



A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer";
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
: ''shul'',
Ladino
Ladino, derived from Latin, may refer to:
* The register of Judaeo-Spanish used in the translation of religious texts, such as the Ferrara Bible
*Ladino people, a socio-ethnic category of Mestizo or Hispanicized people in Central America especi ...
: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
house of worship
A place of worship is a specially designed structure or space where individuals or a group of people such as a congregation come to perform acts of devotion, veneration, or religious study. A building constructed or used for this purpose is somet ...
. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main
sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a saf ...
and sometimes smaller
chapels
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type ...
), where
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including
Weddings
A wedding is a ceremony where two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriage vo ...
,
Bar Mitzvahs or
Bat Mitzvahs,
Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have
rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and
Hebrew school
Hebrew school is Jewish education focusing on topics of Jewish history, learning the Hebrew language, and finally learning their Torah Portion, in preparation for the ceremony in Judaism of entering adulthood, known as a Bar or Bat Mitzvah. Hebr ...
, sometimes Jewish
preschools
A preschool, also known as nursery school, pre-primary school, or play school or creche, is an educational establishment or learning space offering early childhood education to children before they begin compulsory education at primary school ...
, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display.
Synagogues are
consecrated
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different grou ...
spaces used for the purpose of
Jewish prayer
Jewish prayer ( he, תְּפִלָּה, ; plural ; yi, תּפֿלה, tfile , plural ; Yinglish: davening from Yiddish 'pray') is the prayer recitation that forms part of the observance of Rabbinic Judaism. These prayers, often with i ...
, study, assembly, and reading of the
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
(read in its entirety once a year in weekly Torah portions during religious Services). However, a Synagogue is not always necessary for Jewish worship, due to adaptations during times of Jewish persecution in countries and regions that banned Judaism, frequently destroying and/or reappropriating Synagogues into Churches or even government buildings. ''
Halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
'' (Jewish "law," or
Mitzvot
In its primary meaning, the Hebrew word (; he, מִצְוָה, ''mīṣvā'' , plural ''mīṣvōt'' ; "commandment") refers to a commandment commanded by God to be performed as a religious duty. Jewish law () in large part consists of discus ...
, from the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah ...
-- the "Oral Torah") state that communal Jewish worship can be carried out wherever a ''
minyan
In Judaism, a ''minyan'' ( he, מניין \ מִנְיָן ''mīnyān'' , lit. (noun) ''count, number''; pl. ''mīnyānīm'' ) is the quorum of ten Jewish adults required for certain religious obligations. In more traditional streams of Jud ...
'' (a group of at least 10 Jewish adults) is assembled. Worship can also happen alone or with fewer than 10 people, but there are certain prayers that are considered by ''halakha'' as solely communal, and these can therefore be recited only by a ''minyan'', depending on sect of Judaism. In terms of its specific ritual and liturgical functions, the Synagogue does not replace the symbol of the long-destroyed
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusa ...
(1st or 2nd Temple).
Terminology
Israelis
Israelis ( he, יִשְׂרָאֵלִים, translit=Yīśrāʾēlīm; ar, الإسرائيليين, translit=al-ʾIsrāʾīliyyin) are the citizens and nationals of the State of Israel. The country's populace is composed primarily of Jew ...
use the
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
term ' "house of assembly".
Ultra-Orthodox Hasidic Jews have traditionally used the
Western Yiddish (German-Yiddish) term ' (cognate with the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, 'school') in everyday speech.
Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefar ...
and
Romaniote Jews
The Romaniote Jews or the Romaniotes ( el, Ῥωμανιῶτες, ''Rhomaniótes''; he, רומניוטים, Romanyotim) are a Greek-speaking ethnic Jewish community native to the Eastern Mediterranean. They are one of the oldest Jewish comm ...
generally use the term ''kal'' (from the Hebrew ''ḳahal'', meaning "community").
Spanish Jews
Spanish and Portuguese Jews, also called Western Sephardim, Iberian Jews, or Peninsular Jews, are a distinctive sub-group of Sephardic Jews who are largely descended from Jews who lived as New Christians in the Iberian Peninsula during the ...
call the synagogue an and Portuguese Jews call it a .
Persian Jews
Persian Jews or Iranian Jews ( fa, یهودیان ایرانی, ''yahudiān-e-Irāni''; he, יהודים פרסים ''Yəhūdīm Parsīm'') are the descendants of Jews who were historically associated with the Persian Empire, whose successor ...
and some
Karaite Jews
Karaite Judaism () or Karaism (, sometimes spelt Karaitism (; ''Yahadut Qara'it''); also spelt Qaraite Judaism, Qaraism or Qaraitism) is a Jewish religious movement characterized by the recognition of the written Torah alone as its supreme au ...
also use the term ''
kenesa
A kenesa ( Karaim: כְּנִיסָא ''kǝnîsāʾ'') is an Eastern European or Persian Karaite synagogue.
Kenesas are similar to Rabbinical synagogues. In Eastern Europe, they are laid out along north-south axis (facing Jerusalem). Starting f ...
'', which is derived from
Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
, and some
Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained i ...
use ''kenis'' or ''qnis''. Most
Reform
Reform ( lat, reformo) means the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The use of the word in this way emerges in the late 18th century and is believed to originate from Christopher Wyvill#The Yorkshire Associati ...
and
Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization i ...
Jews use the word ''temple'' interchangeably with Synagogue. The
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word ''synagogue'' is used in
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
to cover the preceding possibilities.
Origins

Although synagogues existed a long time before the destruction of the
Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
in 70 CE, communal worship in the time while the Temple still stood focused mostly on ''
korban
In Judaism, the korban ( ''qorbān''), also spelled ''qorban'' or ''corban'', is any of a variety of sacrificial offerings described and commanded in the Torah. The plural form is korbanot, korbanoth or korbans.
The term Korban primarily re ...
ot'' brought by the ''
Kohanim
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally be ...
'' (Aaronic priesthood line of Rabbinical succession) in the
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusa ...
. The all-day
Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day's ...
service, was an event in which the congregation both observed the movements of the ''kohen gadol'' ("
high priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rever ...
") as he presided over the day's traditions and processions, and administered prayers for success.
According to Jewish tradition, the men of the
Great Assembly
According to Jewish tradition the Men of the Great Assembly ( he, כְּנֶסֶת הַגְּדוֹלָה) or Anshei Knesset HaGedolah (, "The Men of the Great Assembly"), also known as the Great Synagogue, or ''Synod'', was an assembly of 120 sc ...
(around 5th century BCE) formalized and standardized the language of the Jewish prayers. Prior to that people prayed as they saw fit, with each individual praying in his or her own way, and there were no standard prayers that were recited.
Johanan ben Zakai
:''See Yohanan for more rabbis by this name''.
Yohanan ben Zakkai ( he, יוֹחָנָן בֶּן זַכַּאי, ''Yōḥānān ben Zakkaʾy''; 1st century CE), sometimes abbreviated as Ribaz () for Rabbi Yohanan ben Zakkai, was one of the Tan ...
, one of the leaders at the end of the
Second Temple period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Jewis ...
, promulgated the idea of creating individual houses of worship in whatever locale Jews found themselves. This contributed to the continuity of the Jewish people by maintaining a unique identity and a portable way of worship despite the destruction of the Temple, according to many historians.
Synagogues in the sense of purpose-built spaces for worship, or rooms originally constructed for some other purpose but reserved for formal, communal prayer, however, existed long before the destruction of the Second Temple.
The earliest archaeological evidence for the existence of very early synagogues comes from Egypt, where stone synagogue dedication inscriptions dating from the 3rd century BCE prove that synagogues existed by that date.
More than a dozen Jewish (and possibly
Samaritan) Second Temple period synagogues have been identified by archaeologists in
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, and in other countries belonging to the
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
world.
Any Jew or group of Jews can build a synagogue. Synagogues have been constructed by ancient Jewish "kings" (the English word "king" has a different context lost in English translation; more appropriately translating to "leader"), by wealthy patrons, as part of a wide range of human institutions including secular educational institutions, governments, and hotels, by the entire Jewish community of living in a particular village or region, or by sub-groups of Jewish people arrayed according to occupation, ethnicity (i.e. the Sephardi,
Yemeni
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and sh ...
, Polish or
Persian Jews
Persian Jews or Iranian Jews ( fa, یهودیان ایرانی, ''yahudiān-e-Irāni''; he, יהודים פרסים ''Yəhūdīm Parsīm'') are the descendants of Jews who were historically associated with the Persian Empire, whose successor ...
of a town), style of religious observance (i.e., Reform, Orthodox synagogue), or by the followers of a particular Rabbi (only in very small congregations or ultra-orthodox Hasidism).
It has been theorized that the synagogue became a place of worship in the region upon the destruction of the Second Temple during the
First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
; however, others speculate that there had been places of prayer, apart from the Temple, during the Hellenistic period. The popularization of prayer over sacrifice during the years prior to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE had prepared the Jews for life in the diaspora, where prayer would serve as the focus of Jewish worship.
Despite the possibility of synagogue-like spaces prior to the First Jewish–Roman War, the synagogue emerged as a stronghold for Jewish worship upon the destruction of the Temple. For Jews living in the wake of the Revolt, the synagogue functioned as a "portable system of worship". Within the synagogue, Jews worshiped by way of prayer rather than sacrifices, which had previously served as the main form of worship within the Second Temple.
Second Temple period
In 1995, Howard Clark Kee argued that synagogues were not a developed feature of Jewish life prior to the First Jewish-Roman War (66-73 CE). Kee interpreted his findings as evidence that the mentions of synagogues in the New Testament, including Jesus's visitations of synagogues in various Jewish settlements in Israel, were anachronistic. However, by 2018, Mordechai Aviam reported that there were now at least nine synagogues excavated known to pre-date the
destruction of the Jerusalem Temple in 70 CE, including in Magdala, Gamla, Masada, Herodium, Modi‘in (Kh. Umm el-‘Umdan), Qiryat Sepher (Kh. Bad ‘Issa), and Kh. Diab. Aviam concluded that he thought almost every Jewish settlement at the time, whether it was a polis or a village, had a synagogue.
*
Gamla
Gamla, alt. sp. Gamala ( he, גַּמְלָא, The Camel) was an ancient Jewish city on the Golan Heights. It is believed to have been founded as a Seleucid fort during the Syrian Wars which was turned into a city under Hasmonean rule in 81 ...
- a synagogue was discovered near the city gate at Gamla, a site in the Golan northeast of the Sea of Galilee. This city was destroyed by the Roman army in 67 CE and was never rebuilt.
*
Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the Dea ...
- a synagogue was discovered on the western side of Masada, just south of the palace complex at the northern end of the site. One of the unique finds at this synagogue was a group of 14 scrolls, which included biblical, sectarian, and apocryphal documents.
*
Herodium
Herodion ( grc, Ἡρώδειον, ar, هيروديون, he, הרודיון), Herodium (Latin), or Jabal al-Fureidis ( ar, جبل فريديس, , "Mountain of the Little Paradise") is an ancient Jewish fortress and town, located in what is now ...
- a synagogue from the 1st century was discovered in Herod's palace fortress at Herodium.
*
Magdala
Magdala (Aramaic: מגדלא, ''Magdala'', meaning "tower"; Hebrew: , ''Migdal''; ar, المجدل, ''al-Majdal'') was an ancient Jewish city on the shore of the Sea of Galilee, north of Tiberias. In the Babylonian Talmud it is known as Magda ...
- also known as the Migdal Synagogue, this synagogue was discovered in 2009. One of the unique features of this synagogue, which is located on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee, is an intricately carved stone
block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
that was found in the center of the main room.
* Modi'in - Discovered between
Modi'in
Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut ( he, מוֹדִיעִין-מַכַּבִּים-רֵעוּת) is an Israeli city located in central Israel, about southeast of Tel Aviv and west of Jerusalem, and is connected to those two cities via Highway 443. In t ...
and
Latrun
Latrun ( he, לטרון, ''Latrun''; ar, اللطرون, ''al-Latrun'') is a strategic hilltop in the Latrun salient in the Ayalon Valley, and a depopulated Palestinian village. It overlooks the road between Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, 25 kilometers ...
is the
oldest synagogue within modern Israel that has been found to date, built during the second century BCE. It includes three rooms and a nearby
mikve
Mikveh or mikvah (, ''mikva'ot'', ''mikvoth'', ''mikvot'', or (Yiddish) ''mikves'', lit., "a collection") is a bath used for the purpose of ritual immersion in Judaism to achieve ritual purity.
Most forms of ritual impurity can be purifi ...
.
File:Gamla Synagogue (7).JPG, First century synagogue at Gamla
File:Masada 051013 Synagogue 01.jpg, First century synagogue at Masada
File:Magdala-588.jpg, First century synagogue at Magdala
File:Herodion Synagogue IMG 0708.JPG, First century synagogue at Herodium
Middle Ages
Rabbi and philosopher,
Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
(1138–1204), described the various customs in his day with respect to local synagogues:
Synagogues and houses of study must be treated with respect. They are swept and sprinkled ith water
The Ith () is a ridge in Germany's Central Uplands which is up to 439 m high. It lies about 40 km southwest of Hanover and, at 22 kilometres, is the longest line of crags in North Germany.
Geography
Location
The Ith is immediatel ...
to lay the dust. In Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, in Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
and in the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
, it is customary to kindle lamps in the synagogues and to spread mats on the floor upon which the worshippers sit. In the lands of Edom (Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwine ...
), they sit in synagogues upon chairs r benches
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Irelan ...
File:Sepphoris (Tzippori) 290314 12.jpg, Mosaic in the Tzippori Synagogue
Tzippori Synagogue (Sepphoris Synagogue) is an ancient synagogue discovered in Sepphoris, a Roman-era Jewish city in the Galilee, now an archaeological site and a national park in Israel.
History
Based on numismatic evidence, the synagogue appe ...
File:Ruins of the Ancient Synagogue at Bar'am.jpg, Ruins of the ancient synagogue of Kfar Bar'am
Kafr Bir'im, also Kefr Berem ( ar, كفر برعم, he, כְּפַר בִּרְעָם), was a former village in Mandatory Palestine, located in modern-day northern Israel, south of the Lebanese border and northwest of Safed. The village was s ...
Samaritan synagogues

Name and history
The Samaritan house of worship is also called a synagogue.
During the 3rd and 2nd centuries BCE, during the Hellenistic period, the Greek word used in the
Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
by Samaritans and Jews was the same: ''proseucheμ'' (literally, a place of prayer); a later, 3rd or 4th century CE inscription, uses a similar Greek term: ''eukteμrion'' (prayer house).
The oldest Samaritan synagogue discovered so far is from
Delos
The island of Delos (; el, Δήλος ; Attic: , Doric: ), near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island are ...
in the
Aegean Islands, with an inscription dated between 250 and 175 BCE, while most Samaritan synagogues excavated in the wider
Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
and ancient
Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first- ...
in particular, were built during the 4th-7th centuries, at the very end of the Roman and throughout the Byzantine period.
Distinguishing elements
The elements which distinguish Samaritan synagogues from contemporary Jewish ones are:
* Alphabet: the use of the
Samaritan script
The Samaritan script is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic.
Samaritan is a direc ...
* Orthography. When the Samaritan script is used, there are some Hebrew words which would be spelled in a way typical only for the
Samaritan Pentateuch
The Samaritan Torah ( Samaritan Hebrew: , ''Tōrāʾ''), also called the Samaritan Pentateuch, is a text of the Torah written in the Samaritan script and used as sacred scripture by the Samaritans. It dates back to one of the ancient version ...
, for instance "forever" is written 'lmw instead of l'lm.
When Greek is the language used in inscriptions, typically, Samaritans may contract two
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
words into one, such ''har'' (mountain) and Gerizim becoming, in Greek, ''Argarizein''.
* Orientation: the façade, or entrance of the Samaritan synagogue, is typically facing towards
Mount Gerizim
Mount Gerizim (; Samaritan Hebrew: ''ʾĀ̊rgā̊rīzēm''; Hebrew: ''Har Gərīzīm''; ar, جَبَل جَرِزِيم ''Jabal Jarizīm'' or جَبَلُ ٱلطُّورِ ''Jabal at-Ṭūr'') is one of two mountains in the immediate vicinit ...
, which is the most holy site to Samaritans, while Jewish synagogues would be oriented towards Jerusalem and the Temple Mount.
* Decoration: the mosaic floor and other architectural elements or artifacts are sometimes decorated with typical symbols.
As the Samaritans have historically adhered more strictly to the
commandment forbidding the creation of any "graven image", they would not use any depictions of man or beast.
Representations of the signs of the zodiac, of human figures or even Greek deities such as the god
Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
, as seen in Byzantine-period Jewish synagogues, would be unimaginable in Samaritan buildings of any period.
:A representation of Mount Gerizim is a clear indication of Samaritan identity.
On the other hand, although the existence of a Samaritan temple on Mount Gerizim is both mentioned by Josephus and confirmed by archaeological excavation at its summit, the temple's early destruction in the 2nd century BCE led to its memory disappearing from Samaritan tradition, so that no temple-related items would be found in Samaritan synagogue depictions.
Religious implements, such as are also known from ancient Jewish synagogue mosaics (
menorah,
shofar
A shofar ( ; from he, שׁוֹפָר, ) is an ancient musical horn typically made of a ram's horn, used for Jewish religious purposes. Like the modern bugle, the shofar lacks pitch-altering devices, with all pitch control done by varying the ...
,
shewbread
Showbread ( he, לחם הפנים ''Leḥem haPānīm'', literally: "Bread of the Faces"), in the King James Version: shewbread, in a biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-de ...
table,
trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard ...
s, incense shovels, and specifically the façade of what looks like a temple or a Torah shrine) are also present in Samaritan ones, but the objects are always related to the desert
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
, the
Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an e ...
within the Tabernacle, or the
Torah shrine
A Torah ark (also known as the ''Heikhal'', or the ''Aron Kodesh'') refers to an ornamental chamber in the synagogue that houses the Torah scrolls.
History
The ark, also known as the ''ark of law'', or in Hebrew the ''Aron Kodesh'' or ''aron ha- ...
in the synagogue itself.
Samaritans believe that at the end of time the Tabernacle and its utensils will be recovered from the place they were buried on Mount Gerizim and as such play an important role in Samaritan beliefs.
Since the same artists, such as mosaicists, worked for all ethno-religious communities of the time, some depictions might be identical in Samaritan and Jewish synagogues, Christian churches and pagan temples, but their significance would differ.
:Missing from Samaritan synagogue floors would be images often found in Jewish ones: the
lulav
''Lulav'' (; he, לולב) is a closed frond of the date palm tree. It is one of the Four Species used during the Jewish holiday of Sukkot. The other Species are the ''hadass'' (Myrtus, myrtle), '' aravah'' (willow), and ''etrog'' (citron). Wh ...
(palm-branch) and
etrog
Etrog ( he, אֶתְרוֹג, plural: '; Ashkenazi Hebrew: ', plural: ') is the yellow citron or ''Citrus medica'' used by Jews during the week-long holiday of Sukkot as one of the four species. Together with the ''lulav'', ''hadass'', and '' ...
(lemon-like fruit) have a different ritual use by Samaritans celebrating
Sukkot
or ("Booths, Tabernacles")
, observedby = Jews, Samaritans, a few Protestant denominations, Messianic Jews, Semitic Neopagans
, type = Jewish, Samaritan
, begins = 15th day of Tishrei
, ends = 21st day of Tishre ...
, and do not appear on mosaic floors.
* Ritual baths near the synagogue after 70 CE: Jews abandoned the habit of building
mikva'ot
Tractate Miqwaʾoth (Hebrew: מקואות, lit. "Pools of Water"; in Talmudic Hebrew: ''Miqwaʾoth'') is a section of the Mishna discussing the laws pertaining to the building and maintenance of a mikvah, a Jewish ritual bath. Like most of Seder T ...
next to their houses of worship after the
70 CE destruction of the
Jerusalem Temple
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusa ...
, but Samaritans continued with the practice.
Archaeological finds
Ancient Samaritan synagogues are mentioned by literary sources or have been found by archaeologists in the Diaspora, in the wider Holy Land, and specifically in Samaria.
Diaspora
*
Delos Synagogue The synagogue of Delos, Greece, is one of the oldest synagogues known today, its proposed origin dating between 150 and 128 BCE, although its identification as a synagogue has been disputed.
Discovery and excavation
The structure was discovered in ...
: a Samaritan inscription has been dated to between 250 and 175 BCE.
*
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and
Tarsus: ancient literature offers hints that Samaritan synagogues may have existed in these cities between the fourth and sixth centuries CE.
*
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capi ...
and
Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
: short inscriptions found there and using the Samaritan and Greek alphabet may originate from Samaritan synagogues.
The wider Holy Land
*
Sha'alvim
Sha'alvim ( he, שַׁעַלְבִים) is a religious kibbutz in central Israel and one of only two affiliated with Poalei Agudat Yisrael (Hafetz Haim being the other). Located near the city of Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut, it falls under the jurisdic ...
synagogue, discovered in Judea, northwest of Jerusalem. Probably built in the 4th or 5th century CE and destroyed in the 5th or 6th.
*
Tell Qasile
Tell Qasile is an archaeological site near the Yarkon River in Tel Aviv, Israel. Over 3,000 years old, the site contains the remains of a port city founded by the Philistines in the 12th century BC.
Prior to 1948, it was on the village lands of ...
synagogue, built at the beginning of the 7th century CE
*
Beth Shean
Beit She'an ( he, בֵּית שְׁאָן '), also Beth-shean, formerly Beisan ( ar, بيسان ), is a town in the Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level.
Beit She'an is be ...
, "Synagogue A". A room added to an existing building in the late 6th or early 7th century CE served as a Samaritan synagogue.
Samaria
* El-Khirbe synagogue, discovered c. 3 km from
Sebaste, was built in the 4th century CE and remained in use into the Early Islamic period, with a break during the late 5th–early 6th century
*
Khirbet Samara
Khirbet Samara ( he, ח'ירבת סמארה) is an archeological site located in the West Bank. It lies near the Israeli settlement of Einav, 9 km east of Taibe.
The site was first surveyed by the Palestine Exploration Fund in the late 19th ...
synagogue, c. 20 km northwest of
Nablus
Nablus ( ; ar, نابلس, Nābulus ; he, שכם, Šəḵem, ISO 259-3: ; Samaritan Hebrew: , romanized: ; el, Νεάπολις, Νeápolis) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a populati ...
and built in the 4th century CE
* Zur Natan synagogue, c. 29 km west of Nablus and built in the 5th century CE
Christianity
In the
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
, the word appears 56 times, mostly in the
Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark, and Gospel of Luke, Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical ...
, but also in the
Gospel of John
The Gospel of John ( grc, Εὐαγγέλιον κατὰ Ἰωάννην, translit=Euangélion katà Iōánnēn) is the fourth of the four canonical gospels. It contains a highly schematic account of the ministry of Jesus, with seven "sig ...
() and the
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
(). It is used in the sense of 'assembly' in the
Epistle of James
The Epistle of James). is a general epistle and one of the 21 epistles ( didactic letters) in the New Testament.
James 1:1 identifies the author as "James, a servant of God and of the Lord Jesus Christ" who is writing to "the twelve tribes ...
(). Alternatively, the epistle of James (in Greek, clearly Ἰάκωβος or יעקב, anglicized to Jacob) refers to a place of assembly that was indeed Jewish, with Jacob ben Joseph perhaps an elder there. The specific word in James (Jacob) 2:2 could easily be rendered "synagogue," from the Greek συναγωγὴν.
During the first Christian centuries,
Jewish Christian
Jewish Christians ( he, יהודים נוצרים, yehudim notzrim) were the followers of a Jewish religious sect that emerged in Judea during the late Second Temple period (first century AD). The Nazarene Jews integrated the belief of Jesus ...
are hypothesized to have used houses of worship known in academic literature as synagogue-churches. Scholars have claimed to have identified such houses of worship of the Jews who had accepted
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
as the
Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of ''mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach'' ...
in Jerusalem
and
Nazareth
Nazareth ( ; ar, النَّاصِرَة, ''an-Nāṣira''; he, נָצְרַת, ''Nāṣəraṯ''; arc, ܢܨܪܬ, ''Naṣrath'') is the largest city in the Northern District of Israel. Nazareth is known as "the Arab capital of Israel". In ...
.
Architectural design

There is no set
blueprint
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing or engineering drawing using a contact print process on light-sensitive sheets. Introduced by Sir John Herschel in 1842, the process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number ...
for synagogues and the architectural shapes and interior designs of synagogues vary greatly. In fact, the influence from other local religious buildings can often be seen in synagogue arches, domes and towers.
Historically, synagogues were built in the prevailing architectural style of their time and place. Thus, the synagogue in
Kaifeng, China looked very like Chinese temples of that region and era, with its outer wall and open garden in which several buildings were arranged. The styles of the earliest synagogues resembled the temples of other cults of the
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The surviving synagogues of medieval Spain are embellished with
mudéjar
Mudéjar ( , also , , ca, mudèjar , ; from ar, مدجن, mudajjan, subjugated; tamed; domesticated) refers to the group of Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period despite the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for ...
plasterwork. The surviving medieval synagogues in
Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
and
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
are typical
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
structures.
With the emancipation of Jews in Western European countries, which not only enabled Jews to enter fields of enterprise from which they were formerly barred, but gave them the right to build synagogues without needing special permissions, synagogue architecture blossomed. Large Jewish communities wished to show not only their wealth but also their newly acquired status as citizens by constructing magnificent synagogues. These were built across Western Europe and in the United States in all of the historicist or revival styles then in fashion. Thus there were
Neoclassical,
Neo-Byzantine
Neo-Byzantine architecture (also referred to as Byzantine Revival) was a revival movement, most frequently seen in religious, institutional and public buildings. It incorporates elements of the Byzantine style associated with Eastern and Orthod ...
,
Romanesque Revival
Romanesque Revival (or Neo-Romanesque) is a style of building employed beginning in the mid-19th century inspired by the 11th- and 12th-century Romanesque architecture. Unlike the historic Romanesque style, Romanesque Revival buildings tended to ...
,
Moorish Revival
Moorish Revival or Neo-Moorish is one of the exotic revival architectural styles that were adopted by architects of Europe and the Americas in the wake of Romanticist Orientalism. It reached the height of its popularity after the mid-19th centur ...
,
Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
, and
Greek Revival
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but ...
. There are
Egyptian Revival
Egyptian Revival is an architectural style that uses the motifs and imagery of ancient Egypt. It is attributed generally to the public awareness of ancient Egyptian monuments generated by Napoleon's conquest of Egypt and Admiral Nelson's defeat ...
synagogues and even one
Mayan Revival
Mayan Revival is a modern architectural style popular in the Americas during the 1920s and 1930s that drew inspiration from the architecture and iconography of pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures.
History
Origins
Though the name of the s ...
synagogue. In the 19th century and early 20th century heyday of historicist architecture, however, most historicist synagogues, even the most magnificent ones, did not attempt a pure style, or even any particular style, and are best described as eclectic.
In the post-war era, synagogue architecture abandoned historicist styles for modernism.
