Straight-pull Rifles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Bolt-action is a type of manual
Bolt-action is a type of manual
 Most of the bolt-action designs use a rotating bolt (or "turn pull") design, which involves the shooter doing an upward "rotating" movement of the handle to unlock the bolt from the breech and cock the
Most of the bolt-action designs use a rotating bolt (or "turn pull") design, which involves the shooter doing an upward "rotating" movement of the handle to unlock the bolt from the breech and cock the
 The Mauser bolt-action system is based on 19th-century Mauser bolt-action rifle designs and was finalized in the
The Mauser bolt-action system is based on 19th-century Mauser bolt-action rifle designs and was finalized in the
 The
The



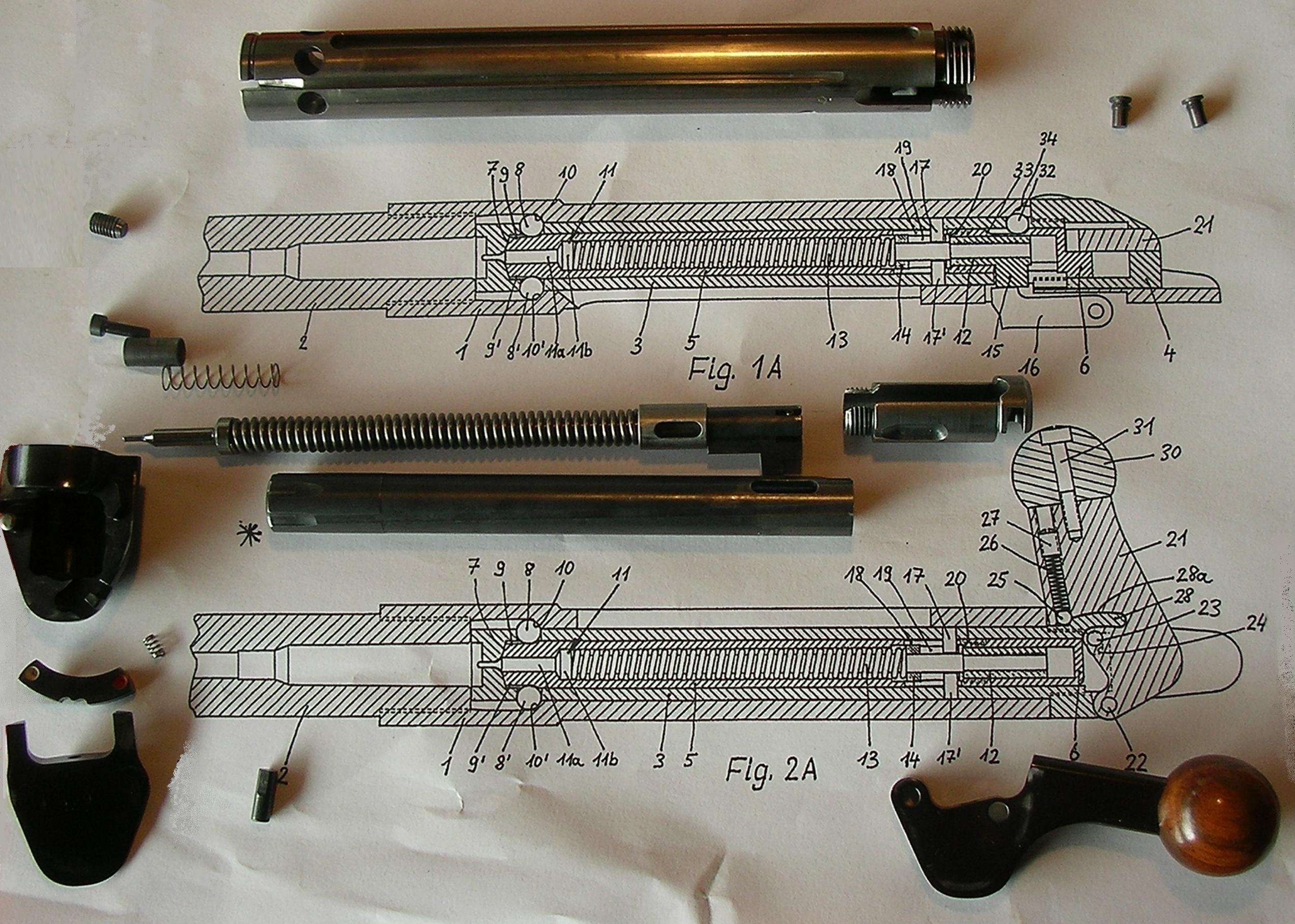 Straight-pull bolt-actions differ from conventional turn-pull bolt-action mechanisms in that the bolt can be cycled back and forward without rotating the handle and thus only a linear motion is required, as opposed to a traditional bolt-action, where the user has to axially rotate the bolt in addition to the linear motions to perform chambering and
Straight-pull bolt-actions differ from conventional turn-pull bolt-action mechanisms in that the bolt can be cycled back and forward without rotating the handle and thus only a linear motion is required, as opposed to a traditional bolt-action, where the user has to axially rotate the bolt in addition to the linear motions to perform chambering and Brand new 2021: Savage Impulse, the new straight-pull rifle from the USA
/ref> Strasser, and Steel Action. Most straight bolt rifles have a firing mechanism without a hammer, but there are some hammer-fired models, such as the Merkel Helix. Firearms using a hammer usually have a comparably longer


 Bolt-action is a type of manual
Bolt-action is a type of manual firearm action
In firearms terminology, an action is the functional mechanism of a breech-loading firearm that handles (loads, locks, fires, extracts and ejects) the ammunition cartridges, or the method by which that mechanism works. Actions are technically n ...
that is operated by ''directly'' manipulating the bolt via a bolt handle, which is most commonly placed on the right-hand side of the weapon (as most users are right-handed).
