|
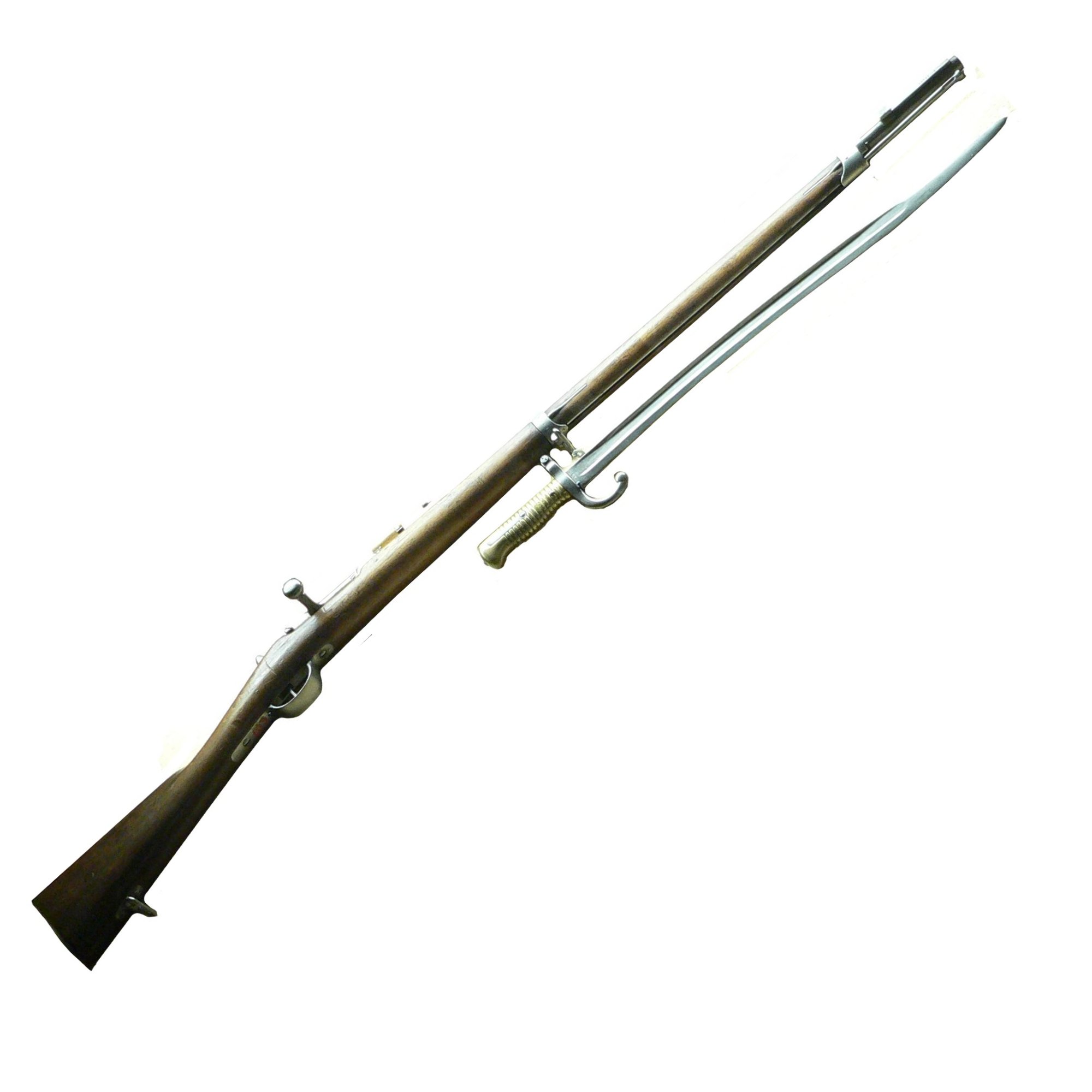
Needle Gun
A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with rifling) is a firearm that has a needle-like firing pin, which can pass through the paper cartridge case to strike a percussion cap at the bullet base. Types Pauly A diagram of a needle-gun cartridge, showing the paper cartridge case, the sabot, and acorn-shaped bullet. The first experimental needle gun was designed by Jean Samuel Pauly, a Swiss gunsmith. In Paris in 1808, in association with French gunsmith François Prélat, Pauly created the first fully self-contained cartridges: the cartridges incorporated a copper base with integrated mercury fulminate primer powder (the major innovation of Pauly), a round bullet and either brass or paper casing. The cartridge was loaded through the breech and fired with a needle. The needle-activated central-fire breech-loading gun became a major feature of firearms thereafter. The corresponding firearm was also developed by Pauly. Pauly made an improved version which was protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreyse Needle Gun
Dreyse may refer to: * Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (1787–1867), German firearms inventor * Hitch Dreyse, a fictional character in '' Attack on Titan'' (''Shingeki no Kyojin'') series who serves in the military police. * Dreyse needle gun, a German service rifle 1841-1873 * Dreyse M1907 The Dreyse Model 1907 is a semi-automatic pistol designed by Louis Schmeisser. The gun was named after Nikolaus von Dreyse, the designer of the Dreyse Needle Gun. The Waffenfabrik von Dreyse company was acquired by Rheinische Metallwaren & Masc ..., a German semi-automatic pistol 1907-1945 * Waffenfabrik von Dreyse, a firearms manufacturing company taken over in 1901 by Rheinische Metallwaaren- und Maschinenfabrik Sömmerda; later, Rheinmetall {{disambig, surname Surnames of German origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Nicolaus Von Dreyse
Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse (20 November 1787 – 9 December 1867) was a German firearms inventor and manufacturer. He is most famous for submitting the Dreyse needle gun in 1836 to the Prussian army, which was adopted for service in December 1840 as the ''Leichte Perkussions-Gewehr M 1841'' – a name deliberately chosen to mislead about the rifle's mechanism – later renamed Zündnadelgewehr M 1841 in 1855. Biography Dreyse was born in Sömmerda (then ruled by the Archbishopric of Mainz), the son of a locksmith. Dreyse worked from 1809 to 1814 in the Parisian gun factory of Jean-Samuel Pauly, a Swiss who designed several experimental breech-loading military rifles. After returning to Sömmerda in 1824, he founded a company to manufacture percussion caps. It was there that he designed the needle rifle. While the gun is thought of by some to be the first bolt-action rifle, in reality it bears little resemblance to modern bolt-action rifles, except for the bolt princip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
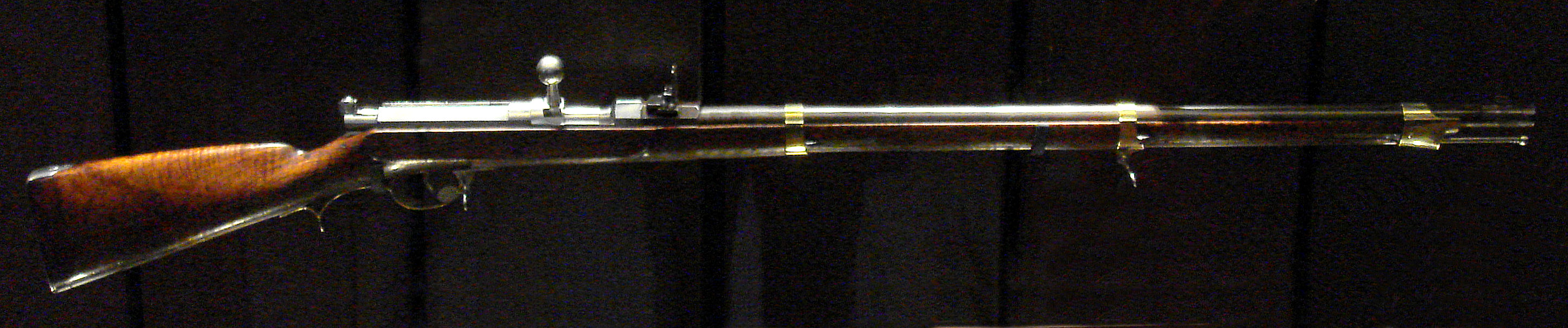
Minié Rifle
The Minié rifle was an important infantry rifle of the mid-19th century. A version was adopted in 1849 following the invention of the Minié ball in 1847 by the French Army captain Claude-Étienne Minié of the Chasseurs d'Orléans and Henri-Gustave Delvigne. The bullet was designed to allow rapid muzzle loading of rifles, and was an innovation that brought about the widespread use of the rifle as the main battlefield weapon for individual soldiers. The French adopted it following difficulties encountered by the French army in North Africa, where their