|
Cystadenoma
Cystadenoma (or "cystoma") is a type of cystic adenoma. When malignant, it is called cystadenocarcinoma. Classification When not otherwise specified, the ICD-O coding is 8440/0. However, the following classifications also exist: By form * serous cystadenoma (8441-8442) * papillary cystadenoma (8450-8451, 8561) * mucinous cystadenoma (8470-8473) By location * Bile duct cystadenoma (8161) or biliary cystadenoma is a slow-growing tumour arising from bile ducts of the liver. The presence of endocrine cells in the tumour also indicates its origin from the glands surrounding the bile ducts. The incidence is 1–5 in 100,000 people. Females are affected more than males at 9:1 ratio. Mean age of presentation is at 45 years old. About 30% of biliary cystadenoma can progressively become malignant over time. * Endometrioid cystadenoma (8380) * Appendix: The term ''mucinous cystadenoma'' is an obsolete term for appendiceal mucinous neoplasm Topic Completed: 1 October 2017. Revised: 11 Decem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICD-O
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries. It is currently in its third revision (ICD-O-3). ICD-10 includes a list of morphology codes. They stem from ICD-O second edition (ICD-O-2) that was valid at the time of publication. Axes The classification has two axes: topography and morphology. Morphology The morphology axis addresses the microscopic structure (histology) of the tumor. This axis has particular importance because the Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine ("SNOMED") has adopted the ICD-O classification of morphology. SNOMED has been changing continuously, and several different versions of SNOMED are in use. Accordingly, mapping of ICD-O codes to SNOMED requires careful assessment of whether entities are indeed true matches. Topography The topogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
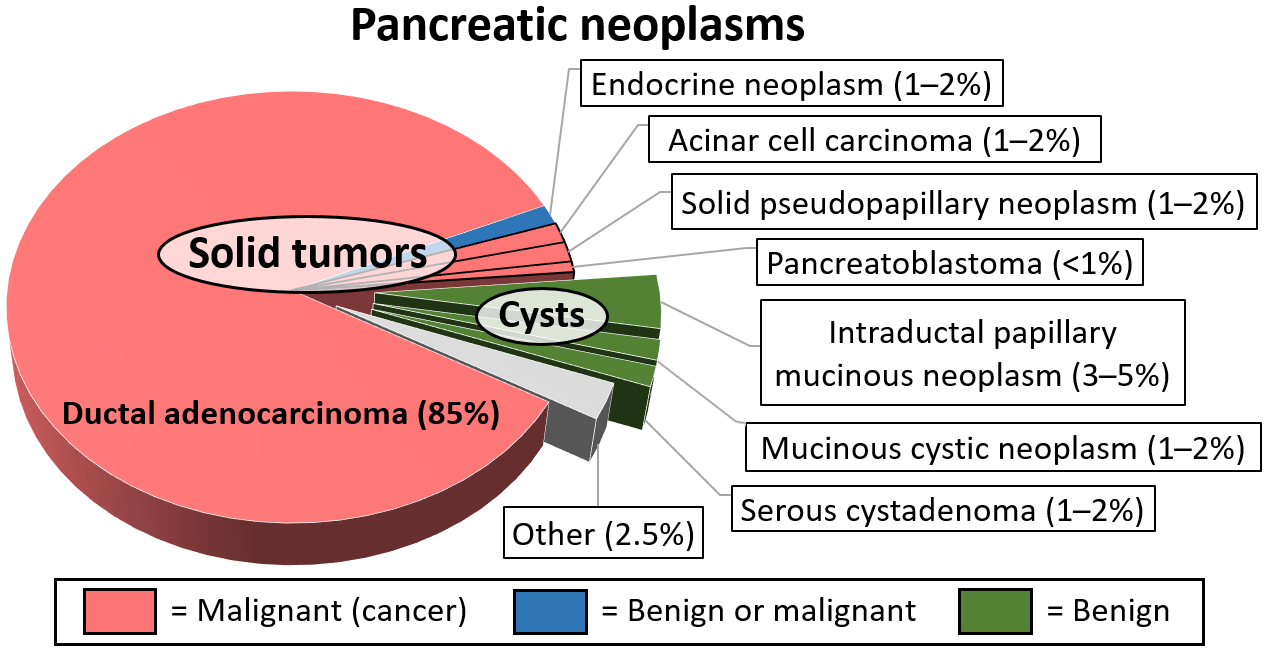
Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of the pancreas. It is usually found in the tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. In contrast to some of the other cyst-forming tumors of the pancreas (such as the intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and the pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma), serous cystic neoplasms are almost always entirely benign. There are some exceptions; rare case reports have described isolated malignant serous cystadenocarcinomas. In addition, serous cystic neoplasms slowly grow, and if they grow large enough they can press on adjacent organs and cause symptoms. Signs and symptoms In most cases, serous cystadenomas of the pancreas are asymptomatic. However, large cysts may cause symptoms related to their size. Classification Pathologists classify serous cystic neoplasms into two broad groups. Those that are benign, that have not spread to other organs, are designated "serous cystadenoma". Serous cystadenomas can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warthin's Tumor
Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers (lymph node-like stroma). It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, who described two cases in 1929. Signs and symptoms Warthin's tumor primarily affects older individuals (age 60–70 years). There is a slight male predilection according to recent studies. The tumor is slow growing, painless, and usually appears in the tail of the parotid gland near the angle of the Human mandible, mandible. In 5–14% of cases, Warthin's tumor is bilateral, but the two masses usually are at different times. Warthin's tumor is highly unlikely to become malignant. Locations The gland most likely affected is the parotid gland. In fact, it is the only tumor virtually restricted to the parotid gland. Warthin's tumor is the second most common benign parotid tumor after pleomorphic adenoma, but its prevalence is steadil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, formi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms. Histopathology Adenoma is a benign tumor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm
Appendix cancer are very rare cancers of the vermiform appendix. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are rare tumors with malignant potential. Primary lymphomas can occur in the appendix. Breast cancer, colon cancer, and tumors of the female genital tract may metastasize to the appendix. Diagnosis Carcinoid tumors are the most common tumors of the appendix. Other common forms are mucinous adenocarcinomas, adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified (NOS), and signet ring cell adenocarcinoma listed from highest to lowest incidence. Carcinoid A carcinoid is a neuroendocrine tumor (NET) of the intestines. Incidence rates among carcinoids occur at about .15 per 100,000 per year. This subgroup makes up a large amount of neoplasias both malignant and benign. Almost 3 out of 4 of these tumors are associated with the region at the end of the appendix, and tend to be diagnosed in the 4th to 5th decades in life. Both women and Caucasian individuals show a minor prevalence regarding Neuroendocr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidrocystoma
Hidrocystoma (also known as cystadenoma, a Moll's gland cyst, and a sudoriferous cyst) is an adenoma of the sweat glands.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Hidrocystomas are cysts of sweat ducts, usually on the eyelids. They are not tumours (a similar-sounding lesion called hidroadenoma is a benign tumour). The three types of "sweat" glands are: True sweat glands or eccrine glands, sebaceous glands, which have an oily secretion around hair follicles, and apocrine glands, which have more oily product than eccrine glands and are found on the face, armpit, and groin. Hidrocystomas usually arise from apocrine glands. They are also called cysts of Moll or sudoriferous cysts. A type of hidroadenoma that arises from eccrine glands is uncommon. Other related conditions on the eyelids include chalazion (a granulomatous reaction to sebaceous glands on the eyelid), lacrimal duct cysts (cysts related to tear ducts), and nas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
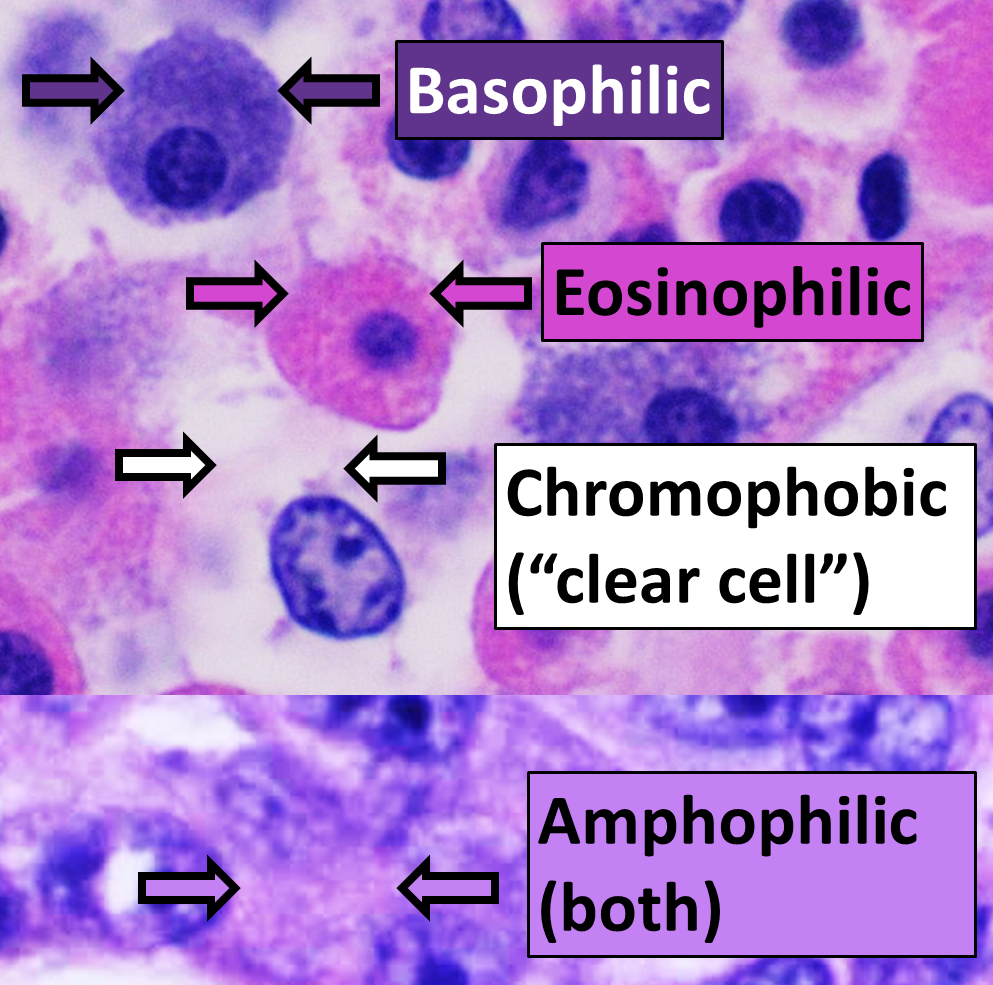
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serous
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fluid fills the inside of body cavities. Serous fluid originates from serous glands, with secretions enriched with proteins and water. Serous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both mucous and serous cells. A common trait of serous fluids is their role in assisting digestion, excretion, and respiration. In medical fields, especially cytopathology, serous fluid is a synonym for effusion fluids from various body cavities. Examples of effusion fluid are pleural effusion and pericardial effusion. There are many causes of effusions which include involvement of the cavity by cancer. Cancer in a serous cavity is called a serous carcinoma. Cytopathology evaluation is recommended to evaluate the causes of effusions in these cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papillary
Papilla (Latin, 'nipple') or papillae may refer to: In animals * Papilla (fish anatomy), in the mouth of fish * Basilar papilla, a sensory organ of lizards, amphibians and fish * Dental papilla, in a developing tooth * Dermal papillae, part of the skin * Major duodenal papilla, in the duodenum * Minor duodenal papilla, in the duodenum * Genital papilla, a feature of the external genitalia of some animals * Interdental papilla, part of the gums * Lacrimal papilla, on the bottom eyelid * Lingual papillae, small structures on the upper surface of the tongue * Renal papilla, part of the kidney In plants and fungi * Papilla (mycology), a nipple-shaped protrusion in the center of the cap * Stigmatic papilla, part of the stigma (botany) See also * * * Blister A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |