Salivary gland cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Salivary gland tumours, also known as mucous gland adenomas or
 There are many diagnostic methods that can be used to determine the type of salivary gland tumour and if it is benign or malignant. Examples of diagnostic methods include:
Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health. The head, neck, mouth, and throat will be checked for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
Endoscopy: A procedure to look at organs and tissues inside the body to check for abnormal areas. For salivary gland cancer, an endoscope is inserted into the mouth to look at the mouth, throat, and larynx. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing.
MRI or CT Scan: These tests can confirm the presence of a tumour. An MRI or CT Scan can also show whether metastasis has occurred.
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle. An FNA is the most common type of biopsy used for salivary gland cancer, and has been shown to produce accurate results when differentiating between benign and malignant tumours.
Radiographs: An OPG (orthopantomogram) can be taken to rule out mandibular involvement. A chest radiograph may also be taken to rule out any secondary tumours.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be used to initially assess a tumour that is located superficially in either the submandibular or parotid gland. It can distinguish an intrinsic from an extrinsic neoplasm. Ultrasonic images of malignant tumours include ill-defined margins. Furthermore, high resolution ultrasound can identify the exact tumour location within the parotid gland, its relationship to the retromandibular vein and assist surgical excision.
There are many diagnostic methods that can be used to determine the type of salivary gland tumour and if it is benign or malignant. Examples of diagnostic methods include:
Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health. The head, neck, mouth, and throat will be checked for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
Endoscopy: A procedure to look at organs and tissues inside the body to check for abnormal areas. For salivary gland cancer, an endoscope is inserted into the mouth to look at the mouth, throat, and larynx. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing.
MRI or CT Scan: These tests can confirm the presence of a tumour. An MRI or CT Scan can also show whether metastasis has occurred.
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle. An FNA is the most common type of biopsy used for salivary gland cancer, and has been shown to produce accurate results when differentiating between benign and malignant tumours.
Radiographs: An OPG (orthopantomogram) can be taken to rule out mandibular involvement. A chest radiograph may also be taken to rule out any secondary tumours.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be used to initially assess a tumour that is located superficially in either the submandibular or parotid gland. It can distinguish an intrinsic from an extrinsic neoplasm. Ultrasonic images of malignant tumours include ill-defined margins. Furthermore, high resolution ultrasound can identify the exact tumour location within the parotid gland, its relationship to the retromandibular vein and assist surgical excision.

 Due to the diverse nature of salivary gland
Due to the diverse nature of salivary gland 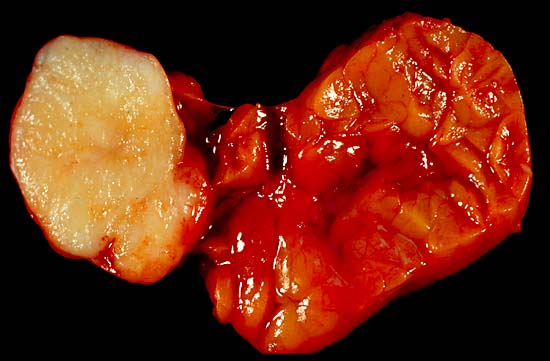 Benign epithelial tumors
* Pleomorphic adenoma
*
Benign epithelial tumors
* Pleomorphic adenoma
*
 Treatment may include the following:
*
Treatment may include the following:
*
Salivary gland cancer
entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms {{DEFAULTSORT:Salivary Gland Cancer Rare cancers * Salivary gland pathology
neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, are tumours
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
that form in the tissues of salivary glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glan ...
. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the man ...
, submandibular
The submandibular ganglion (or submaxillary ganglion in older texts) is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. (The others are the otic ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion, and ci ...
, and sublingual
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their primary ...
glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800 to 1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
cavity. Patients with these types of tumours may be asymptomatic.
Presentation
Salivary gland tumours usually present as a lump or swelling in the affected gland which may or may not have been present for a long time. The lump may be accompanied by symptoms of duct blockage (e.g.xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side eff ...
). Usually, in their early stages it is not possible to distinguish a benign tumour from a malignant one. One of the key differentiating symptoms of a malignant growth is nerve involvement; for example, signs of facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
damage (e.g. facial palsy
Facial nerve paralysis is a common problem that involves the paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve. The pathway of the facial nerve is long and relatively convoluted, so there are a number of causes that may result in facial ...
) are associated with malignant parotid tumours. Facial pain and paraesthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
are also very often associated with malignant tumours. Other red flag symptoms which may suggest malignancy and warrant further investigation are fixation of the lump to the overlying skin, ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o ...
ation and induration (hardening) of the mucosa.
