Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in
Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
to the southwest,
Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
to the west,
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
to the north,
Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
to the northeast,
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
to the southeast,
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
to the northwest,
South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
to the south and the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's
third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the
secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by
Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. Its
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
is
Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
and its most populated city is
Omdurman
Omdurman (standard ar, أم درمان ''Umm Durmān'') is a city in Sudan. It is the most populated city in the country, and thus also in the State of Khartoum. Omdurman lies on the west bank of the River Nile, opposite and northwest of the ...
(part of the metropolitan area of Khartoum).
Sudan's history goes back to the
Pharaonic period, witnessing the
Kingdom of Kerma ( 2500–1500 BC), the subsequent rule of the
Egyptian New Kingdom
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioca ...
( 1500 BC–1070 BC) and the rise of the
Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian language, Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Akkadian language, Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, ce ...
( 785 BC–350 AD), which would in turn
control Egypt itself for nearly a century. After the fall of Kush, the
Nubians formed the three Christian kingdoms of
Nobatia,
Makuria
Makuria (Old Nubian: , ''Dotawo''; gr, Μακουρία, Makouria; ar, المقرة, al-Muqurra) was a Nubian kingdom located in what is today Northern Sudan and Southern Egypt. Makuria originally covered the area along the Nile River from the ...
, and
Alodia, with the latter two lasting until around 1500. Between the 14th and 15th centuries, most of Sudan was gradually settled by
Arab nomads. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, central and eastern Sudan were dominated by the
Funj sultanate, while
Darfur
Darfur ( ; ar, دار فور, Dār Fūr, lit=Realm of the Fur) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju ( ar, دار داجو, Dār Dājū, links=no) while ruled by the Daju, ...
ruled the west and the Ottomans the east.
During the
Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
and
Ottoman periods,
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
played a big role and was demanded from the Sudanese Kashif as the regular remittance of tribute. In 1811, Mamluks established a state at
Dunqulah as a base for their
slave trading
The history of slavery spans many cultures, nationalities, and Slavery and religion, religions from Ancient history, ancient times to the present day. Likewise, its victims have come from many different ethnicities and religious groups. The socia ...
. Under
Turco-Egyptian rule of Sudan after the 1820s, the practice of trading slaves was entrenched along a north–south axis, with slave raids taking place in southern parts of the country and slaves being transported to Egypt and the
Ottoman empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
From the early 19th century, the entirety of Sudan was conquered by the Ottomans under the
Muhammad Ali dynasty. It was under Turkish rule that Sudan acquired its modern borders and began the process of political, agricultural, and economic development. In 1881, nationalist sentiment in Egypt led to the
Orabi Revolt Orabi is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Ahmed ‘Urabi ("Orabi" in Egyptian Arabic; 1841–1911), Egyptian rebel and patriot
*Ibrahim Orabi (born 1912), Egyptian sport wrestler
*Mohamed Orabi (born 1951), Egyptian diplomat and ...
, "weakening" the power of the Egyptian monarchy, and eventually leading to the occupation of Egypt by the United Kingdom. At the same time, religious-nationalist fervour in Sudan erupted in the
Mahdist Uprising led by the self-proclaimed
Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a Messianism, messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the Eschatology, end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a de ...
Muhammad Ahmad
Muhammad Ahmad ( ar, محمد أحمد ابن عبد الله; 12 August 1844 – 22 June 1885) was a Nubian Sufi religious leader of the Samaniyya order in Sudan who, as a youth, studied Sunni Islam. In 1881, he claimed to be the Mahdi, an ...
, and resulting in the establishment of the
Caliphate of Omdurman. The Mahdist forces were eventually defeated by a joint Egyptian-British military force, restoring the authority of the Egyptian monarch. However, Egyptian sovereignty in Sudan would henceforth be rather nominal, as the true power in both Egypt and Sudan was now the United Kingdom. In 1899, under British pressure, Egypt agreed to share sovereignty over Sudan with the United Kingdom as a
condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
. In effect, Sudan was governed as a British possession. The 20th century saw the growth of both Egyptian and Sudanese nationalism focusing on ending the United Kingdom's occupation. The
Egyptian revolution of 1952 toppled the monarchy and demanded the withdrawal of British forces from all of Egypt and Sudan.
Muhammad Naguib, one of the two co-leaders of the revolution, and Egypt's first President, who was half-Sudanese and had been raised in Sudan, made securing Sudanese independence a priority of the revolutionary government. The following year, under Egyptian and Sudanese pressure, the United Kingdom agreed to Egypt's demand for both governments to terminate their shared sovereignty over Sudan and to grant Sudan independence. On 1 January 1956, Sudan was duly declared an independent state.
After Sudan became independent, the
Jaafar Nimeiry
Jaafar Muhammad an-Nimeiry (otherwise spelled in English as Jaafar Nimeiry, Gaafar Nimeiry or Ja'far Muhammad Numayri; ar, جعفر محمد النميري; 26 April 192830 May 2009) was a Sudanese politician who served as the president of Sud ...
regime began
Islamist rule.
This exacerbated the rift between the Islamic North, the seat of the government, and the
Animists
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, huma ...
and Christians in the South. Differences in language, religion, and political power erupted in a
civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
between government forces, influenced by the
National Islamic Front
The National Islamic Front ( ar, الجبهة الإسلامية القومية; transliterated: ''al-Jabhah al-Islamiyah al-Qawmiyah'') was an Islamist political organization founded in 1976 and led by Dr. Hassan al-Turabi that influenced th ...
(NIF), and the southern rebels, whose most influential faction was the
Sudan People's Liberation Army
The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the South Sudan, Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 198 ...
(SPLA), which eventually led to the independence of
South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
in 2011. Between 1989 and 2019, Sudan experienced a 30-year-long
military dictatorship
A military dictatorship is a dictatorship in which the military exerts complete or substantial control over political authority, and the dictator is often a high-ranked military officer.
The reverse situation is to have civilian control of the m ...
led by
Omar al-Bashir, who was accused of
human rights abuses
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
, including torture, persecution of minorities,
allegations of sponsoring global terrorism, and
ethnic genocide due to its actions in the
War in the Darfur region that broke out in 2003. Overall, the regime's actions killed an estimated 300,000 to 400,000 people.
Protests erupted in 2018, demanding Bashir's resignation, which resulted in a
coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
on 11 April 2019 and Bashir's imprisonment.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was Sudan's state religion and
Islamic laws
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
were applied from 1983 until 2020 when the country became a
secular state
A secular state is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a State (polity), state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens ...
.
Sudan is
developing
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
country, ranking 172th in the
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
.The
economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
has been described as lower-middle income, with over 35% population living in poverty, largely relies on agriculture due to long-term international sanctions and isolation, as well as a long history of internal instability and factional violence, to some extent on
oil production in the oil fields of South Sudan. Sudan is a member of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
,
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
,
COMESA
The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is a regional economic community in Africa with twenty-one member states stretching from Tunisia to Eswatini. COMESA was formed in December 1994, replacing a Preferential Trade Area whic ...
,
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
and the
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Etymology
The country's name ''Sudan'' is a name given historically to the large
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
region of West Africa to the immediate West of modern-day Sudan. Historically, Sudan referred to both the
geographical region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, stretching from Senegal on the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
Coast to
Northeast Africa and the modern Sudan. The name derives from the Arabic ' (), or "The Land of the
Blacks
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in s ...
". The name is one of various
toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s sharing similar
etymologies
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
, in reference to the more or less dark skin of the inhabitants. Prior to this, Sudan was known as Nubia and Ta Nehesi or Ta Seti by Ancient Egyptians named for the Nubian and
Medjay archers or Bow men.
History
Prehistoric Sudan (before c. 8000 BC)


By the eighth millennium BC, people of a
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
culture had settled into a sedentary way of life there in fortified
mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also bee ...
villages, where they supplemented hunting and fishing on the Nile with
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
gathering and
cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
herding.
Neolithic peoples created cemeteries such as
R12 R12 may refer to:
Automobiles
* BMW R12, a motorcycle
* Renault 12, a French family car
Aviation
* Bell R-12, an American utility helicopter
* Caudron R.12, a French experimental biplane
* Republic XR-12 Rainbow, an American experimental reco ...
. During the fifth millennium BC, migrations from the drying Sahara brought neolithic people into the Nile Valley along with agriculture. The population that resulted from this cultural and genetic mixing developed a social hierarchy over the next centuries which became the Kingdom of Kush (with the capital at Kerma) at 1700 BC. Anthropological and archaeological research indicate that during the predynastic period Nubia and Nagadan Upper Egypt were ethnically, and culturally nearly identical, and thus, simultaneously evolved systems of pharaonic kingship by 3300 BC.
Kingdom of Kush (c. 1070 BC–350 AD)
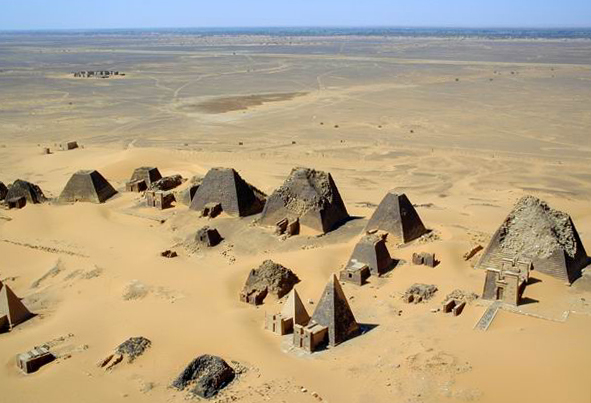


The
Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian language, Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Akkadian language, Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, ce ...
was an ancient
Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
n state centered on the confluences of the
Blue Nile and
White Nile
The White Nile ( ar, النيل الأبيض ') is a river in Africa, one of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the other being the Blue Nile. The name comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color. ...
, and the
Atbarah River and the
Nile River
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
. It was established after the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
collapse and the disintegration of the
New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioca ...
, centered at Napata in its early phase.
After King
Kashta
Kashta was an 8th century BC king of the Kingdom of Kush, Kushite Dynasty in ancient Nubia and the successor of Alara of Nubia, Alara. His nomen ''k3š-t3'' (transcribed as Kashta, possibly pronounced /kuʔʃi-taʔ/) "of the land of Kush" is ofte ...
("the Kushite") invaded Egypt in the eighth century BC, the Kushite kings ruled as pharaohs of the
Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt for nearly a century before being defeated and driven out by the
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
ns.
[ At the height of their glory, the Kushites conquered an empire that stretched from what is now known as South Kordofan to the Sinai. Pharaoh Piye attempted to expand the empire into the Near East but was thwarted by the Assyrian king ]Sargon II
Sargon II (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is general ...
.
Between 800 BCE and 100 AD were built the Nubian pyramids
The Nubian pyramids were built by the rulers of the ancient Kushite kingdoms. The area of the Nile valley known as Nubia, which lies within the north of present-day Sudan, was the site of three Kushite kingdoms during antiquity. The capital of th ...
, among them can be named El-Kurru
El-Kurru was the first of the three royal cemeteries used by the Kushite royals of Napata, also referred to as Egypt's 25th Dynasty, and is home to some of the royal Nubian Pyramids. It is located between the 3rd and 4th cataracts of the Nile ab ...
, Kashta
Kashta was an 8th century BC king of the Kingdom of Kush, Kushite Dynasty in ancient Nubia and the successor of Alara of Nubia, Alara. His nomen ''k3š-t3'' (transcribed as Kashta, possibly pronounced /kuʔʃi-taʔ/) "of the land of Kush" is ofte ...
, Piye, Tantamani
Tantamani ( egy, tnwt-jmn, Neo-Assyrian: , grc, Τεμένθης ), also known as Tanutamun or Tanwetamani (d. 653 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Kush located in Northern Sudan, and the last pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. His pren ...
, Shabaka, Pyramids of Gebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal ( ar, جبل بركل) is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima, Sudan, Karima in Northern, Sudan, Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometime ...
, Pyramids of Meroe (Begarawiyah)
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
, the Sedeinga pyramids, and Pyramids of Nuri.Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
by Assyria. Sennacherib's successor Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his ...
went further and invaded Egypt itself to secure his control of the Levant. This succeeded, as he managed to expel Taharqa from Lower Egypt. Taharqa fled back to Upper Egypt and Nubia, where he died two years later. Lower Egypt came under Assyrian vassalage but proved unruly, unsuccessfully rebelling against the Assyrians. Then, the king Tantamani
Tantamani ( egy, tnwt-jmn, Neo-Assyrian: , grc, Τεμένθης ), also known as Tanutamun or Tanwetamani (d. 653 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Kush located in Northern Sudan, and the last pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. His pren ...
, a successor of Taharqa, made a final determined attempt to regain Lower Egypt from the newly re-instated Assyrian vassal Necho I. He managed to retake Memphis killing Necho in the process and besieged cities in the Nile Delta. Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (Neo-Assyrian language, Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "Ashur (god), Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king o ...
, who had succeeded Esarhaddon, sent a large army in Egypt to regain control. He routed Tantamani near Memphis and, pursuing him, sacked Thebes. Although the Assyrians immediately departed Upper Egypt after these events, weakened, Thebes peacefully submitted itself to Necho's son Psamtik I less than a decade later. This ended all hopes of a revival of the Nubian Empire, which rather continued in the form of a smaller kingdom centered on Napata. The city was raided by the Egyptian 590 BC, and sometime soon after to the late-3rd century BC, the Kushite resettled in Meroë.
Medieval Christian Nubian kingdoms (c. 350–1500)
 On the turn of the fifth century the
On the turn of the fifth century the Blemmyes
The Blemmyes ( grc, Βλέμμυες, Latin: ''Blemmyae'') were an Eastern Desert people who appeared in written sources from the 7th century BC until the 8th century AD.. By the late 4th century, they had occupied Lower Nubia and established a k ...
established a short-lived state in Upper Egypt and Lower Nubia, probably centered around Talmis (Kalabsha
New Kalabsha is a promontory located near Aswan in Egypt.
Created during the International Campaign to Save the Monuments of Nubia, it houses several important temples, structures, and other remains that have been relocated here from the site ...
), but before 450 they were already driven out of the Nile Valley by the Nobatians. The latter eventually founded a kingdom on their own, Nobatia.
By the sixth century there were in total three Nubian kingdoms: Nobatia in the north, which had its capital at Pachoras ( Faras); the central kingdom, Makuria
Makuria (Old Nubian: , ''Dotawo''; gr, Μακουρία, Makouria; ar, المقرة, al-Muqurra) was a Nubian kingdom located in what is today Northern Sudan and Southern Egypt. Makuria originally covered the area along the Nile River from the ...
centred at Tungul (Old Dongola
Old Dongola (Old Nubian: ⲧⲩⲛⲅⲩⲗ, ''Tungul''; ar, دنقلا العجوز, ''Dunqulā al-ʿAjūz'') is a deserted town in what is now Northern State, Sudan, located on the east bank of the Nile opposite the Wadi Howar. An important c ...
), about south of modern Dongola
Dongola ( ar, دنقلا, Dunqulā), also spelled ''Dunqulah'', is the capital of the state of Northern Sudan, on the banks of the Nile, and a former Latin Catholic bishopric (14th century). It should not be confused with Old Dongola, an ancien ...
; and Alodia, in the heartland of the old Kushitic kingdom, which had its capital at Soba
Soba ( or , "buckwheat") is a thin Japanese noodle made from buckwheat. The noodles are served either chilled with a dipping sauce, or hot in a noodle soup. The variety ''Nagano soba'' includes wheat flour.