Most bolt-action firearms use a rotating bolt design, where the handle must first be rotated upward to unlock the bolt from the receiver, then pulled back to open the breech
Breech may refer to:
* Breech (firearms), the opening at the rear of a gun barrel where the cartridge is inserted in a breech-loading weapon
* breech, the lower part of a pulley block
* breech, the penetration of a boiler where exhaust gases leav ...
and allowing any spent cartridge case
A cartridge or a round is a type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile ( bullet, shot, or slug), a propellant substance (usually either smokeless powder or black powder) and an ignition device ( primer) within a metal ...
to be extracted and ejected. This also cocks the striker within the bolt (either on opening or closing of the bolt depending on the gun design) and engages it against the sear
The Sahar Elevated Access Road, abbreviated to SEAR, is a dedicated, elevated, express access road in Mumbai that connects the Western Express Highway (WEH) near Hanuman Nagar junction in Vile Parle, with the forecourts of Terminal T2 of the C ...
. When the bolt is returned to the forward position, a new cartridge
Cartridge may refer to:
Objects
* Cartridge (firearms), a type of modern ammunition
* ROM cartridge, a removable component in an electronic device
* Cartridge (respirator), a type of filter used in respirators
Other uses
* Cartridge (surname), a ...
(if available) is pushed out of the magazine and into the barrel chamber
Chamber or the chamber may refer to:
In government and organizations
* Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests
*Legislative chamber, in politics
* Debate chamber, the space or room that houses delib ...
, and finally the breech is closed tight by rotating the handle down so the bolt head relocks on the receiver.
Bolt-action firearms are generally repeating firearm
A repeating firearm or repeater is any firearm (either a handgun or long gun) that is capable of being fired repeatedly before having to manually reload new ammunition into the weapon.
Unlike single-shot firearms, which can only hold and fir ...
s, but some single-shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many cent ...
breechloaders also use bolt-action design as a breechblock mechanism. The majority of these firearms are rifles, but there are some bolt-action variants of shotguns and handguns as well. Examples of these date as far back as the early 19th century, notably in the Dreyse needle gun Dreyse may refer to:
* Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (1787–1867), German firearms inventor
* Hitch Dreyse, a fictional character in ''Attack on Titan'' (''Shingeki no Kyojin'') series who serves in the military police.
* Dreyse needle gun, a German ...
. From the late 19th century all the way through both World Wars
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
, bolt-action rifles were the standard infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
service weapon
A service rifle (or standard-issue rifle) is a rifle a military issues to regular infantry. In modern militaries, this is typically a versatile and rugged battle rifle, assault rifle, or carbine suitable for use in nearly all environments. Most ...
s for most of the world's military forces. In modern military and law enforcement, bolt-action firearms have been mostly replaced by semi-automatic and selective-fire
Selective fire is the capability of a weapon to be adjusted to fire in semi-automatic, fully automatic, and/or burst mode. The modes are chosen by means of a selector switch, which varies depending on the weapon's design. Some selective-fire we ...
firearms, and have remained prevalent only as sniper rifles due to the design's inherent potential for superior accuracy and precision, as well as ruggedness and reliability compared to autoloading designs.
History
The first bolt-action rifle was produced in 1824 byJohann Nikolaus von Dreyse
Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (20 November 1787 – 9 December 1867) was a German firearms inventor and manufacturer. He is most famous for submitting the Dreyse needle gun in 1836 to the Prussian army, which was adopted for service in December 1840 ...
, following work on breechloading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally bre ...
rifles that dated to the 18th century. Von Dreyse would perfect his ''Nadelgewehr'' (Needle Rifle) by 1836, and it was adopted by the Prussian Army in 1841. While it saw limited service in the German Revolutions of 1848
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, it was not fielded widely until the 1864 victory over Denmark. In 1850 a metallic centerfire bolt-action breechloader was patented by Béatus Beringer. In 1852 another metallic centerfire bolt-action breechloader was patented by Joseph Needham and improved upon in 1862 with another patent. Two different systems for primers –the mechanism to ignite a metallic cartridge's powder charge – were invented in the 1860s as well, the Berdan and the Boxer systems.
The United States purchased 900 Greene rifles (an under hammer, percussion capped, single-shot bolt-action that used paper cartridges and an ogival bore rifling system) in 1857, which saw service at the Battle of Antietam in 1862, during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
; however, this weapon was ultimately considered too complicated for issue to soldiers and was supplanted by the Springfield Model 1861
The Springfield Model 1861 was a Minié-type rifled musket used by the United States Army and Marine Corps during the American Civil War. Commonly referred to as the "Springfield" (after its original place of production, Springfield, Massachus ...
, a conventional muzzle loading rifle. During the American Civil War, the bolt-action Palmer carbine was patented in 1863, and by 1865, 1000 were purchased for use as cavalry weapons. The French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
adopted its first bolt-action rifle, the Chassepot rifle
The Chassepot (pronounced ''SHAS-poh''), officially known as ''Fusil modèle 1866'', was a bolt-action military breechloading rifle. It is famous for having been the arm of the French forces in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. It replace ...
, in 1866 and followed with the metallic cartridge bolt-action Gras rifle
The Fusil Modèle 1874 or Gras was the French Army's primary service rifle from 1874 to 1886. Designed by Colonel Basile Gras, the Gras was a metallic cartridge adaptation of the single-shot, breech-loading, black powder Chassepot rifle. It was ...
in 1874.
European armies continued to develop bolt-action rifles through the latter half of the 19th century, first adopting tubular magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges with ...
s as on the Kropatschek
A Kropatschek is any variant of a rifle designed by Alfred von Kropatschek. Kropatschek's rifles used a tubular magazine (constructed of nickel-plated steel) of his design, of the same type used in the Japanese Murata Type 22 and the German ...
rifle and the Lebel rifle
The Lebel Model 1886 rifle (French: ''Fusil Modèle 1886 dit "Fusil Lebel"'') also known as the ''"Fusil Mle 1886 M93"'', after a bolt modification was added in 1893, is an 8 mm bolt-action infantry rifle that entered service in the French A ...