File:Synagogue Aleppo.jpg, Central Synagogue of Aleppo
The Central Synagogue of Aleppo, ( he, בית הכנסת המרכזי בחאלֶבּ, ar, كنيس حلب المركزي, Kanīs Ḥalab al-Markazī), also known as the Great Synagogue of Aleppo, Joab's Synagogue or Al-Bandara Synagogue ( ar, ...
, Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
, Syria (5th century)
File:Kochi Jewish Synagogue C.jpg, Paradesi Synagogue
The Paradesi Synagogue aka Cochin Jewish Synagogue or the Mattancherry Synagogue (Malayalam: പരദേശി ജൂതപള്ളി) is a synagogue located in Mattancherry Jew Town, a suburb of the city of Kochi, Kerala, in India. It wa ...
, Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
, India (1568)
File:Sofia Synagogue 11c.jpg, Sofia Synagogue
The Sofia Synagogue ( bg, Софийска синагога, ''Sofiyska sinagoga'') is the largest synagogue in Southeastern Europe, one of two functioning in Bulgaria (with the other one in Plovdiv) and the third-largest in Europe. , Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
, Bulgaria (1909)
File:Frank Lloyd Wright - Beth Sholom Synagogue - Elkins Park, PA (7175161021).jpg, Beth Sholom Congregation, Elkins Park
Elkins Park is an unincorporated community in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. It is split between Cheltenham and Abington Townships in the northern suburbs outside of Philadelphia, which it borders along Cheltenham Avenue roughly from Ce ...
, USA (1959)
File:Jerusalem Great Synagogue.jpg, Great Synagogue of Jerusalem (1982)
File:Synagoge muenchen(softeis) ShiftN cropped.jpg, Ohel Jakob synagogue, Munich, Germany (2006)
Interior elements
Bimah (platform)
All synagogues contain a ''
Bimah'', a large, raised, reader's platform (called (reading dais) by Sephardim), where the Torah scroll is placed to be read. In Sephardi synagogues it is also used as the prayer leader's reading desk. This is also so in the Ashkenazi United Synagogue in England, UK, who adopted some of the Sephardi customs.
File:Saluzzo Synagogue 11 - Bimah et Arche Sainte.jpg, Bimah of the Saluzzo Synagogue
Saluzzo (; pms, Salusse ) is a town and former principality in the province of Cuneo, in the Piedmont region, Italy.
The city of Saluzzo is built on a hill overlooking a vast, well-cultivated plain. Iron, lead, silver, marble, slate etc. are fo ...
, Saluzzo
Saluzzo (; pms, Salusse ) is a town and former principality in the province of Cuneo, in the Piedmont region, Italy.
The city of Saluzzo is built on a hill overlooking a vast, well-cultivated plain. Iron, lead, silver, marble, slate etc. are fo ...
, Italy
File:Touro Synagogue National Historic Site TOSY1085.jpg, Bimah of the Touro Synagogue
The Touro Synagogue or Congregation Jeshuat Israel ( he, קהל קדוש ישועת ישראל) is a synagogue built in 1763 in Newport, Rhode Island. It is the Oldest synagogues in the United States, oldest synagogue building still standing in t ...
in Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is an American seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, ...
, USA
File:Inside old synagogue Krakow.JPG, Cast-iron Bimah of the Old Synagogue, Kraków, Old Synagogue in Kraków, Poland
Table or lectern
In Ashkenazi synagogues, the
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
was read on a reader's table located in the center of the room, while the leader of the prayer service, the hazzan, stood at his own lectern or table, facing the Ark. In Sephardic synagogues, the table for reading the Torah (reading dais) was commonly placed at the opposite side of the room from the Torah Ark, leaving the center of the floor empty for the use of a ceremonial procession carrying the Torah between the Ark and the reading table. Most contemporary synagogues feature a lectern for the rabbi.
Torah Ark
The Torah Ark, called in Hebrew ''Aron Kodesh'' or 'holy chest', and alternatively called the ''heikhal''— or 'temple' by Sephardim, Sephardic Jews, is a cabinet in which the
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
scrolls are kept.
The ark in a synagogue is almost always positioned in such a way such that those who face it are facing towards Jerusalem. Thus, sanctuary seating plans in the Western world generally face Mizrah, east, while those east of Israel face west. Sanctuaries in Israel face towards Jerusalem. Occasionally synagogues face other directions for structural reasons; in such cases, some individuals might turn to face Jerusalem when standing for prayers, but the congregation as a whole does not.
The Ark is reminiscent of the
Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an e ...
, which held the tablets inscribed with the Ten Commandments. This is the holiest spot in a synagogue, equivalent to the Holy of Holies. The Ark is often closed with an ornate curtain, the , which hangs outside or inside the ark doors.
Eternal Light

Other traditional features include a continually lit lamp or lantern, usually electric in contemporary synagogues, called the (), the "Eternal Light", used as a way to honor the Divine Presence.
Inner decoration
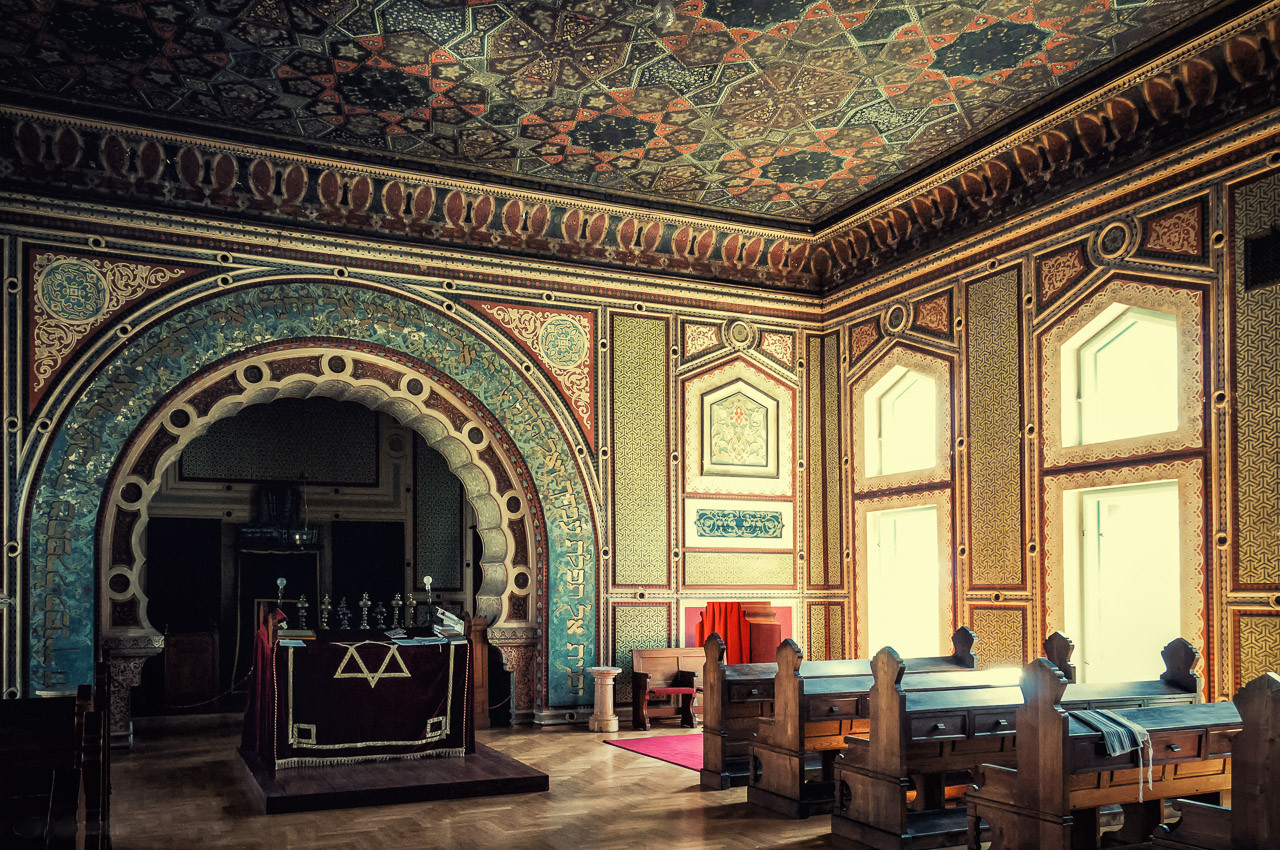

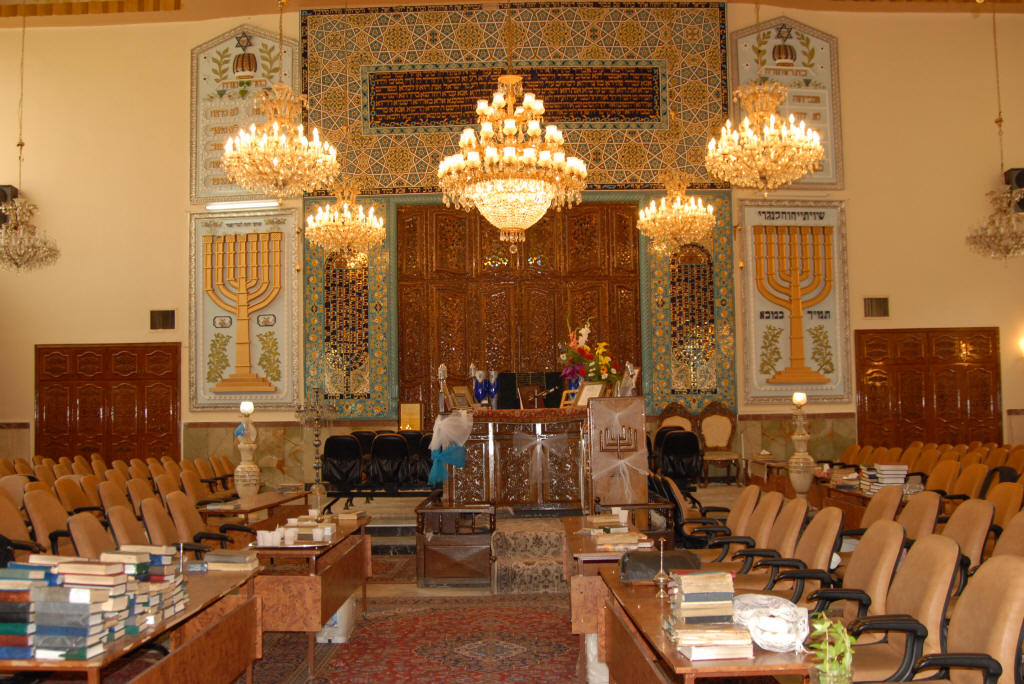
A synagogue may be decorated with artwork, but in the Rabbinic and Orthodox tradition, three-dimensional sculptures and depictions of the human body are not allowed as these are considered akin to idolatry.
