i titles of Samoa. After her death she became a goddess in Polynesian relig ...
was a famous woman warrior who was deified in ancient Samoan religion and whose patronage was highly sought after by successive Samoan rulers.
Today, all of Samoa is united under its two principal royal families: the Sā Malietoa of the ancient Malietoa lineage that defeated the Tongans in the 13th century; and the Sā Tupua, Queen Salamasina's descendants and heirs who ruled Samoa in the centuries that followed her reign. Within these two principal lineages are the four highest titles of Samoa - the elder titles of Malietoa and Tupua Tamasese of antiquity and the newer Mata'afa and Tuimalealiifano titles, which rose to prominence in 19th-century wars that preceded the colonial period. These four titles form the apex of the Samoan matai system as it stands today.
Contact with Europeans began in the early 18th century. Jacob Roggeveen, a Dutchman, was the first known non-Polynesian to sight the Samoan islands in 1722. This visit was followed by French explorer Louis-Antoine de Bougainville
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (, , ; 12 November 1729 – August 1811) was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American Revolution ...
, who named them the Navigator Islands in 1768. Contact was limited before the 1830s, which is when English missionaries, whalers, and traders began arriving.
19th century
Visits by American trading andwhaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industry ...
vessels were important in the early economic development of Samoa. The Salem brig ''Roscoe'' (Captain Benjamin Vanderford), in October 1821, was the first American trading vessel known to have called, and the ''Maro'' (Captain Richard Macy) of Nantucket, in 1824, was the first recorded United States whaler at Samoa. The whalers came for fresh drinking water, firewood and provisions, and later, they recruited local men to serve as crewmen on their ships. The last recorded whaler visitor was the ''Governor Morton'' in 1870.
Christian missionary work in Samoa began in 1830 when John Williams of the London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational mi ...
arrived in Sapapali'i from the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, langu ...
and Tahiti. According to Barbara A. West, "The Samoans were also known to engage in 'headhunting', a ritual of war in which a warrior took the head of his slain opponent to give to his leader, thus proving his bravery."
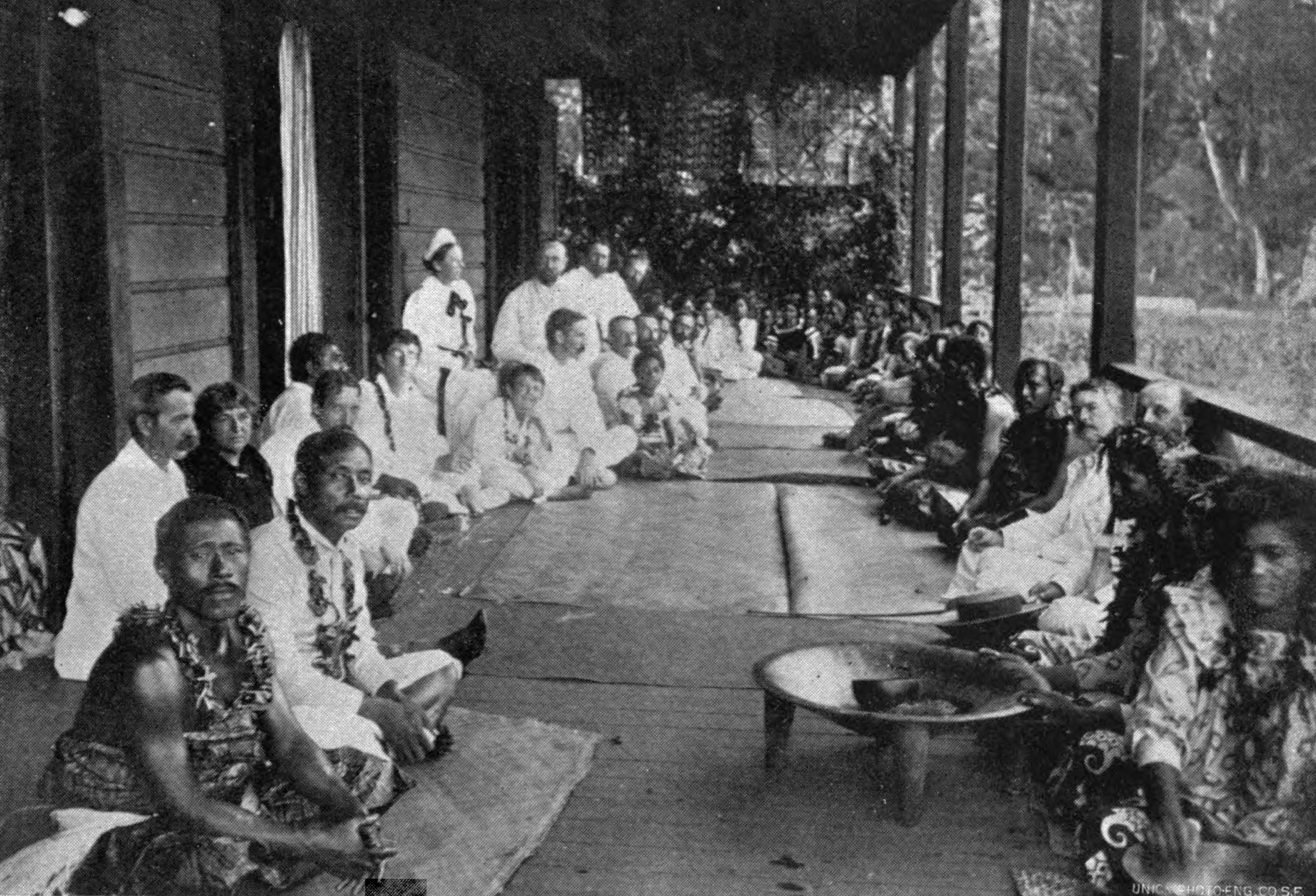
In '' A Footnote to History: Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa'' (1892), Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as ''Treasure Island'', ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll a ...
details the activities of the great powers battling for influence in Samoa – the United States, Germany and Britain – and the political machinations of the various Samoan factions within their indigenous political system.Stevenson, Robert Louis (1892). A Footnote to History: Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa
'' at Gutenberg. Even as they descended into ever greater interclan warfare, what most alarmed Stevenson was the Samoans' economic innocence. In 1894, just months before his death, he addressed the island chiefs:
There is but one way to defend Samoa. Hear it before it is too late. It is to make roads, and gardens, and care for your trees, and sell their produce wisely, and, in one word, to occupy and use your country... if you do not occupy and use your country, others will. It will not continue to be yours or your children's, if you occupy it for nothing. You and your children will in that case be cast out into outer darkness".He had "seen these judgments of God" in Hawaii, where abandoned native churches stood like tombstones "over a grave, in the midst of the white men's sugar fields".


 The Germans, in particular, began to show great commercial interest in the Samoan Islands, especially on the island of Upolu, where German firms monopolised
The Germans, in particular, began to show great commercial interest in the Samoan Islands, especially on the island of Upolu, where German firms monopolised copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from cop ...
and cocoa bean processing. The United States laid its own claim, based on commercial shipping interests in Pearl Harbor in Hawaii and Pago Pago Bay in eastern Samoa, and forced alliances, most conspicuously on the islands of Tutuila and Manu'a, which became American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
.
Britain also sent troops to protect British business enterprise, harbour rights, and consulate office. This was followed by an eight-year civil war, during which each of the three powers supplied arms, training and in some cases combat troops to the warring Samoan parties. The Samoan crisis
The Samoan Crisis was a standoff between the United States, the German Empire, and the British Empire from 1887 to 1889 over control of the Samoan Islands during the First Samoan Civil War.
Background
In 1878, the United States acquired a fuel ...
came to a critical juncture in March 1889 when all three colonial contenders sent warships into Apia harbour, and a larger-scale war seemed imminent. A massive storm on 15 March 1889 damaged or destroyed the warships, ending the military conflict.
The Second Samoan Civil War
The Second Samoan Civil War was a conflict that reached a head in 1898 when Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States were locked in dispute over who should have control over the Samoan island chain, located in the South Pacific Oce ...