. The first bolt-action repeating rifle was patented in Britain in 1855 by an unidentified inventor through the patent agent Auguste Edouard Loradoux Bellford using a gravity-operated tubular magazine in the stock. Another more well-known bolt-action repeating rifle was the Vetterli rifle of 1867 and the first bolt-action repeating rifle to use centerfire cartridges was the weapon designed by the Viennese gunsmith Ferdinand Fruwirth in 1871. Ultimately, the military turned to bolt-action rifles using a box magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges with ...
; the first of its kind was the M1885 Remington–Lee
The Remington–Lee is a bolt-action, box magazine repeating rifle designed principally by James Paris Lee.
Description
It first appeared in 1879, manufactured by the Sharps Rifle Manufacturing Company. Eventually Remington took over producti ...
, but the first to be generally adopted was the British 1888 Lee–Metford. World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
marked the height of the bolt-action rifle's use, with all of the nations in that war fielding troops armed with various bolt-action designs.
During the buildup prior to World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the military bolt-action rifle began to be superseded by semi-automatic rifle
A semi-automatic rifle is an autoloading rifle that fires a single cartridge with each pull of the trigger, and uses part of the fired cartridge's energy to eject the case and load another cartridge into the chamber. For comparison, a bolt-a ...
s and later fully automatic rifles, though bolt-action rifles remained the primary weapon of most of the combatants for the duration of the war; and many American units, especially the USMC
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through co ...
, used bolt-action M1903 Springfield
The M1903 Springfield, officially the United States Rifle, Caliber .30-06, Model 1903, is an American five-round magazine-fed, bolt-action service repeating rifle, used primarily during the first half of the 20th century.
The M1903 was first ...
s until sufficient numbers of M1 Garand
The M1 Garand or M1 rifleOfficially designated as U.S. rifle, caliber .30, M1, later simply called Rifle, Caliber .30, M1, also called US Rifle, Cal. .30, M1 is a semi-automatic rifle that was the service rifle of the U.S Army during World War ...
s were made available. The bolt-action is still common today among sniper rifles, as the design has the potential for superior accuracy, reliability, lesser weight, and the ability to control loading over the faster rate of fire that alternatives allow. There are, however, many semi-automatic sniper rifle designs, especially in the designated marksman
A designated marksman (DM), squad advanced marksman (AD) or squad designated marksman (SDM) is a military marksman role in an infantry squad. The term ''sniper'' was used in Soviet doctrine although the soldiers using the Dragunov SVD were the ...
role.
Today, bolt-action rifles are chiefly used as hunting rifles. These rifles can be used to hunt anything from vermin
Vermin ( colloquially varmint(s) or varmit(s)) are pests or nuisance animals that spread diseases or destroy crops or livestock. Since the term is defined in relation to human activities, which species are included vary by region and enterp ...
to deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
and to large game, especially big game caught on a safari, as they are adequate to deliver a single lethal shot from a safe distance.
Bolt-action shotguns are considered a rarity among modern firearms but were formerly a commonly used action for .410 entry-level shotguns, as well as for low-cost 12-gauge
Gauge ( or ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, ...
shotguns. The M26 Modular Accessory Shotgun System
The M26-MASS (Modular Accessory Shotgun System) is a shotgun configured as an underbarrel ancillary weapon attachment mounted onto the handguard of a service rifle, usually the M16/ M4 family of United States military, essentially making the host ...
(MASS) is the most advanced and recent example of a bolt-action shotgun, albeit one designed to be attached to an M16 rifle or M4 carbine using an underbarrel mount (although with the standalone kit, the MASS can become a standalone weapon). Mossberg 12-gauge bolt-action shotguns were briefly popular in Australia after the 1997 changes to firearms laws, but the shotguns themselves were awkward to operate and had only a three-round magazine, thus offering no practical and real advantages over a conventional double-barrel shotgun.
Some pistols use a bolt-action, although this is uncommon, and such examples are typically specialized target handguns.
Major bolt-action systems
Rotating bolt
 Most of the bolt-action designs use a rotating bolt (or "turn pull") design, which involves the shooter doing an upward "rotating" movement of the handle to unlock the bolt from the breech and cock the
Most of the bolt-action designs use a rotating bolt (or "turn pull") design, which involves the shooter doing an upward "rotating" movement of the handle to unlock the bolt from the breech and cock the firing pin
A firing pin or striker is a part of the firing mechanism of a firearm that impacts the primer in the base of a cartridge and causes it to fire. In firearms terminology, a striker is a particular type of firing pin where a compressed spring ...
, followed by a rearward "pull" to open the breech, extract the spent cartridge case, then reverse the whole process to chamber the next cartridge and relock the breech. There are four major turn bolt-action designs: the Remington M-700, possibly the single most numerous produced rifle in history which is now also used as basis for most custom competition rifle actions, along with the Mauser system, the Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's sta ...
system, and the Mosin–Nagant system. All four differ in the way the bolt fits into the receiver, how the bolt rotates as it is being operated, the number of locking lugs holding the bolt in place as the gun is fired, and whether the action is cocked on the opening of the bolt (as in both the Mauser system and the Mosin Nagant system) or the closing of the bolt (as in the Lee–Enfield system). The vast majority of modern bolt-action rifles were made for the commercial market post-war, numbering in the tens of millions by Remington in the unique, and most accurate Model 700, two of the others use the Mauser system, with other designs such as the Lee–Enfield system and the Mosin Nagant system, of only limited usage.