In Japan, soba noodles can be found i ...
(now a suburb of modern-day Khartoum). Still in the sixth century they converted to Christianity. In the seventh century, probably at some point between 628 and 642, Nobatia was incorporated into Makuria.
Between 639 and 641 the Muslim Arabs of the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
Egypt. In 641 or 642 and again in 652
__NOTOC__
Year 652 ( DCLII) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 652 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era be ...
they invaded Nubia but were repelled, making the Nubians one of the few who managed to defeat the Arabs during the Islamic expansion
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territories ...
. Afterward the Makurian king and the Arabs agreed on a unique non-aggression pact that also included an annual exchange of gifts, thus acknowledging Makuria's independence. While the Arabs failed to conquer Nubia they began to settle east of the Nile, where they eventually founded several port towns and intermarried with the local Beja people, Beja.
 From the mid eighth to mid eleventh century the political power and cultural development of Christian Nubia peaked. In 747 Makuria invaded Egypt, which at this time belonged to the declining Umayyad dynasty, Umayyads, and it did so again in the early 960s, when it pushed as far north as Akhmim. Makuria maintained close dynastic ties with Alodia, perhaps resulting in the temporary unification of the two kingdoms into one state. The culture of the medieval Nubians has been described as "''Afro-Byzantine''", but was also increasingly influenced by Arab culture. The state organisation was extremely centralised, being based on the Byzantine bureaucracy of the sixth and seventh centuries. Arts flourished in the form of pottery paintings and especially wall paintings. The Nubians developed an alphabet for their language, Old Nubian, Old Nobiin, basing it on the Coptic alphabet, while also utilizing Medieval Greek, Greek, Coptic language, Coptic and Arabic. Women enjoyed high social status: they had access to education, could own, buy and sell land and often used their wealth to endow churches and church paintings. Even the royal succession was matrilineal, with the son of the king's sister being the rightful heir.
From the late 11th/12th century, Makuria's capital Dongola was in decline, and Alodia's capital declined in the 12th century as well. In the 14th and 15th centuries Bedouin tribes overran most of Sudan, migrating to the Butana, the Gezira (state), Gezira, Kordofan and Darfur. In 1365 a civil war forced the Makurian court to flee to Gebel Adda in Lower Nubia, while Dongola was destroyed and left to the Arabs. Afterwards Makuria continued to exist only as a petty kingdom. After the prosperous reign of king Joel of Dotawo, Joel ( 1463–1484) Makuria collapsed. Coastal areas from southern Sudan up to the port city of Suakin was succeeded by the Adal Sultanate in the fifteenth century. To the south, the kingdom of Alodia fell to either the Arabs, commanded by tribal leader Abdallah Jamma, or the Funj, an African people originating from the south. Datings range from the Hijri year, 9th century after the Hijra ( 1396–1494), the late 15th century, 1504 to 1509. An alodian rump state might have survived in the form of the kingdom of Fazughli, lasting until 1685.
From the mid eighth to mid eleventh century the political power and cultural development of Christian Nubia peaked. In 747 Makuria invaded Egypt, which at this time belonged to the declining Umayyad dynasty, Umayyads, and it did so again in the early 960s, when it pushed as far north as Akhmim. Makuria maintained close dynastic ties with Alodia, perhaps resulting in the temporary unification of the two kingdoms into one state. The culture of the medieval Nubians has been described as "''Afro-Byzantine''", but was also increasingly influenced by Arab culture. The state organisation was extremely centralised, being based on the Byzantine bureaucracy of the sixth and seventh centuries. Arts flourished in the form of pottery paintings and especially wall paintings. The Nubians developed an alphabet for their language, Old Nubian, Old Nobiin, basing it on the Coptic alphabet, while also utilizing Medieval Greek, Greek, Coptic language, Coptic and Arabic. Women enjoyed high social status: they had access to education, could own, buy and sell land and often used their wealth to endow churches and church paintings. Even the royal succession was matrilineal, with the son of the king's sister being the rightful heir.
From the late 11th/12th century, Makuria's capital Dongola was in decline, and Alodia's capital declined in the 12th century as well. In the 14th and 15th centuries Bedouin tribes overran most of Sudan, migrating to the Butana, the Gezira (state), Gezira, Kordofan and Darfur. In 1365 a civil war forced the Makurian court to flee to Gebel Adda in Lower Nubia, while Dongola was destroyed and left to the Arabs. Afterwards Makuria continued to exist only as a petty kingdom. After the prosperous reign of king Joel of Dotawo, Joel ( 1463–1484) Makuria collapsed. Coastal areas from southern Sudan up to the port city of Suakin was succeeded by the Adal Sultanate in the fifteenth century. To the south, the kingdom of Alodia fell to either the Arabs, commanded by tribal leader Abdallah Jamma, or the Funj, an African people originating from the south. Datings range from the Hijri year, 9th century after the Hijra ( 1396–1494), the late 15th century, 1504 to 1509. An alodian rump state might have survived in the form of the kingdom of Fazughli, lasting until 1685.
Islamic kingdoms of Sennar and Darfur (c. 1500–1821)
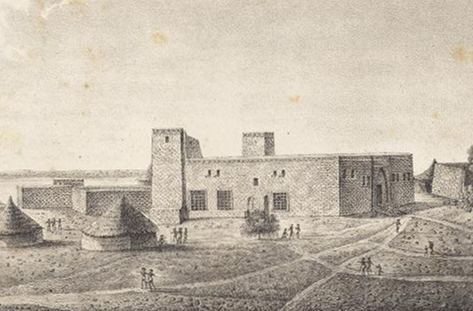 In 1504 the Funj are recorded to have founded the Kingdom of Sennar, in which Abdallah Jamma's realm was incorporated. By 1523, when Jewish traveler David Reubeni visited Sudan, the Funj state already extended as far north as Dongola. Meanwhile, Islam began to be preached on the Nile by Sufism, Sufi holymen who settled there in the 15th and 16th centuries and by David Reubeni's visit king Amara Dunqas, previously a Pagan or nominal Christian, was recorded to be Muslim. However, the Funj would retain un-Islamic customs like the divine kingship or the consumption of alcohol until the 18th century. Sudanese Folk religion, folk Islam preserved many rituals stemming from Christian traditions until the recent past.
Soon the Funj came in conflict with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, who had occupied Suakin around 1526 and eventually pushed south along the Nile, reaching the third Nile cataract area in 1583/1584. A subsequent Ottoman attempt to capture Dongola was battle of Hannik, repelled by the Funj in 1585. Afterwards, Hannik, located just south of the third cataract, would mark the border between the two states. The aftermath of the Ottoman invasion saw the attempted usurpation of Ajib the Great, Ajib, a minor king of northern Nubia. While the Funj eventually killed him in 1611/1612 his successors, the Abdallabi tribe, Abdallab, were granted to govern everything north of the confluence of Blue and White Niles with considerable autonomy.
During the 17th century the Funj state reached its widest extent, but in the following century it began to decline. A coup in 1718 brought a dynastic change, while another one in 1761–1762 resulted in the Hamaj Regency, Hamaj regency, where the Hamaj (a people from the Ethiopian borderlands) effectively ruled while the Funj sultans were their mere puppets. Shortly afterwards the sultanate began to fragment; by the early 19th century it was essentially restricted to the Gezira.
In 1504 the Funj are recorded to have founded the Kingdom of Sennar, in which Abdallah Jamma's realm was incorporated. By 1523, when Jewish traveler David Reubeni visited Sudan, the Funj state already extended as far north as Dongola. Meanwhile, Islam began to be preached on the Nile by Sufism, Sufi holymen who settled there in the 15th and 16th centuries and by David Reubeni's visit king Amara Dunqas, previously a Pagan or nominal Christian, was recorded to be Muslim. However, the Funj would retain un-Islamic customs like the divine kingship or the consumption of alcohol until the 18th century. Sudanese Folk religion, folk Islam preserved many rituals stemming from Christian traditions until the recent past.
Soon the Funj came in conflict with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, who had occupied Suakin around 1526 and eventually pushed south along the Nile, reaching the third Nile cataract area in 1583/1584. A subsequent Ottoman attempt to capture Dongola was battle of Hannik, repelled by the Funj in 1585. Afterwards, Hannik, located just south of the third cataract, would mark the border between the two states. The aftermath of the Ottoman invasion saw the attempted usurpation of Ajib the Great, Ajib, a minor king of northern Nubia. While the Funj eventually killed him in 1611/1612 his successors, the Abdallabi tribe, Abdallab, were granted to govern everything north of the confluence of Blue and White Niles with considerable autonomy.
During the 17th century the Funj state reached its widest extent, but in the following century it began to decline. A coup in 1718 brought a dynastic change, while another one in 1761–1762 resulted in the Hamaj Regency, Hamaj regency, where the Hamaj (a people from the Ethiopian borderlands) effectively ruled while the Funj sultans were their mere puppets. Shortly afterwards the sultanate began to fragment; by the early 19th century it was essentially restricted to the Gezira.
 The coup of 1718 kicked off a policy of pursuing a more orthodox Islam, which in turn promoted the Arabisation of the state. In order to legitimise their rule over their Arab subjects the Funj began to propagate an Banu Umayya, Umayyad descend. North of the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, as far downstream as Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah, the Nubians adopted the tribal identity of the Arab Ja'alin tribe, Jaalin. Until the 19th century Arabic had succeeded in becoming the dominant language of central riverine Sudan and most of Kordofan.
West of the Nile, in Darfur, the Islamic period saw at first the rise of the Tunjur kingdom, which replaced the old Daju kingdom in the 15th century and extended as far west as Wadai Empire, Wadai. The Tunjur people were probably Arabised Berbers and, their ruling elite at least, Muslims. In the 17th century the Tunjur were driven from power by the Fur people, Fur Sultanate of Darfur, Keira sultanate. The Keira state, nominally Muslim since the reign of Sulayman Solong (r. 1660–1680), was initially a small kingdom in northern Jebel Marra, but expanded west- and northwards in the early 18th century and eastwards under the rule of Muhammad Tayrab of Darfur, Muhammad Tayrab (r. 1751–1786), peaking in the conquest of Kordofan in 1785. The apogee of this empire, now roughly the size of present-day Nigeria, would last until 1821.
The coup of 1718 kicked off a policy of pursuing a more orthodox Islam, which in turn promoted the Arabisation of the state. In order to legitimise their rule over their Arab subjects the Funj began to propagate an Banu Umayya, Umayyad descend. North of the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, as far downstream as Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah, the Nubians adopted the tribal identity of the Arab Ja'alin tribe, Jaalin. Until the 19th century Arabic had succeeded in becoming the dominant language of central riverine Sudan and most of Kordofan.
West of the Nile, in Darfur, the Islamic period saw at first the rise of the Tunjur kingdom, which replaced the old Daju kingdom in the 15th century and extended as far west as Wadai Empire, Wadai. The Tunjur people were probably Arabised Berbers and, their ruling elite at least, Muslims. In the 17th century the Tunjur were driven from power by the Fur people, Fur Sultanate of Darfur, Keira sultanate. The Keira state, nominally Muslim since the reign of Sulayman Solong (r. 1660–1680), was initially a small kingdom in northern Jebel Marra, but expanded west- and northwards in the early 18th century and eastwards under the rule of Muhammad Tayrab of Darfur, Muhammad Tayrab (r. 1751–1786), peaking in the conquest of Kordofan in 1785. The apogee of this empire, now roughly the size of present-day Nigeria, would last until 1821.
Turkiyah and Mahdist Sudan (1821–1899)

 In 1821, the Ottoman ruler of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, had invaded and conquered northern Sudan. Although technically the Vali (governor), Vali of Egypt under the Ottoman Empire, Muhammad Ali styled himself as Khedive of a virtually independent Egypt. Seeking to add Sudan to his domains, he sent his third son Ismail (not to be confused with Isma'il Pasha, Ismaʻil Pasha mentioned later) to conquer the country, and subsequently incorporate it into Egypt. With the exception of the Shaiqiya and the Darfur sultanate in Kordofan, he was met without resistance. The Egyptian policy of conquest was expanded and intensified by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha's son, Ismaʻil, under whose reign most of the remainder of modern-day Sudan was conquered.
The Egyptian authorities made significant improvements to the Sudanese infrastructure (mainly in the north), especially with regard to irrigation and cotton production. In 1879, the International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919), Great Powers forced the removal of Ismail and established his son Tewfik Pasha in his place. Tewfik's corruption and mismanagement resulted in the 'Urabi revolt, which threatened the Khedive's survival. Tewfik appealed for help to the British, who subsequently occupied Egypt in 1882. Sudan was left in the hands of the Khedivial government, and the mismanagement and corruption of its officials.
During the Khedivial period, dissent had spread due to harsh taxes imposed on most activities. Taxation on irrigation wells and farming lands were so high most farmers abandoned their farms and livestock. During the 1870s, European initiatives against the slave trade had an adverse impact on the economy of northern Sudan, precipitating the rise of Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdist forces. Muhammad Ahmad, Muhammad Ahmad ibn Abd Allah, the ''
In 1821, the Ottoman ruler of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, had invaded and conquered northern Sudan. Although technically the Vali (governor), Vali of Egypt under the Ottoman Empire, Muhammad Ali styled himself as Khedive of a virtually independent Egypt. Seeking to add Sudan to his domains, he sent his third son Ismail (not to be confused with Isma'il Pasha, Ismaʻil Pasha mentioned later) to conquer the country, and subsequently incorporate it into Egypt. With the exception of the Shaiqiya and the Darfur sultanate in Kordofan, he was met without resistance. The Egyptian policy of conquest was expanded and intensified by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha's son, Ismaʻil, under whose reign most of the remainder of modern-day Sudan was conquered.
The Egyptian authorities made significant improvements to the Sudanese infrastructure (mainly in the north), especially with regard to irrigation and cotton production. In 1879, the International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919), Great Powers forced the removal of Ismail and established his son Tewfik Pasha in his place. Tewfik's corruption and mismanagement resulted in the 'Urabi revolt, which threatened the Khedive's survival. Tewfik appealed for help to the British, who subsequently occupied Egypt in 1882. Sudan was left in the hands of the Khedivial government, and the mismanagement and corruption of its officials.
During the Khedivial period, dissent had spread due to harsh taxes imposed on most activities. Taxation on irrigation wells and farming lands were so high most farmers abandoned their farms and livestock. During the 1870s, European initiatives against the slave trade had an adverse impact on the economy of northern Sudan, precipitating the rise of Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdist forces. Muhammad Ahmad, Muhammad Ahmad ibn Abd Allah, the ''Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a Messianism, messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the Eschatology, end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a de ...
'' (Guided One), offered to the ''ansars'' (his followers) and those who surrendered to him a choice between adopting Islam or being killed. The Mahdiyah (Mahdist regime) imposed traditional Sharia Sharia, Islamic laws. On 12 August 1881, an incident occurred at Battle of Aba, Aba Island, sparking the outbreak of what became the Mahdist War.
From his announcement of the Mahdiyya in June 1881 until the Siege of Khartoum, fall of Khartoum in January 1885, Muhammad Ahmad led a Mahdist War, successful military campaign against the Turco-Egyptian government of the Sudan, known as the Turkiyah. Muhammad Ahmad died on 22 June 1885, a mere six months after the conquest of Khartoum. After a power struggle amongst his deputies, Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, with the help primarily of the Baggara of western Sudan, overcame the opposition of the others and emerged as the unchallenged leader of the Mahdiyah. After consolidating his power, Abdallahi ibn Muhammad assumed the title of ''Khalifa'' (successor) of the Mahdi, instituted an administration, and appointed Ansar (Sudan), Ansar (who were usually Baggara) as emirs over each of the several provinces.
