survey article on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A review article is an
article
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
G ...
that summarizes the current state of understanding on a topic within a certain discipline. A review article is generally considered a secondary source since it may analyze and discuss the method and conclusions in previously published studies. It resembles a survey article or, in news publishing, overview article, which also surveys and summarizes previously published primary and secondary sources, instead of reporting new facts and results. Survey articles are however considered tertiary sources
A tertiary source is an index or textual consolidation of already published primary and secondary sourcestertiary review.
Academic publications that specialize in review articles are known as review journals. Review journals have their own requirements for the review articles they accept, so review articles may vary slightly depending on the journal they are being submitted to.
Review articles teach about:
* the main people working in a field
* recent major advances and discoveries
* significant gaps in the research
* current debates
* suggestions of where research might go next
A

 When finding sources, it is ideal to search through multiple
When finding sources, it is ideal to search through multiple
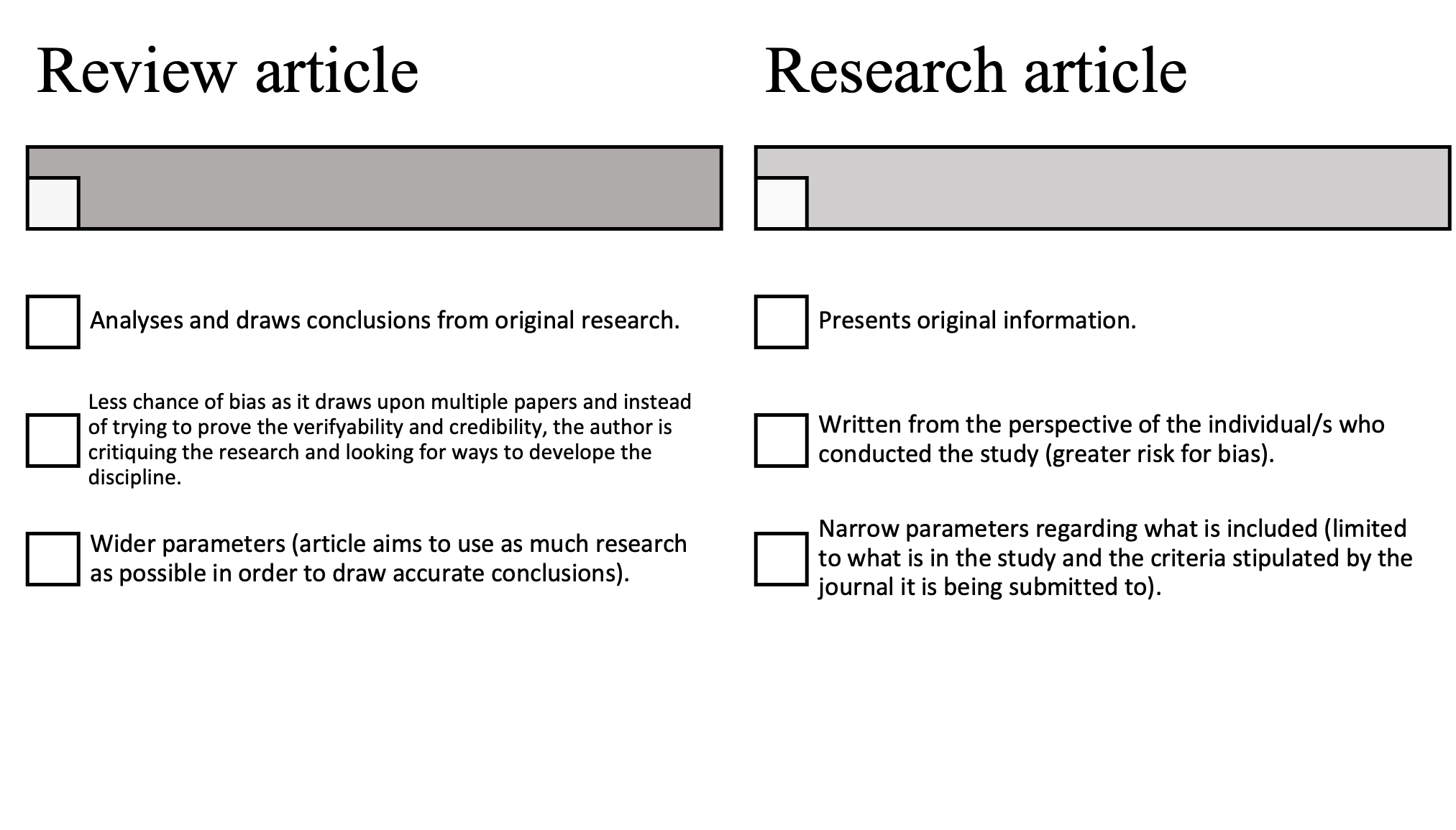 * A research article presents original information from the perspective of the author, whereas a review article analyses that statement and information.