Mauser
 The Mauser bolt-action system is based on 19th-century Mauser bolt-action rifle designs and was finalized in the
The Mauser bolt-action system is based on 19th-century Mauser bolt-action rifle designs and was finalized in the Gewehr 98
The Gewehr 98 (abbreviated G98, Gew 98, or M98) is a German bolt-action rifle made by Mauser, firing cartridges from a five-round internal clip-loaded magazine. It was the German service rifle from 1898 to 1935, when it was replaced by the Kar ...
designed by Paul Mauser. It is the most common bolt-action system in the world, being in use in nearly all modern hunting rifles and the majority of military bolt-action rifles until the middle of the 20th century. The Mauser system is stronger than that of the Lee–Enfield due to two locking lugs just behind the bolt head, which make it better able to handle higher-pressure cartridges (i.e. magnum cartridge
A magnum cartridge is a firearm cartridge with a larger case size than, or derived from, a similar cartridge of the same projectile (bullet) caliber and case shoulder shape. The term derives from the .357 Magnum, the original cartridge with this d ...
s). The 9.3×64mm Brenneke and 8×68mm S magnum rifle cartridge "families" were designed for the Mauser M 98 bolt-action. A novel safety feature was the introduction of a third locking lug present at the rear of the bolt that normally did not lock the bolt, since it would introduce asymmetrical locking forces. The Mauser system features "cock on opening", meaning the upward rotation of the bolt when the rifle is opened cocks the action. A drawback of the Mauser M 98 system is that it cannot be cheaply mass-produced very easily. Many Mauser M 98-inspired derivatives feature technical alterations, such as omitting the third safety locking lug, to simplify production.
The controlled-feed Mauser M 98 bolt-action system's simple, strong, safe, and well-thought-out design inspired other military and hunting/sporting rifle designs that became available during the 20th century, including the:
*Gewehr 98
The Gewehr 98 (abbreviated G98, Gew 98, or M98) is a German bolt-action rifle made by Mauser, firing cartridges from a five-round internal clip-loaded magazine. It was the German service rifle from 1898 to 1935, when it was replaced by the Kar ...
/ Standardmodell/Karabiner 98k
The Karabiner 98 kurz (; "carbine 98 short"), often abbreviated Karabiner 98k, Kar98k or K98k and also sometimes incorrectly referred to as a K98 (a K98 is a Polish carbine and copy of the Kar98a), is a bolt-action rifle chambered for the 7.92× ...
*M24 series
The FN Model 24 series is a line of Mauser Gewehr 98 pattern bolt-action battle rifles produced by the Belgian Fabrique Nationale. They are similar to the Czech vz. 24 rifle, featuring open sights, 8×57mm IS chambering, carbine-length barrels ...
*vz. 24
The vz. 24 rifle is a bolt-action carbine designed and produced in Czechoslovakia from 1924 to 1942. It was developed from the German Mauser Gewehr 98 line, and features a very similar bolt design. The rifle was designed in Czechoslovakia shor ...
/vz. 33
The puška vz. 33Československé ruční palné zbraně a kulomety, Miroslav Šáda, Praha, Naše vojsko, 1971 ("rifle model 1933", sometimes referred to as krátká puška vz. 33 – "short rifle model 33") was a Czechoslovak bolt-action car ...
* Type 24 rifle
*M1903 Springfield
The M1903 Springfield, officially the United States Rifle, Caliber .30-06, Model 1903, is an American five-round magazine-fed, bolt-action service repeating rifle, used primarily during the first half of the 20th century.
The M1903 was first ...
*Pattern 1914 Enfield
The Rifle, .303 Pattern 1914 (or P14) was a British service rifle of the First World War period. A bolt action weapon with an integral 5-round magazine, it was principally contract manufactured by companies in the United States. It served as ...
*M1917 Enfield
The M1917 Enfield, the "American Enfield", formally named "United States Rifle, cal .30, Model of 1917" is an American modification and production of the .303-inch (7.7 mm) Pattern 1914 Enfield (P14) rifle (listed in British Service as Rifle No. ...
*Arisaka
The Arisaka rifle ( ja, 有坂銃, Arisaka-jū) is a family of Japanese military bolt-action service rifles, which were produced and used since approximately 1897, when it replaced the Murata rifle (, ) family, until the end of World War II in ...
Type 38/ Type 99
*M48 Mauser
The Zastava M48 (Serbo-Croatian: ''Puška M.48 7,9 mm'' / Пушка M.48 7,9 mm, "Rifle M.48 7.9 mm") is a post World War II Yugoslav version of the German Karabiner 98k designed by Mauser and the Belgian designed M24 series. It was the s ...
* Kb wz. 98a/Karabinek wz. 1929
The Karabinek wz.29 (Kbk wz.29; Polish: carbine model 29) was a Polish bolt-action short rifle based on the German Kar98AZ. Identifying attributes include a 98/05 style mast bayonet lug ending directly beneath the front sight and winged protectiv ...
*FR8
The FR 7 and FR 8 are bolt-action rifles adopted by Spain in the 1950s. The "FR" stands for ''Fusil Reformado'' in Spanish ("Converted Rifle" in English).
The FR 7 is a variant of the "Spanish M93 Mauser" bolt action while the FR 8 is based on th ...
*modern hunting/sporting rifles like the CZ 550, Heym Express Magnum
The Heym Express Magnum is a luxury bolt-action rifle designed for the purpose of hunting big game. The rifle is available in 5 different calibers from the .375 H&H Magnum to the powerful .450 Rigby. Rather similar in appearance to the Karabiner ...
, Winchester Model 70
The Winchester Model 70 is a bolt-action sporting rifle. It has an iconic place in American sporting culture and has been held in high regard by shooters since it was introduced in 1936, earning the moniker "The Rifleman's Rifle". The action has s ...
and the Mauser M 98
The Mauser M 98 are a series of currently (2020) produced bolt-action hunting rifles.
The production of the controlled round feed Mauser 98 bolt action system for the German military ceased at the end of World War II in 1945. The new Mauser M 98 ...
