straight-five engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The straight-five engine (also referred to as an inline-five engine; abbreviated I5 or L5) is a
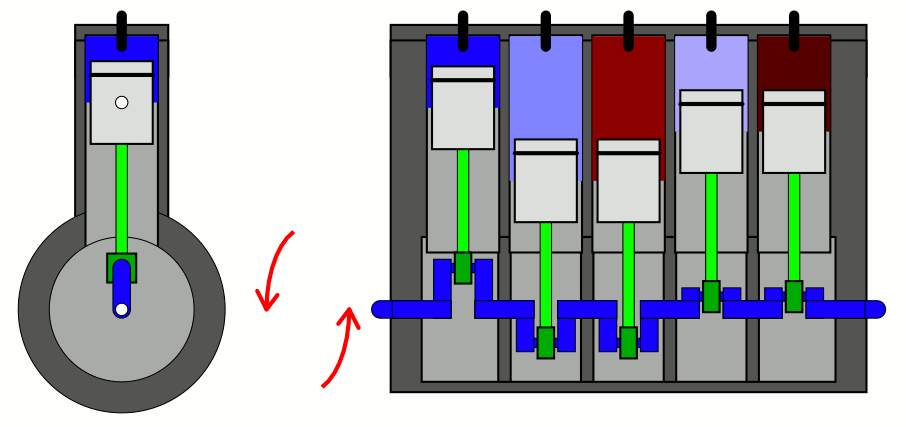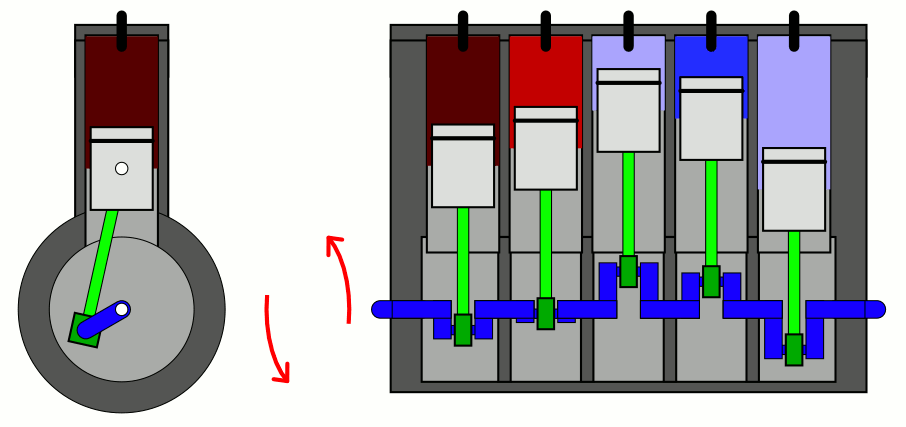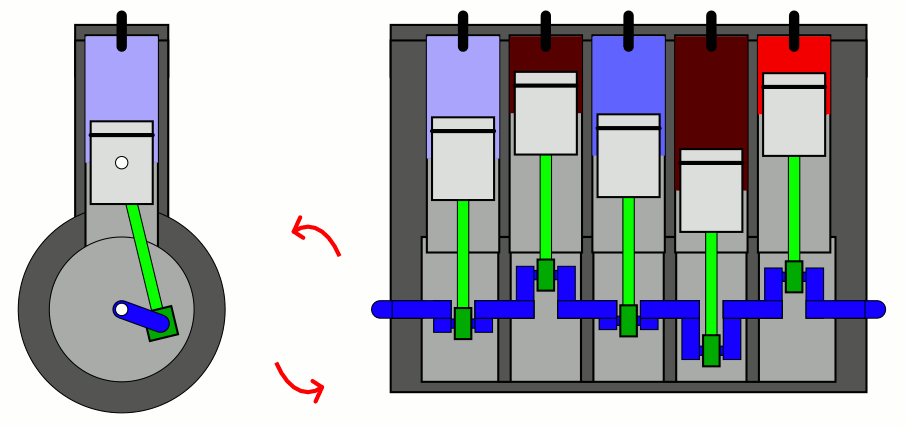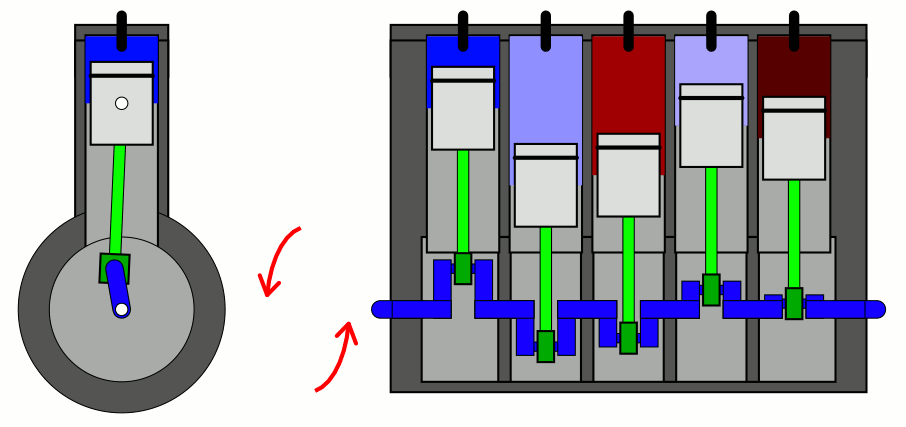 Straight-five engines are typically shorter than
Straight-five engines are typically shorter than
piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common fea ...
with five cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankshaft.
Although less common than straight-four engines and straight-six engine
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine bal ...
s, straight-five engines have occasionally been used by automobile manufacturers since the late 1930s, particularly the Mercedes Benz's diesel engines from 1974 to 2006 and Audi's petrol engines from 1979 to the present. Straight-five engines are smoother running than straight-four engines and shorter than straight-six engines. However, achieving consistent fuelling across all cylinders was problematic prior to the adoption of fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All com ...
.
Characteristics
 Straight-five engines are typically shorter than
Straight-five engines are typically shorter than straight-six engine
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine bal ...
s, making them easier to fit transversely in an engine bay. They are also smoother than straight-four
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the e ...
engines, and are narrower than V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
s and flat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, w ...
s.
Engine balance and vibration
Five-cylinder engines have a crankshaft with 72 degree angles. Amongstfour-stroke engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directio ...
s, an advantage of engines with five or more cylinders is that the power strokes are overlapping (if the engine has an even firing order
The firing order of an internal combustion engine is the sequence of ignition for the cylinders.
In a spark ignition (e.g. gasoline/petrol) engine, the firing order corresponds to the order in which the spark plugs are operated. In a diesel engi ...
).
On the other hand, the odd number of cylinders in a straight-five engine results in imperfect primary and secondary engine balance
Engine balance refers to how the forces (resulting from combustion or rotating/reciprocating components) are balanced within an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The most commonly used terms are ''primary balance'' and ''secondary bala ...
(unlike a straight-six engine
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine bal ...
). Counterweights on the crankshaft (also used in straight-four engines) can be used to reduce the vibrations from these imbalances.Robert Bosch GmbH, ''Bosch Automotive Handbook, 6th edition'' p. 459-463, Professional Engineering Publishing 2004, .
Firing order
Mostfour-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direct ...
straight-five engines use a firing order of 1-2-4-5-3. This firing order results in the minimal primary (crank speed) rocking couple, and is used by the Volvo Modular engine, VW/Audi straight-five engine, General Motors Atlas engine and Honda G engine. Straight-five engines typically have a 72 degree crankshaft design.
All two stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of t ...
straight-five engines are limited in having a single firing order for a given crank configuration; because a complete cycle occurs every 360 degrees, there is no chance to share piston phases without having simultaneous ignitions, so the straight-five is at no disadvantage in this case. Some two-stroke outboard engines, e.g. the ''Mercury Marine Force 150'' engine use a firing order of 1-5-2-3-4.
Carburettors and fuel injection
The use of straight-fivepetrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
engines in mass production cars only became truly viable with the advent of reliable fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All com ...
. This is because of the unavoidable problems of a carburettor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meteri ...
supplying an odd number of cylinders and the length of the inlet manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a ...
between the carburetor varying greatly between cylinders at the ends of the engine and those nearer the carburetor. Unlike other engine layouts, these problems are not easily solved by using multiple carburettors.
Diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-ca ...
s have always used fuel injection, therefore large displacement straight-five diesel engines were commonly seen decades before straight-five petrol engines.