Diagnosis
 There are many diagnostic methods that can be used to determine the type of salivary gland tumour and if it is benign or malignant. Examples of diagnostic methods include:
Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health. The head, neck, mouth, and throat will be checked for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
Endoscopy: A procedure to look at organs and tissues inside the body to check for abnormal areas. For salivary gland cancer, an endoscope is inserted into the mouth to look at the mouth, throat, and larynx. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing.
MRI or CT Scan: These tests can confirm the presence of a tumour. An MRI or CT Scan can also show whether metastasis has occurred.
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle. An FNA is the most common type of biopsy used for salivary gland cancer, and has been shown to produce accurate results when differentiating between benign and malignant tumours.
Radiographs: An OPG (orthopantomogram) can be taken to rule out mandibular involvement. A chest radiograph may also be taken to rule out any secondary tumours.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be used to initially assess a tumour that is located superficially in either the submandibular or parotid gland. It can distinguish an intrinsic from an extrinsic neoplasm. Ultrasonic images of malignant tumours include ill-defined margins. Furthermore, high resolution ultrasound can identify the exact tumour location within the parotid gland, its relationship to the retromandibular vein and assist surgical excision.
There are many diagnostic methods that can be used to determine the type of salivary gland tumour and if it is benign or malignant. Examples of diagnostic methods include:
Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health. The head, neck, mouth, and throat will be checked for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
Endoscopy: A procedure to look at organs and tissues inside the body to check for abnormal areas. For salivary gland cancer, an endoscope is inserted into the mouth to look at the mouth, throat, and larynx. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing.
MRI or CT Scan: These tests can confirm the presence of a tumour. An MRI or CT Scan can also show whether metastasis has occurred.
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle. An FNA is the most common type of biopsy used for salivary gland cancer, and has been shown to produce accurate results when differentiating between benign and malignant tumours.
Radiographs: An OPG (orthopantomogram) can be taken to rule out mandibular involvement. A chest radiograph may also be taken to rule out any secondary tumours.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be used to initially assess a tumour that is located superficially in either the submandibular or parotid gland. It can distinguish an intrinsic from an extrinsic neoplasm. Ultrasonic images of malignant tumours include ill-defined margins. Furthermore, high resolution ultrasound can identify the exact tumour location within the parotid gland, its relationship to the retromandibular vein and assist surgical excision.
Classification

 Due to the diverse nature of salivary gland
Due to the diverse nature of salivary gland tumours
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
, many different terms and classification systems have been used. Perhaps the most widely used currently is that system proposed by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
in 2005, which classifies salivary neoplasms as primary or secondary, benign or malignant, and also by tissue of origin. This system defines five broad categories of salivary gland neoplasms: Benign epithelial tumors
* Pleomorphic adenoma
*
Benign epithelial tumors
* Pleomorphic adenoma
* Warthin's tumor
Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers (lymph node-like stroma). It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, w ...
* Myoepithelioma
* Basal cell adenoma
* Oncocytoma
* Canalicular adenoma
* Lymphadenoma
** ''Sebaceous lymphadenoma
Sebaceous lymphadenoma is a benign tumour of the salivary gland.
Diagnosis
Sebaceous lymphadenoma is a tissue diagnosis, e.g. salivary gland biopsy.
It may be confused with a number of benign and malignant neoplasms, including Warthin tumour, mu ...
''
** '' Nonsebaceous lymphadenoma''
* Ductal papilloma
** '' Inverted ductal papilloma''
** ''Intraductal papilloma
Intraductal papillomas of the breast are benign lesions with an incidence of approximately 2-3% in humans. They result from abnormal proliferation of the epithelial cells lining the breast ducts.
Two types of intraductal papillomas are generally ...
''
** '' Sialadenoma papilliferum''
* Cystadenoma
Cystadenoma (or "cystoma") is a type of cystic adenoma. When malignant, it is called cystadenocarcinoma.
Classification
When not otherwise specified, the ICD-O coding is 8440/0. However, the following classifications also exist:
By form
* serous ...
* Malignant epithelial tumors
** Acinic cell carcinoma
** Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is the most common type of minor salivary gland malignancy in adults. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma can also be found in other organs, such as bronchi, lacrimal sac, and thyroid gland.
Mucicarmine staining is one stain us ...
** Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites. This tumor most often occurs in the salivary glands, but it can also be found in many anatomic sites, including the breast, lacrimal gland, lung, brain ...
** Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
** Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma
** Clear cell carcinoma, not otherwise specified
** Basal cell adenocarcinoma
** Sebaceous carcinoma Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma is an uncommon malignant cutaneous tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebace ...