*modern sniper rifles like the Sako TRG
The Sako TRG is a bolt-action sniper rifle line designed and manufactured by Finnish firearms manufacturer SAKO of Riihimäki. The TRG-21 and TRG-22 are designed to fire standard .308 Winchester ( 7.62×51mm NATO) sized cartridges, while the TRG ...
, Accuracy International Arctic Warfare
The Accuracy International Arctic Warfare rifle is a bolt-action sniper rifle designed and manufactured by the British company Accuracy International. It has proved popular as a civilian, police, and military rifle since its introduction in th ...
and GOL Sniper Magnum
The GOL-Sniper Magnum is a bolt-action sniper rifle designed by the German company Gol-Matic GmbH of Birkenau, Hesse. The rifle is available in tactical as well as sporting and match configurations. GOL-Sniper rifles are based on custom Magnum ...
Versions of the Mauser action designed prior to the Gewehr 98's introduction, such as that of the Swedish Mauser
"Swedish Mausers" are a family of bolt-action rifles based on an improved variant of Mauser's earlier Model 1893, but using the 6.5×55mm cartridge, and incorporating unique design elements as requested by Sweden. These are the m/94 (Model 1894 ...
rifles and carbines, lack the third locking lug and feature a "cock on closing" operation.
Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield bolt-action system was introduced in 1889 with the Lee–Metford and laterLee–Enfield rifle
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's sta ...
s (the bolt system is named after the designer James Paris Lee and the barrel rifling after the Royal Small Arms Factory at the London Borough of Enfield
The London Borough of Enfield () is a London borough in North London. It borders the London boroughs of Barnet to the west, Haringey to the south, and Waltham Forest to the southeast. To the north are the districts of Hertsmere, Welwyn Hat ...
), and is a "cock on closing" action in which the forward thrust of the bolt cocks the action. This enables a shooter to keep eyes on sights and targets uninterrupted by cycling the bolt. The ability of the bolt between lugs and chamber to flex also keeps the shooter safer in case of catastrophic chamber overpressure. The disadvantage of the rearward-located bolt lugs is that a larger part of the receiver, between chamber and lugs, must be made stronger and heavier to resist stretching forces. Also, the bolt ahead of the lugs may flex on firing which, although a safety advantage, may eventually lead to increased head space. Repeated firing over time can lead to receiver "stretch" and excessive headspace, which if perceived as a problem can be remedied by changing the removable bolt head to a larger sized one (the Lee–Enfield bolt manufacture involved a mass production method where at final assembly the bolt body was fitted with one of three standard size bolt heads for correct headspace). In the years leading up to WWII, the Lee–Enfield bolt system was used in numerous commercial sporting and hunting rifles manufactured by such firms in the UK as BSA, LSA, and Parker–Hale, as well as by SAF Lithgow in Australia. Vast numbers of ex-military SMLE Mk III rifles were sporterised post WWII to create cheap, effective hunting rifles, and the Lee–Enfield bolt system is used in the M10 and No 4 Mk IV rifles manufactured by Australian International Arms. Rifle Factory Ishapore of India manufactures a hunting and sporting rifle chambered in .315 which also employs the Lee Enfield action.
*Lee–Enfield (all marks and models)
* Ishapore 2A1
*Various hunting/sporting rifles manufactured by BSA, LSA, SAF Lithgow, and Parker Hale
Parker-Hale Ltd. was a British firearms, air rifle and firearms accessory manufacturer, located in the Gun Quarter of the city of Birmingham, England. It was founded by Alfred Gray Parker and Arthur Hale.
History
Alfred Gray Parker founded a ri ...
*Australian International Arms M10 and No 4 Mk IV hunting/sporting rifles
*Rifle Factory Ishapore's hunting Lee Enfield rifle in .315
Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant action, created in 1891 and named after the designers Sergei Mosin and Léon Nagant, differs significantly from the Mauser and Lee–Enfield bolt-action designs. The Mosin–Nagant design has a separate bolthead that rotates with the bolt and the bearing lugs, in contrast to the Mauser system where the bolthead is a non-removable part of the bolt. The Mosin–Nagant is also unlike the Lee–Enfield system where the bolthead remains stationary and the bolt body itself rotates. The Mosin–Nagant bolt is a somewhat complicated affair, but is extremely rugged and durable; like the Mauser, it uses a "cock on open" system. Although this bolt system has been rarely used in commercial sporting rifles (the Vostok brand target rifles being the most recognized) and never outside of Russia, large numbers of military surplus Mosin–Nagant rifles have beensporterized
Sporterising, sporterisation or sporterization is the practice of modifying military-type firearms either to make them suitable for civilian sporting use or to make them legal under the law.
Modifying for sporting use
Modifying for sporting use c ...
for use as hunting rifles in the years since WWII.
Other designs
Both theU.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
's M24 Sniper Weapon System
The M24 Sniper Weapon System (SWS) or M24 is the military and police version of the Remington Model 700 rifle, ''M24'' being the model name assigned by the United States Army after adoption as their standard sniper rifle in 1988. The M24 is ref ...
and U.S. Marine Corps' M40 sniper rifles are built from the Remington Model 700 rifle, in different degrees of modification, the main difference being the custom fitted heavy contour barrel and action length. The M24 utilizes the Long action and the M40 employs the short action bolt-face. The reason for this is that the M24 was originally intended to chamber the longer .300 Winchester Magnum
The .300 Winchester Magnum (also known as .300 Win Mag or .300 WM) (7.62×67mmB, 7.62x66BR) is a belted, bottlenecked magnum rifle cartridge that was introduced by the Winchester Repeating Arms Company in 1963. The .300 Winchester Magnum is a m ...
round. The M40, however, was not intended to be chambered in the more powerful .300 Winchester Magnum round, yet the Marine Corps' intention was to migrate to the .300 Winchester Magnum cartridge. The Marine Corps' delay has led to a change in migratory direction, the current goal is for the M40 to become a rifle chambered in .338 Lapua Magnum.