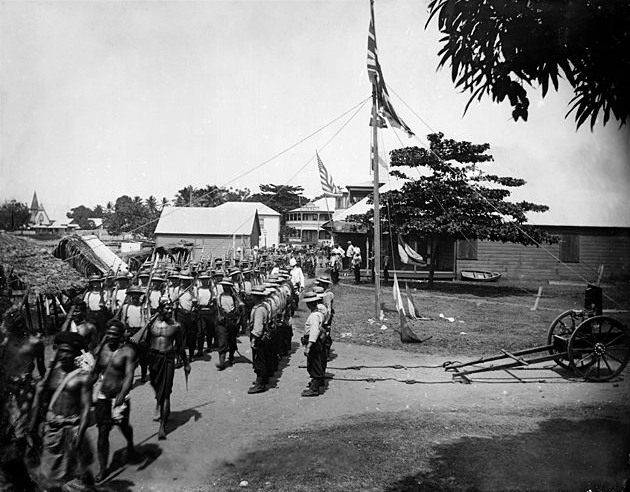
reached a head in 1898 when Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States were locked in dispute over who should control the Samoan Islands. The Siege of Apia
The siege of Apia, or the battle of Apia, occurred during the Second Samoan Civil War in March 1899 at Apia. Samoan forces loyal to Malietoa Tanumafili I were besieged by a larger force of Samoan rebels loyal to Mata'afa Iosefo. Supporting Mali ...
occurred in March 1899. Samoan forces loyal to Prince Tanu Tanu may refer to:
People
* Malietoa Tanumafili I (1879–1939), Samoan prince
* Tanu Nona (1902–1980), Australian pearler and politician
* Tanu Roy (born 1980), Indian actress and model
* Tanu (born 1997), a Finnish/Assyrian rapper
Places
* Ta ...
were besieged by a larger force of Samoan rebels loyal to Mata'afa Iosefo
Mata'afa Iosefo (1832 – 6 February 1912) was a Paramount Chief of Samoa who was one of the three rival candidates for the kingship of Samoa during colonialism. He was also referred to as Tupua Malietoa To'oa Mata'afa Iosefo. He was crowned the K ...
. Supporting Prince Tanu were landing parties from four British and American warships. After several days of fighting, the Samoan rebels were finally defeated.

 American and British warships shelled Apia on 15 March 1899, including the USS ''Philadelphia''. Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States quickly resolved to end the hostilities and divided the island chain at the Tripartite Convention of 1899, signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574
The eastern island-group became a territory of the United States (the Tutuila Islands in 1900 and officially Manu'a in 1904) and was known as American Samoa. The western islands, by far the greater landmass, became German Samoa. The United Kingdom had vacated all claims in Samoa and in return received (1) termination of German rights in Tonga, (2) all of the Solomon Islands south of Bougainville, and (3) territorial alignments in West Africa.
American and British warships shelled Apia on 15 March 1899, including the USS ''Philadelphia''. Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States quickly resolved to end the hostilities and divided the island chain at the Tripartite Convention of 1899, signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574
The eastern island-group became a territory of the United States (the Tutuila Islands in 1900 and officially Manu'a in 1904) and was known as American Samoa. The western islands, by far the greater landmass, became German Samoa. The United Kingdom had vacated all claims in Samoa and in return received (1) termination of German rights in Tonga, (2) all of the Solomon Islands south of Bougainville, and (3) territorial alignments in West Africa.
German Samoa (1900–1914)
TheGerman Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
governed the western part of the Samoan archipelago from 1900 to 1914. Wilhelm Solf was appointed the colony's first governor. In 1908, when the non-violent Mau a Pule resistance movement arose, Solf did not hesitate to banish the Mau leader Lauaki Namulau'ulu Mamoe to Saipan in the German Northern Mariana Islands.
The German colonial administration governed on the principle that "there was only one government in the islands." Thus, there was no Samoan ''Tupu'' (king), nor an ''alii sili'' (similar to a governor), but two ''Fautua'' (advisors) were appointed by the colonial government. ''Tumua'' and ''Pule'' (traditional governments of Upolu and Savai'i) were for a time silent; all decisions on matters affecting lands and titles were under the control of the colonial Governor.
In the first month of World War I, on 29 August 1914, troops of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force landed unopposed on Upolu and seized control from the German authorities, following a request by Great Britain for New Zealand to perform this "great and urgent imperial service."
New Zealand rule (1914–1961)
From the end of World War I until 1962, New Zealand controlled Western Samoa as a Class C Mandate under trusteeship through the League of Nations, then through the United Nations. Between 1919 and 1962, Samoa was administered by theDepartment of External Affairs In many countries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government department responsible for the state's diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entit ...
, a government department which had been specially created to oversee New Zealand's Island Territories and Samoa."External Affairs Bill", in ''New Zealand Parliamentary Debates'', Vol. 185 (3 October–5 November 1919), p.337. In 1943, this department was renamed the Department of Island Territories
The Department of Island Territories is a now-defunct New Zealand government department that was tasked with administrating New Zealand's three Pacific Islands territories—the Cook Islands (until 1965), Niue, and Tokelau, and the country's League ...
after a separate Department of External Affairs In many countries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government department responsible for the state's diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entit ...
was created to conduct New Zealand's foreign affairs. During the period of New Zealand control, their administrators were responsible for two major incidents.
Flu pandemic
In the first incident, approximately one fifth of the Samoan population died in the influenza epidemic of 1918–1919. In 1918, during the final stages of World War I, the Spanish flu had taken its toll, spreading rapidly from country to country. On Samoa, there had been no epidemic of pneumonic influenza in Western Samoa before the arrival of the SS ''Talune'' fromAuckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about It ...
on 7 November 1918. The NZ administration allowed the ship to berth in breach of quarantine; within seven days of this ship's arrival, influenza became epidemic in Upolu and then spread rapidly throughout the rest of the territory. Samoa suffered the most of all Pacific islands, with 90% of the population infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women and 10% of children died. The cause of the epidemic was confirmed in 1919 by a Royal Commission of Inquiry into the Epidemic concluded that there had been no epidemic of pneumonic influenza in Western Samoa before the arrival of the ''Talune'' from Auckland on 7 November 1918.
The pandemic undermined Samoan confidence in New Zealand's administrative capacity and competence. Some Samoans asked that the rule of the islands be transferred to the Americans or the British.
Mau movement
The second major incident arose out of an initially peaceful protest by the Mau (which literally translates as "strongly held opinion"), a non-violent popular movement which had its beginnings in the early 1900s on Savai'i, led by Lauaki Namulauulu Mamoe, an orator chief deposed by Solf. In 1909, Lauaki was exiled toSaipan
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a commonwealth of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 es ...
and died en route back to Samoa in 1915.
By 1918, Western Samoa had a population of some 38,000 Samoans and 1,500 Europeans.
However, native Samoans greatly resented New Zealand's colonial rule, and blamed inflation and the catastrophic 1918 flu epidemic on its misrule. By the late 1920s the resistance movement against colonial rule had gathered widespread support. One of the Mau leaders was Olaf Frederick Nelson, a half Samoan and half Swedish merchant. Nelson was eventually exiled during the late 1920s and early 1930s, but he continued to assist the organisation financially and politically. In accordance with the Mau's non-violent philosophy, the newly elected leader, High Chief Tupua Tamasese Lealofi, led his fellow uniformed Mau in a peaceful demonstration in downtown Apia on 28 December 1929.
The New Zealand police attempted to arrest one of the leaders in the demonstration. When he resisted, a struggle developed between the police and the Mau. The officers began to fire randomly into the crowd and used a Lewis machine gun, mounted in preparation for the demonstration, to disperse the demonstrators. Mau leader and paramount chief Tupua Tamasese Lealofi III
Tupua Tamasese Lealofi-o-ā'ana III (4 May 1901 – 29 December 1929) was a paramount chief of Samoa, holder of the Tupua Tamasese dynastic title and became the leader of the country's pro-independence Mau movement from early 1928 until his assa ...
was shot from behind and killed while trying to bring calm and order to the Mau demonstrators. Ten others died that day and approximately 50 were injured by gunshot wounds and police batons. That day would come to be known in Samoa as Black Saturday.
On 13 January 1930, the New Zealanders banned the organisation. As many as 1500 Mau men took to the bush, pursued by an armed force of 150 marines and seamen from the light cruiser HMS ''Dunedin'', and 50 military police. Villages were raided, often at night and with fixed bayonets. In March, through the mediation of local Europeans and missionaries, Mau leaders met New Zealand’s Minister of Defence and agreed to disperse.