muskets were outranged by long-barreled weapons which were handcrafted by their Algerian opponents. The Minié rifle belonged to the category of rifled muskets. Mechanism The rifle used a conical-cylindrical shaped soft lead bullet, slightly smaller than the barrel bore, with three exterior grease-filled peripheral grooves and a conical hollow in its base. When fired, the expanding gas forcibly pushed on the skirted base of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patriot, revolutionary and republican. He contributed to Italian unification and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. He is considered one of the greatest generals of modern times and one of Italy's " fathers of the fatherland", along with Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour, Victor Emmanuel II of Italy and Giuseppe Mazzini. Garibaldi is also known as the "''Hero of the Two Worlds''" because of his military enterprises in South America and Europe. Garibaldi was a follower of the Italian nationalist Mazzini and embraced the republican nationalism of the Young Italy movement. He became a supporter of Italian unification under a democratic republican government. However, breaking with Mazzini, he pragmatically allied himself with the monarchist Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mentana
The Battle of Mentana was fought on November 3, 1867, near the village of Mentana, located north-east of Rome (then in the Papal States, now modern Lazio), between French-papal troops and the Italian volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, who were attempting to capture Rome, then the main centre of the peninsula still outside of the newly unified Kingdom of Italy. The battle ended in a victory by the French-papal troops. Background When the first Italian Parliament met in Turin, Victor Emmanuel II of Savoy was proclaimed King of Italy on March 17, 1861, and Rome was declared capital of Italy on March 27, 1861. However, the Italian government could not take its seat in Rome because Emperor Napoleon III maintained a French garrison there to prop up Pope Pius IX. This created an unstable political situation that led to much strife, both internal and external. In 1862 Giuseppe Garibaldi, the hero of the unification, organized an expedition from Sicily, under the slogan ''Roma o Morte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Alphonse Chassepot
Antoine Alphonse Chassepot (1833–1905) was a French inventor and gunsmith. Born in 1833 in the town of Mutzig in Alsace, he is best known for inventing the breech-loading, center-fire needle gun rifle named after him: the Chassepot. Officially known as the ''Fusil modèle 1866'', the rifle was adopted by the French army in 1866, for which Chassepot received the Cross of the Légion d'honneur and a gratuity of 30,000 francs The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription ''francorum rex'' (King of the Franks) used on early French coins and until the 18th centu .... References 1833 births 1905 deaths 19th-century French inventors 19th-century French engineers Firearm designers {{France-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compare Dreyse-Chassepot
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and in the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berdan Rifle