* A research article presents original content, whereas a review article synthesises that content and makes sense of it within the context of the discipline.
* A research article has more narrow parameters on what is included (often depending on the journal it is being pitched to), whereas a review article is more open, being able to incorporate multiple research papers albeit still being contained within journal guidelines.
* A research article presents original information from the perspective of the author, whereas a review article analyses that statement and information.
* A research article presents original content, whereas a review article synthesises that content and makes sense of it within the context of the discipline.
* A research article has more narrow parameters on what is included (often depending on the journal it is being pitched to), whereas a review article is more open, being able to incorporate multiple research papers albeit still being contained within journal guidelines.
meta-study
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
summarizes a large number of already published experimental or epidemiological studies and provides statistical analysis of their result.
Review articles have increased in impact and relevance alongside the increase in the amount of research that needs to be synthesised. They are a concise way of collating information for practitioners or academics that are not able to read the plethora of original research that is being published.
Categories
There are various categories of review articles, including narrative reviews, systematic reviews, andmeta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
. Review articles do not introduce new results, but rather state existing results, drawing conclusions on the results presented. Review articles can be categorised by using the same domain, underlying theory, or research method
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness t ...
. Sometimes these categories overlap.
Narrative reviews describe the published information on a theme or topic, but often does not include the methodological process involved in researching the topic. This can lead to narrative review articles being bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group ...
ed, missing important theoretical details pertaining to the original research, and innovative suggestions to further develop the field through further studies.
A systematic review is more detailed and structured than a narrative review. It details the aims, hypothesis, and research method clearly so as to remain transparent and neutral. This review format adheres to explicit criteria when selecting what research is included in the review. Common methods used to analyse selected research articles include text mining
Text mining, also referred to as ''text data mining'', similar to text analytics, is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extract ...
, citation, co-citation analysis, and topic model
In statistics and natural language processing, a topic model is a type of statistical model for discovering the abstract "topics" that occur in a collection of documents. Topic modeling is a frequently used text-mining tool for discovery of hidden ...
ling. These types of reviews also include a discussion on the theoretical implications of such research. Systematic reviews are more highly regarded and selected than narrative reviews due to their specificity and neutrality. In the field of clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of healthcare science that determines the safety and effectiveness ( efficacy) of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treatm ...
, the Cochrane organisation publishes systematic reviews (called ''Cochrane Reviews'') on healthcare topics in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
The Cochrane Library (named after Archie Cochrane) is a collection of databases in medicine and other healthcare specialties provided by Cochrane and other organizations. At its core is the collection of Cochrane Reviews, a database of systemat ...
.
A meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
summarises quantitative results from a variety of research articles on a chosen topic. Given that these articles are formulating conclusions from multiple data sets, meta-analyses adhere to specific guidelines stipulated by the journals where they are published. A meta-analysis lends itself more to statistical research, often converting the original research into one common metric referred to as "effect sizes", so as to easily identify patterns and anomalies among publications. Systematic reviews may include meta-analysis results. The first edition of the ''Handbook of Research Synthesis'' aided the development of various analysis techniques that could be used in systematic review articles, thereby developing this form of literature.