Supporters of the Mau continued to be arrested, so women came to the fore rallying supporters and staging demonstrations. The political stalemate was broken following the victory of the Labour Party victory in New Zealand's 1935 general election. A 'goodwill mission' to Apia in June 1936 recognised the Mau as a legitimate political organisation, and Olaf Nelson was allowed to return from exile. In September 1936, Samoans exercised for the first time the right to elect themembers of the advisory ''Fono of Faipule
The Fono of Faipule was a legislature in Western Samoa during the colonial era. It consisted of representatives (''faipule'') from each district.Mau movement winning 31 of the 39 seats."A Step Towards Self-Government"
''Pacific Islands Monthly'', September 1959, p29
 The 1960 constitution, which formally came into force with independence from New Zealand in 1962, builds on the British pattern of
The 1960 constitution, which formally came into force with independence from New Zealand in 1962, builds on the British pattern of
 On Upolu
On Upolu
:1.
:6. Fa'asaleleaga ( Safotulafai) :7. Gaga'emauga (
2
3
4


 Samoa lies south of the equator, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand, in the
Samoa lies south of the equator, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand, in the


 The
The
 Samoa reported a population of 194,320 in its 2016 census. About three-quarters of the population live on the main island of Upolu.
Samoa reported a population of 194,320 in its 2016 census. About three-quarters of the population live on the main island of Upolu.

 The fa'a Samoa, or traditional Samoan way, remains a strong force in Samoan life and politics. As one of the oldest Polynesian cultures, the fa'asamoa developed over a period of 3,000 years, withstanding centuries of European influence to maintain its historical customs, social and political systems, and language. Cultural customs such as the
The fa'a Samoa, or traditional Samoan way, remains a strong force in Samoan life and politics. As one of the oldest Polynesian cultures, the fa'asamoa developed over a period of 3,000 years, withstanding centuries of European influence to maintain its historical customs, social and political systems, and language. Cultural customs such as the
File:Catholic church in Samoa-2.jpg, Roman Catholic Immaculate Conception of Mary cathedral.
File:Siva Afi - Fire spinning.jpg, A Samoan fire dancer.
File:Fale on Manono Island.jpg, A fale on Manono Island
File:Apia Samoa Temple-new.jpg, LDS
 As with other Polynesian cultures ( Hawaiian, Tahitian and
As with other Polynesian cultures ( Hawaiian, Tahitian and
piccom.org As in many other countries, hip hop music is popular. In addition, the integration of hip hop elements into Samoan tradition also "testifies to the transferability of the dance forms themselves," and to the "circuits through which people and all their embodied knowledge travel." Dance both in its traditional form and its more modern forms has remained a central cultural currency to Samoans, especially youths. The arts organisation ''Tautai'' ''Pacific Arts Trust'' was an informal collective of visual artists including
 The main sports played in Samoa are rugby union, Samoan cricket and
The main sports played in Samoa are rugby union, Samoan cricket and
Government of Samoa
General information
Samoa
'' The World Factbook''.
University of Colorado
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Samoa
from the BBC News *
Samoa Tourism AuthorityKey Development Forecasts for Samoa
from
''Pacific Islands Monthly'', September 1959, p29
Independence
As ''Western Samoa'' (1962–1997)
After repeated efforts by the Samoan independence movement, the New ZealandWestern Samoa Act 1961
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
of 24 November 1961 terminated the Trusteeship Agreement and granted the country independence as the ''Independent State of Western Samoa'', effective on 1 January 1962. Western Samoa, the first small-island country in the Pacific to become independent, signed a Treaty of Friendship with New Zealand later in 1962. Western Samoa joined the Commonwealth of Nations on 28 August 1970. While independence was achieved at the beginning of January, Samoa annually celebrates 1 June as its independence day.
On 15 December 1976, Western Samoa was admitted to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
as the 147th member state. It asked to be referred to in the United Nations as the ''Independent State of Samoa''.
Travel writer Paul Theroux
Paul Edward Theroux (born April 10, 1941) is an American novelist and travel writer who has written numerous books, including the travelogue, '' The Great Railway Bazaar'' (1975). Some of his works of fiction have been adapted as feature films. He ...
noted marked differences between the societies in Western Samoa and American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
in 1992.
As ''Samoa'' (1997 onwards)
On 4 July 1997 the government amended the constitution to change the name of the country from ''Western Samoa'' to ''Samoa'', the name it had been called by in the United Nations since it joined.American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
protested against the name change, asserting that it diminished its own identity.
In 2002, New Zealand prime minister Helen Clark formally apologised for New Zealand's role in the Spanish influenza outbreak in 1918 that killed over a quarter of Samoa's population and for the Black Saturday killings in 1929.
On 7 September 2009, the government changed the rule of the road, from right to left, in common with most other Commonwealth countries, most notably countries in the region such as Australia and New Zealand, home to large numbers of Samoans. This made Samoa the first country in the 21st century to switch to driving on the left.
At the end of December 2011, Samoa changed its time zone offset from UTC−11 to UTC+13, effectively jumping forward by one day, omitting Friday, 30 December from the local calendar. This also had the effect of changing the shape of the International Date Line, moving it to the east of the territory. This change aimed to help the nation boost its economy in doing business with Australia and New Zealand. Before this change, Samoa was 21 hours behind Sydney, but the change means it is now three hours ahead. The previous time zone, implemented on 4 July 1892, operated in line with American traders based in California. In October 2021, Samoa ceased daylight saving time.
In 2017, Samoa signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), or the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty, is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons with the ultimate goal being their total elimination. I ...
.
In June 2017, Parliament amended Article 1 of the Samoan Constitution to make Christianity the state religion.
In May 2021, Fiamē Naomi Mataʻafa
Afioga Fiamē Naomi Mataafa (born 29 April 1957) () is a Samoan politician and High Chiefess ('' matai'') who has served as the seventh Prime Minister of Samoa and leader of the Faatuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) party since 2021.
Th ...
became Samoa's first female prime minister. Mataʻafa's FAST party narrowly won the election, ending the rule of long-term Prime Minister Tuila'epa Sa'ilele Malielegaoi of the Human Rights Protection Party
The Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP, sm, Vaega Faaupufai e Puipuia Aia Tatau a Tagata) is a Samoan political party. It was founded in 1982 and dominated Samoan party politics for decades thereafter, leading every government until their defea ...
(HRPP), although the constitutional crisis complicated and delayed this. On 24 May 2021, she was sworn in as the new prime minister, though it was not until July that the Supreme Court ruled that her swearing-in was legal, thus ending the constitutional crisis and bringing an end to Tuila'epa's 22-year premiership. The FAST party's success in the 2021 election and subsequent court rulings also ended nearly four decades of HRPP rule.
In August 2022, Samoa’s Legislative Assembly reappointed Tuimaleali’ifano Vaaletoa Sualauvi II as the Head of State for a second term of five years.
Government and politics
 The 1960 constitution, which formally came into force with independence from New Zealand in 1962, builds on the British pattern of
The 1960 constitution, which formally came into force with independence from New Zealand in 1962, builds on the British pattern of parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
, modified to take account of Samoan customs. The national modern Government of Samoa is referred to as the ''Malo''.
Fiame Mata'afa Faumuina Mulinu'u II, one of the four highest-ranking paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and arch ...
s in the country, became Samoa's first Prime Minister. Two other paramount chiefs at the time of independence were appointed joint heads of state for life. Tupua Tamasese Mea'ole died in 1963, leaving Malietoa Tanumafili II
Malietoa Tanumafili II (4 January 1913 – 11 May 2007), addressed Susuga Malietoa Tanumafili II, was the Malietoa, the title of one of Samoa's four paramount chiefs, and the head of state, or ''O le Ao o le Malo'', a position that he held for ...
sole head of state until his death on 11 May 2007. The next Head of State was Tui Atua Tupua Tamasese Efi
Tui or TUI may refer to:
Places
* Tui, Pontevedra, Spain
* Tui, Iran, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
* Tui, North Khorasan, North Khorasan Province, Iran
* Tui Province, Burkina Faso
* Tuis District, Costa Rica
* Tui railway station, New Zeala ...