Seating
Originally, synagogues were made devoid of much furniture, the Jewish congregants in
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
(North Africa),
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
, the
Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
and Yemen having a custom to sit upon the floor, which had been strewn with mats and cushions, rather than upon chairs or benches. In other European towns and cities, however, Jewish congregants would sit upon chairs and benches. Today, the custom has spread in all places to sit upon chairs and benches.
Until the 19th century, in an Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi synagogue, all seats most often faced the Torah Ark. In a Sephardi Jews, Sephardic synagogue, seats were usually arranged around the perimeter of the sanctuary, but when the worshipers stood up to pray, everyone faced the Ark.
Special seats
Many current synagogues have an elaborate chair named for the prophet Elijah, which is only sat upon during the ceremony of Brit milah.
In ancient synagogues, a special chair placed on the wall facing Jerusalem and next to the Torah Shrine was reserved for the prominent members of the congregation and for important guests.
[The Interactive Bible]
''Synagogue Moses' Seat: Metaphor of Pride''
/ref> Such a stone-carved and inscribed seat was discovered at archaeological excavations in the synagogue at Chorazin in Galilee and dates from the 4th–6th century; another one was discovered at the Delos Synagogue The synagogue of Delos, Greece, is one of the oldest synagogues known today, its proposed origin dating between 150 and 128 BCE, although its identification as a synagogue has been disputed.
Discovery and excavation
The structure was discovered in ...
, complete with a footstool.
Rules for attendees
Removing one's shoes
In Yemen, the Jewish custom was to remove one's shoes immediately prior to entering the synagogue, a custom that had been observed by Jews in other places in earlier times. The same practice of removing one's shoes before entering the synagogue was also largely observed among Jews in Morocco in the early 20th-century. On the island of Djerba in Tunisia, Jews still remove their shoes when entering a synagogue. The custom of removing one's shoes is no longer practiced in Israel, the United Kingdom, or the United States. However, in Karaite Judaism, the custom of removing one's shoes prior to entering a synagogue is still observed worldwide.
Gender separation
In Orthodox synagogues, men and women do not sit together. The synagogue features a partition () dividing the men's and women's seating areas, or a separate women's section located on a balcony.
Denominational differences
Reform Judaism
 The German–Jewish Reform movement, which arose in the early 19th century, made many changes to the traditional look of the synagogue, keeping with its desire to simultaneously stay Jewish yet be accepted by the surrounding culture.
The Hamburg Temple, first Reform synagogue, which opened in Hamburg in 1811, introduced changes that made the synagogue look more like a church. These included: the installation of an Organ (music), organ to accompany the prayers (even on Shabbat, when musical instruments are proscribed by halakha), a choir to accompany the hazzan, and vestments for the synagogue rabbi to wear.
In following decades, the central reader's table, the Bimah, was moved to the front of the Reform sanctuary—previously unheard-of in Orthodox synagogues.
Gender separation was also removed.
The German–Jewish Reform movement, which arose in the early 19th century, made many changes to the traditional look of the synagogue, keeping with its desire to simultaneously stay Jewish yet be accepted by the surrounding culture.
The Hamburg Temple, first Reform synagogue, which opened in Hamburg in 1811, introduced changes that made the synagogue look more like a church. These included: the installation of an Organ (music), organ to accompany the prayers (even on Shabbat, when musical instruments are proscribed by halakha), a choir to accompany the hazzan, and vestments for the synagogue rabbi to wear.
In following decades, the central reader's table, the Bimah, was moved to the front of the Reform sanctuary—previously unheard-of in Orthodox synagogues.
Gender separation was also removed.
Synagogue as community center
Synagogues often take on a broader role in modern Jewish communities and may include additional facilities such as a catering hall, kosher kitchen, religious school, library, day care center and a smaller chapel for daily services.
Synagogue offshoots
Since many Orthodox and some non-Orthodox Jews prefer to collect a minyan (a quorum of ten) rather than pray alone, they commonly assemble at pre-arranged times in offices, living rooms, or other spaces when these are more convenient than formal synagogue buildings. A room or building that is used this way can become a dedicated small synagogue or prayer room. Among Ashkenazi Jews they are traditionally called (, pl. or , Yiddish for "little house"), and are found in Orthodox communities worldwide.
Another type of communal prayer group, favored by some contemporary Jews, is the ''chavurah'' (, pl. ''chavurot'', ), or prayer fellowship. These groups meet at a regular place and time, either in a private home or in a synagogue or other institutional space. In classical antiquity, antiquity, the Pharisees lived near each other in ''chavurot'' and dined together to ensure that none of the food was unfit for consumption.
List of "great synagogues"
Some synagogues bear the title "great synagogue".
Israel
 * The Belz Great Synagogue, Jerusalem
* The Great Synagogue of Jerusalem
* The Belz Great Synagogue, Jerusalem
* The Great Synagogue of Jerusalem
Europe
Russia, Ukraine and Belarus
 * The Moscow Choral Synagogue
* The Grand Choral Synagogue of St. Petersburg
* The Kharkiv Choral Synagogue
* The Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv), Ukraine
* The Moscow Choral Synagogue
* The Grand Choral Synagogue of St. Petersburg
* The Kharkiv Choral Synagogue
* The Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv), Ukraine
Poland
* The Great Synagogues of Great Synagogue, Warsaw, Warsaw and Great Synagogue, Łódź, Łódź, destroyed by Nazis during World War II.
* The Włodawa Synagogue, Great Synagogue of Włodawa
Czech Republic
* The Great Synagogue (Plzeň), Great Synagogue of Plzeň
Hungary
 * The Dohány Street Synagogue in
* The Dohány Street Synagogue in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Hungary
* The Szeged Synagogue, Synagogue of Szeged
Austria
* The Leopoldstädter Tempel of Vienna, destroyed during the "Kristallnacht" pogrom. Served as model for many other important synagogues.