 Regional relations remained tense throughout much of the Mahdiyah period, largely because of the Khalifa's brutal methods to extend his rule throughout the country. In 1887, a 60,000-man Ansar army invaded
Regional relations remained tense throughout much of the Mahdiyah period, largely because of the Khalifa's brutal methods to extend his rule throughout the country. In 1887, a 60,000-man Ansar army invaded Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, penetrating as far as Gondar. In March 1889, king Yohannes IV of Ethiopia marched on Metemma; however, after Yohannes fell in battle, the Ethiopian forces withdrew. Abd ar-Rahman an-Nujumi, the Khalifa's general, attempted an invasion of Egypt in 1889, but British-led Egyptian troops defeated the Ansar at Tushkah. The failure of the Egyptian invasion broke the spell of the Ansar's invincibility. The Belgium, Belgians prevented the Mahdi's men from conquering Equatoria, and in 1893, the Italians repelled an Ansar attack at Agordat (in Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
) and forced the Ansar to withdraw from Ethiopia.
In the 1890s, the British sought to re-establish their control over Sudan, once more officially in the name of the Egyptian Khedive, but in actuality treating the country as a British colony. By the early 1890s, British, French, and Belgian claims had converged at the Nile headwaters. Britain feared that the other powers would take advantage of Sudan's instability to acquire territory previously annexed to Egypt. Apart from these political considerations, Britain wanted to establish control over the Nile to safeguard a planned irrigation dam at Aswan. Herbert Kitchener led military campaigns against the Mahdist Sudan from 1896 to 1898. Kitchener's campaigns culminated in a decisive victory in the Battle of Omdurman on 2 September 1898. A year later, the Battle of Umm Diwaykarat on 25 November 1899 resulted in the death of Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, subsequently bringing to the end of the Mahdist War.
Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956)
 In 1899, Britain and Egypt reached an agreement under which Sudan was run by a governor-general appointed by Egypt with British consent. In reality, Sudan was effectively administered as a Crown colony. The British were keen to reverse the process, started under Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali Pasha, of uniting the Nile Valley under Egyptian leadership and sought to frustrate all efforts aimed at further uniting the two countries.
Under the Delimitation, Sudan's border with Abyssinia was contested by raiding tribesmen trading slaves, breaching boundaries of the law. In 1905 Local chieftain Sultan Yambio reluctant to the end gave up the struggle with British forces that had occupied the Kordofan region, finally ending the lawlessness. The continued British administration of Sudan fuelled an increasingly strident nationalist backlash, with Egyptian nationalist leaders determined to force Britain to recognise a single independent union of Egypt and Sudan. With a formal end to Ottoman rule in 1914, Sir Reginald Wingate was sent that December to occupy Sudan as the new Military Governor. Hussein Kamel of Egypt, Hussein Kamel was declared Sultan of Egypt and Sudan, as was his brother and successor, Fuad I of Egypt, Fuad I. They continued upon their insistence of a single Egyptian-Sudanese state even when the Sultanate of Egypt was retitled as the Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Egypt and Sudan, but it was Saad Zaghloul who continued to be frustrated in the ambitions until his death in 1927.
In 1899, Britain and Egypt reached an agreement under which Sudan was run by a governor-general appointed by Egypt with British consent. In reality, Sudan was effectively administered as a Crown colony. The British were keen to reverse the process, started under Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali Pasha, of uniting the Nile Valley under Egyptian leadership and sought to frustrate all efforts aimed at further uniting the two countries.
Under the Delimitation, Sudan's border with Abyssinia was contested by raiding tribesmen trading slaves, breaching boundaries of the law. In 1905 Local chieftain Sultan Yambio reluctant to the end gave up the struggle with British forces that had occupied the Kordofan region, finally ending the lawlessness. The continued British administration of Sudan fuelled an increasingly strident nationalist backlash, with Egyptian nationalist leaders determined to force Britain to recognise a single independent union of Egypt and Sudan. With a formal end to Ottoman rule in 1914, Sir Reginald Wingate was sent that December to occupy Sudan as the new Military Governor. Hussein Kamel of Egypt, Hussein Kamel was declared Sultan of Egypt and Sudan, as was his brother and successor, Fuad I of Egypt, Fuad I. They continued upon their insistence of a single Egyptian-Sudanese state even when the Sultanate of Egypt was retitled as the Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Egypt and Sudan, but it was Saad Zaghloul who continued to be frustrated in the ambitions until his death in 1927.
 From 1924 until independence in 1956, the British had a policy of running Sudan as two essentially separate territories; the north and south. The Lee Stack, assassination of a Governor-General of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in Cairo was the causative factor; it brought demands of the newly elected Wafd Party, Wafd government from colonial forces. A permanent establishment of two battalions in Khartoum was renamed the Sudan Defence Force acting as under the government, replacing the former garrison of Egyptian army soldiers, saw action afterward during the Abyssinia Crisis, Walwal Incident. The Wafdist parliamentary majority had rejected Abdel Khalek Sarwat Pasha, Sarwat Pasha's accommodation plan with Austen Chamberlain in London; yet Cairo still needed the money. The Sudanese Government's revenue had reached a peak in 1928 at £6.6 million, thereafter the Wafdist disruptions, and Italian borders incursions from Somaliland, London decided to reduce expenditure during the Great Depression. Cotton and gum exports were dwarfed by the necessity to import almost everything from Britain leading to a balance of payments deficit at Khartoum.
In July 1936 the Liberal Constitutional leader, Muhammed Mahmoud was persuaded to bring Wafd delegates to London to sign the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty, "the beginning of a new stage in Anglo-Egyptian relations", wrote Anthony Eden. The British Army was allowed to return to Sudan to protect the Canal Zone. They were able to find training facilities, and the RAF was free to fly over Egyptian territory. It did not, however, resolve the problem of Sudan: the Sudanese Intelligentsia agitated for a return to metropolitan rule, conspiring with Germany's agents.
Mussolini made it clear that he could not invade Abyssinia without first conquering Egypt and Sudan; they intended unification of Libya with Italian East Africa. The British Imperial General Staff prepared for military defence of the region, which was thin on the ground. The British ambassador blocked Italian attempts to secure a Non-Aggression Treaty with Egypt-Sudan. But Mahmoud was a supporter of the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem; the region was caught between the Empire's efforts to save the Jews, and moderate Arab calls to halt migration.
The Sudanese Government was directly involved militarily in the East African Campaign (World War II), East African Campaign. Formed in 1925, the Sudan Defence Force played an active part in responding to incursions early in World War Two. Italian troops occupied Kassala and other border areas from Italian East Africa, Italian Somaliland during 1940. In 1942, the SDF also played a part in the invasion of the Italian colony by British and Commonwealth forces. The last British governor-general was Robert George Howe.
The Egyptian revolution of 1952 finally heralded the beginning of the march towards Sudanese independence. Having abolished the monarchy in 1953, Egypt's new leaders, Mohammed Naguib, whose mother was Sudanese, and later Gamal Abdel Nasser, believed the only way to end British domination in Sudan was for Egypt to officially abandon its claims of sovereignty. In addition, Nasser knew it would be difficult for Egypt to govern an impoverished Sudan after its independence. The British on the other hand continued their political and financial support for the Mahdist successor, Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, whom it was believed would resist Egyptian pressure for Sudanese independence. Rahman was capable of this, but his regime was plagued by political ineptitude, which garnered a colossal loss of support in northern and central Sudan. Both Egypt and Britain sensed a great instability fomenting, and thus opted to allow both Sudanese regions, north and south to have a free vote on whether they wished independence or a British withdrawal.
From 1924 until independence in 1956, the British had a policy of running Sudan as two essentially separate territories; the north and south. The Lee Stack, assassination of a Governor-General of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in Cairo was the causative factor; it brought demands of the newly elected Wafd Party, Wafd government from colonial forces. A permanent establishment of two battalions in Khartoum was renamed the Sudan Defence Force acting as under the government, replacing the former garrison of Egyptian army soldiers, saw action afterward during the Abyssinia Crisis, Walwal Incident. The Wafdist parliamentary majority had rejected Abdel Khalek Sarwat Pasha, Sarwat Pasha's accommodation plan with Austen Chamberlain in London; yet Cairo still needed the money. The Sudanese Government's revenue had reached a peak in 1928 at £6.6 million, thereafter the Wafdist disruptions, and Italian borders incursions from Somaliland, London decided to reduce expenditure during the Great Depression. Cotton and gum exports were dwarfed by the necessity to import almost everything from Britain leading to a balance of payments deficit at Khartoum.
In July 1936 the Liberal Constitutional leader, Muhammed Mahmoud was persuaded to bring Wafd delegates to London to sign the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty, "the beginning of a new stage in Anglo-Egyptian relations", wrote Anthony Eden. The British Army was allowed to return to Sudan to protect the Canal Zone. They were able to find training facilities, and the RAF was free to fly over Egyptian territory. It did not, however, resolve the problem of Sudan: the Sudanese Intelligentsia agitated for a return to metropolitan rule, conspiring with Germany's agents.
Mussolini made it clear that he could not invade Abyssinia without first conquering Egypt and Sudan; they intended unification of Libya with Italian East Africa. The British Imperial General Staff prepared for military defence of the region, which was thin on the ground. The British ambassador blocked Italian attempts to secure a Non-Aggression Treaty with Egypt-Sudan. But Mahmoud was a supporter of the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem; the region was caught between the Empire's efforts to save the Jews, and moderate Arab calls to halt migration.
The Sudanese Government was directly involved militarily in the East African Campaign (World War II), East African Campaign. Formed in 1925, the Sudan Defence Force played an active part in responding to incursions early in World War Two. Italian troops occupied Kassala and other border areas from Italian East Africa, Italian Somaliland during 1940. In 1942, the SDF also played a part in the invasion of the Italian colony by British and Commonwealth forces. The last British governor-general was Robert George Howe.
The Egyptian revolution of 1952 finally heralded the beginning of the march towards Sudanese independence. Having abolished the monarchy in 1953, Egypt's new leaders, Mohammed Naguib, whose mother was Sudanese, and later Gamal Abdel Nasser, believed the only way to end British domination in Sudan was for Egypt to officially abandon its claims of sovereignty. In addition, Nasser knew it would be difficult for Egypt to govern an impoverished Sudan after its independence. The British on the other hand continued their political and financial support for the Mahdist successor, Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, whom it was believed would resist Egyptian pressure for Sudanese independence. Rahman was capable of this, but his regime was plagued by political ineptitude, which garnered a colossal loss of support in northern and central Sudan. Both Egypt and Britain sensed a great instability fomenting, and thus opted to allow both Sudanese regions, north and south to have a free vote on whether they wished independence or a British withdrawal.
Independence (1956–present)
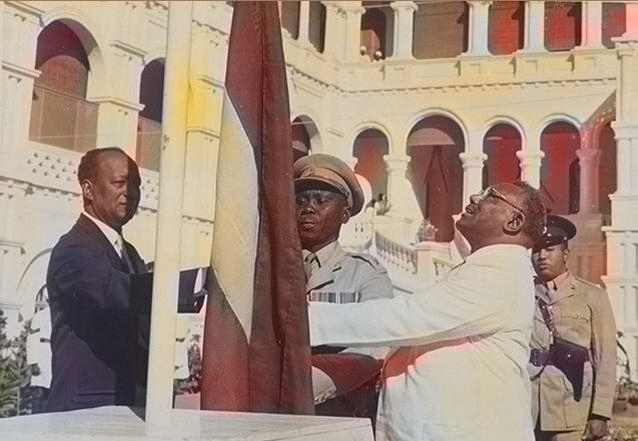 A polling process was carried out resulting in the composition of a democratic parliament and Ismail al-Azhari was elected first Prime Minister and led the first modern Sudanese government. On 1 January 1956, in a special ceremony held at the People's Palace, the Egyptian and British flags were lowered and the new Sudanese flag, composed of green, blue and yellow stripes, was raised in their place by the prime minister Ismail al-Azhari.
Dissatisfaction culminated in a second 1969 Sudanese coup d'état, coup d'état on 25 May 1969. The coup leader, Col. Gaafar Nimeiry, became prime minister, and the new regime abolished parliament and outlawed all political parties. Disputes between Marxist and non-Marxist elements within the ruling military coalition resulted in 1971 Sudanese coup d'état, a briefly successful coup in July 1971, led by the Sudanese Communist Party. Several days later, anti-communist military elements restored Nimeiry to power.
In 1972, the Addis Ababa Agreement (1972), Addis Ababa Agreement led to a cessation of the north–south civil war and a degree of self-rule. This led to ten years hiatus in the civil war but an end to American investment in the Jonglei Canal project. This had been considered absolutely essential to irrigate the Upper Nile region and to prevent an environmental catastrophe and wide-scale famine among the local tribes, most especially the Dinka. In the civil war that followed their homeland was raided, looted, pillaged, and burned. Many of the tribe were murdered in a bloody civil war that raged for over 20 years.
A polling process was carried out resulting in the composition of a democratic parliament and Ismail al-Azhari was elected first Prime Minister and led the first modern Sudanese government. On 1 January 1956, in a special ceremony held at the People's Palace, the Egyptian and British flags were lowered and the new Sudanese flag, composed of green, blue and yellow stripes, was raised in their place by the prime minister Ismail al-Azhari.
Dissatisfaction culminated in a second 1969 Sudanese coup d'état, coup d'état on 25 May 1969. The coup leader, Col. Gaafar Nimeiry, became prime minister, and the new regime abolished parliament and outlawed all political parties. Disputes between Marxist and non-Marxist elements within the ruling military coalition resulted in 1971 Sudanese coup d'état, a briefly successful coup in July 1971, led by the Sudanese Communist Party. Several days later, anti-communist military elements restored Nimeiry to power.
In 1972, the Addis Ababa Agreement (1972), Addis Ababa Agreement led to a cessation of the north–south civil war and a degree of self-rule. This led to ten years hiatus in the civil war but an end to American investment in the Jonglei Canal project. This had been considered absolutely essential to irrigate the Upper Nile region and to prevent an environmental catastrophe and wide-scale famine among the local tribes, most especially the Dinka. In the civil war that followed their homeland was raided, looted, pillaged, and burned. Many of the tribe were murdered in a bloody civil war that raged for over 20 years.
 Until the early 1970s, Sudan's agricultural output was mostly dedicated to internal consumption. In 1972, the Sudanese government became more pro-Western and made plans to export food and cash crops. However, commodity prices declined throughout the 1970s causing economic problems for Sudan. At the same time, debt servicing costs, from the money spent mechanizing agriculture, rose. In 1978, the International Monetary Fund, IMF negotiated a Structural Adjustment Program with the government. This further promoted the mechanised export agriculture sector. This caused great hardship for the pastoralists of Sudan (see Nuba peoples#Effect of private agriculture schemes, Nuba peoples). In 1976, the Ansars had mounted a bloody but unsuccessful coup attempt. But in July 1977, President Nimeiry met with Ansar leader Sadiq al-Mahdi, opening the way for a possible reconciliation. Hundreds of political prisoners were released, and in August a general amnesty was announced for all oppositionists.