, who was elected by the legislature on 17 June 2007 for a fixed five-year term, and was re-elected unopposed in July 2012. He was succeeded by Tuimalealiifano Va'aletoa Sualauvi II in 2017. Tuimaleali’ifano was reappointed for a second term of five years in 2022.
The unicameral legislature (the Fono) consists of 51 members serving 5-year terms. Forty-nine are '' matai'' title-holders elected from territorial districts by Samoans; the other two are chosen by non-Samoans with no chiefly affiliation on separate electoral rolls. At least, 10% of the MPs are women. Universal suffrage was adopted in 1990, but only chiefs (matai) may stand for election to the Samoan seats. There are more than 25,000 matais in the country, about 5% of whom are women. The prime minister, chosen by a majority in the Fono, is appointed by the head of state to form a government. The prime minister's choices for the 12 cabinet positions are appointed by the head of state, subject to the continuing confidence of the Fono.
Prominent women in Samoan politics include the late Laulu Fetauimalemau Mata'afa
The music of Finland can be roughly divided into categories of folk music, classical and contemporary art music, and contemporary popular music.
The folk music of Finland belongs to a broader musical tradition, that has been common amongst B ...
(1928–2007) from Lotofaga
Lotofaga is a village on the south coast of Upolu island in Samoa. Lotofaga is also the name of the larger Lotofaga Electoral Constituency (''Faipule District'') which includes Lotofaga village and two other villages, Vavau and Matatufu.
The v ...
constituency, the wife of Samoa's first prime minister. Their daughter Fiame Naomi Mataʻafa is a high chief and a long-serving senior member of cabinet, who was elected Prime Minister in 2021. Other women in politics include Samoan scholar and eminent professor Aiono Fanaafi Le Tagaloa
Aiono Fanaafi Le Tagaloa OM (25 June 1932 – 14 August 2014) was a chief ( ''matai''), scholar, historian and professor of Samoa. An authority on Samoan culture and language, she was one of the most educated female ''matai'' in the country wit ...
, orator-chief Matatumua Maimoana and Safuneitu'uga Pa'aga Neri ( the Minister of Communication and Technology).
The judicial system incorporates English common law and local customs. The Supreme Court of Samoa
The Supreme Court of Samoa () is the superior court dealing with the administration of justice in Samoa.
It was established by Part VI of the Constitution of Samoa. It consists of the Chief Justice of Samoa and other judges as appointed by the H ...
is the court of highest jurisdiction. The Chief Justice of Samoa is appointed by the head of state upon the recommendation of the prime minister.
Administrative divisions
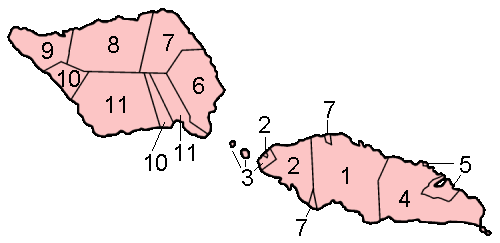
Samoa comprises eleven ''itūmālō'' (political districts). These are the traditional eleven districts which predate European arrival. Each district has its own constitutional foundation (''fa'avae'') based on the traditional order of title precedence found in each district's ''faalupega'' (traditional salutations). The capital village of each district administers and coordinates the affairs of the district and confers each district's paramount title, amongst other responsibilities. For example: A'ana has its capital atLeulumoega
Leulumoega Tuai is a village situated on the northwest coast Upolu island in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main ...
. The paramount ''Lufilufi
Lufilufi is a historical village situated on the north coast of Upolu island in Samoa. The village is part of the electoral constituency (''Faipule District'') Anoamaa East which is within the larger political district of Atua. The village's popula ...
. The paramount ''Falefa
Falefā is located on the north eastern coast of Upolu island in Samoa. It was the ancient capital during the ‘''Malo’'' (‘government’) of ''Tupu Tafa'ifa'' (King) Fonoti. After having defeated his siblings Va'afusuaga and Samalaulu for co ...
and Salani) and Mata'afa (based in Amaile and Lotofaga). The two main political families who confer the respective titles are 'Aiga Sā Fenunuivao and ' Aiga Sā Levālasi. The paramount ''pāpā'' title of Ātua is the Tui Ātua. The orator group which confers this title - the ''Faleono'' (House of Six) - is based at Lufilufi.
Tuamasaga
Tuamāsaga is a district of Samoa, with a population (2016 Census) of 95,907. The geographic area of Tuamasaga covers the central part of Upolu island.
History & Politics
Malie & the Malietoa
The paramount ''matai'' title of Tuamasaga is the ...
has its capital at Afega. The paramount ''Malietoa
Mālietoa ( ''Mālietoa'') is a state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa. It is the titular head of one of the two great royal families of Samoa: Sā Malietoa. Literally translated as "great warrior", the title's orig ...
title, based in Malie Malie is a village on the island of Upolu in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two s ...
. The main political family that confers the Malietoa title is 'Aiga Sā Malietoa, with Auimatagi as the main speaker for the family. The paramount ''pāpā'' titles of Tuamasaga are Gatoaitele (conferred by Afega) and Vaetamasoalii (conferred by Safata).
The eleven ''itūmālō'' are identified to be:
 On Upolu
On Upolu :1.
Tuamasaga
Tuamāsaga is a district of Samoa, with a population (2016 Census) of 95,907. The geographic area of Tuamasaga covers the central part of Upolu island.
History & Politics
Malie & the Malietoa
The paramount ''matai'' title of Tuamasaga is the ...
( Afega)1
:2. A'ana (Leulumoega
Leulumoega Tuai is a village situated on the northwest coast Upolu island in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main ...
)
:3. Aiga-i-le-Tai
Aiga-i-le-Tai is a district of Samoa which includes the small islands of Manono, Apolima and tiny uninhabited Nu'ulopa lying in the Apolima Strait between the country's two main islands of Upolu and Savai'i.
The district includes part of the ma ...
(Mulifanua
Mulifanua is a village on the north-western tip of the island of Upolu, in Samoa. In the modern era, it is the capital of Aiga-i-le-Tai district. Mulifanua wharf is the main ferry terminal for inter-island vehicle and passenger travel across th ...
)2
:4. Atua
Atua are the gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians (see also ); the Polynesian word literally means "power" or "strength" and so the concept is similar to that of ''mana''. Today, it is also used for th ...
(Lufilufi
Lufilufi is a historical village situated on the north coast of Upolu island in Samoa. The village is part of the electoral constituency (''Faipule District'') Anoamaa East which is within the larger political district of Atua. The village's popula ...
)3
:5. Va'a-o-Fonoti ( Samamea)
On Savai'i :6. Fa'asaleleaga ( Safotulafai) :7. Gaga'emauga (
Saleaula
Sale'aula is a village on the central north coast of Savai'i island in Samoa and is the traditional center of the Gaga'emauga political district. Chief council meetings are held at Vaitu’utu’u malae in the village. The village has a populati ...
)4
:8. Gaga'ifomauga (Safotu
Safotu is a village on the central north coast of Savai'i island in Samoa. Safotu is in the district Gagaifomauga and has a population of 1270. Traditionally, it attained the status of 'Pule,' customary political authority, and has been the main ...
)
:9. Vaisigano
Vaisigano is a political district at the western tip of Savai'i island in Samoa. The capital of the district is Asau.
This area is also referred to as 'Itu Asau' (Asau district) in the Samoan language.
The population of Vaisigano is 6,543 ...
( Asau)
:10. Satupa'itea ( Satupa'itea)
:11. Palauli
Palauli is a district and village of Samoa, with a population (2016 Census) of 9,300. It consists of two sections on the southern side of Savai'i. The capital is Vailoa which is also referred to as Vailoa i Palauli (Vailoa in Palauli district).
...
(Vailoa
Vailoa (Vailoa i Palauli) is a village on the island of Savaiʻi in Samoa. Vailoa is the capital of Palauli district on the south east of the island.
)
1
2
3
4
Human rights
Major areas of concern include the under-representation of women, domestic violence and poor prison conditions.Homosexual acts
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to peop ...
are illegal in Samoa.