Structure of a review article
Review articles initially identify the scope and aim. If submitting the review article to a journal, the author must familiarise themselves with the theme of the journal as well as its conditions for submission. Some journals only accept review articles whereas others strictly publish original research. Once the scope of the journal the author intends to submit to is identified, then identify the own personal scope and aim for the article. Experienced author, Angus Crake emphasises the need to define a scope that is “manageable, not too large or small” and to “focus on recent advances if the field is well established”. This equates to a succinct, refreshing review article that adds a new perspective to the field whilst still being grounded in academia. When finding sources, it is ideal to search through multiple
When finding sources, it is ideal to search through multiple database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases sp ...
s and search engine
A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches. They search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a ...
s. This ensures a wide berth of knowledge that presents multiple perspectives and allows for a reasonably balanced article. Some disciplines encourage the use of certain search engines. For example, science-based review articles heavily utilise Medline
MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online, or MEDLARS Online) is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering medic ...
, Embase and CINAHL
CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature) is an index of English-language and selected other-language journal articles about nursing, allied health, biomedicine and healthcare.
Ella Crandall, Mildred Grandbois, and Molli ...
.
The title, abstract and keywords chosen bring awareness to the audience of the article, and should describe what the article is about. Search engine optimisation
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines. SEO targets unpaid traffic (known as "natural" or "organic" results) rather than direc ...
is important when publishing articles within a discipline where the literature is already saturated.
Like most academic articles, a review article includes an ‘ abstract’ at the start. The ‘Abstract’ section of the review article should include: a synopsis of the topic being discussed or the issue studied, an overview of the study participants used in the empirical study being reviewed, a discussion of the results found and conclusions drawn by the scholars conducting the study, an explanation of how such findings have already or could potentially impact the theory and practice within the relevant discipline. Within this section, context and the relevance of the review is included. The jargon used will depend on the intended audience.
The discussion section of the article presents multiple perspectives, stating limitations and potential extensions of the study being reviewed. Also, within this section, similarities and dissonances among studies are stated.
The presentation of both the shortcomings and advancements of the research papers under review is important for comprehensiveness. Daft (1985, p 198) emphasised this by saying “''Previous work is always vulnerable. Criticising is easy, and of little value; it is more important to explain how research builds upon previous findings rather than to claim previous research is inadequate and incompetent."''
Within this section of the review article is the suggestion of improvements and areas to further extend the research in reference. The bibliography included at the end of review articles is equally important as it leads to further information on the study being discussed and is a way for academics and students alike to further their research. These are secondary sources. Meyers and Sinding say,
“''... The review selects from these (research) papers, juxtaposes them, and puts them in a narrative that holds them together… clearly the best reviews are not only concerned with what was done in the past, but also present a means to sculpt the future.”''
Method of research
Reference management software such as Papers,EndNote
A note is a string of text placed at the bottom of a page (paper), page in a book or document or at the end of a chapter, volume, or the whole text. The note can provide an author's comments on the main text or citations of a reference work in ...
, and Zotero
Zotero () is a free and open-source reference management software to manage bibliographic data and related research materials, such as PDF files. Features include web browser integration, online syncing, generation of in-text citations, footno ...
are useful for when it comes to actually structuring and writing your review article.
Peer review process
The process of review articles being peer-reviewed is critical to their credibility. The peer review process is a way to ensure the article is as polished and accurate as possible. Most often, those reviewing the article are fellow academics or experts within the field under discussion in the paper. Sending out a peer review allows for gaps in the paper to be acknowledged so that the review can be as well-informed and comprehensive as possible. Peers will often recommend other research articles and studies to be included in the review, which can add strength to the article. Confusion amongst peers also indicates that your paper is not clear or lacking synergy.Relevance within academic literature
A key aim of review articles is to pose other potential avenues of research, stating the limitations of theempirical studies
Empirical research is research using empirical evidence. It is also a way of gaining knowledge by means of direct and indirect observation or experience. Empiricism values some research more than other kinds. Empirical evidence (the record of one ...
under review and how future studies of the same nature can be improved. They also present findings of other studies within the same discipline, comparing results and drawing conclusions based on each individual finding. Essentially, they are an evaluation of already published academic research.