Until the early 1970s, Sudan's agricultural output was mostly dedicated to internal consumption. In 1972, the Sudanese government became more pro-Western and made plans to export food and cash crops. However, commodity prices declined throughout the 1970s causing economic problems for Sudan. At the same time, debt servicing costs, from the money spent mechanizing agriculture, rose. In 1978, the International Monetary Fund, IMF negotiated a Structural Adjustment Program with the government. This further promoted the mechanised export agriculture sector. This caused great hardship for the pastoralists of Sudan (see Nuba peoples#Effect of private agriculture schemes, Nuba peoples). In 1976, the Ansars had mounted a bloody but unsuccessful coup attempt. But in July 1977, President Nimeiry met with Ansar leader Sadiq al-Mahdi, opening the way for a possible reconciliation. Hundreds of political prisoners were released, and in August a general amnesty was announced for all oppositionists.
Bashir Era (1989–2019)
 On 30 June 1989, Colonel Omar al-Bashir led a bloodless 1989 Sudanese coup d'état, military coup.
On 30 June 1989, Colonel Omar al-Bashir led a bloodless 1989 Sudanese coup d'état, military coup.[''The New York Times''. 16 March 1996. p. 4.] Sudan became a one-party state under the National Congress (Sudan), National Congress Party (NCP). During the 1990s, Hassan al-Turabi, then Speaker of the National Assembly, reached out to Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist groups and invited Osama bin Laden to the country. Before the Elections in Sudan, 2000 presidential election, al-Turabi introduced a bill to reduce the President's powers, prompting al-Bashir to dissolve parliament, order a dissolution and declare a state of emergency. When al-Turabi urged a boycott of the President's re-election campaign signing agreement with
Before the Elections in Sudan, 2000 presidential election, al-Turabi introduced a bill to reduce the President's powers, prompting al-Bashir to dissolve parliament, order a dissolution and declare a state of emergency. When al-Turabi urged a boycott of the President's re-election campaign signing agreement with Sudan People's Liberation Army
The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the South Sudan, Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 198 ...
, al-Bashir suspected they were plotting to overthrow the government.South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
; the region of Abyei will hold Abyei status referendum, its own referendum at a future date.
 The
The Sudan People's Liberation Army
The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the South Sudan, Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 198 ...
(SPLA) was the primary member of the Eastern Front (Sudan), Eastern Front, a coalition of rebel groups operating in eastern Sudan. After the peace agreement, their place was taken in February 2004 after the merger of the larger Fulani people, fulani and Beja Congress with the smaller Rashaida Free Lions. A peace agreement between the Sudanese government and the Eastern Front was signed on 14 October 2006, in Asmara. On 5 May 2006, the Darfur Peace Agreement was signed, aiming at ending the conflict which had continued for three years up to this point. The Chad–Sudan Conflict (2005–2007) had erupted after the Battle of Adré triggered a declaration of war by Chad. The leaders of Sudan and Chad signed an agreement in Saudi Arabia on 3 May 2007 to stop fighting from the Darfur conflict spilling along their countries' border.
In July 2007 the country was hit by 2007 Sudan floods, devastating floods, with over 400,000 people being directly affected. Since 2009, a series of Sudanese nomadic conflicts, ongoing conflicts between rival nomadic tribes in Sudan and South Sudan have caused a large number of civilian casualties.
Partition and rehabilitation
The Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile in the early 2010s between Sudan People's Armed Forces, the Army of Sudan and the Sudan Revolutionary Front started as a dispute over the oil-rich region of Abyei in the months leading up to South Sudan, South Sudanese independence in 2011, though it is also related to civil war in Darfur that is nominally resolved. The events would later be known as the 2011–2013 Sudanese protests, Sudanese Intifada, which would end only in 2013 after al-Bashir promised he would not seek re-election in 2015. He later broke his promise and sought re-election in 2015, winning through a boycott from the opposition who believed that the elections would not be free and fair. Voter turnout was at a low 46%.
On 13 January 2017, US president Barack Obama signed an Executive Order that lifted many sanctions placed against Sudan and assets of its government held abroad. On 6 October 2017, the following US president Donald Trump lifted most of the remaining sanctions against the country and its petroleum, export-import, and property industries.
2019 Sudanese Revolution and transitional government
 On 19 December 2018, Sudanese protests (2018–19), massive protests began after a government decision to triple the price of goods at a time when the country was suffering an acute shortage of foreign currency and inflation of 70 percent. In addition, President al-Bashir, who had been in power for more than 30 years, refused to step down, resulting in the convergence of opposition groups to form a united coalition. The government retaliated by arresting more than 800 opposition figures and protesters, leading to the death of approximately 40 people according to the Human Rights Watch, although the number was much higher than that according to local and civilian reports. The protests continued after the overthrow of his government on 11 April 2019 after a massive sit-in in front of the Sudanese Armed Forces main headquarters, after which the chiefs of staff decided to intervene and they ordered the arrest of President al-Bashir and declared a three-month state of emergency.
On 19 December 2018, Sudanese protests (2018–19), massive protests began after a government decision to triple the price of goods at a time when the country was suffering an acute shortage of foreign currency and inflation of 70 percent. In addition, President al-Bashir, who had been in power for more than 30 years, refused to step down, resulting in the convergence of opposition groups to form a united coalition. The government retaliated by arresting more than 800 opposition figures and protesters, leading to the death of approximately 40 people according to the Human Rights Watch, although the number was much higher than that according to local and civilian reports. The protests continued after the overthrow of his government on 11 April 2019 after a massive sit-in in front of the Sudanese Armed Forces main headquarters, after which the chiefs of staff decided to intervene and they ordered the arrest of President al-Bashir and declared a three-month state of emergency. The transitional institutions and procedures included the creation of a joint military-civilian Sovereignty Council of Sudan as head of state, a new Chief Justice of Sudan as head of the judiciary branch of power, Nemat Abdullah Khair, and a new prime minister. The former Prime Minister, Abdalla Hamdok, a 61-year-old economist who worked previously for the UN Economic Commission for Africa, was sworn in on 21 August. He initiated talks with the IMF and World Bank aimed at stabilising the economy, which was in dire straits because of shortages of food, fuel and hard currency. Hamdok estimated that US$10bn over two years would suffice to halt the panic, and said that over 70% of the 2018 budget had been spent on civil war-related measures. The governments of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates had invested significant sums supporting the military council since Bashir's ouster.
The transitional institutions and procedures included the creation of a joint military-civilian Sovereignty Council of Sudan as head of state, a new Chief Justice of Sudan as head of the judiciary branch of power, Nemat Abdullah Khair, and a new prime minister. The former Prime Minister, Abdalla Hamdok, a 61-year-old economist who worked previously for the UN Economic Commission for Africa, was sworn in on 21 August. He initiated talks with the IMF and World Bank aimed at stabilising the economy, which was in dire straits because of shortages of food, fuel and hard currency. Hamdok estimated that US$10bn over two years would suffice to halt the panic, and said that over 70% of the 2018 budget had been spent on civil war-related measures. The governments of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates had invested significant sums supporting the military council since Bashir's ouster.
2021 coup and the al-Burhan Regime
The Sudanese government announced on 21 September 2021 that there was a failed attempt at a Coup d'état, coup d’état from the military that had led to the arrest of 40 military officers.
One month after the attempted coup, another military coup on 25 October 2021 resulted in the capture of the civilian government, including former Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok. The coup was led by general Abdel Fattah al-Burhan who subsequently declared a state of emergency.
On November 21, 2021, Hamdok was reinstated as prime minister after a political agreement was signed by Abdel Fattah al-Burhan to restore the transition to civilian rule (although Burhan retained control). The 14-point deal called for the release of all political prisoners detained during the coup and stipulated that a 2019 constitutional declaration continued to be the basis for a political transition. Hamdok fired the chief of police Khaled Mahdi Ibrahim al-Emam and his second in command Ali Ibrahim.
On January 2, 2022, Hamdok announced his resignation from the position of Prime Minister following one of the most deadly protests to date.
By March, 2022 over 1,000 people including 148 children had been detained for opposing the coup, there were 25 allegations of rape
Geography

 Sudan is situated in North Africa, with an coastline bordering the
Sudan is situated in North Africa, with an coastline bordering the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. It has land borders with Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
, Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
, and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
. With an area of , it is the third-largest country on the continent (after Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and Democratic Republic of the Congo) and the List of countries and dependencies by area, fifteenth-largest in the world.
Sudan lies between latitudes 8th parallel north, 8° and 23rd parallel north, 23°N. The terrain is generally flat plains, broken by several mountain ranges. In the west, the Deriba Caldera (), located in the Marrah Mountains, is the highest point in Sudan. In the east are the Red Sea Hills.
The Blue Nile and White Nile
The White Nile ( ar, النيل الأبيض ') is a river in Africa, one of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the other being the Blue Nile. The name comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color. ...
rivers meet in Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
to form the Nile, which flows northwards through Egypt to the Mediterranean Sea. The Blue Nile's course through Sudan is nearly long and is joined by the Dinder River, Dinder and Rahad Rivers between Sennar and Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
. The White Nile within Sudan has no significant tributaries.
There are several dams on the Blue and White Niles. Among them are the Sennar Dam, Sennar and Roseires Dams on the Blue Nile, and the Jebel Aulia Dam on the White Nile. There is also Lake Nubia on the Sudanese-Egyptian border.
Rich mineral resources are available in Sudan including asbestos, chromite, cobalt, copper, gold, granite, gypsum, iron, kaolin, lead, manganese, mica, natural gas, nickel, petroleum, silver, tin, uranium and zinc.
Climate
The amount of rainfall increases towards the south. The central and the northern part have extremely dry, desert areas such as the Nubian Desert to the northeast and the Bayuda Desert to the east; in the south, there are grasslands and tropical savanna. Sudan's rainy season lasts for about four months (June to September) in the north, and up to six months (May to October) in the south.
The dry regions are plagued by Dust storm, sandstorms, known as haboob, which can completely block out the sun. In the northern and western semi-desert areas, people rely on the scant rainfall for basic agriculture and many are nomadic, travelling with their herds of sheep and camels. Nearer the River Nile, there are irrigation, well-irrigated farms growing cash crops. The sunshine duration is very high all over the country but especially in deserts where it could soar to over 4,000 h per year.
Environmental issues
Desertification is a serious problem in Sudan. There is also concern over soil erosion. Agricultural expansion, both public and private, has proceeded without Conservation movement, conservation measures. The consequences have manifested themselves in the form of deforestation, soil desiccation, and the lowering of soil fertility and the water table.
The nation's wildlife is threatened by poaching. As of 2001, twenty-one mammal species and nine bird species are endangered, as well as two species of plants. Critically endangered species include: the northern bald ibis, waldrapp, northern white rhinoceros, tora hartebeest, rhim gazelle, slender-horned gazelle, and hawksbill turtle. The Scimitar oryx, Sahara oryx has become extinct in the wild.
Politics
The politics of Sudan formally took place within the framework of a Federal republic, federal representative democracy, representative democratic republic until April 2019, when President Omar al-Bashir's regime was overthrown in a 2019 Sudanese coup d'état, military coup led by Vice President Ahmed Awad Ibn Auf. As an initial step he established the Transitional Military Council (2019), Transitional Military Council to manage the country's internal affairs. He also suspended the Constitution of Sudan, constitution and dissolved the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament — the National Legislature of Sudan, National Legislature, with its National Assembly of Sudan, National Assembly (lower chamber) and the Council of States of Sudan, Council of States (upper chamber). Ibn Auf however, remained in office for only a single day and then resigned, with the leadership of the Transitional Military Council then being handed to Abdel Fattah al-Burhan. On 4 August 2019, a new Constitutional Declaration was signed between the representatives of the Transitional Military Council and the Forces of Freedom and Change, and on 21 August 2019 the Transitional Military Council was officially replaced as head of state by an 11-member Sovereignty Council, and as head of government by a civilian Prime Minister.
Sharia law
Under al-Bashir
During the regime of Omar al-Bashir, the legal system in Sudan was based on Islamic Sharia law. The 2005 Comprehensive Peace Agreement, Naivasha Agreement, ending the civil war between north and south Sudan, established some protections for non-Muslims in Khartoum. Sudan's application of Sharia law is geographically inconsistent.
Stoning was a judicial punishment in Sudan. Between 2009 and 2012, several women were sentenced to death by stoning. Flogging was a legal punishment. Between 2009 and 2014, many people were sentenced to 40–100 lashes.
After al-Bashir
Following the ouster of al-Bashir, the interim constitution signed in August 2019 contained no mention of Sharia law.
Foreign relations
 Sudan has had a troubled relationship with many of its neighbours and much of the international community, owing to what is viewed as its radical Islamic stance. For much of the 1990s, Uganda, Kenya and
Sudan has had a troubled relationship with many of its neighbours and much of the international community, owing to what is viewed as its radical Islamic stance. For much of the 1990s, Uganda, Kenya and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
formed an ad hoc alliance called the "Front Line States" with support from the United States to check the influence of the National Islamic Front
The National Islamic Front ( ar, الجبهة الإسلامية القومية; transliterated: ''al-Jabhah al-Islamiyah al-Qawmiyah'') was an Islamist political organization founded in 1976 and led by Dr. Hassan al-Turabi that influenced th ...
government. The Sudanese Government supported anti-Ugandan rebel groups such as the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA).
As the National Islamic Front regime in Khartoum gradually emerged as a real threat to the region and the world, the U.S. began to list Sudan on its list of State Sponsors of Terrorism. After the US listed Sudan as a state sponsor of terrorism, the National Islamic Front, NIF decided to develop relations with Iraq, and later Iran, the two most controversial countries in the region.
From the mid-1990s, Sudan gradually began to moderate its positions as a result of increased U.S. pressure following the 1998 United States embassy bombings, 1998 U.S. embassy bombings, in Tanzania and Kenya, and the new development of oil fields previously in rebel hands. Sudan also has a territorial dispute with Egypt over the Hala'ib Triangle. Since 2003, the foreign relations of Sudan had centered on the support for ending the Second Sudanese Civil War and condemnation of government support for militias in the war in Darfur.
Sudan has extensive economic relations with China. China obtains ten percent of its oil from Sudan. According to a former Sudanese government minister, China is Sudan's largest supplier of arms.
In December 2005, Sudan became one of the few states to recognise Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara.
In 2015, Sudan participated in the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen against the Shia Islam, Shia Houthis and forces loyal to former President Ali Abdullah Saleh, who was deposed in the 2011 uprising.
In June 2019, Sudan was suspended from the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
over the lack of progress towards the establishment of a civilian-led transitional authority since its initial meeting following the coup d'état of 11 April 2019.
In July 2019, UN ambassadors of 37 countries, including Sudan, have signed a joint letter to the UNHRC defending China's Xinjiang re-education camps, treatment of Uyghurs in the Xinjiang region.
On 23 October 2020, U.S. President Donald Trump announced that Sudan will start to Israel–Sudan normalization agreement, normalize ties with Israel, making it the third Arab state to do so as part of the U.S.-brokered Abraham Accords. On 14 December the U.S. Government removed Sudan from its State Sponsor of Terrorism list; as part of the deal, Sudan agreed to pay $335 million in compensation to victims of the 1998 embassy bombings.
The dispute between Sudan and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
over the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam escalated in 2021. An advisor to the Sudanese leader Abdel Fattah al-Burhan spoke of a water war "that would be more horrible than one could imagine".
In February 2022, it is reported that a Sudanese envoy have visited Israel to promote ties between the countries.
Armed Forces
The Sudanese Armed Forces is the regular forces of Sudan and is divided into five branches: the Sudanese Army, Sudanese Navy (including the Marine Corps), Sudanese Air Force, Border Patrol and the Internal Affairs Defence Force, totalling about 200,000 troops. The military of Sudan has become a well-equipped fighting force; a result of increasing local production of heavy and advanced arms. These forces are under the command of the National Assembly and its strategic principles include defending Sudan's external borders and preserving internal security.