Germany
* The New Synagogue (Berlin), New Synagogue of Berlin
Netherlands
* The Portuguese Synagogue (Amsterdam), Portuguese Synagogue of Amsterdam
Scandinavia
* The Stockholm Synagogue, Great Synagogue of Stockholm
France and Belgium
* The Grand Synagogue of Paris
* The Great Synagogue of Europe, Great Synagogue of Brussels (also known as the Great Synagogue of Europe)
Italy
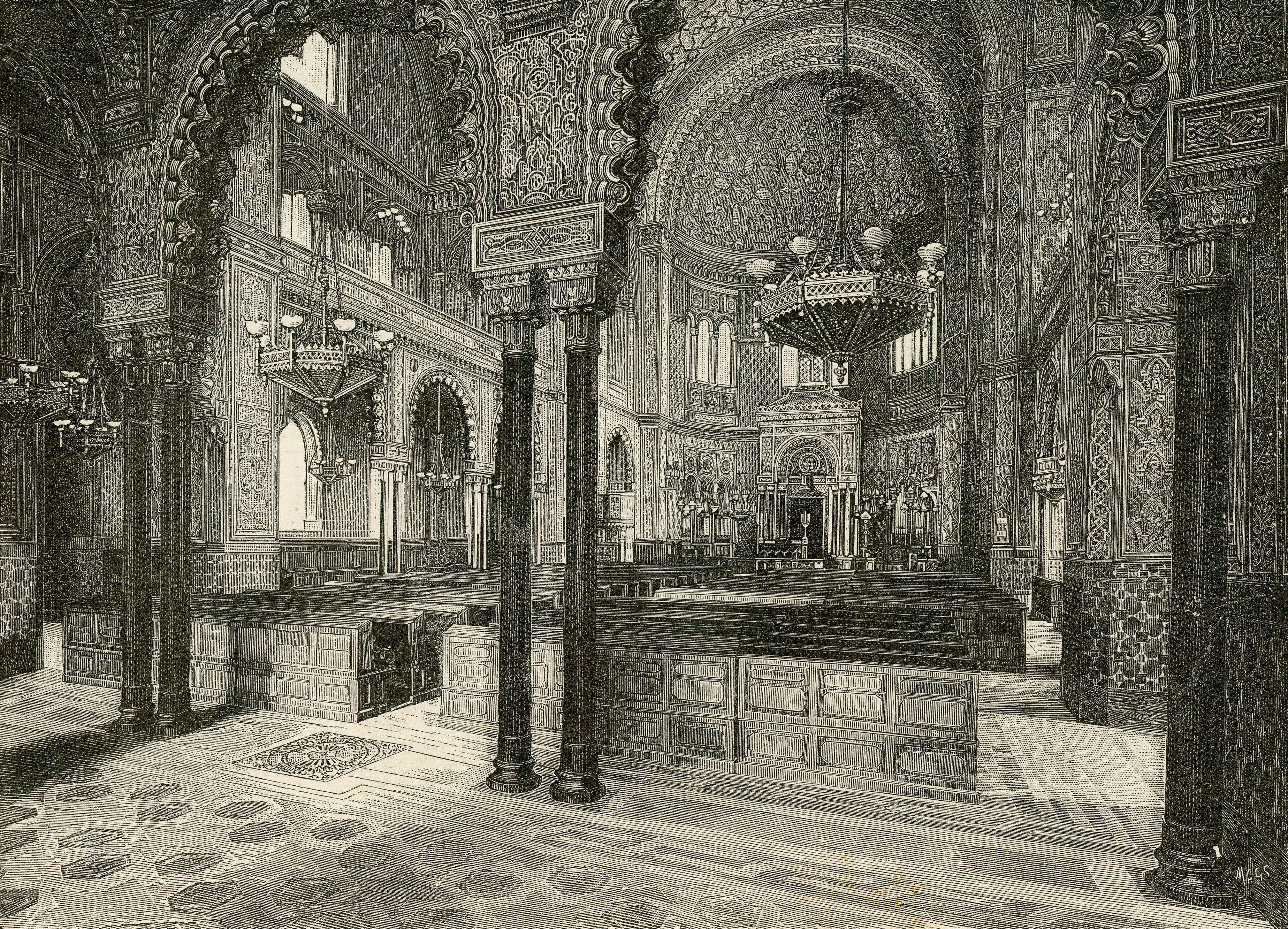 * The Great Synagogue of Florence
* The Great Synagogue of Rome
* The Synagogue of Trieste
* The Great Synagogue of Florence
* The Great Synagogue of Rome
* The Synagogue of Trieste
Romania
* The Cetate Synagogue of Timișoara,
* The Fabric Synagogue of Timișoara, Romania
* The Templul Coral, Choral Temple of Bucharest
Serbia
* The Novi Sad Synagogue, Synagogue of Novi Sad
* The Subotica Synagogue, Synagogue of Subotica
Bosnia and Herzegovina
* The Sarajevo Synagogue, Synagogue of Sarajevo
* The Jewish Community of Doboj, Synagogue of Doboj
Bulgaria
* The Sofia Synagogue, Synagogue of Sofia


Turkey (European part)
* The Edirne Synagogue, Grand Synagogue of Edirne
United Kingdom
* The Great Synagogue of London, destroyed by aerial bombing in the London Blitz in 1941
Tunisia
* The :fr:Grande synagogue de Tunis, Great Synagogue of Tunis
* The El Ghriba synagogue of Djerba
Australia
* The Great Synagogue (Sydney), Great Synagogue of Sydney
World's largest synagogues

Israel
* The largest synagogue in the world is the Ger (Hasidic dynasty)#Center, Great Beth Midrash Gur, in Jerusalem, Israel, whose main sanctuary seats up to 20,000, and has an area of approximately , while the entire complex has an area of approximately . Construction on the edifice took more than 25 years.
* Kehilat Kol HaNeshama, a Reform synagogue located in Baka, Jerusalem, is the largest Reform (and largest non-Orthodox) Jewish synagogue in Israel.
Europe
* The Dohány Street Synagogue in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Hungary, is the largest synagogue in Europe by square footage and number of seats. It seats 3,000, and has an area of and height of (apart from the towers, which are ).
* The Synagogue of Trieste is the largest synagogue in Western Europe.
* The Great Synagogue of Rome is one of the greatest in Europe.
* The Portuguese Synagogue (Amsterdam), Portuguese Synagogue in Amsterdam, also called "Esnoga", was built in 1675. At that time it was the largest synagogue in the world. Apart from the buildings surrounding the synagogue, it has an area of , is high. It was built to accommodate 1227 men and 440 women.Sofia Synagogue
The Sofia Synagogue ( bg, Софийска синагога, ''Sofiyska sinagoga'') is the largest synagogue in Southeastern Europe, one of two functioning in Bulgaria (with the other one in Plovdiv) and the third-largest in Europe. is located in Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
, Bulgaria, seating about 1,200.
* The Subotica Synagogue is located in Subotica, Serbia, seating more than 900.
* Great Synagogue (Plzeň) in the Czech Republic is the second-largest synagogue in Europe, and the third-largest in the world.
North America
* Baron Hirsch Synagogue, an Orthodox synagogue in Memphis, Tennessee, was the largest in the United States at the time of its dedication in 1957, seating 2,200 worshippers with an additional accommodation for 1,000 in its main sanctuary. The synagogue moved in 1988, but the building remains in use as a church.
* The Satmar (Hasidic dynasty), Satmar synagogue in Kiryas Joel, New York, which is said to seat "several thousand", is also very large.
* Congregation Yetev Lev D'Satmar (Rodney Street, Brooklyn) is also said to seat "several thousand".
* Temple Emanu-El of New York, a Temple, Reform Temple, is located in New York City, with an area of , seating 2,500. It is the largest Reform synagogue in the world.
* Congregation Yetev Lev D'Satmar (Hooper Street, Brooklyn) seats between 2,000 and 4,000 congregants.
* The main sanctuary of Adas Israel Congregation (Washington, D.C.) seats 1,500.
* Temple Emanu-El (Miami Beach, Florida) located in Miami Beach, Florida, seats approximately 1,400 people.
* Congregation Shaare Zion, an Orthodox Sephardic synagogue located in Brooklyn, New York (state), New York, is the largest Syrian Jewish congregation in New York City. It is attended by over 1,000 worshipers on weekends.
* Beth Tzedec Congregation in Toronto, Ontario, is the largest Conservative synagogue in North America.
* Temple Israel (Memphis, Tennessee), Temple Israel, a Reform synagogue in Memphis, Tennessee seats 1,335 to 1,500 people in its main sanctuary. The massive synagogue complex contains over 125,000 sq ft (11,613 m2) on 30 acres.
World's oldest synagogues
* The oldest synagogue fragments are stone-carved synagogue dedication inscriptions found in Middle and Lower Egypt and dating from the 3rd century BCE.Delos Synagogue The synagogue of Delos, Greece, is one of the oldest synagogues known today, its proposed origin dating between 150 and 128 BCE, although its identification as a synagogue has been disputed.
Discovery and excavation
The structure was discovered in ...
, dates from between 150 and 128 BCE, or earlier and is located on the island of Delos
The island of Delos (; el, Δήλος ; Attic: , Doric: ), near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island are ...
.
* The Dura-Europos synagogue, synagogue of Dura Europos, a Seleucid city in north eastern Syria, dates from the third century CE. It is unique. The walls were painted with figural scenes from the Old Testament. The paintings included Abraham and Isaac, Moses and Aaron, Solomon, Samuel and Jacob, Elijah and Ezekiel. The synagogue chamber, with its surviving paintings, is reconstructed in the National Museum in Damascus.
* The Old Synagogue (Erfurt), Old Synagogue in Erfurt, Germany, parts of which date to c.1100, is the oldest intact synagogue building in Europe. It is now used as a museum of local Jewish history.
*The Kochangadi Synagogue (1344 A.D. to 1789 A.D.) in Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
in the Kerala, built by the Cochin Jews, Malabar Jews. It was destroyed by Tipu Sultan in 1789 A.D. and was never rebuilt. An inscription tablet from this synagogue is the oldest relic from any synagogue in India. List of synagogues in Kerala, Eight other synagogues exist in Kerala though not in active use anymore.
 * The
* The Paradesi Synagogue
The Paradesi Synagogue aka Cochin Jewish Synagogue or the Mattancherry Synagogue (Malayalam: പരദേശി ജൂതപള്ളി) is a synagogue located in Mattancherry Jew Town, a suburb of the city of Kochi, Kerala, in India. It wa ...
is the oldest active synagogue in the Commonwealth of Nations, located in Kochi, Kerala, in India. It was built in 1568 by Paradesi Jews, Paradesi community in the Kingdom of Cochin. Paradesi is a word used in several Indian languages, and the literal meaning of the term is "foreigners", applied to the synagogue because it was historically used by "White Jews", a mixture of Jews of the Middle East, and European exiles. It is also referred to as the Cochin Jewish Synagogue or the Mattancherry Synagogue. The synagogue is located in the quarter of Old Cochin known as Jew Town and is the only one of the List of synagogues in Kerala, eight synagogues in the area still in use.