State religion
In June 2017, an Act was passed changing the country's constitution to include a reference to the Trinity. As amended, Article 1 of the Samoan Constitution states that "Samoa is a Christian nation founded on God the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit". According to '' The Diplomat'', "What Samoa has done is shift references to Christianity into the body of the constitution, giving the text far more potential to be used in legal processes." The preamble to the constitution already described the country as "an independent State based on Christian principles and Samoan custom and traditions."Military and police
Samoa has no formal defence structure or regular armed forces. It has informal defence ties with New Zealand, which is required to consider any request for assistance from Samoa under the bilateral Treaty of Friendship of 1962. Officers of the national police force, the Samoa Police Service, are regularly unarmed, but may be armed in exceptional circumstances with ministerial approval. In 2022 there is about 900–1,100 police officers in Samoa.Geography


 Samoa lies south of the equator, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand, in the
Samoa lies south of the equator, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand, in the Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n region of the Pacific Ocean. The total land area is , consisting of the two large islands of Upolu and Savai'i (which together account for 99% of the total land area) and eight small islets.
The islets are:
*the three islets in the Apolima Strait
The Apolima Strait is about 13 km wide and separates the two largest islands of Samoa: Savai'i to the northwest, and Upolu to the southeast.
Three small islands lie in the strait. Two of them, Manono and Apolima, have small village settl ...
( Manono Island, Apolima
Apolima is the smallest of the four inhabited islands of Samoa. It lies in the Apolima Strait, between the country's two largest islands: Upolu to the east, and Savai'i to the west.
The island has one village settlement, Apolima Tai, with a po ...
and Nu'ulopa)
*the four Aleipata Islands
The Aleipata Islands are a group of four uninhabited islands off the eastern end of Upolu Island, Samoa. The islands are eroded volcanic tuff rings, and consist of a small northern pair on Upolu's barrier reef, and a larger southern pair outside ...
off the eastern end of Upolu ( Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Namua
Namu'a is a small, uninhabited island off the east coast of Upolu island in Samoa. It is one of four small islands in the Aleipata Islands grouping.
The island is a 10-minute boat ride from Upolu Island, and has beach fale accommodation for vis ...
, and Fanuatapu
Fanuatapu, an uninhabited island, is a volcanic tuff ring off the eastern tip of Upolu Island, Samoa. It is the smallest and easternmost of the four Aleipata Islands, with an area of 15 hectares. It has an automated lighthouse.
See also
* Samo ...
)
* Nu'usafe'e, which is less than in area and lies about off the south coast of Upolu at the village of ''Vaovai''
The main island of Upolu is home to nearly three-quarters of Samoa's population, and to the capital city, Apia
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga.
T ...
.
The Samoan islands result geologically from volcanism, originating with the Samoa hotspot
The Samoa hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the south Pacific Ocean.
The hotspot model describes a hot upwelling plume of magma through the Earth's crust as an explanation of how volcanic islands are formed. The hotspot idea came from J. ...
, which probably results from a mantle plume. While all of the islands have volcanic origins, only Savai'i, the westernmost island in Samoa, remains volcanically active, with the most recent eruptions at Mt Matavanu
Mt Matavanu is an active volcano on the island of Savai'i in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i ...
(1905–1911), Mata o le Afi
Mata o le Afi ("Eye of the Fire" or "Source of the Fire") is an active volcano on the island of Savai'i in Samoa. It last erupted in 1902.
1902 eruption
An eruption began on 30 October 1902. It was preceded by a series of thirteen earthquakes, wh ...
(1902) and Mauga Afi
Mauga Afi ("Burning Mountain" or "Mountain of Fire") is a volcanic mountain in the Gagaʻifomauga district on the island of Savai'i in Samoa. It has an elevation of 1847m.
The most recent eruption of Mauga Afi was around 1768 and was observed by ...
(1725). The highest point in Samoa is Mt Silisili, at . The Saleaula
Sale'aula is a village on the central north coast of Savai'i island in Samoa and is the traditional center of the Gaga'emauga political district. Chief council meetings are held at Vaitu’utu’u malae in the village. The village has a populati ...
lava fields situated on the central north coast of Savai'i result from the Mt Matavanu eruptions, which left of solidified lava.
Savai'i is the largest of the Samoan islands and the sixth-largest Polynesian island (after New Zealand's North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
, South and Stewart Islands
Sikaiana (formerly called the Stewart Islands) is a small atoll NE of Malaita in Solomon Islands in the south Pacific Ocean. It is almost in length and its lagoon, known as Te Moana, is totally enclosed by the coral reef. Its total land s ...
and the Hawaiian islands of Hawaiʻi and Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which ...
). The population of Savai'i is 42,000 people.
Climate
Samoa has an equatorial climate, with an average annual temperature of and a main rainy season from November to April, although heavy rain may fall in any month.Ecology
Samoa forms part of theSamoan tropical moist forests
The Samoan tropical moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Samoan Islands of the Pacific Ocean.
Approximately 30% of Samoa's biodiversity is endemic, found only in Samoa, with new species still being discovered in ...
ecoregion. Since human habitation began, about 80% of the lowland rainforests have disappeared. Within the ecoregion about 28% of plants and 84% of land birds are endemic.
Economy

 The
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
has classified Samoa as an economically developing country since 2014. Samoa's gross domestic product in purchasing-power parity was estimated at $1.13 billion U.S. dollars
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
, ranking the country 204th in the world. The services sector accounted for 66% of GDP, followed by industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
at 23.6% and 10.4% respectively. For the same year, the Samoan labour force was estimated at 50,700.
The Central Bank of Samoa
The Central Bank of Samoa ( sm, Faletupe Tutotonu o Samoa), situated in the capital Apia beside the main government buildings, issues the Samoan currency, the Samoan tālā as well as regulates and manages the exchange rate with foreign currenci ...
issues and regulates Samoa's currency, the Samoan tālā
The tālā is the currency of Samoa. It is divided into 100 ''sene''. The terms ''tālā'' and ''sene'' are the equivalents or transliteration of the English words ''dollar'' and ''cent'', in the Samoan language. Its symbol is $, or ''WS$'' to d ...
.
The economy of Samoa has traditionally depended on agriculture and fishing at the local level. In modern times, development aid, private family remittances from overseas
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland. Money sent home by migrants competes with ...
, and agricultural exports have become key factors in the nation's economy. Agriculture employs two-thirds of the labour force and furnishes 90% of exports, featuring coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
cream, coconut oil
frameless , right , alt = A cracked coconut and a bottle of coconut oil
Coconut oil (or coconut butter) is an edible oil derived from the wick, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat; in warmer climates du ...
, noni (juice of the ''nonu'' fruit, as it is known in Samoan), and copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from cop ...
.
Sixty percent of Samoa's electricity comes from renewable hydro
Hydro from Ancient Greek word ὕδωρ (húdōr), meaning ''water''.
Hydro may also refer to:
Energy technologies
* Water-derived power or energy:
** Hydropower, derived from water
** Hydroelectricity, in electrical form
* "Hydro", AC mains ...
, solar, and wind sources, with the remainder produced by diesel generators. The Electric Power Corporation set a goal of 100% renewable energy
100% renewable energy means getting all energy from renewable resources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issue ...
by 2021.
Agriculture
In the period before German colonisation (from the late 19th century), Samoa produced mostly copra. German merchants and settlers were active in introducing large-scale plantation operations and in developing new industries, notably cocoa beans and rubber, relying on imported labourers from China and Melanesia. When the value ofnatural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
fell drastically, about the end of the Great War ( World War I) in 1918, the New Zealand government encouraged the production of bananas, for which there is a large market in New Zealand.
Because of variations in altitude, Samoa can cultivate a large range of tropical and subtropical crops. Land is not generally available to outside interests. Of the total land area of , about 24.4% is in permanent crops and another 21.2% is arable. About 4.4% is Western Samoan Trust Estates Corporation (WSTEC).
The staple products of Samoa are copra (dried coconut meat), cocoa beans (for chocolate), rubber, and bananas. The annual production of both bananas and copra has been in the range of 13,000 to 15,000 metric tons (about 14,500 to 16,500 short tons). If the Asiatic rhinoceros beetle in Samoa were eradicated, Samoa could produce in excess of 40,000 metric tons (44,000 short tons) of copra. Samoan cocoa beans are of very high quality and are used in fine New Zealand chocolates. Most are Criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish race-based colonial caste system (the European descendants)
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South Ameri ...
