synchrotron emission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the 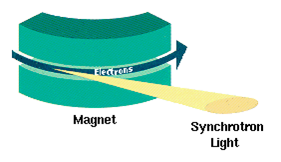


Cosmic Magnetobremsstrahlung (synchrotron Radiation)
by Ginzburg, V. L., Syrovatskii, S. I., ARAA, 1965
Developments in the Theory of Synchrotron Radiation and its Reabsorption
by Ginzburg, V. L., Syrovatskii, S. I., ARAA, 1969
Lightsources.org
BioSync
– a structural biologist's resource for high energy data collection facilities
X-Ray Data Booklet
{{Authority control Particle physics Synchrotron-related techniques Electromagnetic radiation Experimental particle physics
electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, inf ...
emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.
Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle ...
s, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from ...
.
Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation
''Bremsstrahlung'' (), from "to brake" and "radiation"; i.e., "braking radiation" or "deceleration radiation", is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typicall ...
, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly relativistic range (≈85% of the speed of light), the emission is termed ''gyro-synchrotron radiation''.
In astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the h ...
, synchrotron emission occurs, for instance, due to ultra-relativistic motion of a charged particle around a black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
. When the source follows a circular geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. ...
around the black hole, the synchrotron radiation occurs for orbits close to the photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated.
The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it ...
where the motion is in the ultra-relativistic regime.


History
Synchrotron radiation was first observed by technician Floyd Haber, on April 24, 1947, at the 70 MeV electron synchrotron of theGeneral Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
research laboratory in Schenectady, New York
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
. While this was not the first synchrotron built, it was the first with a transparent vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
, allowing the radiation to be directly observed.
As recounted by Herbert Pollock:
Description
A direct consequence ofMaxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
...
is that accelerated charged particles always emit electromagnetic radiation. Synchrotron radiation is the special case of charged particles moving at relativistic speed undergoing acceleration perpendicular to their direction of motion, typically in a magnetic field. In such a field, the force due to the field is always perpendicular to both the direction of motion and to the direction of field, as shown by the Lorentz force law
Lorentz is a name derived from the Roman surname, Laurentius, which means "from Laurentum". It is the German form of Laurence. Notable people with the name include:
Given name
* Lorentz Aspen (born 1978), Norwegian heavy metal pianist and keyboar ...
.
The power carried by the radiation is found (in SI units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes Pleonasm#Acronyms and initialisms, pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most wid ...
) by the relativistic Larmor formula:
where
* is the vacuum permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric consta ...
,
* is the particle charge,
* is the magnitude of the acceleration,
* is the speed of light,
* is the Lorentz factor
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term is a quantity expressing how much the measurements of time, length, and other physical properties change for an object while that object is moving. The expression appears in several equations in special relativit ...
.
The force on the emitting electron is given by the Abraham–Lorentz–Dirac force.
When the radiation is emitted by a particle moving in a plane, the radiation is linearly polarized when observed in that plane, and circularly polarized
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to t ...
when observed at a small angle.
Synchrotron radiation from accelerators
Circular accelerators will always produce gyromagnetic radiation as the particles are deflected in the magnetic field. However, the quantity and properties of the radiation are highly dependent on the nature of the acceleration taking place. For example, due to the difference in mass, the factor of in the formula for the emitted power means that electrons radiate energy at approximately 1013 times the rate of protons. Energy loss from synchrotron radiation in circular accelerators was originally considered a nuisance, as additional energy must be supplied to the beam in order to offset the losses. However, beginning in the 1980s, circular electron accelerators known aslight sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic ener ...
have been constructed to deliberately produce intense beams of synchrotron radiation for research.
Synchrotron radiation in astronomy
Synchrotron radiation is also generated by astronomical objects, typically where relativistic electrons spiral (and hence change velocity) through magnetic fields. Two of its characteristics includepower-law
In statistics, a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities, where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity, independent of the initial size of those quantities: one qua ...
energy spectra and polarization. It is considered to be one of the most powerful tools in the study of extra-solar magnetic fields wherever relativistic charged particles are present. Most known cosmic radio sources emit synchrotron radiation. It is often used to estimate the strength of large cosmic magnetic fields as well as analyze the contents of the interstellar and intergalactic media.