The United States Army's Joint Munitions and Lethality Contracting Center has awarded Remington a Firm Fixed Price (FFP) Indefinite Delivery/ Indefinite Quantity (ID/IQ) contract (W15QKN-10-R-0403) for the upgrade of up to 3,600 M24 Sniper Weapon Systems (SWS) currently fielded to the Army pending type classification as the “M24E1”. The major configuration change for this system is the caliber conversion from 7.62mm NATO (.308 Winchester) to .300 Winchester Magnum to provide soldiers with additional precision engagement capability and range. The contract is for a five-year period and has a guaranteed minimum value of $192K with a potential value of up to $28.2 million. This award follows a full and open competitive evaluation lasting nine months, which began with the release of the Army's Request for Proposal (RFP) on January 13, 2010. The program will be executed under the authority of Project Manager Soldier Weapons, Picatinny Arsenal, NJ, and managed by its subordinate unit, Product Manager Individual Weapons. In 2009 the U.S. Army has changed the weapon name from M24E1 to the XM2010 Enhanced Sniper Rifle
The M2010 Enhanced Sniper Rifle (ESR), formerly known as the XM2010 and M24 Reconfigured Sniper Weapon System, is a sniper rifle developed by PEO Soldier for the United States Army. It is derived from and replaced the M24 Sniper Weapon System, an ...
.
 The
The Vetterli rifle
The Vetterli rifles were a series of Swiss army service rifles in use from 1869 to 1889,Barnes, p.196, "10.4x38R Swiss Vetterli M69/81". when they were replaced with Schmidt–Rubin rifles. Modified Vetterlis were also used by the Italian Army.
...
was the first bolt-action repeating rifle introduced by an army. It was used by the Swiss army from 1869 to circa 1890. Modified Vetterlis were also used by the Italian Army
"The safeguard of the republic shall be the supreme law"
, colors =
, colors_labels =
, march = ''Parata d'Eroi'' ("Heroes's parade") by Francesco Pellegrino, ''4 Maggio'' (May 4) ...
. Another notable design is the Norwegian Krag–Jørgensen
The Krag–Jørgensen is a repeating bolt-action rifle designed by the Norwegians Ole Herman Johannes Krag and Erik Jørgensen in the late 19th century. It was adopted as a standard arm by Norway, Denmark, and the United States. About 300 we ...
, which was used by Norway, Denmark, and briefly the United States. It is unusual among bolt-action rifles in that is loaded through a gate on the right side of the receiver, and thus can be reloaded without opening the bolt. The Norwegian and Danish versions of the Krag have two locking lugs, while the American version has only one. In all versions, the bolt handle itself serves as an emergency locking lug. The Krag's major disadvantage compared to other bolt-action designs is that it is usually loaded by hand, one round at a time, although a box-like device was made that could drop five rounds into the magazine, all at once via a stripper or en bloc clip. This made it slower to reload than other designs which used stripper or en bloc clips. Another historically important bolt-action system was the Gras system, used on the French Mle 1874 Gras rifle
The Fusil Modèle 1874 or Gras was the French Army's primary service rifle from 1874 to 1886. Designed by Colonel Basile Gras, the Gras was a metallic cartridge adaptation of the single-shot, breech-loading, black powder Chassepot rifle. It was ...
, Mle 1886 Lebel rifle
The Lebel Model 1886 rifle (French: ''Fusil Modèle 1886 dit "Fusil Lebel"'') also known as the ''"Fusil Mle 1886 M93"'', after a bolt modification was added in 1893, is an 8 mm bolt-action infantry rifle that entered service in the French A ...
(which was the first to introduce ammunition loaded with nitrocellulose-based smokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared t ...
), and the Berthier series of rifles.
Straight pull



 Straight-pull bolt-actions differ from conventional turn-pull bolt-action mechanisms in that the bolt can be cycled back and forward without rotating the handle and thus only a linear motion is required, as opposed to a traditional bolt-action, where the user has to axially rotate the bolt in addition to the linear motions to perform chambering and
Straight-pull bolt-actions differ from conventional turn-pull bolt-action mechanisms in that the bolt can be cycled back and forward without rotating the handle and thus only a linear motion is required, as opposed to a traditional bolt-action, where the user has to axially rotate the bolt in addition to the linear motions to perform chambering and primary extraction
In breechloading firearms, primary extraction is the initial phase (the first few millimeters) of the extraction of a spent casing from the firearm chamber. After the primary extraction comes the secondary extraction where the bolt is moved furt ...
. The bolt locking of a straight pull action is achieved differently without needing manual inputs, therefore the entire operating cycle needs the shooter to perform only two movements (pull back and push forward) instead of four (rotate up, pull back, push forward, and rotate down), greatly increasing the gun's rate of fire.
In 1993 the German Blaser company introduced the Blaser R93, a new straight pull action where locking is achieved by a series of concentric "claws" that protrude/retract from the bolthead, a design that is referred to as ''Radialbundverschluss'' ("radial connection"). As of 2017 the Rifle Shooter magazine listed its successor Blaser R8 as one of the three most popular straight pull rifles together with Merkel Helix and Browning Maral. Some other notable modern straight pull rifles are made by Beretta
Fabbrica d'Armi Pietro Beretta (; "Pietro Beretta Weapon Factory") is a privately held Italian firearms manufacturing company operating in several countries. Its firearms are used worldwide for a variety of civilian, law enforcement, and milita ...
, C.G. Haenel, Chapuis, Heym Heym is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Georg Heym (1887–1912), German author
* Stefan Heym (1913–2001), German author
See also
* Heym (gun manufacturer)
* Chayyim, the basis for this name
* Haim (disambiguation)
* Hei ...