-Forastero hybrids. Coffee grows well, but production has been uneven. WESTEC is the biggest coffee producer.
Other agricultural industries have proven less successful. Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks ...
production was originally established by Germans in the early 20th century. Old train tracks for transporting cane can be seen at some plantations east of Apia
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga.
T ...
. Pineapples grow well in Samoa, but have not moved beyond local consumption to become a major export.
Demographics
Health
A measles outbreak began in October 2019. As of 7 December, there have been 68 deaths (0.31 per 1,000, based on a population of 201,316) and over 4,460 cases (2.2% of the population) of measles in Samoa, mainly children under four years old, and 10 reported cases in Fiji. It is expected that 70 people will die and up to 6,500 people will be infected.Ethnic groups
The population is 96%Samoans
Samoans or Samoan people ( sm, tagata Sāmoa) are the indigenous Polynesian people of the Samoan Islands, an archipelago in Polynesia, who speak the Samoan language. The group's home islands are politically and geographically divided between t ...
, 2% dual Samoan-New Zealander
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
and 1.9% other, according to a 2011 estimate in the CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
.
Languages
Samoan (''Gagana Fa'asāmoa'') and English are the official languages. Including second-language speakers, there are more speakers of Samoan than English in Samoa. Samoan Sign Language is also commonly used among the deaf population of Samoa. To emphasize the importance of full inclusion with sign language, elementary Samoan Sign Language was taught to members of the Samoa Police Service, Red Cross Society, and public during the 2017 International Week of the Deaf.Religion
Since 2017, Article 1 of the Samoan Constitution states that "Samoa is a Christian nation founded of God the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit". Samoans' religious adherence includes the following: Christian Congregational Church of Samoa 31.8%, Roman Catholic 19.4%, Methodist 15.2%,Assembly of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
13.7%, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints 7.6%, Seventh-day Adventist 3.9%, Worship Centre 1.7%, other Christian 5.5%, other 0.7%, none 0.1%, unspecified 0.1% (2011 estimate). The Head of State until 2007, Malietoa Tanumafili II
Malietoa Tanumafili II (4 January 1913 – 11 May 2007), addressed Susuga Malietoa Tanumafili II, was the Malietoa, the title of one of Samoa's four paramount chiefs, and the head of state, or ''O le Ao o le Malo'', a position that he held for ...
, was a Baháʼí. Samoa hosts the seventh (of nine current) Baháʼí Houses of Worship in the world; completed in 1984 and dedicated by the Head of State, it is located in Tiapapata, from Apia
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga.
T ...
.
Education
The Samoan government provides eight years of primary and secondary education that is tuition-free and is compulsory through age 16. Samoa's main post-secondary educational institution is the National University of Samoa, established in 1984. The country is also home to several branches of the multi-national University of the South Pacific and the Oceania University of Medicine. Education in Samoa has proved to be effective as a 2012 UNESCO report stated that 99 per cent of Samoan adults are literate. The Human Rights Measurement Initiative (HRMI) finds that Samoa is fulfilling only 88.0% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to education based on the country's level of income. HRMI breaks down the right to education by looking at the rights to both primary education and secondary education. While taking into consideration Samoa's income level, the nation is achieving 97.7% of what should be possible based on its resources (income) for primary education but only 78.3% for secondary education.Culture

 The fa'a Samoa, or traditional Samoan way, remains a strong force in Samoan life and politics. As one of the oldest Polynesian cultures, the fa'asamoa developed over a period of 3,000 years, withstanding centuries of European influence to maintain its historical customs, social and political systems, and language. Cultural customs such as the
The fa'a Samoa, or traditional Samoan way, remains a strong force in Samoan life and politics. As one of the oldest Polynesian cultures, the fa'asamoa developed over a period of 3,000 years, withstanding centuries of European influence to maintain its historical customs, social and political systems, and language. Cultural customs such as the Samoa 'ava ceremony
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
are significant and solemn rituals at important occasions including the bestowal of '' matai'' chiefly titles. Items of great cultural value include the finely woven '' 'ie toga''.
Samoan mythology Samoan culture tells stories of many different deities. There were deities of the forest, the seas, rain, harvest, villages, and war. There were two types of deities, ''atua'', who had non-human origins, and ''aitu'', who were of human origin.
Tag ...
includes many gods with creation stories and figures of legend such as Tagaloa
In Samoan mythology, Tagaloa (also known as Tagaloa-Lagi or Tagaloa, Lagi of the Heavens/Skies) is generally accepted as the supreme ruler,
and the goddess of war Nafanua
Nafanua was a historical ''ali'i'' (chief/queen) and ''toa'' (warrior) of Samoa from the Sā Tonumaipe'ā clan, who took four ''pāpā'' (district) titles, the leading ali'i titles of Samoa. After her death she became a goddess in Polynesian relig ...
, the daughter of Saveasi'uleo, ruler of the spirit realm Pulotu
Pulotu is the resting place of those passed on in the Polynesian narrative of Tonga and Samoa, the world of darkness "lalo fonua" (as opposed to the human world of light).
Tonga
In the Tongan narrative, Pulotu is presided over by Havea Hikul ...
. Other legends include the well known story of Sina and the Eel
Sina and the Eel is a myth of origins in Samoan mythology, which explains the origins of the first coconut tree.
In the Samoan language the legend is called ''Sina ma le Tuna.'' ''Tuna'' is the Samoan word for 'eel'.
The story is also well kno ...
which explains the origins of the first coconut tree.
Some Samoans are spiritual and religious, and have subtly adapted the dominant religion of Christianity to 'fit in' with fa'a Samoa and vice versa. Ancient beliefs continue to co-exist side by side with Christianity, particularly in regard to the traditional customs and rituals of fa'a Samoa. The Samoan culture is centred on the principle of vāfealoa'i, the relationships between people. These relationships are based on respect, or fa'aaloalo. When Christianity was introduced in Samoa, most Samoan people converted. Currently 98% of the population identify themselves as Christian.
Some Samoans live a communal way of life, participating in activities collectively. Examples of this are the traditional Samoan '' fale'' (houses) which are open with no walls, using blinds made of coconut palm fronds during the night or bad weather.
The Samoan '' siva'' dance has unique gentle movements of the body in time to music and tells a story, although the Samoan male dances can be more snappy. The '' sasa'' is also a traditional dance where rows of dancers perform rapid synchronised movements in time to the rhythm of wooden drums ''(pate
Pate, pâté, or paté may refer to:
Foods Pâté 'pastry'
* Pâté, various French meat forcemeat pies or loaves
* Pâté haïtien or Haitian patty, a meat-filled puff pastry dish
* ''Pate'' or ''paté'' (anglicized spellings), the Virgin Isla ...
)'' or rolled mats. Another dance performed by males is called the '' fa'ataupati'' or the slap dance, creating rhythmic sounds by slapping different parts of the body. This is believed to have been derived from slapping insects on the body.
The form and construction of traditional architecture of Samoa
The architecture of Samoa is characterised by openness, with the design mirroring the culture and life of the Samoan people who inhabit the Samoa Islands.
was a specialised skill by ''Tufuga fai fale'' that was also linked to other cultural artforms.
Apia Samoa Temple
The Apia Samoa Temple (formerly the Samoan Temple) was the 24th constructed and 22nd operating temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). It was the first built in Samoa and the third to be built in Polynesia. After ...
Tattooing
 As with other Polynesian cultures ( Hawaiian, Tahitian and
As with other Polynesian cultures ( Hawaiian, Tahitian and Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
) with significant and unique tattoos, Samoans have two gender specific and culturally significant tattoos. For males, it is called the Pe'a and consists of intricate and geometrical patterns tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing pro ...
ed that cover areas from the knees up towards the ribs. A male who possesses such a tatau is called a soga'imiti. A Samoan girl or ''teine'' is given a malu
is a word in the Samoan language for a female-specific tattoo of cultural significance. The covers the legs from just below the knee to the upper thighs just below the buttocks, and is typically finer and delicate in design compared to the , ...
, which covers the area from just below her knees to her upper thighs.