The Berdan rifle (''винтовка Бердана''/''vintovka Berdana'' in Russian) is a Russian rifle created by the American firearms expert and inventor Hiram Berdan in 1868. It was standard issue in the Russian army from 1870 to 1891, when it was replaced by the Mosin–Nagant rifle. It was widely used in Russia as a hunting weapon, and sporting variants, including shotguns, were produced until the mid-1930s. The ''Russian'' Berdan I (M1868) and Berdan II (M1870) rifles of .42 caliber are distinct from the ''Spanish'' Berdan 15mm (.58+ cal) conversion rifles adopted by Spain as the M1857/67 Berdan (and related engineer, artillery & short rifles). Berdan I Two different versions of the later single-shot Berdan rifle were adopted as service weapons by Imperial Russia. The first version, manufactured by Colt in the US, is known as model 1868, or Berdan I. It is a hammerless "trapdoor" breechblock design, and was manufactured in limited numbers (the contract stipulated 30,000) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Schaumburg-Lippe
Schaumburg-Lippe, also Lippe-Schaumburg, was created as a county in 1647, became a principality in 1807, a free state in 1918, and was until 1946 a small state in Germany, located in the present day state of Lower Saxony, with its capital at Bückeburg and an area of 340 km² (131 sq. mi.) and over 40,000 inhabitants. History Schaumburg-Lippe was formed as a county in 1647 through the division of the County of Schaumburg by treaties between the Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel and the Count of Lippe. The division occurred because Count Otto V of Holstein-Schaumburg had died in 1640 leaving no male heir. Initially Schaumburg-Lippe's position was somewhat precarious: it had to share a wide variety of institutions and facilities with the County of Schaumburg (which belonged to Hesse-Kassel), including the representative assembly and the highly productive Bückeberg mines, and the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel retained some feudal rights over it. It was furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Königgrätz
The Battle of Königgrätz (or Sadowa) was the decisive battle of the Austro-Prussian War in which the Kingdom of Prussia defeated the Austrian Empire. It took place on 3 July 1866, near the Bohemian city of Hradec Králové (German: Königgrätz) and village of Sadová, now in the Czech Republic. Prussian forces, totaling around 285,000 troops, used their superior training and tactical doctrine and the Dreyse needle gun to win the battle and the entire war at Königgrätz on their own. Prussian artillery was ineffective and almost all of the fighting on the Prussian side was done by the First Army under Prince Friedrich Karl and one division from the Second Army. The Prussian 7th Infantry Division and 1st Guards Infantry Division attacked and destroyed 38 out of 49 infantry battalions of four Austrian corps at the Swiepwald and Chlum at the center of the battlefield, deciding the outcome of the struggle and forcing an Austrian retreat at 15:00, before any Prussian reinfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 1866 between the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia, with each also being aided by various allies within the German Confederation. Prussia had also allied with the Kingdom of Italy, linking this conflict to the Third Italian War of Independence, Third Independence War of Italian unification. The Austro-Prussian War was part of the wider Austria-Prussia rivalry, rivalry between Austria and Prussia, and resulted in Prussian dominance over the German states. The major result of the war was a shift in power among the German states away from Austrian and towards Prussian hegemony. It resulted in the abolition of the German Confederation and its partial replacement by the unification of Germany, unification of all of the northern German sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