Since the War in Darfur, Darfur crisis in 2004, safe-keeping the central government from the armed resistance and rebellion of paramilitary rebel groups such as the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement, Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), the Sudan Liberation Army, Sudanese Liberation Army (SLA) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) have been important priorities. While not official, the Sudanese military also uses nomad militias, the most prominent being the Janjaweed, in executing a counter-insurgency war. Somewhere between 200,000
International organisations in Sudan
Several UN agents are operating in Sudan such as the World Food Program (WFP); the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP); the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO); the United Nations Children Fund (UNICEF); the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR); the United Nations Mine Service (UNMAS), the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) and the World Bank. Also present is the International Organisation for Migration (IOM).
Since Sudan has experienced civil war for many years, many non-governmental organisations (NGOs) are also involved in humanitarian efforts to help internally displaced people. The NGOs are working in every corner of Sudan, especially in the southern part and western parts. During the civil war, international nongovernmental organisations such as the Red Cross were operating mostly in the south but based in the capital Khartoum. The attention of NGOs shifted shortly after the war broke out in the western part of Sudan known as Darfur. The most visible organisation in South Sudan is the Operation Lifeline Sudan (OLS) consortium. Some international trade organisations categorise Sudan as part of the Greater Horn of Africa
Even though most of the international organisations are substantially concentrated in both South Sudan and the Darfur region, some of them are working in the northern part as well. For example, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization is successfully operating in Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, the capital. It is mainly funded by the European Union and recently opened more vocational training. The Canadian International Development Agency is operating largely in northern Sudan.
Human rights
Since 1983, a combination of civil war and famine has taken the lives of nearly two million people in Sudan. It is estimated that as many as 200,000 people had been taken into Slavery in modern Africa, slavery during the Second Sudanese Civil War.
Sudan ranks 172 of 180 countries in terms of freedom of the press according to Reporters Without Borders. More curbs of press freedom to report official corruption are planned.
Muslims who convert to Christianity can face the death penalty for apostasy, see Persecution of Christians in Sudan and the death sentence against Mariam Yahia Ibrahim Ishag (who actually was raised as Christian). According to a 2013 UNICEF report, 88% of women in Sudan had undergone female genital mutilation.[UNICEF 2013]
, p. 27. Sudan's Status (law), Personal Status law on marriage has been criticised for restricting women's rights and allowing child marriage. Evidence suggests that support for female genital mutilation remains high, especially among rural and less well educated groups, although it has been declining in recent years. LGBT rights in Sudan, Homosexuality is illegal; as of July 2020 it was no longer a capital offense, with the highest punishment being life imprisonment.
Darfur
 A letter dated 14 August 2006, from the executive director of Human Rights Watch found that the Sudanese government is both incapable of protecting its own citizens in Darfur and unwilling to do so, and that its militias are guilty of crimes against humanity. The letter added that these human-rights abuses have existed since 2004. Some reports attribute part of the violations to the rebels as well as the government and the Janjaweed. The U.S. State Department's human-rights report issued in March 2007 claims that "''[a]''ll parties to the conflagration committed serious abuses, including widespread killing of civilians, rape as a tool of war, systematic torture, robbery and recruitment of child soldiers."
Over 2.8 million civilians have been displaced and the death toll is estimated at 300,000 killed. Both government forces and militias allied with the government are known to attack not only civilians in Darfur, but also humanitarian workers. Sympathisers of rebel groups are arbitrarily detained, as are foreign journalists, human rights defender, human-rights defenders, student activists and displaced people in and around Khartoum, some of whom face torture. The rebel groups have also been accused in a report issued by the U.S. government of attacking humanitarian workers and of killing innocent civilians. According to UNICEF, in 2008, there were as many as 6,000 child soldiers in Darfur.
A letter dated 14 August 2006, from the executive director of Human Rights Watch found that the Sudanese government is both incapable of protecting its own citizens in Darfur and unwilling to do so, and that its militias are guilty of crimes against humanity. The letter added that these human-rights abuses have existed since 2004. Some reports attribute part of the violations to the rebels as well as the government and the Janjaweed. The U.S. State Department's human-rights report issued in March 2007 claims that "''[a]''ll parties to the conflagration committed serious abuses, including widespread killing of civilians, rape as a tool of war, systematic torture, robbery and recruitment of child soldiers."
Over 2.8 million civilians have been displaced and the death toll is estimated at 300,000 killed. Both government forces and militias allied with the government are known to attack not only civilians in Darfur, but also humanitarian workers. Sympathisers of rebel groups are arbitrarily detained, as are foreign journalists, human rights defender, human-rights defenders, student activists and displaced people in and around Khartoum, some of whom face torture. The rebel groups have also been accused in a report issued by the U.S. government of attacking humanitarian workers and of killing innocent civilians. According to UNICEF, in 2008, there were as many as 6,000 child soldiers in Darfur.
Disputed areas and zones of conflict
* In April 2012, the South Sudanese army captured the Heglig oil field from Sudan, which the Sudanese army later recaptured.
* Kafia Kingi and Radom National Park was a part of Bahr el Ghazal (region of South Sudan), Bahr el Ghazal in 1956. Sudan has recognised South Sudanese independence according to the borders for 1 January 1956.
* The Abyei Area is disputed region between Sudan and South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
. It is currently under Sudanese rule.
* The states of South Kurdufan and Blue Nile (state), Blue Nile are to hold "popular consultations" to determine their constitutional future within Sudan.
* The Hala'ib Triangle is disputed region between Sudan and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. It is currently under Egyptian administration.
* Bir Tawil is a terra nullius occurring on the border between Egypt and Sudan, claimed by neither state.
Administrative divisions
Sudan is divided into States of Sudan, 18 states (''wilayat'', Grammatical number, sing. ''wilayah''). They are further divided into 133 Districts of Sudan, districts.

Regional bodies
In addition to the states, there also exist regional administrative bodies established by peace agreements between the central government and rebel groups.
* The Darfur Regional Government was established by the Darfur Peace Agreement to act as a co-ordinating body for the states that make up the region of Darfur.
* The Eastern Sudan States Coordinating Council was established by the Eastern Sudan Peace Agreement between the Sudanese Government and the rebel Eastern Front (Sudan), Eastern Front to act as a coordinating body for the three eastern states.
* The Abyei, Abyei Area, located on the border between South Sudan and the Republic of the Sudan, currently has a special administrative status and is governed by an Abyei Area Administration. It was due to hold a Abyei status referendum, 2011, referendum in 2011 on whether to be part of South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
or part of the Republic of Sudan.
Economy


 In 2010, Sudan was considered the 17th-fastest-growing economy in the world and the rapid development of the country largely from oil profits even when facing international sanctions was noted by ''The New York Times'' in a 2006 article. Because of the secession of
In 2010, Sudan was considered the 17th-fastest-growing economy in the world and the rapid development of the country largely from oil profits even when facing international sanctions was noted by ''The New York Times'' in a 2006 article. Because of the secession of South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, which contained about 75 percent of Sudan's oilfields, Sudan entered a phase of stagflation, GDP growth slowed to 3.4 percent in 2014, 3.1 percent in 2015 and was projected to recover slowly to 3.7 percent in 2016 while inflation remained as high as 21.8% . Sudan's GDP fell from US$123.053 billion in 2017 to US$40.852 billion in 2018.
Even with the oil profits before the secession of South Sudan, Sudan still faced formidable economic problems, and its growth was still a rise from a very low level of per capita output. The economy of Sudan has been steadily growing over the 2000s, and according to a World Bank report the overall growth in GDP in 2010 was 5.2 percent compared to 2009 growth of 4.2 percent.South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, however, placed most major oilfields out of the Sudanese government's direct control and oil production in Sudan fell from around to under . Production has since recovered to hover around for 2014–15.
In order to export oil, South Sudan relies on a pipeline to Port Sudan on Sudan's Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
coast, as South Sudan is a landlocked country, as well as the oil refining facilities in Sudan. In August 2012, Sudan and South Sudan agreed a deal to transport South Sudanese oil through Sudanese pipelines to Port Sudan.
The People's Republic of China is one of Sudan's major trading partners, China owns a 40 percent share in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company. The country also sells Sudan small arms, which have been used in military operations such as the conflicts in Darfur and South Kordofan conflict, South Kordofan.
While historically agriculture remains the main source of income and employment hiring of over 80 percent of Sudanese, and makes up a third of the economic sector, oil production drove most of Sudan's post-2000 growth. Currently, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is working hand in hand with Khartoum government to implement sound macroeconomic policies. This follows a turbulent period in the 1980s when debt-ridden Sudan's relations with the IMF and World Bank soured, culminating in its eventual suspension from the IMF.
According to the Corruptions Perception Index, Sudan is one of the most corrupt nations in the world. According to the Global Hunger Index of 2013, Sudan has an GHI indicator value of 27.0 indicating that the nation has an 'Alarming Hunger Situation.' It is rated the fifth hungriest nation in the world. According to the 2015 Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
(HDI) Sudan ranked the List of countries by Human Development Index, 167th place in human development, indicating Sudan still has one of the lowest human development rates in the world. In 2014, 45% of the population lives on less than US$3.20 per day, up from 43% in 2009.
Science and research
Sudan has around 25–30 universities; instruction is primarily in Arabic or English. Education at the secondary and university levels has been seriously hampered by the requirement that most males perform military service before completing their education.Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, according to the Sudanese National Centre for Research. In 2015, Sudan published only about 500 scientific papers.
Demographics
 In Sudan's 2008 census, the population of northern, western and eastern Sudan was recorded to be over 30 million. This puts present estimates of the population of Sudan after the secession of
In Sudan's 2008 census, the population of northern, western and eastern Sudan was recorded to be over 30 million. This puts present estimates of the population of Sudan after the secession of South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
at a little over 30 million people. This is a significant increase over the past two decades, as the 1983 census put the total population of Sudan, including present-day South Sudan, at 21.6 million. The population of Greater Khartoum (including Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, Omdurman
Omdurman (standard ar, أم درمان ''Umm Durmān'') is a city in Sudan. It is the most populated city in the country, and thus also in the State of Khartoum. Omdurman lies on the west bank of the River Nile, opposite and northwest of the ...
, and Khartoum North) is growing rapidly and was recorded to be 5.2 million.
Aside from being a refugee-generating country, Sudan also hosts a large population of refugees from other countries. According to United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, UNHCR statistics, more than 1.1 million refugees and asylum seekers lived in Sudan in August 2019. The majority of this population came from South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
(858,607 people), Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
(123,413), Syria (93,502), Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
(14,201), the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
(11,713) and Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
(3,100). Apart from these, the UNHCR report 1,864,195 Internally displaced person, Internally Displaced Persons (IDP's). Sudan is a party to the 1951 Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees.
Ethnic groups
The Sudanese Arabs, Arab population is estimated at 70% of the national total. They are almost entirely Muslims and speak predominantly Sudanese Arabic. Other ethnicities include Beja people, Beja, Fur people, Fur, Nubians, Armenians and Copts in Sudan, Copts.Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. The vast majority of Arab tribes in Sudan migrated into Sudan in the 12th century, intermarried with the indigenous Nubian and other African populations and gradually introduced Islam.
Urban areas
Languages
Approximately 70 languages are native to Sudan.[Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2009. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, 16th ed. Dallas: SIL International. Online version]
"Languages of Sudan"
/ref> Sudan has multiple regional sign languages, which are not mutually intelligible. A 2009 proposal for a unified Sudanese Sign Language had been worked out.
Prior to 2005, Arabic was the nation's sole official language.
Religion
At the 2011 division which split off South Sudan, over 97% of the population in the remaining Sudan adheres to Islam.
Health
Sudan has a life expectancy of 65.1 years according to the latest data for the year 2019 from macrotrends.net Infant mortality in 2016 was 44.8 per 1,000.
UNICEF estimates that 87% of Sudanese females between the ages of 15 to 49 have had female genital mutilation performed on them.
Education
 Education in Sudan is free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 13 years, although more than 40% of children do not go to schools due to the economic situation. Environmental and social factors also increase the difficulty of getting to school, especially for girls. Primary education consists of eight years, followed by three years of secondary education. The former educational ladder 6 + 3 + 3 was changed in 1990. The primary language at all levels is Arabic. Schools are concentrated in urban areas; many in the west have been damaged or destroyed by years of civil war. In 2001 the World Bank estimated that primary enrollment was 46 percent of eligible pupils and 21 percent of secondary students. Enrollment varies widely, falling below 20 percent in some provinces. The literacy rate is 70.2% of total population, male: 79.6%, female: 60.8%.
Education in Sudan is free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 13 years, although more than 40% of children do not go to schools due to the economic situation. Environmental and social factors also increase the difficulty of getting to school, especially for girls. Primary education consists of eight years, followed by three years of secondary education. The former educational ladder 6 + 3 + 3 was changed in 1990. The primary language at all levels is Arabic. Schools are concentrated in urban areas; many in the west have been damaged or destroyed by years of civil war. In 2001 the World Bank estimated that primary enrollment was 46 percent of eligible pupils and 21 percent of secondary students. Enrollment varies widely, falling below 20 percent in some provinces. The literacy rate is 70.2% of total population, male: 79.6%, female: 60.8%.
Culture
Sudanese culture melds the behaviors, practices, and beliefs of about 578 ethnic groups, communicating in numerous different dialects and languages, in a region microcosmic of Africa, with geographic extremes varying from sandy desert to tropical forest. Recent evidence suggests that while most citizens of the country identify strongly with both Sudan and their religion, Arab and African supranational identities are much more polarising and contested.
Music
 Sudan has a rich and unique musical culture that has been through chronic instability and repression during the modern history of Sudan. Beginning with the imposition of strict Salafi interpretation of ''sharia'' law in 1983, many of the country's most prominent poets and artists, like Mahjoub Sharif, were imprisoned while others, like Mohammed el Amin (returned to Sudan in the mid-1990s) and Mohammed Wardi (returned to Sudan 2003), fled to Cairo. Traditional music suffered too, with traditional Zār ceremonies being interrupted and drums confiscated . At the same time European militaries contributed to the development of Sudanese music by introducing new instruments and styles; military bands, especially the Scottish bagpipes, were renowned, and set traditional music to march (music), military march music. The march ''March Shulkawi No 1'', is an example, set to the sounds of the Shilluk people, Shilluk. Northern Sudan listens to different music than the rest of Sudan. A type of music called Aldlayib uses a musical instrument called the Tambur. The Tambur has five strings, is made from wood and makes music accompanied by the voices of human applause and singing artists.
Sudan has a rich and unique musical culture that has been through chronic instability and repression during the modern history of Sudan. Beginning with the imposition of strict Salafi interpretation of ''sharia'' law in 1983, many of the country's most prominent poets and artists, like Mahjoub Sharif, were imprisoned while others, like Mohammed el Amin (returned to Sudan in the mid-1990s) and Mohammed Wardi (returned to Sudan 2003), fled to Cairo. Traditional music suffered too, with traditional Zār ceremonies being interrupted and drums confiscated . At the same time European militaries contributed to the development of Sudanese music by introducing new instruments and styles; military bands, especially the Scottish bagpipes, were renowned, and set traditional music to march (music), military march music. The march ''March Shulkawi No 1'', is an example, set to the sounds of the Shilluk people, Shilluk. Northern Sudan listens to different music than the rest of Sudan. A type of music called Aldlayib uses a musical instrument called the Tambur. The Tambur has five strings, is made from wood and makes music accompanied by the voices of human applause and singing artists.