It is important that review articles do not introduce new results, but rather, reiterate existing results. However, they are able to draw conclusions on the results presented (within reason). Review articles hold importance as they forecast to see new research opportunities by synthesising the existing research and identifying gaps in this research. They were born out of the necessity to categorise and make sense of the ongoing plethora of research publications being released annually. Between 1991 and 2008, there were forty times more papers published within the field of biodiversity alone. This overload of research papers makes it difficult for scientists and clinicians to remain up to date on current findings and developments within their discipline.Difference from a research article
Research article
Academic publishing is the subfield of publishing which distributes academic research and scholarship. Most academic work is published in academic journal articles, books or theses. The part of academic written output that is not formally publ ...
s form the basis of review articles. Review articles use the original information presented in research articles to draw conclusions and pose suggestions for future research.
Research and empirical articles are reporting the results of the author's study, thereby deeming it a primary source
In the study of history as an academic discipline, a primary source (also called an original source) is an artifact, document, diary, manuscript, autobiography, recording, or any other source of information that was created at the time under ...
. They often include raw data and statistics, using the words “participants”, “sample”, “subjects”, and “experiment” frequently throughout. Review articles are academic but are not empirical. As opposed to ''presenting'' the results of a study (which would be a research article
Academic publishing is the subfield of publishing which distributes academic research and scholarship. Most academic work is published in academic journal articles, books or theses. The part of academic written output that is not formally publ ...
), review articles ''evaluate'' the results of already published studies.
 * A research article presents original information from the perspective of the author, whereas a review article analyses that statement and information.
* A research article presents original content, whereas a review article synthesises that content and makes sense of it within the context of the discipline.
* A research article has more narrow parameters on what is included (often depending on the journal it is being pitched to), whereas a review article is more open, being able to incorporate multiple research papers albeit still being contained within journal guidelines.
* A research article presents original information from the perspective of the author, whereas a review article analyses that statement and information.
* A research article presents original content, whereas a review article synthesises that content and makes sense of it within the context of the discipline.
* A research article has more narrow parameters on what is included (often depending on the journal it is being pitched to), whereas a review article is more open, being able to incorporate multiple research papers albeit still being contained within journal guidelines.
Academic publishing
Review articles inacademic journal
An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and d ...
s analyze or discuss research previously published by others, rather than reporting new experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome oc ...
al results.
An expert's opinion is valuable, but an expert's assessment of the literature can be more valuable. When reading individual articles, readers could miss features that are apparent to an expert clinician-researcher. Readers benefit from the expert's explanation and assessment of the validity and applicability of individual studies.
Review articles come in the form of literature reviews
A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provid ...
and, more specifically, systematic reviews; both are a form of secondary literature. Literature reviews provide a summary of what the authors believe are the best and most relevant prior publications. Systematic reviews determine an objective list of criteria, and find all previously published original papers that meet the criteria; they then compare the results presented in these papers.
Some academic journal
An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and d ...
s likewise specialize in review of a field; they are known as review journals.
The concept of "review article" is separate from the concept of peer-reviewed literature. A review article, even one that is requested or "peer-invited", will be either peer-reviewed or non-peer-reviewed depending on how submissions are treated.
Writing review articles can be a popular task among students. At times, teachers from schools and universities assign this task
Impact
According to a 2021 study in the ''American Sociological Review'', "papers cited by formal review articles generally experience a dramatic loss in future citations. Typically, the review gets cited instead of the specific articles mentioned in the review." The study identifies an exception to this trend: articles that are characterized by the review as being bridges between clusters of scholarship tend to get disproportionate future attention. An analysis was conducted by McAlister et al. of review articles in six different medical journals. Of the six journals, less than 25% included a description, evaluation, or synthesis of evidence that had been provided. Only one-third of the articles had a clinical topic at the forefront, and only half of the articles presentedquantitative data
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philoso ...
that support the suggestions made at the end of the piece.
Historically, review journals have a higher impact than primary research journals. The year 2006 showed the top 10 most impactful journals to be compiled exclusively of review articles. In addition to this, review articles are cited more frequently than research articles. There are currently no studies commenting on the effect of review articles on the impactfullness of journals that usually only publish research papers. This prevents one from saying with certainty that review articles could replace original research papers in large journals. Of the 538 review articles published in pathology journals within the year 2005, a mere 21% of them have been cited over ten times following their issuance. Furthermore, in a 2000-2006 comparison of journals; The American Journal of Pathology, The Journal of Pathology, and Laboratory Investigation, published both with and without review articles included, it was found that journals published with review articles had a greater impact on readers than those that did not include review articles.