Contemporary culture
Albert Wendt
Albert Tuaopepe Wendt (born 27 October 1939) is a Samoan poet and writer who lives in New Zealand. He is one of the most influential writers in Oceania. His notable works include ''Sons for the Return Home'', published in 1973 (adapted into a ...
is a significant Samoan writer whose novels and stories tell the Samoan experience. In 1989, his novel ''Flying Fox in a Freedom Tree'' was made into a feature film in New Zealand, directed by Martyn Sanderson. Another novel ''Sons for the Return Home'' had also been made into a feature film in 1979, directed by Paul Maunder.
The late John Kneubuhl
John Alexander Kneubuhl (July 2, 1920 – February 20, 1992) was an American Samoan screenwriter, playwright and Polynesian historian. He wrote for American television series such as '' The Fugitive'', ''Gunsmoke'', ''The Wild Wild West'', ''Star ...
, born in American Samoa, was an accomplished playwright and screenwriter and writer. His play ''Think of Garden'' premiered in Auckland in 1993 a year after his death, it was directed by Nathaniel Lees
Nathaniel Lees is a New Zealand theatre actor and director and film actor of Samoan descent, best known for film roles in ''The Matrix Reloaded'', ''The Matrix Revolutions'' and '' The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers'' and for starring in ''You ...
, is set in 1929 and is about Samoa's struggle for independence.
Sia Figiel
Sia Figiel (born 1967 Apia, Samoa) is an American contemporary Samoan novelist, poet, and painter.
Early life
Sia Figiel grew up amidst traditional Samoan singing and poetry, which heavily influenced her writing. Figiel's greatest influence a ...
won the 1997 Commonwealth Writers' Prize for fiction in the south-east Asia/South Pacific region with her novel "Where We Once Belonged".
Momoe Malietoa Von Reiche is an internationally recognised poet and artist.
Tusiata Avia
Donna Tusiata Avia (born 1966) is a New Zealand poet and children's author.
Background
Avia was born and raised in Christchurch, New Zealand. Her father is Samoan and her mother is Palagi (New Zealand European). Avia graduated from the Unive ...
is a performance poet. Her first book of poetry ''Wild Dogs Under My Skirt'' was published by Victoria University Press in 2004.
Dan Taulapapa McMullin is an artist and writer.
Other Samoan poets and writers include Sapa'u Ruperake Petaia, Eti Sa'aga and Savea Sano Malifa
Savea Sano Malifa '' OM'' (also known as Fata Sano Malifa) is a Samoan poet, journalist, newspaper editor, and publisher. He is the founder and editor-in-chief of the '' Samoa Observer'', the main newspaper in Samoa. He is the author of the novel ...
, the editor of the Samoa Observer
The ''Samoa Observer'' is the largest newspaper group in Samoa published in both English and Samoan. The ''Samoa Observer'' is published Monday to Friday, the ''Weekend Observer'' on Saturdays and the ''Sunday Samoan'' on Sundays with all editi ...
.
In music, popular local bands include The Five Stars, Penina o Tiafau and Punialava'a.
The Yandall Sisters' cover of the song ''Sweet Inspiration'' reached number one on the New Zealand charts in 1974.
King Kapisi
Bill Rangi Urale is a New Zealand-Samoan hip-hop artist.
Music career
He was signed up as an artist with Festival Mushroom Records (NZ). In 2000 he released his critically acclaimed debut album ''Savage Thoughts'', followed by a second album, ...
was the first hip hop artist to receive the prestigious New Zealand APRA Silver Scroll Award in 1999 for his song ''Reverse Resistance''. The music video for ''Reverse Resistance'' was filmed in Savai'i at his villages.
Other successful Samoan hip hop artists include rapper Scribe, Dei Hamo
Sanerivi "Sani" Sagala (born 24 August 1974), better known by his stage name Dei Hamo, is a New Zealand hip hop artist, producer and director.
Dei Hamo, which can be translated as "The Samoan", has won various awards for his chart-topping music a ...
, Savage and Tha Feelstyle
Kas Futialo, known by the stage name Tha Feelstyle, is a New Zealand hip hop artist of Samoan descent. His first album was '' Break It To Pieces'' in 2004. Tha Feelstyle was born in Samoa and moved to New Zealand in the 1980s. He raps in English ...
whose music video ''Suamalie'' was filmed in Samoa.
Lemi Ponifasio
Salā Lemi Ponifasio (born in Lano Samoa), is globally renowned for his progressive application to theatre, politicking, and engagement with indigenous, Māori and Pacific peoples. He was the Arts Foundation Laureate in 2011, and was the recipi ...
is a director and choreographer who is prominent internationally with his dance Company MAU.
Neil Ieremia's company Black Grace
Black Grace is one of New Zealand's leading contemporary dance companies. Founded by Neil Ieremia in 1995, Ieremia draws from his Samoan and New Zealand roots to create innovative dance works that reach across social, cultural and generationa ...
has also received international acclaim with tours to Europe and New York.
Hip hop has had a significant impact on Samoan culture. According to Katerina Martina Teaiwa, PhD from the University of Hawaii at Manoa, "Hip hop culture in particular is popular amongst Samoan youth."Dances of Life , American Samoapiccom.org As in many other countries, hip hop music is popular. In addition, the integration of hip hop elements into Samoan tradition also "testifies to the transferability of the dance forms themselves," and to the "circuits through which people and all their embodied knowledge travel." Dance both in its traditional form and its more modern forms has remained a central cultural currency to Samoans, especially youths. The arts organisation ''Tautai'' ''Pacific Arts Trust'' was an informal collective of visual artists including
Fatu Feu'u
Fatu Akelei Feu'u (born 1946) is a noted Samoan painter from the village of Poutasi in the district of Falealili in Samoa. He has established a reputation as the elder statesman of Pacific art in New Zealand.
Biography
Feu'u emigrated to Ne ...
, Johnny Penisula, Shigeyuki Kihara
Yuki Kihara (born 1975) is an interdisciplinary artist of Japanese and Samoan descent. In 2008, her work was the subject of a solo exhibition at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York; it was the first time a New Zealander and the first time ...
, Michel Tuffery
Michael "Michel" Cliff Tuffery (born 27 May 1966) is a New Zealand artist of Samoan, Tahitian and Cook Islands descent. He is one of New Zealand's most well known artists and his work is held in many art collections in New Zealand and around ...
, and Lily Laita in the 1980s and formalised into a trust in 1995 and is now a leading Pacific arts organisation directed by Courtney Sina Meredith. Marilyn Kohlhase ran a Pacific focused gallery called '' Okaioceanikart'' from 2007 - 2013.
Director Sima Urale
Sima Urale is a New Zealand filmmaker. Her films explore social and political issues and have been screened worldwide. She is one of the few Polynesian film directors in the world with more than 15 years in the industry. Her accolades include th ...
is a filmmaker. Urale's short film ''O Tamaiti'' won the prestigious Best Short Film at the Venice Film Festival in 1996. Her first feature film ''Apron Strings'' opened the 2008 NZ International Film Festival. The feature film '' Siones Wedding'', co-written by Oscar Kightley
Oscar Vai To'elau Kightley (born 14 September 1969) is a Samoan-born New Zealand actor, television presenter, writer, journalist, director, and comedian. He acted in and co-wrote the successful 2006 film '' Sione's Wedding''.
Biography
Kightley ...
, was financially successful following premieres in Auckland and Apia. The 2011 film The Orator
''The Orator'', also known as ( Italian), ( Etruscan) or (Latin), is an Etruscan bronze sculpture from the late second or the early first century BC. Aulus Metellus was an Etruscan senator in the Roman republic, originally from Perugia or Cort ...
was the first ever fully Samoan film, shot in Samoa in the Samoan language with a Samoan cast telling a uniquely Samoan story. Written and directed by Tusi Tamasese
Tusi Tamasese (born in 1975 or 1976 in Samoa) is a Samoan New Zealander film director.
He is of high chiefly descent, of the Tupua Tamasese lineage.
He came to New Zealand at the age of 18 with the intention to go to university, but, lacking a ...
, it received much critical acclaim and attention at film festivals throughout the world.
Sport
 The main sports played in Samoa are rugby union, Samoan cricket and
The main sports played in Samoa are rugby union, Samoan cricket and netball
Netball is a ball sport played on a court by two teams of seven players. It is among a rare number of sports which have been created exclusively for female competitors. The sport is played on indoor and outdoor netball courts and is specifical ...