* Jew's Court, Steep Hill, Lincoln, England, is arguably the oldest synagogue in Europe in current use.
Oldest synagogues in the United States
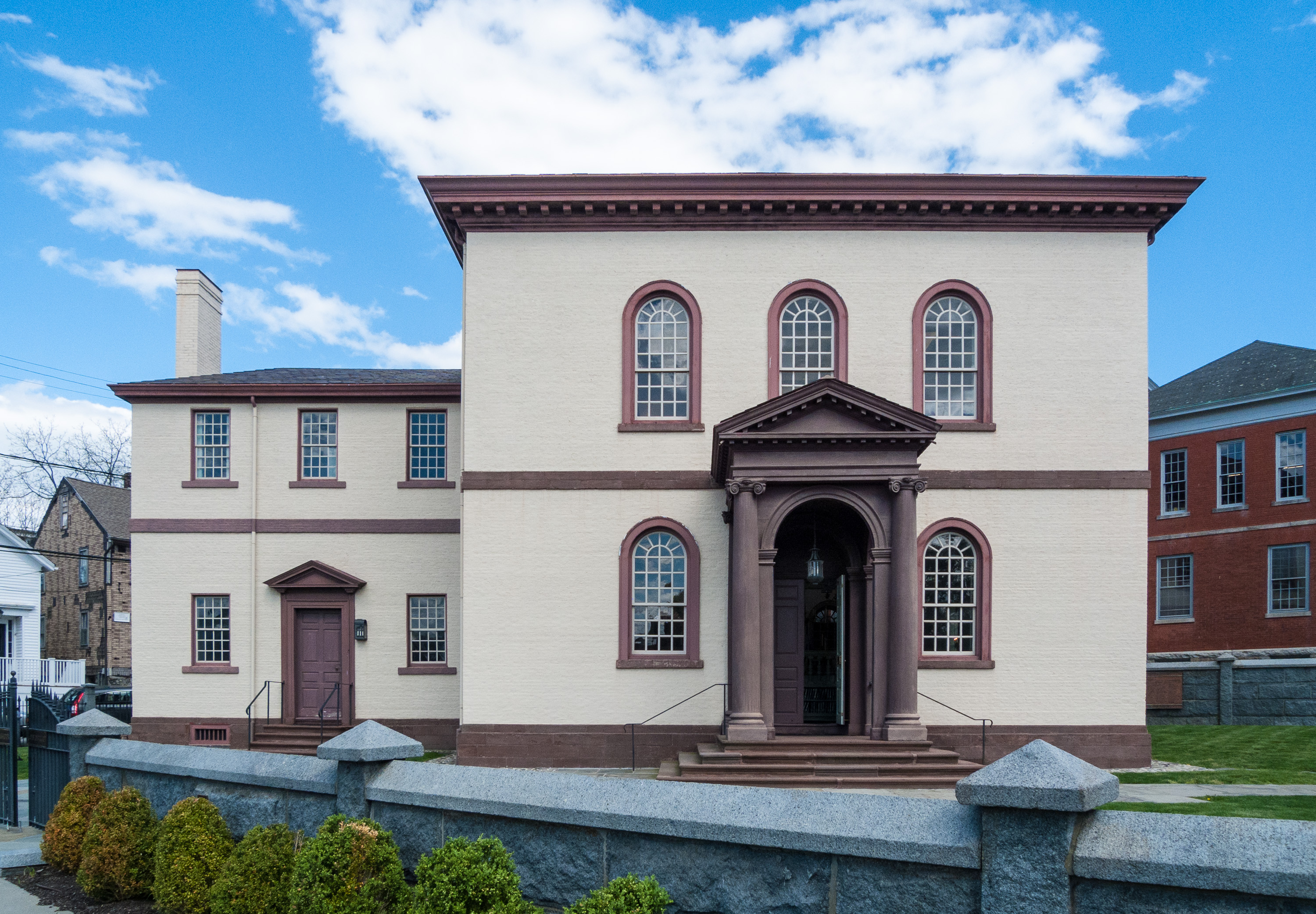


 * Congregation Shearith Israel, in New York City, founded in 1654, is the oldest congregation in the United States. Its present building dates from 1897.
* The
* Congregation Shearith Israel, in New York City, founded in 1654, is the oldest congregation in the United States. Its present building dates from 1897.
* The Touro Synagogue
The Touro Synagogue or Congregation Jeshuat Israel ( he, קהל קדוש ישועת ישראל) is a synagogue built in 1763 in Newport, Rhode Island. It is the Oldest synagogues in the United States, oldest synagogue building still standing in t ...
in Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is an American seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, ...
, is the oldest Jewish house of worship in North America that is still standing. It was built in 1759 for the Jeshuat Israel congregation, which was established in 1658.
Other famous synagogues
* The Worms Synagogue in Germany, built in 1175 and razed on Kristallnacht in 1938, was painstakingly reconstructed using many of the original stones. It is still in use as a synagogue.
* The Synagogue of El Transito of Toledo, Spain, was built in 1356 by Samuel ha-Levi, treasurer of King Pedro I of Crown of Castile, Castile. This is one of the best examples of Mudéjar architecture in Spain. The design of the synagogue recalls the Nasrid style of architecture that was employed during the same period in the decorations of the palace of the Alhambra in Granada as well as the Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba, Mosque of Córdoba. Since 1964, this site has hosted a Sephardi museum.
* The Hurva Synagogue, located in the Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter of the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, was Jerusalem's main Ashkenazi synagogue from the 16th century until 1948, when it was destroyed by the Arab Legion several days after the conquest of the city. After the Six-Day War, an arch was built to mark the spot where the synagogue stood. A complete reconstruction, to plans drawn up by architect Nahum Meltzer, opened in March 2010.
* The Abdallah Ibn Salam Mosque or Oran, Algeria, built in 1880, but converted into a mosque in 1975 when most Algerian Jews had left the country for France following independence.
*The Nidhe Israel Synagogue ("Bridgetown Synagogue") of Barbados, located in the capital city of Bridgetown, was first built in 1654. It was destroyed in the hurricane of 1831 and reconstructed in 1833.
* The Curaçao synagogue or ''Snoa'' in Willemstad, Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles was built by Sephardic Portuguese Jews from Amsterdam and Recife, Brazil. It is modeled after the Esnoga in Amsterdam. Congregation Mikvé Israel built this synagogue in 1692; it was reconstructed in 1732.
* The Bialystoker Synagogue on New York's Lower East Side, is located in a landmark building dating from 1826 that was originally a Methodist Episcopal Church. The building is made of quarry stone mined locally on Pitt Street, Manhattan. It is an example of federal architecture. The ceilings and walls are hand-painted with zodiac frescos, and the sanctuary is illuminated by stained glass windows. The bimah and floor-to-ceiling ark are handcarved.
* The Great Synagogue of Florence, Tempio Maggiore, Florence, 1874–82, is an example of the magnificent, cathedral-like synagogues built in almost every major European city in the 19th century and early 20th century.
* Boston's 1920 Vilna Shul is a rare surviving intact Immigrant Era synagogue.
Gallery
File:CZZSVg018348-07.jpg, The Great Synagogue of Tunis, Tunisia
File:Zarzis Synagogue.JPG, The Zarzis Synagogue, Tunisia
File:Alte Synagoge Erfurt.JPG, The Old Synagogue (Erfurt) is the oldest intact synagogue building in Europe.
File:Berlin Neue Synagoge 2005.jpg, The New Synagogue (Berlin), New Synagogue in Berlin, Germany
File:Frankfurt Hauptsynagoge 1885.jpg, The main synagogue of the city of Frankfurt am Main (Germany) before the Kristallnacht
File:Köln synagoge pano.jpg, The Roonstrasse Synagogue in Cologne, Germany
File:RoyLindmanBethYaakovSynagogueGeneva 001.jpg, Beth Yaakov Synagogue, Switzerland
File:Basler Synagoge(ws) retouched.jpg, The Great Synagogue of Basel in Basel, Switzerland
File:Åbo synagoga, den 27 juni 2007, bild 1.jpg, The Turku Synagogue in Turku, Finland
File:SynaStPersburgExt.JPG, The Grand Choral Synagogue of St. Petersburg, Russia
File:SynagogueSantiago.jpg, The Great Synagogue of Santiago, Chile, Santiago, Chile
File:GerardDoustraatSynagogue.jpg, The Synagogue in the Gerard Doustraat in Amsterdam, Netherlands
File:EsnogaAmsterdam.jpg, The Portuguese Synagogue (Amsterdam), Portuguese Synagogue in Amsterdam, Netherlands
File:Synagogue - Budapest.jpg, The Dohány Street Synagogue in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Hungary
File:Synagogue, Szombathely, Hungary.jpg, Synagogue, Szombathely, Hungary
File:Old new synagogue in Prague - inside.jpg, Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
interior of the 13th-century Old New Synagogue of Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
, Czech Republic
File:Great Synagogue Plzen CZ general view.JPG, The Great Synagogue (Plzeň), Great Synagogue in Plzeň, Czech Republic
File:Lesko synagoga.jpg, The Lesko Synagogue in Lesko, Poland
File:Synagoga Bobowa.JPG, The Bobowa Synagogue in Bobowa, Poland
File:Beogradska sinagoga.jpg, Belgrade Synagogue, Sukkat Shalom Synagogue in Belgrade, Serbia
File:Sinagoga u Subotici, 00.JPG, Subotica Synagogue, Jakab and Komor Square Synagogue in Subotica, Serbia
File:Синагога у Новом Саду 3.JPG, The Novi Sad Synagogue, Jewish Street Synagogue in Novi Sad, Serbia
File:Sinagoga Kadoorie10.jpg, Kadoorie Synagogue in Porto, Portugal, the largest synagogue in the Iberian Peninsula
File:Besht Shul1 Medzhibozh.jpg, The Baal Shem Tov's shul in Medzhybizh, Ukraine (c. 1915), destroyed and recently rebuilt.