Cinema
The cinema of Sudan began with cinematography by the History of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, British colonial presence in the early 20th century. After independence in 1956, a vigorous documentary film tradition was established, but financial pressures and serious constraints imposed by the Islamist government led to the decline of filmmaking from the 1990s onwards. Since the 2010s, several initiatives have shown an encouraging revival of filmmaking and public interest in film shows and festivals, albeit limited mainly to Khartoum.
The use of Photography of Sudan, photography in Sudan goes back to the 1880s and the Turkish Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian rule. As in other countries, the growing importance of photography for mass media like newspapers, as well as for amateur photographers led to a wider photographic documentation and Photojournalism#Golden age, use of photographs in Sudan during the 20th century and beyond. In the 21st century, photography in Sudan has undergone important changes, mainly due to digital photography and distribution through social media and the internet.
Clothing
 Most Sudanese wear either traditional or western attire. A traditional garb widely worn by Sudanese men is the jalabiya, galabiya, which is a loose-fitting, long-sleeved, collarless ankle-length garment also common to
Most Sudanese wear either traditional or western attire. A traditional garb widely worn by Sudanese men is the jalabiya, galabiya, which is a loose-fitting, long-sleeved, collarless ankle-length garment also common to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. The galabiya is often accompanied by a large turban and a scarf, and the garment may be white, colored, striped, and made of fabric varying in thickness, depending on the season of the year and personal preferences.
The most common dress for Sudanese women is the ''thobe'' or ''thawb'', pronounced ''tobe'' in Sudanese dialect. The thobe is a white or colorful long, one piece cloth that women wrap around their inner garments, usually covering their head and hair.
Due to a 1991 penal code (''Public Order Law''), women were not allowed to wear trousers in public, because it was interpreted as an "obscene outfit." The punishment for wearing trousers could be up to 40 lashes, but after being found guilty in 2009, one woman was fined the equivalent of 200 U.S. dollars instead.
Sport
Like in many countries, football is the most popular sport also in Sudan. The Sudan Football Association was founded in 1936 and thus it became one of the oldest football associations to exist in Africa. However, before the foundation of the Football Association, Sudan had started experiencing football brought to the country by the British colonizers since early 20th century via Egypt. Other Sudanese clubs founded at that time include Al-Hilal (Omdurman), Al-Hilal Omdurman, Al-Merrikh SC, Al-Merrikh, which led to popularization of football in the country. The Khartoum League became the first national league to be played in Sudan, laying ground for the future development of Sudanese football.
Since September 2019, there has been an official national league for women's football clubs that started on the basis of informal women's clubs since the beginning of the 2000s. In 2021, the Sudan women's national football team participated for the first time in the 2021 Arab Women's Cup, Arab Women's Cup, held in Cairo, Egypt.
Sudan's national beach volleyball team competed at the 2018–2020 CAVB Beach Volleyball Continental Cup in both the women's and the men's section. In June 2022, Patricia Seif El Din El Haj, the first Sudanese woman Wrestling, wrestler to participate in an African championship, was photographed by Reuters photographer Mohamed Nureldin Abdallah, as she got ready to travel to Nigeria in order to prepare for the 2024 Summer Olympics, 2024 Summer Olympic games.
See also
* Outline of Sudan
References
Bibliography
; Books
*
* Berry, LaVerle B., ed. (2015).
Sudan: A Country Study
'. Library of Congress (Washington, D.C.) .
*
*
* Winston Churchill, Churchill, Winston (1899; 2000). ''The River War, The River War: An Historical Account of the Reconquest of the Soudan''. Carroll & Graf (New York City). .
*
* Paul Clammer, Clammer, Paul (2005). ''Sudan: The Bradt Travel Guide''. Bradt Travel Guides (Chalfont St. Peter); Globe Pequot Press. (Guilford, Connecticut). .
*
* Evans-Pritchard, Blake; Polese, Violetta (2008). ''Sudan: The City Trail Guide''. City Trail Publishing. .
*
* Mandour Elmahdi, El Mahdi, Mandour. (1965). A Short History of the Sudan. Oxford University Press. .
* Fadlalla, Mohamed H. (2005). ''The Problem of Dar Fur'', iUniverse (New York City). .
* Fadlalla, Mohamed H. (2004). ''Short History of Sudan''. iUniverse (New York City). .
* Fadlalla, Mohamed H. (2007). ''UN Intervention in Dar Fur'', iUniverse (New York City). .
*
*
*
* Jok, Jok Madut (2007). ''Sudan: Race, Religion and Violence''. Oneworld Publications (Oxford). .
* Köndgen, Olaf (2017). ''The Codification of Islamic Criminal Law in the Sudan. Penal Codes and Supreme Court Case Law under Numayri and al-Bashir''. Brill (Leiden, Boston). .
*
*
*
*
*
* Godfrey Mwakikagile, Mwakikagile, Godfrey (2001). ''Slavery in Mauritania and Sudan: The State Against Blacks'', in ''The Modern African State: Quest for Transformation''. Nova Science Publishers (Huntington, New York). .
*
* Peterson, Scott (2001). ''Me Against My Brother: At War in Somalia, Sudan and Rwanda—A Journalist Reports from the Battlefields of Africa''. Routledge (London; New York City). .
* Gérard Prunier, Prunier, Gérard (2005). ''Darfur: The Ambiguous Genocide''. Cornell University Press (Ithaca, New York). .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Zilfū, ʻIṣmat Ḥasan (translation: Clark, Peter) (1980). ''Karari: The Sudanese Account of the Battle of Omdurman''. Frederick Warne & Co (London). .
; Articles
* "Sudan." Background Notes, U.S. Department of State, 2009
online
* "Quo Vadis bilad as-Sudan? The Contemporary Framework for a National Interim Constitution". ''Law in Africa'' (Cologne; 2005). Vol. 8, pp. 63–82. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
; Weblinks
*
External links
Government of Sudan
website
Archaeological sites in Sudan
*
*
*
*
Sudan
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
*
Sudan profile
from BBC News
CIMIC activities in the African Union Mission in Sudan
The conflict in South Sudan
– ''The Economist''
UNAMID UNITED NATIONS – AFRICAN UNION HYBRID OPERATION IN DARFUR
{{Authority control
Sudan,
1956 establishments in Africa
Arabic-speaking countries and territories
English-speaking countries and territories
Federal republics
Least developed countries
Member states of the African Union
Member states of the Arab League
Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Member states of the United Nations
Military dictatorships
Saharan countries
States and territories established in 1956
Countries in Africa
East African countries

 By the eighth millennium BC, people of a
By the eighth millennium BC, people of a  The
The  On the turn of the fifth century the
On the turn of the fifth century the  From the mid eighth to mid eleventh century the political power and cultural development of Christian Nubia peaked. In 747 Makuria invaded Egypt, which at this time belonged to the declining Umayyad dynasty, Umayyads, and it did so again in the early 960s, when it pushed as far north as Akhmim. Makuria maintained close dynastic ties with Alodia, perhaps resulting in the temporary unification of the two kingdoms into one state. The culture of the medieval Nubians has been described as "''Afro-Byzantine''", but was also increasingly influenced by Arab culture. The state organisation was extremely centralised, being based on the Byzantine bureaucracy of the sixth and seventh centuries. Arts flourished in the form of pottery paintings and especially wall paintings. The Nubians developed an alphabet for their language, Old Nubian, Old Nobiin, basing it on the Coptic alphabet, while also utilizing Medieval Greek, Greek, Coptic language, Coptic and Arabic. Women enjoyed high social status: they had access to education, could own, buy and sell land and often used their wealth to endow churches and church paintings. Even the royal succession was matrilineal, with the son of the king's sister being the rightful heir.
From the late 11th/12th century, Makuria's capital Dongola was in decline, and Alodia's capital declined in the 12th century as well. In the 14th and 15th centuries Bedouin tribes overran most of Sudan, migrating to the Butana, the Gezira (state), Gezira, Kordofan and Darfur. In 1365 a civil war forced the Makurian court to flee to Gebel Adda in Lower Nubia, while Dongola was destroyed and left to the Arabs. Afterwards Makuria continued to exist only as a petty kingdom. After the prosperous reign of king Joel of Dotawo, Joel ( 1463–1484) Makuria collapsed. Coastal areas from southern Sudan up to the port city of Suakin was succeeded by the Adal Sultanate in the fifteenth century. To the south, the kingdom of Alodia fell to either the Arabs, commanded by tribal leader Abdallah Jamma, or the Funj, an African people originating from the south. Datings range from the Hijri year, 9th century after the Hijra ( 1396–1494), the late 15th century, 1504 to 1509. An alodian rump state might have survived in the form of the kingdom of Fazughli, lasting until 1685.
From the mid eighth to mid eleventh century the political power and cultural development of Christian Nubia peaked. In 747 Makuria invaded Egypt, which at this time belonged to the declining Umayyad dynasty, Umayyads, and it did so again in the early 960s, when it pushed as far north as Akhmim. Makuria maintained close dynastic ties with Alodia, perhaps resulting in the temporary unification of the two kingdoms into one state. The culture of the medieval Nubians has been described as "''Afro-Byzantine''", but was also increasingly influenced by Arab culture. The state organisation was extremely centralised, being based on the Byzantine bureaucracy of the sixth and seventh centuries. Arts flourished in the form of pottery paintings and especially wall paintings. The Nubians developed an alphabet for their language, Old Nubian, Old Nobiin, basing it on the Coptic alphabet, while also utilizing Medieval Greek, Greek, Coptic language, Coptic and Arabic. Women enjoyed high social status: they had access to education, could own, buy and sell land and often used their wealth to endow churches and church paintings. Even the royal succession was matrilineal, with the son of the king's sister being the rightful heir.
From the late 11th/12th century, Makuria's capital Dongola was in decline, and Alodia's capital declined in the 12th century as well. In the 14th and 15th centuries Bedouin tribes overran most of Sudan, migrating to the Butana, the Gezira (state), Gezira, Kordofan and Darfur. In 1365 a civil war forced the Makurian court to flee to Gebel Adda in Lower Nubia, while Dongola was destroyed and left to the Arabs. Afterwards Makuria continued to exist only as a petty kingdom. After the prosperous reign of king Joel of Dotawo, Joel ( 1463–1484) Makuria collapsed. Coastal areas from southern Sudan up to the port city of Suakin was succeeded by the Adal Sultanate in the fifteenth century. To the south, the kingdom of Alodia fell to either the Arabs, commanded by tribal leader Abdallah Jamma, or the Funj, an African people originating from the south. Datings range from the Hijri year, 9th century after the Hijra ( 1396–1494), the late 15th century, 1504 to 1509. An alodian rump state might have survived in the form of the kingdom of Fazughli, lasting until 1685.
 In 1504 the Funj are recorded to have founded the Kingdom of Sennar, in which Abdallah Jamma's realm was incorporated. By 1523, when Jewish traveler David Reubeni visited Sudan, the Funj state already extended as far north as Dongola. Meanwhile, Islam began to be preached on the Nile by Sufism, Sufi holymen who settled there in the 15th and 16th centuries and by David Reubeni's visit king Amara Dunqas, previously a Pagan or nominal Christian, was recorded to be Muslim. However, the Funj would retain un-Islamic customs like the divine kingship or the consumption of alcohol until the 18th century. Sudanese Folk religion, folk Islam preserved many rituals stemming from Christian traditions until the recent past.
Soon the Funj came in conflict with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, who had occupied Suakin around 1526 and eventually pushed south along the Nile, reaching the third Nile cataract area in 1583/1584. A subsequent Ottoman attempt to capture Dongola was battle of Hannik, repelled by the Funj in 1585. Afterwards, Hannik, located just south of the third cataract, would mark the border between the two states. The aftermath of the Ottoman invasion saw the attempted usurpation of Ajib the Great, Ajib, a minor king of northern Nubia. While the Funj eventually killed him in 1611/1612 his successors, the Abdallabi tribe, Abdallab, were granted to govern everything north of the confluence of Blue and White Niles with considerable autonomy.
During the 17th century the Funj state reached its widest extent, but in the following century it began to decline. A coup in 1718 brought a dynastic change, while another one in 1761–1762 resulted in the Hamaj Regency, Hamaj regency, where the Hamaj (a people from the Ethiopian borderlands) effectively ruled while the Funj sultans were their mere puppets. Shortly afterwards the sultanate began to fragment; by the early 19th century it was essentially restricted to the Gezira.
In 1504 the Funj are recorded to have founded the Kingdom of Sennar, in which Abdallah Jamma's realm was incorporated. By 1523, when Jewish traveler David Reubeni visited Sudan, the Funj state already extended as far north as Dongola. Meanwhile, Islam began to be preached on the Nile by Sufism, Sufi holymen who settled there in the 15th and 16th centuries and by David Reubeni's visit king Amara Dunqas, previously a Pagan or nominal Christian, was recorded to be Muslim. However, the Funj would retain un-Islamic customs like the divine kingship or the consumption of alcohol until the 18th century. Sudanese Folk religion, folk Islam preserved many rituals stemming from Christian traditions until the recent past.
Soon the Funj came in conflict with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, who had occupied Suakin around 1526 and eventually pushed south along the Nile, reaching the third Nile cataract area in 1583/1584. A subsequent Ottoman attempt to capture Dongola was battle of Hannik, repelled by the Funj in 1585. Afterwards, Hannik, located just south of the third cataract, would mark the border between the two states. The aftermath of the Ottoman invasion saw the attempted usurpation of Ajib the Great, Ajib, a minor king of northern Nubia. While the Funj eventually killed him in 1611/1612 his successors, the Abdallabi tribe, Abdallab, were granted to govern everything north of the confluence of Blue and White Niles with considerable autonomy.
During the 17th century the Funj state reached its widest extent, but in the following century it began to decline. A coup in 1718 brought a dynastic change, while another one in 1761–1762 resulted in the Hamaj Regency, Hamaj regency, where the Hamaj (a people from the Ethiopian borderlands) effectively ruled while the Funj sultans were their mere puppets. Shortly afterwards the sultanate began to fragment; by the early 19th century it was essentially restricted to the Gezira.
 The coup of 1718 kicked off a policy of pursuing a more orthodox Islam, which in turn promoted the Arabisation of the state. In order to legitimise their rule over their Arab subjects the Funj began to propagate an Banu Umayya, Umayyad descend. North of the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, as far downstream as Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah, the Nubians adopted the tribal identity of the Arab Ja'alin tribe, Jaalin. Until the 19th century Arabic had succeeded in becoming the dominant language of central riverine Sudan and most of Kordofan.
West of the Nile, in Darfur, the Islamic period saw at first the rise of the Tunjur kingdom, which replaced the old Daju kingdom in the 15th century and extended as far west as Wadai Empire, Wadai. The Tunjur people were probably Arabised Berbers and, their ruling elite at least, Muslims. In the 17th century the Tunjur were driven from power by the Fur people, Fur Sultanate of Darfur, Keira sultanate. The Keira state, nominally Muslim since the reign of Sulayman Solong (r. 1660–1680), was initially a small kingdom in northern Jebel Marra, but expanded west- and northwards in the early 18th century and eastwards under the rule of Muhammad Tayrab of Darfur, Muhammad Tayrab (r. 1751–1786), peaking in the conquest of Kordofan in 1785. The apogee of this empire, now roughly the size of present-day Nigeria, would last until 1821.
The coup of 1718 kicked off a policy of pursuing a more orthodox Islam, which in turn promoted the Arabisation of the state. In order to legitimise their rule over their Arab subjects the Funj began to propagate an Banu Umayya, Umayyad descend. North of the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, as far downstream as Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah, the Nubians adopted the tribal identity of the Arab Ja'alin tribe, Jaalin. Until the 19th century Arabic had succeeded in becoming the dominant language of central riverine Sudan and most of Kordofan.
West of the Nile, in Darfur, the Islamic period saw at first the rise of the Tunjur kingdom, which replaced the old Daju kingdom in the 15th century and extended as far west as Wadai Empire, Wadai. The Tunjur people were probably Arabised Berbers and, their ruling elite at least, Muslims. In the 17th century the Tunjur were driven from power by the Fur people, Fur Sultanate of Darfur, Keira sultanate. The Keira state, nominally Muslim since the reign of Sulayman Solong (r. 1660–1680), was initially a small kingdom in northern Jebel Marra, but expanded west- and northwards in the early 18th century and eastwards under the rule of Muhammad Tayrab of Darfur, Muhammad Tayrab (r. 1751–1786), peaking in the conquest of Kordofan in 1785. The apogee of this empire, now roughly the size of present-day Nigeria, would last until 1821.

 In 1821, the Ottoman ruler of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, had invaded and conquered northern Sudan. Although technically the Vali (governor), Vali of Egypt under the Ottoman Empire, Muhammad Ali styled himself as Khedive of a virtually independent Egypt. Seeking to add Sudan to his domains, he sent his third son Ismail (not to be confused with Isma'il Pasha, Ismaʻil Pasha mentioned later) to conquer the country, and subsequently incorporate it into Egypt. With the exception of the Shaiqiya and the Darfur sultanate in Kordofan, he was met without resistance. The Egyptian policy of conquest was expanded and intensified by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha's son, Ismaʻil, under whose reign most of the remainder of modern-day Sudan was conquered.
The Egyptian authorities made significant improvements to the Sudanese infrastructure (mainly in the north), especially with regard to irrigation and cotton production. In 1879, the International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919), Great Powers forced the removal of Ismail and established his son Tewfik Pasha in his place. Tewfik's corruption and mismanagement resulted in the 'Urabi revolt, which threatened the Khedive's survival. Tewfik appealed for help to the British, who subsequently occupied Egypt in 1882. Sudan was left in the hands of the Khedivial government, and the mismanagement and corruption of its officials.
During the Khedivial period, dissent had spread due to harsh taxes imposed on most activities. Taxation on irrigation wells and farming lands were so high most farmers abandoned their farms and livestock. During the 1870s, European initiatives against the slave trade had an adverse impact on the economy of northern Sudan, precipitating the rise of Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdist forces. Muhammad Ahmad, Muhammad Ahmad ibn Abd Allah, the ''
In 1821, the Ottoman ruler of Egypt, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, had invaded and conquered northern Sudan. Although technically the Vali (governor), Vali of Egypt under the Ottoman Empire, Muhammad Ali styled himself as Khedive of a virtually independent Egypt. Seeking to add Sudan to his domains, he sent his third son Ismail (not to be confused with Isma'il Pasha, Ismaʻil Pasha mentioned later) to conquer the country, and subsequently incorporate it into Egypt. With the exception of the Shaiqiya and the Darfur sultanate in Kordofan, he was met without resistance. The Egyptian policy of conquest was expanded and intensified by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha's son, Ismaʻil, under whose reign most of the remainder of modern-day Sudan was conquered.
The Egyptian authorities made significant improvements to the Sudanese infrastructure (mainly in the north), especially with regard to irrigation and cotton production. In 1879, the International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919), Great Powers forced the removal of Ismail and established his son Tewfik Pasha in his place. Tewfik's corruption and mismanagement resulted in the 'Urabi revolt, which threatened the Khedive's survival. Tewfik appealed for help to the British, who subsequently occupied Egypt in 1882. Sudan was left in the hands of the Khedivial government, and the mismanagement and corruption of its officials.
During the Khedivial period, dissent had spread due to harsh taxes imposed on most activities. Taxation on irrigation wells and farming lands were so high most farmers abandoned their farms and livestock. During the 1870s, European initiatives against the slave trade had an adverse impact on the economy of northern Sudan, precipitating the rise of Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdist forces. Muhammad Ahmad, Muhammad Ahmad ibn Abd Allah, the '' In 1899, Britain and Egypt reached an agreement under which Sudan was run by a governor-general appointed by Egypt with British consent. In reality, Sudan was effectively administered as a Crown colony. The British were keen to reverse the process, started under Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali Pasha, of uniting the Nile Valley under Egyptian leadership and sought to frustrate all efforts aimed at further uniting the two countries.
Under the Delimitation, Sudan's border with Abyssinia was contested by raiding tribesmen trading slaves, breaching boundaries of the law. In 1905 Local chieftain Sultan Yambio reluctant to the end gave up the struggle with British forces that had occupied the Kordofan region, finally ending the lawlessness. The continued British administration of Sudan fuelled an increasingly strident nationalist backlash, with Egyptian nationalist leaders determined to force Britain to recognise a single independent union of Egypt and Sudan. With a formal end to Ottoman rule in 1914, Sir Reginald Wingate was sent that December to occupy Sudan as the new Military Governor. Hussein Kamel of Egypt, Hussein Kamel was declared Sultan of Egypt and Sudan, as was his brother and successor, Fuad I of Egypt, Fuad I. They continued upon their insistence of a single Egyptian-Sudanese state even when the Sultanate of Egypt was retitled as the Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Egypt and Sudan, but it was Saad Zaghloul who continued to be frustrated in the ambitions until his death in 1927.
In 1899, Britain and Egypt reached an agreement under which Sudan was run by a governor-general appointed by Egypt with British consent. In reality, Sudan was effectively administered as a Crown colony. The British were keen to reverse the process, started under Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali Pasha, of uniting the Nile Valley under Egyptian leadership and sought to frustrate all efforts aimed at further uniting the two countries.
Under the Delimitation, Sudan's border with Abyssinia was contested by raiding tribesmen trading slaves, breaching boundaries of the law. In 1905 Local chieftain Sultan Yambio reluctant to the end gave up the struggle with British forces that had occupied the Kordofan region, finally ending the lawlessness. The continued British administration of Sudan fuelled an increasingly strident nationalist backlash, with Egyptian nationalist leaders determined to force Britain to recognise a single independent union of Egypt and Sudan. With a formal end to Ottoman rule in 1914, Sir Reginald Wingate was sent that December to occupy Sudan as the new Military Governor. Hussein Kamel of Egypt, Hussein Kamel was declared Sultan of Egypt and Sudan, as was his brother and successor, Fuad I of Egypt, Fuad I. They continued upon their insistence of a single Egyptian-Sudanese state even when the Sultanate of Egypt was retitled as the Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Egypt and Sudan, but it was Saad Zaghloul who continued to be frustrated in the ambitions until his death in 1927.
 From 1924 until independence in 1956, the British had a policy of running Sudan as two essentially separate territories; the north and south. The Lee Stack, assassination of a Governor-General of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in Cairo was the causative factor; it brought demands of the newly elected Wafd Party, Wafd government from colonial forces. A permanent establishment of two battalions in Khartoum was renamed the Sudan Defence Force acting as under the government, replacing the former garrison of Egyptian army soldiers, saw action afterward during the Abyssinia Crisis, Walwal Incident. The Wafdist parliamentary majority had rejected Abdel Khalek Sarwat Pasha, Sarwat Pasha's accommodation plan with Austen Chamberlain in London; yet Cairo still needed the money. The Sudanese Government's revenue had reached a peak in 1928 at £6.6 million, thereafter the Wafdist disruptions, and Italian borders incursions from Somaliland, London decided to reduce expenditure during the Great Depression. Cotton and gum exports were dwarfed by the necessity to import almost everything from Britain leading to a balance of payments deficit at Khartoum.
In July 1936 the Liberal Constitutional leader, Muhammed Mahmoud was persuaded to bring Wafd delegates to London to sign the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty, "the beginning of a new stage in Anglo-Egyptian relations", wrote Anthony Eden. The British Army was allowed to return to Sudan to protect the Canal Zone. They were able to find training facilities, and the RAF was free to fly over Egyptian territory. It did not, however, resolve the problem of Sudan: the Sudanese Intelligentsia agitated for a return to metropolitan rule, conspiring with Germany's agents.
Mussolini made it clear that he could not invade Abyssinia without first conquering Egypt and Sudan; they intended unification of Libya with Italian East Africa. The British Imperial General Staff prepared for military defence of the region, which was thin on the ground. The British ambassador blocked Italian attempts to secure a Non-Aggression Treaty with Egypt-Sudan. But Mahmoud was a supporter of the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem; the region was caught between the Empire's efforts to save the Jews, and moderate Arab calls to halt migration.
The Sudanese Government was directly involved militarily in the East African Campaign (World War II), East African Campaign. Formed in 1925, the Sudan Defence Force played an active part in responding to incursions early in World War Two. Italian troops occupied Kassala and other border areas from Italian East Africa, Italian Somaliland during 1940. In 1942, the SDF also played a part in the invasion of the Italian colony by British and Commonwealth forces. The last British governor-general was Robert George Howe.
The Egyptian revolution of 1952 finally heralded the beginning of the march towards Sudanese independence. Having abolished the monarchy in 1953, Egypt's new leaders, Mohammed Naguib, whose mother was Sudanese, and later Gamal Abdel Nasser, believed the only way to end British domination in Sudan was for Egypt to officially abandon its claims of sovereignty. In addition, Nasser knew it would be difficult for Egypt to govern an impoverished Sudan after its independence. The British on the other hand continued their political and financial support for the Mahdist successor, Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, whom it was believed would resist Egyptian pressure for Sudanese independence. Rahman was capable of this, but his regime was plagued by political ineptitude, which garnered a colossal loss of support in northern and central Sudan. Both Egypt and Britain sensed a great instability fomenting, and thus opted to allow both Sudanese regions, north and south to have a free vote on whether they wished independence or a British withdrawal.
From 1924 until independence in 1956, the British had a policy of running Sudan as two essentially separate territories; the north and south. The Lee Stack, assassination of a Governor-General of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in Cairo was the causative factor; it brought demands of the newly elected Wafd Party, Wafd government from colonial forces. A permanent establishment of two battalions in Khartoum was renamed the Sudan Defence Force acting as under the government, replacing the former garrison of Egyptian army soldiers, saw action afterward during the Abyssinia Crisis, Walwal Incident. The Wafdist parliamentary majority had rejected Abdel Khalek Sarwat Pasha, Sarwat Pasha's accommodation plan with Austen Chamberlain in London; yet Cairo still needed the money. The Sudanese Government's revenue had reached a peak in 1928 at £6.6 million, thereafter the Wafdist disruptions, and Italian borders incursions from Somaliland, London decided to reduce expenditure during the Great Depression. Cotton and gum exports were dwarfed by the necessity to import almost everything from Britain leading to a balance of payments deficit at Khartoum.
In July 1936 the Liberal Constitutional leader, Muhammed Mahmoud was persuaded to bring Wafd delegates to London to sign the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty, "the beginning of a new stage in Anglo-Egyptian relations", wrote Anthony Eden. The British Army was allowed to return to Sudan to protect the Canal Zone. They were able to find training facilities, and the RAF was free to fly over Egyptian territory. It did not, however, resolve the problem of Sudan: the Sudanese Intelligentsia agitated for a return to metropolitan rule, conspiring with Germany's agents.
Mussolini made it clear that he could not invade Abyssinia without first conquering Egypt and Sudan; they intended unification of Libya with Italian East Africa. The British Imperial General Staff prepared for military defence of the region, which was thin on the ground. The British ambassador blocked Italian attempts to secure a Non-Aggression Treaty with Egypt-Sudan. But Mahmoud was a supporter of the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem; the region was caught between the Empire's efforts to save the Jews, and moderate Arab calls to halt migration.
The Sudanese Government was directly involved militarily in the East African Campaign (World War II), East African Campaign. Formed in 1925, the Sudan Defence Force played an active part in responding to incursions early in World War Two. Italian troops occupied Kassala and other border areas from Italian East Africa, Italian Somaliland during 1940. In 1942, the SDF also played a part in the invasion of the Italian colony by British and Commonwealth forces. The last British governor-general was Robert George Howe.
The Egyptian revolution of 1952 finally heralded the beginning of the march towards Sudanese independence. Having abolished the monarchy in 1953, Egypt's new leaders, Mohammed Naguib, whose mother was Sudanese, and later Gamal Abdel Nasser, believed the only way to end British domination in Sudan was for Egypt to officially abandon its claims of sovereignty. In addition, Nasser knew it would be difficult for Egypt to govern an impoverished Sudan after its independence. The British on the other hand continued their political and financial support for the Mahdist successor, Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, whom it was believed would resist Egyptian pressure for Sudanese independence. Rahman was capable of this, but his regime was plagued by political ineptitude, which garnered a colossal loss of support in northern and central Sudan. Both Egypt and Britain sensed a great instability fomenting, and thus opted to allow both Sudanese regions, north and south to have a free vote on whether they wished independence or a British withdrawal.
 A polling process was carried out resulting in the composition of a democratic parliament and Ismail al-Azhari was elected first Prime Minister and led the first modern Sudanese government. On 1 January 1956, in a special ceremony held at the People's Palace, the Egyptian and British flags were lowered and the new Sudanese flag, composed of green, blue and yellow stripes, was raised in their place by the prime minister Ismail al-Azhari.
Dissatisfaction culminated in a second 1969 Sudanese coup d'état, coup d'état on 25 May 1969. The coup leader, Col. Gaafar Nimeiry, became prime minister, and the new regime abolished parliament and outlawed all political parties. Disputes between Marxist and non-Marxist elements within the ruling military coalition resulted in 1971 Sudanese coup d'état, a briefly successful coup in July 1971, led by the Sudanese Communist Party. Several days later, anti-communist military elements restored Nimeiry to power.
In 1972, the Addis Ababa Agreement (1972), Addis Ababa Agreement led to a cessation of the north–south civil war and a degree of self-rule. This led to ten years hiatus in the civil war but an end to American investment in the Jonglei Canal project. This had been considered absolutely essential to irrigate the Upper Nile region and to prevent an environmental catastrophe and wide-scale famine among the local tribes, most especially the Dinka. In the civil war that followed their homeland was raided, looted, pillaged, and burned. Many of the tribe were murdered in a bloody civil war that raged for over 20 years.
A polling process was carried out resulting in the composition of a democratic parliament and Ismail al-Azhari was elected first Prime Minister and led the first modern Sudanese government. On 1 January 1956, in a special ceremony held at the People's Palace, the Egyptian and British flags were lowered and the new Sudanese flag, composed of green, blue and yellow stripes, was raised in their place by the prime minister Ismail al-Azhari.
Dissatisfaction culminated in a second 1969 Sudanese coup d'état, coup d'état on 25 May 1969. The coup leader, Col. Gaafar Nimeiry, became prime minister, and the new regime abolished parliament and outlawed all political parties. Disputes between Marxist and non-Marxist elements within the ruling military coalition resulted in 1971 Sudanese coup d'état, a briefly successful coup in July 1971, led by the Sudanese Communist Party. Several days later, anti-communist military elements restored Nimeiry to power.