. Rugby union is the national football code of Samoa. In Samoan villages, volleyball is also popular.
Rugby union is the national sport in Samoa and the national team
A national sports team (commonly known as a national team or a national side) is a team that represents a nation, rather than a particular club or region, in an international sport.
The term is most commonly associated with team sports, for exa ...
, nicknamed the Manu Samoa, is consistently competitive against teams from vastly more populous nations. Samoa has competed at every Rugby World Cup
The Rugby World Cup is a men's rugby union tournament contested every four years between the top international teams. The tournament is administered by World Rugby, the sport's international governing body. The winners are awarded the Webb ...
since 1991
File:1991 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Boris Yeltsin, elected as Russia's first president, waves the new flag of Russia after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, orchestrated by Soviet hardliners; Mount Pinatubo erupts in the Ph ...
, and made the quarter finals in 1991, 1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake stri ...
and the second round of the 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school shoot ...
World Cup. At the 2003 world cup, Manu Samoa came close to beating eventual world champions, England. Samoa also played in the Pacific Nations Cup
The Pacific Nations Cup is an international rugby union competition held between three Pacific states: Fiji, Samoa and Tonga. The 2019 edition of the tournament will also include the national teams of Canada, Japan and United States. First held ...
and the Pacific Tri-Nations
The Pacific Tri-Nations was the traditional rugby union series between Tonga, Fiji and Samoa. It was established in 1982 with the Samoan team, then known as Western Samoa, winning the tournament. In 2006 it was replaced by the IRB Pacific 5 Nation ...
. The sport is governed by the Samoa Rugby Football Union
Rugby Samoa ( sm, Lakapi Samoa) is the governing body of the sport of rugby union in Samoa. Founded as the ''Apia Rugby Union'' in 1924, it was affiliated to the New Zealand Rugby Football Union the same year.Jones, p10 It joined the Internationa ...
, who are members of the Pacific Islands Rugby Alliance
The Pacific Islands Rugby Alliance (PIRA) was set up in 2002 as a basis of co-operation between the Fiji, Samoa and Tonga Rugby Unions. Niue and the Cook Islands also became members of the Alliance and supplied players to the Pacific Islanders
...
, and thus, also contribute to the international Pacific Islanders rugby union team
The Pacific Islanders was a combined international rugby union team that played from 2004 to 2008. It represented Fiji, Samoa and Tonga; Niue and the Cook Islands also supplied players to the squad for their tour in 2004. The team did not play at R ...
.
At club level, there is the National Provincial Championship and Pacific Rugby Cup
The World Rugby Pacific Challenge, formerly the IRB Pacific Rugby Cup, is an annual rugby union football tournament held in Oceania since 2006. It is contested by national 'A' teams (formed from the best locally based players, with most not alre ...
. They also took home the cup at Wellington and the Hong Kong Rugby Sevens in 2007—for which the Prime Minister of Samoa, also Chairman of the national rugby union, Tuila’epa Sa’ilele Malielegaoi, declared a national holiday. They were also the IRB World Sevens Series Champions in 2010 capping a year of achievement for the Samoans, following wins in the US, Australia, Hong Kong and Scotland Sevens tournaments.
Prominent Samoan players include Pat Lam
Patrick Richard Lam (born 29 September 1968) is a rugby union coach and former player. He is currently Director of Rugby at Bristol Bears in England's Premiership Rugby.
Born in New Zealand, he represented New Zealand in schools and under-21 ...
and Brian Lima
Brian Pala Lima '' OM'' (born 25 January 1972) is a Samoan former rugby union player who was inducted into the IRB Hall of Fame in 2011.
He earned the nickname of "The Chiropractor" for his shuddering hits both on and off the pitch that supposedl ...
. In addition, many Samoans have played for or are playing for New Zealand.
Rugby league is mostly played by Samoans living in New Zealand and Australia. Samoa reached the quarter finals of the 2013 Rugby League World Cup
The 2013 Rugby League World Cup was the fourteenth staging of the Rugby League World Cup and took place in England, Wales, France and Ireland. between 26 October and 30 November 2013.
It was the main event of the year's Festival of World C ...
, the team comprising players from the NRL
The National Rugby League (NRL) is an Australasian rugby league club competition which contains clubs from New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, the Australian Capital Territory and New Zealand. The NRL formed in 1998 as a joint partnership ...
and Super League plus domestic players. Many Samoans and New Zealanders or Australians of Samoan descent play in the Super League and National Leagues in Britain, including Francis Meli, Ta'ane Lavulavu of Workington Town, Maurie Fa'asavalu of St Helens, David Fatialofa of Whitehaven and Setaimata Sa, who signed with London Irish rugby club. Other noteworthy players from NZ and Australia have represented the Samoan National team. The 2011 domestic Samoan rugby league competition contained 10 teams with plans to expand to 12 in 2012. Samoa reached the final of the 2021 Rugby League World Cup
The 2021 Rugby League World Cup (RLWC2021) was a collection of world cups in the sport of rugby league, held in England from 15 October to 19 November 2022. England won hosting rights for the competition on 27 October 2016. The bid received £2 ...
to face Australia.
Samoans have been very visible in boxing, kickboxing
Kickboxing is a combat sport focused on kicking and punching. The combat takes place in a boxing ring, normally with boxing gloves, mouthguards, shorts, and bare feet to favour the use of kicks. Kickboxing is practiced for self-defense, genera ...
, wrestling, and sumo; some Samoan sumo wrestlers, most famously Musashimaru and Konishiki, have reached the highest rank of '' Ozeki'' and '' yokozuna''.
American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team with ...
is occasionally played in Samoa, reflecting its wide popularity in American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
, where the sport is played under high school sanction. About 30 ethnic Samoans, many from American Samoa, currently play in the National Football League. A 2002 article from ''ESPN
ESPN (originally an initialism for Entertainment and Sports Programming Network) is an American international basic cable sports channel owned by ESPN Inc., owned jointly by The Walt Disney Company (80%) and Hearst Communications (20%). The co ...
'' estimated that a Samoan male (either an American Samoan or a Samoan living in the mainland United States) is 40 times more likely to play in the NFL than a non-Samoan American.
See also
* Outline of SamoaFootnotes
References
Further reading
*Watson, R M, ''History of Samoa'' (Wellington, 1918) *Meleisea, Malama. ''The Making of Modern Samoa: Traditional Authority and Colonial Administration in the Modern History of Western Samoa''. (Suva, 1987) Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific. *Schnee, Dr. Heinrich (former Deputy Governor of German Samoa and last Governor of German East Africa). 1926. ''German Colonization, Past and Future: The Truth about the German Colonies.'' London: George Allen & Unwin. *Eustis, Nelson.979
Year 979 ( CMLXXIX) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Byzantine Empire
* March 24 – Second Battle of Pankaleia: An Ibero-Byzantine expeditionar ...
1980. '' Aggie Grey of Samoa.'' Adelaide, South Australia: Hobby Investments. .
*
*Mead, Margaret. 1928, ''Coming of Age in Samoa: A Study of Adolescence and Sex in Primitive Societies''.
*Freeman, Derek. 1983. ''Margaret Mead in Samoa: the Making and Unmaking of an Anthropological Myth''.
*Urmenyhazi Attila. 2013 ''Samoan & Marquesan Life in Oceania: a probing travelogue''. – National Library of Australia, Bib ID: 6377055.
*Mallon, Sean. 2002. ''Samoan Art and Artists''. O Measina a Samoa. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
*
External links
* GovernmentGovernment of Samoa
General information
Samoa
'' The World Factbook''.
Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.University of Colorado
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Samoa
from the BBC News *
Samoa Tourism Authority
from
International Futures
International Futures (IFs) is a global integrated assessment model designed to help with thinking strategically and systematically about key global systems (economic, demographic, education, health, environment, technology, domestic governance, ...
*
{{Authority control
1962 establishments in Oceania
Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean
Countries in Polynesia
English-speaking countries and territories
Island countries
Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
Member states of the United Nations
Small Island Developing States
States and territories established in 1962
Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations
Christian states
Countries in Oceania
Former least developed countries
Country name changes