File:Synagoge auf Gelaende der Universtaet Tel Aviv.jpg, The Cymbalista Synagogue and Jewish Heritage Center at Tel Aviv University
File:Kherson-Synagogue01.jpg, The synagogue of Kherson, Ukraine
File:Or Zaruaa synagogue, founded by Rabbi Amram Aburbeh in Nahlat Ahim, Jerusalem, Israel exterior photo; showing location on 3 Refali street..jpg, Or Zaruaa Synagogue, Jerusalem, Israel founded in 1926.
File:Hurva synagogue.jpg, The Hurva Synagogue towered over the Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter of Jerusalem from 1864 until 1948, when it was destroyed in war
File:Hakhurba-synagogue01m.jpg, The remains of the Hurva Synagogue as they appeared from 1977 to 2003. The synagogue has been rebuilt in 2010.
File:Istanbul Ashkenazi Sinagogue Interior.JPG, The Ashkenazi Synagogue of Istanbul, Turkey
File:Karaite synagogue cali.jpg, The interior of a Karaite Judaism, Karaite synagogue
File:Jewish synagouge kochi india.jpg, The Paradesi Synagogue
The Paradesi Synagogue aka Cochin Jewish Synagogue or the Mattancherry Synagogue (Malayalam: പരദേശി ജൂതപള്ളി) is a synagogue located in Mattancherry Jew Town, a suburb of the city of Kochi, Kerala, in India. It wa ...
in Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
, India
File:Kiev34.jpg, The Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv), Great Choral Synagogue in Kyiv, Ukraine
File:Great Synagogue of Rome 01.JPG, Great Synagogue of Rome, Italy
File:RoyLindmanAbuhavSynagogueZefatIsrael 001.jpg, Abuhav synagogue, Israel
File:Ari Ashkenazi Synagogue, exterior.jpg, Ari Ashkenazi Synagogue, Israel
File:RoyLindmanSantaMarialaBlancaSynagogue 002.jpg, Santa María la Blanca, Spain
File:RoyLindmanCordobaSynagogue 003.jpg, Córdoba Synagogue, Spain
File:RoyLindmanElTransito 003.jpg, El Transito Synagogue, Spain
File:Sofia Synagogue.jpg, Sofia Synagogue
The Sofia Synagogue ( bg, Софийска синагога, ''Sofiyska sinagoga'') is the largest synagogue in Southeastern Europe, one of two functioning in Bulgaria (with the other one in Plovdiv) and the third-largest in Europe. , Bulgaria
File:BUCTemplulCoral.jpg, Templul Coral, The Choral Temple, Bucharest, Romania
File:Sinagoga din Targu Mures.jpg, Synagogue of Târgu Mureș, Romania
File:Caravan shul interior.jpg, Interior of a "caravanim, caravan shul" (synagogue housed in a trailer-type facility), Neve Yaakov, Jerusalem
File:Ohev Sholom - The National Synagogue.JPG, Ohev Sholom – The National Synagogue in Washington, D.C.
File:ASCALON STUDIOS, David Ascalon, Lincoln Square Synagogue Ark New York.jpg, Sanctuary ark, Lincoln Square Synagogue, New York City (2013), created by David Ascalon
File:Central Synagogue Lex jeh.jpg, The Central Synagogue (Manhattan), Central Synagogue in Manhattan, New York City
File:Temple Emanu-El Synagogue.jpg, Temple Emanu-El, Neo-Byzantine style synagogue in Miami Beach, Florida
File:Bevis Marks Synagogue 01.JPG, Bevis Marks Synagogue, City of London, the oldest synagogue in the United Kingdom
File:Stockholms synagoga 2010.JPG, Stockholm Synagogue, Sweden
File:Brisbane Synagogue.jpg, Brisbane Hebrew Congregation, Brisbane Synagogue, Australia
File:אום אל קנאטיר 2.jpg, Umm el-Qanatir#ancient synagogue, Ein Keshatot synagogue (active 5th-8th centuries), Israel
See also
*Great Synagogue (disambiguation)
*List of synagogues
*List of synagogues in the United States
*Mandi (Mandaeism)
*Place of worship
*Prayer book
*Rabbi
*Siddur
*Zionist churches
*Synagogue Church
*Temple
Notes
References
*
* Messinas, Elias (2022). ''The Synagogues of Greece: A Study of Synagogues in Macedonia and Thrace: With Architectural Drawings of all Synagogues of Greece''. Seattle: KDP. .
* Young, Penny (2014). ''Dura Europos: A City for Everyman''. Diss, Norfolk, UK: Twopenny Press. .
External links
Jewish Encyclopedia: Synagogue
Chabad Lubavitch Center & Synagogue Finder
Orthodox Union Synagogue Finder
United Synagogue of Conservative Judaism Synagogue Finder
Union for Reform Judaism Synagogue Finder
Reconstructionist Synagogue Finder
{{Authority control
Synagogues,
Jewish holy places
Jewish buildings
Building types



 A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer";
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer";  Although synagogues existed a long time before the destruction of the
Although synagogues existed a long time before the destruction of the 
 Other traditional features include a continually lit lamp or lantern, usually electric in contemporary synagogues, called the (), the "Eternal Light", used as a way to honor the Divine Presence.
Other traditional features include a continually lit lamp or lantern, usually electric in contemporary synagogues, called the (), the "Eternal Light", used as a way to honor the Divine Presence.
 A synagogue may be decorated with artwork, but in the Rabbinic and Orthodox tradition, three-dimensional sculptures and depictions of the human body are not allowed as these are considered akin to idolatry.
A synagogue may be decorated with artwork, but in the Rabbinic and Orthodox tradition, three-dimensional sculptures and depictions of the human body are not allowed as these are considered akin to idolatry.
 The German–Jewish Reform movement, which arose in the early 19th century, made many changes to the traditional look of the synagogue, keeping with its desire to simultaneously stay Jewish yet be accepted by the surrounding culture.
The Hamburg Temple, first Reform synagogue, which opened in Hamburg in 1811, introduced changes that made the synagogue look more like a church. These included: the installation of an Organ (music), organ to accompany the prayers (even on Shabbat, when musical instruments are proscribed by halakha), a choir to accompany the hazzan, and vestments for the synagogue rabbi to wear.
In following decades, the central reader's table, the Bimah, was moved to the front of the Reform sanctuary—previously unheard-of in Orthodox synagogues.
Gender separation was also removed.
The German–Jewish Reform movement, which arose in the early 19th century, made many changes to the traditional look of the synagogue, keeping with its desire to simultaneously stay Jewish yet be accepted by the surrounding culture.
The Hamburg Temple, first Reform synagogue, which opened in Hamburg in 1811, introduced changes that made the synagogue look more like a church. These included: the installation of an Organ (music), organ to accompany the prayers (even on Shabbat, when musical instruments are proscribed by halakha), a choir to accompany the hazzan, and vestments for the synagogue rabbi to wear.
In following decades, the central reader's table, the Bimah, was moved to the front of the Reform sanctuary—previously unheard-of in Orthodox synagogues.
Gender separation was also removed.
 * The Belz Great Synagogue, Jerusalem
* The Great Synagogue of Jerusalem
* The Belz Great Synagogue, Jerusalem
* The Great Synagogue of Jerusalem
 * The Moscow Choral Synagogue
* The Grand Choral Synagogue of St. Petersburg
* The Kharkiv Choral Synagogue
* The Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv), Ukraine
* The Moscow Choral Synagogue
* The Grand Choral Synagogue of St. Petersburg
* The Kharkiv Choral Synagogue
* The Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv), Ukraine
 * The Dohány Street Synagogue in
* The Dohány Street Synagogue in  * The Great Synagogue of Florence
* The Great Synagogue of Rome
* The Synagogue of Trieste
* The Great Synagogue of Florence
* The Great Synagogue of Rome
* The Synagogue of Trieste

 * The
* The 

 * Congregation Shearith Israel, in New York City, founded in 1654, is the oldest congregation in the United States. Its present building dates from 1897.
* The
* Congregation Shearith Israel, in New York City, founded in 1654, is the oldest congregation in the United States. Its present building dates from 1897.
* The