, Lynx, Rößler Rößler is a surname and may refer to:
* Hole Rößler (born 1949), German modern pentathlete
* Matthias Rößler (born 1955), German politician (CDU)
* Robert Rößler (1838–1883), German poet
* Rößler firearms, an Austrian firearms manufa ...
, Savage Arms
Savage Arms is an American gunmaker based in Westfield, Massachusetts, with operations in Canada. Savage makes a variety of rimfire and centerfire rifles, as well as Stevens single-shot rifles and shotguns. The company is best known for the ...
,/ref> Strasser, and Steel Action. Most straight bolt rifles have a firing mechanism without a hammer, but there are some hammer-fired models, such as the Merkel Helix. Firearms using a hammer usually have a comparably longer
lock time
Lock time or action time refers to the time interval (often measured in milliseconds) from when the trigger of a firearm is activated until the firing pin strikes the primer, and depends on the design of the firing mechanism. A long lock time inc ...
than hammerless mechanisms.
In the sport of biathlon
The biathlon is a winter sport that combines cross-country skiing and rifle shooting. It is treated as a race, with contestants skiing through a cross-country trail whose distance is divided into shooting rounds. The shooting rounds are not time ...
, because shooting speed is an important performance factor and semi-automatic guns are illegal for race use, straight pull actions are quite common and are used almost exclusively in the Biathlon World Cup
The Biathlon World Cup is a top-level biathlon season-long competition series. It has been held since the winter seasons of 1977–78 for men and 1982–83 for women. The women's seasons until 1986–87 season were called the European Cup, alt ...
. The first company to make the straight pull action for .22 caliber .22 caliber, or 5.6 mm caliber, refers to a common firearms bore diameter of 0.22 inch (5.6 mm).
Cartridges in this caliber include the very widely used .22 Long Rifle and .223 Remington / 5.56×45mm NATO.
.22 inch is also a popular ...
was J. G. Anschütz
J. G. Anschütz GmbH & Co. KG is a sporting firearms manufacturer based in Ulm, Germany, that makes rimfire and centerfire rifles as well as air rifles and air pistols for target and competition shooting, as well as hunting. Anschütz rifl ...
; the action is specifically the straight pull ball bearing lock action, which features spring-loaded ball bearings on the side of the bolt which lock into a groove inside the bolt's housing. With the new design came a new dry fire method; instead of the bolt being turned up slightly, the action is locked back to catch the firing pin.
Operating the bolt
Typically, the bolt consists of a tube of metal inside of which the firing mechanism is housed, and which has at the front or rear of the tube several metal knobs, or "lugs", which serve to lock the bolt in place. The operation can be done via arotating bolt
Rotating bolt is a method of locking the breech (or rear barrel) of a firearm closed for firing. Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse developed the first rotating bolt firearm, the " Dreyse needle gun", in 1836. The Dreyse locked using the bolt handle ...
, a lever, cam action, a locking piece, or a number of systems. Straight pull designs have seen a great deal of use, though manual turn bolt designs are what is most commonly thought of in reference to a bolt-action design due to the type ubiquity. As a result, the bolt-action term is often reserved for more modern types of rotating bolt designs when talking about a specific weapon's type of action. However, both straight pull and rotating bolt rifles are types of bolt-action rifles. Lever-action
The toggle-link action used in the iconic Winchester Model 1873 rifle, one of the most famous lever-action firearms
Lever-action is a type of action for repeating firearms that uses a manually operated cocking handle located around the trigger g ...
and pump-action
Pump action or slide action is a repeating firearm action that is operated manually by moving a sliding handguard on the gun's forestock. When shooting, the sliding forend is pulled rearward to eject any expended cartridge and typically to coc ...
weapons must still operate the bolt, but they are usually grouped separately from bolt-actions that are operated by a handle directly attached to a rotating bolt. Early bolt-action designs, such as the Dreyse needle gun Dreyse may refer to:
* Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (1787–1867), German firearms inventor
* Hitch Dreyse, a fictional character in ''Attack on Titan'' (''Shingeki no Kyojin'') series who serves in the military police.
* Dreyse needle gun, a German ...
and the Mauser Model 1871
The Mauser Model 1871 adopted as the ''Gewehr'' 71 or ''Infanterie-Gewehr'' 71, or "Infantry Rifle 71" ("I.G.Mod.71" was stamped on the rifles themselves) was the first rifle model in a distinguished line designed and manufactured by Paul Mauser ...
, locked by dropping the bolt handle or bolt guide rib into a notch in the receiver, this method is still used in .22 rimfire rifles. The most common locking method is a rotating bolt with two lugs on the bolt head, which was used by the Lebel Model 1886 rifle
The Lebel Model 1886 rifle (French: ''Fusil Modèle 1886 dit "Fusil Lebel"'') also known as the ''"Fusil Mle 1886 M93"'', after a bolt modification was added in 1893, is an 8 mm bolt-action infantry rifle that entered service in the French A ...
, Model 1888 Commission Rifle
The Gewehr 88 (commonly called the Model 1888 commission rifle) was a late 19th-century German bolt-action rifle, adopted in 1888.
The invention of smokeless powder in the late 19th century immediately rendered all of the large-bore black powder ...
, Mauser M 98
The Mauser M 98 are a series of currently (2020) produced bolt-action hunting rifles.
The production of the controlled round feed Mauser 98 bolt action system for the German military ceased at the end of World War II in 1945. The new Mauser M 98 ...
, Mosin–Nagant and most bolt-action rifles. The Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's sta ...
has a lug and guide rib, which lock on the rear end of the bolt into the receiver.