In terms of the growth of review articles, the rate has been exponential. The number of papers on the topic of ‘pathology’ has increased 2.3 times between the years 1991 to 2006. Within the science discipline, the number of review articles in the Science Citation Index
The Science Citation Index Expanded – previously entitled Science Citation Index – is a citation index originally produced by the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) and created by Eugene Garfield. It was officially launched in 1964 and ...
increased from 14,815 to 45,829 between 1991 and 2005. Following the same trend, the number of dedicated review journals within the Science Citation Index database grew from 163 to 198 between 1999 and 2006. Although, the percentage of review articles in review journals that formed the foundation of review literature decreased by 17% between 1999 and 2005. This indicates that most review articles are being allocated to original research journals as opposed to strictly review journals. This is also dependent on the quality of the review articles published.
Separate to the quality of articles, the number of review articles published poses its own challenge to those searching for succinct but comprehensive research analysis. This makes it equally as difficult for experts to navigate through the synthesised review articles as it is to sift through the primary research itself. Additionally, the inclusion of poorly referenced, inadequately researched, and overly biased review articles serve to muddy the water and make it even harder to determine quality writing.
Social, behavioural and health science disciplines
Following the release of the ‘Handbook of Research Synthesis’, the use of review articles within the social, behavioural and health science disciplines has proliferated. 2007 statistics showed that systematic review articles were produced at a rate of 2,500 per year on theMEDLINE
MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online, or MEDLARS Online) is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering medic ...
platform (Moher et al., 2007). The increased in prevalence of review articles within these disciplines can be attributed to the pull towards “evidence-based practice
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the idea that occupational practices ought to be based on scientific evidence. While seemingly obviously desirable, the proposal has been controversial, with some arguing that results may not specialize to indiv ...
”. This term was coined by Sackett (2000) and refers to the combination of available research, practitioner expertise, and consumer values. Due to the inundation of original research in the field, there is a need for review articles which highlight relevant studies, results and trends. The varying methods and participants used among original research studies can provide inconsistent results, thereby presenting a challenge in synthesising information using one common metric. The conjunction of meta-analyses and systematic reviews has proven to be more effective in organising data and drawing conclusions, especially when it comes to clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s within the medical field.
Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science
The Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science (JAMS) is a highly acclaimed peer-reviewed journal for the marketing discipline. It aims for 10%-20% of published content to be review articles, which is indicative of the value they add to journals. A 2012-2016Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Nik ...
analysis of the top six marketing journals found that JAMS attracted the most papers, publishing 31% of all review articles. The number of papers published per year in JAMS has increased from 40 to 60, allowing for an additional 8-10 review articles to be accepted annually, and thereby highlighting the growth in popularity of review articles.
This particular marketing journal established the ‘Review Paper Editorial Initiative’. This initiative encompasses a system in which the authors of peer review articles submit a detailed proposal of their paper, outlining key figures as well as a description of the process they undertook or are planning on undertaking for their review article. From this proposal, JAMS may grant an assurance that the paper will be accepted into the journal given that the final product is executed as detailed in the proposal. This instils confidence in authors and academics aiming to write and publish review articles within a saturated field. It also encourages papers to be written within areas that need further synthesis and research.
See also
*Case series
A case series (also known as a clinical series) is a type of medical research study that tracks subjects with a known exposure, such as patients who have received a similar treatment, or examines their medical records for exposure and outcome. Cas ...
, sometimes called a ''clinical review'' because it reviews or summarizes the records for a series of patients at a single medical clinic
* Living review
In academic publishing, a "living" review is a review article that is updated at intervals to reflect the latest research. Living reviews are typically published online. Unlike in a print journal, readers are notified of newer versions. While ea ...
References
Further reading
* {{Academic publishing Meta-analysis Academic publishing * Research Academia Literature