Sulfite Ester on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite
REGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
/ref>
 The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent
The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent  Evidence from 17O NMR spectroscopic data suggests that protonation of the sulfite ion gives a mixture of isomers:
Evidence from 17O NMR spectroscopic data suggests that protonation of the sulfite ion gives a mixture of isomers:

 Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
(systematic name
A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivi ...
: sulfate(IV) ion), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reve ...
of bisulfite
The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion . Salts containing the ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite diss ...
. Although its acid (sulfurous acid
Sulfuric(IV) acid (United Kingdom spelling: sulphuric(IV) acid), also known as sulfurous (UK: sulphurous) acid and thionic acid, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula .
Raman spectroscopy, Raman spectra of solutions o ...
) is elusive, its salts are widely used.
Sulfites are substances that naturally occur in some foods and the human body. They are also used as regulated food additives. When in food or drink, sulfites are often lumped together with sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
.SeREGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
/ref>
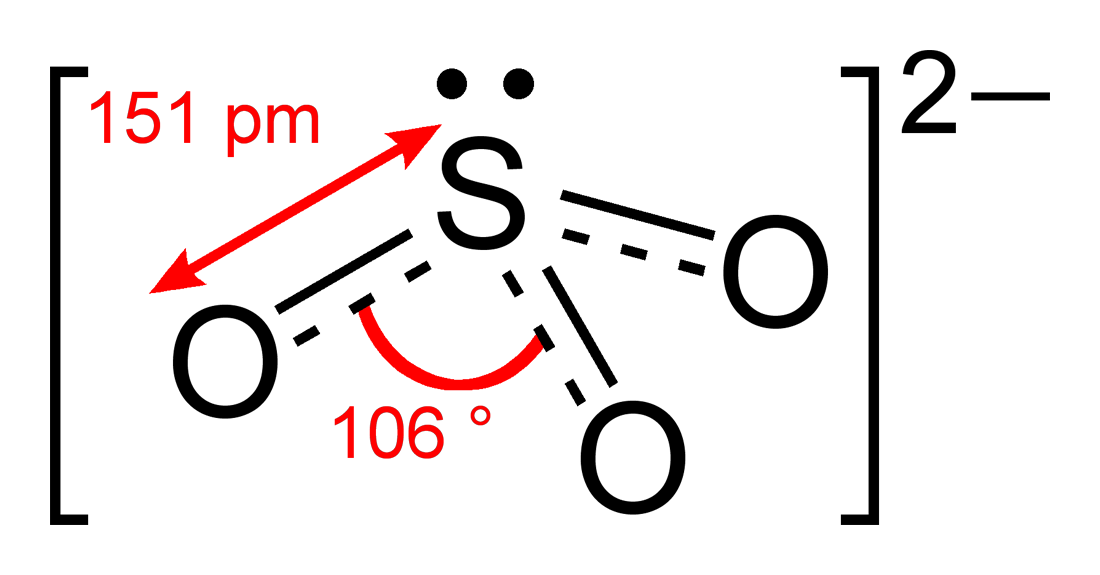
Structure
 The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent
The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent resonance structures
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or '' ...
. In each resonance structure, the sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom with a formal charge
In chemistry, a formal charge (F.C. or ), in the covalent view of chemical bonding, is the hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of rela ...
of zero (neutral), and sulfur is singly bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, which each carry a formal charge of −1, together accounting for the −2 charge on the anion. There is also a non-bonded lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
on the sulfur, so the structure predicted by VSEPR theory
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ( , ) is a conceptual model, model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gill ...
is trigonal pyramidal, as in ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
(NH3). In the hybrid resonance structure, the S−O bonds are equivalently of bond order
In chemistry, bond order is a formal measure of the multiplicity of a covalent bond between two atoms. As introduced by Gerhard Herzberg, building off of work by R. S. Mulliken and Friedrich Hund, bond order is defined as the difference between t ...
one and one-third.
 Evidence from 17O NMR spectroscopic data suggests that protonation of the sulfite ion gives a mixture of isomers:
Evidence from 17O NMR spectroscopic data suggests that protonation of the sulfite ion gives a mixture of isomers:

Commercial uses
Sulfites are used as a foodpreservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
or enhancer. They may come in various forms, such as:
* Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, which is not a sulfite, but a closely related chemical oxide
* Potassium bisulfite
Potassium bisulfite (or potassium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximately correctly mentioned formula chemical formula KHSO3. Potassium bisulfite in fact is not an actual compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in wat ...
or potassium metabisulfite
Potassium metabisulfite, K2S2O5, also known as potassium pyrosulfite, is a white crystalline powder with a pungent odour. It is mainly used as an antioxidant or chemical sterilant. As a disulfite, it is chemically very similar to sodium metabi ...