** Sebaceous lymphadenocarcinoma
** Cystadenocarcinoma
** Low-grade cribriform cystadenocarcinoma
** Mucinous adenocarcinoma
** Oncocytic carcinoma
** Salivary duct carcinoma
** Salivary duct carcinoma, not otherwise specified
** Adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified
** Myoepithelial carcinoma
** Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
** Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma
** Carcinosarcoma
Carcinosarcomas are malignant tumors that consist of a mixture of carcinoma (or epithelial cancer) and sarcoma (or mesenchymal/connective tissue cancer). Carcinosarcomas are rare tumors, and can arise in diverse organs, such as the skin, salivary ...
** Metastasizing pleomorphic adenoma
** Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on th ...
** Large cell carcinoma
Large-cell carcinoma (LCC, LCLC) is a heterogeneous group of undifferentiated malignant neoplasms that lack the cytologic and architectural features of small cell carcinoma and glandular or squamous differentiation. LCC is categorized as a type of ...
** Lymphoepithelial carcinoma
** Sialoblastoma
* Soft tissue tumors
** Hemangioma
A hemangioma or haemangioma is a usually benign vascular tumor derived from blood vessel cell types. The most common form, seen in infants, is an infantile hemangioma, known colloquially as a "strawberry mark", most commonly presenting on the ski ...
* Hematolymphoid tumors
** Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition w ...
** Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a cancer of B cells, a type of lymphocyte that is responsible for producing antibodies. It is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among adults, with an annual incidence of 7–8 cases per 100,000 ...
** Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma
* Secondary tumors (i.e. a tumor which has metastasized
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
to the salivary gland from a distant location)
Others, not included in the WHO classification above, include:
* Intraosseous (central) salivary gland tumors
* Hybrid tumors (i.e. a tumor displaying combined forms of histologic tumor types)
** Hybrid carcinoma
** Others
* Others
** Keratocystoma
** Sialolipoma
Treatment
Most patients with early-stage lesions that are resectable generally tend to undergo surgery as their initial therapeutic approach, whereas those with advanced or unresectable cancers tend to be treated with radiotherapy (RT) alone or chemoradiotherapy (CRT), which hampered the comparison of the efficacy of RT alone with that of surgery combined with adjuvant RT. But some effort had been made to reflect the role of surgery in salivary gland tumours. Treatment may include the following:
*
Treatment may include the following:
* Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
Complete surgical resection, with adequate free margins, is currently the mainstay treatment for salivary gland tumours. However elective treatment of the N0 neck region remains a controversial topic
* Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radi ...
If a salivary gland tumour is cancerous, Radiation Therapy may be necessary
Fast neutron therapy has been used successfully to treat salivary gland tumors, and has shown to be significantly more effective than photons in studies treating unresectable salivary gland tumors.
* Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
Currently little is known about the efficacy of chemotherapy in treating salivary gland tumours. Chemotherapy, which plays an important role in systemic therapy, is generally reserved for the palliative treatment of symptomatic locally recurrent and/or metastatic disease that is not amenable to further surgery or radiation. Conventional chemotherapy regimens, such as cisplatin and 5-FU or CAP (cisplatin, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide) are still utilized as first-line therapy for patients with advanced lesions.
Targeted Therapy - Due to the poor results with chemotherapy, it's urgent to explore novel therapeutic interventions for this disease. And great expectations have been put into individualized therapies: in particular, the EGF receptors family (EGFR and HER2), KIT and androgen receptors are the most commonly investigated molecular targets in SGCs. Their expression seems not to be linked to its pathogenetic role in the development of SGCs, but more to the histogenetic origin of the tumor cells. Various targeted agents, such as imatinib, cetuximab, gefitinib, trastuzumab, had been used for exploring new treatment for salivary gland tumours, but on account of the rare incidence of salivary gland tumours, the number of cases available on targeted therapy for analysis is relatively small.
Epidemiology
Little is known about the total incidence of salivary gland tumours as most benign tumours go unrecorded in national cancer registries. The majority of salivary tumours are benign (65-70%). Within the parotid gland 75 - 80% of tumours are benign. Around 50% of the tumours found in the submandibular glands are benign. Sublingual gland tumours are very rare but if present, they are most likely to be malignant. In the United States, salivary gland cancers are uncommon with an incidence rate of 1.7 in 100000 between 2009 and 2013.See also
*Head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms ...
* Salivary gland pathology
References
External links
Salivary gland cancer
entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms {{DEFAULTSORT:Salivary Gland Cancer Rare cancers * Salivary gland pathology