Usage in automobiles
Diesel engines
The 1938 Lancia 3Ro trucks introduced a straight-five diesel engine to replace the previous straight-three engine. Built for the Italian and German armed forces during World War II and later for civilian usage, the truck remained in production until 1950. The first mass-production straight-five passenger car engine was the 1974 Mercedes-Benz OM617, a naturally-aspirated engine introduced in the ''Mercedes-Benz 300D (W114/W115)'' models. In 1978, aturbocharged
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
version was introduced in the ''Mercedes-Benz 300SD Turbo'' models. Mercedes-Benz continued to produce straight-five engines for the next 28 years, until the Mercedes-Benz OM647 engine ended production in 2006.
In 1978, the Audi 2.0 R5 D engine was introduced in the ''Audi 100'' sedan. In 1983, a turbocharged version was introduced, initially for the U.S market Audi 100. Several Volvo cars were produced with Audi straight-five diesel engines, prior to the introduction of the Volvo D5 turbo-diesel engine; this engine was produced from 2001 to 2017 and was used in several diesel hybrid applications (marketed as "twin engine" models).
Other mass-production straight-five diesel engines include the 1999-2001 VM Motori 531 turbo-diesel engine, the 1998-2007 Land Rover Td5 turbo-diesel engine, the 2006-2019 Ford Duratorq 3.2 turbo-diesel engine and the 1998-2009 Fiat JTD 2.4 turbo-diesel engine.
Petrol engines
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of ...
had an inline-five engine developed in the late 1930s to early 1940s for a compact economy car design, which never saw production due to lack of demand for small cars in the United States.
The first production straight-five petrol engine was the Audi 2.1 R5 introduced in the Audi 100 in 1979. Audi has continued use of straight-five petrol engines (in both naturally aspirated and turbocharged
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
versions) to the present day. The Audi TT RS and Audi RS3 currently use straight-five engines. In motorsport, the first car to use a straight-five engine was the Audi Quattro
The Audi Quattro is a road and rally car, produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi, part of the Volkswagen Group. It was first shown at the 1980 Geneva Motor Show on 3 March. Production continued through 1991.
Background
The wor ...
rally car; other racing cars which used straight-five engines include the 1985-1986 Audi Sport Quattro E2 and the 1989 Audi 90 Quattro IMSA GTO. For the year 1987 factory team tested a 1000 hp version of the inline-5 powered Audi S1 Sport Quattro.
Several Volkswagen-branded straight-five engines have been produced, beginning with the Volkswagen WH/WN 1.9 litre 10v engine used in the 1981 Volkswagen Passat. The final Volkswagen straight-five petrol engine was the Volkswagen EA855
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post- ...
2.5 litre 20v engine used in the North American Passat models until 2014.
The Volvo Modular engine was introduced in the 1991 Volvo 850 sedan and was used in various Volvo models, along with the ''Ford Focus ST'' and ''Ford Focus RS'' models. All of the straight-five petrol engines used by Volvo and Ford were built at the Volvo Skövde engine plant in Skövde
Skövde () is a locality and urban centre in Skövde Municipality and Västra Götaland County, in the Västergötland (Western Gothland region) in central Southern Sweden.
Skövde is situated some 150 km northeast of Gothenburg, between ...
, Sweden, until their discontinuation in 2016.
Other straight-five petrol engines include
* 1989-1998 Honda G-series 2.0-2.5 litre 20v engines
* 1995-2006 Fiat Family C 2.0-2.4 litre 20v engine
* 2004-2012 General Motors Vortec 3500/ 3700 3.5-3.7 litre 20v engines
In recent years the engine has been falling out of favour, with Volvo announcing in 2014 it would discontinue building them, for example.
Usage in motorcycles
Very few motorcycles have used five-cylinder engines. However, the 1965 ''Honda RC148'' and 1966 ''Honda RC149'' 125 cc four-stroke racing motorcycles used straight-five engines based on the 50 cc straight-twin engine from the Honda RC116 Grand Prix racing motorcycle. These straight-five engines were an unusual design in that they were configured as a straight-six engine with one of the middle cylinders removed.See also
* Straight engine * V5 engine * VR5 engineReferences
{{Piston engine configurations Straight-05 5