* Sodium bisulfite
Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is not a real compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions compose ...
, sodium metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite or sodium pyrosulfite (IUPAC spelling; Br. E. sodium metabisulphite or sodium pyrosulphite) is an inorganic compound of chemical formula Na2S2O5. The substance is sometimes referred to as disodium metabisulfite. It is used a ...
or sodium sulfite
Sodium sulfite (sodium sulphite) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2SO3. A white, water-soluble solid, it is used commercially as an antioxidant and preservative. It is also suitable for the softening of lignin in the pulping an ...
Wine
Sulfites occur naturally in allwine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
s to some extent. Sulfites are commonly introduced to arrest fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
at a desired time, and may also be added to wine as preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
s to prevent spoilage and oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
at several stages of the winemaking
Winemaking, wine-making, or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its Ethanol fermentation, fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over ...
. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) protects wine not only from oxidation, but also from bacteria.
Organic wines are not necessarily sulfite-free, but generally have lower amounts and regulations stipulate lower maximum sulfite contents for these wines. In general, white wines contain more sulfites than red wines and sweeter wines contain more sulfites than drier ones.
In the United States, wines bottled after mid-1987 must have a label stating that they contain sulfites if they contain more than 10 parts per million (ppm).
In the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
an equivalent regulation came into force in November 2005. This includes sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, and the limit is on the milligrams per kilogram or per litre of sulfur dioxide equivalent. In 2012, a new regulation for organic wines came into force. In the United Kingdom, similar laws apply. Bottles of wine that contain over 10 mg/L (ppm) of "sulfites" (or sulfur dioxide) are required to bear "contains sulphites" on the label. This does not differ if sulfites are naturally occurring or added in the winemaking process.
Other foods
Sulfites are often used aspreservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
s in dried fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed prior to cooking or being eaten on its own. Drying may occur either naturally, by sun, through the use of industrial dehydrators, or by freeze drying. ...
s, preserved radish
The radish (''Raphanus sativus'') is a flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae. Its large taproot is commonly used as a root vegetable, although the entire plant is edible and its leaves are sometimes used as a leaf vegetable. Origina ...
, and dried potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
products.
Most beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
s no longer contain sulfites, although some alcoholic ciders contain them. Although shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
are sometimes treated with sulfites on fishing vessels, the chemical may not appear on the label. In 1986, the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
in the United States banned the addition of sulfites to all fresh fruit and vegetables that are eaten raw.
E numbers
E numbers for sulfites aspreservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
food additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for ...
are:
In addition, two non-preservative food additives are produced by reacting with sulfite and hence have "sulfite" in the name:
Both are types of caramel coloring
Caramel color or caramel coloring is a water-soluble food coloring. It is made by heat treatment of carbohydrates (sugars), in general in the presence of acids, alkalis, or salts, in a process called caramelization. It is more fully oxidized than ...
. The sulfite in these additives have a tight chemical bond with the caramel and are not easily freed.
Health effects
Allergic reactions to sulfites appear to be very rare in the general population, but more common inhyperallergic
''Hyperallergic'' is an online arts magazine, based in Brooklyn, New York. Founded by the art critic Hrag Vartanian and his husband Veken Gueyikian in October 2009, the site describes itself as a "forum for serious, playful, and radical thinki ...
individuals.
Sulfites are counted among the top nine food allergens, but a reaction to sulfite is seldom a true allergy. Some people have positive skin allergy tests to sulfites indicating true (IgE
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
-mediated) allergy. Chronic skin conditions in the hands, perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
, and face have been reported in individuals that regularly use cosmetics or medications containing sulfites. Occupational exposure to sulfites has been reported to cause persistent skin symptoms.
It may cause breathing difficulty within minutes after eating a food containing it. Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
tics and possibly people with salicylate sensitivity
Salicylate sensitivity is any adverse effect that occurs when a usual amount of salicylate is ingested. People with salicylate intolerance are unable to consume a normal amount of salicylate without adverse effects.
Salicylate sensitivity diff ...
(or aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
sensitivity) are at an elevated risk for reaction to sulfites. Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typicall ...
and life-threatening reactions are rare. Other potential symptoms include sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
, swelling of the throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
, hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and typically ...
, and migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
.
A 2017 study has shown negative impacts of sulfites on bacteria found in the human microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
.