History of detection
This type of radiation was first detected in a jet emitted byMessier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local uni ...
in 1956 by Geoffrey R. Burbidge, who saw it as confirmation of a prediction by Iosif S. Shklovsky in 1953. However, it had been predicted earlier (1950) by Hannes Alfvén
Hannes Olof Gösta Alfvén (; 30 May 1908 – 2 April 1995) was a Swedish electrical engineer, plasma physicist and winner of the 1970 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). He described the class of MHD waves now ...
and Nicolai Herlofson. Solar flares
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phe ...
accelerate particles that emit in this way, as suggested by R. Giovanelli in 1948 and described by J.H. Piddington in 1952.
T. K. Breus noted that questions of priority on the history of astrophysical synchrotron radiation are complicated, writing:
From supermassive black holes
It has been suggested thatsupermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical obj ...
s produce synchrotron radiation in "jets", generated by the gravitational acceleration of ions in their polar magnetic fields. The nearest such observed jet is from the core of the galaxy Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local uni ...
. This jet is interesting for producing the illusion of superluminal
Faster-than-light (also FTL, superluminal or supercausal) travel and communication are the conjectural propagation of matter or information faster than the speed of light (). The special theory of relativity implies that only particles with zero ...
motion as observed from the frame of Earth. This phenomenon is caused because the jets are travelling very near the speed of light ''and'' at a very small angle towards the observer. Because at every point of their path the high-velocity jets are emitting light, the light they emit does not approach the observer much more quickly than the jet itself. Light emitted over hundreds of years of travel thus arrives at the observer over a much smaller time period, giving the illusion of faster than light travel, despite the fact that there is actually no violation of special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The laws o ...
.
Pulsar wind nebulae
A class ofastronomical source
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, ...
s where synchrotron emission is important is pulsar wind nebula
A pulsar wind nebula (PWN, plural PWNe), sometimes called a plerion (derived from the Greek "πλήρης", ''pleres'', meaning "full"), is a type of nebula sometimes found inside the shell of a supernova remnant (SNR), powered by winds generate ...
e, also known as plerion
A pulsar wind nebula (PWN, plural PWNe), sometimes called a plerion (derived from the Greek "πλήρης", ''pleres'', meaning "full"), is a type of nebula sometimes found inside the shell of a supernova remnant (SNR), powered by winds generate ...
s, of which the Crab nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations Messier object, M1, New General Catalogue, NGC 1952, Taurus (constellation), Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name ...
and its associated pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Ea ...
are archetypal.
Pulsed emission gamma-ray radiation from the Crab has recently been observed up to ≥25 GeV, probably due to synchrotron emission by electrons trapped in the strong magnetic field around the pulsar.
Polarization in the Crab nebula at energies from 0.1 to 1.0 MeV, illustrates this typical property of synchrotron radiation.
Interstellar and intergalactic media
Much of what is known about the magnetic environment of theinterstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
and intergalactic medium
Intergalactic may refer to:
* "Intergalactic" (song), a song by the Beastie Boys
* ''Intergalactic'' (TV series), a 2021 UK science fiction TV series
* Intergalactic space
* Intergalactic travel, travel between galaxies in science fiction and ...
is derived from observations of synchrotron radiation. Cosmic ray electrons moving through the medium interact with relativistic plasma and emit synchrotron radiation which is detected on Earth. The properties of the radiation allow astronomers to make inferences about the magnetic field strength and orientation in these regions. However, accurate calculations of field strength cannot be made without knowing the relativistic electron density.
See also
* * * * * * *Notes
References
* Brau, Charles A. Modern Problems in Classical Electrodynamics. Oxford University Press, 2004. . * Jackson, John David. Classical Electrodynamics. John Wiley & Sons, 1999. *External links
Cosmic Magnetobremsstrahlung (synchrotron Radiation)
by Ginzburg, V. L., Syrovatskii, S. I., ARAA, 1965
Developments in the Theory of Synchrotron Radiation and its Reabsorption
by Ginzburg, V. L., Syrovatskii, S. I., ARAA, 1969
Lightsources.org
BioSync
– a structural biologist's resource for high energy data collection facilities
X-Ray Data Booklet
{{Authority control Particle physics Synchrotron-related techniques Electromagnetic radiation Experimental particle physics