Bolt knob
The bolt knob is the part of the bolt handle that the user grips when loading and reloading the firearm and thereby acts as a cocking handle. On many older firearms, the bolt knob is welded to the bolt handle, and as such becoming an integral part of the bolt handle itself. On many newer firearms, the bolt knob is instead threaded onto the handle, allowing the user to change the original bolt knob for an aftermarket one, either for aesthetical reasons, achieving better grip or similar. The type of threads used vary between firearms. European firearms often use either M6 1 or M8 1.25 threads, for example M6 is used on theSIG Sauer 200 STR
The SIG Sauer 200 STR (Scandinavian Target Rifle), also known as the SIG Sauer 200 STR Match, is a bolt-action rifle mostly used as a target/competition rifle for national competitions by Norwegian, Swedish and Danish sport shooters. It is a var ...
, Blaser R93, Blaser R8, CZ 457 and Bergara rifles, while M8 is used on the Sako TRG
The Sako TRG is a bolt-action sniper rifle line designed and manufactured by Finnish firearms manufacturer SAKO of Riihimäki. The TRG-21 and TRG-22 are designed to fire standard .308 Winchester ( 7.62×51mm NATO) sized cartridges, while the TRG ...
and SIG Sauer 404 {{Infobox weapon
, is_ranged = yes
, name = Sauer 404
, image =
, image_size =
, caption =
, origin = {{flag, Germany
, type = Bolt-action repeating rifle
, designer = Sauer & Sohn
, design_date =
, manufacturer = J. P. Sauer & Sohn Gm ...
. Many American firearms instead use 1/4" 28 TPI (6.35 0.907 mm) or 5/16" 24 TPI (7.9375 1.058 mm) threads. Some other thread types are also used, for example, No. 10 32 TPI (4.826 0.794 mm) as used by Mausingfield. There also exists aftermarket slip-on bolt handle covers which are mounted without having to remove the existing bolt handle. These are often made of either rubber or plastic.
Reloading
Most bolt-action firearms are fed by an internal magazine loaded by hand, by en bloc, or stripper clips, though a number of designs have had a detachable magazine or independent magazine, or even no magazine at all, thus requiring that each round be independently loaded. Generally, the magazine capacity is limited to between two and ten rounds, as it can permit the magazine to be flush with the bottom of the rifle, reduce the weight, or prevent mud and dirt from entering. A number of bolt-actions have atube magazine
A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device for a repeating firearm, either integral within the gun (internal/fixed magazine) or externally attached (detachable magazine). The magazine functions by holding several cartridges with ...
, such as along the length of the barrel. In weapons other than large rifles, such as pistols and cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
s, there were some manually operated breech-loading weapons. However, the Dreyse Needle fire rifle was the first breech loader
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breech ...
to use a rotating bolt design. Johann Nicholas von Dreyse
Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (20 November 1787 – 9 December 1867) was a German firearms inventor and manufacturer. He is most famous for submitting the Dreyse needle gun in 1836 to the Prussian army, which was adopted for service in December 1840 ...
's rifle of 1838 was accepted into service by Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
in 1841, which was in turn developed into the Prussian Model in 1849. The design was a single shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many cent ...
breech-loader and had the now familiar arm sticking out from the side of the bolt, to turn and open the chamber
Chamber or the chamber may refer to:
In government and organizations
* Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests
*Legislative chamber, in politics
* Debate chamber, the space or room that houses delib ...
. The entire reloading sequence was a more complex procedure than later designs, however, as the firing pin
A firing pin or striker is a part of the firing mechanism of a firearm that impacts the primer in the base of a cartridge and causes it to fire. In firearms terminology, a striker is a particular type of firing pin where a compressed spring ...
had to be independently primed and activated, and the lever was used only to move the bolt.
See also
*Antique guns
An antique firearm is a term to describe a firearm that was designed and manufactured prior to the beginning of the 20th century. Although the exact definition of what constitutes an "antique firearm" varies between countries, the advent of smok ...
*British military rifles
The origins of the modern British military rifle are within its predecessor the Brown Bess musket. While a musket was largely inaccurate over , due to a lack of rifling and a generous tolerance to allow for muzzle-loading, it was cheap to prod ...
*Service rifle
A service rifle (or standard-issue rifle) is a rifle a military issues to regular infantry. In modern militaries, this is typically a versatile and rugged battle rifle, assault rifle, or carbine suitable for use in nearly all environments. Mos ...
Other firearm actions
*Break action
Break action is a type of firearm action in which the barrel or barrels are hinged much like a door and rotate perpendicularly to the bore axis to expose the breech and allow loading and unloading of cartridges. A separate operation may be requir ...
*Falling block action
A falling-block action (also known as a sliding-block or dropping-block action) is a single-shot firearm action in which a solid metal breechblock slides vertically in grooves cut into the breech of the weapon and is actuated by a lever.
Desc ...
*Lever action
The toggle-link action used in the iconic Winchester Model 1873 rifle, one of the most famous lever-action firearms
Lever-action is a type of action for repeating firearms that uses a manually operated cocking handle located around the trigger ...
* Pump action
*Rolling block
A rolling-block action is a form of firearm action where the sealing of the breech is done with a specially shaped breechblock able to rotate on a pin. The breechblock is shaped like a section of a circle.
The breechblock is locked into place by ...
*Rotating bolt
Rotating bolt is a method of locking the breech (or rear barrel) of a firearm closed for firing. Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse developed the first rotating bolt firearm, the " Dreyse needle gun", in 1836. The Dreyse locked using the bolt handle ...
* Semi automatic rifle
*Automatic rifle
An automatic rifle is a type of autoloading rifle that is capable of fully automatic fire. Automatic rifles are generally select-fire weapons capable of firing in semi-automatic and automatic firing modes (some automatic rifles are capable of ...
** Blowback operated
**Recoil operated
Recoil operation is an operating mechanism used to implement locked breech, autoloading firearms. Recoil operated firearms use the energy of recoil to cycle the action, as opposed to gas operation or blowback operation using the pressure of the ...
**Gas operated
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spent ...
References
Further reading
*External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bolt Action Firearm actions *