Use and labeling regulations
In 1986, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration banned the use of sulfites as preservatives on foods intended to be eaten fresh (such as salad ingredients). This has contributed to the increased use oferythorbic acid
Erythorbic acid (isoascorbic acid, D-araboascorbic acid) is a stereoisomer (C5 epimer) of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It is synthesized by a reaction between methyl 2-keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose or ...
and its salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
as preservatives.
They also cannot be added to foods high in vitamin B1
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thia ...
such as meats because sulfites can destroy vitamin B1 from foods
Generally, U.S. labeling regulations do not require products to indicate the presence of sulfites in foods unless it is added specifically as a preservative; still, many companies voluntarily label sulfite-containing foods. Sulfites used in food processing (but not as a preservative) are required to be listed if they are not incidental additives (21 CFR 101.100(a)(3)), and if there are more than 10 ppm in the finished product (21 CFR 101.100(a)(4))
Sulfites that are allowed to be added in food in the US are sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, sodium sulfite
Sodium sulfite (sodium sulphite) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2SO3. A white, water-soluble solid, it is used commercially as an antioxidant and preservative. It is also suitable for the softening of lignin in the pulping an ...
, sodium bisulfite
Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is not a real compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions compose ...
, potassium bisulfite
Potassium bisulfite (or potassium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximately correctly mentioned formula chemical formula KHSO3. Potassium bisulfite in fact is not an actual compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in wat ...
, sodium metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite or sodium pyrosulfite (IUPAC spelling; Br. E. sodium metabisulphite or sodium pyrosulphite) is an inorganic compound of chemical formula Na2S2O5. The substance is sometimes referred to as disodium metabisulfite. It is used a ...
, and potassium metabisulfite
Potassium metabisulfite, K2S2O5, also known as potassium pyrosulfite, is a white crystalline powder with a pungent odour. It is mainly used as an antioxidant or chemical sterilant. As a disulfite, it is chemically very similar to sodium metabi ...
.
Products likely to contain sulfites at less than 10 ppm (fruits and alcoholic beverages) do not require ingredients labels, and the presence of sulfites usually is undisclosed.
In Australia and New Zealand, sulfites must be declared in the statement of ingredients when present in packaged foods in concentrations of 10 mg/kg (ppm) or more as an ingredient; or as an ingredient of a compound ingredient; or as a food additive or component of a food additive; or as a processing aid or component of a processing aid.
Sulfites that can be added to foods in Canada are potassium bisulfite, potassium metabisulfite, sodium bisulfite, sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite (also known as sodium hydrosulfite) is a white crystalline powder with a sulfurous odor. Although it is stable in dry air, it decomposes in hot water and in acid solutions.
Structure
left, 220px, Packing of sodium dithionit ...
, sodium metabisulfite, sodium sulfite, sulfur dioxide and sulfurous acid
Sulfuric(IV) acid (United Kingdom spelling: sulphuric(IV) acid), also known as sulfurous (UK: sulphurous) acid and thionic acid, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula .
Raman spectroscopy, Raman spectra of solutions o ...
. These can also be declared using the common names sulfites, sulfates, sulfiting agents.
In the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, "EU law requires food labels to indicate "contains sulfites" (when exceeding 10 milligrams per kilogram or per litre) without specifying the amount".
Metabolic diseases
People withmolybdenum cofactor deficiency
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency is a rare human disease in which the absence of molybdopterin – and consequently its molybdenum complex, commonly called molybdenum cofactor – leads to accumulation of toxic levels of sulphite and neurological d ...
cannot perform a number of metabolic functions, including the breakdown of sulfite. This causes an accumulation of sulfite in the blood, leading to neurological damage and death within months of birth unless treated. Treatment in the form of fosdenopterin, requiring daily injections, became available in 2009.
See also
*HSObisulfite
The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion . Salts containing the ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite diss ...
ion
*H2SO3 sulfurous acid
Sulfuric(IV) acid (United Kingdom spelling: sulphuric(IV) acid), also known as sulfurous (UK: sulphurous) acid and thionic acid, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula .
Raman spectroscopy, Raman spectra of solutions o ...
*SO2 sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
* Sulfite esters
*Other sulfur oxyacids
*Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most conomicallyimportant sulfur oxide". It is prepared on an industrial scale as a precursor to ...
(uncharged SO3; a sulfate precursor)
*'' Grant v The Australian Knitting Mills''
* Transition metal sulfito complex
References
{{Reflist * Sulfur oxyanions