In 1972, the Addis Ababa Agreement (1972), Addis Ababa Agreement led to a cessation of the north–south civil war and a degree of self-rule. This led to ten years hiatus in the civil war but an end to American investment in the Jonglei Canal project. This had been considered absolutely essential to irrigate the Upper Nile region and to prevent an environmental catastrophe and wide-scale famine among the local tribes, most especially the Dinka. In the civil war that followed their homeland was raided, looted, pillaged, and burned. Many of the tribe were murdered in a bloody civil war that raged for over 20 years.
 Until the early 1970s, Sudan's agricultural output was mostly dedicated to internal consumption. In 1972, the Sudanese government became more pro-Western and made plans to export food and cash crops. However, commodity prices declined throughout the 1970s causing economic problems for Sudan. At the same time, debt servicing costs, from the money spent mechanizing agriculture, rose. In 1978, the International Monetary Fund, IMF negotiated a Structural Adjustment Program with the government. This further promoted the mechanised export agriculture sector. This caused great hardship for the pastoralists of Sudan (see Nuba peoples#Effect of private agriculture schemes, Nuba peoples). In 1976, the Ansars had mounted a bloody but unsuccessful coup attempt. But in July 1977, President Nimeiry met with Ansar leader Sadiq al-Mahdi, opening the way for a possible reconciliation. Hundreds of political prisoners were released, and in August a general amnesty was announced for all oppositionists.
Until the early 1970s, Sudan's agricultural output was mostly dedicated to internal consumption. In 1972, the Sudanese government became more pro-Western and made plans to export food and cash crops. However, commodity prices declined throughout the 1970s causing economic problems for Sudan. At the same time, debt servicing costs, from the money spent mechanizing agriculture, rose. In 1978, the International Monetary Fund, IMF negotiated a Structural Adjustment Program with the government. This further promoted the mechanised export agriculture sector. This caused great hardship for the pastoralists of Sudan (see Nuba peoples#Effect of private agriculture schemes, Nuba peoples). In 1976, the Ansars had mounted a bloody but unsuccessful coup attempt. But in July 1977, President Nimeiry met with Ansar leader Sadiq al-Mahdi, opening the way for a possible reconciliation. Hundreds of political prisoners were released, and in August a general amnesty was announced for all oppositionists.
 On 30 June 1989, Colonel Omar al-Bashir led a bloodless 1989 Sudanese coup d'état, military coup. The new military government suspended political parties and introduced an Islamic legal code on the national level. Later, al-Bashir carried out purges and executions in the upper ranks of the army, the banning of associations, political parties, and independent newspapers, and the imprisonment of leading political figures and journalists. On 16 October 1993, al-Bashir appointed himself "President of Sudan, President" and disbanded the Revolutionary Command Council. The executive and legislative powers of the council were taken by al-Bashir.
In the Sudanese general election, 1996, 1996 general election, he was the only candidate by law to run for election.''The New York Times''. 16 March 1996. p. 4. Sudan became a one-party state under the National Congress (Sudan), National Congress Party (NCP). During the 1990s, Hassan al-Turabi, then Speaker of the National Assembly, reached out to Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist groups and invited Osama bin Laden to the country. The United States subsequently listed Sudan as a State Sponsors of Terrorism, state sponsor of terrorism. Following Al Qaeda's 1998 United States embassy bombings, bombing of the U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania, the U.S. launched Operation Infinite Reach and targeted the Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory, which the U.S. government falsely believed was producing chemical weapons for the terrorist group. Al-Turabi's influence began to wane, and others in favour of more pragmatic leadership tried to change Sudan's international isolation. The country worked to appease its critics by expelling members of the Egyptian Islamic Jihad and encouraging bin Laden to leave.
On 30 June 1989, Colonel Omar al-Bashir led a bloodless 1989 Sudanese coup d'état, military coup. The new military government suspended political parties and introduced an Islamic legal code on the national level. Later, al-Bashir carried out purges and executions in the upper ranks of the army, the banning of associations, political parties, and independent newspapers, and the imprisonment of leading political figures and journalists. On 16 October 1993, al-Bashir appointed himself "President of Sudan, President" and disbanded the Revolutionary Command Council. The executive and legislative powers of the council were taken by al-Bashir.
In the Sudanese general election, 1996, 1996 general election, he was the only candidate by law to run for election.''The New York Times''. 16 March 1996. p. 4. Sudan became a one-party state under the National Congress (Sudan), National Congress Party (NCP). During the 1990s, Hassan al-Turabi, then Speaker of the National Assembly, reached out to Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist groups and invited Osama bin Laden to the country. The United States subsequently listed Sudan as a State Sponsors of Terrorism, state sponsor of terrorism. Following Al Qaeda's 1998 United States embassy bombings, bombing of the U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania, the U.S. launched Operation Infinite Reach and targeted the Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory, which the U.S. government falsely believed was producing chemical weapons for the terrorist group. Al-Turabi's influence began to wane, and others in favour of more pragmatic leadership tried to change Sudan's international isolation. The country worked to appease its critics by expelling members of the Egyptian Islamic Jihad and encouraging bin Laden to leave.
 The
The  On 19 December 2018, Sudanese protests (2018–19), massive protests began after a government decision to triple the price of goods at a time when the country was suffering an acute shortage of foreign currency and inflation of 70 percent. In addition, President al-Bashir, who had been in power for more than 30 years, refused to step down, resulting in the convergence of opposition groups to form a united coalition. The government retaliated by arresting more than 800 opposition figures and protesters, leading to the death of approximately 40 people according to the Human Rights Watch, although the number was much higher than that according to local and civilian reports. The protests continued after the overthrow of his government on 11 April 2019 after a massive sit-in in front of the Sudanese Armed Forces main headquarters, after which the chiefs of staff decided to intervene and they ordered the arrest of President al-Bashir and declared a three-month state of emergency. Over 100 people died on 3 June after security forces dispersed the sit-in using tear gas and live ammunition in what is known as the Khartoum massacre, resulting in Sudan's suspension from the African Union. Sudan's youth had been reported to be driving the protests. The protests came to an end when the Forces for Freedom and Change (an alliance of groups organizing the protests) and Transitional Military Council (2019), Transitional Military Council (the ruling military government) signed the July 2019 Political Agreement and the August 2019 Draft Constitutional Declaration.
On 19 December 2018, Sudanese protests (2018–19), massive protests began after a government decision to triple the price of goods at a time when the country was suffering an acute shortage of foreign currency and inflation of 70 percent. In addition, President al-Bashir, who had been in power for more than 30 years, refused to step down, resulting in the convergence of opposition groups to form a united coalition. The government retaliated by arresting more than 800 opposition figures and protesters, leading to the death of approximately 40 people according to the Human Rights Watch, although the number was much higher than that according to local and civilian reports. The protests continued after the overthrow of his government on 11 April 2019 after a massive sit-in in front of the Sudanese Armed Forces main headquarters, after which the chiefs of staff decided to intervene and they ordered the arrest of President al-Bashir and declared a three-month state of emergency. Over 100 people died on 3 June after security forces dispersed the sit-in using tear gas and live ammunition in what is known as the Khartoum massacre, resulting in Sudan's suspension from the African Union. Sudan's youth had been reported to be driving the protests. The protests came to an end when the Forces for Freedom and Change (an alliance of groups organizing the protests) and Transitional Military Council (2019), Transitional Military Council (the ruling military government) signed the July 2019 Political Agreement and the August 2019 Draft Constitutional Declaration.
 The transitional institutions and procedures included the creation of a joint military-civilian Sovereignty Council of Sudan as head of state, a new Chief Justice of Sudan as head of the judiciary branch of power, Nemat Abdullah Khair, and a new prime minister. The former Prime Minister, Abdalla Hamdok, a 61-year-old economist who worked previously for the UN Economic Commission for Africa, was sworn in on 21 August. He initiated talks with the IMF and World Bank aimed at stabilising the economy, which was in dire straits because of shortages of food, fuel and hard currency. Hamdok estimated that US$10bn over two years would suffice to halt the panic, and said that over 70% of the 2018 budget had been spent on civil war-related measures. The governments of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates had invested significant sums supporting the military council since Bashir's ouster. On 3 September, Hamdok appointed 14 civilian ministers, including the first female foreign minister and the first Coptic Christian, also a woman. As of August 2021, the country was jointly led by Chairman of the Transitional Sovereign Council, Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, and Prime Minister Abdallah Hamdok.
The transitional institutions and procedures included the creation of a joint military-civilian Sovereignty Council of Sudan as head of state, a new Chief Justice of Sudan as head of the judiciary branch of power, Nemat Abdullah Khair, and a new prime minister. The former Prime Minister, Abdalla Hamdok, a 61-year-old economist who worked previously for the UN Economic Commission for Africa, was sworn in on 21 August. He initiated talks with the IMF and World Bank aimed at stabilising the economy, which was in dire straits because of shortages of food, fuel and hard currency. Hamdok estimated that US$10bn over two years would suffice to halt the panic, and said that over 70% of the 2018 budget had been spent on civil war-related measures. The governments of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates had invested significant sums supporting the military council since Bashir's ouster. On 3 September, Hamdok appointed 14 civilian ministers, including the first female foreign minister and the first Coptic Christian, also a woman. As of August 2021, the country was jointly led by Chairman of the Transitional Sovereign Council, Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, and Prime Minister Abdallah Hamdok.

 Sudan has had a troubled relationship with many of its neighbours and much of the international community, owing to what is viewed as its radical Islamic stance. For much of the 1990s, Uganda, Kenya and
Sudan has had a troubled relationship with many of its neighbours and much of the international community, owing to what is viewed as its radical Islamic stance. For much of the 1990s, Uganda, Kenya and  A letter dated 14 August 2006, from the executive director of Human Rights Watch found that the Sudanese government is both incapable of protecting its own citizens in Darfur and unwilling to do so, and that its militias are guilty of crimes against humanity. The letter added that these human-rights abuses have existed since 2004. Some reports attribute part of the violations to the rebels as well as the government and the Janjaweed. The U.S. State Department's human-rights report issued in March 2007 claims that "''[a]''ll parties to the conflagration committed serious abuses, including widespread killing of civilians, rape as a tool of war, systematic torture, robbery and recruitment of child soldiers."
Over 2.8 million civilians have been displaced and the death toll is estimated at 300,000 killed. Both government forces and militias allied with the government are known to attack not only civilians in Darfur, but also humanitarian workers. Sympathisers of rebel groups are arbitrarily detained, as are foreign journalists, human rights defender, human-rights defenders, student activists and displaced people in and around Khartoum, some of whom face torture. The rebel groups have also been accused in a report issued by the U.S. government of attacking humanitarian workers and of killing innocent civilians. According to UNICEF, in 2008, there were as many as 6,000 child soldiers in Darfur.
A letter dated 14 August 2006, from the executive director of Human Rights Watch found that the Sudanese government is both incapable of protecting its own citizens in Darfur and unwilling to do so, and that its militias are guilty of crimes against humanity. The letter added that these human-rights abuses have existed since 2004. Some reports attribute part of the violations to the rebels as well as the government and the Janjaweed. The U.S. State Department's human-rights report issued in March 2007 claims that "''[a]''ll parties to the conflagration committed serious abuses, including widespread killing of civilians, rape as a tool of war, systematic torture, robbery and recruitment of child soldiers."
Over 2.8 million civilians have been displaced and the death toll is estimated at 300,000 killed. Both government forces and militias allied with the government are known to attack not only civilians in Darfur, but also humanitarian workers. Sympathisers of rebel groups are arbitrarily detained, as are foreign journalists, human rights defender, human-rights defenders, student activists and displaced people in and around Khartoum, some of whom face torture. The rebel groups have also been accused in a report issued by the U.S. government of attacking humanitarian workers and of killing innocent civilians. According to UNICEF, in 2008, there were as many as 6,000 child soldiers in Darfur.

 In Sudan's 2008 census, the population of northern, western and eastern Sudan was recorded to be over 30 million. This puts present estimates of the population of Sudan after the secession of
In Sudan's 2008 census, the population of northern, western and eastern Sudan was recorded to be over 30 million. This puts present estimates of the population of Sudan after the secession of  Education in Sudan is free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 13 years, although more than 40% of children do not go to schools due to the economic situation. Environmental and social factors also increase the difficulty of getting to school, especially for girls. Primary education consists of eight years, followed by three years of secondary education. The former educational ladder 6 + 3 + 3 was changed in 1990. The primary language at all levels is Arabic. Schools are concentrated in urban areas; many in the west have been damaged or destroyed by years of civil war. In 2001 the World Bank estimated that primary enrollment was 46 percent of eligible pupils and 21 percent of secondary students. Enrollment varies widely, falling below 20 percent in some provinces. The literacy rate is 70.2% of total population, male: 79.6%, female: 60.8%.
Education in Sudan is free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 13 years, although more than 40% of children do not go to schools due to the economic situation. Environmental and social factors also increase the difficulty of getting to school, especially for girls. Primary education consists of eight years, followed by three years of secondary education. The former educational ladder 6 + 3 + 3 was changed in 1990. The primary language at all levels is Arabic. Schools are concentrated in urban areas; many in the west have been damaged or destroyed by years of civil war. In 2001 the World Bank estimated that primary enrollment was 46 percent of eligible pupils and 21 percent of secondary students. Enrollment varies widely, falling below 20 percent in some provinces. The literacy rate is 70.2% of total population, male: 79.6%, female: 60.8%.
 Sudan has a rich and unique musical culture that has been through chronic instability and repression during the modern history of Sudan. Beginning with the imposition of strict Salafi interpretation of ''sharia'' law in 1983, many of the country's most prominent poets and artists, like Mahjoub Sharif, were imprisoned while others, like Mohammed el Amin (returned to Sudan in the mid-1990s) and Mohammed Wardi (returned to Sudan 2003), fled to Cairo. Traditional music suffered too, with traditional Zār ceremonies being interrupted and drums confiscated . At the same time European militaries contributed to the development of Sudanese music by introducing new instruments and styles; military bands, especially the Scottish bagpipes, were renowned, and set traditional music to march (music), military march music. The march ''March Shulkawi No 1'', is an example, set to the sounds of the Shilluk people, Shilluk. Northern Sudan listens to different music than the rest of Sudan. A type of music called Aldlayib uses a musical instrument called the Tambur. The Tambur has five strings, is made from wood and makes music accompanied by the voices of human applause and singing artists.
Sudan has a rich and unique musical culture that has been through chronic instability and repression during the modern history of Sudan. Beginning with the imposition of strict Salafi interpretation of ''sharia'' law in 1983, many of the country's most prominent poets and artists, like Mahjoub Sharif, were imprisoned while others, like Mohammed el Amin (returned to Sudan in the mid-1990s) and Mohammed Wardi (returned to Sudan 2003), fled to Cairo. Traditional music suffered too, with traditional Zār ceremonies being interrupted and drums confiscated . At the same time European militaries contributed to the development of Sudanese music by introducing new instruments and styles; military bands, especially the Scottish bagpipes, were renowned, and set traditional music to march (music), military march music. The march ''March Shulkawi No 1'', is an example, set to the sounds of the Shilluk people, Shilluk. Northern Sudan listens to different music than the rest of Sudan. A type of music called Aldlayib uses a musical instrument called the Tambur. The Tambur has five strings, is made from wood and makes music accompanied by the voices of human applause and singing artists.
 Most Sudanese wear either traditional or western attire. A traditional garb widely worn by Sudanese men is the jalabiya, galabiya, which is a loose-fitting, long-sleeved, collarless ankle-length garment also common to
Most Sudanese wear either traditional or western attire. A traditional garb widely worn by Sudanese men is the jalabiya, galabiya, which is a loose-fitting, long-sleeved, collarless ankle-length garment also common to